Abstract
Background
Neuronal and glial cell interaction is essential for synaptic homeostasis and may be affected in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). We measured cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) neuronal and glia markers along the AD continuum, to reveal putative protective or harmful stage-dependent patterns of activation.
Methods
We included healthy controls (n = 36) and Aβ-positive (Aβ+) cases (as defined by pathological CSF amyloid beta 1-42 (Aβ42)) with either subjective cognitive decline (SCD, n = 19), mild cognitive impairment (MCI, n = 39), or AD dementia (n = 27). The following CSF markers were measured: a microglial activation marker—soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (sTREM2), a marker of microglial inflammatory reaction—monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1), two astroglial activation markers—chitinase-3-like protein 1 (YKL-40) and clusterin, a neuron-microglia communication marker—fractalkine, and the CSF AD biomarkers (Aβ42, phosphorylated tau (P-tau), total tau (T-tau)). Using ANOVA with planned comparisons, or Kruskal-Wallis tests with Dunn’s pairwise comparisons, CSF levels were compared between clinical groups and between stages of biomarker severity using CSF biomarkers for classification based on amyloid pathology (A), tau pathology (T), and neurodegeneration (N) giving rise to the A/T/N score.
Results
Compared to healthy controls, sTREM2 was increased in SCD (p < .01), MCI (p < .05), and AD dementia cases (p < .001) and increased in AD dementia compared to MCI cases (p < .05). MCP-1 was increased in MCI (p < .05) and AD dementia compared to both healthy controls (p < .001) and SCD cases (p < .01). YKL-40 was increased in dementia compared to healthy controls (p < .01) and MCI (p < .05). All of the CSF activation markers were increased in subjects with pathological CSF T-tau (A+T−N+ and A+T+N+), compared to subjects without neurodegeneration (A−T−N− and A+T−N−).
Discussion
Microglial activation as indicated by increased sTREM2 is present already at the preclinical SCD stage; increased MCP-1 and astroglial activation markers (YKL-40 and clusterin) were noted only at the MCI and AD dementia stages, respectively, and in Aβ+ cases (A+) with pathological T-tau (N+). Possible different effects of early and later glial activation need to be explored.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12974-019-1399-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Early diagnosis, Cerebrospinal fluid, ELISA, sTREM2, YKL-40, Chitinase-3-like protein 1, MCP-1, Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, Fractalkine, CX3CL1, Clusterin, Apolipoprotein J, Microglia, Neuroinflammation
Background
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) may be described as a biological continuum that includes the hallmark pathological processes of amyloid-beta (Aβ) dysmetabolism, formation of amyloid deposits (A), neurofibrillary tangles (T), neurodegeneration (N), determined by measuring cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) levels of Aβ42, phosphorylated tau (P-tau), and total tau (T-tau) respectively. The presence or absence of pathological markers can be summarized as an A/T/N score, an unbiased classification of pathology and severity along the AD continuum [1, 2]. In contrast, the clinical classification of the AD continuum is based on subjective accounts of cognitive deficits, performance on cognitive tests, and functioning in daily life [3–6]. Patients who report experience of decline in cognitive function while performing within the normal range on cognitive tests, may be categorized as having subjective cognitive decline (SCD) [3]. In contrast, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) requires the presence of subjective cognitive decline in combination with impaired cognitive performance yet retaining preserved independence in functional ability [4–6]. We and others have made large efforts towards standardization of criteria for these stages, e.g., as part of the EU JPND-funded BIOMARKAPD study, and Norwegian national efforts [7, 8].
While genetic evidence indicates that Aβ dysmetabolism is causal in familial AD, the initial sequence of events and causality in sporadic AD is still not determined. However, reduced Aβ clearance and deficient innate immune activity related to the triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) and clusterin (Apo J) function may play a role [9–11]. While central nervous system (CNS) interstitial Aβ is released from neurons dependent on activity, clearance is a result of neuronal, astro-, and microglial uptake and degradation as well as transport to the glymphatic system, blood, and (CSF) [12–14]. Microglia normally subserve synaptic homeostasis and synapse elimination [15, 16]. They are CNS myeloid-derived innate immune effector cells, which together with reactive astrocytes also may acquire inflammatory properties. Genetic evidence supports a role for loss of balanced TREM2 activation, innate immunity, and microglial activity in AD pathogenesis [9, 17–19]. Further, experimental studies support neuroinflammatory responses as drivers of AD pathogenesis, and there is evidence for associations to neuroinflammation and deficient microglia Aβ function in MCI due to AD and more advanced AD [14, 20–22], though the initial microglial activation might be compensatory and advantageous. Aβ clearance decreases with age and could in combination with genetic liabilities for compromised innate immune clearance capacity contribute to age-related disease inception [23, 24]. Notably, a recent translocator protein (TSPO) ligand positron-emission tomography (PET) study detecting activated microglia showed higher binding in AD “slow decliners” [25]. Moreover, a longitudinal TSPO-PET study demonstrated reduced microglia activation over time in patients at the MCI stage, but increased activation in patients at the AD stage of dementia [26]. These findings may be interpreted as an early beneficial role of microglial activation and a later inflammatory peak. Experimental evidence suggests that TREM2 increases in parallel with amyloid deposition, possibly limiting Aβ plaque-associated pathology [27, 28]. Thus, initial microglial activation might induce phagocytosis of Aβ, stalling formation of oligomers, and restricting neurotoxicity from deposited Aβ in plaques, while further inflammatory activation might accelerate neurodegeneration. If supported, this distinction could aid patient stratification and guide intervention trials that include immune modification components.
Glial activation occurs as part of altered immune cytokine activities, which also change towards increased inflammatory activity during AD progression. However, micro- and astroglial activation are interlinked, and genetic evidence suggests that innate immunity could be a prime mover in the AD cascade [9]. Based on the described findings of early microglial activation, our starting point was to investigate these events in CSF samples via soluble TREM2 (sTREM2) as a microglial activation marker, and clusterin and chitinase-3-like protein 1 (YKL-40) which both are suggestive of astroglial activation, a marker for neuron-microglia communication (chemokine ligand 1; CX3CL1; fractalkine) and a well-established marker for microglial mobilization and inflammatory reaction (monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, MCP-1).
Soluble TREM2 is released upon microglial activation, leading to increased levels of CSF sTREM2 in AD [29, 30]. This receptor might subserve Aβ uptake by peptides being bound to its ligands APOE and clusterin [31–34]. Clusterin is abundantly expressed by astrocytes and select neuronal populations, e.g., within the hippocampus, and may modulate Aβ metabolism as a chaperone protein [35]. In binding Aβ, clusterin may increase clearance and inhibit plaque formation in processes that are coupled to immune responses [35–37]. YKL-40 is produced mainly by astrocytes, but also microglia, often surrounding amyloid plaques. While early expression levels vary, increased expression has been reported at the MCI stage associated with neuroinflammation [38, 39]. Experimental data suggest a role for YKL-40 in microglia-astroglia crosstalk [38, 40]. Fractalkine is a CXC chemokine (CX3CL1) that is highly expressed by neurons in the hippocampus and cortex, while its receptors (CX3CR1) are found on microglia [41]. Fractalkine neuron-to-microglia communication strengthens the neuroprotective role of microglia, by inhibiting TNFα secretion [42], reducing neurotoxicity, and reducing microglial activation [43, 44]. The expression level of fractalkine has been reported to reflect progression of AD [45]. MCP-1 is a CC chemokine produced by micro- and astroglia and endothelial cells with receptors (CCR2) largely restricted to immune cells but also found on neurons. In the brain, MCP-1 attracts microglial and peripheral immune cells to sites of inflammation. It may stimulate microglia to change from resting to activated morphology, and the level of CSF MCP-1 increases with advancing pathology in AD [46].
These individual markers have been studied in predementia and in AD dementia stages with variable reported findings (see Additional file 1: Table S1). To our knowledge, none of the included CSF immune markers (sTREM2, MCP-1, YKL-40, fractalkine, and clusterin) have been studied in a defined SCD group; however, both CSF sTREM2 and YKL-40 have been studied in preclinical AD (SCD cases and asymptomatic subjects) with pathological (low) CSF Aβ. Neither sTREM2 nor YKL-40 was reportedly increased in this mixed group [29, 30, 38, 40]. Clusterin and fractalkine have been little studied in MCI [47, 48], but sTREM2, MCP-1, and YKL-40 have all shown contradictory results, either unchanged [49–52] or increased [29, 30, 38, 40, 53, 54] compared to controls. Except for YKL-40 [38, 51] and fractalkine [47] which respectively have been found unchanged or reduced compared to controls, all the other immune markers have shown contradictory results in AD dementia compared to controls, either unchanged [29, 49, 51, 55–59], reduced [60, 61], or increased CSF values [38, 50, 53, 54, 62–65].
Intrathecal levels of glial- and inflammation markers may reflect both CNS AD pathogenic processes and responsivity, as well as inflammatory reactivity upon stimulation such as therapeutic interventions and infectious agents. To our knowledge, CSF sTREM2, MCP-1, YKL-40, clusterin, and fractalkine have never been analyzed in the same cohorts across predementia AD stages. Thus, we currently lack information on putative disparate or concerted micro- and astroglial patterns of activation and inflammation related to clinical and neuropathological changes in predementia AD. As activation may be bi- or multiphasic along the AD continuum, highly standardized protocols and measurements on standardized platforms, tightly controlled clinical staging, and biomarker-based stratification may be necessary to detect relevant differences.
Microglial activation per se does not need to be inflammatory, but may be a compensatory response at the synapse. Following Fan et al. [26], we hypothesize that the earliest stage of demonstrable microglial activation occurs at the pre-clinical stage, only coincident with other inflammatory and astroglial activation markers at later stages. We also explore relations between CSF biomarker-derived A/T/N stages and glial activation markers.
Methods
Subjects
For the purposes of the present study, we selected 121 participants from two Norwegian cohorts. Healthy controls with normal CSF (n = 36), participants with SCD (n = 18), and MCI (n = 20) patients, both with CSF Aβ42 confirmed amyloid pathology, were selected from the Norwegian multicenter study, “Dementia Disease Initiation” (DDI) [7]. A patient group meeting the National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association (NIA-AA) criteria for dementia due to AD [6] (n = 27) and an additional 19 MCI patients with CSF Aβ42 confirmed amyloid pathology were included from the Norwegian part of the Gothenburg-Oslo MCI (MCI-GO) cohort [66]. Classification of A/T/N groups [1] was done using CSF Aβ42 (A), phosphorylated tau (P-tau) (T), and total-Tau (T-tau) (N). All subjects were assigned binary scores for each category, rated positive when the CSF biomarker value was defined as pathological. The cut-off for CSF was Aβ42 < 708 pg/ml for amyloid plaque pathology, subsequently denoted Aβ-positive (Aβ+) and A+ cases. This Aβ optimal cut-off was determined by a PET [18F]-Flutemetamol uptake study [67]. Cases with Aβ42 values close to cutoff (± 30 ng/ml) were excluded from this study material. The abnormality cut-off values for CSF T-tau and P-tau were set in accordance with reference values from Sjögren et al. [68]. For P-tau, the cut-off value was ≥ 80 pg/ml, and values above this threshold were classified as a T+ score. For T-tau, cut-off values were > 300 pg/ml for age < 50 years, > 450 pg/ml for age 50–69 years, and > 500 pg/ml for age ≥ 70 years. Subjects were denoted N+ cases when their T-tau value exceeded the respective thresholds.
Further criteria for inclusion were age between 40 and 80 years and a native language of Norwegian, Swedish, or Danish. Exclusion criteria were brain trauma or disorders, including clinical stroke, dementia, severe psychiatric disorder, and severe somatic disease that might influence the cognitive functions, intellectual disability, or other developmental disorders.
Both DDI and MCI-GO employ a standardized protocol for participant selection, assessment, and disease stage classification according to published criteria [3, 4, 6]. All patients were interviewed and examined by a physician trained in diagnosing cognitive disorders. They all underwent cognitive testing, either cerebral MRI or CT, blood screening, and standard lumbar puncture as part of the clinical assessment.
Classification of SCD and MCI
Participants were classified as SCD according to the SCD-I framework, which requires normal objective cognitive performance on neuropsychological tests while experiencing a subjective decline in any cognitive domain [3]. MCI was classified according to the NIA-AA criteria which require the presence of subjective cognitive impairment or decline in combination with lower performance than expected in one or more cognitive domains, yet preserved independence in functional ability and not fulfilling the criteria of dementia [4, 6]. Performance was classified as normal or abnormal according to published norms (adjusted for age, sex, and educational effects) for the different tests [69–71]. Due to mutually exclusive criteria, the cut-off values for SCD vs. MCI (defined as normal or abnormal cognition) were ≤ 1.5 standard deviation below normative mean on either Consortium to Establish a Registry for AD (CERAD) word list (delayed recall), Visual Object and Space Perception (VOSP) silhouettes, Trail Making Test part B (TMT-B), or Controlled Oral Word Association Test (COWAT). For the DDI cohort global cognitive status was also assessed by the Clinical Dementia Rating Scale (CDR), whereas the Global Deterioration Scale was used for MCI-GO [72, 73].
CSF collection and handling
Lumbar punctures were performed similarly on four sites all following a detailed BIOMARKAPD SOPs as described previously [8]. Briefly described, sampling was done before noon and CSF was collected in polypropylene tubes (Thermo Fisher Scientific, MA, USA) which were centrifuged within 4 h at 2000g for 10 min at room temperature. The supernatant was subsequently transferred to new defined tubes, directly frozen at − 80 °C on site and kept at − 80 °C until thawed for analysis. All CSF samples were analyzed either at the Department of Interdisciplinary Laboratory Medicine or Section of Clinical Molecular Biology (EpiGen) at Akershus University Hospital. The exception was the sTREM2 analysis, which was assayed at the Department of Pharmacology at the University of Oslo.
Protein biomarker measurements
Commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) based on monoclonal antibodies were used to measure CSF levels of the following protein biomarkers: Aβ42, T-tau, and P-tau. They were determined using Innotest β-Amyloid (1-42), Innotest T-tau Ag, and Innotest P-tau (181P)(Fujirebio, Ghent, Belgium), respectively.
CSF sTREM2 was also analyzed using a sandwich ELISA as described earlier [49] with some modifications; the plates were coated over night with the capture antibody (0.25 μg/ml; AF1828, R&D Systems, MN, USA) and samples incubated for 2 h prior to TREM2 detection with a rabbit-monoclonal anti-human TREM2 antibody (0.5 μg/ml; SEK11084, Sino Biologics, Beijing, China).
The QuickPlex SQ 120 system from Meso Scale Discovery (MSD, MD, USA) was used to measure YKL-40, MCP-1, and fractalkine in a U-plex format and clusterin in an R-plex format, where YKL-40 and clusterin were in a singleplex setup and MCP-1 and fractalkine were in the same multiplex setup. The MSD analyses were carried out according to the manufacturers’ procedures, with the adjustments that CSF samples were diluted 200 times prior to YKL-40 and clusterin analyses, and the multiplex setup was used with 100 μl neat CSF and 25 μl buffer.
All the lower limits of quantifications (LLOQs) were defined as the lowest concentration at which the coefficient of variation (CV) of the calculated concentration was < 20% in > 75% of the analyses or the mean CV was < 20% in our test set. All biomarker values in all samples were well above LLOQ. All samples were analyzed in duplicates and reanalyzed if relative deviations (RDs) exceeded 20%. In addition, quality control samples with RD threshold of 15% assured inter-plate and inter-day variation.
Statistical analysis
Normality was assessed through the inspection of Q-Q plots, histograms, and the Shapiro-Wilks test of normality.
In order to explore and adjust for age and sex, and APOE-ɛ4 allelic effects on CSF inflammatory markers in healthy aging, simple and multiple regression analyses (controlling for several covariates) were performed between these variables and CSF immune markers within the healthy control group. If a significant relationship was observed between these covariates and an inflammatory marker in the healthy control group, the standardized residuals from the pertinent regression model was obtained for the entire sample and used in further analysis in order to adjust for these covariates in between-group comparisons. To assess differences in biomarker levels between groups, we performed one-way ANOVAs with planned comparisons for variables with normal distributions. We performed Kruskal-Wallis test with Dunn’s non-parametric pairwise post hoc test with Bonferroni corrections to assess group differences in variables with non-normal distributions (CSF Aβ42, CSF T-tau, CSF P-tau, MMSE, and A/T/N groups). Non-parametric pairwise comparisons and ANOVA contrasts were performed in a hierarchical manner. We compared Aβ + SCD, MCI, and AD dementia groups to healthy controls, and finally we compared the SCD with the MCI group and both SCD and MCI to the AD dementia group. The dichotomous variable “sex” was assessed using a chi-square test. For the A/T/N groups, A−T−N− and A+T−N− were compared to all other groups. Only one patient had A+T+N− classification, and this patient was excluded from both statistical analysis and figure.
To assess clinical stage dependent relationships between the innate immune response to AD pathology, correlational analyses between the inflammatory markers (sTREM2, YKL40, MCP-1, fractalkine, and clusterin) and CSF AD biomarkers (Aβ42, T-Tau, and P-tau) were performed using Pearson’s r within the pertinent symptomatic groups (SCD, MCI, and AD dementia).
All analyses were performed in the Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 25, and the significance level was defined as p < .05.
Ethics
The regional medical research ethics committee approved this study. Participants gave their written informed consent before taking part in the study. All further study conduct was in line with the guidelines provided by the Declaration of Helsinki (1964; revised 2013) and the Norwegian Health and Research Act (2009).
Results
See Table 1 for further characterization of the study cohort.The mean concentration and standard deviations for sTREM2, MCP-1, YKL-40, fractalkine, and clusterin at the different clinical stages are shown in Table 2.
Table 1.
Demographic characteristics, AD biomarkers, and ATN groups of the participants by diagnostic category
| Variable | Groups | X2(p) | Dunn’s pair-wise comparisons | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Healthy controls (n = 36) | 2. Aβ + SCD (n = 18) | 3. Aβ + MCI (n = 40) | 4. AD dementia (n = 27) | 1 vs 2 | 1 vs 3 | 1 vs 4 | 2 vs 3 | 2 vs 4 | 3 vs 4 | ||
| Age | 61.1 (9.2) | 67.2 (6.6) | 66.6 (7.4) | 67.6 (5.2) | X2 = 14.4 (< .01) | n.s. | < .05 | < .05 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| Female % | 19 (53%) | 8 (44%) | 23 (57%) | 13 (48%) | X2 = 1.6 (n.s.) | a | a | a | a | a | a |
| MMSE | 29.4 (0.7) | 29.2 (0.8) | 27.9 (2.0) | 19.0 (5.8) | X2 = 83.7 (< .001) | n.s. | < .001 | < .001 | < .01 | < .001 | < .001 |
| APOE-ɛ4 positivity (%) | 16 (44%) | 13 (72%) | 23 (57%) | 9 (33%) | X2 = 6.8 (n.s.) | a | a | a | a | a | a |
| CSF Aβ42 | 1044 (185) | 530 (98) | 474 (112) | 473 (93) | b | b | b | b | b | b | |
| CSF Total tau | 298 (97) | 487 (249) | 635 (290) | 961 (417) | X2 = 58.0 (< .001) | < .05 | < .001 | < .001 | n.s. | < .01 | < .05 |
| CSF P-tau | 51 (13) | 74 (33) | 86 (40) | 89 (43) | X2 = 37.2 (< .001) | < .05 | < .001 | < .001 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| A−T−N−, n (%) | 36 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | b | b | b | b | b | b | |
| A+T−N−, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 10 (55%) | 13 (33%) | 0 (0%) | b | b | b | b | b | b | |
| A+T−N+, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (5%) | 10 (25%) | 19 (70%) | b | b | b | b | b | b | |
| A+T+N+, n (%) | 0 (0%) | 7 (40%) | 16 (40%) | 8 (30%) | b | b | b | b | b | b | |
Abbreviations: n.s. non-significant, Aβ+ indicates CSF Aβ42 below the normal range
aNon-parametric post hoc analysis not performed due to non-significant Kruskal-Wallis test. All p values are Bonferroni corrected
b No statistical tests applied
Table 2.
Between-group CSF inflammation marker comparisons
| Variable | Groups | F(p) | ANOVA contrasts (p) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Healthy controls (n = 36) | 2. Aβ + SCD (n = 18) | 3. Aβ + MCI (n = 40) | 4. AD dementia (n = 27) | 1 vs 2 | 1 vs 3 | 1 vs 4 | 2 vs 3 | 2 vs 4 | 3 vs 4 | ||
| CSF sTREM2 | 3.1 (0.9) | 4.6 (1.9) | 4.0 (1.8) | 4.8 (1.7) | F = 7.0 (p < .001) | < .01b | < .05b | < .001b | n.s. b | n.s. b | < .05b |
| CSF MCP-1 | 483 (124) | 510 (133) | 581 (160) | 645 (249) | F = 5.3 (p < .01) | n.s.b | < .05b | < .001b | n.s.b | < .05b | n.s.b |
| CSF YKL-40 | 145 (46) | 188 (80) | 182 (69) | 221 (70) | F = 3.4 (p < .05) | n.s. b | n.s. b | < .01b | n.s. b | n.s. b | < .05b |
| CSF fractalkine | 1823 (446) | 1924 (461) | 1790 (469) | 1983 (569) | F = 1.0 (p = n.s.) | a | a | a | a | a | a |
| CSF clusterin | 2286 (828) | 2305 (719) | 2611 (817) | 2777 (769) | F = 2.6 (p = n.s.) | a | a | a | a | a | a |
Abbreviations: n.s. non-significant (p > .05), Aβ+ indicates CSF Aβ42 below the normal range
aContrasts not performed due to non-significant ANOVA
bEqual distribution assumed
Age, sex, and APOE-ɛ4 allelic relationship with CSF immune markers in healthy controls
Neither APOE-ɛ4 status nor sex was associated with any of the CSF inflammatory markers in healthy controls when using simple regression analysis. When age and CSF T-tau were included in multiple regression models, both age (β = .477, p < .001) and T-tau (β = .384, p < .01) were shown to predict CSF YKL-40 (adjusted R2 = .497, F[2, 33] = 18.280, p < .001) (Additional file 2). The same was not true for CSF sTREM2, where the relationship between age and sTREM2 was not found in healthy controls (β = .248, p = n.s.), when controlling for the effects of T-tau (β = .478, p < .01) in a multiple regression analysis (adjusted R2 = .342, F[2, 32] = 9819, p < .001). No relationships were found between age and CSF MCP-1, clusterin, or fractalkine within the healthy control group in any regression models. Thus, only YKL-40 was adjusted for age-effect prior to analysis of between-group differences in clinical staging.
CSF activation and inflammation marker comparisons based on clinical staging
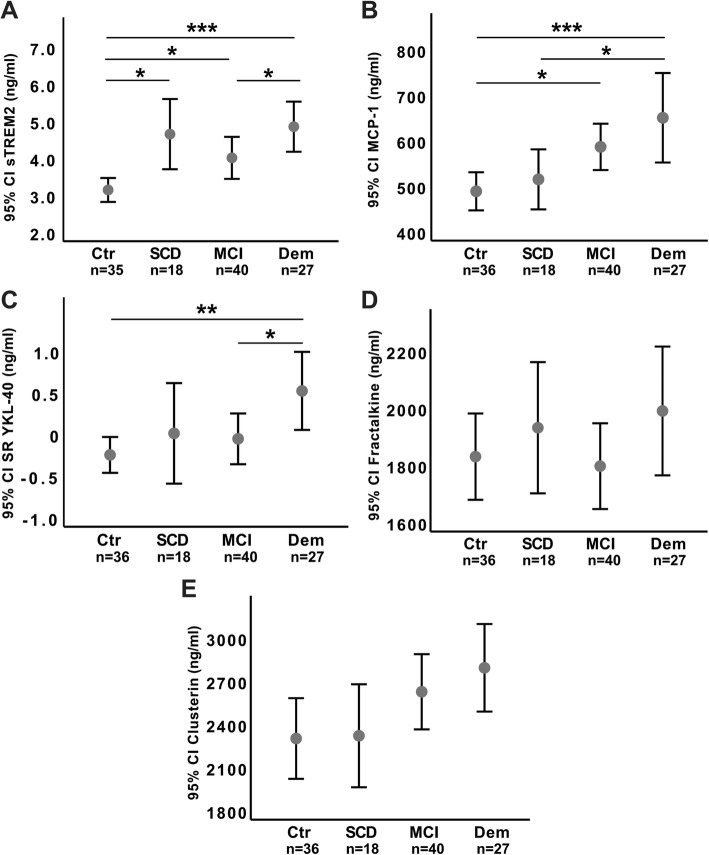
CSF level comparisons between clinical groups are summarized in Table 2, illustrated in Fig. 1, and further compared in Additional file 3: Figure S2. CSF sTREM2, YKL-40, and MCP-1 were increased at more advanced clinical stages, but differed according to which cognitive stage they showed abnormal levels.
Fig. 1.
Between-group CSF immune marker comparisons based on clinical staging. Fig. text: The Y-axis with sTREM2 (a), MCP-1 (b), fractalkine (d), and clusterin (e) reported as CSF concentration in nanograms per milliliter, while the Y-axis for YKL-40 (c) are residuals standardized for age. Error bars are shown as mean and 95% confidence interval (CI). Abbreviation: Ctr: healthy controls (n = 36), SCD: CSF Aβ42+ subjects with subjective cognitive decline (n = 19), MCI: CSF Aβ42+ subjects with mild cognitive impairment (n = 39), Dem: Aβ42+ subjects with Alzheimer’s disease dementia (n = 27). Statistically significant differences are marked with asterisks, where * indicates p < .05, ** indicates p < .01, and *** indicates p < .001
CSF sTREM2 values were higher in Aβ + SCD subjects (t(116) = 3.282, p < .01), Aβ + MCI subjects (t(116) = 2.364, p < .05), and subjects with AD dementia (t(116) = 4.213, p < .001), compared to healthy controls. A higher CSF sTREM2 level was also found in subjects with AD dementia compared to Aβ + MCI subjects (t(116) = 2.135, p < .05).
No difference in the CSF YKL-40 level was found between healthy controls, and Aβ + SCD or Aβ + MCI subjects. However, an increased level of CSF YKL-40 was found in subjects with AD dementia compared to both Aβ + MCI subjects (t(117) = 2.370, p < .05) and healthy controls (t(117) = 3.096, p < .01).
No differences in CSF MCP-1 levels were demonstrated between Aβ + SCD and healthy controls. However, CSF MCP-1 levels were equally increased in Aβ + MCI subjects and subjects with AD dementia, and levels where higher in these groups compared to healthy controls ((t(117) = 2.480, p < .05) and (t(117) = 3.704, p < .001) respectively).
Finally, no significant differences between clinical groups were found for either CSF fractalkine or CSF clusterin. The between-group ANOVA analysis for clusterin was, however, borderline significant (F(3, 117) = 2.574, p = .057), with markedly higher CSF clusterin levels in the dementia group compared to the control group (Fig. 1).
CSF activation and inflammation marker comparisons based on A/T/N biomarker classification
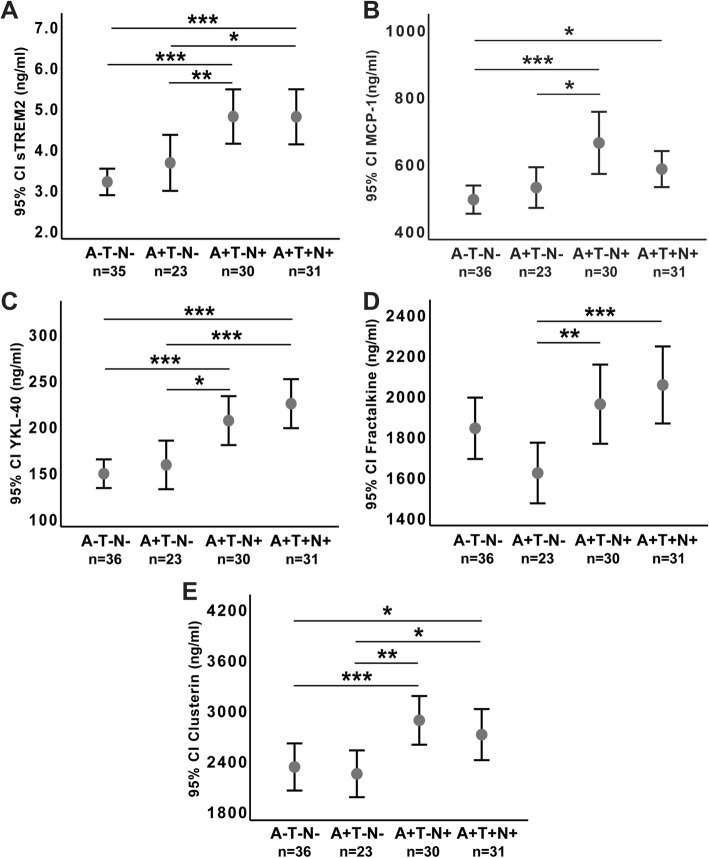
CSF level comparisons between A/T/N groups are illustrated in Fig. 2.
Fig. 2.
Between-group CSF immune marker comparisons based on ATN staging. Fig. text: The association with ATN groups. Y-axis shows concentration of inflammatory markers in CSF in nanograms per milliliter. A+ indicating CSF Aβ42 below the reference range, T+ indicating CSF p-tau above the reference range and N+ here indicating T-tau above the reference range for age. Minus (−) indicating normal values within the reference range. Error bars are shown as mean and 95% confidence interval (CI). Statistically significant differences are marked with asterisks, where * indicates p < .05, ** indicates p < .01, and *** indicates p < .001
No differences in CSF sTREM2, YKL-40, MCP-1, or CSF clusterin levels were found between healthy controls with normal CSF (A−T−N− n = 36) compared to participants with cognitive symptoms with A+T−N− (n = 23). However, the levels of these markers were all equally increased in A+T−N+ (n = 30) and A+T+N+ (n = 31), p < .01–p < .001 and p < .05–p < 01 respectively, please see Table 1 and Fig. 2 for details. Within the SCD group, there were no significant differences between those with pathological levels of T-tau and/or P-tau (n = 9) and those with normal CSF levels, for either CSF sTREM2, YKL-40, MCP-1, clusterin, or fractalkine (independent samples T-test), nor no significant correlations between CSF MCP-1 or clusterin and T-tau or P-tau. However, there were significant positive correlations between CSF sTREM2, YKL-40, and fractalkine with both T-tau and P-tau within the SCD group (Table 3).
Table 3.
Correlation analyses between inflammatory and AD CSF biomarkers by diagnostic category
| All symptomatic subjects (SCD, MCI, AD dementia) (n = 85) | |||||
| Variable | CSF sTREM2 | CSF YKL-40 | CSF MCP-1 | CSF Fractalkine | CSF Clusterin |
| CSF Aβ42 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| CSF T-tau | .318, p < .01 | .589, p < .001 | .276, p < .05 | .507, p < .001 | .400, p < .001 |
| CSF P-tau | .289, p < .01 | .444, p < .001 | n.s. | .368, p < .001 | .290, p < .01 |
| SCD (n = 18) | |||||
| Variable | CSF sTREM2 | CSF YKL-40 | CSF MCP-1 | CSF Fractalkine | CSF Clusterin |
| CSF Aβ42 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | .568, p < .05 |
| CSF T-tau | .629, p < .01 | .730, p < .001 | n.s. | .616, p < .01 | n.s. |
| CSF P-tau | .655, p < .01 | .679, p < .01 | n.s. | .536, p < .05 | n.s. |
| MCI (n = 40) | |||||
| Variable | CSF sTREM2 | CSF YKL-40 | CSF MCP-1 | CSF Fractalkine | CSF Clusterin |
| CSF Aβ42 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| CSF T-tau | n.s. | .409, p < .01 | n.s. | .479, p < .01 | .330, p < .05 |
| CSF P-tau | .335, p < .05 | .347, p < .05 | n.s. | .375, p < .05 | .364, p < .05 |
| AD dementia (n = 29) | |||||
| Variable | CSF sTREM2 | CSF YKL-40 | CSF MCP-1 | CSF Fractalkine | CSF Clusterin |
| CSF Aβ42 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
| CSF T-tau | n.s. | .660, p < .001 | n.s. | .550, p < .01 | .415, p < .05 |
| CSF P-tau | n.s. | .439, p < .05 | n.s. | n.s. | n.s. |
Reported values are Pearson’s r and associated p value
n.s. non-significant (p > .05)
CSF fractalkine was increased in A+T−N+ (n = 30) and A+T+N+ (n = 31) compared to patients with pathological CSF Aβ without tau pathology or neurodegeneration markers A+N−T− (n = 23) (p < .001 and p < .01 respectively), in accordance with the association between fractalkine and T-tau (Table 3). CSF fractalkine was lower (1603 ng/ml, SD 345) in A+T−N− than in A−T−N− healthy controls (1823 ng/ml, SD 446), but this difference did not reach statistical significance (p = .057). CSF clusterin levels were equally increased in both A+T−N+ (n = 30) and A+T+N+ (n = 31) compared to healthy controls with normal CSF (A−T−N−, n = 36) (p < .01 and p < .05 respectively) and also in accordance with the association with T-tau (Table 3).
There were no significant correlations between sTREM2, YKL-40, MCP-1, or fractalkine and CSF Aβ42 in our cohort, neither in subgroups controlled separately nor when all symptomatic subjects were combined. There was, however, a correlation between CSF clusterin and CSF Aβ42 (β = 0.568, p < 0.05) in the SCD group. CSF T-tau correlated strongest with all of the before mentioned activation markers when all symptomatic subjects were combined, in addition to several of the subgroups. For details, please see Table 3.
Discussion
In this study, we have demonstrated microglial activation in Aβ + SCD cases, as shown by increased sTREM2. Since there were no differences in objective cognitive performance between the healthy controls and the SCD group (see Table 1), increased CSF sTREM2 in the Aβ + SCD group suggests microglial activation even before objective cognitive decline. Furthermore, we did not find evidence for neither astroglial activation at this stage (no significant increase of YKL-40 or clusterin) nor for a microglial inflammatory response (no significant increase in MCP-1 levels). CSF MCP-1 levels were increased in the Aβ + MCI group compared to healthy controls, indicative of an inflammatory response at the MCI stage. This interpretation is corroborated by the increase in astroglial markers at the dementia stage, indicative of involvement of astrocytes in the inflammatory process as loss of cognitive abilities progresses even further. These differences may represent functionally important stages of innate immune activation and neuroinflammation along the AD continuum and are summarized in Additional file 3: Figure S2.
Increasing inflammation with increasing neurodegeneration, but not Aβ pathology alone
All of the inflammatory markers were increased in CSF in subjects with pathological T-tau (A+T−N+ and A+T+N+), indicating neurodegeneration, compared to those subjects without neurodegeneration (A−T−N− and A+T−N−). Interestingly, neither glial activation markers nor inflammatory markers were significantly increased in cases with only Aβ+ pathology (A+T−N−) compared to healthy controls (A−T−N−), though CSF fractalkine showed a non-significant reduction. For both CSF fractalkine and CSF clusterin, the increase with increasing neurodegeneration may be masked when comparing the clinical groups, as these contain subjects with and without neurodegeneration, but it became evident when we employed the A/T/N classification. For CSF fractalkine, we found no between group differences between the control group/A−T−N− compared to the other clinical groups. However, when comparing A/T/N groups as a measure of AD biomarker severity, the Aβ42-positive group without neurodegeneration (A+T−N−, 13 subjects with MCI and 9 with SCD) showed significantly lower CSF fractalkine levels compared to the Aβ42-positive groups with neurodegeneration (A+T−N+, 1 SCD subject, 10 MCI subjects, and 19 AD dementia, and A+T+N+, 7 SCD subjects, 16 MCI subjects, and 8 AD dementia). CSF fractalkine showed a clear association to T-tau in all clinical subgroups, see Table 3. Moreover, CSF clusterin was also associated with T-tau in both the MCI and dementia subgroups, but not the SCD group. While the between-group ANOVA analysis for clusterin did not reach the threshold for statistical significance, the dementia group did show markedly higher levels compared to the control group. This negative result may have been due to the inclusion of a heterogeneous sample with relatively small subgroups. When our cohort was categorized according to the A/T/N biomarker classification scheme, however, the difference between the groups without (A−T−N− and A+T−N−) and those with neurodegeneration (A+T−N+ and A+T+N+) was clearly evident (Fig. 2). Thus, findings relative to clinical and A/T/N stages are in general accordance, both consistent with a restricted microglial activation accompanying amyloid pathology (A+) without more extensive inflammatory activation, the latter accompanying neurodegeneration, and established cognitive impairment at the MCI and dementia stages.
Our findings in the clinical stages are in accordance with imaging data suggestive of a biphasic microglial response, though the sTREM2 level in our material at the SCD stage was only nominally higher but not significantly different from that at the MCI stage [25, 26]. Aging is associated with subtle microglial priming, facilitating phagocytosis and homeostatic recovery but also further development of potentially detrimental inflammatory properties that may increase Aβ and tau pathologies [74, 75]. A sequence of events is not established, as microglia may be primed by several types of stimuli including Aβ, but our description of the relation between inflammatory and neurodegeneration markers is consistent with the above description.
Our findings may help interpret studies of immunomodulating therapies towards reducing the Aβ deposition by increasing the microglial clearance [76]. A too advanced stage of AD may have contributed to trial failures with several phase III studies being discontinued due to lack of treatment efficacy or side effects. Cerebral Aβ aggregation starts 10 to 15 years before mild cognitive decline [77] and 20 to 30 years before dementia onset [78]. The present findings suggest that the innate immune system and astroglial cells may undergo sequential changes towards an inflammatory activation also during the preclinical part of this period, represented by sTREM2 and YKL-40, respectively. Immunomodulating therapies might have different effects depending on the state of immune activation, i.e., whether monocyte and astroglial inflammatory components are activated or not [26]. Thus, immune activation should be investigated in greater detail by analyzing CSF markers pro- and anti-inflammatory markers throughout the AD continuum, which we plan to explore in a subsequent study.
A limitation of these findings is that these markers are expressed or secreted by multiple cell types and are not completely specific to neuronal, microglial, or astrocyte expression. Fractalkine is mainly expressed on neurons in the CNS [79], but expression is also seen in astrocytes [80], especially in neuroinflammatory models [81–83]. Also, the choroid plexus has been shown to express fractalkine in experimental activation models [84]. MCP-1 is expressed by astrocytes [85, 86], microglia [87] and neurons [88]. YKL-40 is primarily expressed by astrocytes and to a lesser degree by microglia [89]. Although clusterin is mainly expressed by astrocytes [90–93], and especially reactive astrocytes [94], expression has also been shown in neurons [92–95] and degenerating oligodendrocytes [91]. TREM2, on the other hand, seems to be specific to microglia in the brain [96–99]. However, in peripheral tissue, TREM2 has been shown to be expressed by several myeloid cells, including tissue macrophages and dendritic cells [100].
In addition to a relatively small sample size, a further limitation in this work is the cross-sectional design, as longitudinal sampling is necessary for a better interpretation of the sequence of events along the AD continuum. Furthermore, a more extensive mapping of inflammatory cytokine markers will be needed.
Conclusion
We here demonstrate increased microglial activation at a preclinical AD stage, with increased CSF sTREM2 levels in Aβ + SCD. The MCP-1 level was significantly enhanced at the Aβ + MCI stage, and CSF YKL-40 in AD dementia, suggesting a shift towards a more harmful stage of immune activation as AD progresses. Furthermore, our findings suggest that inflammation is associated with neurodegeneration, but not with amyloid pathology alone.
Additional files
Table S1. Literature overview CSF immune markers in AD clinical groups. (DOCX 72 kb)
Figure S1. Correlation between CSF YKL-40 and age. (PDF 805 kb)
Figure S2. Between-group comparisons of microglial- and astroglial activation with inflammation based on clinical staging. (PDF 277 kb)
Acknowledgements
We thank Erna Utnes (Akershus University Hospital, Norway) for assistance with data collection and handling and Department of Interdisciplinary Laboratory Medicine for analyzing the established AD markers; Aβ42, T-tau, and P-tau.
Funding
The project was funded by Norwegian Research Council, NASATS (Dementia Disease Initiation) and the JPND (APGeM) and funding from the regional health authorities (Helse Sør-Øst and Helse Nord). This paper represents independent research partly funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London. The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health. K.H. has been financially supported by Civitan Alzheimerfondet.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to data restrictions to keep the privacy of the patients, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request and with permission of the Regional Ethics Committee.
Abbreviations
- AD
Alzheimer’s disease
- ANOVA
Analysis of variance
- Aβ1-42
Amyloid beta 1-42 peptide
- CCR2
CC chemokine receptor type 2, MCP-1 receptor
- CDR
Clinical Dementia Rating Scale
- CERAD
Consortium to Establish a Registry for Alzheimer’s Disease
- COWAT
Controlled Oral Word Association Test
- CSF
Cerebrospinal fluid
- CT
Computer tomography
- CV
Coefficient of variation
- CX3CL1
Fractalkine
- CX3CR1
Fractalkine receptor
- DDI
Dementia Disease Initiation
- LLOQ
Lower limit of quantification
- MCI
Mild cognitive impairment
- MCI-GO
Gothenburg-Oslo MCI
- MCP-1
Monocyte chemoattractant protein 1
- MMSE
Mini-Mental State Examination
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MSD
Meso Scale Discovery
- n.s.
Non-significant
- NIA-AA
National Institute on Aging–Alzheimer’s Association
- PET
Positron emission tomography
- P-tau
Phosphorylated tau
- Q-Q plots
Quantile-quantile plots
- RD
Relative deviation
- SCD
Subjective cognitive decline
- SD
Standard deviation
- SOP
Standard operating procedure
- SPSS
Statistical Package for Social Sciences
- sTREM2
Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2
- TMT-B
Trail Making Test part B
- T-tau
Total tau
- VOSP
Visual Object and Space Perception
- YKL-40
Chitinase-3-like protein 1
- Aβ+
Pathological amyloid beta 142 peptide in the cerebrospinal fluid
Authors’ contributions
KN interpreted the inflammatory markers and patient data, performed the statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript with discussions and contributions from BEK, KH, SBT, PS, LN, and TF during the process. TF planned the project, in collaboration with all authors. KH re-validated the sTREM2 ELISA and assayed CSF sTREM2. MW and BG performed the MSD ELISA analyses with aid from SBT in method development. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The project has been considered by the Norwegian Regional Ethics Committee (approval number for the DDI project: 2013/115, approval number for the genetic analysis (APGEM): 2014/1164, approval number for the biobank: 2011/1051). The local data protection officer at Akershus University Hospital has also approved the study with the according approval number 13-056, 14-156 and 13-088. Data handling was in accordance with local and national regulations, with security precautions for storage and regulated biobank facilities. Both sexes are equally included, patients and controls give informed consent to participate in the study. The DDI has a patient and caregiver representative in the steering group. User participation is ensured with open meetings and written information.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Dr. Aarsland has received research support and/or honoraria from Astra-Zeneca, H. Lundbeck, Novartis Pharmaceuticals, and GE Health and serves as paid consultant for H. Lundbeck, Eisai, Heptares, and Axovant. Dag Aarsland is a Royal Society Wolfson Research Merit Award Holder and would like to thank the Wolfson Foundation and the Royal Society for their support. Dr. Fladby is inventor and co-founder of Inventor Pre Diagnostics A/S. All other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Kaja Nordengen, Phone: +47 679 66 981, Email: kaja.nordengen@medisin.uio.no.
Bjørn-Eivind Kirsebom, Email: bjorn-eivind.kirsebom@unn.no.
Kristi Henjum, Email: kristi.henjum@medisin.uio.no.
Per Selnes, Email: per.selnes@medisin.uio.no.
Berglind Gísladóttir, Email: berglind.gisladottir@ahus.no.
Marianne Wettergreen, Email: marianne.wettergreen@ahus.no.
Silje Bøen Torsetnes, Email: silje.torsetnes@medisin.uio.no.
Gøril Rolfseng Grøntvedt, Email: goril.r.grontvedt@ntnu.no.
Knut K. Waterloo, Email: knut.waterloo@uit.no
Dag Aarsland, Email: daarsland@gmail.com.
Lars N. G. Nilsson, Email: lars.nilsson@medisin.uio.no
Tormod Fladby, Email: tormod.fladby@medisin.uio.no.
References
- 1.Jack CR, Jr, Bennett DA, Blennow K, Carrillo MC, Dunn B, Haeberlein SB, et al. NIA-AA research framework: toward a biological definition of Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2018;14(4):535–562. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2018.02.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jack CR, Jr, Bennett DA, Blennow K, Carrillo MC, Feldman HH, Frisoni GB, et al. A/T/N: an unbiased descriptive classification scheme for Alzheimer disease biomarkers. Neurology. 2016;87(5):539–547. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jessen F, Amariglio RE, van Boxtel M, Breteler M, Ceccaldi M, Chetelat G, et al. A conceptual framework for research on subjective cognitive decline in preclinical Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 2014;10(6):844–852. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2014.01.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Albert MS, DeKosky ST, Dickson D, Dubois B, Feldman HH, Fox NC, et al. The diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 2011;7(3):270–279. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Sperling RA, Aisen PS, Beckett LA, Bennett DA, Craft S, Fagan AM, et al. Toward defining the preclinical stages of Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & Dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 2011;7(3):280–292. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR, Jr, Kawas CH, et al. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 2011;7(3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fladby T, Palhaugen L, Selnes P, Waterloo K, Brathen G, Hessen E, et al. Detecting at-risk Alzheimer's disease cases. J Alzheimers Dis. 2017;60(1):97–105. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Reijs BL, Teunissen CE, Goncharenko N, Betsou F, Blennow K, Baldeiras I, et al. The central biobank and virtual biobank of BIOMARKAPD: a resource for studies on neurodegenerative diseases. Front Neurol. 2015;6:216. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2015.00216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Villegas-Llerena C, Phillips A, Garcia-Reitboeck P, Hardy J, Pocock JM. Microglial genes regulating neuroinflammation in the progression of Alzheimer's disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2016;36:74–81. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2015.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Jonsson T, Stefansson H, Steinberg S, Jonsdottir I, Jonsson PV, Snaedal J, et al. Variant of TREM2 associated with the risk of Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(2):107–116. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1211103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lambert JC, Heath S, Even G, Campion D, Sleegers K, Hiltunen M, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and CR1 associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nat Genet. 2009;41(10):1094–1099. doi: 10.1038/ng.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cirrito JR, Yamada KA, Finn MB, Sloviter RS, Bales KR, May PC, et al. Synaptic activity regulates interstitial fluid amyloid-beta levels in vivo. Neuron. 2005;48(6):913–922. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.10.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mandrekar S, Jiang Q, Lee CY, Koenigsknecht-Talboo J, Holtzman DM, Landreth GE. Microglia mediate the clearance of soluble Abeta through fluid phase macropinocytosis. J Neurosci. 2009;29(13):4252–4262. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5572-08.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tarasoff-Conway JM, Carare RO, Osorio RS, Glodzik L, Butler T, Fieremans E, et al. Clearance systems in the brain-implications for Alzheimer disease. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11(8):457–470. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2015.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Neniskyte U, Gross CT. Errant gardeners: glial-cell-dependent synaptic pruning and neurodevelopmental disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2017;18(11):658–670. doi: 10.1038/nrn.2017.110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Colonna M, Butovsky O. Microglia function in the central nervous system during health and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Immunol. 2017;35:441–468. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-051116-052358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Guerreiro R, Wojtas A, Bras J, Carrasquillo M, Rogaeva E, Majounie E, et al. TREM2 variants in Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2013;368(2):117–127. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1211851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.International Genomics of Alzheimer’s Disease Consortium (IGAP) Convergent genetic and expression data implicate immunity in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015;11(6):658–671. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2014.05.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yeh FL, Hansen DV, Sheng M. TREM2, microglia, and neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Mol Med. 2017;23(6):512–533. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2017.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Sarlus H, Heneka MT. Microglia in Alzheimer's disease. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(9):3240–3249. doi: 10.1172/JCI90606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Southam KA, Vincent AJ, Small DH. Do microglia default on network maintenance in Alzheimer's disease? J Alzheimers Dis. 2016;51(3):657–669. doi: 10.3233/JAD-151075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J, Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet Neurol. 2015;14(4):388–405. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)70016-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hickman SE, Allison EK, El Khoury J. Microglial dysfunction and defective beta-amyloid clearance pathways in aging Alzheimer's disease mice. J Neurosci. 2008;28(33):8354–8360. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0616-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Patterson BW, Elbert DL, Mawuenyega KG, Kasten T, Ovod V, Ma S, et al. Age and amyloid effects on human central nervous system amyloid-beta kinetics. Ann Neurol. 2015;78(3):439–453. doi: 10.1002/ana.24454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hamelin L, Lagarde J, Dorothee G, Leroy C, Labit M, Comley RA, et al. Early and protective microglial activation in Alzheimer's disease: a prospective study using 18F-DPA-714 PET imaging. Brain. 2016;139(Pt 4):1252–1264. doi: 10.1093/brain/aww017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Fan Z, Brooks DJ, Okello A. Edison P. Brain: An early and late peak in microglial activation in Alzheimer's disease trajectory; 2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Brendel M, Kleinberger G, Probst F, Jaworska A, Overhoff F, Blume T, et al. Increase of TREM2 during aging of an Alzheimer's disease mouse model is paralleled by microglial activation and amyloidosis. Front Aging Neurosci. 2017;9:8. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2017.00008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang Y, Ulland TK, Ulrich JD, Song W, Tzaferis JA, Hole JT, et al. TREM2-mediated early microglial response limits diffusion and toxicity of amyloid plaques. J Exp Med. 2016;213(5):667–675. doi: 10.1084/jem.20151948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Suarez-Calvet M, Kleinberger G, Araque Caballero MA, Brendel M, Rominger A, Alcolea D, et al. sTREM2 cerebrospinal fluid levels are a potential biomarker for microglia activity in early-stage Alzheimer's disease and associate with neuronal injury markers. EMBO Mol Med. 2016;8(5):466–476. doi: 10.15252/emmm.201506123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Gispert JD, Suarez-Calvet M, Monte GC, Tucholka A, Falcon C, Rojas S, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid sTREM2 levels are associated with gray matter volume increases and reduced diffusivity in early Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2016;12(12):1259–1272. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2016.06.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Atagi Y, Liu CC, Painter MM, Chen XF, Verbeeck C, Zheng H, et al. Apolipoprotein E is a ligand for triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) J Biol Chem. 2015;290(43):26043–26050. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.679043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bailey CC, DeVaux LB, Farzan M. The triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 binds apolipoprotein E. J Biol Chem. 2015;290(43):26033–26042. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.677286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yeh FL, Wang Y, Tom I, Gonzalez LC, Sheng M. TREM2 binds to apolipoproteins, including APOE and CLU/APOJ, and thereby facilitates uptake of amyloid-Beta by microglia. Neuron. 2016;91(2):328–340. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2016.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pasinetti GM, Johnson SA, Oda T, Rozovsky I, Finch CE. Clusterin (SGP-2): a multifunctional glycoprotein with regional expression in astrocytes and neurons of the adult rat brain. J Comp Neurol. 1994;339(3):387–400. doi: 10.1002/cne.903390307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Li X, Ma Y, Wei X, Li Y, Wu H, Zhuang J, et al. Clusterin in Alzheimer's disease: a player in the biological behavior of amyloid-beta. Neurosci Bull. 2014;30(1):162–168. doi: 10.1007/s12264-013-1391-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Yu JT, Tan L. The role of clusterin in Alzheimer's disease: pathways, pathogenesis, and therapy. Mol Neurobiol. 2012;45(2):314–326. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8237-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Deming Y, Xia J, Cai Y, Lord J, Holmans P, Bertelsen S, et al. A potential endophenotype for Alzheimer's disease: cerebrospinal fluid clusterin. Neurobiol Aging. 2016;37:208.e1–.e9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 38.Gispert JD, Monte GC, Falcon C, Tucholka A, Rojas S, Sanchez-Valle R, et al. CSF YKL-40 and pTau181 are related to different cerebral morphometric patterns in early AD. Neurobiol Aging. 2016;38:47–55. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2015.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Llorens F, Thune K, Tahir W, Kanata E, Diaz-Lucena D, Xanthopoulos K, et al. YKL-40 in the brain and cerebrospinal fluid of neurodegenerative dementias. Mol Neurodegener. 2017;12(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13024-017-0226-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Antonell A, Mansilla A, Rami L, Llado A, Iranzo A, Olives J, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid level of YKL-40 protein in preclinical and prodromal Alzheimer's disease. J Alzheimers Dis. 2014;42(3):901–908. doi: 10.3233/JAD-140624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chen P, Zhao W, Guo Y, Xu J, Yin M. CX3CL1/CX3CR1 in Alzheimer's disease: a target for neuroprotection. Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:8090918. doi: 10.1155/2016/8090918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zujovic V, Benavides J, Vige X, Carter C, Taupin V. Fractalkine modulates TNF-alpha secretion and neurotoxicity induced by microglial activation. Glia. 2000;29(4):305–315. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1136(20000215)29:4<305::AID-GLIA2>3.0.CO;2-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mizuno T, Kawanokuchi J, Numata K, Suzumura A. Production and neuroprotective functions of fractalkine in the central nervous system. Brain Res. 2003;979(1–2):65–70. doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(03)02867-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Pabon MM, Bachstetter AD, Hudson CE, Gemma C, Bickford PC. CX3CL1 reduces neurotoxicity and microglial activation in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. J Neuroinflammation. 2011;8:9. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-8-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Strobel S, Grunblatt E, Riederer P, Heinsen H, Arzberger T, Al-Sarraj S, et al. Changes in the expression of genes related to neuroinflammation over the course of sporadic Alzheimer's disease progression: CX3CL1, TREM2, and PPARgamma. J Neural Transm. 2015;122(7):1069–1076. doi: 10.1007/s00702-015-1369-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Deshmane SL, Kremlev S, Amini S, Sawaya BE. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): an overview. J Interf Cytokine Res. 2009;29(6):313–326. doi: 10.1089/jir.2008.0027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Perea JR, Lleo A, Alcolea D, Fortea J, Avila J, Bolos M. Decreased CX3CL1 levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with Alzheimer's disease. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:609. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Desikan RS, Thompson WK, Holland D, Hess CP, Brewer JB, Zetterberg H, et al. The role of clusterin in amyloid-beta-associated neurodegeneration. JAMA Neurol. 2014;71(2):180–187. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2013.4560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Henjum K, Almdahl IS, Arskog V, Minthon L, Hansson O, Fladby T, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 in aging and Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2016;8(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13195-016-0182-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Liu D, Cao B, Zhao Y, Huang H, McIntyre RS, Rosenblat JD, et al. Soluble TREM2 changes during the clinical course of Alzheimer's disease: a meta-analysis. Neurosci Lett. 2018;686:10–16. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.08.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Mattsson N, Tabatabaei S, Johansson P, Hansson O, Andreasson U, Mansson JE, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid microglial markers in Alzheimer's disease: elevated chitotriosidase activity but lack of diagnostic utility. NeuroMolecular Med. 2011;13(2):151–159. doi: 10.1007/s12017-011-8147-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Westin K, Buchhave P, Nielsen H, Minthon L, Janciauskiene S, Hansson O. CCL2 is associated with a faster rate of cognitive decline during early stages of Alzheimer's disease. PLoS One. 2012;7(1):e30525. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Brosseron F, Traschutz A, Widmann CN, Kummer MP, Tacik P, Santarelli F, et al. Characterization and clinical use of inflammatory cerebrospinal fluid protein markers in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2018;10(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s13195-018-0353-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Galimberti D, Schoonenboom N, Scheltens P, Fenoglio C, Bouwman F, Venturelli E, et al. Intrathecal chemokine synthesis in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol. 2006;63(4):538–543. doi: 10.1001/archneur.63.4.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Blasko I, Lederer W, Oberbauer H, Walch T, Kemmler G, Hinterhuber H, et al. Measurement of thirteen biological markers in CSF of patients with Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord. 2006;21(1):9–15. doi: 10.1159/000089137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lidstrom AM, Hesse C, Rosengren L, Fredman P, Davidsson P, Blennow K. Normal levels of clusterin in cerebrospinal fluid in Alzheimer's disease, and no change after acute ischemic stroke. J Alzheimers Dis. 2001;3(5):435–442. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2001-3501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Prikrylova Vranova H, Henykova E, Mares J, Kaiserova M, Mensikova K, Vastik M, et al. Clusterin CSF levels in differential diagnosis of neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurol Sci. 2016;361:117–121. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2015.12.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Richens JL, Vere KA, Light RA, Soria D, Garibaldi J, Smith AD, et al. Practical detection of a definitive biomarker panel for Alzheimer's disease; comparisons between matched plasma and cerebrospinal fluid. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet. 2014;5(2):53–70. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yang C, Wang H, Li C, Niu H, Luo S, Guo X. Association between clusterin concentration and dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Metab Brain Dis. 2018. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 60.Kleinberger G, Yamanishi Y, Suarez-Calvet M, Czirr E, Lohmann E, Cuyvers E, et al. TREM2 mutations implicated in neurodegeneration impair cell surface transport and phagocytosis. Sci Transl Med. 2014, 6, 243:243ra86. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 61.Puchades M, Hansson SF, Nilsson CL, Andreasen N, Blennow K, Davidsson P. Proteomic studies of potential cerebrospinal fluid protein markers for Alzheimer's disease. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2003;118(1–2):140–146. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2003.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Heslegrave A, Heywood W, Paterson R, Magdalinou N, Svensson J, Johansson P, et al. Increased cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 concentration in Alzheimer's disease. Mol Neurodegener. 2016;11:3. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0071-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Piccio L, Deming Y, Del-Aguila JL, Ghezzi L, Holtzman DM, Fagan AM, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid soluble TREM2 is higher in Alzheimer disease and associated with mutation status. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131(6):925–933. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1533-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Deming Y, Black K, Carrell D, Cai Y, Del-Aguila JL, Fernandez MV, et al. Chitinase-3-like 1 protein (CHI3L1) locus influences cerebrospinal fluid levels of YKL-40. BMC Neurol. 2016;16(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s12883-016-0742-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Nilselid AM, Davidsson P, Nagga K, Andreasen N, Fredman P, Blennow K. Clusterin in cerebrospinal fluid: analysis of carbohydrates and quantification of native and glycosylated forms. Neurochem Int. 2006;48(8):718–728. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2005.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Selnes P, Fjell AM, Gjerstad L, Bjornerud A, Wallin A, Due-Tonnessen P, et al. White matter imaging changes in subjective and mild cognitive impairment. Alzheimer's & dementia : the journal of the Alzheimer's Association. 2012;8(5 Suppl):S112–S121. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.07.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kalheim LF, Fladby T, Coello C, Bjornerud A, Selnes P. [18F]-Flutemetamol uptake in cortex and white matter: comparison with cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers and [18F]-Fludeoxyglucose. J Alzheimers Dis. 2018;62(4):1595–1607. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Sjogren M, Vanderstichele H, Agren H, Zachrisson O, Edsbagge M, Wikkelso C, et al. Tau and Abeta42 in cerebrospinal fluid from healthy adults 21-93 years of age: establishment of reference values. Clin Chem. 2001;47(10):1776–1781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Warrington EK, James M. The visual object and space perception battery. Thames Valley Test Company: Bury St Edmunds, England; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 70.Heaton RK. Revised COmprehensive norms for an expanded Halstead-Reitan battery: demographically adjusted neuropsychological norms for African American and Caucasian adults: professional manual: psychological assessment resources. 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Sotaniemi M, Pulliainen V, Hokkanen L, Pirttila T, Hallikainen I, Soininen H, et al. CERAD-neuropsychological battery in screening mild Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neurol Scand. 2012;125(1):16–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2010.01459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Hughes CP, Berg L, Danziger WL, Coben LA, Martin RL. A new clinical scale for the staging of dementia. Br J Psychiatry. 1982;140:566–572. doi: 10.1192/bjp.140.6.566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Reisberg B, Ferris SH, de Leon MJ, Crook T. Global Deterioration Scale (GDS) Psychopharmacol Bull. 1988;24(4):661–663. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Li JW, Zong Y, Cao XP, Tan L, Tan L. Microglial priming in Alzheimer's disease. Annals of translational medicine. 2018;6(10):176. doi: 10.21037/atm.2018.04.22. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Hoeijmakers L, Heinen Y, van Dam AM, Lucassen PJ, Korosi A. Microglial priming and Alzheimer's disease: a possible role for (early) immune challenges and epigenetics? Front Hum Neurosci. 2016;10:398. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2016.00398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Morgan D. The role of microglia in antibody-mediated clearance of amyloid-beta from the brain. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2009;8(1):7–15. doi: 10.2174/187152709787601821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Jansen WJ, Ossenkoppele R, Tijms BM, Fagan AM, Hansson O, Klunk WE, et al. Association of Cerebral Amyloid-beta Aggregation with Cognitive Functioning in persons without dementia. JAMA psychiatry. 2018;75(1):84–95. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Fagan AM, Xiong C, Jasielec MS, Bateman RJ, Goate AM, Benzinger TL, et al. Longitudinal change in CSF biomarkers in autosomal-dominant Alzheimer's disease. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(226):226ra30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 79.Harrison JK, Jiang Y, Chen S, Xia Y, Maciejewski D, McNamara RK, et al. Role for neuronally derived fractalkine in mediating interactions between neurons and CX3CR1-expressing microglia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(18):10896–10901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.18.10896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Hulshof S, van Haastert ES, Kuipers HF, van den Elsen PJ, De Groot CJ, van der Valk P, et al. CX3CL1 and CX3CR1 expression in human brain tissue: noninflammatory control versus multiple sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2003;62(9):899–907. doi: 10.1093/jnen/62.9.899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Maciejewski-Lenoir D, Chen S, Feng L, Maki R, Bacon KB. Characterization of fractalkine in rat brain cells: migratory and activation signals for CX3CR-1-expressing microglia. J Immunol. 1999;163(3):1628–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Hughes PM, Botham MS, Frentzel S, Mir A, Perry VH. Expression of fractalkine (CX3CL1) and its receptor, CX3CR1, during acute and chronic inflammation in the rodent CNS. Glia. 2002;37(4):314–327. doi: 10.1002/glia.10037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Yoshida H, Imaizumi T, Fujimoto K, Matsuo N, Kimura K, Cui X, et al. Synergistic stimulation, by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interferon-gamma, of fractalkine expression in human astrocytes. Neurosci Lett. 2001;303(2):132–136. doi: 10.1016/S0304-3940(01)01699-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Mills JH, Alabanza LM, Mahamed DA, Bynoe MS. Extracellular adenosine signaling induces CX3CL1 expression in the brain to promote experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuroinflammation. 2012;9:193. doi: 10.1186/1742-2094-9-193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Kalehua AN, Nagel JE, Whelchel LM, Gides JJ, Pyle RS, Smith RJ, et al. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and macrophage inflammatory protein-2 are involved in both excitotoxin-induced neurodegeneration and regeneration. Exp Cell Res. 2004;297(1):197–211. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.02.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Wittendorp MC, Boddeke HW, Biber K. Adenosine A3 receptor-induced CCL2 synthesis in cultured mouse astrocytes. Glia. 2004;46(4):410–418. doi: 10.1002/glia.20016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Dicou E, Vincent JP, Mazella J. Neurotensin receptor-3/sortilin mediates neurotensin-induced cytokine/chemokine expression in a murine microglial cell line. J Neurosci Res. 2004;78(1):92–99. doi: 10.1002/jnr.20231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Banisadr G, Gosselin RD, Mechighel P, Kitabgi P, Rostene W, Parsadaniantz SM. Highly regionalized neuronal expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1/CCL2) in rat brain: evidence for its colocalization with neurotransmitters and neuropeptides. J Comp Neurol. 2005;489(3):275–292. doi: 10.1002/cne.20598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Bonneh-Barkay D, Bissel SJ, Kofler J, Starkey A, Wang G, Wiley CA. Astrocyte and macrophage regulation of YKL-40 expression and cellular response in neuroinflammation. Brain Pathol. 2012;22(4):530–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2011.00550.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.de Silva HV, Harmony JA, Stuart WD, Gil CM, Robbins J. Apolipoprotein J: structure and tissue distribution. Biochemistry. 1990;29(22):5380–5389. doi: 10.1021/bi00474a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Liu L, Persson JK, Svensson M, Aldskogius H. Glial cell responses, complement, and clusterin in the central nervous system following dorsal root transection. Glia. 1998;23(3):221–238. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1098-1136(199807)23:3<221::AID-GLIA5>3.0.CO;2-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Kullberg S, Aldskogius H, Ulfhake B. Microglial activation, emergence of ED1-expressing cells and clusterin upregulation in the aging rat CNS, with special reference to the spinal cord. Brain Res. 2001;899(1–2):169–186. doi: 10.1016/S0006-8993(01)02222-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Charnay Y, Imhof A, Vallet PG, Hakkoum D, Lathuiliere A, Poku N, et al. Clusterin expression during fetal and postnatal CNS development in mouse. Neuroscience. 2008;155(3):714–724. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.06.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Danik M, Chabot JG, Hassan-Gonzalez D, Suh M, Quirion R. Localization of sulfated glycoprotein-2/clusterin mRNA in the rat brain by in situ hybridization. J Comp Neurol. 1993;334(2):209–227. doi: 10.1002/cne.903340205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.O'Bryan MK, Cheema SS, Bartlett PF, Murphy BF, Pearse MJ. Clusterin levels increase during neuronal development. J Neurobiol. 1993;24(4):421–432. doi: 10.1002/neu.480240402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Frank S, Burbach GJ, Bonin M, Walter M, Streit W, Bechmann I, et al. TREM2 is upregulated in amyloid plaque-associated microglia in aged APP23 transgenic mice. Glia. 2008;56(13):1438–1447. doi: 10.1002/glia.20710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Takahashi K, Rochford CD, Neumann H. Clearance of apoptotic neurons without inflammation by microglial triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells-2. J Exp Med. 2005;201(4):647–657. doi: 10.1084/jem.20041611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Jiang T, Tan L, Zhu XC, Zhang QQ, Cao L, Tan MS, et al. Upregulation of TREM2 ameliorates neuropathology and rescues spatial cognitive impairment in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014;39(13):2949–2962. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Jiang T, Yu JT, Zhu XC, Tan MS, Gu LZ, Zhang YD, et al. Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 knockdown exacerbates aging-related neuroinflammation and cognitive deficiency in senescence-accelerated mouse prone 8 mice. Neurobiol Aging. 2014;35(6):1243–1251. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.11.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Bouchon A, Dietrich J, Colonna M. Cutting edge: inflammatory responses can be triggered by TREM-1, a novel receptor expressed on neutrophils and monocytes. J Immunol. 2000;164(10):4991–4995. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.164.10.4991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. Literature overview CSF immune markers in AD clinical groups. (DOCX 72 kb)
Figure S1. Correlation between CSF YKL-40 and age. (PDF 805 kb)
Figure S2. Between-group comparisons of microglial- and astroglial activation with inflammation based on clinical staging. (PDF 277 kb)
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to data restrictions to keep the privacy of the patients, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request and with permission of the Regional Ethics Committee.