Abstract
Background
Patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN-1) develop multiple pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasias (PNENs). Size at diagnosis and growth during follow-up are crucial parameters. According to the WHO 2017, grading is another important parameter. The impact of grading compared to size (WHO 2000) on the clinical course needs to be evaluated.
Methods
Sixty PNENs of six patients with MEN-1 were retrospectively evaluated.
Results
Fifty-one tumors with a diameter of < 20 mm were graded as G1. Two of 9 tumors with diameters of ≥20 mm were graded as G2. Tumor size of ≥20 mm correlated significantly with higher proliferation (p = 0.000617). Lymph node metastases were documented in two patients with a total of 19 tumors. In one patient, all 13 tumors (diameter: 0.4 to 100 mm) were classified as G1. However, metastases were documented in 9/29 lymph nodes. In the other patient, 5 tumors (3.5 to 20 mm) were classified as G1. The sixth tumor (30 mm) was classified as G2 (Ki-67: 8%). Metastases were revealed in 2/20 lymph nodes.
Conclusions
Tumor size of ≥20 mm seems to correlate with more aggressive MEN-1 related pancreatic disease, regardless of individual proliferation. Tumors ≥20 mm and tumors graded as G2 should be treated surgically regardless of their size.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s13023-019-1034-4) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: MEN-1, Multiple endocrine neoplasia, Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, NET, Intertumor heterogeneity
Introduction
Patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN-1) develop multiple pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasias (PNENs) which show various sizes and may be functioning (F)- or non-functioning (NF)-PNENs.
Independent of their size mostly F-PNENs are an indication for surgery in an attempt to control hormone excess. The majority of (NF)-PNENs are measuring < 20 mm with a low oncologic risk [1, 2]. The treatment ranges from watchful waiting to partial and total pancreatectomy, the latter resulting in a diabetic metabolic status [1–6]. NF-PNENs ≥20 mm are discussed an indication for surgical intervention [7].
The “20mm size cut-off” was recommended by the WHO 2000 [8] based on clinical follow-up studies of sporadic PNENs showing locally invasive growth as well as local and distant metastasis more often at the time of diagnosis and during clinical follow-up. Size is easily assessed and documented radiologically [9–11], but it seems to be only one of various potential factors that determine the biological tumor behavior. Tumor biology may additionally be characterized by the mitotic count and proliferation index obtained on tissue samples using the WHO grading system [12].
The malignant potential of neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) is divided into three groups (G1, G2 and G3) according to their proliferation rates, measured by mitotic count and by the percentage of cells with immunohistochemically expressed Ki-67 (G1: < 3%; G2: 3–20%, G3: > 20%) [13–15].
In MEN-1 patients, the impact of PNENs grading in correlation with size has not been evaluated to plan either surveillance or surgery; multiple pubmed searches yielded no suggestive results with any combinations of two of the following keywords: MEN-1, multiple endocrine neoplasia, pancreas, grading, size, surgery.
Materials and methods
Sixty PNENs belonging to 6 MEN-1 patients (2 females, age 38 and 61; 4 males, age 15, 29, 33 and 60) were studied (Table 1).
Table 1.
Mutation, TNM, surgery, Ki-67 (%) of the largest tumor, and follow-up of 6 MEN-1 patients
| Patient | Mutation | Gender | Age | T | N | M | Ki-67% | function | Surgery | Follow-up Status |
Years | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENETS | UICC | |||||||||||
| A | Exon 2, del 4 bp (c.247_250delCTGT); - > Termination after amino acid 116 |
m | 29 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | F (WDHA-Syndrome) | TP | DF | 12 |
| B | Intron 4, G > A -9 bp - > Alternative splicing |
f | 60 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 8 | NF | TP | PD (M?) | 10 |
| C | Exon 9, Q405X, CAG > TAG (Gln > Stop) - > Termination after amino acid 404 |
m | 60 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | NF | TP | DF | 7 |
| D | Exon 3, Codon 179 GAG>AAG (Glu > Lys) - > AS Exchange |
m | 15 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 3 | F (Hyper-insulinism) | DP | DF | 29 |
| E | Exon 4, p.I247N, ATT > AAT (Ile > Asn) WORLDWIDE INDEX-CASE |
f | 38 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | NF | TP | DF [+] | 4 |
| F | Exon 3, del4bp (amino acid 210/211) - > Termination after amino acid 209 |
m | 33 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 | F (subclinical Hyper-insulinism) | DP, E | PD (N) | 21 |
T tumor classification of the largest tumor, N lymph node, Ki-67 Index in %, M distant metastasis, m male, f female
F functioning, NF non-functioning
TP fotal pancreatectomy, DP distal pancreatic resection, E enucleation
DF disease free, PD pogressive disease; [+]: died unrelated to MEN-1
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional review board (approval number: 1053/2013) and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments.
Biochemical and clinical pre- and postoperative staging
Preoperatively the biochemical screening and follow-up was performed according to the recently revised ENETS guidelines [16]. In all patients CgA levels were determined preoperatively and during follow-up.
The number, location and appearance of the PNENs were evaluated by endoscopic ultrasound (EUS; fine-needle aspiration cytology was not performed), computerized tomography (CT), and/or by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pancreas. To exclude distant metastasis somatostatin-receptor (SSR)-mediated scintigraphy was applied at the time of diagnosis.
Surgery
The indications for surgery were functioning (n = 3; organic hyperinsulinism [n = 2; patients D and F], Water Diarrhea Hypokalemia Achlorhydria (WDHA) syndrome [n = 1; patient A]) or multiple non-functioning tumors > 20 mm (n = 3; patients B, C, E).
Total pancreatectomy was performed in patients A, B, C and E (patients B and C suffering from insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus type 2 preoperatively) because of the large amount of PNENs distributed throughout the pancreas without any chance to save “normal” pancreatic tissue. In patient D, a left pancreatic resection was carried out to save parts of the pancreatic body and the head. In patient F, a left pancreatic resection was performed and three PNENs were enucleated from the pancreatic head (Thompson procedure [17]). Extended lymph node dissection was performed in all patients. At the time of surgery, no liver or other distant metastases were documented in any of the patients (cM0). All operations performed were open operations.
Immunohistochemistry
Each of the 60 PNENs (functioning and non-functioning) and all lymph nodes dissected were evaluated histologically and immunohistochemically.
Staining with chromogranin A (CgA), synaptophysin, Ki-67, Islet-1, TTF1 and CDX2 was performed.
The tumors were classified according to the WHO classification of 2017 [14, 17, 18] and staged according to the European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society (ENETS) consensus proposal of 2006 and the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC)/Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) classification of 2010 [17–19].
Tumor tissue was routinely formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining involved 3 μm sections of each block. One representative block of each primary tumor and lymph node metastasis was selected, and 3 μm sections were cut. Immunostainings with chromogranin A (CgA), synaptophysin and against proliferation marker Ki-67 antigen (MIB-1 monoclonal mouse, Novocastra, Newcastle, UK; dilution 1:20), CDX2 (1H9 monoclonal mouse, abcam, Cambridge, UK, undiluted), Islet-1 (1H9 monoclonal mouse, abcam, Cambridge, UK, dilution 1:400) and TTF-1 (SP141 monoclonal rabbit, Ventana, Tucson, Arizona, USA, undiluted) were performed using an automatic immunostainer (Ventana Medical Systems Inc., BenchMark® or BenchMark® ULTRA, Tucson, Arizona, USA). For antigen retrieval, slides for Ki-67, CDX2 and Islet-1 staining were boiled with a commercially available puffer (Ventana Medical Systems Inc., Cell Conditioning 1, Tucson, Arizona, USA) for 256, 256 and 64 min, respectively. In case of Ki-67 staining a commercially available amplification kit (Ventana Medical Systems Inc., Amplification Kit, Tucson, Arizona, USA) was used.
The Ki-67 labeling index with antibody MIB-1 was used for grading and was assessed in 500 tumor cells in areas in which the highest nuclear labeling was observed using an eye grid ocular. The classification was as follows: G1: Ki-67 < 3, G2: Ki-67 3-20, and G3: Ki-67 > 20%.
Follow-up
All 6 patients were followed clinically and biochemically 4, 7, 10, 12, 21 and 29 years after diagnosis.
Functional imaging by Gallium-DOTANOC-PET-CT was performed in 4 of 6 patients (patients A, B, C and F) 7, 10, 12 and 21 years after surgery. Two patients were clinically cured. However, they refused biochemical and radiological follow-up examinations 4 (patient E) and 29 (patient D) years after pancreatic surgery, therefore cure was not definitively documented.
Statistical analysis
Comparisons of the distribution of G2 tumors in the group of tumors measuring < 20 mm and ≥ 20 mm and in various subgroups were performed with the chi-square test. Statistical significance was set at a p-value of 0.05.
Expression of Islet-1, TTF1 and CDX2 was evaluated semiquantitatively.
Results
Overall 60 neuroendocrine lesions were documented in the surgical specimens (details can be seen in Table 2 and Additional file 1: Table S1).
Table 2.
Proliferation index (Ki-67) and immunohistochemical staining of Islet-1, TTF1 and CDX2
| Patient | Function | PNEN | Location | Ki-67 (%) | Islet-1 (%) | TTF1 (%) | CDX2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | F (WDHA-syndrome) | 1 | Head | 1 | +++ | + | – |
| 2 | Body | 1 | +++ | – | – | ||
| 3 | Tail | 2 | +++ | – | – | ||
| B | NF | 1 | Head | 2 | +++ | – | – |
| 2 | Body | 8 | +++ | – | – | ||
| 3 | 1 | + | ++ | – | |||
| 4 | 1 | ++ | – | – | |||
| 5 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 6 | Tail | 1 | +++ | – | – | ||
| C | NF | 1 | Duodenum | 1 | + | – | ++ |
| 2 | Head | 1 | +++ | – | – | ||
| 3 | Body | 1 | +++ | – | ++ | ||
| 4 | 2 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 5 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 6 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 7 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 8 | Tail | 1 | +++ | – | – | ||
| 9 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 10 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 11 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 12 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 13 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 14 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 15 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| D | F (Hyper-insulinism) | 1 | Body/Tail | 1 | +++ | – | – |
| 2 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 3 | 3 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 4 | 2 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 5 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| E | NF | 1 | Head | 1 | n.f. | n.f. | n.f. |
| 2 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 3 | Head/Body | 1 | +++ | – | – | ||
| 4 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 5 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 6 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 7 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 8 | Tail | 1 | +++ | – | – | ||
| 9 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 10 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 11 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 12 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 13 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 14 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 15 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 16 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 17 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 18 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| F | F (subclinical Hyper-insulinism) | 1 | Head/Body | 1 | +++ | – | – |
| 2 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 3 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 4 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 5 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 6 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 7 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 8 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 9 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 10 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 11 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 12 | 1 | +++ | – | – | |||
| 13 | Tail | 1 | +++ | – | – |
Positivity of cells (+: ≤ 10%; ++: > 10 to < 100%; +++: 100%)
The tumors were distributed all over the organs: 5 in the pancreatic head, 17 on the junction between the pancreatic head and body, 10 in the body, 5 on the junction between the body and tail, 22 in the tail, and one 5 mm tumor originated in the duodenum.
Imaging by CT or MRI served to localize 10 (16.7%) out of 60 tumors, all measuring ≥10 mm. Five more tumors (5%; between 5 and 9 mm) were documented either by EUS (n = 2) or intraoperative ultrasound (IOUS; n = 3).
SSR-scintigraphy was negative in all patients (radiologically [r] M0) in terms of distant metastasis.
Forty (66.7%) pancreatic lesions (including the single duodenal lesion) were microadenomas (largest size/diameter: ≤5 mm) [18], 11 (18.3%) were NENs between > 6 mm and < 20 mm, and 9 (15.0%) tumors were ≥ 20 mm, respectively (Table 3).
Table 3.
Correlation of size and grading - Subgroup analysis
| pT | Group | Size (mm) | G1 | G2 | Ʃ | % | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENETS | AJCC/UICC | |||||||
| 1 | 1 | A | I | ≤5 | 39 + 1a | 0 | 40 | 66.7 |
| II | 6 ≤ 10 | 8 | 0 | 8 | 13.3 | |||
| III | 11 < 20 | 3 | 0 | 3 | 5.0 | |||
| 2 | 2 | B | IV | ≥20–40 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 11.7 |
| 3 | > 40 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3.3 | |||
| 58 | 2 | 60 | 100 | |||||
P: pathological; T: tumor, size in mm; G: Grading; G1: Ki-67 < 3; G2: Ki-67 3-20%; aduodenum;
ENETS: European Neuroendocrine Tumor Society
AJCC: American Joint Committee on Cancer; UICC: Union for International Cancer Control
Group A (tumor diameter < 20 mm) vs group B (tumor diameter ≥ 20 mm): p = 0.000617
Group I (tumor diameter ≤ 5 mm) vs Groups II to IV (> 6 mm): p = 0.041932
Groups I + II (tumor diameter ≤ 10 mm) vs Groups III + IV (> 11 mm): p = 0.004018
According to the TNM classification of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors issued by the ENETS and AJCC/UICC [20], 51 (85.0%) were classified as stage I (pT1, N0, c/rM0), 6 (10%) as IIA (pT2, N0, c/r M0), one as IIB (pT3, N0, M0 c/r), and 2 (3.3%) as IIIB (anyT, N1, c/rM0) according to the ENETS staging system. Applying the AJCC staging system, 51 tumors were staged as IA (pT1, pN0, c/rM0), 7 tumors as IB (pT2, pN0, c/rM0), and the two patients with positive lymph nodes as IIB.
Size and proliferation (Ki-67) index
Applying the proliferation marker Ki-67, 58 (96.6%) lesions were classified as G1 and two (3%) as G2, respectively. The proliferation rates ranged from 1 to 8%. No tumor was classified as G3.
All 51 tumors with a diameter < 20 mm were graded as G1. Seven of 9 tumors (size = tumor diameter ≥ 20 mm] were graded as G1 and two as G2, respectively.
Table 3 summarizes the various subgroups of tumors based on their different tumor diameters.
Comparing the distribution of G2 tumors in groups I to III (size < 20 mm) and in group IV (≥20 mm), significantly more G2 tumors were found in group IV (0/51 [0%] vs. 2/9 [22%]; chi-square test: p = 0.000617).
Comparing groups I + II (size ≤10 mm) and groups III + IV (size > 10 mm), significantly more G2 tumors were found in the group of tumors > 10 mm (0/48 [0%] vs. 2/12 [16.7%]; chi-square test: p = 0.004018).
Significance could also be documented comparing group I (size ≤5 mm) with groups II to IV (size > 6 mm; 0/40 [0%] vs. 2/20 [10%]; chi-square test: p = 0.041932).
Individual analyses of 6 patients and follow-up
In patient A (3 tumors examined in detail), the largest (80 mm; T3 according to ENETS, T2 according to UICC; G1, N0) and the second largest tumor (40 mm; Fig. 1) were by definition classified as vipomas (proven by VIP expression in more than 70% of the tumor cells; concordant with high blood VIP levels presurgically). Clinically, the patient suffered from severe WDHA syndrome [21].
Fig. 1.
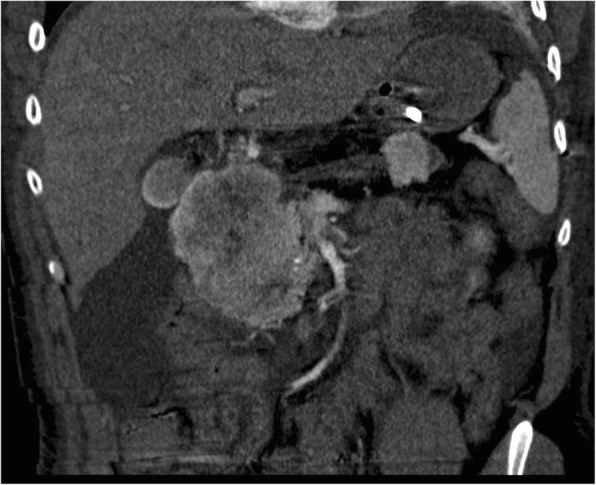
CT-image of two large tumors (80 mm and 40 mm) of patient A that were both immunohistochemically positive for VIP
Twelve years after total pancreatectomy the patient is free of neuroendocrine tumor disease, his insulin-dependent diabetes is well controlled, and he had no complications secondary to it so far.
Patient B with 6 PNENs was staged as IIIA. The largest lesion located in the pancreatic head was a moderately proliferating G2 tumor (Ki-67: 8%; TTF1 positiv) 30 mm in diameter (pT2). The proliferation rate of this tumor was identical to the two affected regional lymph nodes (pN1–2/20; Table 4, Ki-67: 6 and 8% in hotspots).
Table 4.
Patient B: Size, proliferation and immunohistochemistry of the primary tumors and lymph node metastasis
| PNEN/ LN | Location | Size (mm) | Ki-67 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Head | 30 | 8 |
| 2 | Body | 25 | 1 |
| 3 | 6.3 | 1 | |
| 4 | 4 | 1 | |
| 5 | 3.5 | 1 | |
| 6 | Tail | 20 | 1 |
| LN 1 | 8 | ||
| LN 2 | 6 |
PNEN: Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasia; LN = lymph node; Grading: G;
G1: Ki-67 <3%; G2: Ki-67 3-20%)
10 years after total pancreatectomy, the Gallium DOTANOC-PET-CT and MRT revealed multiple small (≤10 mm) liver metastases.
In patient C, 15 tumors were examined, including one in the duodenum (which was positive for CDX2). The leading tumor measured 25 mm, corresponding to pT2 N0 cMo. All tumors were graded as G1.
Seven years after total pancreatectomy, the patient is free of neuroendocrine tumor burden.
Patient D presented with hypoglycemia. Organic hyperinsulinism was confirmed clinically and biochemically in this patient at age 15. Preoperatively, one tumor was diagnosed in the pancreatic tail (20 mm), while three others (15, 6, 5 mm) were localized by intraoperative sonography in the pancreatic body. After left pancreatic resection, five neuroendocrine neoplasias were described in final histology. The largest (20 mm) with 3% positivity for Ki-67 presented by definition as a low G2 NET. More than 70% of the neuroendocrine cells of this tumor showed immunopositivity for insulin (=insulinoma).
Twenty-nine years after surgery, the patient is clinically cured. Now 42 years of age, he refuses any follow-up examinations.
Seventeen tumors (all smaller than 10 mm) were evaluated in the specimen obtained from patient E after total pancreatectomy. None showed a proliferation rate higher than 1%, corresponding to G1. The original histopathological report described another non-functioning tumor of 22 mm in diameter (the only one located by CT preoperatively) in the pancreatic head with a Ki-67 of < 1%. Therefore, the tumor was classified as pT2.
Clinically free of symptoms, she died of liver cirrhosis based on alcohol abuse four years later.
Patient F had 13 tumors ranging from less than 1 mm in size to 100mm (!). The large tumor described in CT was located in the pancreatic tail. All lesions, including the large one, were graded as G1. At the time of surgery, lymph node metastases were diagnosed in 9 of 29 lymph nodes. All lymph nodes were invaded by a G1 tumor. The patient had (subclinical) hyperinsulinism. Immunohistochemically, the largest tumor was negative for insulin, but some smaller tumors showed insulin-positive neuroendocrine cells dispersed (less than 70%) in the lesions.
Twenty-one years after subtotal pancreatic left resection and enucleation of three pancreatic head tumors and lymph node dissection, low normal fasting glucose levels correspond to high normal insulin and C-peptide levels. The patient is free of clinical symptoms. Ga-DOTANOC-PET-CT reveals multiple lymph node metastases in the upper abdomen.
Discussion
All NENs are potentially malignant lesions [22]. The majority of PNENs are histologically well differentiated and slow-growing tumors that differ in their biological behavior. In the WHO 2000 classification, NF- and F-tumors (except insulinoma) were thought to show low-grade malignancy [23]. Clinical behavior is influenced by various clinical-pathological features such as size, local−/angioinvasion and histological differentiation [24].
Currently, the ENETS and the WHO 2017 each propose a formal classification for PNENs based on proliferative tumor activity as measured by mitotic count and the expression of nuclear antigen Ki-67, subdividing the NENs into G1, G2 and G3, respectively [14, 18]. Grading is combined with site-specific (TNM) staging to improve prognostic strength.
To our knowledge, the prognostic impact of PNEN grading in correlation to size (pT) has not yet been evaluated in MEN-1 because the number of patients with pancreatic surgery is low. However, as shown here there seem to be no significant differences in the biological behavior of sporadic and hereditary PNENs.
Due to the genetic background of MEN-1, every single neuroendocrine cell of the pancreas is a potential progenitor of a NEN. Therefore, organs are pervaded by neuroendocrine micro- and macro-lesions in up to 90% of genetically affected patients [19]. As expected, the majority of neuroendocrine lesions in the six MEN-1 patients were non-functioning and developed predominantly as microadenomas (≤ 5 mm in diameter; 66.7%).
Fifty-eight (96.6%) of the 60 lesions were graded as G1 and two (3.3%) tumors as G2 [14, 18]. No lesion was graded as G3. G2 tumors were found only in lesions ≥20 mm (ENETS/AJCC pT2), while all tumors < 20 mm (ENETS/AJCC pT1) were graded as G1.
Within one pancreatic gland, NENs of various sizes and different Ki-67 indices were found, demonstrating intertumor heterogeneity within one patient. These findings underline the observation that size – an important parameter for the definition of T in the TNM classification – appears to be an independent predictor of survival, and the evaluation of Ki-67 alone cannot be utilized for this purpose. This is comparable to the situation in sporadic PNENs [25]. Grading may help to better estimate metastasizing capacity. As every single tumor is a potential risk for systemic disease [26], early diagnosis and surgical excision of MEN-1-related PNENs can improve survival [3].
Imaging with novel radiolabeled somatostatin analogs (Ga68-DOTANOC), PET/CT or MRI allows to measure size, to verify local invasion of the primary tumor(s), and to evaluate the presence of metastatic disease. Functioning imaging is the key element in the management of patients with MEN-1 to determine appropriate therapeutic strategies. With regard to our series, somatostatin receptor imaging was performed in all patients and yielded negative results in respect to distant metastases before surgery. During follow up DOPA-Peptide-PET-CTs were used in all patients and could detect metastatic lesions in two, which amended the treatment regimens.
The indication, timing and extent of surgery in NF-PENs has to be individualized on the basis of size and proliferation activity, keeping in mind the potential morbidity of pancreatic resection and the risk of long-term insulin dependence.
Tumor size is easily assessed with EUS or cross-sectional imaging, while Ki-67 grading on histological samples obtained by EUS-guided fine-needle aspiration is technically complex [27].
The current analysis is in accordance with some authors who currently agree that NF-PNENs ≤10 mm can be followed conservatively: all 48 NF-NENs analyzed in this investigation were graded as G1. The management of NF-PNENs sized 11 to < 20 mm is a matter of debate. The progression-free survival may be identical in patients undergoing active surveillance compared to surgery [28, 29].
The procedures currently discussed are either resection or follow-up. Lopez et al. have recommended surgical treatment for NF-PNENs in MEN-1 with a size between 10 and 20 mm, should rapid progression – defined by 5 mm tumor growth annually – be observed [30]. The current findings indirectly emphasize the recommendation that NF-PNENs ≥20 mm (pT2) should be treated surgically as they likely yield a more aggressive clinical course, especially if an elevated Ki-67 index is documented additionally.
Conclusion
This small-scale series with 60 NENs harvested from 6 MEN-1 pancreatic glands adds additional information regarding the importance of size (pT) in combination with proliferation (G). In this series, significantly more tumors ≥20 mm were classified as G2 (Ki-67 index: > 2 to 20%) yielding indirectly a higher capacity of malignancy.
When tumors reach the cutoff (20 mm; leading tumors), it may be recommended to obtain tissue specimens of this tumor to select patients at risk of highly proliferating neoplasms who may require early surgical intervention to prevent invasive growth, regional and distant metastasis. PNENs with Ki-67 positive cells > 2% should probably be treated surgically early on, regardless of their size.
Additional file
Table S1. Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasia in MEN-1: Size, TNM, proliferation. A, B, C, E: total pancreatectomy; D: left pancreatic resection; F: Thompson procedure. (DOCX 22 kb)
Acknowledgements
Special thanks to the technicians and keepers of the archives at our institution.
This paper is not based on a previous communication to a society or a meeting.
Funding
This study was not funded by a third party.
Availability of data and materials
All data and material analyzed in this study is available.
Abbreviations
- AJCC
American Joint Committee on Cancer
- CDX 2
Caudal related homeobox transcription factor 2
- CgA
Chromogranin A
- CT
Computerized tomography
- DOTANOC
DOTA-Na13-Octreotide
- ENETS
European neuroendocrine tumor society
- EUS
Endoscopic ultrasound
- Ga68
Positron-emitting Gallium isotope (half-life: 68 min)
- IOUS
Intraoperative ultrasound
- Ki-67
Kiel – 67
- MEN
Multiple endocrine neoplasia
- MIB-1
Molecular immunology borstel – 1
- MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging
- NEN
Neuroendocrine neoplasia
- NET
Neuroendocrine tumor
- PET
Positron emission tomography
- PNEN
Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasia
- PNET
Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor
- SSR
Somatostatin receptor
- TNM
Tumor (T), lymph node (N), metastasis (M) – classification
- TTF 1
Thyroid transcription factor 1
- UICC
Union for International Cancer Control
- VIP
Vasoactive intestinal peptide
- WDHA
Water Diarrhea Hypokalemia Achlorhydria
- WHO
World Health Organization
Authors’ contributions
All authors contributed substantially to this manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All procedures performed in this study involving human material were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was obtained from all participants.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Andreas Selberherr, Phone: +43-1-40400, Email: andreas.selberherr@meduniwien.ac.at.
Oskar Koperek, Email: Oskar.Koperek@meduniwien.ac.at.
Philipp Riss, Email: Philipp.Riss@meduniwien.ac.at.
Christian Scheuba, Email: Christian.Scheuba@meduniwien.ac.at.
Martin B. Niederle, Email: Martin.Niederle@meduniwien.ac.at
Reto Kaderli, Email: Reto.Kaderli@insel.ch.
Aurel Perren, Email: Aurel.Perren@pathology.unibe.ch.
Bruno Niederle, Email: Bruno.Niederle@meduniwien.ac.at.
References
- 1.Doherty GM, Thompson NW. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1: duodenopancreatic tumours. J Intern Med. 2003;253(6):590–598. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.2003.01163.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gauger PG, Thompson NW. Early surgical intervention and strategy in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001;15(2):213–223. doi: 10.1053/beem.2001.0136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kouvaraki MA, Shapiro SE, Cote GJ, et al. Management of pancreatic endocrine tumors in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. World J Surg. 2006;30(5):643–653. doi: 10.1007/s00268-006-0360-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Akerstrom G, Hessman O, Skogseid B. Timing and extent of surgery in symptomatic and asymptomatic neuroendocrine tumors of the pancreas in MEN 1. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2002;386(8):558–569. doi: 10.1007/s00423-001-0274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gauger PG, Doherty GM, Broome JT, et al. Completion pancreatectomy and duodenectomy for recurrent MEN-1 pancreaticoduodenal endocrine neoplasms. Surgery. 2009;146(4):801–806. doi: 10.1016/j.surg.2009.06.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Adkisson CD, Stauffer JA, Bowers SP, et al. What extent of pancreatic resection do patients with MEN-1 require? JOP. 2012;13(4):402–408. doi: 10.6092/1590-8577/657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Triponez F, Sadowski SM, Pattou F, et al. Long-term follow-up of MEN1 patients who do not have initial surgery for small </=2 cm nonfunctioning pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors, an AFCE and GTE study: association francophone de Chirurgie Endocrinienne & Groupe d'Etude des Tumeurs endocrines. Ann Surg. 2018;268(1):158–164. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hamilton SR, Aaltonen LA. World Health Organization classification of tumours. Pathology and Genetics of Tumours of the Digestive System. 3. Lyon: IARC Press; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Imazu H, Uchiyama Y, Matsunaga K, et al. Contrast-enhanced harmonic EUS with novel ultrasonographic contrast (Sonazoid) in the preoperative T-staging for pancreaticobiliary malignancies. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2010;45(6):732–738. doi: 10.3109/00365521003690269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Queneau PE, Sauve G, Koch S, et al. The impact on clinical practice of endoscopic ultrasonography used for the diagnosis and staging of pancreatic adenocarcinoma. JOP. 2001;2(3):98–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lewis MA, Thompson GB, Young WF., Jr Preoperative assessment of the pancreas in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. World J Surg. 2012;36(6):1375–1381. doi: 10.1007/s00268-012-1539-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Pezzilli R, Partelli S, Cannizzaro R, et al. Ki-67 prognostic and therapeutic decision driven marker for pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasms (PNENs): a systematic review. Advances in medical sciences. 2016;61(1):147–153. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2015.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Bosman FT. WHO classification of tumours of the digestive system. 4. Lyon: IARC Press; 2010. [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rindi G, Kloppel G, Alhman H, et al. TNM staging of foregut (neuro) endocrine tumors: a consensus proposal including a grading system. Virchows Arch. 2006;449(4):395–401. doi: 10.1007/s00428-006-0250-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lloyd RV, Osamura RY, Klöppel G, et al. WHO classification of tumours of endocrine organs. 4. Lyon: IARC Press; 2017. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Falconi M, Eriksson B, Kaltsas G, et al. ENETS consensus guidelines update for the Management of Patients with functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors and non-functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Neuroendocrinology. 2016;103(2):153–171. doi: 10.1159/000443171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Thompson NW. Current concepts in the surgical management of multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 pancreatic-duodenal disease. Results in the treatment of 40 patients with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome, hypoglycaemia or both. J Intern Med. 1998;243(6):495–500. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.1998.00307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Klimstra DS, Arnold R, Capella C, et al. Neuroendocrine neoplasms of the pancreas. In: Bosman F, Carneiro F, Hruban RH, Theise ND, editors. World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Digestive System. Fourth ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer; 2010. p. 279–337.
- 19.Anlauf M, Schlenger R, Perren A, et al. Microadenomatosis of the endocrine pancreas in patients with and without the multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 syndrome. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30(5):560–574. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000194044.01104.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kloppel G, Rindi G, Perren A, et al. The ENETS and AJCC/UICC TNM classifications of the neuroendocrine tumors of the gastrointestinal tract and the pancreas: a statement. Virchows Arch. 2010;456(6):595–597. doi: 10.1007/s00428-010-0924-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Verner JV, Morrison AB. Islet cell tumor and a syndrome of refractory watery diarrhea and hypokalemia. Am J Med. 1958;25(3):374–380. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(58)90075-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kloppel G, Rindi G, Anlauf M, et al. Site-specific biology and pathology of gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Virchows Arch. 2007;451(Suppl 1):S9–27. doi: 10.1007/s00428-007-0461-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Solcia E, Kloppel G, Sobin LH. Histological typing of endocrine tumours. 2. Berlin: WHO International Histological Classification of Tumors. Springer; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kloppel G, Perren A, Heitz PU. The gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine cell system and its tumors: the WHO classification. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2004;1014:13–27. doi: 10.1196/annals.1294.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Rindi G, Falconi M, Klersy C, et al. TNM staging of neoplasms of the endocrine pancreas: results from a large international cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2012;104(10):764–777. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 26.Perren A, Anlauf M, Henopp T, et al. Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 (MEN1): loss of one MEN1 allele in tumors and monohormonal endocrine cell clusters but not in islet hyperplasia of the pancreas. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92(3):1118–1128. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-1944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Weynand B, Borbath I, Bernard V, et al. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumour grading on endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration: high reproducibility and inter-observer agreement of the Ki-67 labelling index. Cytopathology. 2014;25(6):389–395. doi: 10.1111/cyt.12111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Triponez F, Sadowski SM, Pattou F, et al. Long-term Follow-up of MEN1 Patients Who Do Not Have Initial Surgery for Small </=2 cm Nonfunctioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors, an AFCE and GTE Study: Association Francophone de Chirurgie Endocrinienne & Groupe d'Etude des Tumeurs Endocrines. Ann Surg. 2017;268(1):158–64. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 29.Partelli S, Tamburrino D, Lopez C, et al. Active Surveillance versus Surgery of Nonfunctioning Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms </=2 cm in MEN1 Patients. Neuroendocrinology. 2016;103(6):779–786. doi: 10.1159/000443613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lopez CL, Albers MB, Bollmann C, et al. Minimally invasive versus open pancreatic surgery in patients with multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1. World J Surg. 2016;40(7):1729–1736. doi: 10.1007/s00268-016-3456-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. Pancreatic neuroendocrine neoplasia in MEN-1: Size, TNM, proliferation. A, B, C, E: total pancreatectomy; D: left pancreatic resection; F: Thompson procedure. (DOCX 22 kb)
Data Availability Statement
All data and material analyzed in this study is available.


