Abstract
Only a few studies have described sperm chromosome intranuclear positioning changes in men with reproductive failure and an incorrect somatic karyotype. We studied the influence of Robertsonian translocations on the acrocentric chromosome positioning in human sperm cells. The basis of the analysis was the localization of NORs (nucleolar organizing regions) in sperm nuclei from three Robertsonian translocation carriers, namely, rob(13;22), rob(13;15) and rob(13;14), with a known meiotic segregation pattern. All three carriers presented with a similar percentage of genetically normal sperm cells (i.e., approximately 40%). To visualize NORs, we performed 2D-FISH with directly labelled probes. We used the linear and radial topologies of the nucleus to analyse the NORs distribution. We found an affected positioning of NORs in each case of the Robertsonian translocations. Moreover, the NORs tended to group, most often in two clusters. Both in Robertsonian carriers and control sperm cells, NORs mostly colocalized in the medial areas of the nuclei. In the case of the Roberstonian carriers, NORs were mostly concentrated in the peripheral part of the medial area, in contrast to control sperm cells in which the distribution was more dispersed towards the internal area.
Introduction
Robertsonian translocations (ROBs), named after the American biologist W.R.B. Robertson, were first described in 1916 in grasshoppers1. Since the first description of ROBs, they have been an object of fascination for geneticists and a subject of numerous and comprehensive studies due to their following characteristics: specificity of the creation of these translocations2,3; potential influence on speciation4; presence of NOR sequences on chromosomes engaged in the creation of ROBs5; and influence on reproductive failure6,7.
Robertsonian translocation is a central fusion of the long arms of two acrocentric chromosomes. Acrocentric fusions have been proposed to occur via incomplete homologous or non-homologous recombination between short arm repeats or through the repair of short arm DNA damage, which is corrected by a similar short arm DNA sequence on a nearby non-homologous acrocentric chromosome. In most cases, the regions of breaks are located just above the centromere. A singleton chromosome with two centromeres is then formed (a dicentric chromosome), one of which loses the shape of the centromere and remains inactive. A simultaneously created fragment (acentric) without a centromere is lost during subsequent cell divisions6,8. Consequently, in humans, ROB carriers have 45 chromosomes. In most cases, no phenotypic significance is linked to the loss of the short chromosome arms probably because these arms contain only nucleolus organizing regions called NORs9. All 10 short arms of acrocentrics have a specific genomic organization, and they share several highly similar blocks of repetitive DNA, including satellite III and beta satellite. The short arms also share NORs, which exist as clusters of approximately 400 copies of 43 kb ribosomal DNA (rDNA) organized in a head-to-tail fashion and localized between centromeric and telomeric heterochromatin5,10.
Among five pairs of human acrocentric chromosomes (13, 14, 15, 21 and 22), which can form 10 nonhomologous ROBs, the most commonly occurring ones are rob(13;14) (q10;q10) (67–75%) and rob(14;21) (q10;q10) (approximately 10%)11–25. The majority of heterologous ROBs are inherited from a carrier parent.
ROBs are common in man with an incidence of 1 in 1000–1230 births6,11,14. Among men with reproductive failure, ROBs occur over 9 times more often, that is, with a frequency greater than 0.8%6,9. Problems with fertility in ROB carriers are mostly because during meiosis, the rearranged chromosomes in pachytene form a configuration composed of three chromosomes (trivalent) as a result of paired homologous fragments. In anaphase, these three chromosomes segregate to gametes, resulting in the following segregation types: alternate, adjacent 1, adjacent 2, and 3:0. Fertilization with a spermatozoon created after adjacent or 3:0 segregation leads to trisomy or monosomy in zygotes, and the majority of which are eliminated early12,15.
Meiotic segregation patterns have been recognized in about 150 carriers of the following different nonhomologous ROBs: der(13;14), der(13;15), der(13;21), der(13;22), der(14;15), der(14;21), der(14;22), der(15;21), der(15;22) and der(21;22)17–29. On average, in most carriers of different nonhomologous ROBs, the frequency of genetically balanced segregants is around 80%, and the numbers of offspring with normal or balanced karyotypes are similar which can indicate a homogenous segregation behaviour of Robertsonian translocations independent of the chromosome pairs involved16,18,19,25. Many ROB carriers have oligoasthenoteratozoospermia with varying degree of intensity16. Interestingly, carriers with normal sperm parameters or oligoasthenoteratozoospermic (OAT) carriers display similar frequencies of genetic imbalance, suggesting that the segregation pattern and impairment of spermatogenesis are most probably independent processes19,25. ROB carriers are often infertile (meaning: no conception), but it happens that they are the sons or the brothers of fertile carriers of the same translocation. It is therefore hard to clearly assess the influence of these translocations on infertility12,14.
The aim of this study was to investigate if the presence of Robertsonian translocation interferes with changes of acrocentric chromosome positioning in human sperm cells. The topology and organization of chromosomes in human sperm cells is a subject of numerous studies due to suggestions that intranuclear architecture is of considerable importance for the correct decondensation of chromatin in the male pronucleus30–32. In this context, it seems important that changes in the chromosomal topology were detected in men with reproductive failures and correct somatic karyotype33,34. However, in our earlies studies, we found changes in the spatial arrangement of chromosomes in sperm cells with chromosome abnormalities, namely, with aneuploidies35, with small additional marker chromosome36, and with reciprocal translocations37. In the studies reported here we investigated the positioning of acrocentric chromosomes in sperm cells from ROBs carriers by analysing the localization of NORs. NORs were chosen as the target region of our interest because the analysis how ROBs affect the positioning of NORs seems to be interesting in view of observed tendency for clustering in control sperm cells in fertile men with normal karyotype38,39. To visualize NORs, we performed 2D-FISH with directly labelled probes. The conservation of the distal sequence to rDNA among the five human acrocentric chromosomes provides a unique opportunity to visualize NORs by FISH signals, which are consistent between NORs40. We analysed a radial and longitudinal localization of NORs in sperm nuclei from three carriers of different ROBs with known meiotic segregation patterns. We found altered distribution of NORs in each case of the Robertsonian translocation. Such an observation stemmed mostly from the comparison of the localization of NORs in sperm cells from a control donor with normal karyotype vs ROB carriers.
Results
Meiotic segregation patterns
The meiotic segregation patterns were examined for the ROB carriers on the basis of ca. 2100–3400 sperm cells counted. As presented in Table 1, in the case of rob(13;15) (R2) and rob(13;14) (R3) carriers, the segregation patterns were similar, and the percentage of sperm cells of the alternate and adjacent segregation types did not significantly differ. The majority of the sperm cells (greater than 75%) were normal and genetically balanced. In the case of rob(13;22) (R1), the percentage of normal sperm cells after the alternate/normal segregation, was similar to results for R2 and R3 (41.5%, 42.9%, and 40.0%, respectively). In turn, the percentage of genetically balanced sperm cells, that is, after the alternate/balanced segregation, and the sum of the unbalanced sperm cells was 10% higher for R1 than for R2 and R3.
Table 1.
Meiotic segregation patterns in sperm cells of three Robertsonian translocation carriers (R1, R2 and R3) and the number of acrocentric chromosomes with NOR sequence.
| Segregation type | No. of chromosomes with NOR | R1 = rob (13; 22) | R2 = rob (13; 15) | R3 = rob (13; 14) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| sperm genotype* | % | Total % | sperm genotype** | % | Total % | sperm genotype*** | % | Total % | ||
| 2:1 Alternate normal/balanceda |
5 | 23 | 41.5 | 86.8 | 23 | 42.9 | 78.4 | 23 | 40.0 | 75.8 |
| 3 | 22, −13, −22, +der (13;22) | 45.3 | 22, −13, −15, +der (13;15) | 35.5 | 22, −13, −14, +der (13;14) | 35.8 | ||||
| 2:1 Adjacent-1b | 4 | 23, −22, +der (13; 22) | 2.6 | 9.9 | 23, −15, +der (13; 15) | 6.5 | 20.5 | 23, −14, +der (13; 14) | 4.8 | 18.7 |
| 4 | 22, −13 | 1.5 | 22, −13 | 3.3 | 22, −13 | 2.4 | ||||
| 2:1 Adjacent-2 | 4 | 23, −13, +der (13; 22) | 3.6 | 23, −13, +der (13; 15) | 5.8 | 23, −13, +der (13; 14) | 6.5 | |||
| 4 | 22, −22 | 2.2 | 22, −15 | 4.9 | 22, −14 | 5.0 | ||||
| 3:0 and/or 2n | 5 | 24, +der (13;22) | 1.3 | 1.3 | 24, +der (13, 15) | 0.6 | 0.6 | 24, +der (13;14) | 2.0 | 2.0 |
| ∑ unbalancedc | 11.2 | ∑ unbalanced | 21.1 | ∑ unbalanced | 20.7 | |||||
| unexplained | 2.0 | unexplained | 0.5 | unexplained | 3.5 | |||||
One-way ANOVA was used to compare results (p ≤ 0.01 was considered to be statistically significant).
aValue of R1 (total % of Alternate/balanced) was significantly different from the R2, R2/2 and R3 results.
bValue of R1 (total % of Adjacent) was significantly different from the R2, R2, R2/2 and R3 results; also, R3 was different from the R2 result.
cValue of R1 (total % of unbalanced) was significantly different from the R2, R2/2 and R3 results.
As it is known and as detailed in Table 1, the sperm cells from Robertsonian carriers always have 5 acrocentric chromosomes with the NOR sequence after the alternate/normal and after the 3:0 segregation, while the sperm cells after the alternate/balanced segregation have 3 acrocentric chromosomes with the NOR sequence. Sperm cells that are products of adjacent-1 and adjacent-2 segregations have 4 acrocentric chromosomes with NOR sequences.
Linear localization of NORs in sperm cells
The number of analysed relevant sperm nuclei (i.e., having simultaneously red NORs signal/s and a single green signal of the centromere of chromosome 7) is presented in Table 2. According to the data shown in Table 2, the analyses concerning the intranuclear localization of the NOR sequences (both linear and radial aspects) were performed in 1139 sperm cells (390 + 398 + 351) from three ROB carriers (R1, R2 and R3, respectively) and in 474 sperm cells from a control donor. In these sperm cells, we localized 2205 (720 + 786 + 699, respectively) and 1122 FISH signals originating from the NOR sequences from ROB carriers and control donor, respectively (Table 2). Theoretically speaking, the number of expected NORs recognized as discrete FISH signals observed per cell should be the same as the number of acrocentric chromosomes bearing the NOR sequence in a particular sperm cell. However, the number of discrete FISH signals observed per nucleus in most sperm cells was lower due to acrocentric chromosomes displaying tendencies of colocalization. As a consequence, the sum of observed FISH signals coming from NORs was approximately half the total of acrocentric chromosomes in analysed sperm cells (Table 2).
Table 2.
The number of sperm cells in which analysis of NORs localization (recognized as FISH signals) was performed. The sum of observed NORs discrete signals versus the number of expected NOR signals if all NOR-bearing chromosomes were independently dispersed.
| Carrier | No. of analyzed sperm cells | No. of expected NOR signals = ∑ of chromosomes with NOR sequence | ∑ of observed NORs signals | % of expected NORs signals |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 rob(13;22) | 390 | 1494 | 720 | 48% |
| R2 rob(13;15) | 398 | 1604 | 786 | 49% |
| R3 rob(13;14) | 351 | 1342 | 699 | 52% |
| ∑/mean value | 1139/380 | 4440/1480 | 2205/735 | 50% |
| Control | 474 | 2370 | 1122 | 47% |
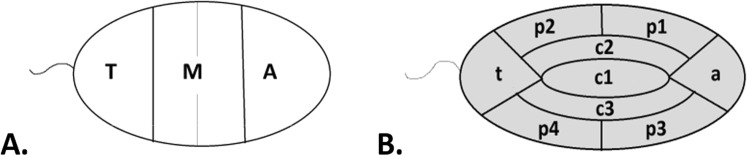
The linear organization of NORs was assessed using the scheme depicted in Fig. 1A. Table 3 shows the results of distribution of discrete FISH signals visualized for NORs in three linear areas (A), (M) and (T). In the sperm cells of carriers R1, R2 and R3 as well as in the sperm cells of the Control, the majority of NORs (i.e., 54.0%, 56.7%, 51.1% and 58.4%, respectively) were localized in the (M) area, while the minority of NORs were localized in the (T) area (12.0%, 11.4%, 16.4% and 15.0%, respectively). Significant differences concerned mostly the (A) area. In all carriers, i.e., R1, R2 and R3, considerably more NORs appeared in the (A) area than in the Control sperm cells (34.0%, 31.9% and 32.5% vs. 26.6%, respectively). The differences between the carriers concerned only values in areas (M) and (T), which differed for R3 from the values for R1 and for R2 (see Table 3).
Figure 1.
A scheme of the sperm cell nucleus areas used for the localization of FISH signals from NORs (nuclear organizing regions). (A) Linear division. The division of the sperm cell nucleus into three longitudinal areas was marked as follows: A = apical, closer to the acrosome; M = medial; and T = area close to tail. (B) Radial division. The division of the sperm cell nucleus into nine radial areas was marked as follows: (c1) = central; (c2 + c3) = internal; (p1 + p3) = peripheral, near the apical area; (p2 + p4) = peripheral, near the tail area; (a) = apical area; and (t) = tail area.
Table 3.
Linear localization of NORs in sperm cells nuclei. Percentage (%) of NORs (recognized as FISH signals) in marked linear areas A, M, and T as defined in Fig. 1A.
| Carrier | Linear areas of nucleus• | Sperm cells with NORs localized only in the M area | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | M | T | |||
| % of NORs | % of sperm cells | % of NORs | |||
| R1 rob(13;22) | 34.0* | 54.0* H | 12.0 L | 43.9 | 40.1* |
| Number of analyzed objects | 245/720 | 389/720 | 86/720 | 171/390 | 289/720 |
| ∑ of all analyzed NORs signals = 720 ∑ of all analyzed sperm cells = 390 |
|||||
| R2 rob(13;15) | 31.9* | 56.7 H | 11.4* L | 60.1* | 56.9* |
| Number of analyzed objects | 251/786 | 446/786 | 89/786 | 238/398 | 449/786 |
| ∑ of all analyzed NORs signals =786 ∑ of all analyzed sperm cells = 398 |
|||||
| R3 rob(13;14) | 32.5* | 51.1* 1H | 16.4 1L | 56.4* 2 | 54.2*2 |
| Number of analyzed objects | 227/699 | 357/699 | 115/699 | 198/351 | 375/699 |
| ∑ of all analyzed NORs signals = 699 ∑ of all analyzed sperm cells = 351 |
|||||
| Control | 26.6 | 58.4 H | 15.0 L | 47.5 | 45.5 |
| Number of analyzed objects | 299/1122 | 655/1122 | 168/1122 | 225/474 | 510/1122 |
| ∑ of all analyzed NORs signals = 1122 ∑ of all analyzed sperm cells = 474 |
|||||
•Linear areas according to the scheme in Fig. 1A. One-way ANOVA was used to compare results (p ≤ 0.01 was considered to be statistically significant). *Values significantly different from mean control value C.
aSignificantly different from the R1 and R2 results.
bSignificantly different from the R1 result.
LLowest values between areas (A, M and T).
HHighest values between areas (A, M and T).
During the analysis of linear distribution of NORs signals, it was also noted that in a significant percentage of the sperm cells (from approximately 44% to 60%), all signals were located only in the (M) area. Table 3 also presents individual results for carriers R1, R2, R3 and the Control. Compared to the Control value (47.5%), the result for R1 (43.9%) was similar, whereas significant differences were found for R2 and R3 (60.1% and 56.4%, respectively).
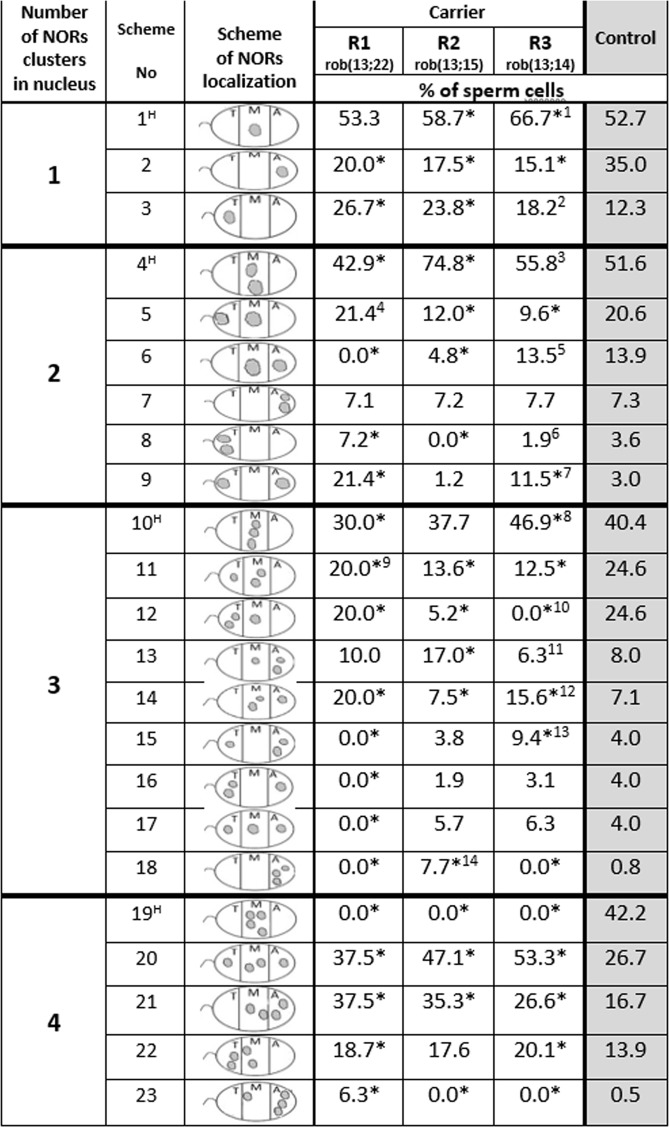
Table 4 shows in detail the results indicating the NOR tendency for clustering. In the case of Control sperm cells, the presence of five discrete NOR signals, which would be expected if all the acrocentric chromosomes were randomly or independently localized, was only observed in 0.4% of nuclei. The presence of four NOR signals was small (9.4%). A single NOR signal was observed in 16.6% of Control sperm cells. In most Control sperm cells, NORs formed two (41.4%) or three (32.1%) discrete signals. In the case of R1, R2 and R3 carriers, sperm cells with five discrete NOR signals were not observed, and sperm cells with four signals were rare (approximately 4%). In all three R1, R2, and R3 carriers, the percentage of sperm cells with two separate NOR signals (38.5%, 43.2% and 44.4%, respectively) was similar to Control sperm cells (41,4%). Significant differences occurred among R1, R2 and R3 carrier sperm cells with three NOR signals, and the number of cells with three NOR signals was less than that in Control sperm cells (23.0%, 23.0% and 23.1%, respectively). The number of sperm cells from R1, R2 and R3 carriers with one NOR signal, was significantly more than that of the control (34.4%, 29.6% and 28.2%, respectively). Thus, the highest percentage of sperm cells in R1, R2, R3 and Control (about 40%) was sperm cells with two NOR signals (Table 4). Moreover, in the case of R1, R2, and R3 carriers, the sperm cells with one or two NOR signals jointly constituted as many as 73% but only 58% in the Control sperm cells. In the case of the Control, however, the majority (73.5%) of sperm cells jointly consisted of sperm cells with two or three NOR signals.
Table 4.
Clustering of NORs in sperm cells. Percentage (%) of sperm cells in which NORs (recognized as FISH signals) form one, two, three, four or five clusters.
| Number of NORs clusters | 1 | 2 | ∑(1 + 2) | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carrier | % of sperm cells | |||||
| R1 rob(13;22) | 34.4* a | 38.5 Hb | 72.9* | 23.0* ,A | 4.1* L | 0.0 |
| Numer of sperm cells | 134/390 | 150/390 | 284/390 | 90/390 | 16/390 | 0.0 |
| ∑ of analyzed sperm cells = 390 ∑ of analyzed NORs signals = 720 |
||||||
| R2 rob(13;15) | 29.6* | 43.2 H | 72.8* | 23.0* A | 4.2* L | 0.0 |
| Numer of sperm cells | 118/398 | 172/398 | 290/398 | 91/398 | 17/398 | 0.0 |
| ∑ of analyzed sperm cells = 398 ∑ of analyzed NORs signals = 786 |
||||||
| R3 rob(13;14) | 28.2* | 44.4 H | 72.6* | 23.1* A | 4.3* L | 0.0 |
| Numer of sperm cells | 99/351 | 156/351 | 255/351 | 81/351 | 15/351 | 0.0 |
| ∑ of analyzed sperm cells = 351 ∑ of analyzed NORs signals = 699 |
||||||
| Control | 16.6 | 41.4 H | 58.0 | 32.1 | 9.4 | 0.4 L |
| Numer of sperm cells | 79/474 | 197/474 | 276/474 | 153/474 | 45/474 | 2/474 |
| ∑ of analyzed sperm cells = 474 ∑ of analyzed NORs signals = 1122 |
||||||
One-way ANOVA was used to compare results (p ≤ 0.01 was considered to be statistically significant).
*Values significantly higher than the Control value (p < 0.01).
aSignificantly different from the R2 and R3 results.
bSignificantly different from the R2 and R3 results.
HSignificantly higher than the remaining results.
LSignificantly lower than the remaining results.
ASignificantly different from the remaining results.
Similar results indicating the tendency of NOR signals to group were also found in these sperm cells, in which all signals were found only in the (M) area (Table 5) (also see right side of Table 3). In most Control sperm cells, NORs formed two (45.3%) or three (27.6%) discrete signals, but NORs in most sperm cells from R1, R2 and R3 formed two (37.4%, 53.9% and 44.0%, respectively) or one cluster (46.8%, 28.9% and 33.3%, respectively) (Table 5). Differences both in relation to Control values and among R1, R2 and R3 were statistically significant.
Table 5.
Clustering of NORs in the case of sperm cells in which all NORs (recognized as FISH signals) were located only in the M (medial) area of the sperm cell nucleus (M area marked in the scheme in Fig. 1A).
| Number of NORs cluster only in M area of nucleus | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 or 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carrier | % of sperm cells | |||
| R1 rob(13;22) | 46.8* | 37.4* | 15.8* | 0.0* |
| Number of sperm cells with NORs signals only in M = 171 = 43.9% ∑ of all analyzed sperm cells = 390 |
80/171 | 64/171 | 27/171 | 0/171 |
| R2 rob(13;15) | 28.9* | 53.9* | 17.2* | 0.0* |
| Number of sperm cells with NORs signals only in M = 238 = 60.1% ∑ of all analyzed sperm cells = 398 |
69/239 | 129/239 | 41/239 | 0/239 |
| R3 rob(13;14) | 33.3* a | 44.0 b | 22.7* c | 0.0* |
| Number of sperm cells with NORs signals only in M = 198 = 56.4% ∑ of all analyzed sperm cells = 351 |
66/198 | 87/198 | 45/198 | 45/198 |
| Control | 18.7 | 45.3 | 27.6 | 8.4 |
| Number of sperm cells with NORs signals only in M = 225 = 47.5% ∑ of all analyzed sperm cells = 474 |
42/225 | 102/225 | 62/225 | 19/225 |
One-way ANOVA was used to compare results (p ≤ 0.01 was considered to be statistically significant).
*Values significantly different from Control value (p < 0.01).
aAll of the values of R1, R2 and R3 were significantly different.
bAll of the values of R1, R2 and R3 were significantly different.
cAll of the values of R1, R2 and R3 were significantly different.
Figure 2 shows schemes of different NOR localizations in nuclei (recognized as red FISH signals) (For their corresponding representative images see Suppl. Fig. S1). Simultaneously, the percentages of sperm cells in which NORs were found in particular localizations in R1, R2, R3 and the Control are also shown (for total amount of sperm cells with given numbers of NOR clusters see Table 4). As a criterion for the order of schemes (i.e., number 1–23), we assumed the decreasing percentages of the relevant sperm cells in the Control. A considerable part of the detailed results for R1, R2 and R3 was different in relation to Control and/or in relation to one another. For R1, R2 and R3, there were few spermatozoa with four NOR signals (see Table 4 and scheme numbers 19–23 in Fig. 2). These differences may be attributed to the fact that the number of the analysed NOR signals was higher in the case of the Control (see Tables 2 and 4). However, despite the differences, the interesting similarity of the results for R1, R2, R3 and the Control was noticeable because in the case of one, two, or three clusters of NORs, the most sperm cells were compatible with the same scheme, that is, number 1, 4, and 10, respectively. Scheme numbers 1, 4 and 10 concerned signals localization only in the medial (M) area. With respect to the Control, the largest difference existed in sperm cells with four NOR signals. In the case of R1, R2 and R3, no sperm cells in which all four signals were concentrated only in the M area (i.e., according to scheme No 19) were found.
Figure 2.
Percentage (%) of sperm cells with NORs localizations (recognized as FISH signals) according to schemes No. 1 – 23 (for representative images of FISH, see Suppl. Fig. S1). One-way ANOVA was used to compare results (values p ≤ 0.01 was considered to be significantly different). *Values were significantly different from the Control value (p < 0.01). HNr of the scheme, the frequency of sperm cells was the highest (p < 0.001) in R1, R2, R3 and Control. 1Significantly different from the R1 and R2 results. 2Significantly different from the R1 result. 3All of the values of R1, R2 and R3 were significantly different. 4Significantly different from the R2 and R3 results. 5All values R1, R2 and R3 were significantly different. 6Significantly different from R1 result. 7All of the values of R1, R2 and R3 were significantly different. 8Significantly different from the R1 and R3 results. 9Significantly different from the R2 and R3 results. 10All of the values the R1, R2 and R3 were significantly different. 11All of the values of R1, R2 and R3 were significantly different. 12All of the values of R1, R2 and R3 were significantly different. 13Significantly different from the R1 and R2 results. 14Significantly different from the R1 and R2 results.
Radial localization of NORs in sperm cells
The radial organization of NORs was assessed using the scheme depicted in Fig. 1B. Table 6 shows the results of distribution of discrete FISH signals visualized for NORs in nine radial areas. The illustration of these results is shown in Fig. 3 (for more detailed data see Suppl. Fig. S2). The results in the depicted areas are analysed as a sum, i.e., p1 + p3, p2 + p4 and c2 + c3, because both sides of the sperm nucleus, namely front and back, could not be distinguished using the fluorescent microscope in this study. Due to the flattened shape of the sperm cells, fixed nuclei were arranged on the slide randomly on the “front” or the “back” side (see Fig. 1B). Therefore, the “mirror reflection effect” must be considered in the analysis of the results of intranuclear topology of FISH signals.
Table 6.
Radial localization of NORs in sperm cells nuclei. Percentage (%) of NORs (recognized as FISH signals) in radial areas (a), (c1), (c2 + c3), (p1 + p3), (p2 + p4) and (t) as defined in Fig. 1B and depicted in Fig. 2.
| Radial areas in sperm cell• | a | c1 | c2 + c3 | p1 + p3 | p2 + p4 | t |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carrier | % of NORs | |||||
| R1 rob(13;22) | 21.9* A | 12.4 B | 15.6* | 26.2 H | 17.9 C | 6.0 L |
| Number of NORs signals | 158/720 | 89/720 | 112/720 | 189/720 | 129/720 | 43/720 |
| ∑ of NORs signals = 720 | ||||||
| ∑ of sperm cells = 390 | ||||||
| R2 rob(13;15) | 13.2 1,D | 10.0 | 18.8 E | 38.2* 2,H | 13.8* 3 | 6.0 L |
| Number of NORs signals | 104/786 | 78/786 | 148/786 | 300/786 | 108/786 | 48/786 |
| ∑ of NORs signals = 786 | ||||||
| ∑ of sperm cells = 398 | ||||||
| R3 rob(13;14) | 18.0 F | 12.9 G | 16.7* | 29.2* H | 14.6 | 8.6 L |
| Number of NORs signals | 126/699 | 90/699 | 117/699 | 204/699 | 102/699 | 60/699 |
| ∑ of NORs signals = 699 | ||||||
| ∑ of sperm cells = 351 | ||||||
| Control | 16.1 I | 12.4 J | 21.9 K | 23.4 M | 18.0 | 8.2 L |
| Number of NORs signals | 181/1122 | 139/1122 | 246/1122 | 262/1122 | 201/1122 | 92/1122 |
| ∑ of NORs signals = 1122 | ||||||
| ∑ of sperm cells = 474 | ||||||
•Radial areas according to the scheme shown in Fig. 1B. Radial areas were labeled as follows: (c1) = central; (c2 + c3) = internal,(p1 + p3) = peripheral, near the apical area, (p2 + p4) peripheral, near the tail area, (a) = apical area and (t) = tail area. One-way ANOVA was used to compare results (p ≤ 0.01 was considered to be significantly different). *Values significantly different from Control value (p < 0.01).
HIn cases when the R1, R2 and R3 values in the (p1 + p3) area were highest.
LIn cases when the of R1, R2, R3 and Control values in the t area were highest.
AValue not different only from the (p2 + p4) value.
BValue not different only from the (c2 + c3) value.
CValue not different only from the (c2 + c3) value
DValues of (a), (c1) and (p2 + p4) were not different.
EValue of (c2 + c3) was different from the other areas.
FValue not different only from the (c2 + c3) and (p2 + p4) values.
GValue not different only from the (p2 + p4) values.
IValue not different only from the (c1) and (p2 + p4) values.
JValue not different only from the (a) value.
KValue not different only from the (p1 + p3) and (p2 + p4) values.
MValue not different only from the (c2 + c3) value.
aSignificantly different from the R1 and R3 values.
bSignificantly different from the R1 and R3 values.
cSignificantly different from the R1 value.
Figure 3.
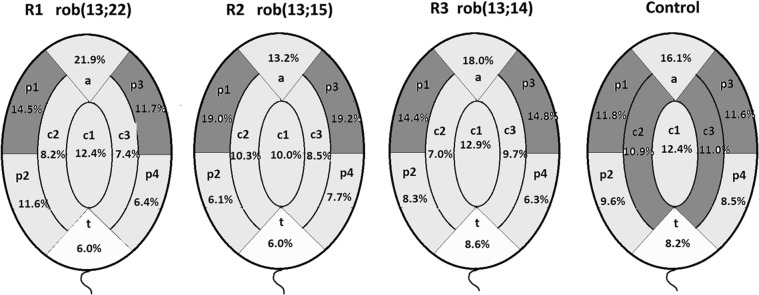
Illustration of the results of the radial localization of NORs in sperm cells from Robertsonian translocation carriers (R1, R2 and R3) and the Control. Values based on the data from Table 6. Values in dark grey mark areas, including (p1 + p3) and in the case of the Control also (c2 + c3), were significantly higher, while the values in the white areas (t) were found to be the lowest (data in Table 6). The division of the sperm cell nucleus into radial areas according to the scheme in Fig. 1B.
Regardless of the significant differences in the results among R1, R2 and R3, the highest percentage of discrete NORs signals (i.e., 26.2%, 38.2%, and 29.2%, respectively) in the sperm cells of all three ROBs were localized in the (p1 + p3) area, while the lowest were localized in the (t) area (6.0%, 6.0% and 8.6%, respectively) (Table 6).
In the case of Control sperm cells, the lowest percent of discrete NORs signals was also found in the (t) area. However, considerably more NORs appeared both in the (p1 + p3) and in (c2 + c3) areas (Fig. 3, Table 6 data). These data indicated a more scattered dispersion of NOR locations in the Control sperm nuclei compared to the locations in sperm nuclei from R1, R2 and R3.
Correlated to the data presented in Fig. 3 (for more details see Suppl. Fig. S2C), the results in radial area p1 were similar to the results in p3 in every studied case (R1, R2, R3 and Control). Hypothetically, such symmetry could indicate a lack of the tendency for preferential localization of NORs on one side of the sperm nucleus or the other (i.e., p1 or p3). However, due to the inability to differentiate between the “back” and the “front” side of fixed sperm nuclei, we could not rule out that the existence of such a preference might remain undetected.
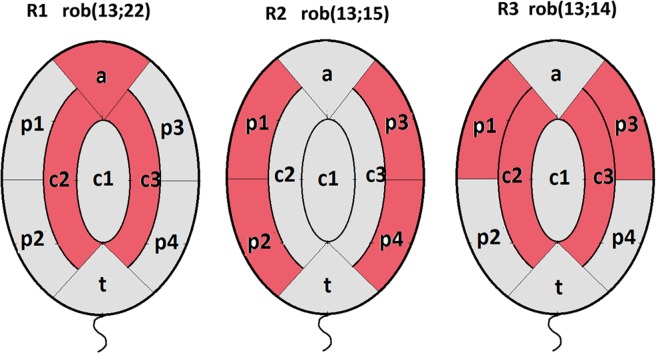
The significant differences in the individual results of R1, R2 and R3 (Table 6) compared to the Control are shown in Fig. 4. For each of the carriers R1, R2, and R3, the differences compared to the Control are marked across different areas, which indirectly illustrate the differences between carriers. Significant differences were not present only in the (c1) and (t) areas.
Figure 4.
Illustration of the differences in the radial localization of NORs in sperm cells from Robertsonian translocation carriers (R1, R2 and R3) compared to the Control (values based on the data from Table 6). The red background illustrates areas with results that were significantly different from the Control values (data in Table 6). The division of the sperm cell nucleus into radial areas according to the scheme shown in Fig. 1B.
Discussion
The relationship between the human sperm intranuclear architecture and the sperm cell function is not fully recognized30,41. However, there is a generally accepted view that changes in sperm chromosome organization may be critical for pronuclear chromatin remodelling, which in consequence may disturb the transmission of paternal chromosomal information to the zygote31.
Sperm cell chromosomes are approximately 6 times more tightly condensed when compared to the chromosomes of somatic cells42,43, and sperm FISH studies have shown that whole chromosomes are preferentially ordered along the head-tail axis and occupy individual territories33,43–46. Several concepts have been presented for the model of intranuclear architecture of human sperm cells. First a structural layout of the sperm DNA/chromatin has been presented in the so-called donut-loop model32. The so-called hairpin-loop model, the model based on double normalized, preferential 2D-FISH data, assumes that heterochromatin of chromosome centromeres form an inner one to three clusters in the interior area of the nucleus called the chromocentre. At the same time, chromosome telomeres have been preferentially located at the nuclear periphery of the nucleus forming dimers and tetramers43,44,46. More recent studies performed using a confocal microscope (3D-FISH) have shed additional light on the knowledge of topology of sperm chromosomes33,39,45. Confocal microscope data have suggested that sperm nuclei centromeres cluster to form multiple chromocentres (with an average of 7 chromocentres observed per cell) that display a more segmented organization occupying discrete locations with preferential (92%) intermediate and peripheral localizations. Moreover, the organization of dimers or tetramers of telomeres is more segmental with a significant proportion of telomeres clustering to form a “belt” in the mid part of the sperm nucleus39.
The results of the research performed so far indicate that all the factors that have been analysed with respect to their negative influence on spermatogenesis (e.g., chromosomal reciprocal translocations and high DNA fragmentation) can disrupt the architecture of sperm nucleus33,35–37,47,48.
Having analysed the dispersions of NORs in the reported studies (recognized as 2D-FISH discrete signals), we found changes in the nuclear architecture in spermatozoa from Robertsonian translocation carriers in comparison to control sperm cells.
To date, only few studies have examined the effects of chromosomes with Robertsonian translocations on nuclear organization in mammalian germ cells49–52. In mouse germ cells from heterozygous carriers of multiple Robertsonian translocations, Garagna et al.49 showed an altered nuclear organization in spermatocytes and spermatids. Berríos et al.50 showed that meiotic architecture of mouse spermatocytes with Robertsonian chromosomes is prone to modification by chromosomal rearrangements. Moreover, the results of Solé et al.51 provided the first evidence of a chromosome territorial alteration in the presence of a Robertsonian translocation in metaphase I of human spermatocytes. In turn, the results presented by Acloque et al.52 showed that boar Robertsonian translocation t(13;17) does not significantly alter sperm nucleus architecture, but they suggested that centromere remodelling after chromosome fusion locally impacts chromosome positioning52.
In the present study, the topology of NORs in sperm cells from three Robertsonian carriers, namely rob(13;22), rob(13;15) and rob(13;14), was analysed. The common feature of these translocations was that they were related to chromosome 13, and all three carriers had the same percentage of normal sperm cells (i.e., approximately 40%). Moreover, in each case, the minority of the sperm cells (i.e., less than 25%) were genetically unbalanced (Table 1). These results were in line with other studies, in which a majority (72.2–96.6%) of sperm originated by alternate segregation17–29.
We found an altered distribution of NORs in each case of examined ROBs. Such an observation stems mostly from the comparison of the dispersion of NOR signals in the Control sperm cells with normal karyotype (Table 3 for linear and Table 6 with Fig. 4 for radial distribution). The difference with respect to the Control mainly concerned the higher percentage (%) of discrete NOR signals found in the apical area (Table 3). However, in the sperm cells of ROB carriers and of the Control, the majority of NORs (i.e., greater than 50%) were localized in the (M) area (Table 3).
Interestingly, we observed a tendency of NOR clustering and colocalization in particular areas of the nucleus both in ROB carriers and in the Control. Both in ROB carriers and Control sperm cells, we found out that NORs showed a tendency towards two discrete FISH signals (Table 4). In the case of the sperm cells from ROB carriers, one or two signals were observed in as many as 72% of the sperm cells. This percentage was significantly more than in the Control (58%), which can indicate a lower tendency towards grouping (Table 4). In the case of clusters formed by two or three acrocentric chromosomes (73.5% of Control sperm cells), it is unknown whether they were preferentially formed by the same chromosomes in different sperm cells or if the grouping was random in individual sperm cells. Unfortunately, the applied FISH probes did not allow us to make such a distinction. NORs are located on the short arms of the five acrocentric chromosomes between centromeric and telomeric heterochromatin. Because the sequences in this region are conserved, the FISH signals are consistent among different NORs40.
In addition, our research showed that both in sperm cells of ROB carriers and the Control, the discrete NORs signals were localized mostly in the medial area of the nucleus (Table 3 and Fig. 2). However, in the case of the ROB carriers, the localization mostly appeared in the peripheral part of the medial area in contrast to Control sperm cells in which the distribution was more dispersed towards the internal area (Fig. 3, Table 6).
In contrast to transcriptionally non-active haploid sperm cells, there are 10 NOR sequences in most diploid human cells that contribute to the formation of nucleoli which are the sites of ribosome biogenesis10,16. NORs coalesce to form mostly one to several nucleoli which disintegrated during mitosis40,51,53,54 (for the representative image of 2D-FISH of NORs in diploid cell see Suppl. Fig. S3). The localization of nucleoli has been examined also during mammalian spermatogenesis. NORs have been observed using silver staining during the entire period of the meiotic prophase up to methaphase I55,56. It has been suggested that the association among NOR-bearing chromosomes mainly depends on the presence of constitutive heterochromatin, which is a key element in the nuclear architecture of spermatocytes52. Moreover, it has been shown that the round spermatid contains a distinct nucleolus, indicating that some, if not all, of NORs are clustered together in a structural unit57. Because later stages of the spermatid do not exhibit a predominant nucleolus, it has been suggested that the structure has begun to segregate into separate chromosomes58.
The first evidence of the tendency of NORs to colocalize in mature human sperm cells from fertile control men was suggested in a report of Gurevitz et al.38. The analysis of dispersion was narrowed only to sperm cells showing five discrete FISH signals, which limited the comparison with our data38. The results demonstrated that the centromeres of the five acrocentric chromosomes are positioned close to each other as reflected by their non-random proximity but that their localization is not stable among the different sperm cell nuclei.
In Syrian hamster sperm cells, which have five NOR-bearing chromosomes, sperm nuclei are most commonly (64%) observed to have four or five irregularly distributed distinct FISH signals (using 28S rRNA gene as a probe)58. A clear tendency for colocalization at the equatorial region of the nucleus has also been observed in equine sperm cells59.
A tendency of non-random colocalization of human acrocentric chromosomes in the central area within the sperm nucleus has also been noted by a 3D-FISH45. Ioannou et al.39 showed that the radial and longitudinal topology of NORs is non-randomly organized and highly reproducible among the sperm cells from 10 fertile control men enrolled in the study. In these studies, a single or five distinct NOR signals were rarely observed in sperm cells (<10%), but NORs predominantly formed three to four discrete signals (>63%)39. In our research, NORs in sperm cells from the fertile Control predominantly formed two or three NORs signals (73.5%). The above data together can suggests that in control sperm cells with “healthy nuclear state” NORs predominantly form two to four clusters relatively evenly dispersed in the medial/internal area. In the studies performed so far, it is not possible to determine if clusters are preferentially form by NORs located on these same acrocentric chromosomes39. It can only be speculated that the tendency of NORs towards cluster formation depends mainly on the presence of constitutive heterochromatin, which embeds rDNAs, suggesting that it is probably not chromosome specific.
The results of the present studies showed that similar to the existence of reciprocal translocations37, the existence of Robertsonian translocations affects the sperm chromosome topology. It is known that there are often infertility problems among ROBs carriers and it is assumed that these problems stem from meiotic disorders. It is therefore difficult to assess the potential implications of the observed repositioning of NORs on the sperm cell function at the current state of the art. Still, an open question remains of how the nucleolus initially forms de novo during early embryogenesis in humans5. Some inconsistencies among the previously published data undoubtedly complicate the interpretation30,31,39,44. Some authors suggest that even if spermatogenesis is compromised, the reorganization of the nuclear architecture is a robust process and topological differences between infertile and fertile males are rather modest48. By contrast, the differences in the localization of sperm chromosomes between sperm cells of fertile and infertile men indirectly confirm the hypothesis that changes in the organization of sperm chromosomes may disrupt the transmission of paternal chromosomal information to the zygote30,31. However, it must be noted that the conclusions regarding the repositioning of the chromosomes of infertile sperm cells are based on significant differences between the investigated parameters with respect to control sperm cells. By contrast, the observations of the target loci in individual sperm cells (also in the control) (2D or 3D-FISH) show such a great variation that we can put a hypothesis that the model(s) layout31,39,44,60 is not directly reflected in any single sperm cell. To paraphrase, sperm cells apparently do not know that they should follow a particular layout.
In summary, according to our knowledge, this is the first study based on human sperm cells, whose goal was to investigate if ROBs carriers show changes in the localization of sperm cell acrocentric chromosomes. On the basis of the NORs analysis in three different ROBs we can only suggest the following: (1) in ROBs carriers there can be perturbations in nuclear organization of sperm acrocentrics, (2) in the case of NORs clusters, there is a tendency to repositioning toward the periphery of the nucleus, and (3) between the carriers, there can be individual differences in nuclear spatial arrangement of the loci that we examined. There are two probable sources of these differences. First, different acrocentric chromosomes are involved in different ROBs. Second, in the sperm cells of over half of ROB carriers, there is an aneuploidy of chromosomes that are not involved in translocations – in our earlier study we showed the presence of dislocated centromere positions in human sperm cells with aneuploidies35. However, the answer to the question whether carriers of different ROBs show particular topological features will require future studies on a larger group of carriers of different ROBs.
Materials and Methods
Male participants
This study was approved by the Local Bioethical Committee at the Poznan University of Medical Sciences, Poland, and informed consent was obtained from all subjects. We should like also to confirm that all experiments were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. The collected patient group consisted of three Robertsonian carriers (ROBs) with reproductive failures. The carriers aged between 30 to 35 years were selected for the study after attending infertility clinics due to the lack of conception over a 5-year period. Two patients were diagnosed as rob(13;22) and rob(13;14) in Lviv (N. Huleyuk), and one patient from Moscow (V. Chernykh) was diagnosed as a carrier of rob(13;15). The Robertsonian carriers were coded as follows: R1 = rob(13;22), R2 = rob(13;15), and R3 = rob(13;14). The analysis of meiotic segregation patters and analysis of localization of NORs were performed in sperm nuclei of carriers R1, R2 and R3. Additionally, analyses of NORs were performed in control sperm nuclei. Sperm cells from a normozoospermic volunteer, who has proven fertility, a normal karyotype, and has attended the Andrology Outpatient in Poznań (M. Kurpisz), served as the control.
Semen collection and processing
Semen samples were obtained by masturbation after 3–5 days of sexual abstinence. After liquefaction of ejaculate (at room temperature), routine semen analyses were performed according to the World Health Organization 2010 criteria61. General semen assessment of carriers R1, R2, R3 and the control volunteer is presented in Suppl. Table S1. Sperm cells were separated from seminal plasma by centrifugation at 600 g for 8 minutes. An aliquot of sperm suspension was washed three times in phosphate buffer saline (PBS; pH 7.4) and processed for FISH analysis.
FISH (fluorescence in situ hybridization) procedure and DNA probes
After a PBS wash, sperm cells were fixed with a fresh, cold fixative solution (methanol: acetic acid 3:1 v/v, −20 °C) for 20 min. After three rinses with the fixative, sperm samples were spread onto slides and air-dried. Prior to FISH reactions, mild decondensation of nuclei was performed, which is a prerequisite for sperm nuclei analysis. Slides were washed two times in PBS and plunged into a solution of 10 mM dithiothreitol (DTT, Sigma, St. Louis, MO, USA) in 0.1 M Tris-HCL (pH 8.5) for 5–10 min in 43 °C. The decondensation of sperm nuclei was verified under a phase-contrast microscope. Under this mild procedure, the sperm cells had a well-defined boundary, and the sperm tails were attached to their heads and nuclei were minimally swollen47. Importantly, it has been shown previously that this procedure does not alter the morphology and nuclear topology38,62. The slides were rinsed twice in 2x SSC, dehydrated in an ethanol dilution from 70% to 100% and air-dried.
FISH experiments for analysis of meiotic segregation patterns were performed using red or green directly labelled probes from Cytocell Technologies Ltd. (Cambridge, UK) according to the manufacturer’s guideline. This study used 13 wcp red (whole chromosome paint, Texas Red) and 14, 15 or 22 wcp green (whole chromosome paint, FITC) probes. The use of wcp probes required only a moderate sperm decondensation to provide high hybridization efficiency. The wcp method allowed the distinguishment of both normal spermatozoa (with two clearly separated signals of different colour) and balanced spermatozoa (with two signals of different colour coupled one with the other). FISH experiments for the identification of nuclear organizing regions (NORs) were performed using directly labelled Acro-P-Arms NOR red probes from Kreatech Biotechnology B.V. (distributed by Leica Biosystems, UE). Simultaneously, we used an alpha-satellite centromeric chromosome 7 green probe (FITC) to control hybridization efficiency. We utilized the manufacturer’s standard protocol. The hybridization mixture (probes plus hybridization buffer) was applied to the slide, covered with a coverslip and sealed with Fixogum. The probes and cellular DNA were co-denatured simultaneously for 5 min at 75 °C.
Hybridization was performed overnight in a moist chamber at 37 °C. Post-hybridization washes of slides were performed by incubation without agitation for 2 min in 0.4x SCC at 72 °C followed by incubation for 30 sec in 2x SCC/0.5% Tween 20 at 24 °C. Slides were air-dried for several minutes at RT, and 15 µl of DAPI/antifade counterstain was applied. Hybridization signals were observed using the Olympus Bx41 microscope fitted with filters for DAPI/FITC/TEXAS Red and an oil immersed objective 100 × (1.25 NA). Images were captured and archived using a CCD camera and ISIS (MetaSystems, Germany) software. The overall efficiency of FISH was approximately 98–99%. Sperm nuclei were scored according to standard, published criteria37. The analysis criterion was not the size of the FISH signal/s but the number of clearly separated, distinguished signals.
Determination of NOR positioning in sperm nuclei of Robertsonian carriers and control volunteers
To determine the intranuclear position of NORs in examined sperm nuclei, we applied the graphic schemes shown in Fig. 1A,B for the longitudinal and radial localizations, respectively. The schemes included typical ellipsoid shape of the sperm cell where the length to width ratio is ca. 2. The linear analysis was performed as per previous studies for 2D FISH37. As presented in Fig. 1A, three contractual linear areas based on the tail-head distance, namely A, M and T, within the nucleus were designated. The distribution of each FISH signal was assigned to a selected area. In the case of Fig. 1B, nine contractual radial areas, namely a, c1, c2, c3, p1, p2, p3, p4, and t, were designated.
Statistical analysis
The data were analysed using STATISTICA version 7.0 (StatSoft, Tulsa, OK, USA.). One-way ANOVA test was utilized to compare results between patients and control values, and the Chi-squared test was used to compare the frequencies of adjacent and alternate segregation patterns as well as to compare the distribution of signals in nuclear areas. Statistically significant differences were considered as p-value ≤ 0.01.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Science Centre, grant no. 2015/17/D/NZ5/03442 to M.O. and grant no. 2015/17/B/NZ2/01157 to M.K.
Author Contributions
E.W. conceptualized the project, performed the NOR analyses, interpreted results, and wrote the manuscript; M.O. provided funding and performed the meiotic segregation patterns analyses; N.H. and V.B.Ch. identified ROB carriers by GTG karyotyping; M.K. provided funding, provided biological material, and finalized the manuscript.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary information accompanies this paper at 10.1038/s41598-019-38478-x.
References
- 1.Robertson, W. R. B. Chromosome studies. I. Taxonomic relationships shown in the chromosomes of Tettigidae and Acrididae. V-shaped chromosomes and their significance in Acrididae, Locustidae and Gryllidae: chromosome and variation. J. Morph. 27, 179-331 (1916).
- 2.Page SL, et al. Breakpoint diversity illustrates distinct mechanisms for Robertsonian translocation formation. Hum. Mol. Gene.t. 1996;5:1279–1288. doi: 10.1093/hmg/5.9.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Bandyopadhyay R, et al. Parental origin and timing of de novo Robertsonian translocation formation. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002;71:1456–62. doi: 10.1086/344662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Song J, et al. A family with Robertsonian translocation: a potential mechanism of speciation in humans. Mol. Cytogenet. 2016;18(9):48. doi: 10.1186/s13039-016-0255-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.McStay B. Nucleolar organizer regions: genomic ‘dark matter’ requiring illumination. Genes Dev. 2016;15(30):1598–610. doi: 10.1101/gad.283838.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kim SR, Shaffer LG. Roberstonian translocations: mechanisms of formation, aneuploidy, and uniparental disomy and diagnostic considerations. Genet. Test. 2002;6:163–168. doi: 10.1089/109065702761403315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mau-Holzmann UA. Somatic chromosomal abnormalities in infertile men and women. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2005;111:317–336. doi: 10.1159/000086906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Han JY, Choo KH, Shaffer LG. Molecular cytogenetic characterization of 17 rob(13q14q) Robertsonian translocations by FISH, narrowing the region containing the breakpoints. Am. J Hum. Genet. 1994;55:960–967. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Morel F, et al. Meiotic segregation of translocations during male gametogenesis. Review. Int. J. Androl. 2004;27:200–212. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2004.00490.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stults DM, Killen MW, Pierce HH, Pierce AJ. Genomic architecture and inheritance of human ribosomal RNA gene clusters. Genome Res. 2008;18:13–18. doi: 10.1101/gr.6858507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Therman E, Susman B, Denniston C. The nonrandom participation of human acrocentric chromosomes in Robertsonian translocations. Ann. Hum. Genet. 1989;53:49–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-1809.1989.tb01121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Keymolen K, et al. Pregnancy outcome in carriers of Robertsonian translocations. Am. J. Med. Genet. A. 2011;155A:2381–2385. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.33941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhao WW, et al. Robertsonian translocations: an overview of 872 Robertsonian translocations identified in a diagnostic laboratory in China. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0122647. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Nielsen J, Wohlert M. Chromosome abnormalities found amond 34,910 newborn children: results from a 13-year incidence study in Arhus, Denmark. Hum. Genet. 1991;85:49–54. doi: 10.1007/BF01213097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Shaffer LG. Risk estimates for uniparental disomy following prenatal detection of a nonhomologous Robertsonian translocation. Prenat. Diagn. 2006;26:303–307. doi: 10.1002/pd.1384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Roux C, et al. Segregation of chromosomes in sperm of Roberstonian translocation carriers. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2005;111:291–296. doi: 10.1159/000086902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Anton E, Blanco J, Egozcue J, Vidal F. Sperm FISH studies in seven male carriers of Robertsonian translocation t(13;14)(q10; q10) Hum. Reprod. 2004;19:1345–1351. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deh232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Anton E, Blanco J, Vidal F. Meiotic behavior of three D;G Robertsonian translocations: segregation and interchromosomal effect. J. Hum. Genet. 2010;55:541–545. doi: 10.1038/jhg.2010.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ogur G, et al. Chromosomal segregation in spermatozoa of 14 Robertsonian translocation carriers. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2006;12:209–215. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gah253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Brugnon F, et al. Apoptosis and meiotic segregation in ejaculated sperm from Robertsonian translocation carrier patients. Hum. Reprod. 2010;25:1631–1642. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deq113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mahjoub M, et al. Chromosomal segregation in spermatozoa of five Robertsonian translocation carriers t(13;14) J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2011;28:607–13. doi: 10.1007/s10815-011-9560-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Bernicot I, et al. Analysis using fish of sperm and embryos from two carriers of rare rob(13;21) and rob(15;22) robertsonian translocation undergoing PGD. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2012;55:245–51. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2012.02.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rogenhofer N, et al. Case report: elevated sperm aneuploidy levels in an infertile Robertsonian translocation t(21;21) carrier with possible interchromosomal effect. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2012;29:343–346. doi: 10.1007/s10815-012-9720-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Vozdova M, et al. Balanced chromosomal translocations in men: relationships among semen parameters, chromatin integrity, sperm meiotic segregation and aneuploidy. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2013;30:391–405. doi: 10.1007/s10815-012-9921-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pylyp LY, Zukin VD, Bilko NM. Chromosomal segregation in sperm of Robertsonian translocation carriers. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2013;30:1141–11415. doi: 10.1007/s10815-013-0067-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Godo A, et al. Altered segregation pattern and numerical chromosome abnormalities interrelate in spermatozoa from Robertsonian translocation carriers. Reprod. Biomed. Online. 2015;31:79–88. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2015.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Luciani JM, Guichaoua MR, Mattei A, Morazzani MR. Pachytene analysis of a man with a 13q;14q translocation and infertility. Behavior of the trivalent and nonrandom association with the sex vesicle. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1984;38:14–22. doi: 10.1159/000132023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Dutrillaux B, Lejeune J. Study of progeny of individuals bearing a t(DqDq) translocation. Ann. Genet. 1970;13:11–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Acar H, Yildirim MS, Cora T, Ceylaner S. Evaluation of segregation patterns of 21;21 Robertsonian translocation along with sex chromosomes and interchromosomal effects in sperm nuclei of carrier by FISH technique. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2002;63:232–236. doi: 10.1002/mrd.10166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ioannou D, Tempest HG. Does genome organization matter in spermatozoa? A refined hypothesis to awaken the silent vessel. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2018;2:1–17. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2017.1421278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zalensky A, Zalenskaya I. Organization of chromosomes in spermatozoa: an additional layer of epigenetic information? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2007;35:609–611. doi: 10.1042/BST0350609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Ward WS. Function of sperm chromatin structural elements in fertilization and development. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 2010;16:30–36. doi: 10.1093/molehr/gap080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Alladin N, et al. The three-dimensional image analysis of the chromocenter in motile and immotile human sperm. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2013;59:146–152. doi: 10.3109/19396368.2013.772679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Finch KA, et al. Nuclear organisation in human sperm: preliminary evidence for altered sex chromosome centromere position in infertile males. Human Reprod. 2008;23:1263–1270. doi: 10.1093/humrep/den112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Olszewska M, Wiland E, Kurpisz M. Positioning of chromosome 15, 18, X and Y centromeres in sperm cells of fertile individuals and infertile patients with increased level of aneuploidy. Chromosome Res. 2008;16:875–890. doi: 10.1007/s10577-008-1246-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Olszewska M, Wanowska E, Wiland E, Kurpisz M. Genetic dosage and position effect of small supernumerary marker chromosome (sSMC) in human sperm nuclei in infertile male patient. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:17408. doi: 10.1038/srep17408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wiland E, Zegało M, Kurpisz M. Interindividual differences and alterations in the topology of chromosomes in human sperm nuclei of fertile donors and carriers of reciprocal translocations. Chromosome Res. 2008;16:291–305. doi: 10.1007/s10577-007-1194-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gurevitch M, et al. Acrocentric centromere organization within the chromocenter of the human sperm nucleus. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2001;60:507–516. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ioannou D, Millan NM, Jordan E, Tempest HG. A new model of sperm nuclear architecture following assessment of the organization of centromeres and telomeres in three-dimensions. Sci. Rep. 2017;7:41585. doi: 10.1038/srep41585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Floutsakou I, et al. The shared genomic architecture of human nucleolar organizer regions. Genome Res. 2013;23:2003–2012. doi: 10.1101/gr.157941.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Miller D, Brinkworth M, Iles D. Paternal DNA packaging in spermatozoa: more than the sum of its parts? DNA, histones, protamines and epigenetics. Reproduction. 2010;139:287–301. doi: 10.1530/REP-09-0281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Noblanc A, Kocer A, Drevet JR. Recent knowledge concerning mammalian sperm chromatin organization and its potential weaknesses when facing oxidative challenge. Basic Clin. Androl. 2014;24:6. doi: 10.1186/2051-4190-24-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mudrak O, Tomilin N, Zalensky A. Chromosome architecture in the decondensing human sperm nucleus. J. Cell Sci. 2005;118:4541–4550. doi: 10.1242/jcs.02581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Zalenskaya I, Zalensky AO. Non-random-positioning of chromosomes in human sperm nuclei. Chromosomes Res. 2004;12:163–173. doi: 10.1023/B:CHRO.0000013166.04629.97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Manvelyan M, et al. Chromosome distribution in human sperm - A 3D multicolor banding-study. Mol. Cytogenet. 2008;1:25. doi: 10.1186/1755-8166-1-25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Zalensky, et al. Well-defined genome architecture in the human sperm nucleus. Chromosoma. 1995;103:577–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00357684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wiland E, Fraczek M, Olszewska M, Kurpisz M. Topology of chromosome centromeres in human sperm nuclei with high levels of DNA damage. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:31614. doi: 10.1038/srep31614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Ioannou D, et al. Nuclear organization of sperm remains remarkably unaffected in the presence of defective spermatogenesis. Chromosome Res. 2011;19:741–753. doi: 10.1007/s10577-011-9238-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Garagna S, et al. Alteration of nuclear architecture in male germ cells of chromosomally derived subfertile mice. J Cell Sci. 2001;114:4429–4434. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.24.4429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Berríos S, et al. Robertsonian chromosomes and the nuclear architecture of mouse meiotic prophase spermatocytes. Biol. Res. 2014;47:16. doi: 10.1186/0717-6287-47-16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Solé, et al. Altered bivalent positioning in metaphase I human spermatocytes from Robertsonian translocation carriers. J Assist Reprod. Genet. 2017;34:131–138. doi: 10.1007/s10815-016-0809-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Acloque H, et al. Sperm Nuclear Architecture Is Locally Modified in Presence of a Robertsonian Translocation t(13;17) PLoS One. 2013;8:e78005. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Berrios S. Nuclear architecture of mouse spermatocytes:chromosome topology, heterochromatin, and nucleolus. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2017;151:61–71. doi: 10.1159/000460811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kalmárová M, et al. Positioning of the NOR-Bearing Chromosomes in Relation to Nucleoli in Daughter Cells after Mitosis. Physiol. Res. 2008;57:421–425. doi: 10.33549/physiolres.931430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Schmid M, Müller H, Stasch S, Engel W. Silver staining of nucleolus organizer regions during human spermatogenesis. Spermatogeneza. Hum. Genet. 1983;64:363–370. doi: 10.1007/BF00292368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Sarrate Z, Blanco J, Vidal F. Acrocentric bivalents positioned preferentially nearby to the XY pair in metaphase I human spermatocytes. Fertil. Steril. 2012;98:1241–1245. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2012.07.1110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sousa M, Carvalheiro JA. Cytochemical study of the nucleolus and nucleolus-related structures during human spermatogenesis. Ana. Embryol. (Berl). 1994;190:479–487. doi: 10.1007/BF00235495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Nadel B, De Lara J, Ward WS. Structure of the rRNA genes in the hamster sperm nucleus. J. Androl. 1995;16:517–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wnuk M, et al. Nucleolar organizer regions (NORs) distribution and behavior in spermatozoa and meiotic cells of the horse (Equus caballus) Theriogenology. 2012;77:579–587. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2011.08.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mudrak OS, Nazarov IB, Jones EL, Zalensky AO. Positioning of chromosomes in human spermatozoa is determined by ordered centromere arrangement. PLoS One. 2012;7:e52944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.World Health Organization WHO, laboratory manual for the examination of human semen and sperm-cervical mucus interaction, 5th ed., Cambridge University Press, New York (2010).
- 62.Celik-Ozenci C, et al. Human sperm maintain their shape following decondensation and denaturation for fluorescent in situ hybridization: shape analysis and objective morphometry. Biol Reprod. 2003;69:1347–1355. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.103.019596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.