Abstract
Recently, a novel mobile colistin resistance gene, mcr-8, was identified in Klebsiella pneumoniae. Here, we report the identification of mcr-8 and its variant, mcr-8.4, in Raoultella ornithinolytica isolates which also belong to Enterobacteriaceae family. The mcr-8 gene was located on transferrable plasmids with difference sizes. Notably, the transferability of mcr-8-carrying plasmids was enhanced once they entered into Escherichia coli hosts and multiple β-lactamase genes could co-transfer with mcr-8. These findings expand our knowledge of mcr-8-carrying bacterial species.
Keywords: colistin resistance, mcr-8, mcr-8.4, β-lactamase, Raoultella ornithinolytica
Introduction
Colistin (polymyxin E), a polypeptide antibiotic, was originally isolated from the soil bacterium Paenibacillus polymyxa subsp. colistin (Poirel et al., 2017). Colistin is effective against most Gram-negative bacteria and was considered as one of the last-resort antibiotics for the treatment of human infections caused by multidrug resistant Gram-negative bacteria, especially, carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) (Li et al., 2006). However, in 2016, the first plasmid mediated colistin resistance gene mcr-1 was identified in Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Liu et al., 2016). To date, the mcr-1 gene has been detected in Enterobacteriaceae isolated from food, animals, human and environment in over 50 countries across five different continents (Hembach et al., 2017; Huang et al., 2017). Subsequently, plasmid-mediated colistin resistance genes mcr-2, mcr-3, mcr-4, mcr-5, mcr-6, and mcr-7 have been identified in various bacterial species from humans and animals (Partridge et al., 2018). Recently, we reported the identification of mcr-8 located on an InFII-type conjugative plasmid in Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from chickens and pigs in China (Wang et al., 2018).
Raoultella ornithinolytica is closely related to Klebsiella and belongs to Enterobacteriaceae family (Beye et al., 2018; Hajjar et al., 2018). R. ornithinolytica is usually found in animals, soil, and botanical environment. This organism caused human infections, initially rare, are increasing according to several reports (Sun et al., 2015; Ponce-Alonso et al., 2016; Beye et al., 2018). So far, multi-drug resistance has been detected in R. ornithinolytica (Walckenaer et al., 2004; Castanheira et al., 2009; Khajuria et al., 2013), including mcr-1 positive isolates (Luo et al., 2017). Here, we report the emergence of mcr-8 in R. ornithinolytica.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial Isolation and Identification
A total of 300 cloaca samples were collected from chicken in commercial poultry farms of Shandong Province, China, in 2016. All the samples were screened on the CHROMAgar Orientation agar plate (bioMérieux, Lyon, France) containing 2 μg/ml colistin. The identification of bacterial species was performed using MALDI-TOF MS (BruKer Daltonik, Bremen, Germany), and then confirmed by 16S rDNA sequence analysis as described previously (Zhang et al., 2015; Luo et al., 2017). The presence of mcr (mcr-1 to mcr-8) in R. ornithinolytica was determined by PCR amplification and followed by Sanger sequencing as described previously (Wang et al., 2018).
Before collection the study samples, we have drafted an application “Detection of plasmid mediated colistin resistance genes of Enterobacteriaceae in Shandong, China,” within which chicken are designed to be used as research object in this antimicrobial resistance study. Those experiments are guaranteed to conduct in accordance with the principles of the Beijing Municipality Review of Welfare and Ethics of Laboratory Animals, as well as rules and regulations from China Agricultural University’s committee on animal welfare and ethics. Finally, this application was approved by committee on Animal Welfare and Ethics in China Agricultural University.
S1-PFGE and Southern Blotting
S1 nuclease-PFGE and Southern blotting were performed to locate the mcr-8 gene in both donor and recipient strains as described previously (Zheng et al., 2017). Briefly, agarose gel plugs embedded strains were digested with S1 nuclease (TakaRa, Dalian, China), and Southern blotting was performed using the DIG-High Prime DNA Labeling and Detection Starter Kit II (Roche Diagnostics). The genomic DNA of the Salmonella enterica serovar Braenderup H9812 strain restricted with XbaI was used as the DNA marker. The mcr-8 probe was the one, which we previously reported (Wang et al., 2018).
Conjugation Assay
The horizontal transferability of mcr-8 was examined using conjugation assay with E. coli J53 (azide-resistant) or E. coli EC600 (rifampicin-resistant) as the recipient strain. Considering colistin resistance spontaneous mutants might be confused with colistin transconjugants, the conjugation assay with E. coli J53 were performed twice, first was selected on LB agar plates containing 4 μg/ml colistin and 100 μg/ml azide, second was selected on 16 μg/ml amoxicillin and 100 μg/ml azide LB agar plates. In parallel, QDRO1 and QDRO2, and recipient strains J53 were plated on conjugation plates as control. Transconjugants were confirmed by PCR targeting the mcr-8 and β-lactamase genes, blaTEM-1B and blaOXA-1 in QDRO1 and QDRO2 transconjugants, respectively, as well as XbaI enzyme digested pulsed field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). For analysis of the transfer ability of mcr-8 in the same genus, we further performed conjugation assay using the above identified QDRO1 and QDRO2 transconjugants (T-QDRO1 and T-QDRO2) as donor strains and E. coli EC600 as recipient strain. The transfer frequency was calculated as the number of transconjugants per recipient as previous reported (Zhao et al., 2017).
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Test
The MICs of wild strains and transconjugants to antimicrobial agents (listed in Table 1) were determined by broth microdilution method, and the results were interpreted according to CLSI and European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). The E. coli ATCC 25922 was used as a quality control strain.
Table 1.
The minimum inhibitory concentrations of tested antimicrobial agents for the studied bacterial isolates.
| Bacterial isolate1 | MICs (μg/ml)2 |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CST | PB | AMC | AZT | CAZ | GEN | TET | FFC | CHL | CIP | |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO1 | 16 | 8 | 128/64 | 2 | 64 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 128 |
| T-QDRO1 | 16 | 4 | 32/16 | 2 | 16 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 4 | 4 | 0.004 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO2 | 8 | 4 | 128/64 | 8 | 32 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 128 |
| T-QDRO2 | 8 | 4 | 32/16 | 4 | 16 | 0.25 | 0.5 | 4 | 4 | 0.004 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO3 | 4 | 4 | 128/64 | 2 | 64 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 16 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO4 | 8 | 8 | 64/32 | 2 | 32 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 128 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO5 | 16 | 8 | 128/64 | 4 | 32 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 64 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO6 | 8 | 8 | 64/32 | 4 | 32 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 32 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO7 | 8 | 8 | 64/32 | 4 | 16 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 0.008 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO8 | 16 | 16 | 128/64 | 4 | 32 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 64 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO9 | 32 | 16 | 128/64 | 4 | 32 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 64 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO10 | 64 | 32 | 128/64 | 4 | 64 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 128 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO11 | 4 | 4 | 64/32 | 2 | 32 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 64 |
| R. ornithinolytica QDRO12 | 8 | 8 | 128/64 | 4 | 32 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 128 |
| R. planticola QDRP1 | 8 | 8 | 64/32 | 4 | 8 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 16 |
| R. planticola QDRP2 | 4 | 4 | 64/32 | 4 | 16 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 8 |
| R. terrigena QDRT1 | 2 | 2 | 32/16 | 4 | 8 | >512 | >256 | >256 | >256 | 0.016 |
1T-QDRO1 and T-QDRO2 represent the transconjugations of R.ornithinolytica QDRO1 and R.ornithinolytica QDRO2. 2Antimicrobial agents are abbreviated as follows: CST, colistin; PB, polymyxin B; AMC, amoxicillin-clavulanate; AZT, aztreonam; CAZ, ceftazidime; GEN, gentamycin; TET, tetracycline; FFC, florfenicol; CHL, chloramphenicol; CIP, ciprofloxacin. The bold numbers mean the isolates are resistant to the tested antimicrobial agent.
Genome Sequencing and Analysis of Antibiotic Resistance Genes
Genomic DNA of the isolates were extracted using the Wizard Genomic DNA Purification kit (Promega), then subjected to WGS on the Illumina HiSeq 2500 platform according to the manufacturer’s protocols, which produced 150-bp paired-end reads. For each isolate analyzed by WGS, at least 100-fold coverage of raw reads was collected. The draft genomes were assembled using CLC Genomics Workbench 9.0 (CLC Bio, Aarhus, Denmark). Reference sequences of antibiotic resistance genes were from database ARG-ANNOT (de Man and Limbago, 2016).
Results and Discussion
Presence and Location of mcr-8 in Raoultella spp
A total of 15 Raoultella spp strains obtained from 300 chicken cloaca samples, among which 12 R. ornithinolytica, 2 R. planticola, and 1 R. terrigena. PCR assays showed that two R. ornithinolytica strains, named QDRO1 and QDRO2, were positive for mcr-8, but no other mcr genes were identified in this 15 Raoultella spp strains. S1-PFGE and Southern blotting assay indicated that mcr-8 were located on ∼90-kb and ∼200-kb plasmids in QDRO1 and QDRO2, respectively (Figure 1). These two mcr-8-carrying plasmids were named as pQDRO1 and pQDRO2, respectively.
FIGURE 1.
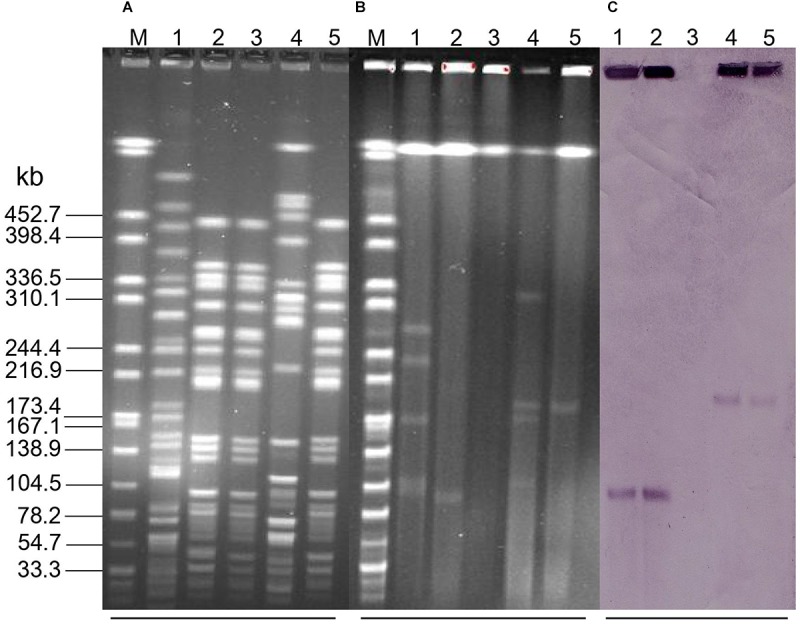
The location of mcr-8 in Raoultella ornithinolytica QDRO1 and QDRO2 isolates and their transconjugants. (A) XbaI-digested PFGE of the R. ornithinolytica QDRO1 and QDRO2 isolates, transconjugants, and recipient Escherichia coli J53. (B) S1-PFGE and (C) the corresponding Southern hybridization using the mcr-8-specific probe. Lane M, marker H9812; Lane 1, R. ornithinolytica QDRO1; Lane 2, transconjugant T-QDRO1; Lane 3, recipient E. coli J53; Lane 4, R. ornithinolytica QDRO2; Lane 5, transconjugant T-QDRO2.
Transferability of mcr-8 Gene
Conjugation assays showed that the pQDRO1 and pQDRO2 plasmids were transferable from R. ornithinolytica to recipient E. coli strains. The transfer frequencies of the pQDRO1 and pQDRO2 plasmids to E. coli J53 were 2.28 ± 1.64 × 10-8 and 1.71 ± 1.01 × 10-8, respectively. Meanwhile, transconjugants from amoxicillin and azide plates were resistant to colistin and mcr-8 positive. These suggested that mcr-8 was co-transferred with β-lactamase genes. As expected, donor strains QDRO1 and QDRO2, and recipient J53 did not grow on colistin and azide plates, or amoxicillin and azide plates. To determine whether the adaptation of mcr-8-carrying plasmids in E. coli could affect their transfer frequencies, we further performed the conjugation assays using the transconjugants as donor strains and E. coli EC600 as recipient strain. We found that the transfer frequencies of the pQDRO1 and pQDRO2 plasmids increased 103 and 104 folds, respectively, compared with the transfer frequencies of plasmids from R. ornithinolytica QDRO1 and QDRO2 to E. coli, respectively. To determine if the transfer frequencies of plasmids could be affected by the recipient bacteria, we performed the conjugation assays using the parental strains R. ornithinolytica QDRO1 and QDRO2 as donors and E. coli EC600 as recipients. The transfer frequencies of the pQDRO1 and pQDRO2 plasmids from R. ornithinolytica to E. coli EC600 were 4.17 ± 1.35 × 10-7 and 3.09 ± 1.29 × 10-7, respectively. We further performed the conjugation assays using the obtained transconjugants as donor strains and E. coli J53 as recipient strain. The transfer frequencies of pQDRO1 and pQDRO2 were 2.74 ± 1.31 × 10-4 and 3.71 ± 1.98 × 10-4, respectively. Similar to the previous results, increased transfer frequencies were observed for the pQDRO1 and pQDRO2 plasmids once they adapted to the E. coli host. These findings demonstrated that mcr-8 gene is able to transfer between different bacterial species, which may further promote the dissemination of drug resistance.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility
Antimicrobial susceptibility test showed that this 15 Raoultella spp strains were all resistant to colistin, polymyxin B, amoxicillin-clavulanate, aztreonam, ceftazidime, tetracycline, florfenicol, chloramphenicol, and only R. ornithinolytica QDRO7 and R. terrigena QDRT1 were sensitivity to ciprofloxacin (Table 1). Both transconjugants were not only resistant to colistin and polymyxin B, but also resistant to β-lactam antibiotics, such as amoxicillin-clavulanate, aztreonam and ceftazidime, which implied that β-lactamase producing genes might be co-transferred with mcr-8.
Whole Genome Sequencing Analysis
WGS analysis showed that a 16.5-kb contig (GenBank: QWIX00000000) of R. ornithinolytica QDRO1 carrying mcr-8 showed 100% query coverage and 99% identity to the corresponding segment of the mcr-8-carrying plasmid pKP91 from K. pneumoniae (Genbank number: MG736312) by Blastin in the NCBI database. A mcr-8 variant, termed mcr-8.4 (Genbank number: MH791448), was found in this 16.5-kb contig. Compared with mcr-8, mcr-8.4 gene carried an A1209C transversion, which resulted in Serine to Arginine substitution. Similarly, the 25.5-kb mcr-8-carrying contig (Genbank number: MK097469) of R. ornithinolytica QDRO2 showed 83% query coverage and 99% identity to the corresponding segment of the mcr-8-carrying plasmid pKP91 from K. pneumoniae. Genetic structure analysis of the two mcr-8-carrying contigs showed that two copies of ΔIS903B located upstream and downstream of mcr-8.4 in R. ornithinolytica QDRO1, while, only one copy of ΔIS903B located upstream of mcr-8 in R. ornithinolytica QDRO2 (Supplementary Figure S1). Plasmid replicon type was carried out using the Center for Genomic Epidemiology1, and showed that R. ornithinolytica QDRO1 contained IncHI2, IncA/C2, IncX3, and IncFII-type plasmids, and R. ornithinolytica QDRO2 contained IncHI2, IncFIB, IncHI1B, and IncFII-type plasmids. To further identify the replicon type of plasmids pQDRO1 and pQDRO2, we detected the replicon genes, which found in wild strains, in transconjugants of R. ornithinolytica QDRO1 and QDRO2 using primers listed in Supplementary Table S1. Results showed that the plasmids pQDRO1 and pQDRO2 both belong to IncFII-type, which is same with plasmid pKP91.
Analysis of the whole genome sequences of QDRO1 and QDRO2 isolates showed that these two strains contained multiple resistance genes (Table 1). As shown, except mcr-8.4, R. ornithinolytica QDRO1 also contained aadA1, aph(3′)-Ia, strA, strB, aac(6′)-Ib, and armA, fosA, mph(E), floR, cml, qnrB4, sul, tet(B), tet(34), blaTEM-1B, blaOXA-1, blaDHA-1. Similarly, except mcr-8, R. ornithinolytica QDRO2 contained aac(3)-IVa, aph(4)-Ia, aadA2, fosA, mph(A), mph(E), cat, floR, cml, QnrS4, oqxAB, QnrB52, sul1, sul2 and sul3, tet(A), tet(34), tet(O), tet(B), blaTEM-1B, blaOXA-1, blaSHV -73.
Our above antimicrobial susceptibility assay suggests that β-lactamase genes might be co-transferred with mcr-8. In order to determine the co-transfer of these genes, PCR amplification was performed to detect the presence of β-lactamase genes in transconjugants using primers listed in Supplementary Table S1. blaTEM-1B and blaDHA-1 were detected in QDRO1 transconjugant, while blaOXA-1 and blaSHV -73 were present in QDRO2 transconjugant. These findings indicated that blaTEM-1B, blaDHA-1, blaOXA-1, and blaSHV -73 could co-transfer with mcr-8.
Conclusion
This study identified colistin resistance genes mcr-8 and its variant, mcr-8.4, in R. ornithinolytica. The two mcr-8-carrying IncFII-type plasmids could be transferred to E. coli by conjugation. In addition, the transferability of the two plasmids were enhanced once they entered into E. coli hosts, which might further accelerate the dissemination of mcr-8 among Enterobacteriaceae. It is worth noting that the co-transferability of mcr-8 with several β-lactamase genes may further facilitate the dissemination of mcr-8 among Enterobacteriaceae.
Author Contributions
ZS, SZ, and YaoW conceived and designed the experiments. XW, YaoW, YZ, and ZW performed the experiments. ZS and XW analyzed the data. XW, YanW, and ZS wrote the manuscript.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Funding. The study was supported by grants from National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0501304 and 2016YFD0501305).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fmicb.2019.00228/full#supplementary-material
References
- Beye M., Hasni I., Seng P., Michelle C., La Scola B., Raoult D., et al. (2018). Genomic analysis of a Raoultella ornithinolytica strain causing prosthetic joint infection in an immunocompetent patient. Sci. Rep. 8:9462. 10.1038/s41598-018-27833-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castanheira M., Deshpande L., Dipersio J., Kang J., Weinstein M., Jones R. (2009). First descriptions of blaKPC in Raoultella spp. (R. planticola and R. ornithinolytica): report from the sentry antimicrobial surveillance program. J. Clin. Microbiol. 47 4129–4130. 10.1128/JCM.01502-09 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Man T. J., Limbago B. (2016). SSTAR, a stand-alone easy-to-use antimicrobial resistance gene predictor. mSphere 1 e50–e15. 10.1128/mSphere.00050-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar R., Schwenter F., Su S., Gasse M., Sebajang H. (2018). Community-acquired infection to Raoultella ornithinolytica presenting as appendicitis and shock in a healthy individual. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2018:rjy097. 10.1093/jscr/rjy097 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hembach N., Schmid F., Alexander J., Hiller C., Rogall E. T., Schwartz T. (2017). Occurrence of the mcr-1 colistin resistance gene and other clinically relevant antibiotic resistance genes in microbial populations at different municipal wastewater treatment plants in Germany. Front. Microbiol. 8:1282. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01282 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang X., Yu L., Chen X., Zhi C., Yao X., Liu Y., et al. (2017). High prevalence of colistin resistance and mcr-1 gene in Escherichia coli isolated from food animals in China. Front. Microbiol. 8:562. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00562 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khajuria A., Praharaj A., Grover N., Kumar M. (2013). First report of blaNDM-1 in Raoultella ornithinolytica. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 57 1092–1093. 10.1128/AAC.02147-12 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J., Nation R., Turnidge J., Milne R., Coulthard K., Rayner C., et al. (2006). Colistin: the re-emerging antibiotic for multidrug-resistant gram-negative bacterial infections. Lancet Infect. Dis. 6 589–601. 10.1016/S1473-3099(06)70580-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Wang Y., Walsh T., Yi L., Zhang R., Spencer J., et al. (2016). Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: a microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 16 161–168. 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00424-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo J., Yao X., Lv L., Doi Y., Huang X., Huang S. (2017). Emergence of mcr-1 in Raoultella ornithinolytica and Escherichia coli isolates from retail vegetables in China. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 61 e1139–e1117. 10.1128/AAC.01139-17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Partridge S., Di Pilato V., Doi Y., Feldgarden M., Haft D., Klimke W. (2018). Proposal for assignment of allele numbers for mobile colistin resistance (mcr) genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 73 2625–2630. 10.1093/jac/dky262 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poirel L., Jayol A., Nordmann P. (2017). Polymyxins: antibacterial activity, susceptibility testing, and resistance mechanisms encoded by plasmids or chromosomes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 30 557–596. 10.1128/CMR.00064-16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponce-Alonso M., Rodriguez-Rojas L., Del C., Cantón R., Morosini M. (2016). Comparison of different methods for identification of species of the genus Raoultella: report of 11 cases of Raoultella causing bacteraemia and literature review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 22 252–257. 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.10.035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun F., Yin Z., Feng J., Qiu Y., Zhang D., Luo W., et al. (2015). Production of plasmid-encoding NDM-1 in clinical Raoultella ornithinolytica and Leclercia adecarboxylata from China. Front. Microbiol. 6:458. 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00458 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walckenaer E., Poirel L., Leflon-Guibout V., Nordmann P., Nicolas-Chanoine M. (2004). Genetic and biochemical characterization of the chromosomal class A beta-lactamases of Raoultella (formerly Klebsiella) Planticola and Raoultella ornithinolytica. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 48 305–312. 10.1128/AAC.48.1.305-312.2004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X., Wang Y., Zhou Y., Li J., Yin W., Wang S., et al. (2018). Emergence of a novel mobile colistin resistance gene, mcr-8, in NDM-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 7:122. 10.1038/s41426-018-0124-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang L., Gao Y., Lai L., Li S. (2015). Whole-cell-based identification of electrochemically active bacteria in microbial fuel cells by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 29 2211–2218. 10.1002/rcm.7387 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao F., Feng Y., Lű X., McNally A., Zong Z. (2017). Remarkable diversity of Escherichia coli carrying mcr-1 from hospital sewage with the identification of two new mcr-1 variants. Front. Microbiol. 8:2094. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02094 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng B., Huang C., Xu H., Guo L., Zhang J., Wang X., et al. (2017). Occurrence and genomic characterization of ESBL-producing. MCR-1-harboring Escherichia coli in farming soil. Front. Microbiol. 8:2510. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02510 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


