Abstract
Conducting systematic reviews of qualitative studies to incorporate patient perspectives within the early stages of core outcome set (COS) development can be resource intensive. We aimed to identify an expedited approach to be used as part of the wider COS development process. Specifically, we undertook a rapid review of qualitative studies of patients’ views and experiences of type 2 diabetes. We searched MEDLINE from inception to June 2017 to identify studies reporting qualitative empirical findings of perspectives of people with type 2 diabetes. Qualitative methodological filters were used to minimize irrelevant references. Drawing on content analysis, data synthesis involved identifying text in eligible studies relevant to outcomes of type 2 diabetes and interpreting and categorizing this according to the 38 core domains of the Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials taxonomy. Of 146 studies screened, 26 were included. Four hundred and fifty-eight outcomes were derived from the included studies. In comparison to the outcomes extracted from clinical trials, more life impact outcomes were derived from the qualitative studies, but fewer physiological/clinical outcomes. Outcomes relating to ‘mortality/survival’ and ‘role functioning’ were more prevalent in studies conducted in low/middle-income countries. This rapid review and synthesis of qualitative studies identified outcomes that had not previously been identified by a systematic review of clinical trials. It also identified differences in the types of outcomes given prominence to in the clinical trials and qualitative literatures. Incorporating qualitative evidence on patient perspectives from the outset of the COS development process can help to ensure outcomes that matter to patients are not overlooked. Our method provides a pragmatic and resource-efficient way to do this. For those developing international COS, our method has potential for incorporating the perspectives of patients from diverse countries in the early stages of COS development.
Keywords: type 2 diabetes, core outcome set, patient perspectives, qualitative, rapid review
Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus, characterized by abnormal glucose metabolism and an inadequate compensatory insulin secretion response, accounts for over 90% of all cases of diabetes.1 Treatment of type 2 diabetes often targets abnormal glucose levels, yet outcomes measured in clinical trials of glucose-lowering interventions are inconsistent2 and this heterogeneity in outcomes limits the usefulness of trial findings to patients and other decision-makers.3 4 The Selecting Core Outcomes for Randomised Effectiveness trials In Type 2 diabetes (SCORE-IT) study5 aims to address these issues by developing a core outcome set (COS) for use in clinical trials of glucose-lowering interventions in people with type 2 diabetes.
COS represent agreed standardized sets of outcomes that should be measured and reported, as a minimum, in all clinical trials for a specific health condition.6 The development and implementation of COS can improve the relevance and consistency of trial outcomes and allow the results of clinical research to be pooled and compared, thereby reducing waste in research.7 The first step in the development of a COS typically involves a review of existing knowledge (eg, systematic review of outcomes used in previous studies) to inform the consensus process.8 In the case of the SCORE-IT study, this has involved a systematic review of outcomes used in registered clinical trials of glucose-lowering interventions for type 2 diabetes.2 While this is typical of many COS, clinical trials often overlook the outcomes that are important to patients9 10 and so the outcomes identified in such reviews are likely to predominantly reflect the perspectives of researchers and clinicians.11 This is a concern, as there is evidence that the input of patients leads to the identification of core outcomes beyond those identified by practitioners alone.12–15 Furthermore, the Core Outcome Set-Standards for Development project recently established the inclusion of patient stakeholders within the COS development process to be a minimum standard for COS.16
Primary qualitative research is particularly suited to accessing patient perspectives on outcomes, as these studies allow patients to voice their views and experiences in an open-ended way and in their own words.17 The findings from such studies can contribute in several ways to COS development including to the ‘long list’ of outcomes needed in the early stages of the process. However, primary qualitative research can be resource intensive and require study team expertise in qualitative methodology.18 Systematic reviews of qualitative studies potentially provide an alternative to conducting primary qualitative research where suitable published studies are available.17
Previous systematic reviews of qualitative studies have identified outcomes of importance to patients and informed the development of COS in critical illness, bariatric and metabolic surgery, neonatal care and tuberculosis.19 20 Such reviews have identified outcomes that were not reported in systematic reviews of clinical trials, indicating that qualitative evidence is needed to ensure that the initial ‘long list’ of outcomes is comprehensive and does not omit outcomes important to patients.19 21 However, these previous systematic reviews of qualitative studies have undertaken exhaustive literature searches and are likely to be time consuming and resource intensive.22 Systematic reviews inform the early phases of COS and comprise one small aspect of the COS development process. As many developers have limited time and resources, there is a need to identify an expedited approach for identifying outcomes that are important to patients, which can subsequently inform the development of COS. Existing qualitative reviews for a specific condition could be considered; however, in the case of type 2 diabetes, these reviews23 24 have not been conducted in the context of COS development and as such group findings into overarching concepts, many of which have little relevance to COS. Here we report an expedited approach for identifying outcomes reported by people with type 2 diabetes when asked about their lived experience.
Aims
Our aims in undertaking this review were: to identify an expedited approach for incorporating the patient perspective within the initial stages of COS development; to identify outcomes important to people with type 2 diabetes for inclusion in a ‘long list’ of outcomes for the COS consensus process; and to compare outcomes identified from the qualitative literature with those identified via a previous systematic review of outcomes measured in type 2 diabetes clinical trials. We also aimed to compare outcomes identified from qualitative studies of patients living in low/middle-income countries (LMIC) with outcomes identified from qualitative studies conducted in higher income countries (HIC). The prevalence of diabetes in LMICs is high25 and it is important to examine if outcomes voiced by patients living in LMICs differ from those of patients in HICs.
Methods
Search strategy
Using rapid review methodology, which involves streamlining traditional systematic review methods to synthesize evidence within a shortened time frame,26 we searched a single health-related database, MEDLINE, with no date restrictions on 22 June 2017. The search terms, which are indicated in table 1, comprised qualitative methodological filters previously shown to identify qualitative research from the MEDLINE electronic database.27 The research field for type 2 diabetes is vast and so search filters designed for maximum specificity27 were selected to minimize irrelevant references.
Table 1.
MEDLINE search strategy
| Multifield search | ||
| (type 2 diabetes OR type II diabetes) | Abstract | |
| AND | patient* | Abstract |
| AND | (Qualitative OR Themes) | Abstract |
| AND | (symptom OR treatment OR living with) | Abstract |
| NOT | (co-morbid* OR foot ulcers OR retinopathy OR nephropathy OR bariatric surgery OR non-alcoholic fatty liver disease OR cardiovascular disease) | Abstract |
Studies reporting qualitative empirical findings of the views and experiences of people with type 2 diabetes on their condition and treatment were eligible for inclusion. Type 1 diabetes, gestational diabetes, type 2 diabetes in children and maturity onset diabetes of the young were outside the scope of this review. Studies where the primary focus was the treatment of diabetes comorbidities or complications (eg, diabetic foot ulcer, diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, bariatric surgery, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and cardiovascular disease) were also excluded.
Study selection
SLG and NLH identified and screened titles and abstracts from the MEDLINE search for eligibility, batch checked 10% of these to ensure consistency and discussed uncertainties. There was good agreement between reviewers during the batch check; therefore, the two reviewers each reviewed half the remaining abstracts. Full texts were retrieved and reviewed for articles meeting the following inclusion criteria: participants were people with type 2 diabetes or their partners, the focus was type 2 diabetes and not an associated comorbidity, and qualitative data collection methods (interviews or focus groups) were used. SLG and NLH each reviewed half the full-text papers for eligibility.
Data extraction
For each included study the following data were extracted:
Study aim.
Participants (number in study, age, sex, number of years with diabetes).
Geographical location of participants.
Qualitative data collection methods used.
Text excerpts relevant to outcomes.
Our approach to identifying text relevant to outcomes was deductive. It is important to note that none of the qualitative studies explicitly aimed to identify outcomes, although they did contain text that we could interpret as relevant to type 2 diabetes outcomes. Such text comprised any reports about how patients felt or functioned in relation to their diabetes and the healthcare or treatment they had received. Others have previously defined such reports as relevant to outcomes if they describe something that could be used to assess the effect of a healthcare intervention on the patient’s life.28 29 We were also guided by this definition. For example, we interpreted the patient quotation, ‘I just think I like to get my blood glucose inside the right range, as we should’ as about the outcome ‘glycaemic control’. All such text, including participants’ quotations about their views and experiences and the authors’ commentary, was extracted verbatim from both the results and discussion sections of included papers. This text was entered as a separate row in a Microsoft excel spreadsheet (available on request).
SLG and NLH both reviewed and interpreted outcomes from five included studies and checked these for agreement. They each independently reviewed half of the remaining studies.
Quality appraisal
The role of quality appraisal of qualitative studies in systematic reviews, and whether quality assessment should be used to exclude studies, is debated.30 One reviewer (SLG) quality appraised included studies using Critical Appraisal Skills Programme checklist31 to facilitate our understanding of them rather than to exclude any studies.
Data categorization
For the current review, we drew on content analysis to synthesize data from eligible studies. This approach permitted tabulation and frequency counts32 and thereby facilitated comparison with the outcomes reported in the previous systematic review of type 2 diabetes clinical trials. We used the Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials (COMET) taxonomy to categorize text from the studies.
Two reviewers (SLG and NLH) discussed each text excerpt relevant to outcomes to agree how to categorize them, referring back to the original article when necessary to resolve ambiguities. The COMET taxonomy is an outcome classification system suitable for classifying outcomes across all trials, COS, systematic reviews and trial registries33 regardless of the condition being investigated. It has been designed to provide high-level differentiation between outcome domains to facilitate uniformity of outcome classification in electronic databases.33 Additionally, COS developers have used the taxonomy to assist the classification of outcomes prior to the consensus stage.34–36 The taxonomy comprises 38 core domains structured within five top level core areas: death, physiological/clinical, life impact, resource use, and adverse events.
Reviewers categorized text excerpts, considering all 38 core domains of the taxonomy as they did so. Agreement between reviewers (SLG and NLH) was assessed with three batch checks of 10% of all outcomes until 100% agreement was reached. Where uncertainty about an outcome could not be resolved reviewers sought clinical input (JPHW). Where one outcome included multiple components, for example, ‘fear of death’, which encompasses two discrete outcomes ‘fear’ and ‘death’, the outcome was classified under two domains (eg, ‘emotional functioning/well-being’ and ‘mortality/survival’) as recommended.33 Outcome categorization was verified by the developer of the COMET taxonomy (SD), who was provided with a list of the outcomes extracted from the included studies, which she categorized blind, without seeing the categorization by the two reviewers. Her outcome categorization was compared with that of the two reviewers and any discrepancies were discussed and resolved.
Results
Study characteristics
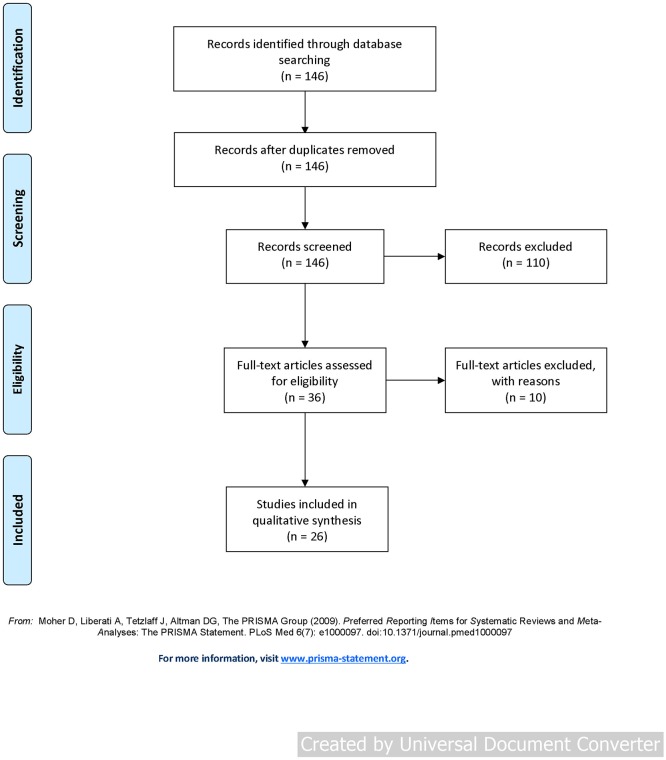
The search returned 146 articles. Of these, 36 were retained after screening titles and abstracts. Following full-text review a further 10 studies were excluded as they did not meet the inclusion criteria. The flow of studies is shown in figure 1.
Figure 1.
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) flow diagram.
These 26 included studies involved either qualitative interviews (69%) or focus groups (31%) with a total of 976 patients (median 23 participants, range 5–246) from five continents. All studies included participants with type 2 diabetes with some studies focusing on particular minority groups.37–42 Time since diagnosis of diabetes ranged from less than 1 year up to 51 years, although this was not reported in all studies. For one study that also included partners of patients,38 content relating to both patients and their partners was included in the synthesis. Another study included both patients and healthcare professionals; however, only data originating from patients were synthesized.43 A summary of included studies is provided in table 2.
Table 2.
Characteristics of included studies
| Study ID | Aim | Year of publication | Location of study | Participants (n) | Participant age | Participant sex | Time with diabetes | Data collection method | Outcomes identified (n) |
| 42 | Explore behavioral factors affecting what patients do for self-care and why they do it. | 1998 | USA | 51 | 29–69 years (mean=52.9) | Male: 26 (51%), female: 25 (49%) | 0.5–1 year: 4 (8%), 1–5 years: 20 (39%), >6 years: 27 (53%) |
Interviews | 24 |
| 44 | Investigate the distress associated with type 2 diabetes. | 2002 | UK | 51 | Not reported | Male: 19 (37%), female: 32 (63%) | Not reported | Focus groups | 16 |
| 60 | Explore the views and health beliefs of patients who had experienced a new structured diabetes shared care service. | 2003 | Ireland | 25 | 30–50 years: 6 (24%); 51–70 years: 13 (52%); >70 years: 6 (24%) |
Male: 15 (60%), female: 10 (40%) | Not reported | Focus groups | 10 |
| 58 | Describe personal understandings of illness among patients. | 2004 | Sweden | 44 | 47–80 years (mean=64) | Male: 23 (52%), female: 21 (48%) | Not reported | Interviews | 5 |
| 39 | Explore the relevance of a reframed model of healthcare consultation. | 2004 | UK | 21 | Not reported | Not reported | Not reported | Interviews | 21 |
| 45 | Investigate patients’ perceptions about their illness and treatment strategies to facilitate patient-centered, culture-sensitive clinical skills. | 2005 | Taiwan | 22 | 44–80 years (mean=60.2) | Male: 12 (55%), female: 10 (45%) | 2–25 years (mean=8.3) | Interviews | 12 |
| 46 | Explore the self-reported healthcare goals, factors influencing these goals, and self-care practices of older patients. | 2005 | USA | 28 | 65–88 years (mean=74) | Male: 12 (43%), female: 16 (57%) | 0–5 years: 11 (39%), >5 to 10 years: 6 (21%), >10 years: 11 (39%) |
Interviews | 15 |
| 47 | Explore medication experiences of patients. | 2006 | USA | 138 | >70 years: 30 (22%), >50 years: 102 (74%) |
Male: 44 (32%), female: 94 (68%) | Mean=13 years | Focus groups | 31 |
| 48 | Identify the obstacles to adherence for patients. | 2007 | Europe | 246 | 40–80 years (mean=63.8) | Male: 122 (49.6%), female: 124 (49.4%) | 1–22 years (mean=10.2) | Focus groups | 16 |
| 61 | Describe the experience of benefit and risk assessment for patients when making treatment decisions. | 2007 | Canada | 18 | Mean=60 years | Male: 8 (44%), female: 10 (55%) | Mean=10.7 years | Interviews | 29 |
| 49 | Explore the lived experience of patients converting to insulin therapy. | 2007 | UK | 8 | 49–72 years | Male: 4 (50%), female: 4 (50%) | Not reported | Interviews | 25 |
| 50 | Understand and document the perspectives of patients regarding the processes and strategies used to self-manage their chronic condition. | 2008 | Taiwan | 41 | 42–81 years | Male: 22 (54%), female: 19 (46%) | Mean=9.19 years | Focus groups | 27 |
| 38 | Describe cultural and family challenges to illness management in foreign-born Chinese-American patients and their spouses. | 2009 | USA | 40 (20 patients, 20 partners) |
Mean=62 years | Male: 16 (40%), female: 24 (60%) | Mean=8.4 years | Interviews | 12 |
| 51 | Explore how women manage their diabetes. | 2009 | USA | 5 | 50–85 years (mean=70.4) | Female: 5 (100%) | 1–18 years (mean=8) | Interviews | 16 |
| 62 | Explore how living with diabetes in everyday life was experienced following a self-management intervention program based on motivational interviewing. | 2011 | Denmark | 22 | 30–72 years | Male: 10 (45%), female: 12 (55%) | 1–11 years | Focus groups | 10 |
| 43 | Explore physicians’ and patients’ views of patients’ difficulty achieving treatment goals. | 2012 | USA | 34 patients, 19 physicians* | 43–70 years (mean=59.8) | Male: 20 (59%), female: 14 (41%) | 3–51 years (mean=12) | Interviews | 10 |
| 41 | Assess self-management skills of Chinese-Americans. | 2012 | USA | 24 (7 poorly controlled, 17 well controlled) | Poorly controlled: mean=56 years, well controlled: mean=60.6 years |
Poorly controlled—male: 3 (43%), female: 4 (57%); well controlled—male: 13 (76%), female: 2 (12%), NA: 2 (12%) |
Poorly controlled: mean=6.4 years; well controlled: mean=6 years | Focus groups | 11 |
| 52 | Describe the experiences and ways of coping of older Singaporean Chinese women. | 2013 | Singapore | 10 | 60–69 years | Female: 10 (100%) | Not reported | Interviews | 26 |
| 53 | Explore the concept of patient values in the context of making decisions about insulin initiation. | 2013 | Malaysia | 21 | 28–67 years | Male: 12 (57%), female: 9 (43%) | Not reported | Interviews | 19 |
| 37 | Gain a deeper understanding of the difficulties Vietnamese patients experience when accessing services and managing their diabetes. | 2013 | Australia | 15 | 60 to >70 years: 15 (100%), >70 years: 11 (73%) |
Male: 4 (27%), female: 11 (73%) | >1 year: 6, >5 years: 9 |
Focus groups | 24 |
| 54 | Better understand barriers to glycemic control from the patient’s perspective. | 2013 | New Zealand | 15 | 33–90 years (mean=63.3) | Male: 5 (33%), female: 10 (67%) | 2–30 years (mean=44.3) | Interviews | 10 |
| 55 | Explore the barriers to diabetes control of middle-aged women. | 2013 | Syria | 12 | 40–65 years | Female: 12 (100%) | 4–23 years | Interviews | 21 |
| 40 | Identify issues in self-management, and opportunities for community pharmacies to offer self-management support to these populations. | 2013 | Australia | 24 | 54–95 years (mean=73) | Male: 10 (42%), female: 14 (58%) |
<5 years: 2, 6–10 years: 8, >10 years: 14 |
Interviews | 14 |
| 56 | Explore patients’ reactions to the diagnosis and their health-related quality of life. | 2014 | Malaysia | 12 | 50–62 years | Male: 5 (42%), female: 7 (58%) |
2.5–21 years | Interviews | 32 |
| 57 | Explore the illness perceptions of patients attending treatment and better understand how they manage their illness. | 2016 | Ethiopia | 39 | >70 years: 30 | Male: 20 (51%), female: 19 (49%) |
1–25 years | Interviews | 31 |
| 59 | Investigate patients’ perceptions and experiences, self-care and engagement with GP-led integrated diabetes care. | 2016 | Australia | 30 | <50 to >65 years (mean=60.2) | Male: 16 (53%), female: 14 (47%) |
Mean=12 years | Interviews | 6 |
*Data not included in synthesis.
GP, general practitioner; NA, not applicable.
Quality appraisal
The majority of included studies justified the research design (85%), explained details about the recruitment strategy (81%), took ethical issues into consideration (89%), provided an in-depth description of the data collection (89%) and analysis processes (69%), provided a clear statement of findings (96%), and discussed the implications of the research (81%). In contrast, only a minority of studies adequately described the relationship between the researcher and participants (39%).
Data categorization
A total of 458 individual outcomes were interpreted from the included studies (median 16 outcomes per study, range 5–32) and categorized according to the COMET taxonomy. Thirty-nine outcomes related to multiple domains and were classified under two or more domains. Thus, 501 outcomes were categorized within the 38 taxonomy domains. Table 3 lists the number of outcomes included in each of the taxonomy domains and the number of studies that included outcomes belonging to each domain.
Table 3.
Outcome categorization according to the COMET taxonomy
| Core area | Core domains | Studies including one or more outcomes in core domain, n (%) | Outcomes included in core domain, n (%) |
| Death | Mortality/survival | 10 (39) | 10 (2) |
| Physiological/clinical | Blood and lymphatic system outcomes | 0 | 0 |
| Cardiac outcomes | 5 (19) | 5 (1) | |
| Congenital, familial and genetic outcomes | 0 | 0 | |
| Endocrine outcomes | 1 (4) | 1 (<1) | |
| Ear and labyrinth outcomes | 0 | 0 | |
| Eye outcomes | 8 (31) | 9 (2) | |
| Gastrointestinal outcomes | 1 (4) | 2 (<1) | |
| General outcomes* | 19 (73) | 42 (8) | |
| Hepatobiliary outcomes | 1 (4) | 1 (<1) | |
| Immune system outcomes | 0 | 0 | |
| Infection and infestation outcomes | 3 (12) | 3 (1) | |
| Injury and poisoning outcomes | 1 (4) | 1 (<1) | |
| Metabolism and nutrition outcomes | 26 (100) | 63 (13) | |
| Musculoskeletal and connective tissue outcomes | 1 (4) | 1 (<1) | |
| Outcomes relating to neoplasms: benign, malignant and unspecified (including cysts and polyps) | 0 | 0 | |
| Nervous system outcomes | 4 (15) | 4 (1) | |
| Pregnancy, puerperium and perinatal outcomes | 0 | 0 | |
| Renal and urinary outcomes | 11 (42) | 13 (3) | |
| Reproductive system and breast outcomes | 0 | 0 | |
| Psychiatric outcomes | 5 (19) | 7 (1) | |
| Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal outcomes | 1 (4) | 1 (<1) | |
| Skin and subcutaneous tissue outcomes | 0 | 0 | |
| Vascular outcomes | 10 (39) | 12 (2) | |
| Life impact | Social functioning | 14 (54) | 28 (6) |
| Role functioning | 16 (62) | 20 (4) | |
| Physical functioning | 24 (92) | 72 (14) | |
| Emotional functioning/well-being | 24 (92) | 106 (21) | |
| Cognitive functioning | 12 (46) | 15 (3) | |
| Global quality of life | 3 (12) | 3 (1) | |
| Perceived health status | 5 (19) | 5 (1) | |
| Delivery of care | 18 (69) | 43 (9) | |
| Personal circumstance | 7 (27) | 12 (2) | |
| Resource use | Economic | 0 | 0 |
| Hospital | 0 | 0 | |
| Need for intervention | 9 (35) | 10 (2) | |
| Societal/carer burden | 2 (8) | 2 (<1) | |
| Adverse events | Adverse events/effects | 8 (31) | 10 (2) |
*The COMET taxonomy defines ‘general outcomes’ to include those affecting the whole body, which cannot be attributed to a certain body system, for example, fatigue, malaise, pain (unspecified, not associated with a particular body system), fever (not attributable to infection), anthropometric measures (eg, weight), ‘global’ measures, ‘symptoms’ (not associated with a particular body system), ‘physical health’ and fitness.45
COMET, Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials.
Of the 501 outcomes, 10 (2%) concerned death, 165 (33%) were physiological/clinical, 304 (61%) were associated with life impact, 12 (2%) related to resource use and 10 (2%) pertained to the adverse events core area. Most outcomes fell within the core domains of ‘emotional functioning/well-being’, ‘physical functioning’ and ‘metabolism and nutrition’. Outcomes relating to each of these three domains were identified in more than 90% of included studies and, when combined, comprised 48% of the total outcomes.
Emotional functioning/well-being
Over one-fifth of the derived outcomes related to ‘emotional functioning/well-being’ (n=106). These outcomes were identified in 24 of the 26 included studies (92%). In 16 studies, patients described being fearful,41 42 44–57 with fears relating to medication side effects, treatment escalation, needing insulin injections, dying, uncertainty about the future, and developing complications, such as foot damage, paralysis and loss of eyesight. Relatedly, 10 studies39 42 47–50 52 55–57 described patients feeling worried or anxious about symptoms, complications, health deterioration, and ultimately dying prematurely as a result of their diabetes. Patients also commented on how diabetes was a burden44 47 58 59 and reported experiencing aggression and frustration,38 39 43 47 49 51 56 57 59–61 sadness and depression,37–39 43 47 52 56 59 guilt43 44 54 and hopelessness.43 44 52 54
Physical functioning
A total of 72 (14%) outcomes concerning physical functioning were derived from 24 included studies (92%). Exercise was identified as an outcome in 16 studies, with patients acknowledging the importance of regular exercise and the benefits it brings; however, some patients labelled it a burdensome activity, which they had difficulty engaging in.37 39 40 42–46 48 50 52 53 56–58 61 In 15 studies, patients referred to the self-monitoring activities they engaged in to manage their diabetes, for example, regularly checking blood glucose levels,37–41 44 47 49 50 52 55–57 61 62 with many emphasizing that the need for a strict self-management regime had become a burden on their lives. Dietary restrictions were a common difficulty relating to self-management, with many patients articulating a desire for dietary freedom, where they could eat what they want, when they want.37 38 44 46 49 57 61
Metabolism and nutrition
Outcomes relating to metabolism and nutrition were identified in all of the 26 included studies, with 63 (13%) outcomes identified in total. In 20 studies, patients made references to their diet, explaining how healthy eating was necessary for controlling their blood sugar levels.37 39–43 46 48 50–56 58–62 In 17 studies, patients spoke about blood glucose-level fluctuations, the importance of glycemic control and the consequences of blood glucose levels falling outside the appropriate range.38 39 41–43 45–47 49–51 53 55–57 60 62 Relatedly, 12 studies referred to hypoglycemia, including patients’ concerns over what would happen if they did experience a hypoglycemic episode, fears about the physical symptoms and the steps they would take to avoid hypoglycemia.37 39 41 44 47 49 52–54 56 57 61
Outcomes identified from studies conducted in LMICs
Of the 26 included studies, four (15%) were conducted in LMICs.63 These four LMIC studies included one upper middle-income country (Malaysia),53 56 one lower middle-income country (Syria)55 and one least developed country (Ethiopia).57 The most prevalent outcome domains among the LMIC studies were ‘mortality/survival’, ‘general outcomes’, ‘metabolism and nutrition’, ‘role functioning’, ‘physical functioning’, ‘emotional functioning/well-being’ and ‘delivery of care’. Outcomes relating to these seven domains were derived from 100% of the LMIC studies. Five of these seven domains were also among the most reported in the studies conducted in HICs; however, outcomes associated with the ‘mortality/survival’ and ‘role functioning’ domains were less frequently reported in HIC studies, at 27% and 55% of studies, respectively. Additionally, outcomes relating to two of the domains, ‘endocrine outcomes’ (eg, pancreatic function) and ‘hepatobiliary outcomes’ (eg, liver complications), were only derived from the LMIC studies.
Comparison with outcomes identified in systematic review of clinical trials
We compared the outcomes derived from the qualitative studies with the outcomes identified from the recent systematic review of type 2 diabetes registered clinical trials.2 Table 4 shows the number of outcomes identified from both reviews according to the five core areas of the COMET taxonomy. In total, 1446 outcomes were identified from the clinical trials review and 458 outcomes from the review of qualitative studies. Both reviews identified a similar proportion of outcomes related to death, resource use and adverse events. However, the systematic review of clinical trials identified a higher proportion of physiological/clinical outcomes (84% vs 33%), whereas the qualitative studies identified a greater proportion of life impact (61% vs 10%) outcomes. Several domains were only identified in one or other of the reviews. Outcomes relating to the ‘blood and lymphatic system’, ‘immune system’, ‘skin and subcutaneous tissue’, ‘economic resource use’ and ‘hospital resource use’ were only extracted from the clinical trials, whereas outcomes associated with ‘injury and poisoning’ (eg, injuries associated with insulin injections), ‘personal circumstances’ (eg, patients’ support networks) and ‘societal/carer burden’ (eg, patients wanting to be independent and not wanting to be a burden to their family) were only identified in the qualitative studies.
Table 4.
Number of outcomes identified in the systematic review of clinical trials and synthesis of qualitative literature according to the five core areas within the COMET taxonomy
| Outcomes identified in systematic review of clinical trials, n (%) | Outcomes identified in synthesis of qualitative literature, n (%) | |
| Death | 3 (<1) | 10 (2) |
| Physiological/clinical | 1221 (84) | 165 (33) |
| Life impact | 145 (10) | 304 (61) |
| Resource use | 31 (2) | 12 (2) |
| Adverse events | 46 (3) | 10 (2) |
COMET, Core Outcome Measures in Effectiveness Trials.
Discussion
This review has identified an expedited approach for incorporating patient perspectives within the early stages of COS development. In contrast to previous similar reviews, which have involved exhaustive searches,19 20 the streamlined nature of the current review enabled rapid identification of patient-centered outcomes that can be used to contribute to the development of the ‘long list’ of outcomes to inform the COS consensus process.
To our knowledge, this is the first review of qualitative studies to identify outcomes that are important to people with type 2 diabetes. The findings will be used, alongside a review of outcomes measured in clinical trials,2 in the development of a COS for type 2 diabetes. Importantly, this review of qualitative studies has identified outcomes that have not previously been measured in type 2 diabetes clinical trials. Without this review, these outcomes would not have been identified for inclusion in the ‘long list’ of outcomes to go forward to the Delphi study.
Most outcomes identified from the qualitative studies related to life impact, whereas in the review of registered clinical trials a relatively small proportion of outcomes related to life impact.2 If clinical trial reviews are used as the only source for developing ‘long list’ of outcomes for COS consensus processes, life impact outcomes may become sidelined in favor of outcomes more frequently measured in clinical trials. This is reflected in the COMET database, where far fewer COS encompass life impact outcomes, in contrast to many COS that encompass physiological/clinical outcomes.33 Thus, the current review supports the recommendation by Dodd and colleagues33 for COS developers to give greater attention to outcomes of life impact. It also illustrates how conducting reviews of qualitative studies can help, alongside other steps such as including patients as participants in COS studies and involving patients and the public in the design of such studies, to ensure COS reflect outcomes that matter to patients.
Given uncertainties about how far COS are applicable beyond those countries that the participants in the development process have been drawn from, it is striking that 84% of published COS studies have not included any participants from LMICs.64 While few qualitative studies had been conducted in LMICs, our review has enabled us to compare outcomes identified in LMIC and HIC studies. Outcomes relating to ‘mortality/survival’ were identified in all LMIC studies, yet almost three-quarters of HIC studies made no references to these outcomes. This is most likely due to the higher prevalence of diabetes-related deaths in LMICs.25 Similarly, all LMIC studies reported outcomes relating to ‘role functioning’ (eg, ability to work and managing family responsibilities) while almost half of the HIC studies made no references to these outcomes. Being unable to function in one’s life roles is likely to be more detrimental to patients living in LMICs.65 Furthermore, three domains relating to diabetes-related complications were only reported in the LMIC studies. Complications are expensive to treat in LMICs, which represent less than 20% of the world’s diabetes care-related expenditure.66 It is possible that national economic factors influence which outcomes are important to patients, indicating the importance of ensuring that the perspectives of patients in LMICs are incorporated into COS development processes.
Strengths and limitations
This study has identified an expedited approach for incorporating the patient perspective into the initial stages of COS development. Our review has enabled evidence from a large number of patients living in a diversity of countries to contribute to the early stages of COS development. We anticipate that such reviews could be performed by COS developers without specialist expertise in qualitative methods, although relevant training would be helpful. Additionally, the method is less resource intensive than other methods for reviewing qualitative evidence which makes it feasible as part of a wider COS process. However, there are some methodological limitations. In line with our expedited approach and recommendations from previous studies,67 68 we only searched one database (MEDLINE) and did not search gray literature. While this approach may mean that some relevant studies may have been missed, our aim was not to provide a comprehensive overview of all research relating to patients’ views and perceptions of type 2 diabetes. Rather, to provide an expedited approach for identifying outcomes that are important to patients, as part of a wider process to incorporate the patient perspective in COS development. In comparison to other qualitative systematic reviews we identified few articles for screening, which reflects the specificity27 of our search terms. Despite these limitations, the number of studies included in this rapid review is comparable to other reviews of qualitative evidence.19 20
A further limitation is that our inclusion of studies relating to a specific experience (eg, patients’ reactions to their diagnosis)56 or intervention (eg, the views of patients who had experienced a new structured diabetes shared care service)60 may have impacted on the outcomes identified. However, when extracting data from such studies we focused on patients’ general views and experiences of diabetes; we did not extract data that focused solely on patients’ perspectives of specific experiences or interventions. An additional limitation is that while many studies in our review were inductive, our approach to reviewing them and deriving outcomes was deductive. Specifically, categorizing text excerpts according to the COMET taxonomy may have transformed their meaning or diluted the patient perspective. However, this categorization enabled us to compare the different literatures in a common ‘currency’, which was key to identifying differences in the types of outcomes given prominence in the clinical trials versus the qualitative literatures, and differences in the qualitative studies from LMICs and HICs. Finally, our review was largely aggregative, collecting findings of previous studies and describing these according to a predefined taxonomy to allow comparison and address specific aims, rather than a configurative review which seeks to interpret the experiences of patients or generate new theory about these.69 Nevertheless, we hope the pragmatic and resource-efficient nature of our method helps the field of COS development by making it easier to incorporate patients’ perspectives.
Conclusion
This rapid review of qualitative studies identified outcomes that are important to people with type 2 diabetes and its findings will inform the development of a COS for clinical trials of glucose-lowering interventions in people with type 2 diabetes. These patient-derived outcomes contrasted with those identified from a systematic review of clinical trials, pointing to the importance of incorporating patient perspectives from the outset of COS development. Additionally, this review also emphasized the importance of ensuring that patients in LMICs are able to input into the development of COS.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Susanna Dodd for verifying the COMET taxonomy outcome classifications during the data categorization stage of the review.
Footnotes
Contributors: SLG: investigation, methodology, writing–original draft preparation, writing–review and editing. BY, JPHW: investigation, writing–review and editing. PRW: conceptualization, funding acquisition, supervision, writing–review and editing. NLH: conceptualization, investigation, project administration, writing–original draft preparation, writing–review and editing.
Funding: This work was supported by the Medical Research Council North West Hub for Trials Methodology Research grant number MR/K025635/1 and the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program (CORBEL, under grant agreement number 654248).
Competing interests: None declared.
Patient consent for publication: Not required.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: All the findings from available data have been published in this manuscript. Original extracted data are available from the corresponding author, NLH, on reasonable request.
References
- 1. American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2010;33:S62–S69. 10.2337/dc10-S062 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Harman NL, James R, Wilding J, et al. . SCORE-IT (selecting core outcomes for randomised effectiveness trials in type 2 diabetes): a systematic review of registered trials. Trials 2017;18 10.1186/s13063-017-2317-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Heneghan C, Goldacre B, Mahtani KR. Why clinical trial outcomes fail to translate into benefits for patients. Trials 2017;18 10.1186/s13063-017-1870-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Tunis SR, Clarke M, Gorst SL, et al. . Improving the relevance and consistency of outcomes in comparative effectiveness research. J Comp Eff Res 2016;5:193–205. 10.2217/cer-2015-0007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Harman N, Williamson P, Demotes-Mainard J, et al. . SCORE-IT - Selecting a Core Outcome Set for Randomised Effectiveness trials In Type 2 Diabetes. Available: http://www.comet-initiative.org/studies/details/956 [Accessed 26 Mar 2018].
- 6. Williamson PR, Altman DG, Blazeby JM, et al. . Developing core outcome sets for clinical trials: issues to consider. Trials 2012;13 10.1186/1745-6215-13-132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Gargon E, Gurung B, Medley N, et al. . Choosing important health outcomes for comparative effectiveness research: a systematic review. PLoS One 2014;9:e99111 10.1371/journal.pone.0099111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Williamson PR, Altman DG, Bagley H, et al. . The comet Handbook: version 1.0. Trials 2017;18 10.1186/s13063-017-1978-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Goodare H, Smith R. The rights of patients in research. BMJ 1995;310:1277–8. 10.1136/bmj.310.6990.1277 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Serrano-Aguilar P, Trujillo-Martín MM, Ramos-Goñi JM, et al. . Patient involvement in health research: a contribution to a systematic review on the effectiveness of treatments for degenerative ataxias. Soc Sci Med 2009;69:920–5. 10.1016/j.socscimed.2009.07.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Macefield RC, Boulind CE, Blazeby JM. Selecting and measuring optimal outcomes for randomised controlled trials in surgery. Langenbecks Arch Surg 2014;399:263–72. 10.1007/s00423-013-1136-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Kirwan J, Heiberg T, Hewlett S, et al. . Outcomes from the patient perspective workshop at OMERACT 6. J Rheumatol 2003;30:868–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Turk DC, Dworkin RH, Revicki D, et al. . Identifying important outcome domains for chronic pain clinical trials: an IMMPACT survey of people with pain. Pain 2008;137:276–85. 10.1016/j.pain.2007.09.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Sinha IP, Gallagher R, Williamson PR, et al. . Development of a core outcome set for clinical trials in childhood asthma: a survey of clinicians, parents, and young people. Trials 2012;13 10.1186/1745-6215-13-103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Noble AJ, Marson AG. Which outcomes should we measure in adult epilepsy trials? the views of people with epilepsy and informal carers. Epilepsy Behav 2016;59:105–10. 10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.01.036 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Kirkham JJ, Davis K, Altman DG, et al. . Core outcome Set-STAndards for development: the COS-STAD recommendations. PLoS Med 2017;14:e1002447 10.1371/journal.pmed.1002447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Keeley T, Williamson P, Callery P, et al. . The use of qualitative methods to inform Delphi surveys in core outcome set development. Trials 2016;17 10.1186/s13063-016-1356-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Humphrey L, Willgoss T, Trigg A, et al. . A comparison of three methods to generate a conceptual understanding of a disease based on the patients' perspective. J Patient Rep Outcomes 2017;1 10.1186/s41687-017-0013-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Coulman KD, MacKichan F, Blazeby JM, et al. . Patient experiences of outcomes of bariatric surgery: a systematic review and qualitative synthesis. Obes Rev 2017;18:547–59. 10.1111/obr.12518 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Hashem MD, Nallagangula A, Nalamalapu S, et al. . Patient outcomes after critical illness: a systematic review of qualitative studies following hospital discharge. Crit Care 2016;20 10.1186/s13054-016-1516-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Coulman KD, Howes N, Hopkins J, et al. . A comparison of health professionals' and patients' views of the importance of outcomes of bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 2016;26:2738–46. 10.1007/s11695-016-2186-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Featherstone RM, Dryden DM, Foisy M, et al. . Advancing knowledge of rapid reviews: an analysis of results, conclusions and recommendations from published review articles examining rapid reviews. Syst Rev 2015;4 10.1186/s13643-015-0040-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Campbell R, Pound P, Pope C, et al. . Evaluating meta-ethnography: a synthesis of qualitative research on lay experiences of diabetes and diabetes care. Soc Sci Med 2003;56:671–84. 10.1016/S0277-9536(02)00064-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Frost J, Garside R, Cooper C, et al. . A qualitative synthesis of diabetes self-management strategies for long term medical outcomes and quality of life in the UK. BMC Health Serv Res 2014;14 10.1186/1472-6963-14-348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Rawal LB, Tapp RJ, Williams ED, et al. . Prevention of type 2 diabetes and its complications in developing countries: a review. Int J Behav Med 2012;19:121–33. 10.1007/s12529-011-9162-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Ganann R, Ciliska D, Thomas H. Expediting systematic reviews: methods and implications of rapid reviews. Implementation Sci 2010;5 10.1186/1748-5908-5-56 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Wong S, Wilczynski N, Haynes R. Developing optimal search strategies for detecting clinically relevant qualitative. Medinfo 2004;107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Higgins J, Green S. Cochrane Handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- 29. Costlow MR, Landsittel DP, James AE, et al. . Model for a patient-centered comparative effectiveness research center. Clin Transl Sci 2015;8:155–9. 10.1111/cts.12257 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Carroll C, Booth A, Lloyd-Jones M. Should we exclude inadequately reported studies from qualitative systematic reviews? An evaluation of sensitivity analyses in two case study reviews. Qual Health Res 2012;22:1425–34. 10.1177/1049732312452937 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Critical appraisal skills programme CASP qualitative checklist. Available: http://www.casp-uk.net/casp-tools-checklists [Accessed 15 Feb 2018].
- 32. Popay J, Roberts H, Sowden A, et al. . Guidance on the conduct of narrative synthesis in sytematic reviews. London: Institute for Health Research, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 33. Dodd S, Clarke M, Becker L, et al. . A taxonomy has been developed for outcomes in medical research to help improve knowledge discovery. J Clin Epidemiol 2018;96:84–92. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.12.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Mercer J, Penner M, Wing K, et al. . Inconsistency in the reporting of adverse events in total ankle arthroplasty: a systematic review of the literature. Foot Ankle Int 2016;37:127–36. 10.1177/1071100715609719 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Thorn JC, Brookes ST, Ridyard C, et al. . Core items for a standardized resource use Measure: expert Delphi consensus survey. Value Health 2018;21:640–9. 10.1016/j.jval.2017.06.011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Kaufman J, Ryan R, Glenton C, et al. . Childhood vaccination communication outcomes unpacked and organized in A taxonomy to facilitate core outcome establishment. J Clin Epidemiol 2017;84:173–84. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.02.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Carolan-Olah MC, Cassar A, Quiazon R, et al. . Diabetes care and service access among elderly Vietnamese with type 2 diabetes. BMC Health Serv Res 2013;13 10.1186/1472-6963-13-447 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Chesla CA, Chun KM, Kwan CML. Cultural and family challenges to managing type 2 diabetes in immigrant Chinese Americans. Diabetes Care 2009;32:1812–6. 10.2337/dc09-0278 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Bissell P, May CR, Noyce PR. From compliance to concordance: barriers to accomplishing a re-framed model of health care interactions. Soc Sci Med 2004;58:851–62. 10.1016/S0277-9536(03)00259-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Barbara S, Krass I. Self management of type 2 diabetes by Maltese immigrants in Australia: can community pharmacies play a supporting role? Int J Pharm Pract 2013;21:305–13. 10.1111/ijpp.12011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Wang Y, Chuang L, Bateman WB. Focus group study assessing self-management skills of Chinese Americans with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Immigr Minor Health 2012;14:869–74. 10.1007/s10903-011-9514-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Hunt LM, Pugh J, Valenzuela M. How patients adapt diabetes self-care recommendations in everyday life. J Fam Pract 1998;46:207–15. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Beverly EA, Ritholz MD, Brooks KM, et al. . A qualitative study of perceived responsibility and self-blame in type 2 diabetes: reflections of physicians and patients. J Gen Intern Med 2012;27:1180–7. 10.1007/s11606-012-2070-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. West C, McDowell J. The distress experienced by people with type 2 diabetes. Br J Community Nurs 2002;7:606–13. 10.12968/bjcn.2002.7.12.10901 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Lai WA, Lew-Ting C-Y, Chie W-C. How diabetic patients think about and manage their illness in Taiwan. Diabet Med 2005;22:286–92. 10.1111/j.1464-5491.2004.01406.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Huang ES, Gorawara-Bhat R, Chin MH. Self-reported goals of older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Am Geriatr Soc 2005;53:306–11. 10.1111/j.1532-5415.2005.53119.x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Hayes RP, Bowman L, Monahan PO, et al. . Understanding diabetes medications from the perspective of patients with type 2 diabetes: prerequisite to medication concordance. Diabetes Educ 2006;32:404–14. 10.1177/0145721706288182 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Vermeire E, Hearnshaw H, Rätsep A, et al. . Obstacles to adherence in living with type-2 diabetes: an international qualitative study using meta-ethnography (EUROBSTACLE). Prim Care Diabetes 2007;1:25–33. 10.1016/j.pcd.2006.07.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Phillips A, Warwickshire. Experiences of patients with type 2 diabetes starting insulin therapy. Nurs Stand 2007;21:35–41. 10.7748/ns.21.23.35.s54 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Lin C-C, Anderson RM, Hagerty BM, et al. . Diabetes self-management experience: a focus group study of Taiwanese patients with type 2 diabetes. J Clin Nurs 2008;17:34–42. 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2007.01962.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Matthews SM, Peden AR, Rowles GD. Patient-provider communication: understanding diabetes management among adult females. Patient Educ Couns 2009;76:31–7. 10.1016/j.pec.2008.11.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Li J, Drury V, Taylor B. 'Diabetes is nothing': the experience of older Singaporean women living and coping with type 2 diabetes. Contemp Nurse 2013;45:188–96. 10.5172/conu.2013.45.2.188 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Lee YK, Low WY, Ng CJ. Exploring patient values in medical decision making: a qualitative study. PLoS One 2013;8:e80051 10.1371/journal.pone.0080051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Janes R, Titchener J, Pere J, et al. . Understanding barriers to glycaemic control from the patient's perspective. J Prim Health Care 2013;5:114–22. 10.1071/HC13114 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Zamzam S, Anoosheh M, Ahmadi F. Barriers to diabetes control from Syrian women's perspectives. Jpn J Nurs Sci 2013;10:121–9. 10.1111/j.1742-7924.2012.00218.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Low LL, Tong SF, Low WY. Mixed feelings about the diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a consequence of adjusting to health related quality of life. Coll Antropol 2014;38:11–20. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Habte BM, Kebede T, Fenta TG, et al. . Explanatory models of adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus from urban centers of central Ethiopia. BMC Res Notes 2016;9 10.1186/s13104-016-2248-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Hörnsten A, Sandström H, Lundman B. Personal understandings of illness among people with type 2 diabetes. J Adv Nurs 2004;47:174–82. 10.1111/j.1365-2648.2004.03076.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Burridge LH, Foster MM, Donald M, et al. . Making sense of change: patients' views of diabetes and GP-led integrated diabetes care. Health Expect 2016;19:74–86. 10.1111/hex.12331 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Smith SM, O'Leary M, Bury G, et al. . A qualitative investigation of the views and health beliefs of patients with type 2 diabetes following the introduction of a diabetes shared care service. Diabet Med 2003;20:853–7. 10.1046/j.1464-5491.2003.01071.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61. Nair KM, Levine MAH, Lohfeld LH, et al. . "I take what I think works for me": a qualitative study to explore patient perception of diabetes treatment benefits and risks. Can J Clin Pharmacol 2007;14:e251–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62. Rosenbek Minet LK, Lønvig E-M, Henriksen JE, et al. . The experience of living with diabetes following a self-management program based on motivational interviewing. Qual Health Res 2011;21:1115–26. 10.1177/1049732311405066 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63. Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development Development assistance Committee (DAC) list of official development assistance (ODA) recipients. Available: http://www.oecd.org/dac/stats/daclist.htm [Accessed 17 Jan 2018].
- 64. Davis K, Gorst SL, Harman N, et al. . Choosing important health outcomes for comparative effectiveness research: an updated systematic review and involvement of low and middle income countries. PLoS One 2018;13:e0190695 10.1371/journal.pone.0190695 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65. Elrayah-Eliadarous HA, Östenson C-G, Eltom M, et al. . Economic and Social impact of diabetes mellitus in a low-income country: a case-control study in Sudan. J Diabetes 2017;9:1082–90. 10.1111/1753-0407.12540 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66. Brown J, Vistisen D, Sicree R, et al. . The economic impacts of diabetes : Atlas D, GAN D. Brussels: International Diabetes Federation, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 67. van Enst WA, Scholten RJPM, Whiting P, et al. . Meta-epidemiologic analysis indicates that Medline searches are sufficient for diagnostic test accuracy systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol 2014;67:1192–9. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.05.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68. Rice DB, Kloda LA, Levis B, et al. . Are Medline searches sufficient for systematic reviews and meta-analyses of the diagnostic accuracy of depression screening tools? A review of meta-analyses. J Psychosom Res 2016;87:7–13. 10.1016/j.jpsychores.2016.06.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69. Kastner M, Antony J, Soobiah C, et al. . Conceptual recommendations for selecting the most appropriate knowledge synthesis method to answer research questions related to complex evidence. J Clin Epidemiol 2016;73:43–9. 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2015.11.022 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]