Abstract
Objectives
The aim was to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of niraparib compared with routine surveillance (RS), olaparib and rucaparib for the maintenance treatment of patients with recurrent ovarian cancer (OC).
Methods
A decision-analytic model estimated the cost per quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained for niraparib versus RS, olaparib, and rucaparib from a US payer perspective. The model considered recurrent OC patients with or without germline BRCA mutations (gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut), who were responsive to their last platinum-based chemotherapy regimen. Model health states were: progression-free disease, progressed disease and dead. Mean progression-free survival (PFS) was estimated using parametric survival distributions based on ENGOT-OV16/NOVA (niraparib phase III trial), ARIEL3 (rucaparib phase III trial) and Study 19 (olaparib phase II trial). Mean overall survival (OS) benefit was estimated as double the mean PFS benefit based on the relationship between PFS and OS observed in Study 19. Costs included: drug, chemotherapy, monitoring, adverse events, and terminal care. EQ-5D utilities were estimated from trial data.
Results
Compared to RS, niraparib was associated with an incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER) of US$68,287/QALY and US$108,287/QALY for gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut, respectively. Compared to olaparib and rucaparib, niraparib decreased costs and increased QALYs, with a cost saving of US$8799 and US$22,236 versus olaparib and US$198,708 and US$73,561 versus rucaparib for gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut, respectively.
Conclusions
Niraparib was estimated to be less costly and more effective compared to olaparib and rucaparib, and the ICER fell within an acceptable range compared to RS. Therefore, niraparib may be considered a cost-effective maintenance treatment for patients with recurrent OC.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1007/s40273-018-0745-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Key Points for Decision Makers
| Niraparib reduced costs and increased quality-adjusted life-years (QALYs) compared to olaparib and rucaparib, dominating both treatments. Therefore, niraparib was cost-effective compared to olaparib and rucaparib in both the gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut populations from a US payer perspective. |
| Niraparib increased costs and QALYs compared to routine surveillance. The resulting incremental cost-effectiveness ratio led to niraparib being considered cost-effective compared to routine surveillance in both the gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut populations from a US payer perspective. |
Introduction
Ovarian cancer (OC) is rare, with an estimated 22,440 new cases (1.3% of new cancer cases) diagnosed in the United States (US) in 2017 [1]. However, it is also the fifth deadliest cancer for women, with an estimated 14,080 deaths (2.3% of cancer deaths) in the US in 2017 and a 5-year survival rate of 46.5% [1, 2]. The presence of a BRCA mutation significantly increases the lifetime risk of developing OC, but patients without a BRCA mutation (~ 80% of all patients) are associated with worse long-term survival than those who carry the mutation [3–5]. OC is treatable, but frequently recurs, with relapse rates up to 95% for patients with advanced disease [6, 7].
Patients with recurrent OC (ROC) typically undergo systemic treatment with repeated courses of platinum-based chemotherapy (PBC), with the aim of increasing progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS). However, PFS decreases with each PBC course, until the disease becomes ‘platinum resistant’. At this point, patients are faced with limited treatment options and poor outcomes [8].
With current treatments offering no chance of cure and with decreasing PFS in between lines of PBC, the use of targeted maintenance treatments (MTs), such as poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi), to extend patients PFS and therefore extend the time between lines of chemotherapy has become an area of focus in the treatment of ROC [9]. By extending time to progression after PBC, MTs can increase the number of patients eligible for further PBC (i.e. patients who progress after 6 months) in the next treatment line, which may extend survival [8].
There are currently three PARPi licensed by the US Food and Drug Administration for use in the US as an MT for patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who have complete or partial response to PBC: niraparib, olaparib and rucaparib [10–12].
ENGOT-OV16/NOVA was a phase III, randomised controlled trial (RCT) wherein patients were divided by their BRCA mutation status and then randomised to receive niraparib or placebo. Patients in the niraparib group had a significantly longer median PFS compared to the placebo group, with a median PFS of 21.0 versus 5.5 months (gBRCAmut [p < 0.001]) and 9.3 versus 3.9 months (non-gBRCAmut [p < 0.001]) [13].
Study 19 and SOLO2 were phase II and III RCTs wherein patients were randomised to receive olaparib or placebo. Patients in the olaparib group had a significantly longer median PFS compared to the placebo group, with median PFS of 8.4 versus 4.8 months (Study 19 intention-to-treat [ITT] [p < 0.001]), 7.4 versus 5.5 months (Study 19 BRCAwt [p = 0.0075]) and 19.1 versus 5.5 months (SOLO2 gBRCAmut [p < 0.0001]) [14–16].
ARIEL3 was a phase III RCT wherein patients were randomised to receive rucaparib or placebo. Three nested cohorts were analysed: patients with BRCA mutations, with homologous recombination deficiencies (HRD) and the ITT population. Across the nested cohorts, median PFS was significantly longer (p < 0.0001) in patients in the rucaparib group than in the placebo group (16.6 versus 5.4 months [BRCA mutation], 13.6 versus 5.4 months [HRD], 10.8 versus 5.4 months [ITT]) [17]. The HRD subgroup was not included in our publication as HRD testing is not commonly used in clinical practice (< 2% of OC patients) [18].
Given the lack of a cure for ROC, there is a real need for effective MTs like niraparib, olaparib and rucaparib. This study sought to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of niraparib compared with routine surveillance (RS), olaparib and rucaparib for the MT of patients with ROC.
Methods
A cost-effectiveness model was developed in Microsoft® Excel 2010 (Redmond, Washington, US) to estimate the expected costs and outcomes of niraparib compared with RS, olaparib and rucaparib for the MT of patients with ROC. The primary outcome was the incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER), expressed as cost/quality-adjusted life-year (QALY) gained. Three systematic literature reviews (SLRs) were undertaken to identify clinical, economic, and health-related quality-of-life evidence of OC MTs (see the electronic supplementary material).
Target Population
The target population in the model was based on the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA trial population: adult patients with platinum-sensitive, recurrent, high-grade, serous epithelial ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who had received at least two platinum-based regimens and were responsive to their last PBC [13]. Since disease prognosis differs by BRCA status, the following populations were modelled separately:
Patients with a deleterious germline BRCA mutation or genetic variant, or suspected deleterious mutation (gBRCAmut cohort)
Patients without the hereditary germline BRCA mutation (non-gBRCAmut cohort)
Interventions
Olaparib and rucaparib are the only two licensed interventions for which niraparib would be considered as an alternative MT option (Sect. 1). Therefore, both were considered as comparators in addition to RS. A feasibility assessment concluded that formal indirect comparisons were not feasible between niraparib and these comparators (Sect. 4). Therefore, six analyses were considered (Table 1).
Table 1.
Analyses undertaken in the model
| gBRCAmut | Non-gBRCAmut |
|---|---|
|
● An analysis comparing niraparib with RS data from the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA study [13] ● A cost-minimisation analysis comparing niraparib with olaparib assuming equal efficacy such that efficacy data from the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA study used for both treatments [13, 19] ● An analysis comparing niraparib with rucaparib considering a naïve side-by-side comparison of results from the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA study for niraparib and the ARIEL3 study for rucaparib [13, 17] |
● An analysis comparing niraparib with RS data from the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA study [13] ● An analysis comparing niraparib with olaparib considering a naïve side-by-side comparison of results from the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA study for niraparib and Study 19 for olaparib [13, 15, 16] ● An analysis comparing niraparib with rucaparib considering a naïve side-by-side comparison of results from the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA study for niraparib and the ARIEL3 study for rucaparib [17] |
RS routine surveillance
Model Structure
A decision-analytic model was constructed to estimate the costs and QALYs of the target population. This structure has been previously adopted in OC publications and Health Technology Assessment submissions [20–22].
The model consists of three health states (HSs): progression-free disease (PFD), progressed disease (PD) and dead (Fig. 1). The PFD HS has been modelled to represent those patients on or off treatment without disease progression according to RECIST v1.1 and clinical criteria defined as per the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA trial protocol.
Fig. 1.
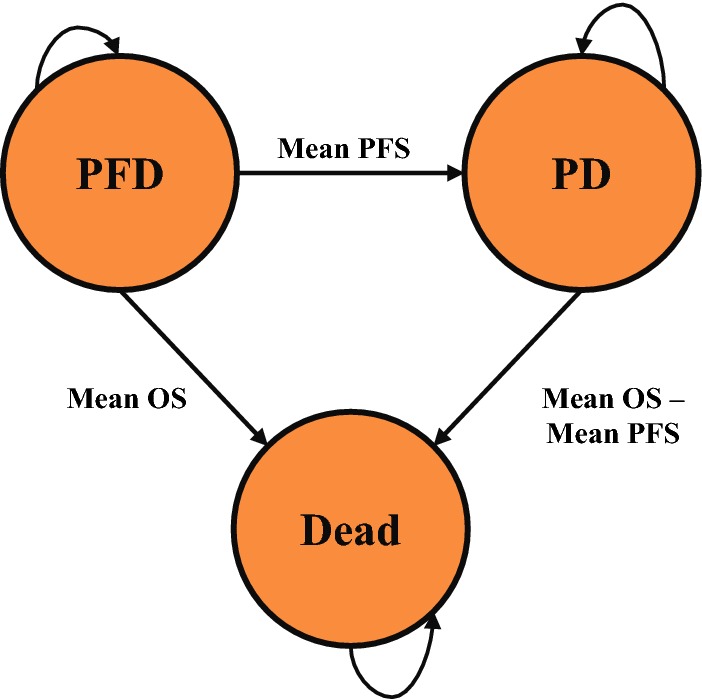
Model states and transitions. OS overall survival, PD progressed disease, PFD progression-free disease, PFS progression-free survival
Upon commencement of MT, patients entered the PFD HS. Patients transitioned to the PD HS after treatment-specific mean PFS, derived from trial data.
Patients then remained in the PD HS for the mean period of time, calculated as the difference between mean OS and mean PFS. Mean OS was calculated by treatment arm and derived from Study 19 for RS, with niraparib, olaparib, and rucaparib OS benefit extrapolated from PFS benefit.
Costs and QALYs for each treatment were accumulated based on the mean time spent in the PFD and PD HSs, from which incremental results and the cost/QALY were determined.
Time Horizon, Cycle Length, Discounting, and Perspective
A lifetime horizon was selected to ensure all differential costs and QALYs accumulated by patients until death were considered. A 30-day cycle length was adopted. A 3.0% annual discount rate was applied for costs and benefits in the cost-effectiveness analysis (CEA) in line with World Health Organization guidelines [23]. The analysis was conducted from a US payer perspective.
Clinical Effectiveness Inputs
The effectiveness and cost of the interventions were calculated based on the treatment-specific mean PFS, OS, and time on MT (TOMT). The treatment-specific means were calculated as the area under the curve using the trapezium rule (Eq. 1).
Trapezium rule
| 1 |
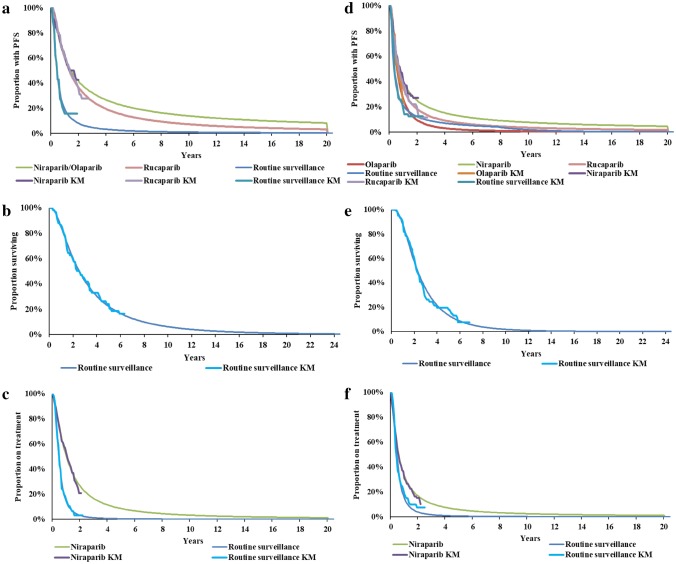
Parametric distributions were fitted to the Kaplan–Meier (KM) data for PFS, OS, and time to treatment discontinuation (TTD) (for TOMT) to extrapolate from the trial duration to the lifetime horizon. National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE) Decision Support Unit (DSU) guidelines were followed in fitting six parametric distributions to the KM data: exponential, Weibull, Gompertz, log-logistic, lognormal, and generalised gamma [24]. The best-fitting distribution was selected based on the lowest Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) and Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) (see the electronic supplementary material), visual inspection of the fitted distributions on the KM plots and validation by an external OC clinical expert. KM and parametric distributions for PFS, OS, and TTD by treatment are presented in Fig. 2, and mean PFS, OS, and TOMT by treatment are presented in Table 2.
Fig. 2.
KM plots and parametric distributions for PFS, OS and TTD. Left: gBRCAmut (a PFS; b OS; c TTD). Right: non-gBRCAmut (d PFS; e OS; f TTD). KM Kaplan–Meier, OS overall survival, PFS progression-free survival, RS routine surveillance, TTD time to treatment discontinuation
Table 2.
Clinical inputs and utilities
| Value | 95% CI | Distribution | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean PFS, OS, TOMT (years) | ||||
| gBRCAmut | ||||
| Niraparib | ||||
| Mean PFS | 4.14 | 2.25–7.20 | Generalised gamma | [13] |
| Mean OS | 10.22 | 6.45–16.35 | Varies based on PFS estimates | Calculation |
| Mean TOMT | 2.00 | 1.60–2.40 | Log-logistic | [13] |
| RS | ||||
| Mean PFS | 0.91 | 0.51–1.95 | Generalised gamma | [13] |
| Mean OS | 3.77 | 2.57–5.56 | Lognormal | [25] |
| Mean TOMT | 0.63 | 0.63–0.67 | Log-logistic | [13] |
| Olaparib | ||||
| Mean PFS | 4.14 | 2.25–7.20 | Assumed equal to niraparib | [13] |
| Mean OS | 10.22 | 6.45–16.35 | Assumed equal to niraparib | [13] |
| Mean TOMT | 2.00 | 1.60–2.40 | Assumed equal to niraparib | [13] |
| Rucaparib | ||||
| Mean PFS | 2.99 | 1.75–5.25 | Generalised gamma | [17] |
| Mean OS | 8.40 | 6.33–11.88 | Varies based on PFS estimates | Calculation |
| Mean TOMT | 2.99 | 1.75–5.25 | Assumed equal to PFS estimate | [17] |
| Non-gBRCAmut | ||||
| Niraparib | ||||
| Mean PFS | 2.59 | 1.59–3.82 | Generalised gamma | [13] |
| Mean OS | 5.82 | 4.29–8.74 | Varies based on PFS estimates | Calculation |
| Mean TOMT | 1.45 | 1.16–1.74 | Log-logistic | [13] |
| RS | ||||
| Mean PFS | 1.14 | 0.65–2.02 | Generalised gamma | [13] |
| Mean OS | 2.94 | 2.26–3.89 | Lognormal | [25] |
| Mean TOMT | 0.65 | 0.65–0.67 | Log-logistic | [13] |
| Olaparib | ||||
| Mean PFS | 1.65 | 1.23–3.87 | Generalised gamma | [16] |
| Mean OS | 3.95 | 3.11–8.40 | Varies based on PFS estimates | Calculation |
| Mean TOMT | 1.65 | 1.23–3.87 | Assumed equal to PFS estimate | [16] |
| Rucaparib | ||||
| Mean PFS | 1.74 | 1.15–2.60 | Generalised gamma | [17] |
| Mean OS | 5.26 | 4.30–6.51 | Varies based on PFS estimates | Calculation |
| Mean TOMT | 1.74 | 1.15–2.60 | Assumed equal to PFS estimate | [17] |
| AE incidence rates (%) | ||||
| Niraparib | ||||
| Anaemia | 25.34 | 16.09–35.87 | Beta | [13] |
| Thrombocytopenia | 33.79 | 21.25–47.60 | Beta | [13] |
| Neutropenia | 19.62 | 12.53–27.84 | Beta | [13] |
| Fatigue | 8.17 | 5.26–11.65 | Beta | [13] |
| Hypertension | 8.17 | 5.26–11.65 | Beta | [13] |
| Nausea | 3.00 | 1.94–4.28 | Beta | [13] |
| Vomiting | 1.91 | 1.23–2.72 | Beta | [13] |
| RS | ||||
| Anaemia | 0.00 | 0.00–0.00 | Beta | [13] |
| Thrombocytopenia | 0.56 | 0.36–0.80 | Beta | [13] |
| Neutropenia | 1.68 | 1.08–2.39 | Beta | [13] |
| Fatigue | 0.56 | 0.36–0.80 | Beta | [13] |
| Hypertension | 2.23 | 1.44–3.19 | Beta | [13] |
| Nausea | 1.12 | 0.72–1.60 | Beta | [13] |
| Vomiting | 0.56 | 0.36–0.80 | Beta | [13] |
| Olaparib | ||||
| Anaemia | 5.14 | 3.49–7.71 | Beta | [26] |
| Thrombocytopenia | 0.00 | 0.00–0.00 | Beta | [26] |
| Neutropenia | 4.05 | 2.62–5.78 | Beta | [26] |
| Fatigue | 6.76 | 4.36–9.63 | Beta | [26] |
| Hypertension | 0.00 | 0.00–0.00 | Beta | [26] |
| Nausea | 1.35 | 0.87–1.93 | Beta | [26] |
| Vomiting | 2.70 | 1.75–3.86 | Beta | [26] |
| Rucaparib | ||||
| Anaemia | 16.67 | 10.67–23.68 | Beta | [17] |
| Thrombocytopenia | 18.01 | 11.52–25.58 | Beta | [17] |
| Neutropenia | 6.99 | 4.50–9.96 | Beta | [17] |
| Fatigue | 12.37 | 7.94–17.60 | Beta | [17] |
| Hypertension | 0.00 | 0.00–0.00 | Beta | [17] |
| Nausea | 15.05 | 9.65–21.40 | Beta | [17] |
| Vomiting | 9.41 | 6.05–13.40 | Beta | [17] |
| Health state utilities | ||||
| Niraparib | ||||
| PFD | 0.849 | 0.843–0.855 | Beta | [13] |
| PD | 0.793 | 0.772–0.813 | Beta | [13] |
| RS | ||||
| PFD | 0.820 | 0.809–0.831 | Beta | [13] |
| PD | 0.775 | 0.748–0.800 | Beta | [13] |
| Olaparib | ||||
| PFD | 0.769 | 0.749–0.788 | Beta | [26] |
| PD | 0.718 | 0.698–0.737 | Beta | [26] |
| Rucaparib | ||||
| PFD | 0.849 | 0.843–0.855 | Assumed equal to niraparib | [13] |
| PD | 0.793 | 0.772–0.813 | Assumed equal to niraparib | [13] |
| AE disutilities | ||||
| Anaemia | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | Beta | [27] |
| Thrombocytopenia | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | Beta | [27] |
| Neutropenia | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | Beta | [27] |
| Fatigue | 0.170 | 0.030–0.398 | Beta | [28] |
| Hypertension | 0.000 | 0.000–0.000 | Beta | Assumption |
| Nausea | 0.230 | 0.056–0.479 | Beta | [28] |
| Vomiting | 0.230 | 0.056–0.479 | Beta | [28] |
AE adverse event, CI confidence interval, OS overall survival, PD progressed disease, PFD progression-free disease, PFS progression-free survival, RS routine surveillance, TOMT time on maintenance treatment
Progression-Free Survival
PFS data sources by model analyses are presented in the electronic supplementary material. PFS KM data for niraparib and RS were from the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA trial. A conservative efficacy assumption was made whereby gBRCAmut olaparib PFS efficacy was assumed equal to niraparib. PFS data for olaparib in the non-gBRCAmut population were from Study 19 BRCAwt data. All rucaparib PFS data were from the ARIEL3 trial, with the non-gBRCAmut population from combined BRCAwt data with high and low loss of heterozygosity.
The generalised gamma distribution had the lowest AIC and BIC. Visual inspection of the plots confirmed this was the best-fitting distribution for the PFS KM data for every population and comparison.
Upon advice from a clinical expert in OC, the long tails of certain distributions which suggested patients may be progression-free beyond 40 years were deemed unrealistic and were, therefore, capped at a recommended 20 years, such that patients could not be progression-free after 20 years. A rule was also applied to RS such that the proportion of patients progression-free cannot be greater than the proportion of patients alive.
It was assumed that the mean non-gBRCAmut PFS benefit of olaparib from Study 19 versus RS in Study 19 was the same as the mean PFS benefit of olaparib from Study 19 versus RS from the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA trial (Eq. 2).
Olaparib PFS benefit
| 2 |
Similarly, it was assumed that the mean PFS benefit of rucaparib from ARIEL3 versus RS in ARIEL3 was the same as the mean PFS benefit of rucaparib from ARIEL3 versus RS from the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA trial (Eq. 3).
Rucaparib PFS benefit
| 3 |
Overall Survival
Study 19 was the only available source of mature OS data and therefore the only appropriate study to explore the PFS:OS relationship. The ITT population in Study 19 was used to assess this relationship. The relationship based on the restricted means of KM data from Study 19 was estimated to be greater than 1:2.24 between mean PFS and OS benefit, with the relationship based on means from parametric distributions being greater than 1:4.63. Therefore, under a conservative assumption, the mean OS increment was assumed to be twice the mean PFS increment for all MTs.
Thus, the mean OS for these treatments was calculated as two times their PFS benefit plus the mean OS for RS from Study 19 (used as an anchor for the BRCAmut and BRCAwt population). Olaparib OS gBRCAmut was assumed equal to the gBRCAmut niraparib population.
Time on Maintenance Treatment
Time to treatment discontinuation (TTD) KM data were reported in the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA trial, and were extrapolated over a lifetime horizon using the aforementioned parametric distributions to obtain mean TOMT for niraparib and RS. Olaparib gBRCAmut TOMT was assumed equal to niraparib gBRCAmut. For olaparib non-gBRCAmut and rucaparib in both gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut, mean TTD was assumed the same as mean PFS. The log-logistic distribution was fitted to all TTD KM data.
Adverse Event Rates
The model included treatment-related adverse events (AEs) ≥ grade 3 reported in ≥ 10% of patients in either treatment arm in the ENGOT-OV16/NOVA trial, or with ≥ 1% difference between the niraparib and RS rate. Corresponding incidence rates for olaparib in the gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut populations were from Study 19. The AE rates for rucaparib were from the ARIEL3 study (Table 2).
Quality-of-Life Inputs
Utilities
Utility data were collected in ENGOT-OV16/NOVA from patients completing the EuroQol–five dimensions–five levels (EQ-5D-5L) questionnaire and were mapped onto the US EQ-5D-3L (three levels) valuation set using a ‘cross-walk’ algorithm [29]. This mapping was performed to match the EQ-5D-3L utility data available for olaparib [26].
Using these mapped data, EQ-5D-3L treatment-specific utilities (TSUs) were derived for each HS for the ITT population. Corresponding TSUs for olaparib were sourced from the olaparib NICE technology appraisal (TA) 381 [26]. ARIEL3 did not present utility data for rucaparib; therefore, utilities for rucaparib were assumed equal to those for niraparib (Table 2).
Disutilities
AE disutility data were identified as part of the SLR for the following symptomatic AEs: fatigue, nausea, and vomiting (Table 2). Other AEs were assigned zero disutility due to being asymptomatic and no negative effect on quality-of-life being reported in published literature [27].
Cost and Resource Use Inputs
Cost inputs included drug acquisition, administration, monitoring, AE, subsequent chemotherapy (SC), and terminal care costs (Table 3). These costs were informed by the economic SLR, supplemented with targeted searches. Where required, costs were updated to US dollars 2017/2018 values using US Bureau of Labor Statistics inflation data [30]. Drug acquisition and HS-dependent monitoring costs were calculated based on a 30-day cycle.
Table 3.
Unit costs and cycle costs
| Cost (US$) | 95% CI | Distribution | Source | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit costs | ||||
| Drug acquisition | ||||
| Niraparib | ||||
| Bottle of 30 100-mg capsules | 6584 | N/A | N/A | [31] |
| One 100-mg capsule | 219.47 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Olaparib | ||||
| Pack of 120 150-mg tablets | 13,886 | N/A | N/A | [31] |
| One 150-mg tablet | 115.72 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Rucaparib | ||||
| Pack of 120 300-mg tablets | 14,702 | N/A | N/A | [31] |
| One 300-mg tablet | 122.52 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Drug administration | ||||
| Oral drugs | 0 | N/A | N/A | Assumption |
| Intravenous subsequent chemotherapy drugs | 143 | 93–204 | Gamma | [32] |
| Monitoring | ||||
| Outpatient visit | 78.09 | 50.54–111.55 | Gamma | [33, 34] |
| CT scan | 541.70 | 350.56–773.77 | Gamma | [33, 34] |
| Blood test | 15.23 | 9.85–21.75 | Gamma | [33, 34] |
| Adverse event | ||||
| Anaemia | 755.92 | 489.19–1079.76 | Gamma | [35] |
| Thrombocytopenia | 732.30 | 473.90–1046.02 | Gamma | [35] |
| Neutropenia | 867.98 | 561.71–1239.83 | Gamma | [35] |
| Fatigue | 0.00 | 0.00–0.00 | Gamma | [36] |
| Hypertension | 215.37 | 139.38–307.64 | Gamma | [35, 36] |
| Nausea | 678.24 | 438.92–968.80 | Gamma | [35] |
| Vomiting | 678.24 | 438.92–968.80 | Gamma | [35] |
| Terminal care | ||||
| Terminal care | 85,904 | 55,592–122,705 | Gamma | [37] |
| Cycle costs | ||||
| Drug acquisition | ||||
| Niraparib (200 mg QD) | 13,168 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Olaparib (600 mg QD) | 13,886 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Rucaparib (1200 mg QD) | 14,702 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Monitoring | ||||
| gBRCAmut | ||||
| Niraparib | ||||
| PFD | 10,952 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| PD | 1539 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| RS | ||||
| PFD | 2772 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| PD | 833 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Olaparib | ||||
| PFD | 10,906 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| PD | 1539 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Rucaparib | ||||
| PFD | 8209 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| PD | 1428 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Non-gBRCAmut | ||||
| Niraparib | ||||
| PFD | 7208 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| PD | 894 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| RS | ||||
| PFD | 3514 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| PD | 528 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Olaparib | ||||
| PFD | 4817 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| PD | 662 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| Rucaparib | ||||
| PFD | 5090 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
| PD | 992 | N/A | N/A | Calculation |
CI confidence interval, CT computed tomography, PD progressed disease, PFD progression-free disease, QD per day, RS routine surveillance
Drug Acquisition Costs
MT drug costs are presented in Table 3. This analysis uses the 30-count bottle quantity to determine the 30-day bottle cost since expert opinion has suggested the 30-count bottle quantity will be prescribed more commonly across the US.
Administration Costs
As niraparib, olaparib, and rucaparib are all administered orally, it was assumed that there were no administration costs. SC regimen drugs that are administered orally were also assumed to have no administration costs.
All other SC was administered intravenously with a unit administration cost (Table 3). This cost was multiplied by the resource use rates for each of the MTs at different stages of the SC (cycles 1–3, 4, 5, 6) to obtain the administration costs of each treatment during SC.
Monitoring Costs
Unit costs of three monitoring methods were identified for use in the model (Table 3). Monitoring resource use rates were separated by HS. The PFD resource use rates were split by cycle (cycle 1, 2–14, and 15 +). The resource use rates were multiplied by the unit monitoring costs to calculate the comparative monitoring costs for each intervention. The resource use by cycle is summarised in the electronic supplementary material, and the subsequent total HS monitoring costs/cycle per treatment are presented in Table 3.
Adverse Event Costs
AE management costs were sourced from literature (Table 3). These costs were multiplied by the AE incidence rates in Table 2 to evaluate the total costs associated with AEs by treatment.
Subsequent Chemotherapy Costs
The unit drug costs associated with the SC regimens were combined into relevant regimens to calculate the mean cost/cycle. These costs were then multiplied by the different regimen usage rates for each MT (see the electronic supplementary material).
Terminal Care Costs
The costs associated with terminal care are one-off and were equal for all interventions (Table 3).
Sensitivity Analyses
One-Way Sensitivity Analyses
One-way sensitivity analyses (OWSAs) were performed to assess the impact of individual parameters on the model. OWSA considered upper and lower confidence intervals of pre-specified probabilistic distributions assigned to each parameter. Where the standard error was unavailable, this was assumed to be 20% of the mean value.
Probabilistic Sensitivity Analyses
Probabilistic sensitivity analyses (PSAs) were conducted to explore uncertainty around key model inputs by varying them simultaneously using assigned distributions and recording the mean model results; 1000 PSA iterations were run to obtain a stable estimate of the mean model results. The variation of parameters is presented in Tables 2 and 3.
Mean PSA results were illustrated through an incremental cost-effectiveness plane (ICEP) and a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve (CEAC).
Scenario Analyses
Scenario analyses were conducted to assess alternate model settings and structural uncertainty of the model (Table 4).
Table 4.
List of scenario analyses
| Scenario | Purpose |
|---|---|
| 1.5% discount rate | To assess the impact of varying the discount rate applied to costs and outcomes on the results of the model |
| 6% discount rate | |
| 10-year time horizon | To assess the impact of varying the time horizon on the results of the model |
| 20-year time horizon | |
| 30-year time horizon | |
| Lognormal distribution for PFS | To assess the impact of varying the parametric distribution for PFS on the model results |
| Log-logistic curve for PFS | |
| Spline normal k = 1 distribution for PFS | |
| Spline odds k = 3 distribution for PFS | |
| Log-logistic distribution for RS OS anchor | To assess the impact of varying the parametric distribution for OS on the model results |
| Lognormal distribution for TTD | To assess the impact of varying the parametric distribution for TTD on the model results |
| No cap on TTD and PFS | To assess the impact of varying the time cap applied to PFS and TTD within the model |
| 15-year cap on TTD and PFS | |
| PFS:OS = 1:3 | To assess the impact of varying the mean PFS and OS difference relationship on the model results |
| PFS:OS = 1:1 | |
| PFS:OS = 1:1.5 | |
| PFS:OS = 1:2.5 | |
| AE disutilities not included | To assess the impact of removing AE disutilities from the model on the results |
AE adverse event, k knotts, OS overall survival, PFS progression-free survival, RS routine surveillance, TTD time to treatment discontinuation
Model Validation
The model underwent internal and external validation. The model was developed internally by two independent health economists. An external health economist reviewed and provided suggestions for improvement of the approach and methodology of modelling mean OS based on mean PFS and conducting scenario analyses using flexible survival curves. Clinical trial data underpinning the model structure and assumptions were ratified by an external clinical expert. All feedback obtained by internal and external ratification went into the final model and this publication.
Results
Base-Case Results
For gBRCAmut, niraparib was associated with an ICER of US$68,287/QALY versus RS, with US$301,174 incremental costs and 4.410 incremental QALYs. Niraparib dominates olaparib and rucaparib, with −US$8799 and −US$198,708 incremental costs and 0.679 and 1.162 incremental QALYs, respectively (Table 5). For non-gBRCAmut, niraparib was associated with an ICER of US$108,287/QALY versus RS, with US$232,598 incremental costs and 2.148 incremental QALYs. Niraparib dominates olaparib and rucaparib, with −US$22,236 and −US$73,561 incremental costs and 1.623 and 0.432 incremental QALYs, respectively (Table 6). Disaggregated results are presented in the electronic supplementary material.
Table 5.
Base-case results for niraparib, RS, olaparib and rucaparib gBRCAmut
| Total costs (US$) | Total LYG | Total QALYs | Incremental costs (US$) | Incremental LYG | Incremental QALYs | ICER (US$) versus baseline (QALYs) | ICER (US$) incremental (QALYs) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS | 95,628 | 3.564 | 2.801 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Niraparib | 396,802 | 8.824 | 7.212 | 301,174 | 5.259 | 4.410 | 68,287 | 68,287 |
| Olaparib | 405,601 | 8.824 | 6.532 | 8799 | 0.000 | −0.679 | 83,078 | Dominated |
| Rucaparib | 595,510 | 7.437 | 6.050 | 198,708 | − 1.387 | − 1.162 | 153,866 | Dominated |
ICER incremental cost-effectiveness ratio, LYG life-years gained, QALYs quality-adjusted life-years, RS routine surveillance
Table 6.
Base-case results for niraparib, RS, olaparib and rucaparib non-gBRCAmut
| Total costs (US$) | Total LYG | Total QALYs | Incremental costs (US$) | Incremental LYG | Incremental QALYs | ICER (US$) versus baseline (QALYs) | ICER (US$) incremental (QALYs) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RS | 100,724 | 2.816 | 2.231 | – | – | – | – | – |
| Niraparib | 333,322 | 5.351 | 4.379 | 232,598 | 2.535 | 2.148 | 108,287 | 108,287 |
| Olaparib | 355,558 | 3.727 | 2.756 | 22,236 | − 1.623 | − 1.623 | 485,304 | Dominated |
| Rucaparib | 406,883 | 4.868 | 3.948 | 73,561 | − 0.483 | − 0.432 | 178,382 | Dominated |
ICER incremental cost-effectiveness ratio, LYG life-years gained, QALYs quality-adjusted life-years, RS routine surveillance
Sensitivity Analyses
One-Way Sensitivity Analyses
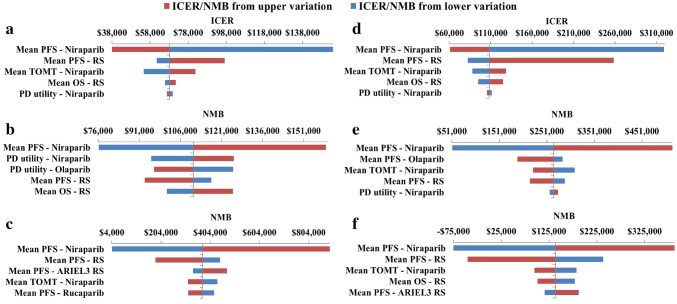
Tornado diagrams illustrate the impact of the five most sensitive parameters on the model. ICERs are presented for niraparib versus RS, and incremental net monetary benefit (NMB) results are presented for niraparib versus olaparib and rucaparib. NMB was reported where the base-case ICER was dominating to allow graphical representation with a willingness to pay (WTP) of US$150,000/QALY (Fig. 3) [38–40]. Across the analyses, the ICERs and NMBs were most sensitive to the estimates of mean PFS of the treatments, RS OS, niraparib TOMT, and PD HS utilities.
Fig. 3.
One-way sensitivity analysis: tornado diagrams for the ICER or NMB of the following comparisons: gBRCAmut: a niraparib versus RS, b niraparib versus olaparib, c niraparib versus rucaparib; non-gBRCAmut: d niraparib versus RS, e niraparib versus olaparib, f niraparib versus rucaparib. ICER incremental cost-effectiveness ratio, NMB net monetary benefit, OS overall survival, PD progressed disease, PFS progression-free survival, RS routine surveillance, TOMT time on maintenance treatment
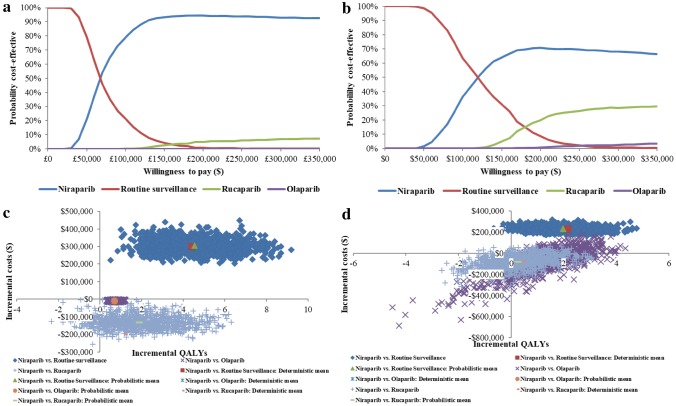
Probabilistic Sensitivity Analyses
PSA results for gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut are similar to the base-case results (see the electronic supplementary material). The ICEP and CEAC for both populations are presented in Fig. 4. At a WTP threshold of US$150,000/QALY, niraparib had a 93% and 64% probability, RS had a 4% and 31% probability, rucaparib had a 3% and 5% probability, and olaparib had a 0% and 0% probability of being cost-effective for gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut, respectively.
Fig. 4.
Probabilistic sensitivity analysis: a cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for gBRCAmut, b incremental cost-effectiveness plane for gBRCAmut, c cost-effectiveness acceptability curve for non-gBRCAmut, d incremental cost-effectiveness plane for non-gBRCAmut. QALY quality-adjusted life-year
Scenario Analyses
The results of the scenario analyses are presented in the electronic supplementary material.
gBRCAmut: Niraparib versus RS results were most sensitive to changing the PFS:OS relationship to 1:1 and using the lognormal distribution for PFS, resulting in increased ICERs of $126,500 and $111,527, respectively.
Niraparib dominated olaparib and rucaparib in all scenarios, with results for olaparib most sensitive to applying no cap on TTD and PFS (increased incremental costs: −US$9931) and results for rucaparib most sensitive to modelling PFS with the lognormal distribution (reduced incremental costs: −US$68,890).
Non-gBRCAmut: For all comparisons, results were most sensitive to changing the PFS distribution to lognormal, where niraparib no longer dominated olaparib and rucaparib. ICERs were US$206,388/QALY, US$113,628/QALY, and US$122,654/QALY for niraparib versus RS, olaparib, and rucaparib, respectively, higher than those in the base case. Niraparib dominated olaparib and rucaparib in the majority of other scenarios.
Discussion
These analyses sought to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of niraparib versus RS, olaparib and rucaparib for the MT of patients with ROC. A decision-analytic model estimated the costs and QALYs for each intervention; this approach has been used before in OC (NICE TA91 [41]). Base-case results versus RS found that niraparib was associated with ICERs of US$68,287/QALY and US$108,287/QALY for gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut, respectively. Furthermore, niraparib dominated olaparib and rucaparib, accruing cost savings/patient of US$8799 and US$22,236 versus olaparib and US$198,708 and US$73,561 versus rucaparib for gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut, respectively.
As there is no set WTP threshold in the US, a threshold of US$150,000/QALY was decided upon based on thresholds used in relevant literature [38–40].
In every comparison, treatment with niraparib led to increased OS versus the comparator treatment (except versus olaparib gBRCAmut, where a conservative equal efficacy assumption was adopted), and in turn, increased QALYs. This was driven by niraparib treatment leading to longer PFS compared to other comparators, which translated into longer OS based on the PFS:OS relationship established by Study 19.
OWSAs showed that the main driver of the model was the mean PFS estimates. Other key drivers included the mean RS OS, niraparib TOMT and PD HS utilities. The incremental NMB was only negative when the mean PFS for niraparib and RS Study 19 were varied in the non-gBRCAmut population versus rucaparib. PSA results were similar to those in the base case, showing that results were robust to variation in model inputs. At a WTP threshold of US$150,000/QALY, niraparib had a 93% and 64% probability of being cost-effective for gBRCAmut and non-gBRCAmut, respectively. Scenario analyses mainly showed similar results to the base case, and were sensitive to alternative PFS distributions and the PFS:OS ratio.
Validation of the model included reviews by clinical experts on the choice of parametric distributions and the clinical data used, lending plausibility to the model results. Additionally, Study 19 reports that 14% of BRCAwt patients were still progression-free at 5-years, and of the parametric distributions evaluated, the chosen generalised gamma models this the closest (12.12%) [42].
Although the initial starting dose of niraparib is more costly than olaparib or rucaparib, 73% of patients are titrated to a lower dose within the first three cycles, and thus, the cycle cost is less (Table 3). Due to these dose reductions, the most commonly used dose for niraparib in ENGOT-OV16/NOVA was 200 mg rather than the indicated starting dose of 300 mg [43], leading to lower costs. Olaparib and rucaparib are flat priced, however, so are more expensive than niraparib, even if a lower dose is used [31].
CEAs have previously considered olaparib for MT in ROC patients from a US perspective [44, 45]. However, ICERs were not reported, and niraparib was not specified as a comparator, so no meaningful comparisons can be made.
The main strength of the analysis is that it is relevant and generalisable to clinical practice in the US. Firstly, the populations evaluated fall within the niraparib’s US licence. Secondly, the clinical evidence base is representative of US patients with ROC as US patients were enrolled in all three trials: ENGOT-OV16/NOVA, Study 19 and ARIEL3. Finally, all costs and resource use in the model were from US sources, where available.
There are several limitations with the analysis which lead to uncertainty in the results. Firstly, the use of naïve side-by-side comparisons between MTs disregards the random nature of the trials and may lead to biased results. A feasibility assessment was conducted which concluded that formal indirect comparisons were not feasible, due to multiple significant confounding factors causing a great degree of heterogeneity in the study design, patient population and PFS outcomes of the RCTs. Based on this assessment, a naïve side-by-side comparison was conducted. The authors’ acknowledge the limitations with this approach and emphasise that caution must be exercised in interpreting the study results as a consequence.
In addition, since there are two studies evaluating the gBRCAmut population for olaparib (Study 19 and SOLO2), at different doses, a naïve side-by-side comparison of niraparib and olaparib was not feasible. Therefore, the conservative assumption was made to assume equal efficacy between niraparib and olaparib to avoid over or under-estimation of incremental benefits with niraparib; a methodology previously accepted during a NICE TA of niraparib [21].
Secondly, clinical benefits beyond the duration of the clinical trials were assumed through the fitting of parametric distributions to the KM data to estimate mean PFS, OS, and TOMT over a lifetime horizon. This assumption may have led to uncertainty in the efficacy results, but was appropriate due to the inherent limitation of short-term trial durations, and was modelled following NICE DSU guidelines with validation by an external OC expert. Scenario analyses considered alternative parametric distributions and shorter time horizons, which found that results were sensitive to alternative PFS distributions, but less sensitive to shorter time horizons.
Thirdly, a 20-year PFS and TTD cap was required. While it is unrealistic that real-life KM data would match these capped curves, based upon clinical recommendations, they were more realistic than uncapped curves, which modelled some patients still being progression-free at 40 years. Scenario analyses were undertaken considering a 15-year cap, no cap, and, given the need for a cap within standard parametric models, a flexible approach for PFS. When a 15-year cap or the flexible curves for PFS were used, the ICER increased compared to RS regardless of BRCA mutation status (except spline odds knotts = 3 PFS distribution for gBRCAmut), and when there was no cap, the ICER decreased against RS regardless of BRCA mutation status. Niraparib dominated olaparib and rucaparib in all scenarios and populations except for the non-gBRCAmut population with a lognormal PFS distribution, log-logistic or spline normal knotts = 3.
Fourthly, a lack of mature OS data meant that a 1:2 PFS:OS relationship was assumed to produce OS data for the MTs, which may have led to uncertainty in the efficacy results. This assumption was, however, clinically appropriate and plausible, as any relationship lower than 1:2 would assume niraparib has far worse OS benefit than olaparib. Furthermore, SLR evidence found no studies evaluating this relationship for MT in OC. Therefore, Study 19 was the only available evidence to derive this relationship. It is not surprising that at least a 1:2 PFS:OS relationship was observed in Study 19. By extending time to progression after PBC, MT will in turn increase the number of patients who are considered for retreatment with PBC in the next treatment line. By increasing PFS and the likelihood of consideration for retreatment with PBC, studies have shown that effective MT can extend OS to a greater extent than already gained through PFS [15, 46]. ENGOT-OV16/NOVA data showed that more niraparib patients retain their platinum-sensitive status compared to placebo, partially justifying the extension of niraparib OS in this analysis. Scenario analyses modelled the effects of applying 1:1 and 1:3 PFS:OS relationships. The 1:3 relationship decreased the ICERs against RS, while the 1:1 relationship nearly doubled the ICERs against RS. Niraparib dominated olaparib and rucaparib in both scenarios.
Finally, the HS and TSU data used for niraparib patients was in the EQ-5D-3L form, which was mapped from EQ-5D-5L data to allow comparison to the olaparib EQ-5D-3L TSU. This was necessary as there was only one source of olaparib utility data available. In addition, due to a lack of data from ARIEL3, utilities for rucaparib were conservatively assumed equal to those for niraparib. This reduced bias by assuming no quality-of-life benefit for niraparib, while also increasing uncertainty in the results.
In the future, consideration should be given to furthering this research by including mature OS data when available to validate the results presented in this publication.
Conclusion
These estimates indicate that at a WTP threshold of US$150,000/QALY, niraparib was cost-effective compared to RS, olaparib and rucaparib from a US payer perspective. However, mature OS data is required to validate these results.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to ongoing regulatory and reimbursement discussions in several ex-US countries, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Jack Hansen-Maughan for his writing and editing assistance and dedicated work on the data analyses (FIECON Ltd).
Author Contributions
All authors were involved in the design and execution of the analysis, interpretation of the results, and the drafting and revision of this manuscript, and provided final approval of the version to be published. All authors vouch for the accuracy of the content included in the full manuscript.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Funding
This analysis was sponsored by TESARO, Inc.
Conflict of interest
Holly Guy, Lydia Walder, and Mark Fisher are employees of FIECON Ltd, a health economics consultancy, which performed the analyses presented in the manuscript, funded by TESARO, Inc.
References
- 1.Ovarian Cancer-Cancer Stat Facts. 2018. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/ovary.html. Accessed Mar 26 2018.
- 2.Siegel Rebecca L, Miller Kimberly D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;2016(66):7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Janavičius R. Founder BRCA1/2 mutations in the Europe: implications for hereditary breast-ovarian cancer prevention and control. EPMA J. 2010;1:397–412. doi: 10.1007/s13167-010-0037-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chetrit A, Hirsh-Yechezkel G, Ben-David Y, Lubin F, Friedman E, Sadetzki S. Effect of BRCA1/2 mutations on long-term survival of patients with invasive ovarian cancer: the National Israeli Study of Ovarian Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:20–25. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2007.11.6905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Moschetta M, George A, Kaye SB, Banerjee S. BRCA somatic mutations and epigenetic BRCA modifications in serous ovarian cancer. Ann Oncol. 2016;27:1449–1455. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdw142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Berek JS, Bast RC., Jr . Epithelial ovarian cancer. In: Kufe DW, Pollock RE, Weichselbaum RR, editors. Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine. 6. Hamilton: BC Decker; 2003. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Recurrence. Ovarian Cancer Res Fund Alliance. 2018. https://ocrfa.org/patients/about-ovarian-cancer/recurrence/. Accessed 26 Mar 2018.
- 8.Khalique S, Hook JM, Ledermann JA. Maintenance therapy in ovarian cancer. Curr Opin Oncol. 2014;26:521–528. doi: 10.1097/CCO.0000000000000110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Evans T, Matulonis U. PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer: evidence, experience and clinical potential. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2017;9:253–267. doi: 10.1177/1758834016687254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Research C for DE and Approved Drugs-Niraparib (ZEJULA). 2018. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/informationondrugs/approveddrugs/ucm548487.htm. Accessed 13 Jul 2018.
- 11.Research C for DE and Approved drugs-FDA approves olaparib tablets for maintenance treatment in ovarian cancer. 2018. https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm572143.htm. Accessed 13 Jul 2018.
- 12.Research C for DE and. Approved drugs-Rucaparib. 2018. https://www.fda.gov/Drugs/InformationOnDrugs/ApprovedDrugs/ucm533891.htm. Accessed 13 Jul 2018.
- 13.Mirza MR, Monk BJ, Herrstedt J, Oza AM, Mahner S, Redondo A, et al. Niraparib maintenance therapy in platinum-sensitive, recurrent ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:2154–2164. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1611310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Pujade-Lauraine E, Ledermann JA, Selle F, Gebski V, Penson RT, Oza AM, et al. Olaparib tablets as maintenance therapy in patients with platinum-sensitive, relapsed ovarian cancer and a BRCA1/2 mutation (SOLO2/ENGOT-Ov21): a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017;18:1274–1284. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30469-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ledermann J, Harter P, Gourley C, Friedlander M, Vergote I, Rustin G, et al. Olaparib maintenance therapy in platinum-sensitive relapsed ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:1382–1392. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1105535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ledermann J, Harter P, Gourley C, Friedlander M, Vergote I, Rustin G, et al. Olaparib maintenance therapy in patients with platinum-sensitive relapsed serous ovarian cancer: a preplanned retrospective analysis of outcomes by BRCA status in a randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15:852–861. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70228-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Coleman RL, Oza AM, Lorusso D, Aghajanian C, Oaknin A, Dean A, et al. Rucaparib maintenance treatment for recurrent ovarian carcinoma after response to platinum therapy (ARIEL3): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;390:1949–1961. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32440-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Flatiron Health Electronic health record (EHR) Database. 2018. Available at: https://flatiron.com/. Accessed 30 Apr 2018.
- 19.Fisher M, Guy H, Walder L. Cost-effectiveness of niraparib versus routine surveillance, olaparib, and rucaparib for the maintenance treatment of adult patients with ovarian cancer in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2018;36(15_suppl):5559. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2018.36.15_suppl.5559. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fisher M, Gore M. Cost-effectiveness of trabectedin plus pegylated liposomal doxorubicin for the treatment of women with relapsed platinum-sensitive ovarian cancer in the UK: analysis based on the final survival data of the OVA-301 trial. Value Health J Int Soc Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2013;16:507–516. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2013.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Niraparib for maintenance treatment of relapsed, platinum-sensitive ovarian, fallopian tube and peritoneal cancer|Guidance and guidelines|NICE. 2018. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/TA528. Accessed 24 Jul 2018.
- 22.Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride, paclitaxel, trabectedin and gemcitabine for treating recurrent ovarian cancer|Guidance and guidelines|NICE. 2018. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta389. Accessed 14 June 2018.
- 23.World Health Organization. (2003). WHO guide to cost-effectiveness analysis. http://www.who.int/choice/publications/p_2003_generalised_cea.pdf. Accessed Mar 2017.
- 24.Latimer, N. NICE DSU Technical Support Document 14: undertaking survival analysis for economic evaluations alongside clinical trials—extrapolation with patient-level data. 2011. http://www.nicedsu.org.uk. Accessed Apr 2017. [PubMed]
- 25.Ledermann JA, Harter P, Gourley C, et al. Overall survival in patients with platinum-sensitive recurrent serous ovarian cancer receiving olaparib maintenance monotherapy: an updated analysis from a randomised, placebo-controlled, double-blind, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016;17:1579–1589. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30376-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.NICE. Olaparib for maintenance treatment of relapsed, platinum-sensitive, BRCA mutation-positive ovarian, fallopian tube and peritoneal cancer after response to second-line or subsequent platinum-based chemotherapy (TA381). https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta381. Accessed May 2017.
- 27.Quality of life in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer treated with niraparib versus placebo (ENGOT-OV16/NOVA): results from a double-blind, phase 3, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(18)30333-4/fulltext. Accessed 2 Aug 2018. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 28.Havrilesky LJ, Broadwater G, Davis DM, Nolte KC, Barnett JC, Myers ER, et al. Determination of quality of life-related utilities for health states relevant to ovarian cancer diagnosis and treatment. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;113:216–220. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2008.12.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.van Hout B, Janssen MF, Feng YS, Kohlmann T, Busschbach J, Golicki D, et al. Interim scoring for the EQ- 5D-5L: mapping the EQ-5D-5L to EQ-5D-3L value sets. Value Health. 2012;15(5):708–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2012.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.United States Department of Labor. CPI medical inflation rates, 2018. https://data.bls.gov/timeseries/CUUR0000SAM?output_view=pct_12mths.
- 31.Truven. RED BOOK Online. Greenwood Village, CO: Truven health analytics; 2018.
- 32.http://Medicare-coding-and-payment-drug-admin-services-physician-fee-schedule.pdf.
- 33.Find-A-Code-ICD 10 Codes, CPT Codes, HCPCS Codes, ICD 9 Codes—online encoder-medical billing and coding. 2018. https://www.findacode.com/. Accessed 26 Mar 2018.
- 34.Physician Fee Schedule Search Results. 2018. https://www.cms.gov/apps/physician-fee-schedule/. Accessed 3 Apr 2018.
- 35.Rashid N, Koh HA, Baca HC, Lin KJ, Malecha SE, Masaquel A. Economic burden related to chemotherapy-related adverse events in patients with metastatic breast cancer in an integrated health care system. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2016 doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S105618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Gala S, Nanavaty M, Proach J. Systematic literature review of cost of adverse events in cancer treatment in the US. Value Health. 2015;18:A200. doi: 10.1016/j.jval.2015.03.1160. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Pyenson B, Connor S, Fitch K, Kinzbrunner B. Medicare cost in matched hospice and non-hospice cohorts. J Pain Symptom Manag. 2004;28:200–210. doi: 10.1016/j.jpainsymman.2004.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.WHO|Thresholds for the cost–effectiveness of interventions: alternative approaches. WHO. 2018. http://www.who.int/bulletin/volumes/93/2/14-138206/en/. Accessed 9 Jul 2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 39.Neumann PJ, Cohen JT, Weinstein MC. Updating cost-effectiveness—the curious resilience of the $50,000-per-QALY threshold. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:796–797. doi: 10.1056/NEJMp1405158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chin LM, Carlson JJ. Cost-Effectiveness analysis of rucaparib maintenance treatment for recurrent ovarian carcinoma after response to platinum therapy. Poster presented at ISPOR 2018, Baltimore, MD.
- 41.Edwards SJ, Barton S, Thurgar E, Trevor N. Topotecan, pegylated liposomal doxorubicin hydrochloride, paclitaxel, trabectedin and gemcitabine for the treatment of recurrent ovarian cancer: a multiple technology appraisal. BMJ-TAG, London, 2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 42.Gourley C, Friedlander M, Matulonis UA, Shirinkin V, Selle F, Scott CL, et al. Clinically significant long-term maintenance treatment with olaparib in patients (pts) with platinum-sensitive relapsed serous ovarian cancer (PSR SOC) J Clin Oncol. 2017;35:5533. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.35.15_suppl.5533. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Berek JS, Matulonis UA, Peen U, Ghatage P, Mahner S, Redondo A, et al. Safety and dose modification for patients receiving niraparib. Ann Oncol. 2018;29:1784–1792. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdy181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Smith HJ, Walters Haygood CL, Arend RC, Leath CA, Straughn JM. PARP inhibitor maintenance therapy for patients with platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Gynecol Oncol. 2015;139:59–62. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2015.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Alvarez-Secord A, Barnett JC, Ledermann JA, Peterson BL, Myers ER, Havrilesky LJ. Cost-effectiveness of Brca1 and Brca2 mutation testing to target parp inhibitor use in platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2013;23(5):846–852. doi: 10.1097/IGC.0b013e31829527bd. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Cook A. 961PICON7: Ovarian cancer, platinum second-line chemotherapy and overall survival|Annals of Oncology|Oxford Academic. Ann Oncol. 2018. https://academic.oup.com/annonc/article/28/suppl_5/mdx372.032/4109046. Accessed 8 Mar 2018.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due to ongoing regulatory and reimbursement discussions in several ex-US countries, but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.