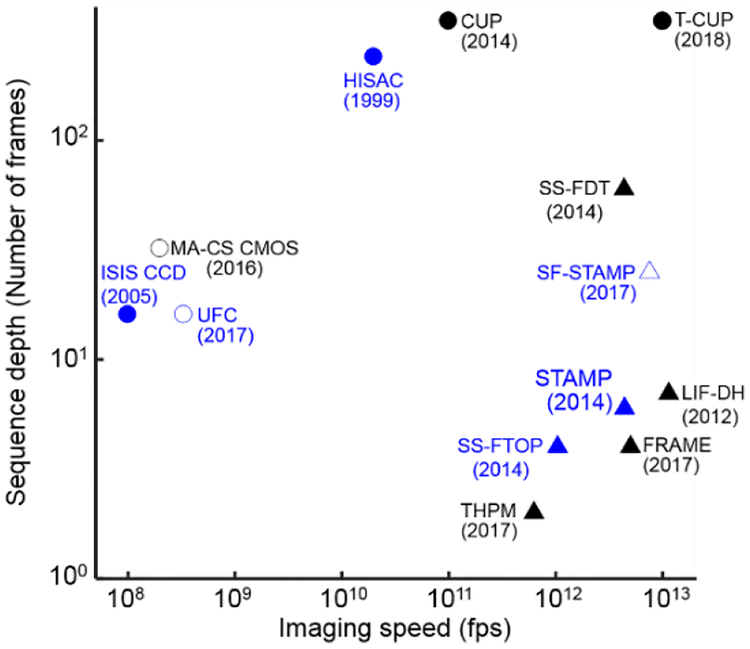
Fig. 13.
Comparison of representative single-shot ultrafast optical imaging techniques in imaging speeds and sequence depths. Triangles and circles represent active and passive detection domains. Blue and black colors represent the direct and reconstruction imaging methods, respectively. Solid and hollow marks represent high and low (including medium) light throughputs. The numbers in the parentheses are the years in which the techniques were published. CUP, Compressed ultrafast photography; T-CUP, Trillion-frames-per-second CUP; FRAME, Frequency recognition algorithm for multiple exposures; HISAC, High-speed sampling camera; ISIS CCD, In-situ storage image sensor CCD; LIF-DH, Light-in-flight recording by digital holography; MA-CS CMOS, Multi-aperture compressed sensing CMOS; SS-FDT, Single-shot Fourier-domain tomography; SS-FOP, Single-shot femtosecond time-resolved optical polarimetry; STAMP, Sequentially timed all-optical mapping photography; SF-STAMP, Spectral-filtering STAMP; THPM, Time-resolved holographic polarization microscopy; UFC, Ultrafast framing camera.