Abstract
Objective:
Some patients lack regular computer access and experience a digital divide that causes them to miss internet-based health innovations. The diffusion of smartphones increased internet access across the socioeconomic spectrum, and increasing the channels through which patients can access their personal health records (PHRs) could help bridge the divide in PHR use. We examined PHR use through a computer-based web browser or mobile device.
Study Design:
Cross-sectional, historical cohort analysis.
Methods:
Among adult patients in the diabetes registry of an integrated delivery system, we studied the devices used to access their PHR during 2016.
Results:
Among 267,208 patients with diabetes, 68% used the PHR in 2016: 60.6% of all log-ins were via computer and 39.4% via mobile device. Among users, 64% used it from both a computer and mobile device, 30% used only a computer, and 7% only a mobile device. After adjustment, patients who were Black, Hispanic, or Asian, lived in lower socioeconomic status (SES) neighborhoods, or had lower engagement were all significantly more likely to use the PHR only by mobile device (p<0.05). Patients using PHR only via mobile device used it less frequently.
Conclusions:
Mobile-accessible PHRs may increase access among patients facing a digital divide in computer use, disproportionately reaching racial/ethnic minorities and lower SES patients. Nonetheless, even with a mobile-optimized and app-accessible PHR, differences in PHR use by race/ethnicity and SES remained. Continued efforts are needed to increase equitable access to PHRs among patients with chronic conditions.
Précis:
Minorities and patients living in poorer neighborhoods were more likely to access their personal health record exclusively with a mobile device.
Introduction
While more than 200,000 health-promoting mobile apps are available for patient download, with 1.7 billion users worldwide, research is needed to identify the clinical usefulness of mobile tools in self-management and care quality for patients.1,2 Importantly, the vast majority of these apps lack any integration with patients’ ongoing healthcare services and providers.3,4 Apps that are integrated with a clinical electronic health record (EHR) and that make patient-reported data available to clinicians may hold the most promise to improve well-coordinated, high-quality healthcare delivery. Within healthcare, this timely expansion to mobile-connected devices complements the growing availability of personal health records (PHRs). PHRs could be particularly relevant for patients with chronic conditions such as diabetes who require ongoing self-management that can be facilitated via PHRs.
However, the long-standing digital divide, defined as the gulf between individuals with and without ready access to the internet, has been well-documented.5 EHR requirements from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS, Stage 3 meaningful use objectives) include that physicians provide patients with electronic access to their health records and tailored patient education via web-based tethered personal health record (PHR) that is linked to the patient’s EHR, also known as a patient portal.6 While meaningful use financial incentives continue to promote the widespread adoption of PHRs among eligible providers, they do not require that PHRs be easily accessible via mobile devices.6 With only computer-based access, many patients might be left out.
As a result of the digital divide, previous research found that use of computer-based PHRs has been consistently lower among racial and ethnic minorities and patients with lower education and health literacy.7–13 Recently, the diffusion of smartphone technology has increased mobile access to the internet and smartphone applications (apps) among individuals most likely affected by the digital divide, including those with lower socioeconomic status (SES) and racial/ethnic minorities.14 Mobile-accessible PHRs can help engage patients in managing their health through convenient and timely access to personal health data, provider messaging, refilling prescriptions, or scheduling appointments.15 With many healthcare innovations, specifically advancements in PHRs, changes have favored those who have social advantage, such as higher education, greater income or wealth, greater knowledge of how to navigate the healthcare system, and non-minority race/ethnicity. In this manuscript, we focus specifically on a different type of technological innovation, the introduction PHRs that are more easily accessible using mobile devices.
Diabetes is more prevalent among lower SES and racial/ethnic minorities.16 Patients with diabetes often have other chronic conditions with complex clinical needs that require ongoing self-management.17–19 Diabetes self-management is crucial, requiring extensive self-monitoring, adherence to medications, proper diet, and adequate exercise.20 Any practical realization of a model for coordinated, safe care must rely heavily on timely availability and use of comprehensive electronic clinical information, not only available to providers through an EHR but also to patients through a PHR.21–23 Previous studies found that PHR use was associated with improved diabetes quality measures.15,24–26 Thus, mobile-accessible PHRs could be particularly relevant for patients with diabetes. Yet, in the absence of mobile-accessible PHRs, we found that lack of computer access accounted for most of the variation in PHR use by race and income.13 Consequently, we expect that mobile access to PHRs may facilitate PHR use among individuals who are mobile dependent. Little is known about use of PHRs that are easily accessible and optimized for use via mobile devices.
Within an integrated delivery system that provided all member with multiple channels to access their PHR, we examined the channel through which an adult population of patients with diabetes used their PHR (i.e., through a computer-based web browser, smartphone-accessible website, or mobile apps). We also assessed the association between patient characteristics and PHR use via mobile device.
Methods
Setting.
Kaiser Permanente Northern California is an integrated delivery system that provides comprehensive care, including inpatient, outpatient and pharmacy services, to more than 3 million members via employer-sponsored, individual, or publicly-sponsored insurance. Members who register to use the password-protected patient PHR can access it free of charge via computer browser, mobile-optimized website, or mobile apps. The computer-based web-portal has been available to members for over 10 years. The mobile-optimize website and Android or iOS apps have been available to members since 2013. The PHR offers a number of services, including the ability to exchange secure messages with providers on their healthcare team, view lab results, request medication refills, view portions of their health records, schedule office visits, and pay bills. The mobile-accessible and computer-browser versions of the PHR offered comparable functions, although features changed slightly over time.
Study Population.
Our study population included all adult (ages 18+) members of an integrated delivery system (IDS), Kaiser Permanente Northern California, who were in the health plan diabetes clinical registry as of the last quarter of 2015. We chose to focus on patients with diabetes in order to examine patients with a chronic condition that would likely have ongoing need for healthcare services and self-management functions available in PHRs. This analysis was part of a larger study focused on how patients with diabetes use technology to manage care. We included all patients who maintained continuous health plan coverage in 2016. Since our study focuses on patient characteristics, we excluded PHR use via designated proxies.
Data and measures.
We used automated datasets to capture PHR use by channel (mobile app, mobile website, or computer browser) in 2016 among the full study population. To calculate PHR use counts, we identified use episodes by counting the number of days during the year with any PHR use (e.g., multiple log-ins in one day counted as a single episode). In addition, we measured if patients used three key PHR functions (order prescription refill, send secure message, or view lab result) at any time in 2016. We also used electronic health record data to capture patient characteristics (age, gender, race/ethnicity) and linked patients’ residential addresses to 2010 U.S. Census measures of education and income to define neighborhood SES at the census block group level. Census block groups are defined as neighborhoods of lower socioeconomic status if at least 20 percent of residents have household incomes below the federal poverty level or at least 25 percent of residents 25 years of age or older have less than a high school education.27 We also identified patients’ additional chronic conditions, in addition to diabetes, during the last quarter of 2015 with the health plan’s clinical chronic condition registries for asthma, coronary artery disease, heart failure, and hypertension. As an indicator of patient engagement in 2015, we used clinical quality registries to create an overall measure of patients’ histories of adherence to chronic condition medications (with 80% or more days covered by medications) and adherence to preventive care recommendations (up-to-date flu shot, blood pressure measure, LDL measure, and HbA1C measure for those with diabetes). We categorized patients as being highly engaged in their care if they were adherent to both their chronic condition oral medications for diabetes, hypertension, or cholesterol (≥80% of proportion of days covered) and recommended preventive care services (flu vaccine and HbA1c, Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Tests, and blood pressure screening) in 2015.
Statistical Analysis.
We studied patient characteristics associated with the channel(s) used to access the PHR during 2016 (both computer and mobile, computer only and mobile only). We used multivariable logistic regression to measure the association between PHR use (any use in 2016 vs. no use) and patient characteristics. We used multinomial logistic regression to measure the association between device used (mobile only, computer only, or both mobile and computer) among PHR users and patient characteristics (age, gender, race/ethnicity, neighborhood SES, number of chronic conditions, and health engagement). For both models, we calculated the adjusted percent of patients using the PHR and device type by patient characteristics, assuming patients in the subgroup had the same other characteristics as the full study population (margins command in Stata). We included the main effects of each covariate and first order interaction of all covariates (except for age group and number of other chronic conditions due to an empty cell problem). All analyses were conducted using Stata 14.28
The Kaiser Foundation Research Institute Institutional Review Board reviewed and approved the study protocol.
Results
Table 1 shows characteristics of the 267,208 patients with diabetes included in the study and adjusted rates of PHR use in 2016. In that year, 49% were aged 65+, 48% were female, 43.7% were White, 22.6% Asian, 21.6% Hispanic, 10.2% Black, 24.0% lived in low SES neighborhoods, and 75.1% had multiple chronic conditions. Nearly a third of all study patients (31.9%) did not use the PHR in 2016. Over half (58.0%) of patients were categorized as highly engaged, meaning that they were adherent to their oral medications for chronic conditions and received the flu vaccine and recommended screenings for HbA1c, Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Tests, and blood pressure in 2015.
Table 1.
Patient characteristics overall and adjusted percent that used the personal health record (PHR) in 2016 by characteristic
| All Patients (N=267,208) | % Used PHR a (N=181,981) |
||
|---|---|---|---|
| Column % | Adjusted Row % (95% CI) | ||
| Age | 18–<30 | 1.4% | 84.7% (82.4%, 86.9%) |
| 30–<45 | 7.8% | 83.6% (83.1%, 84.2%) | |
| 45–<65 | 41.8% | 73.1% (72.9%, 73.4%) | |
| 65+ | 49.1% | 60.9% (60.6%, 61.2%) | |
| Gender | Male | 52.3% | 68.4% (68.2%, 68.7%) |
| Female | 47.7% | 67.8% (67.6%, 68.1%) | |
| Race/ | White | 43.7% | 78.4% (78.2%, 78.6%) |
| Ethnicity | Black | 10.2% | 57.8% (57.2%, 58.4%) |
| Hispanic | 21.6% | 54.3% (53.9%, 54.7%) | |
| Asian | 22.6% | 67.7% (67.4%, 68.1%) | |
| Other | 1.9% | 62.2% (60.9%, 63.6%) | |
| Neighborhood | Higher | 74.8% | 71.1% (70.9%, 71.3%) |
| SES | Low | 24.0% | 59.5% (59.1%, 59.9%) |
| Unknown | 1.1% | 67.4% (65.6%, 69.1%) | |
| Number of | 1 | 24.9% | 68.9% (68.5%, 69.3%) |
| Chronic | 2 | 54.3% | 68.0% (67.7%, 68.2%) |
| Conditions | 3 | 16.2% | 69.1% (68.7%, 69.5%) |
| 4 | 4.2% | 67.2% (66.4%, 68.1%) | |
| 5 | 0.5% | 66.5% (64.0%, 69.0%) | |
| High Health | No | 42.0% | 64.2% (63.9%, 64.5%) |
| Engagementb | Yes | 58.0% | 71.0% (70.8%, 71.3%) |
Adjusted percentages and 95% confidence intervals calculated using logistic regression results assuming patients in each subgroup have the same distribution of other characteristics as the full study population.
Patients defined as highly engaged in their care if they were adherent to both their chronic condition medications and recommended preventive care services in 2015.
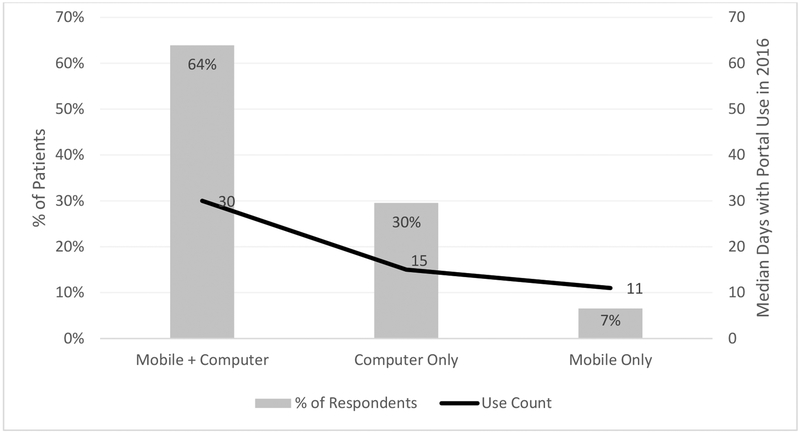
During 2016, 181,981 patients (68.1% of the total number) accessed their PHR 8.9 million times: 60.6% via a computer, 19.9% via mobile device browser, and 19.5% via smartphone apps. Among PHR users, 6.5% used it only with a mobile device, 29.6% only with a computer, and 63.9% used both a computer and mobile devi0063e to access the PHR (Table 2). Patients who accessed the PHR only via a mobile device used it less frequently (median of 11 days with PHR use) than those using only a computer (15 days) or both a computer and mobile device (30 days). Most PHR users used it to view lab results (81.0%), send a secure message (75.8%), and order a prescription refill (66.0%). For the three key functions, use was highest among patients who used both a computer and mobile device and lowest among those who used only a mobile device to access the PHR (Table 2).
Table 2.
Among PHR users (N=181,981), percent of patients who used key PHR functions by device(s) used in 2016
| All PHR users | PHR users by device(s) used in 2016 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Computer and Mobile | Computer only | Mobile only | ||
| Ordered a prescription refill | 66.0% | 73.7% | 54.8% | 40.5% |
| Sent secure message to a provider | 75.8% | 84.1% | 63.2% | 51.8% |
| Viewed lab result | 81.0% | 85.7% | 78.5% | 46.4% |
Adjusted percentages of patients who used the PHR, calculated using results from the multivariable logistic regressions, are shown in Table 1. After adjustment, a higher percentage of patients who were younger (84.7% for ages 18–29), White (78.4%), living in higher SES neighborhoods (71.1%), and highly engaged (71.0%) used the PHR in 2016 compared with those who were older (60.9% for ages 65+), Black (57.8%), Hispanic (54.3%), Asian (67.7%), living in lower SES neighborhoods (59.5%), and not highly engaged in their care (64.2%, all p<0.05).
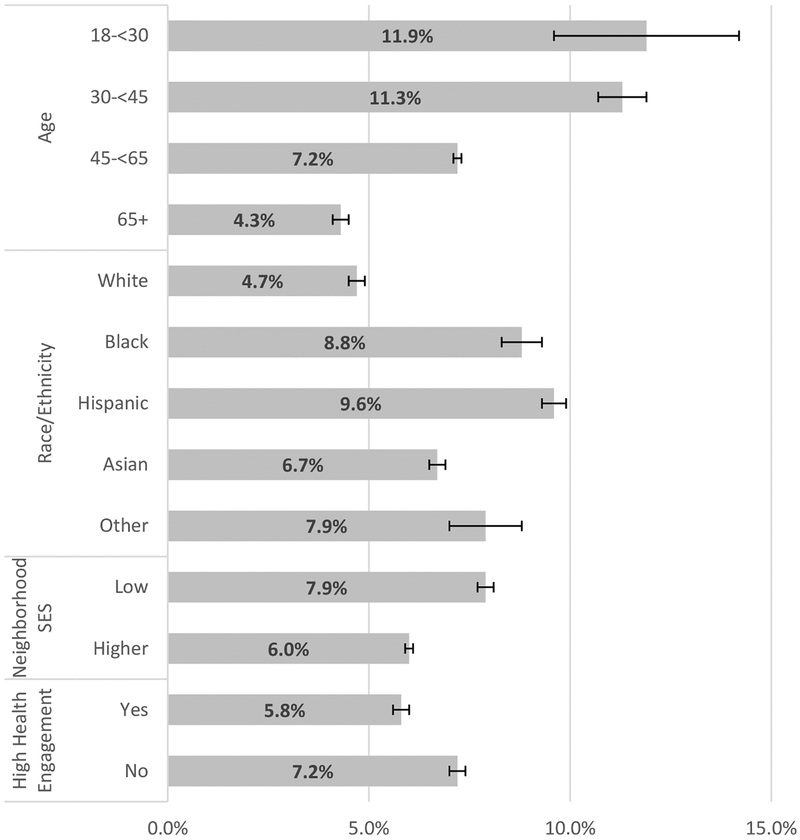
Figure 2 shows the adjusted percentages of PHR users who accessed their PHR only from a mobile device by patient characteristics. After adjustment, a higher percentage of patients who were Black (8.8%), Hispanic (9.6%), Asian (6.7%), living in lower SES neighborhoods (7.9%), younger (11.9% for ages 18–30), or not highly engaged in their health (7.2%) used the PHR only via a mobile device in 2016 relative to those who were White (4.7%), from higher SES neighborhoods (6.0%), older (4.3% for ages 65+), or highly engaged (5.8%, all p<0.05).
Figure 2.
Adjusted percentage of patients using the personal health record (PHR) only by mobile device by patient characteristics in 2016
Note: Adjusted percentages and 95% confidence intervals calculated using logistic regression results assuming patients in each subgroup have the same distribution of other characteristics as the full study population. The model also adjusted for number of chronic conditions and gender. SES=Socioeconomic status.
Discussion
In 2015, a Pew survey found that 64% of U.S. adults owned a smartphone, and 19% relied on smartphones exclusively for internet access.29 In our study of use of a mobile-accessible PHR among patients with diabetes, most PHR users (70%) accessed their PHR with a mobile device at least once and nearly 40% of all PHR logins were done via a mobile device. Among PHR users, nearly 7% accessed the PHR exclusively via a mobile device. Mobile-only PHR users accessed the PHR less frequently than those who used computers. In addition, nearly one-third of patients did not use the PHR at all in 2016. Patients who were Black, Hispanic, or Asian, living in lower SES neighborhoods, or with lower engagement in their care were significantly more likely to access the PHR exclusively using a mobile device in 2016, which is consistent with other reports of mobile-dependent individuals29. It is possible that many of the patients who accessed the PHR only by mobile device were dependent on that device for internet access and would not have had convenient computer access to use the PHR if a mobile option had not been available.
In our previous analyses conducted in 2010, before the PHR was mobile-accessible, we found that computer internet access explained most of the variation in use of secure messaging via the PHR by race/ethnicity and income.13 Thus, the current finding that mobile access is disproportionately reaching members living in lower SES neighborhoods and racial/ethnic minorities is encouraging and suggests that mobile PHR access may, in fact, be helping to bridge the digital divide by reducing disparities in PHR use.
Of note, we found that patients with diabetes that were not considered to be highly engaged in their health (i.e., not previously adherent to chronic condition medications and recommended preventive care services) were significantly more likely to use the PHR exclusively via a mobile device. For patients coping with diabetes and other chronic conditions, which require substantial self-management practices, health engagement is critical to maintaining their health.30 Recent studies of PHR use among patients with diabetes found that it is associated with improved self-management practices and glycemic control.15,24–26 Mobile PHR use could be an important gateway for potentially reaching those patients who previously had limited engagement with preventive care and medication adherence.
The federal government has invested more than $30 billion to promote the widespread adoption of EHRs and tethered PHRs as a way to increase access and quality of care.31 However, these financial incentives do not require that PHRs be easily accessible via mobile devices. In fact, eligible providers caring for patients in regions with low broadband internet access are exempted from meaningful use objectives related to PHRs.6 While it is possible for patients with smartphones to access any available computer-based PHR using their mobile devices, websites that are not optimized for mobile use can be exceedingly difficult to navigate using the relatively small-sized smartphone screens. To the extent that PHR use can improve chronic care management and clinical outcomes32–35, limiting PHR access to patients with easy access to internet-connected computers could contribute to existing disparities in healthcare access and outcomes. Policy makers should consider extending meaningful use PHR objectives to require easy access via mobile devices.
Nonetheless, even with a mobile-accessible PHR, we found that differences in use remained, with Black, Hispanic, and Asian patients and those living in lower SES neighborhoods still significantly less likely to have used the PHR at all in 2016. This finding is similar to previous studies of PHRs that were not mobile accessible.7,10,13,36,37 Mobile-dependent internet users often face important constraints to accessing the internet, such as data usage limits and small screens. It is possible that these constraints limited any PHR use or frequency of use among mobile-dependent individuals. While smartphones have increased mobile access to the internet among underserved groups, they may be insufficient to fully bridge the digital divide.29
Policy makers and healthcare administrators should continue to increase the accessibility of PHRs by making them easy to navigate and available in multiple platforms in order to reach patients with limited computer access or literacy. Increasing promotion and education about mobile-accessible PHR availability and salience to health management, particularly for patients with chronic conditions, could help to further bridge the divide in PHR use. Still, it is likely that PHR use may not be preferred by all patients, so it is equally important to make alternative methods for easily accessing care available.
This study has some limitations. The study was conducted with health plan members of a single health plan in Northern California. Results may differ in other healthcare settings, such as those with higher poverty rates or providing services to the uninsured. . Also, since our results are based on cross-sectional data, they should be interpreted as associations only. We are not able to confirm causality. Our study does not have any direct measure of the types of internet-connected devices patients have easy access to and relies only on the type of device used to access the PHR itself. Thus, in this study we made the assumption that patients that use a device to access the PHR have access to such a device. While we picked a patient population with diabetes in order to examine patients with a chronic condition that would likely have ongoing need for healthcare services and self-management functions available in PHRs and adjusted for number of chronic conditions, individual clinical need varied by patients and over time.
Our findings suggest that offering mobile access to PHRs may increase engagement with healthcare among vulnerable patients facing a digital divide in computer technology access. Patients who were of non-White race/ethnicity, living in lower SES neighborhoods, and with lower prior health engagement were more likely to rely exclusively on mobile devices to access the PHR. Nonetheless, even with access to a mobile-optimized and app-accessible PHR, differences in PHR use by race and neighborhood SES remain. Continued efforts are needed to increase equitable access to PHRs and electronic patient self-management technologies among patients with chronic conditions who may not have convenient computer access.
Supplementary Material
Figure 1.
Percent of patients by device(s) used to access their personal health record (PHR) and median count of days with PHR use in 2016
Note: To calculate PHR use counts, we identified use episodes by counting the number of days during the year with any PHR use, e.g., multiple log-ins in one day counted as a single episode.
Take Away Points:
In an integrated delivery system, mobile access to personal health records (PHRs) may increase PHR use among patients with limited computer access, but differences in PHR use by race/ethnicity and neighborhood socioeconomic status (SES) remained.
70% of PHR users accessed it with a mobile device, with nearly 40% of all logins done using a mobile device.
Patients who were Black, Hispanic, or Asian, or living in lower SES neighborhoods were significantly more likely to use the PHR exclusively via a mobile device. Still, these groups of patients were less likely to use the PHR at all in 2016.
Funding Source:
This research was supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (R01DK085070).
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: “This is the pre-publication version of a manuscript that has been accepted for publication in The American Journal of Managed Care® (AJMC®). This version does not include post-acceptance editing and formatting. The editors and publisher of AJMC® are not responsible for the content or presentation of the prepublication version of the manuscript or any version that a third party derives from it. Readers who wish to access the definitive published version of this manuscript and any ancillary material related to it (eg, correspondence, corrections, editorials, etc) should go to www.ajmc.com or to the print issue in which the article appears. Those who cite this manuscript should cite the published version, as it is the official version of record.”
References
- 1.Cortez NG, Cohen IG, Kesselheim AS. FDA regulation of mobile health technologies. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(4):372–379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kuehn BM. Is there an app to solve app overload? JAMA. 2015;313(14):1405–1407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Uscher-Pines L, Mehrotra A. Analysis of Teladoc use seems to indicate expanded access to care for patients without prior connection to a provider. Health Aff (Millwood). 2014;33(2):258–264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Burke BL Jr., Hall RW. Telemedicine: Pediatric Applications. 2015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Norris P Digital divide: Civic engagement, information poverty, and the Internet worldwide Cambridge University Press; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Medicare Cf, Medicaid Services H. Medicare and Medicaid Programs; Electronic Health Record Incentive Program--Stage 3 and Modifications to Meaningful Use in 2015 Through 2017. Final rules with comment period. Federal register. 2015;80(200):62761. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sarkar U, Karter AJ, Liu JY, et al. Social disparities in internet patient portal use in diabetes: evidence that the digital divide extends beyond access. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2011;18(3):318–321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sarkar U, Karter AJ, Liu JY, et al. The literacy divide: health literacy and the use of an internet-based patient portal in an integrated health system-results from the diabetes study of northern California (DISTANCE). Journal of health communication. 2010;15 Suppl 2:183–196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hsu J, Huang J, Kinsman J, et al. Use of e-Health services between 1999 and 2002: a growing digital divide. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association : JAMIA. 2005;12(2):164–171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Garrido T, Kanter M, Meng D, et al. Race/ethnicity, personal health record access, and quality of care. Am J Manag Care. 2015;21(2):e103–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Goel MS, Brown TL, Williams A, Hasnain-Wynia R, Thompson JA, Baker DW. Disparities in enrollment and use of an electronic patient portal. J Gen Intern Med. 2011;26(10):1112–1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lyles CR, Harris LT, Jordan L, et al. Patient race/ethnicity and shared medical record use among diabetes patients. Medical care. 2012;50(5):434–440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Graetz I, Gordon N, Fung V, Hamity C, Reed ME. The Digital Divide and Patient Portals: Internet Access Explained Differences in Patient Portal Use for Secure Messaging by Age, Race, and Income. Medical care. 2016;54(8):772–779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Smith A Record shares of Americans now own smartphones, have home broadband. Pew Research Center. 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tenforde M, Nowacki A, Jain A, Hickner J. The Association Between Personal Health Record Use and Diabetes Quality Measures. Journal of General Internal Medicine. 2012;27(4):420–424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Peek ME, Cargill A, Huang ES. Diabetes Health Disparities. Medical Care Research and Review. 2007;64(5_suppl):101S–156S. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Higashi T, Wenger NS, Adams JL, et al. Relationship between number of medical conditions and quality of care. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(24):2496–2504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tinetti ME, Bogardus ST, Agostini JV Jr.. Potential pitfalls of disease-specific guidelines for patients with multiple conditions. N Engl J Med. 2004;351(27):2870–2874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Young AS, Chaney E, Shoai R, et al. Information technology to support improved care for chronic illness. J Gen Intern Med. 2007;22 Suppl 3:425–430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes - 2015. Diabetes Care. 2015;38(1). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.O’Connor PJ. Electronic medical records and diabetes care improvement: are we waiting for Godot? Diabetes Care. 2003;26(3):942–943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Burton LC, Anderson GF, Kues IW. Using electronic health records to help coordinate care. Milbank Q. 2004;82(3):457–481, table of contents. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Weiner M, Biondich P. The influence of information technology on patient-physician relationships. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21 Suppl 1:S35–39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Devkota B, Salas J, Sayavong S, Scherrer JF. Use of an Online Patient Portal and Glucose Control in Primary Care Patients with Diabetes. Population health management. 2016;19(2):125–131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Glasgow RE, Christiansen SM, Kurz D, et al. Engagement in a diabetes self-management website: usage patterns and generalizability of program use. Journal of medical Internet research. 2011;13(1). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shimada SL, Allison JJ, Rosen AK, Feng H, Houston TK. Sustained Use of Patient Portal Features and Improvements in Diabetes Physiological Measures. Journal of medical Internet research. 2016;18(7):e179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Geronimus AT, Bound J. Use of census-based aggregate variables to proxy for socioeconomic group: evidence from national samples. American Journal of Epidemiology. 1998;148(5):475–486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Stata A. Stata Base Reference Manual Release 14. 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Smith A US smartphone use in 2015. Pew Research Center. 2015;1. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Funnell MM, Brown TL, Childs BP, et al. National standards for diabetes self-management education. Diabetes care. 2009;32(Supplement 1):S87–S94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Blumenthal D, Tavenner M. The “Meaningful Use” Regulation for Electronic Health Records. New England Journal of Medicine. 2010;363(6):501–504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Goldzweig CL, Initiative QER, West Los Angeles V. Systematic review: secure messaging between providers and patients, and patients’ access to their own medical record: evidence on health outcomes, satisfaction, efficiency and attitudes. Department of Veterans Affairs, Health Services Research & Development Service; 2012. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Harris LT, Koepsell TD, Haneuse SJ, Martin DP, Ralston JD. Glycemic control associated with secure patient-provider messaging within a shared electronic medical record: a longitudinal analysis. Diabetes care. 2013;36(9):2726–2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.McClellan SR, Panattoni L, Chan AS, Tai-Seale M. Patient-initiated Electronic Messages and Quality of Care for Patients With Diabetes and Hypertension in a Large Fee-for-Service Medical Group: Results From a Natural Experiment. Med Care. 2016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhou YY, Kanter MH, Wang JJ, Garrido T. Improved quality at Kaiser Permanente through e-mail between physicians and patients. Health affairs. 2010;29(7):1370–1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sanders MR, Winters P, Fortuna RJ, et al. Internet access and patient portal readiness among patients in a group of inner-city safety-net practices. The Journal of ambulatory care management. 2013;36(3):251–259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yamin CK, Emani S, Williams DH, et al. The digital divide in adoption and use of a personal health record. Archives of internal medicine. 2011;171(6):568–574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.