Abstract
Saphenous neuralgia is characterized by persistent neuropathic pain at the distribution of the saphenous nerve. Injury to the saphenous nerve, and specifically to its infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve has been implicated as a cause of medial knee pain after orthopedic knee surgery or trauma. We present two cases of saphenous neuralgia, one after total knee arthroplasty and the other after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction, that were adequately treated with ultrasound-guided saphenous nerve blocks distal to the adductor canal. Early recognition and treatment of saphenous neuralgia is essential to prevent persistent disabling pain, which significantly affects patients’ quality of life.
Keywords: Knee, neuralgia, pain
Introduction
Saphenous neuralgia is characterized by persistent neuropathic pain at the distribution of the saphenous nerve.1 Total knee arthroplasty (TKA), anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction, knee arthroscopy, tibial intramedullary nailing, and knee trauma, may all be complicated by saphenous nerve injury and especially the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve (IPSN).1,2,3,4
Saphenous neuralgia must be included into the differential diagnosis of any persistent medial knee pain after knee surgery. Early diagnosis and prompt decision-making can obviate subsequent complications.1
We present two cases of saphenous neuralgia, effectively treated with ultrasound-guided saphenous nerve blocks distal to the adductor canal. Both patients provided written informed consent for publication.
Cases Reports
Case 1
A 66-year-old woman presented with severe knee pain, persisting for 2 years after TKA, with initial Numeric Rating Scale (NRS) up to 10/10 at movement and 7/10 at rest at the knee area, with strong neuropathic characteristics, with Leeds Assessmentof of Neuropathic Symptoms and Signs (LANSS) score 17/24. She described paroxysmic, burning pain, with the feeling of “pins and needles” over the knee. Clinical examination revealed allodynia, hyperalgesia, and hypoesthesia at the distribution of the saphenous nerve. After meticulous clinical and radiological examination, with normal laboratory tests and needle electromyography, any other potential etiologies of knee pain were excluded.
Diagnostic injection with 1% lidocaine at the site of maximum tenderness, at the knee scar, led to immediate but short-term relief. Alongside, a trial of systemic administration of gabapentin and duloxetine was commenced. Thereafter, an ultrasound-guided saphenous nerve block (linear 5–12MHz transducer/Vivid I; GE Healthcare, Waukesha, Wisconsin, USA) was conducted distal to the adductor canal, underneath the sartorius muscle5,6 [Figure 1a and b]. Both, ropivacaine 0.375% and triamcinolone 20 mg were administered, producing a 50% pain relief. The patient responded favorably, with the pain symptoms further subsiding at 30%, to having a second saphenous nerve block 2 weeks later. One year post-treatment, the patient appears significantly better (NRS = 2/10), using only paracetamol as a rescue analgesic.
Figure 1.
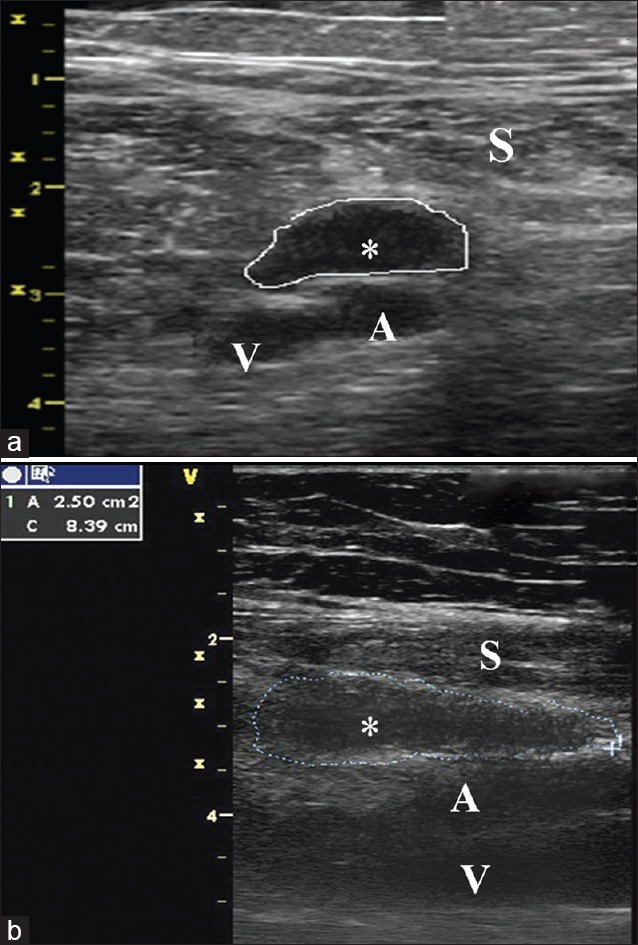
(a and b) Local anesthetic injection out of the subsartorial compartment for saphenous nerve block. The femoral artery (A) and vein (V) are seen below the sartorius (S). Local anesthetic injection is performed in the subsurtorial compartment between the femoral artery and the sartorius muscle (S) Cross sectional (3A) and longitudinal (3B) view of the femoral artery, vein and local anesthetic spread area (*) are also shown
Case 2
A 34-year-old woman presented with severe knee pain, persisting for 18 months after ACL reconstruction, with initial NRS 6/10 and LANSS 19/24 over the distribution of the saphenous nerve. She had paroxysmic, burning pain, provoked by clothing, cold water, and touch, with severe allodynia and hyperalgesia. As before, all other causes of knee pain were excluded.
Diagnostic injection of 1% lidocaine was initially injected over the scar, and the subsequent 50% reduction of pain confirmed the diagnosis. An ultrasound-guided saphenous nerve block was performed with ropivacaine 0.375% and triamcinolone 20 mg. Three consecutive injections followed, with a lockout period of 2 weeks (two with corticosteroid). The pain was significantly reduced (NRS = 3/10), and the patient one year post-treatment experiences only sporadically paroxysmic pain, of low intensity.
Discussion
Saphenous neuralgia presents with a broad spectrum of symptoms, including sharp burning pain, hyperalgesia, allodynia, as well as hypoesthesia and dysesthesia at the distribution of the saphenous nerve.1 A positive Tinel sign can facilitate the diagnosis. An extensive workup consisting of laboratory tests with inflammatory markers and knee radiological imaging should be normal.1 The use of specific diagnosing questionnaires such as LANSS and DN4 is helpful, to support the neuropathic pain diagnosis.1,6 The differential diagnosis is cumbersome, including tendonitis of the distal sartorius, pes anserinus bursitis, ligament pathology, knee joint pathology, peripheral vascular disease, lumbar nerve root compression, and other causes of peripheral neuropathic pain.1,6 Final diagnosis is achieved by symptomatic pain relief after injection of local anesthetic at the distribution of the saphenous nerve.1,7,8
The rate of saphenous nerve injury, and especially of IPSN is approximately 21%–69%, after knee procedures1,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 [Table 1], implicating not only total TKA but also arthroscopic knee surgery.16,17 This is often related to inappropriate trocar/portal placement, or injury secondary to the use of a tourniquet.9 Surgical incisions at the medial part of the knee always entail a risk,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 especially midline incisions with medial parapatellar approach. Therefore, special care should be taken in such incisions if they cannot be avoided. In ACL reconstruction, this complication occurs frequently with both bone-patellar tendon-bone and hamstring autograft technique,12 with an incidence ranging between 14.9% and 59%.2 In this case, knee flexion and hip external rotation may reduce the tension applied on the nerve during harvesting of the semitendinosus and gracilis tendons and prevent postoperative saphenous neuralgia.1,2,3,4 Several authors have recommended the use of horizontal or oblique incisions instead of vertical ones, to expose the tibial insertions of the hamstring tendons, since with this technique there is less chance of infrapattelar saphenous nerve (IPS) injury.2,18 In a cadaveric study, where vertical incisions were used, the IPS was injured in 80% of the knees.19,20 However, there seems to be a safe zone to prevent saphenous nerve injury. Boon et al.19 in a cadaveric study stated that a safe area on the right knee may be at the tibial tuberosity plane, between 3.7 and 5.5 cm, with an angle of incision of 51.6°, and at the left knee was between 3.6 and 4.9 cm, with an angle of incision of 52.5°, respectively. Kartus et al.20 in another cadaveric study described also this great variation of the IPS, and proposed two vertical 25 mm incisions for harvesting consistent bone-patellar tendon–bone autographs, leaving the IPS intact during the procedure. Other causes of damage include traction from medial retractors placed during surgery or adhesions which may develop between the injured nerve and adjacent fascial planes, resulting in neuritis.1,3,7 Some propose that in every case, smaller incisions minimize the possibility of nerve injury, in addition, with proper preparation of the nerve and cutting of the pulleys, which should be performed under direct visual control with a blunt technique. Finally, care should also be taken during anteromedial portal placement for ankle arthroscopy, or during lower leg fasciotomies, where the saphenous nerve may also be damaged along with the saphenous vein.21 However, in all cases, as described in multiple cadaveric studies, there is a great variation in the course of IPS, and therefore, damage of the nerve cannot always be prevented.1 Early identification of saphenous neuralgia and aggressive treatment are essential in alleviating patients’ pain. Systemic drugs for the management of neuropathic pain, in addition to local anesthetic injections and capsaicin or lidocaine patches, have been proposed; with variable results.1,7 Injections of local anesthetic around saphenous nerve neuromas are diagnostic; however, it might be only with the ultrasound-guided saphenous nerve blocks that the pain relief is more persistent.1,7 However, the volume of the local anesthetic injected, the anatomic approach and the success rate of the block show a significant variability among studies.6,7 Clendenen et al., showed ultrasound-guided injections of the IPS to be effective, with a response rate of 56.3%.7 In the adductor canal, the high anatomic variability of the saphenous nerve and the vessel sheath may result to incomplete spread of the local anesthetic, leading to the variable success rate of the block.6 In our cases, the saphenous nerve blocks were undertaken more distal to the adductor canal, providing significant pain reduction. Moreover, the vastus medialis nerve was not blocked avoiding the subsequent weakness of the corresponding muscle, which is important for immediate patient ambulation.6 To the best of our knowledge, there have been no clinical series or comparative trials discussing a technique similar to that used in this series. If the injection provides temporary comfort, there are multiple other options available, such as neurolysis, pulsed radiofrequency, cryoneuroablation, and surgical excision of neuroma, with the insertion of the proximal end into adjacent muscle.1
Table 1.
Saphenous nerve injury after knee surgery
| Reference | Surgical procedure | Incision | Outcome measure | Time postoperative | Result | Study type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Heare et al., 2015 | Intramedullary nailing of an open tibial shaft fracture | 4 cm oblique scar at the junction between middle and distal anteromedial tibia, at the original open fracture site | Pain scores before and after selective anesthetic injection | 1 year | Selective neurolysis and partial neurectomy, w/complete resolution of neuralgia and pain | Case report |
| Figueora et al., 2015 | Arthroscopic ACL (hamstrings) | Longitudinal, <25 mm, 50 mm from the medial articular margin, medial to the tibial tuberosity | Neurology consult 3 weeks after surgery, w/light touch and pinprick sensation exam and electrophysiology | 3 weeks | Area of hypoesthesia in the IPSN territory in 17/22 knees; injury to IPSN el/cally detected in 15 patients; saphenous n. injury also in 2 patients | Case series (prospective) |
| Jameson and Emmerson, 2007 | Arthroscopic ACL (hamstrings) | Longitudinal, 30 mm, over the pes anserinus | Questionnaire sent by post | 13-78 months | LSCN: 29 patients (33%) | Case series (retrospective) |
| SN: 23 patients (26%) | ||||||
| IPSN: 10 patients (12%) | ||||||
| Liden et al., 2007 | Arthroscopic ACL (donor site issues in BTB vs. ST autograft) | BTB: 2 vertical 25 mm incisions; ST: 3 cm oblique over the pes anserinus | Clinical exam; pain assessment | 7 years | Anterior knee pain in 39% of BTB group and 26% of ST group | RCT |
| Sanders et al., 2007 | Arthroscopic ACL (hamstrings) | 2 cm longitudinal over pes anserinus | Patients questionnaire | Variable | SBSN: 14/62 or 23% | Case series (retrospective), followed by cadaveric study to identify anatomic relations |
| IPSN: 12/62 or 19% | ||||||
| Combined: 20/62 or 32% | ||||||
| Papastergiou et al., 2006 | Arthroscopic ACL (hamstrings) | 3 cm vertical versus 3 cm horizontal incision for graft harvesting | Sensory exam for IPSN sensory changes | 1-12 months | Vertical group: sensory changes in 46/116 patients or 39.7% | Case series (retrospective) |
| Horizontal group: sensory changes in 17/114 patients or 14.9% | ||||||
| Portland et al., 2005 | Arthroscopic ACL (BTB) | Vertical versus horizontal incision for graft harvesting | Medical records review; patient questionnaire | At least 3 years | IPSN damage evidence in 20/34 patients or 59% in the vertical group; 18/42 patients or 43% in the horizontal group | Case series (retrospective) |
| Mochizuki et al., 2004 | Arthroscopic ACL (hamstrings) | Vertical incision | Patient questionnaire sent by post | 32 months | 47/86 (55%) reported sensory changes | Case series (retrospective) |
| Sgaglione et al., 1990 | Open ACL (hamstrings) | Medial parapatellar incision | Personal interview | 24-81 months | IPSN numbness in 27/72 patients (38%); significantly bothersome in 1/72 patients (1.4%) | Case series (retrospective) |
| Bertram et al., 2000 | Arthroscopic ACL (hamstrings) | Vertical incision over the pes anserinus | Sensory exam | Immediately | SN neurolysis w/immediate resolution of symptoms | Case report |
| Kachar et al., 2008 | Total knee arthroplasty | Midline skin incision | 11-point Numerical Rating Scale | 21 months | SN neurolysis and neuroma resection w/resolution of symptoms | Case report |
| Leliveld et al., 2012 | Intramedullary nailing of the tibia | 46 medial parapatellar; 26 transtendinous | SF-36; AKPS; study-specific questionnaire | Variable | IPSN deficit in 43/72 (60%); 12 nails removed due to knee pain; pain persisted in 7/12 patients | Case series (retrospective) |
SN=Saphenous nerve, ACL=Anterior cruciate ligament, IPSN=Infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve, LSCN=Lateral sural cutaneous nerve, SBSN=Suprapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve, BTB=Bone-patellar tendon-bone graft, ST=Semitendinosus graft, SF-36=Short form-36, AKPS=Anterior knee pain scale, RCT=Randomized controlled trial
Conclusion
Saphenous neuralgia can be a distressing condition leading to severe disabling pain. Prevention of saphenous nerve injury during knee procedures and high index of suspicion may help minimize its incidence. Saphenous nerve block should always feature at the armentarium of our therapeutic options.
Declaration of patient consent
The authors certify that they have obtained all appropriate patient consent forms. In the form, the patient has given her consent for her images and other clinical information to be reported in the journal. The patients understand that their names and initials will not be published and due efforts will be made to conceal their identity, but anonymity cannot be guaranteed.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- 1.Trescot AM, Brown MN, Karl HW. Infrapatellar saphenous neuralgia – Diagnosis and treatment. Pain Physician. 2013;16:E315–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Figueroa D, Calvo R, Vaisman A, Campero M, Moraga C. Injury to the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve in ACL reconstruction with the hamstrings technique: Clinical and electrophysiological study. Knee. 2008;15:360–3. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2008.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kachar SM, Williams KM, Finn HA. Neuroma of the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve a cause of reversible knee stiffness after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2008;23:927–30. doi: 10.1016/j.arth.2007.07.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Leliveld MS, Verhofstad MH. Injury to the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve, a possible cause for anterior knee pain after tibial nailing? Injury. 2012;43:779–83. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2011.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Adoni A, Paraskeuopoulos T, Saranteas T, Sidiropoulou T, Mastrokalos D, Kostopanagiotou G, et al. Prospective randomized comparison between ultrasound-guided saphenous nerve block within and distal to the adductor canal with low volume of local anesthetic. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2014;30:378–82. doi: 10.4103/0970-9185.137271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Clendenen S, Greengrass R, Whalen J, O’Connor MI. Infrapatellar saphenous neuralgia after TKA can be improved with ultrasound-guided local treatments. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015;473:119–25. doi: 10.1007/s11999-014-3812-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Heare A, Mitchell JJ, Bravman JT. Posttraumatic saphenous neuroma after open tibial fracture. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 2015;44:E461–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bertram C, Porsch M, Hackenbroch MH, Terhaag D. Saphenous neuralgia after arthroscopically assisted anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with a semitendinosus and gracilis tendon graft. Arthroscopy. 2000;16:763–6. doi: 10.1053/jars.2000.4820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sanders B, Rolf R, McClelland W, Xerogeanes J. Prevalence of saphenous nerve injury after autogenous hamstring harvest: An anatomic and clinical study of sartorial branch injury. Arthroscopy. 2007;23:956–63. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2007.03.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Portland GH, Martin D, Keene G, Menz T. Injury to the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: Comparison of horizontal versus vertical harvest site incisions. Arthroscopy. 2005;21:281–5. doi: 10.1016/j.arthro.2004.10.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Papastergiou SG, Voulgaropoulos H, Mikalef P, Ziogas E, Pappis G, Giannakopoulos I, et al. Injuries to the infrapatellar branch(es) of the saphenous nerve in anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with four-strand hamstring tendon autograft: Vertical versus horizontal incision for harvest. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2006;14:789–93. doi: 10.1007/s00167-005-0008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Jameson S, Emmerson K. Altered sensation over the lower leg following hamstring graft anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with transverse femoral fixation. Knee. 2007;14:314–20. doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2007.04.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lidén M, Ejerhed L, Sernert N, Laxdal G, Kartus J. Patellar tendon or semitendinosus tendon autografts for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: A prospective, randomized study with a 7-year followup. Am J Sports Med. 2007;35:740–8. doi: 10.1177/0363546506298275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mochizuki T, Akita K, Muneta T, Sato T. Anatomical bases for minimizing sensory disturbance after arthroscopically-assisted anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction using medial hamstring tendons. Surg Radiol Anat. 2003;25:192–9. doi: 10.1007/s00276-003-0130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sgaglione NA, Warren RF, Wickiewicz TL, Gold DA, Panariello RA. Primary repair with semitendinosus tendon augmentation of acute anterior cruciate ligament injuries. Am J Sports Med. 1990;18:64–73. doi: 10.1177/036354659001800111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hunter LY, Louis DS, Ricciardi JR, O’Connor GA. The saphenous nerve: Its course and importance in medial arthrotomy. Am J Sports Med. 1979;7:227–30. doi: 10.1177/036354657900700403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mochida H, Kikuchi S. Injury to infrapatellar branch of saphenous nerve in arthroscopic knee surgery. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;320:88–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Gali JC, Resina AF, Pedro G, Neto IA, Almagro MA, da Silva PA, et al. Importance of anatomically locating the infrapatellar branch of the saphenous nerve in reconstructing the anterior cruciate ligament using flexor tendons. Rev Bras Ortop. 2014;49:625–9. doi: 10.1016/j.rboe.2013.10.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Boon JM, Van Wyk MJ, Jordaan D. A safe area and angle for harvesting autogenous tendons for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Surg Radiol Anat. 2004;26:167–71. doi: 10.1007/s00276-003-0213-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kartus J, Ejerhed L, Eriksson BI, Karlsson J. The localization of the infrapatellar nerves in the anterior knee region with special emphasis on central third patellar tendon harvest: A dissection study on cadaver and amputated specimens. Arthroscopy. 1999;15:577–86. doi: 10.1053/ar.1999.v15.015057001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pyne D, Jawad AS, Padhiar N. Saphenous nerve injury after fasciotomy for compartment syndrome. Br J Sports Med. 2003;37:541–2. doi: 10.1136/bjsm.37.6.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


