Abstract
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is a lethal disease with a 5-year survival rate of <5%, the lowest of all types of cancer. The diagnosis of pancreatic cancer relies on imaging and tissue biopsy, and the only curative therapy is complete surgical resection. Pancreatic cancer has the propensity to metastasise at an early stage and the majority of patients are diagnosed when surgery is no longer an option. Hence, there is an urgent need to identify biomarkers to enable early diagnosis, and to develop new therapeutic strategies. One approach for this involves targeting cancer-associated glycans. The most widely used serological marker in pancreatic cancer is the carbohydrate antigen CA 19-9 which contains a glycan known as sialyl Lewis A (sLeA). The CA 19-9 assay is used routinely to monitor response to treatment, but concerns have been raised about its sensitivity and specificity as a diagnostic biomarker. In addition to sLeA, a wide range of alterations to other important glycans have been observed in pancreatic cancer. These include increases in the sialyl Lewis X antigen (sLex), an increase in truncated O-glycans (Tn and sTn), increased branched and fucosylated N-glycans, upregulation of specific proteoglycans and galectins, and increased O-GlcNAcylation. Growing evidence supports crucial roles for glycans in all stages of cancer progression, and it is well established that glycans regulate tumour proliferation, invasion and metastasis. The present review describes the biological significance of glycans in pancreatic cancer, and discusses the clinical value of exploiting aberrant glycosylation to improve the diagnosis and treatment of this deadly disease.
Keywords: glycosylation, glycans, pancreatic cancer, treatment, biomarkers
1. Introduction
Pancreatic adenocarcinoma is one of the worlds' most aggressive malignancies with a five year survival rate of less than 5%, the worst prognosis among all cancers (1). The poor survival rate is mostly due to the lack of a reliable early detection method, a tendency to metastasise at an early stage and resistance to available therapeutic options (2,3). In addition, there is often an absence of symptoms in early disease and established disease can have clinical similarities to benign conditions, making it difficult to diagnose (4). The diagnosis of pancreatic cancer relies on imaging and tissue biopsy, and the only curative therapy is complete surgical resection. Non-invasive biomarkers, such as those from serum, could provide a useful complement to imaging and cytology diagnostic methods and have the potential to aid clinical decisions as part of a routine blood test. Currently, the only clinical biomarker used in the management of pancreatic cancer is the serum marker CA19-9, which although used widely for disease monitoring, does not provide adequate accuracy for early detection and diagnosis. Given the usually late diagnosis of pancreatic cancer, highly specific circulating biomarkers for cancer detection and screening are urgently needed, and would be a major breakthrough allowing treatment for more patients.
Glycosylation is an enzymatic process that links glycan sugars to other glyans, lipids or proteins. Glycosylation takes place in the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum and occurs as the consequence of the synchronised action of glycosylation enzymes. The two most common mechanisms by which glycans can be linked to lipids and proteins are O-linked and N-linked glycosylation. In O-linked glycosylation glycans are added sequentially to the hydroxyl oxygen of serine/threonine residues on target proteins and extended to produce various core and terminal structures that can be sialylated and/or fucosylated. In N-linked glycosylation 14 sugar preassembled blocks are transferred co-translationally to the amide group of an asparagine residue. N-glycans contain a common pentasaccharide core region consisting of three mannose and two N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) subunits. This can be further modified by the addition of terminal Gal (galactose), GlcNAc, fucose and sialic acid moieties.
Aberrant glycosylation in cancer was first described nearly 50 years ago (5), and since then it has been well documented that the development and progression of cancer results in fundamental changes in the glycosylation patterns of cell surface and secreted glycoproteins (6). Many of the first cancer-specific antibodies identified were directed against oncofetal antigens expressed on embryonic and tumour cells but not in adult tissues (7) and growing evidence supports crucial roles for glycans during all steps of tumour progression. Glycans can regulate tumour proliferation, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis (8), and aberrant glycosylation has been proposed as a general hallmark of all cancers (6).
Glycans can control cell identity and cell environment interactions. Changes in the glycosylation modification of proteins that are expressed on the cell surface, or secreted by cancer cells, are promising sources of potential biomarkers (9,10). Glycoconjugates with altered glycosylation are often shed into the circulation, allowing the distinction between patients with and without cancer (11–13). Recent research has uncovered new ways that glycosylation can contribute to cancer biology, as well as new strategies to improve treatment by exploiting glycans (14). This review discusses the changes in glycosylation involved in pancreatic cancer, their role in disease development and progression, and the huge potential to exploit glycans to improve diagnosis and treatment.
2. Aberrant glycosylation in pancreatic cancer
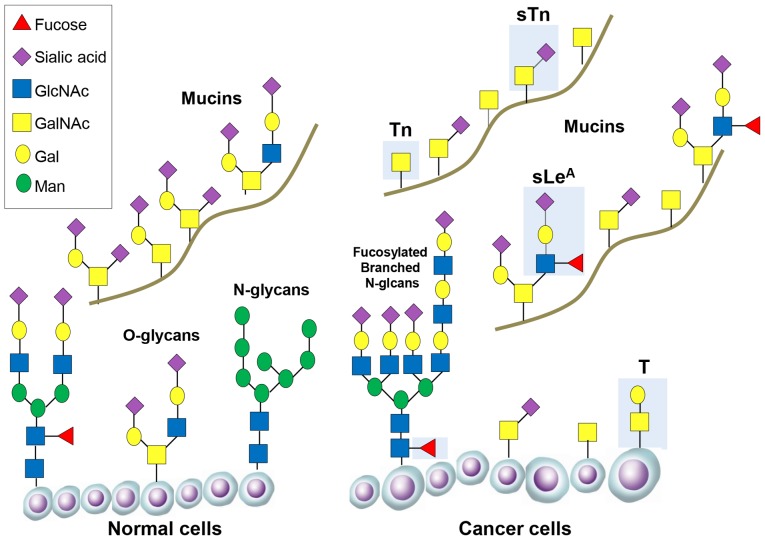
In the normal pancreas glycosylated proteins have important functions, including protection and lubrication of the pancreatic ducts (15). In pancreatic cancer glycosylation of proteins becomes deregulated, and the aberrant expression of specific glycans is associated with disease progression and poor prognosis. Changes to the glycome in pancreatic cancer include increases in the sialyl Lewis antigens (sLeA and sLex), an increase in truncated O-glycans (Tn and sTn), increased branched and fucosylated N-glycans, upregulation of specific proteoglycans and galectins, and increased O-GlcNAcylation (some of these alterations are summarised in Fig. 1 and Table I).
Figure 1.
Changes in glycosylation during cancer progression. Representative O-glycans and N-glycans are shown attached on the surface of normal cells and cancer cells. O-glycans are also shown attached to mucin glycoproteins. Important tumour-associated glycans are shown in the blue boxes, including truncated O-glycans (Tn and sTn) and fucosylated branched N-glycans (sLeA and SLeX). For more information about the structure of each glycan see Table I.
Table I.
Summary of glycan alterations in pancreatic cancer.
| Glycan | Structure | Change | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| sialyl Lewis A (sLeA) | 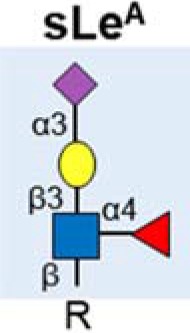 |
Upregulated | (23) |
| Detected by CA 19-9 assay | (16–20) | ||
| Found on various protein carriers including mucins | (15,28,31,32) | ||
| sialyl Lewis X (sLex) | 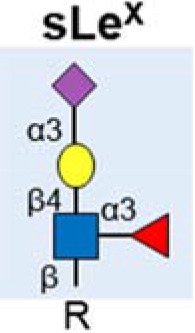 |
Upregulated | (34–37) |
| Linked to invasion | (39) | ||
| Found on numerous proteins implicated in pancreatic cancer | (32,40–42) | ||
| Tn antigen | 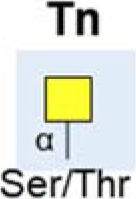 |
Increased | (30,45) |
| Linked to poor prognosis & metastasis | (11,44,45) | ||
| sTn antigen | 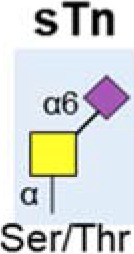 |
Increased | (30,45) |
| Linked to poor prognosis & metastasis | (11,44,45) | ||
| Fucosylated & branched N-glycans | 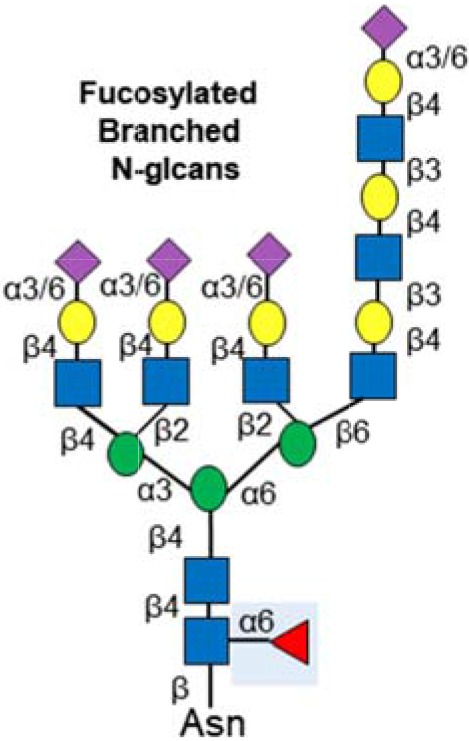 |
Highly branched N-glycans increased in aggressive disease | (57,58) |
| Increased fucosylation | (56,59,60) | ||
| Found on numerous proteins implicated in pancreatic cancer | (50–52) | ||
| O-GlcNAcylation | 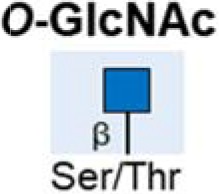 |
Increased | (64) |
| Inhibition can reduce tumour growth and progression | (66,71,72) | ||
| Proteoglycans | 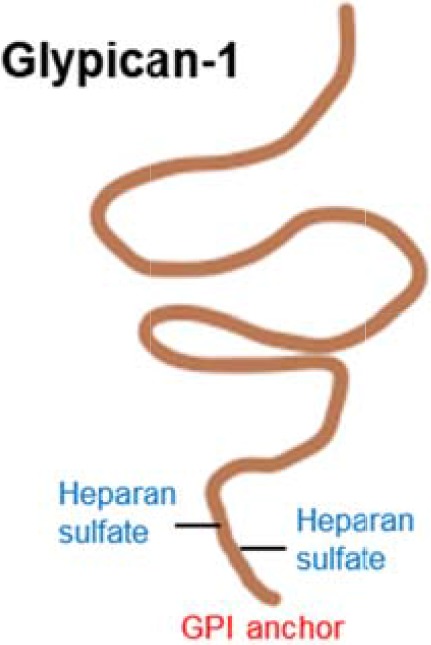 |
Numerous proteoglycans are overexpressed in pancreatic cancer | (74–82) |
| e.g., the heparin sulphate proteoglycan glypican-1 is linked to disease progression and expressed by exosomes | (83,84) | ||
| Galectins |  |
Galectin-1 & Galectin-3 overexpressed | (87–90) |
3. The Sialyl Lewis antigens (sLeA and sLeX)
The most widely used serological assay used in the management of pancreatic cancer detects a cancer associated carbohydrate antigen, called CA 19-9, that contains a glycan known as sialyl Lewis A (sLeA) (16–20). sLeA is part of the Lewis family of blood group antigens, named after the discoverer of a series of antigens found on red blood cells. Studies have shown that sLeA is found at low levels in normal tissue, higher levels in embryonic tissue (21), and is overexpressed in epithelial cancers (22). In the normal pancreas sLeA is found on the epithelial surfaces of the ducts, whereas in pancreatic cancer sLeA can be heavily secreted into the lumen of proliferating ducts and pass into the bloodstream (23).
The CA 19-9 assay detects the sLeA glycan motif, along with the additional glycans, lipids and proteins to which it is attached. sLeA has been found on numerous proteins including mucins, carcinoembryonic antigen and circulating apolipoproteins (24). The CA 19-9 assay is widely used to monitor response to treatment in patients already diagnosed with pancreatic cancer (25,26), but concerns have been raised about its sensitivity and specificity as a diagnostic biomarker, and it is not used in screening (22,27–29). Mucin glycoproteins have multiple roles in pancreatic cancer and are major carriers of glycans including CA 19-9 (15). Altered mucin glycoforms have been observed in both the early stages of pancreatic cancer, and in late stage metastatic disease (30). It has been suggested that measuring the CA19-9 antigen on specific protein carriers (such as mucins), and detecting additional related glycans may improve the performance of the CA19-9 assay (28,31,32). Targeting mucin glycosylation may also limit pancreatic cancer growth (33).
In addition to sLeA, other members of the Lewis antigens also have roles in pancreatic cancer. An isomer of sLeA (known as sialyl Lewis X (sLeX)) is also upregulated in some pancreatic cancers, and can be detected in the blood of many patients (34–37). The sialyl Lewis antigens are the minimal recognition motif for ligands of selectins, a family of lectins with roles in leukocyte trafficking with roles in tumour extravasation and cancer metastasis (38). In pancreatic cancer sLeX has been found on migrating lymphocytes and linked to invasion (39). Increased sLeX antigen on the glycoprotein ceruloplasmin has been described in pancreatic malignancy (37), and numerous proteins implicated in pancreatic cancer (including Kras, SPARC and Wnt7b) have been found to express sLeX glycans (40). Tang et al (2016) profiled the levels of multiple glycans in in the plasma of 200 patients with either benign pancreatic disease or pancreatic cancer (32), and showed increased levels of CA19-9, sLeX and also in sialylated type 1 LacNAc (also known as Dupan-2). Dupan-2 has previously been associated with pancreatic cancer and is increased in some patients (41,42). Each of the three glycans (CA19-9, sLeX and Dupan-2) are increased in some pancreatic cancer patients but not in others, leading the authors to suggest the use of a three glycan panel to improve diagnosis and facilitate pancreatic cancer sub-classification (32).
4. Truncated O-glycans
Immature, truncated O-glycans are characteristic of virtually all epithelial cancer cells (43). In pancreatic cancer, the expression of the truncated cancer-associated O-glycans Tn and sialyl-Tn (sTn) are linked to poor patient outcome (11), and associated with cancer cell growth and metastasis (44,45). The normal pancreas does not express Tn or sTn (46), but levels are high in pancreatic cancer (30,45). Specifically, truncated O-glycans have been detected on Nucleolin, EGFR and Her2 (45,47). COSMC is a molecular chaperone that is essential for correct protein O-glycosylation (48). Knockdown of COSMC promotes aberrant O-glycosylation in pancreatic cancer, and this is linked to anti-apoptotic and pro-metastatic cell behaviour, reduced proliferation and increased migration (45). In addition to COSMC, the GALNT3 enzyme is also linked to the aberrant production of tumor-associated O-glycans in pancreatic cancer. GALNT3 is increased in well/moderately differentiated pancreatic cancer, but lost in poorly differentiated tissues (47,49).
5. N-glycans
Aberrant N-linked glycosylation is common in pancreatic cancer. In particular, pancreatic cancer cells frequently display increased levels of highly branched N-glycans, and alterations to N-glvcan sialylation or fucosylation. Increased levels of N-glycosylation has been found on integrins and ECM adhesion proteins (50) and in proteins involved in pathways important in pancreatic cancer such as TGF-β, TNF, and NF-kappa-B signalling (51). N-glycosylation can also influence the surface expression of receptor tyrosine kinases and enhance the chemosensitivity of drug resistant pancreatic cancer cells (52). N-glycans have shown promise as biomarkers in pancreatic cancer. The sialyltransferase enzymes ST6Gal1 and ST3Gal3 are overexpressed in pancreatic tissue and this is linked to invasive potential (53–55). It is also possible to detect changes to N-glycans in patient blood. Increased fucosylation can be detected in serum from patients with pancreatic cancer (56), and highly branched N-glycans are increased in the blood of patients with aggressive disease (57,58). Fucosylated epitopes occur on specific proteins such as haptoglobin and ribonuclease 1 (RNASE1) and these are currently being explored for use diagnostically (59,60).
6. The HBP pathway
The hexosamine biosynthetic pathway (HBP) produces the amino sugar conjugate O-linked N-acetylglucosamine (O-GlcNAc). Addition of O-GlcNAc to proteins (known as O-GlcNAcylation) can alter key hallmarks of cancer including transcription, cell signalling metabolism and epigenetics (61,62), and may impact cell survival and resistance during chemotherapy (63). O-GlcNAc is added to and removed from proteins by the O-GlcNAc cycling enzymes OGT and OGA. Both these enzymes are dramatically elevated in pancreatic cancer relative to normal pancreas, as are the overall levels of protein O-GlcNAcylation (64). In the normal pancreas OGT allows cells to dynamically respond to glucose levels by modulating O-linked protein glycosylation (65). When pancreatic cancer develops increased O-GlcNAcylation may block cancer cell apoptosis and lead to oncogenic activation of NF-κB signalling (66). Several proteins with defined roles in pancreatic cancer have been shown to be modified by O-GlcNAc including the heat shock protein HSP70 (67), the transcription factor Sp1 (68), the Wnt signalling proteins β-catenin and LRP6 (69), and more recently the transcription factor Sox2 that determines self-renewal in pancreatic cancer and is responsible for tumour initiation (70). Inhibiting O-GlcNAcylation can reduce pancreatic tumour growth and progression suggesting HBP is promising potential therapeutic target (66,71,72).
7. Proteoglycans
In addition to aberrant protein glycosylation, cancer cells can also have alterations in proteoglycans (73). Proteoglycans are heavily glycosylated glycoproteins with attached glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) such as chondroitin sulphate and heparin sulphate that are located on the cell surface or secreted. Numerous proteoglycans have been found to be overexpressed in pancreatic cancer, including syndecan-1, versican, decorin, lumican and biglycan (74–81). Of particular interest, the heparin sulphate proteoglycan glypican-1 is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer cell models and patient tumours (82) and has been shown to contribute to pancreatic cancer progression using mouse models (83,84). A recent study found that glypican-1 is specifically expressed by circulating cancer exosomes, and may serve as non-invasive diagnostic and screening tool to enable early diagnosis of pancreatic cancer (85).
8. Galectins
As well as changes in glycosylation patterns cancer cells may also display altered expression of proteins that interact with glycans. An important example of such proteins is the galectins, which are a group of glycan binding proteins with an established role in cancer biology (86). In pancreatic cancer, Galectin-1 (GAL1) and Galectin-3 (GAL3) are overexpressed (87–90). This is important for cancer progression since GAL1 can induce stroma remodelling, tumour cell proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, inflammation, and metastasis (91,92), and GAL3 can activate pancreatic cancer cells to produce inflammatory cytokines (88). It is likely that galectin specific targeting will have a broad therapeutic potential in pancreatic cancer, either alone or in combination with other therapies (88,93).
9. Conclusions and future perspectives
The survival rates for pancreatic cancer have remained dismal for many years, and as such there is an urgent need to improve diagnosis and treatment. A wide range of alterations to glycans have been detected in pancreatic cancer, and these show promise as both potential circulating biomarkers and as targets for glycan specific therapies. The expression of specific glycans within pancreatic tumours, their presence in patient serum, and their possible ability to facilitate metastases, suggests glycans could help guide precision medicine strategies. Recent profiling has defined 4 molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer (94), and it likely that diversity exists between pancreatic cancers in the variety and type of glycans made and secreted into the blood (24). To fully exploit glycans clinically it will be vital to fully profile the pancreatic cancer glycome and determine how this varies between different tumour types.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Authors' contributions
JM conceived the review, researched the literature and wrote the manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares that there are no competing interests.
References
- 1.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68:7–30. doi: 10.3322/caac.21442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Garrido-Laguna I, Hidalgo M. Pancreatic cancer: From state-of-the-art treatments to promising novel therapies. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2015;12:319–334. doi: 10.1038/nrclinonc.2015.53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Maitra A, Hruban RH. Pancreatic cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2008;3:157–188. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pathmechdis.3.121806.154305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Klöppel G, Adsay NV. Chronic pancreatitis and the differential diagnosis versus pancreatic cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2009;133:382–387. doi: 10.5858/133.3.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Meezan E, Wu HC, Black PH, Robbins PW. Comparative studies on the carbohydrate-containing membrane components of normal and virus-transformed mouse fibroblasts. II. Separation of glycoproteins and glycopeptides by sephadex chromatography. Biochemistry. 1969;8:2518–2524. doi: 10.1021/bi00834a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Munkley J, Elliott DJ. Hallmarks of glycosylation in cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:35478–35489. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Feizi T. Demonstration by monoclonal antibodies that carbohydrate structures of glycoproteins and glycolipids are onco-developmental antigens. Nature. 1985;314:53–57. doi: 10.1038/314053a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pinho SS, Reis CA. Glycosylation in cancer: Mechanisms and clinical implications. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15:540–555. doi: 10.1038/nrc3982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kailemia MJ, Park D, Lebrilla CB. Glycans and glycoproteins as specific biomarkers for cancer. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2017;409:395–410. doi: 10.1007/s00216-016-9880-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Munkley J. Glycosylation is a global target for androgen control in prostate cancer cells. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2017;24:R49–R64. doi: 10.1530/ERC-16-0569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mereiter S, Balmaña M, Gomes J, Magalhães A, Reis CA. Glycomic approaches for the discovery of targets in gastrointestinal cancer. Front Oncol. 2016;6:55. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Adamczyk B, Tharmalingam T, Rudd PM. Glycans as cancer biomarkers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820:1347–1353. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2011.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Munkley J, Vodak D, Livermore KE, James K, Wilson BT, Knight B, Mccullagh P, Mcgrath J, Crundwell M, Harries LW, et al. Glycosylation is an androgen-regulated process essential for prostate cancer cell viability. EBioMedicine. 2016;8:103–116. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2016.04.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Munkley J, Mills IG, Elliott DJ. The role of glycans in the development and progression of prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol. 2016;13:324–333. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2016.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Moniaux N, Andrianifahanana M, Brand RE, Batra SK. Multiple roles of mucins in pancreatic cancer, a lethal and challenging malignancy. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:1633–1638. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Magnani JL, Nilsson B, Brockhaus M, Zopf D, Steplewski Z, Koprowski H, Ginsburg V. A monoclonal antibody-defined antigen associated with gastrointestinal cancer is a ganglioside containing sialylated lacto-N-fucopentaose II. J Biol Chem. 1982;257:14365–14369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Magnani JL, Brockhaus M, Smith DF, Ginsburg V, Blaszczyk M, Mitchell KF, Steplewski Z, Koprowski H. A monosialoganglioside is a monoclonal antibody-defined antigen of colon carcinoma. Science. 1981;212:55–56. doi: 10.1126/science.7209516. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Herlyn M, Sears HF, Steplewski Z, Koprowski H. Monoclonal antibody detection of a circulating tumor-associated antigen. I. Presence of antigen in sera of patients with colorectal, gastric, and pancreatic carcinoma. J Clin Immunol. 1982;2:135–140. doi: 10.1007/BF00916897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Magnani JL, Steplewski Z, Koprowski H, Ginsburg V. Identification of the gastrointestinal and pancreatic cancer-associated antigen detected by monoclonal antibody 19-9 in the sera of patients as a mucin. Cancer Res. 1983;43:5489–5492. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yue T, Partyka K, Maupin KA, Hurley M, Andrews P, Kaul K, Moser AJ, Zeh H, Brand RE, Haab BB. Identification of blood-protein carriers of the CA 19-9 antigen and characterization of prevalence in pancreatic diseases. Proteomics. 2011;11:3665–3674. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201000827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lahdenne P, Pitkänen S, Rajantie J, Kuusela P, Siimes MA, Lanning M, Heikinheimo M. Tumor markers CA 125 and CA 19-9 in cord blood and during infancy: Developmental changes and use in pediatric germ cell tumors. Pediatr Res. 1995;38:797–801. doi: 10.1203/00006450-199511000-00026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Goonetilleke KS, Siriwardena AK. Systematic review of carbohydrate antigen (CA 19-9) as a biochemical marker in the diagnosis of pancreatic cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2007;33:266–270. doi: 10.1016/j.ejso.2006.10.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kalthoff H, Kreiker C, Schmiegel WH, Greten H, Thiele HG. Characterization of CA 19-9 bearing mucins as physiological exocrine pancreatic secretion products. Cancer Res. 1986;46:3605–3607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Tang H, Hsueh P, Kletter D, Bern M, Haab B. The detection and discovery of glycan motifs in biological samples using lectins and antibodies: New methods and opportunities. Adv Cancer Res. 2015;126:167–202. doi: 10.1016/bs.acr.2014.11.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shah UA, Saif MW. Tumor markers in pancreatic cancer: 2013. JOP. 2013;14:318–321. doi: 10.6092/1590-8577/1653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Barton JG, Bois JP, Sarr MG, Wood CM, Qin R, Thomsen KM, Kendrick ML, Farnell MB. Predictive and prognostic value of CA 19-9 in resected pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 2009;13:2050–2058. doi: 10.1007/s11605-009-0849-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Galli C, Basso D, Plebani M. CA 19-9: Handle with care. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2013;51:1369–1383. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2012-0744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Yue T, Maupin KA, Fallon B, Li L, Partyka K, Anderson MA, Brenner DE, Kaul K, Zeh H, Moser AJ, et al. Enhanced discrimination of malignant from benign pancreatic disease by measuring the CA 19-9 antigen on specific protein carriers. PLoS One. 2011;6:e29180. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0029180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tempero MA, Uchida E, Takasaki H, Burnett DA, Steplewski Z, Pour PM. Relationship of carbohydrate antigen 19-9 and Lewis antigens in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 1987;47:5501–5503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Remmers N, Anderson JM, Linde EM, DiMaio DJ, Lazenby AJ, Wandall HH, Mandel U, Clausen H, Yu F, Hollingsworth MA. Aberrant expression of mucin core proteins and o-linked glycans associated with progression of pancreatic cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:1981–1993. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-2662. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Partyka K, Maupin KA, Brand RE, Haab BB. Diverse monoclonal antibodies against the CA 19-9 antigen show variation in binding specificity with consequences for clinical interpretation. Proteomics. 2012;12:2212–2220. doi: 10.1002/pmic.201100676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Tang H, Partyka K, Hsueh P, Sinha JY, Kletter D, Zeh H, Huang Y, Brand RE, Haab BB. Glycans related to the CA19-9 antigen are elevated in distinct subsets of pancreatic cancers and improve diagnostic accuracy over CA19-9. Cell Mol Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;2:201–221.e215. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmgh.2015.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Xu HL, Zhao X, Zhang KM, Tang W, Kokudo N. Inhibition of KL-6/MUC1 glycosylation limits aggressive progression of pancreatic cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:12171–12181. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v20.i34.12171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pour PM, Tempero MM, Takasaki H, Uchida E, Takiyama Y, Burnett DA, Steplewski Z. Expression of blood group-related antigens ABH, Lewis A, Lewis B, Lewis X, Lewis Y and CA 19-9 in pancreatic cancer cells in comparison with the patient's blood group type. Cancer Res. 1988;48:5422–5426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Singh S, Pal K, Yadav J, Tang H, Partyka K, Kletter D, Hsueh P, Ensink E, Kc B, Hostetter G, et al. Upregulation of glycans containing 3′ fucose in a subset of pancreatic cancers uncovered using fusion-tagged lectins. J Proteome Res. 2015;14:2594–2605. doi: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.5b00142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tang H, Singh S, Partyka K, Kletter D, Hsueh P, Yadav J, Ensink E, Bern M, Hostetter G, Hartman D, et al. Glycan motif profiling reveals plasma sialyl-lewis × elevations in pancreatic cancers that are negative for sialyl-lewis A. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2015;14:1323–1333. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M114.047837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Balmaña M, Sarrats A, Llop E, Barrabés S, Saldova R, Ferri MJ, Figueras J, Fort E, de Llorens R, Rudd PM, Peracaula R. Identification of potential pancreatic cancer serum markers: Increased sialyl-Lewis X on ceruloplasmin. Clin Chim Acta. 2015;442:56–62. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2015.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Natoni A, Macauley MS, O'Dwyer ME. Targeting selectins and their ligands in cancer. Front Oncol. 2016;6:93. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2016.00093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Takahashi S, Oda T, Hasebe T, Sasaki S, Kinoshita T, Konishi M, Ueda T, Nakahashi C, Ochiai T, Ochiai A. Overexpression of sialyl Lewis × antigen is associated with formation of extratumoral venous invasion and predicts postoperative development of massive hepatic metastasis in cases with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pathobiology. 2001;69:127–135. doi: 10.1159/000048767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Rho JH, Mead JR, Wright WS, Brenner DE, Stave JW, Gildersleeve JC, Lampe PD. Discovery of sialyl Lewis A and Lewis X modified protein cancer biomarkers using high density antibody arrays. J Proteomics. 2014;96:291–299. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2013.10.030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Metzgar RS, Gaillard MT, Levine SJ, Tuck FL, Bossen EH, Borowitz MJ. Antigens of human pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells defined by murine monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1982;42:601–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kawa S, Tokoo M, Oguchi H, Furuta S, Homma T, Hasegawa Y, Ogata H, Sakata K. Epitope analysis of SPan-1 and DUPAN-2 using synthesized glycoconjugates sialyllact-N-fucopentaose II and sialyllact-N-tetraose. Pancreas. 1994;9:692–697. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199411000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Munkley J. The role of Sialyl-Tn in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17:275. doi: 10.3390/ijms17030275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Radhakrishnan P, Dabelsteen S, Madsen FB, Francavilla C, Kopp KL, Steentoft C, Vakhrushev SY, Olsen JV, Hansen L, Bennett EP, et al. Immature truncated O-glycophenotype of cancer directly induces oncogenic features. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111:E4066–E4075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1406619111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hofmann BT, Schlüter L, Lange P, Mercanoglu B, Ewald F, Fölster A, Picksak AS, Harder S, El Gammal AT, Grupp K, et al. COSMC knockdown mediated aberrant O-glycosylation promotes oncogenic properties in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 2015;14:109. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0386-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Itzkowitz S, Kjeldsen T, Friera A, Hakomori S, Yang US, Kim YS. Expression of Tn, sialosyl Tn, and T antigens in human pancreas. Gastroenterology. 1991;100:1691–1700. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(91)90671-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chugh S, Meza J, Sheinin YM, Ponnusamy MP, Batra SK. Loss of N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 3 in poorly differentiated pancreatic cancer: Augmented aggressiveness and aberrant ErbB family glycosylation. Br J Cancer. 2016;114:1376–1386. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2016.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wang Y, Ju T, Ding X, Xia B, Wang W, Xia L, He M, Cummings RD. Cosmc is an essential chaperone for correct protein O-glycosylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:9228–9233. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0914004107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Taniuchi K, Cerny RL, Tanouchi A, Kohno K, Kotani N, Honke K, Saibara T, Hollingsworth MA. Overexpression of GalNAc-transferase GalNAc-T3 promotes pancreatic cancer cell growth. Oncogene. 2011;30:4843–4854. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pan S, Tamura Y, Chen R, May D, McIntosh MW, Brentnall TA. Large-scale quantitative glycoproteomics analysis of site-specific glycosylation occupancy. Mol Biosyst. 2012;8:2850–2856. doi: 10.1039/c2mb25268f. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Pan S, Chen R, Tamura Y, Crispin DA, Lai LA, May DH, McIntosh MW, Goodlett DR, Brentnall TA. Quantitative glycoproteomics analysis reveals changes in N-glycosylation level associated with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. J Proteome Res. 2014;13:1293–1306. doi: 10.1021/pr4010184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Contessa JN, Bhojani MS, Freeze HH, Rehemtulla A, Lawrence TS. Inhibition of N-linked glycosylation disrupts receptor tyrosine kinase signaling in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68:3803–3809. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Pérez-Garay M, Arteta B, Llop E, Cobler L, Pagès L, Ortiz R, Ferri MJ, de Bolós C, Figueras J, de Llorens R, et al. α2,3-Sialyltransferase ST3Gal IV promotes migration and metastasis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma cells and tends to be highly expressed in pancreatic adenocarcinoma tissues. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45:1748–1757. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2013.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Pérez-Garay M, Arteta B, Pagès L, de Llorens R, de Bolòs C, Vidal-Vanaclocha F, Peracaula R. alpha2,3-sialyltransferase ST3Gal III modulates pancreatic cancer cell motility and adhesion in vitro and enhances its metastatic potential in vivo. PLoS One. 2010;5(pii):e12524. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0012524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hsieh CC, Shyr YM, Liao WY, Chen TH, Wang SE, Lu PC, Lin PY, Chen YB, Mao WY, Han HY, et al. Elevation of β-galactoside α2,6-sialyltransferase 1 in a fructoseresponsive manner promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis. Oncotarget. 2017;8:7691–7709. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Yue T, Goldstein IJ, Hollingsworth MA, Kaul K, Brand RE, Haab BB. The prevalence and nature of glycan alterations on specific proteins in pancreatic cancer patients revealed using antibody-lectin sandwich arrays. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2009;8:1697–1707. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M900135-MCP200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Park HM, Hwang MP, Kim YW, Kim KJ, Jin JM, Kim YH, Yang YH, Lee KH, Kim YG. Mass spectrometry-based N-linked glycomic profiling as a means for tracking pancreatic cancer metastasis. Carbohydr Res. 2015;413:5–11. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2015.04.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zhao J, Qiu W, Simeone DM, Lubman DM. N-linked glycosylation profiling of pancreatic cancer serum using capillary liquid phase separation coupled with mass spectrometric analysis. J Proteome Res. 2007;6:1126–1138. doi: 10.1021/pr0604458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kamada Y, Kinoshita N, Tsuchiya Y, Kobayashi K, Fujii H, Terao N, Kamihagi K, Koyama N, Yamada S, Daigo Y, et al. Reevaluation of a lectin antibody ELISA kit for measuring fucosylated haptoglobin in various conditions. Clin Chim Acta. 2013;417:48–53. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2012.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Barrabés S, Pagès-Pons L, Radcliffe CM, Tabarés G, Fort E, Royle L, Harvey DJ, Moenner M, Dwek RA, Rudd PM, et al. Glycosylation of serum ribonuclease 1 indicates a major endothelial origin and reveals an increase in core fucosylation in pancreatic cancer. Glycobiology. 2007;17:388–400. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwm002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Fardini Y, Dehennaut V, Lefebvre T, Issad T. O-GlcNAcylation: A new cancer hallmark? Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2013;4(99) doi: 10.3389/fendo.2013.00099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Bond MR, Hanover JA. A little sugar goes a long way: The cell biology of O-GlcNAc. J Cell Biol. 2015;208:869–880. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201501101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Liu Y, Cao Y, Pan X, Shi M, Wu Q, Huang T, Jiang H, Li W, Zhang J. O-GlcNAc elevation through activation of the hexosamine biosynthetic pathway enhances cancer cell chemoresistance. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:485. doi: 10.1038/s41419-018-0522-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Qian K, Wang S, Fu M, Zhou J, Singh JP, Li MD, Yang Y, Zhang K, Wu J, Nie Y, et al. Transcriptional regulation of O-GlcNAc homeostasis is disrupted in pancreatic cancer. J Biol Chem. 2018;293:13989–14000. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA118.004709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Konrad RJ, Kudlow JE. The role of O-linked protein glycosylation in beta-cell dysfunction. Int J Mol Med. 2002;10:535–539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Ma Z, Vocadlo DJ, Vosseller K. Hyper-O-GlcNAcylation is anti-apoptotic and maintains constitutive NF-κB activity in pancreatic cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:15121–15130. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.470047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Zachara NE, O'Donnell N, Cheung WD, Mercer JJ, Marth JD, Hart GW. Dynamic O-GlcNAc modification of nucleocytoplasmic proteins in response to stress. A survival response of mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:30133–30142. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M403773200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Banerjee S, Sangwan V, McGinn O, Chugh R, Dudeja V, Vickers SM, Saluja AK. Triptolide-induced cell death in pancreatic cancer is mediated by O-GlcNAc modification of transcription factor Sp1. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:33927–33938. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.500983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Garg B, Giri B, Majumder K, Dudeja V, Banerjee S, Saluja A. Modulation of post-translational modifications in β-catenin and LRP6 inhibits Wnt signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;388:64–72. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.11.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sharma NS, Gupta VK, Dauer P, Kesh K, Hadad R, Giri B, Chandra A, Dudeja V, Slawson C, Banerjee S, et al. O-GlcNAc modification of oncogenic transcription factor Sox2 promotes protein stability and regulates self-renewal in pancreatic cancer. bioRxiv. doi: 10.7150/thno.32615. doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/345223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Dwek RA, Butters TD, Platt FM, Zitzmann N. Targeting glycosylation as a therapeutic approach. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2002;1:65–75. doi: 10.1038/nrd708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Vasconcelos-Dos-Santos A, Oliveira IA, Lucena MC, Mantuano NR, Whelan SA, Dias WB, Todeschini AR. Biosynthetic machinery involved in aberrant glycosylation: Promising targets for developing of drugs against cancer. Front Oncol. 2015;5:138. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Iozzo RV, Sanderson RD. Proteoglycans in cancer biology, tumour microenvironment and angiogenesis. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15:1013–1031. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01236.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Pan S, Chen R, Stevens T, Bronner MP, May D, Tamura Y, McIntosh MW, Brentnall TA. Proteomics portrait of archival lesions of chronic pancreatitis. PLoS One. 2011;6:e27574. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Pan S, Chen R, Reimel BA, Crispin DA, Mirzaei H, Cooke K, Coleman JF, Lane Z, Bronner MP, Goodlett DR, et al. Quantitative proteomics investigation of pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Electrophoresis. 2009;30:1132–1144. doi: 10.1002/elps.200800752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Chen R, Yi EC, Donohoe S, Pan S, Eng J, Cooke K, Crispin DA, Lane Z, Goodlett DR, Bronner MP, et al. Pancreatic cancer proteome: The proteins that underlie invasion, metastasis, and immunologic escape. Gastroenterology. 2005;129:1187–1197. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2005.08.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Chen WB, Lenschow W, Tiede K, Fischer JW, Kalthoff H, Ungefroren H. Smad4/DPC4-dependent regulation of biglycan gene expression by transforming growth factor-beta in pancreatic tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:36118–36128. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M203709200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Koninger J, Giese T, di Mola FF, Wente MN, Esposito I, Bachem MG, Giese NA, Büchler MW, Friess H. Pancreatic tumor cells influence the composition of the extracellular matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;322:943–949. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Koninger J, Giese NA, di Mola FF, Berberat P, Giese T, Esposito I, Bachem MG, Büchler MW, Friess H. Overexpressed decorin in pancreatic cancer: Potential tumor growth inhibition and attenuation of chemotherapeutic action. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:4776–4783. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-1190-03. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Weber CK, Sommer G, Michl P, Fensterer H, Weimer M, Gansauge F, Leder G, Adler G, Gress TM. Biglycan is overexpressed in pancreatic cancer and induces G1-arrest in pancreatic cancer cell lines. Gastroenterology. 2001;121:657–667. doi: 10.1053/gast.2001.27222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Conejo JR, Kleeff J, Koliopanos A, Matsuda K, Zhu ZW, Goecke H, Bicheng N, Zimmermann A, Korc M, Friess H, Büchler MW. Syndecan-1 expression is up-regulated in pancreatic but not in other gastrointestinal cancers. Int J Cancer. 2000;88:12–20. doi: 10.1002/1097-0215(20001001)88:1<12::AID-IJC3>3.0.CO;2-T. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kleeff J, Ishiwata T, Kumbasar A, Friess H, Büchler MW, Lander AD, Korc M. The cell-surface heparan sulfate proteoglycan glypican-1 regulates growth factor action in pancreatic carcinoma cells and is overexpressed in human pancreatic cancer. J Clin Invest. 1998;102:1662–1673. doi: 10.1172/JCI4105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Whipple CA, Young AL, Korc M. A KrasG12D-driven genetic mouse model of pancreatic cancer requires glypican-1 for efficient proliferation and angiogenesis. Oncogene. 2012;31:2535–2544. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Aikawa T, Whipple CA, Lopez ME, Gunn J, Young A, Lander AD, Korc M. Glypican-1 modulates the angiogenic and metastatic potential of human and mouse cancer cells. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:89–99. doi: 10.1172/JCI32412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Melo SA, Luecke LB, Kahlert C, Fernandez AF, Gammon ST, Kaye J, LeBleu VS, Mittendorf EA, Weitz J, Rahbari N, et al. Glypican-1 identifies cancer exosomes and detects early pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2015;523:177–182. doi: 10.1038/nature14581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Ebrahim AH, Alalawi Z, Mirandola L, Rakhshanda R, Dahlbeck S, Nguyen D, Jenkins M, Grizzi F, Cobos E, Figueroa JA, et al. Galectins in cancer: Carcinogenesis, diagnosis and therapy. Ann Transl Med. 2014;2:88. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2014.09.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Qian D, Lu Z, Xu Q, Wu P, Tian L, Zhao L, Cai B, Yin J, Wu Y, Staveley-O'Carroll KF, et al. Galectin-1-driven upregulation of SDF-1 in pancreatic stellate cells promotes pancreatic cancer metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2017;397:43–51. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.03.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Zhao W, Ajani JA, Sushovan G, Ochi N, Hwang R, Hafley M, Johnson RL, Bresalier RS, Logsdon CD, Zhang Z, Song S. Galectin-3 mediates tumor cell-stroma interactions by activating pancreatic stellate cells to produce cytokines via integrin signaling. Gastroenterology. 2018;154:1524–1537.e6. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.12.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Chen R, Pan S, Ottenhof NA, de Wilde RF, Wolfgang CL, Lane Z, Post J, Bronner MP, Willmann JK, Maitra A, Brentnall TA. Stromal galectin-1 expression is associated with long-term survival in resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Biol Ther. 2012;13:899–907. doi: 10.4161/cbt.20842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Chen R, Dawson DW, Pan S, Ottenhof NA, de Wilde RF, Wolfgang CL, May DH, Crispin DA, Lai LA, Lay AR, et al. Proteins associated with pancreatic cancer survival in patients with resectable pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Lab Invest. 2015;95:43–55. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2014.128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Martinez-Bosch N, Fernández-Barrena MG, Moreno M, Ortiz-Zapater E, Munné-Collado J, Iglesias M, André S, Gabius HJ, Hwang RF, Poirier F, et al. Galectin-1 drives pancreatic carcinogenesis through stroma remodeling and Hedgehog signaling activation. Cancer Res. 2014;74:3512–3524. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Orozco CA, Martinez-Bosch N, Guerrero PE, Vinaixa J, Dalotto-Moreno T, Iglesias M, Moreno M, Djurec M, Poirier F, Gabius HJ, et al. Targeting galectin-1 inhibits pancreatic cancer progression by modulating tumor-stroma crosstalk. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2018;115:E3769–E3778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1722434115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Seguin L, Camargo MF, Wettersten HI, Kato S, Desgrosellier JS, von Schalscha T, Elliott KC, Cosset E, Lesperance J, Weis SM, Cheresh DA. Galectin-3, a druggable vulnerability for KRAS-addicted cancers. Cancer Discov. 2017;7:1464–1479. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Bailey P, Chang DK, Nones K, Johns AL, Patch AM, Gingras MC, Miller DK, Christ AN, Bruxner TJ, Quinn MC, et al. Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature. 2016;531:47–52. doi: 10.1038/nature16965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.