Abstract
The aim of this cross-sectional analysis is to investigate the associations between the adherence to the Mediterranean Diet (MD) and semen quality parameters. To assess the adherence to the MD, the Trichopoulou score was used. Semen parameters were assessed as described in the 2010 WHO’s report and the results are showed across tertiles of MD adherence. A total of 106 participants were included. Compared to those in the lowest MD adherence tertile, participants in the top tertile had statistically significant higher BMI and waist circumference and consumed more energy, and also had statistically significant higher semen pH, and total sperm motility and progressive sperm motility percentages, and lower sperm immotility percentages. Moreover, percentage of total and progressive motility were significantly higher among those subjects in the higher adherence to MD in comparison with those in low-medium adherence category. The multivariable linear regression models evaluating the relationship between the sperm quality parameters and tertiles of MD adherence adjusted by age, energy and BMI showed that compared with the lowest tertile, men in the highest tertile had a higher percentage of total sperm motility [β non-standardized coefficient = 12.785]. These findings suggest that adherence to the MD was positively associated with sperm motility.
Introduction
Male reproductive health is declining year by year raising serious concerns and implications about human fertility1. Nowadays infertility affects ∼15% of the world’s population and male factors are responsible for 40–50% of these cases2,3. Although it has been shown to be a problem worldwide, this decrease is stronger in certain geographic regions of the world, specifically in the developed and industrialized countries4,5. Therefore, enhancing research on causes of this decline is urgently needed. There are multiple possible causes of this decline, however, the most plausible seems to be related to environmental and lifestyle factors such as pollution6, smoking7, alcohol consumption8, lack of physical activity9, psychological stress10, overweight or obesity11, and unhealthy diets12.
Accumulating observational literature12–15 supports the hypothesis that specific foods can have beneficial (e.g. fish, shellfish and seafood, poultry, cereals, vegetables and fruits, and low-fat dairy) or deleterious (e.g. processed meat, soy foods, potatoes, full-fat dairy products, coffee, alcohol and sugar-sweetened beverages and sweets) effects on semen quality. Also, a recent meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials (RCTs)16 proposes that some nutrients and dietary supplements (e.g. omega-3, CoQ10, selenium, zinc and carnitines) could beneficially modulate sperm quality parameters and affect male fertility, even though, these last results must be cautiously interpreted due to the limited sample size of the meta-analyzed studies and the considerable observed inter-study heterogeneity. However, there are few studies focused on assessing the possible role of dietary patterns on semen quality parameters, especially in healthy and young population.
One of the healthiest dietary patterns, described as the Mediterranean diet (MD)17,18,19, is characterized by a high consumption of olive oil, fruit, nuts, legumes, vegetables and whole cereals; a moderate intake of fish, poultry and wine; and a low consumption of dairy products, red meat, processed meats, and sweets. Because this dietary pattern has been proved to have beneficial effects in several intermediate metabolic outcomes, such as inflammation, oxidative stress and insulin resistance, all of which are related to sperm function, we can hypothesize that adherence to the MD can have benefits in terms of semen quality parameters.
Therefore, the aim of the present study was to investigate the associations between the adherence to the MD pattern and several recognized semen quality parameters (e.g. semen volume and pH, total sperm count and concentration, sperm motility and vitality, and sperm morphology) in healthy and reproductive-age males, using a validated MD score.
Results
A total of 244 subjects were assessed for eligibility, 119 were enrolled in the study and finally, 106 participants (89.1%) were included in the present analysis because a completed seminogram and dietary measures were obtained at baseline.
The mean age (±SD) of the study population (n = 106) was 24.7 (±4.7) years old. Most men had a normal BMI (n = 74, 69.8%), one participant was underweight (0.9%), 26 were overweight (24.5%), and 5 were obese (4.7%). The median and interquartile range (IQR) values for the semen parameters were: 73.8 × 106 spz. (27.9 × 106−125.5 × 106) for total sperm count, 24.1 × 106 spz./ml (10.8 × 106−43.1 × 106) for sperm concentration, 79.2% (72.3–84–8%) for sperm vitality, 66.3% (47.6–75.0%) form sperm total motility, 46.5% (28.7–57.8%) for sperm progressive motility and 6.4% (5.2–7.9%) for normal sperm morphology. Most men had at least one major semen analysis parameter (volume, total sperm count or concentration, vitality, motility or morphology) below the WHO 2010 reference values (58.5%).
The baseline characteristics of the participants according to the tertiles of MD are shown in Table 1. Compared to those in the lowest tertile, participants in the top tertile had statistically significant higher BMI and waist circumference and consumed more energy. Regarding the sperm parameters, the participants in the higher tertile, compared with the lowest tertile, had statistically significant higher pH (8 vs. 8.5, P-value = 0.023), higher total motility percentage (54.5% vs. 73.2%, P-value = 0.009), higher progressive motility percentage (40.8% vs. 52.2%, P-value = 0.013) and lower sperm immotility (34.3% vs. 29.0%, P-value = 0.045). No significant differences were shown in the rest of parameters.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of the study population according to tertiles of Mediterranean diet adherence.
| Variables | 1st Tertile n = 30 MD score ≤3 | 2nd Tertile n = 49 MD score 4–5 | 3rd Tertile n = 27 MD score ≥6 | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD score*; median [Pc25-Pc75] | 3 [2–3]a | 4 [4–5]b | 6 [6–7]c | <0.001 |
| Demographic parameters | ||||
| Age (years); mean (±SD) | 24.1 (±4.5) | 24.1 (±4.6) | 26.3 (±4.8) | 0.100 |
| Energy (kcal); mean (±SD) | 2418 (±701)a | 2860 (±836)b,c | 3192 (±720)c | 0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2); mean (±SD) | 22.5 (±2.3)a | 24.3 (±3.7)b,c | 24.4 (±2.5)c | 0.021 |
| Waist circumference (cm); mean (±SD) | 78.4 (±5.6)a | 81.5 (±9.3)a,b | 84.6 (±6.8)b | 0.014 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg); mean (±SD) | 126.3 (±11.4) | 129.0 (±9.3) | 127.0 (±11.0) | 0.571 |
| Diastolic blood pressure(mmHg); mean (±SD) | 72.6 (±7.0) | 72.1 (±9.1) | 72.7 (±7.7) | 0.946 |
| Blood parameters | ||||
| Plasma glucose (mg/dl); mean (±SD) | 88.0 (±9.3) | 87.1 (±7.2) | 88.5 (±9.1) | 0.759 |
| Total cholesterol (mg/dl); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 170.8 [150.8–182.3] | 170.8 [147.5–192.0] | 169.0 [149.0–188.0] | 0.878 |
| HDL-c (mg/dl); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 57.7 [54.8–66.3] | 56.0 [47.5–66.0] | 56.0 [48.0–59.0] | 0.467 |
| LDL-c (mg/dl); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 96.7 [76.8–105.5] | 96.7 [73.5–106.0] | 93.0 [79.0–108.0] | 0.911 |
| VLDL-c (mg/dl); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 14.1 [11.0–16.3] | 15.0 [9.5–19.5] | 13.0 [12.0–18.0] | 0.827 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dl); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 75.0 [56.5–81.6] | 76.0 [48.5–99.0] | 66.0 [59.0–88.0] | 0.739 |
| Plasma insulin (mcUI/ml); mean (±SD) | 6.1 (±3.7) | 6.8 (±5.5) | 6.2 (±5.7) | 0.794 |
| C-reactive protein (mg/dl); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 0.2 [0.2–0.2] | 0.2 [0.2–0.2] | 0.2 [0.2–0.2] | 0.985 |
| Folate (ng/ml); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 6.6 [5.7–8.9] | 6.3 [4.7–6.9] | 6.2 [4.6–8.1] | 0.150 |
| Semen/sperm parameters | ||||
| pH; median [Pc25-Pc75] | 8.0 [8.0–8.5]a | 8.0 [8.0–8.5]a,b | 8.5 [8.0–8.5]a,c | 0.023 |
| Volume (ml); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 2.8 [1.9–4.5] | 3.0 [1.9–4.6] | 3.3 [2.1–4.4] | 0.852 |
| Volume <1.5 ml; n (%) | 3 (10) | 8 (16.3) | 4 (14.8) | 0.731 |
| Total sperm count (x106); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 76.6 [30.8–139.5] | 65.0 [24.8–126.0] | 79.0 [43.5–101.0] | 0.675 |
| Total sperm count <39 × 106 spz; n (%) | 9 (30) | 19 (38.8) | 6 (22.2) | 0.321 |
| Sperm concentration (x106); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 27.6 [9.1–53.7] | 23.6 [10.0–38.1] | 25.2 [16.1–35.6] | 0.669 |
| Sperm concentration <15 × 106 spz/ml; n (%) | 11 (36.7) | 19 (38.8) | 5 (18.5) | 0.175 |
| Vitality (%); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 79.2 [69.4–82.2] | 79.3 [72.7–84.2] | 78.9 [72.7–87.9] | 0.662 |
| Vitality <58%; n (%) | 3 (10) | 2 (4.1) | 3 (11.1) | 0.451 |
| Total motility (%); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 54.5 [38.8–72.4]a | 64.4 [43.8–72.7]a,b | 73.2 [64.7–82.2]c | 0.009 |
| Total motility <40% motile; n (%) | 8 (26.7) | 7 (14.3) | 2 (7.4) | 0.127 |
| Progressive motility (%); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 40.8 [20.9–58.8]a | 41.8 [25.9–53.5]a,b | 52.2 [43.3–62.3]c | 0.013 |
| Progressive motility <32% motile; n (%) | 10 (33.3) | 17 (34.7) | 4 (14.8) | 0.160 |
| Non-progressive motility (%); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 11.1 [6.3–14.4] | 12.1 [8.6–16.1] | 12.1 [7.9–15.3] | 0.674 |
| Immotility (%); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 34.3 [25.6–53.0]a | 35.6 [27.3–56.2]a,b | 29.0 [20.1–35.9]a,c | 0.045 |
| Morphology (%); median [Pc25-Pc75] | 6.4 [4.4–8.0] | 6.5 [5.6–7.9] | 6.3 [5.0–8.0] | 0.762 |
| Morphology <4% normal; n (%) | 5 (16.7) | 5 (10.2) | 2 (7.4) | 0.515 |
| Seminogram abnormality; n (%) | 19 (63.3) | 32 (65.3) | 11 (40.7) | 0.094 |
Abbreviations. BMI: Body-mass-index, HDL-c: High-density lipoprotein cholesterol, LDL-c: Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, MD: Mediterranean diet, n: number of subjects, Pc: percentile, spz: spermatozoa, VLDL-c: very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, SD: standard deviation.
*MD score (Trichopoulou et al.)18.
Continuous variables were presented as means (±SD) or medians [25th-75th percentiles (Pc)] and categorical variables are presented as number (n) and percentages (%). Differences in variables across tertiles of MD adherence were tested using ANOVA test or Kruskal–Wallis test for continuous variables. Same superscripts in different columns denote non-significant differences, while different superscript letters denote statistically significant differences in a paired comparison (after multiple comparison post-hoc Bonferroni test). Pearson chi-squared test (Fisher’s exact test) was used to compare categorical variables.
Participants with higher adherence to MD score had a higher consumption of vegetables, legumes, fruits and nuts, cereals, fish and seafood. No significant differences across tertiles of MD adherence were detected in dairy products, meat, MUFA/SFA ratio or alcohol intake (Table 2).
Table 2.
Group food consumption of the study population according to tertiles of Mediterranean diet adherence.
| Variables | 1st Tertile n = 30 MD score ≤3 | 2nd Tertile n = 49 MD score 4–5 | 3rd Tertile n = 27 MD score ≥6 | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD score*; median [Pc25-Pc75] | 3 [2–3]a | 4 [4–5]b | 6 [6–7]c | <0.001 |
| Vegetables (g/d); mean (±SD) | 284.3 (±133.7)a | 458.7 (±243.4)b,c | 561.2 (±200.2)c | <0.001 |
| Legumes (g/d); mean (±SD) | 18.0 (±10.5)a | 24.6 (±18.2)a | 36.6 (±21.8)b | <0.001 |
| Fruits and nuts (g/d); mean (±SD) | 176.3 (±104.4)a | 272.4 (±151.2)b | 353.2 (±137.6)c | <0.001 |
| Dairy products (g/d); mean (±SD) | 361.8 (±225.6) | 316.1 (±188.3) | 331.7 (±308.1) | 0.702 |
| Cereals (g/d); mean (±SD) | 119.2 (±74.4)a | 162.3 (±86.3)a,b | 177.7 (±99.3)b | 0.029 |
| Meat (g/d); mean (±SD) | 194.9 (±68.7) | 229.7 (±112.4) | 212.4 (±104.0) | 0.322 |
| Fish and seafood (g/d); mean (±SD) | 66.5 (±34.7)a | 91.3 (±56.1)a,b | 147.4 (±67.4)c | <0.001 |
| MUFA/SFA (ratio/d); mean (±SD) | 0.83 (±0.28) | 0.82 (±0.23) | 0.85 (±0.25) | 0.911 |
| Alcohol (g/d); mean (±SD) | 7.29 (±12.15) | 9.17 (±8.87) | 10.93 (±6.78) | 0.353 |
Abbreviations. g/d: grams per day, MD: Mediterranean diet, MUFA: monounsaturated fatty acids, Pc: percentile, SD: standard deviation, SFA: saturated fatty acids.
*MD score (Trichopoulou et al.)18.
Continuous variables were presented as means (±SD) or medians [25th-75th percentiles (Pc)]. Differences in variables across tertiles of MD adherence were tested using ANOVA test. Same superscripts in different columns denote non-significant differences while different superscript letters denote statistically significant differences in a paired comparison (after multiple comparison post-hoc Bonferroni test).
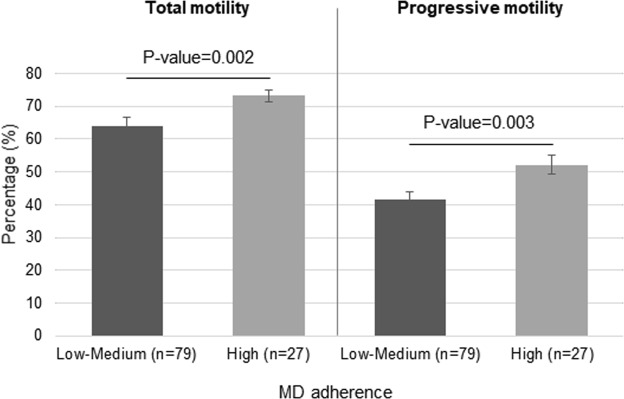
As shown in Fig. 1, in comparison with those participants that had a low-medium adherence to MD, the subjects with a high adherence had significantly higher percentages of total motility (P-value = 0.002) and progressive motility (P-value = 0.003).
Figure 1.
Median of total and progressive motility parameters according to Mediterranean diet adherence. Differences across the categorical MD adherence variable was tested using Mann-Whitney U test.
Table 3 shows the multivariable linear regression models for evaluating the relationship between tertiles of MD adherence adjusted by age, energy and BMI as potential confounder factors, and several sperm parameters. A positive relationship was exhibited between MD adherence and the percentage of total sperm motility after adjusting for confounders, indicating an increase of a 12.8% of total sperm motility in those participants in the top tertile of MD adherence [β non-standardized coefficient = 12.785; P-value = 0.037].
Table 3.
Multivariable linear regression models for tertiles of Mediterranean diet adherence and the principal sperm quality parameters.
| Total sperm count (x106spz.) | Sperm concentration (x106spz./ml) | Sperm vitality (%) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| β non-standardized coefficient | Standard error | P-value | β non-standardized coefficient | Standard error | P-value | β non-standardized coefficient | Standard error | P-value | |
| 1st Tertile | Reference | Reference | Reference | ||||||
| 2nd Tertile | −20.573 | 18.927 | 0.280 | −8.047 | 5.887 | 0.175 | 4.923 | 3.536 | 0.167 |
| 3rd Tertile | −26.148 | 22.808 | 0.254 | −8.132 | 7.094 | 0.254 | 6.669 | 4.261 | 0.121 |
| Age (years) | 2.179 | 1.655 | 0.191 | 0.310 | 0.515 | 0.549 | −0.588 | 0.309 | 0.060 |
| Energy (kcal) | 0.005 | 0.010 | 0.584 | −0.000 | 0.003 | 0.970 | −0.002 | 0.002 | 0.195 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 2.046 | 2.516 | 0.418 | 0.535 | 0.589 | 0.496 | 0.448 | 0.470 | 0.343 |
| R2x100 = 3.4% | R2x100 = 2.7% | R2x100 = 7.1% | |||||||
| F5,105 = 0.698 | F5,105 = 0.545 | F5,105 = 1.533 | |||||||
| P-value = 0.629 | P-value = 0.742 | P-value = 0.186 | |||||||
| Total motility (%) | Progressive motility (%) | Normal sperm forms (%) | |||||||
| β non-standardized coefficient | Standard error | P-value | β non-standardized coefficient | Standard error | P-value | β non-standardized coefficient | Standard error | P-value | |
| 1st Tertile | Reference | Reference | Reference | ||||||
| 2nd Tertile | 1.803 | 5.010 | 0.720 | −1.376 | 4.548 | 0.763 | −0.162 | 0.632 | 0.799 |
| 3rd Tertile | 12.785 | 6.037 | 0.037 | 9.371 | 5.481 | 0.090 | −0.345 | 0.762 | 0.652 |
| Age (years) | 0.224 | 0.438 | 0.610 | 0.435 | 0.398 | 0.277 | −0.021 | 0.055 | 0.705 |
| Energy (kcal) | 0.000 | 0.003 | 0.941 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.764 | 0.001 | 0.000 | 0.068 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 1.803 | 0.666 | 0.074 | 0.962 | 0.605 | 0.115 | 0.214 | 0.084 | 0.012 |
| R2x100 = 11.5% | R2x100 = 11.8% | R2x100 = 9.0% | |||||||
| F5,105 = 2.611 | F5,105 = 2.678 | F5,105 = 1.975 | |||||||
| P-value = 0.029 | P-value = 0.026 | P-value = 0.089 | |||||||
Abbreviations. BMI: Body-mass-index, spz: spermatozoa.
Discussion
In this cross-sectional study conducted in healthy and young population we found that higher adherence to a Mediterranean diet, measured by the validated Trichopolou’s score, was associated with an increased sperm motility. Beyond the potential confounding factors considered in advance for the present study (all participants were non-smokers and healthy), this association was not only independent of the age and BMI of the participants, but also for the total energy consumption.
Our findings are consistent with previous epidemiologic observational studies12 that have reported a positive association between the consumption of individual components of a traditional Mediterranean diet such as fish and seafood20, poultry21, whole cereals22, vegetables21 and fruits22, low-fat dairy23, and the improvement of several sperm quality parameters. The results of the present study are also in line with other studies demonstrating that typical foods highly consumed in western dietary patterns, such us processed meat24, potatoes25, full-fat dairy and total dairy products26, alcohol27, sugar-sweetened beverages28 and sweets21, are detrimentally associated with some quality parameters of semen.
Our study has been based on the analysis of dietary pattern. Dietary pattern analysis has emerged as an alternative and complementary approach to examining the relationship between diet and the risk of health outcomes. Instead of looking at individual nutrients or foods, dietary pattern analysis examines the effects of overall diet. This approach takes into account possible food or nutrient interactions, and positive or negative synergistic effects29. Unfortunately, research assessing possible associations between dietary patterns and sperm quality outcomes is scarce and needs to be promoted in the future.
A recent systematic review and meta-analysis of six observational studies30–35 assessing the association between some a posteriori dietary patterns defined by factor analysis, and semen quality concluded that healthy eating patterns might have a positive association with sperm concentration, but not with other classical sperm quality parameters14. However, due to the small sample size and heterogeneity of the studies, the authors recommended caution in the interpretation of the results.
The traditional MD pattern has been considered one of the healthiest dietary patterns existing36. The MD has consistently been associated with broad healthy benefits on human health, especially in relation to protection against CVD and mortality37. Because this dietary pattern has also demonstrated beneficial effects on inflammation38, oxidation39, insulin sensitivity40, and endothelial function41 among others, we can hypothesize that it can have also benefits in terms of semen quality parameters and male fertility. However, whether adherence to the MD is associated with better semen profile remains largely unexplored.
To our knowledge, there was only one previously published study analyzing the association between MD adherence, defined a priori, and the quality of sperm42. In this cross-sectional study of 225 men from couples attending a fertility clinic in Athens, that has not been included in the aforementioned meta-analysis, men in the lowest tertile of the MD adherence score had higher likelihood of having abnormal sperm concentration, total sperm count and motility, compared to men in the highest tertile of the score. Therefore, our results confirm these previous reported results but only in relation to total and progressive sperm motility, an important parameter related to fertility.
In fact, healthy dietary patterns and specially the MD are rich in several nutrients that have been proven to have benefits in terms of sperm motility43–48 adding biological plausibility to the reported association. Only one study has demonstrated that adherence to a healthy dietary pattern is associated to sperm motility in a posteriori analysis. In the context of the Rochester Young Men’s cohort, adherence to a Prudent diet identified by factor analysis rich in fish, chicken, fruit, vegetables, legumes and whole grains was positively associated with progressive sperm motility33.
The principal strength of the present study is the originality of the work, because this is the first study exploring the association between the MD pattern and sperm quality parameters in a young and healthy population. The use of FFQs, as a comprehensive method to obtain detailed information about the habitual intake of foods allowed us to use a validated and widely used MD score measuring adherence to the MD18.
The main limitation of the study is the cross-sectional nature. Cross-sectional design could not determine whether MD adherence and sperm motility improvements are causally related. Future well-designed observational prospective studies and clinical trials on the current topic are therefore recommended. Although in our study we have excluded several potential confounding factors, these results should be interpreted with caution because of the multifactorial etiology of the sperm quality parameters. Moreover, we cannot discount other possible associations between the adherence to the MD and other sperm parameters by increasing the sample size or by repeating the semen analysis in order to decrease the biological variability. We cannot also discount some analytical error when measuring the sperm parameters, however we have minimized it through strong adherence to standardized protocols. Another limitation it that this study focuses on healthy men and therefore, the results cannot be extrapolated to other populations. Also, in some studies it has been shown that physical activity is associated with an improvement of sperm quality49. Unfortunately, we did not measure physical activity in our participants; therefore, we have not have controlled our models for this variable with the limitations that this entails in the interpretation of the findings. Finally, although an association between adherence to MD and sperm quality was detected, the highest probability of fecundability translation needs to be proven in the future.
In summary, in this healthy and young population, and using a cross-sectional analysis, we demonstrated that adherence to a MD was positively associated with sperm motility parameters. These findings suggest that compliance to a healthy diet may help to improve some semen quality parameters, especially those related to the sperm motility, one of the most important parameter related to fertility. Prospective studies and randomized clinical trials are warranted in the future to increase the scientific evidence in relation to the possible effect of diet on the sperm quality and fecundability.
Material and Methods
Study population
This cross-sectional analysis was conducted with baseline data of participants recruited between December 2015 and February 2017 in the FERTINUTS study, a parallel randomized clinical trial aimed to assess the effects of nut supplementation on sperm quality parameters. The design of the trial has been reported in detail elsewhere (ISRCTN12857940)50. Eligible participants were healthy and young men (aged 18–35 years old) reporting a western-style dietary pattern. Exclusion criteria included severe chronic illness, alcohol or drug abuse, frequent consumption or allergy of nuts, use of supplements (i.e. plant sterol, fish oil supplements, multivitamins, vitamin E or other antioxidant supplements), history of reproductive disorders or vasectomy, current smoking, or use of drugs for chronic diseases.
The protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Hospital Universitari Sant Joan de Reus in October 2015. The study was done according to the Declaration of Helsinki for Medical Research involving Human Subjects and all the participants provided a written informed consent.
Dietary intake and adherence to the Mediterranean diet
Dietary intake was quantified by trained dietitians with a face-to-face 143-item, semi-quantitative, validated food frequency questionnaire (FFQ)51 over the past year and the mean of 3-day dietary records, including 2 workdays and a weekend day. In the FFQ, dietitians asked the participants about the frequency with which they consumed the different items: never, one to three times per month, once per week, two to four times per week, five to six times per week, once per day, two to three times per day, four to six times per day or more than six times per day. The responses were transformed to grams per day. Energy, nutrient intake, and food groups were estimated using Spanish food composition tables52.
In order to assess the adherence to the MD the Trichopoulou score was fitted from FFQ information18. Subjects were assigned a value of 0 if the consumption of components considered beneficial (vegetables, legumes, fruit and nuts, cereals, fish and seafood, monounsaturated -MUFA- to saturated fatty acids -SFA- ratio) was below the median, whereas individuals were assigned a value of 1 if they had a consumption of beneficial food at or above the median. Otherwise, people with consumption of components considered harmful (meat and dairy products) below the median were assigned a value of 1, whereas people with consumption at or above the median were assigned a value of 0. With regards to alcohol, a value of 1 was assigned to subjects consuming a moderate amount (i.e. between 10 and 30 g per day for men) and a value of 0 otherwise. Therefore, the total Trichopoulou score had a potential range from 0 (minimal adherence to MD) to 9 (maximal adherence to MD).
General, anthropometric and blood measurements
General, anthropometrical variables and blood pressure were determined by trained staff at baseline. Briefly, body weight and height were measured using an electronic scale (TANITA TBF-300; Tanita), and BMI was calculated as weight in kilograms divided by squared height in meters. The commonly accepted BMI ranges are: underweight (<18.5 kg/m2), normal weight (18.5 to 25 kg/m2), overweight (25 to 30 kg/m2) and obese (>30 kg/m2). Waist circumference was measured to the nearest 0.5 cm midway between the lowest rib and the iliac crest with an anthropometric tape. Blood pressure was measured in duplicate with a 5 minutes interval by using a semiautomatic oscillometer (Omron HEM-705CP, Netherlands). Blood samples following 12 h fasting conditions were collected in order to measure the following parameters: plasma glucose, total serum cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) cholesterol, triglycerides, insulin, C-reactive protein, and folate (COBAS; Roche Diagnostics Ltd, UK).
Sperm parameters analysis
Semen parameters were assessed as described in the 2010 World Health Organization’s report: “WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen”2 and following the Björndahl checklist53 with at least 3 days of sexual abstinence. All analyses were done in fresh samples with a maximum of 60 minutes after collection. Briefly, semen volume and pH were measured after 30 minutes of liquefaction with a Pasteur pipette and pH-indicator strips, respectively. The lower reference limit for semen volume was 1.5 ml, and in the case of pH, 7.2 was used as a lower threshold value. Total sperm count, and concentration was determined with a 100-µm-deep haemocytometer chamber (Neubauer®), at ×400 magnification counting 200 spermatozoa. The lower reference limit for sperm concentration was 15 × 106 spermatozoa per ml and for sperm count was 39 × 106 spermatozoa per ejaculate. Sperm motility was assessed also at ×400 magnification (counting 200 spermatozoa) and permits to classify the spermatozoa as: a) Progressive motility (PR), b) Non-progressive motility (NP); and c) Immotility (IM). Total motility was expressed as PR + NP. The lower reference limit for total motility and progressive motility were 40% and 32%, respectively. Sperm vitality was estimated using eosin-nigrosine at ×1,000 magnification (evaluating 200 spermatozoa). The lower reference limit for vitality (membrane-intact spermatozoa) was 58%. Sperm morphology was assessed with Hemacolor® (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) staining at ×1,000 magnification (assessing 200 spermatozoa), and expressed as percentage of normal forms. The lower reference limit for normal forms was 4%.
Statistical analysis
The results are shown across tertiles of MD adherence. Continuous variables were presented as means and standard deviation (±SD) or medians [25th-75th percentiles (Pc)] based on the normal or non-normal distribution. Missing blood values for the patients who have all the seminogram and dietary information were imputed using the mean of the variables measured. Normal distribution and homogeneity of variances were evaluated using Kolmogorov-Smirnov and Levene’s test, respectively. Categorical variables were presented as number (n) and percentages (%). Differences between groups were assessed with ANOVA test when the variables were normally distributed and Kruskal-Wallis or Mann-Whitney U tests when they were not. A multiple comparison post-hoc Bonferroni test were used to perform pairwise comparisons between groups. The Pearson chi-squared test was used to compare categorical variables. Multivariate linear regression models (enter method) were fitted to assess the relationship between tertiles of MD adherence and the principal sperm quality parameters. Estimates with β coefficient and standard error were shown. The multivariate linear regression models included the following potential confounders: age (years), energy (kcal) and BMI (kg/m2). The goodness of fit was expressed as: R square multiply per 100 (R2x100) and the variance analysis of the model and its significance (F-value and P-value). All P-values are two-tailed at the <0.05 level. Statistical analyses were conducted with the IBM-SPSS statistical package (version 22.0, SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Acknowledgements
We thank all the participants for their enthusiastic collaboration. We also thank Rocío Moraleda for her nutritional assistance, Santiago Domínguez for his nursery assistance, and Susana Benigno and Carles Munné for their help as editors. Also, the authors thank Dra. Nerea Becerra-Tomás for many valuable comments. Consorcio CIBER, M.P., Fisiopatologia de la Obesidad y Nutrición (CIBERobn), Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII). The Plan Nacional de Investigación Científica, Desarrollo e Innovación Tecnológica, the Instituto de Salud Carlos III - Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria (PI12/0153). The Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER). This work was partially supported by the International Nut and Dried Fruit Council (INC) with the Grant No. 2015 INC Research Grant (PV15110S) and by Human Nutrition Unit funds. INC is a non-profit entity registered at the Register of Foundations of Catalonia, Spain.
Author Contributions
A.S.-H. and J.S.-S. initiated the idea of the trial. A.S.-H., N.B., M.B., and J.S.-S. were involved in study design. A.S.-H. was involved in study conception and execution, acquisition and analysis of data, and wrote the manuscript; N.B. was involved in data analysis; N.B., D.T.C., M.B. and J.S.-S. supervised the analysis and critically revised the manuscript. All authors provided substantial intellectual contributions and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Data Availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Competing Interests
J.S.-S. reports serving on the board of and receiving grant support through his institution from International Nut and Dried Fruit Council; receiving consulting personal fees from Danone, Font Vella Lanjaron, Nuts for Life, and Eroski; and receiving grant support through his institution from Nut and Dried Fruit Foundation and Eroski. M.B. received research funds through her Institution from Pistachio Growers. None of these industries/organizations have participated in the conception of the present study or preparation of this paper. None of the other authors reported a conflict of interest related to the study.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Albert Salas-Huetos, Email: albert.salas@utah.edu.
Jordi Salas-Salvadó, Email: jordi.salas@urv.cat.
References
- 1.Levine H, et al. Temporal trends in sperm count: A systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update. 2017;23:646–659. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmx022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization. WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen. 5th ed., (World Health Organization, 2010).
- 3.Sabanegh, E. S. Male infertility: Problems and solutions. 1st ed., (Humana Press, 2011).
- 4.Carlsen E, Giwercman A, Keiding N, Skakkebaek NE. Evidence for decreasing quality of semen during past 50 years. Br. Med. J. 1992;305:609–613. doi: 10.1136/bmj.305.6854.609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Swan SH, Elkin EP, Fenster L. The question of declining sperm density revisited: An analysis of 101 studies published 1934-1996. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000;108:961–966. doi: 10.1289/ehp.00108961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Deng Z, et al. Association between air pollution and sperm quality: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Pollut. 2016;208:663–669. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2015.10.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Sharma R, Harlev A, Agarwal A, Esteves SC. Cigarette smoking and semen quality: A new meta-analysis examining the effect of the 2010 World Health Organization laboratory methods for the examination of human semen. Eur. Urol. 2016;70:635–645. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.04.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ricci E, et al. Semen quality and alcohol intake: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Reprod. Biomed. Online. 2016;34:38–47. doi: 10.1016/j.rbmo.2016.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Jurewicz J, et al. Lifestyle and semen quality: Role of modifiable risk factors. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2014;60:43–51. doi: 10.3109/19396368.2013.840687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Nargund VH. Effects of psychological stress on male fertility. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2015;12:373–382. doi: 10.1038/nrurol.2015.112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sermondade N, et al. BMI in relation to sperm count: An updated systematic review and collaborative meta-analysis. Hum. Reprod. Update. 2013;19:221–231. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dms050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Salas-Huetos A, Bulló M, Salas-Salvadó J. Dietary patterns, foods and nutrients in male fertility parameters and fecundability: a systematic review of observational studies. Hum. Reprod. Update. 2017;23:371–389. doi: 10.1093/humupd/dmx006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Giahi L, Mohammadmoradi S, Javidan A, Sadeghi MR. Nutritional modifications in male infertility: A systematic review covering 2 decades. Nutr. Rev. 2016;74:118–130. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuv059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Arab A, Rafie N, Mansourian M, Miraghajani M, Hajianfar H. Dietary patterns and semen quality: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Andrology. 2017;10:1–9. doi: 10.1111/andr.12430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ricci E, et al. Dietary habits and semen parameters: a systematic narrative review. Andrology. 2018;6:104–116. doi: 10.1111/andr.12452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Salas-Huetos A, et al. The Effect of Nutrients and Dietary Supplements on Sperm Quality Parameters: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of RandomizedClinical Trials. Adv. Nutr. An Int. Rev. J. 2018;9:833–848. doi: 10.1093/advances/nmy057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Estruch R, et al. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a Mediterranean diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;368:1279–90. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1200303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Trichopoulou A, Costacou T, Bamia C, Trichopoulos D. Adherence to a Mediterranean Diet and Survival in a Greek Population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003;348:2599–2608. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa025039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Estruch Ramón, et al. Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease with a Mediterranean Diet Supplemented with Extra-Virgin Olive Oil or Nuts. New England Journal of Medicine. 2018;378:e34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1800389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Afeiche M, et al. Processed meat intake is unfavorably and fish intake favorably associated with semen quality indicators among men attending a Fertility Clinic. J. Nutr. 2014;144:1091–1098. doi: 10.3945/jn.113.190173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Eslamian G, Amirjannati N, Rashidkhani B, Sadeghi MR, Hekmatdoost A. Intake of food groups and idiopathic asthenozoospermia: A case-control study. Hum. Reprod. 2012;27:3328–3336. doi: 10.1093/humrep/des311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Braga DPDAF, et al. Food intake and social habits in male patients and its relationship to intracytoplasmic sperm injection outcomes. Fertil. Steril. 2012;97:53–59. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Afeiche M, et al. Dairy intake and semen quality among men attending a fertility clinic. Fertil. Steril. 2014;101:1280–1287. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.02.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Afeiche M, et al. Meat intake and reproductive parameters among young men. Epidemiology. 2014;25:323–30. doi: 10.1097/EDE.0000000000000092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mendiola J, et al. Food intake and its relationship with semen quality: A case-control study. Fertil. Steril. 2009;91:812–818. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.01.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Afeiche M, et al. Dairy food intake in relation to semen quality and reproductive hormone levels among physically active young men. Hum. Reprod. 2013;28:2265–75. doi: 10.1093/humrep/det133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Anifandis G, et al. The impact of cigarette smoking and alcohol consumption on sperm parameters and sperm DNA fragmentation (SDF) measured by Halosperm. Arch. Gynecol. Obstet. 2014;290:777–782. doi: 10.1007/s00404-014-3281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chiu YH, et al. Sugar-sweetened beverage intake in relation to semen quality and reproductive hormone levels in young men. Hum. Reprod. 2014;29:1575–1584. doi: 10.1093/humrep/deu102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Hu FB. Dietary pattern analysis: A new direction in nutritional epidemiology. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2002;13:3–9. doi: 10.1097/00041433-200202000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Vujkovic M, et al. Associations between dietary patterns and semen quality in men undergoing IVF/ICSI treatment. Hum. Reprod. 2009;24:1304–1312. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dep024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cutillas-Tolin A, et al. Mediterranean and western dietary patterns are related to markers of testicular function among healthy men. Hum. Reprod. 2015;30:2945–2955. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Liu CY, et al. The association between dietary patterns and semen quality in a general Asian population of 7282 Males. PLoS One. 2015;10:1–12. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0134224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gaskins AJ, Colaci DS, Mendiola J, Swan SH, Chavarro JE. Dietary patterns and semen quality in young men. Hum. Reprod. 2012;27:2899–2907. doi: 10.1093/humrep/des298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jurewicz J, et al. Dietary Patterns and the Frequency of Disomy in Human Sperm. Urology. 2016;93:86–91. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2016.03.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jurewicz J, et al. Dietary Patterns and Their Relationship With Semen Quality. Am. J. Mens. Health. 2018;12:575–583. doi: 10.1177/1557988315627139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Jankovic N, et al. Adherence to a Healthy Diet According to the World Health Organization Guidelines and All-Cause Mortality in Elderly Adults From Europe and the United States. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014;180:978–988. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwu229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Salas-Salvadó, J., Becerra-Tomás, N., García-Gavilán, J. F., Bulló, M. & Barrubés, L. Mediterranean Diet and Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: What do We Know? Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis., 10.1016/j.pcad.2018.04.006 (2018). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 38.Panagiotakos DB, et al. Mediterranean diet and inflammatory response in myocardial infarction survivors. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2009;38:856–866. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyp142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Fitó M, et al. Effect of a Traditional Mediterranean Diet on Lipoprotein Oxidation. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007;167:1195. doi: 10.1001/archinte.167.11.1195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Baratta F, et al. Adherence to Mediterranean Diet and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Effect on Insulin Resistance. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2017;112:1832–1839. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2017.371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Torres-Peña JD, et al. Mediterranean diet improves endothelial function in patients with diabetes and prediabetes: A report from the CORDIOPREV study. Atherosclerosis. 2018;269:50–56. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.12.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Karayiannis D, et al. Association between adherence to the Mediterranean diet and semen quality parameters in male partners of couples attempting fertility. Hum. Reprod. 2017;32:215–222. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dew288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Safarinejad MR. Effect of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid supplementation on semen profile and enzymatic anti-oxidant capacity of seminal plasma in infertile men with idiopathic oligoasthenoteratospermia: A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised study. Andrologia. 2011;43:38–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0272.2009.01013.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Martínez-Soto JC, et al. Dietary supplementation with docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) improves seminal antioxidant status and decreases sperm DNA fragmentation. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 2016;62:387–395. doi: 10.1080/19396368.2016.1246623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Safarinejad MR, Safarinejad S. Efficacy of selenium and/or N-Acetyl-Cysteine for improving semen parameters in infertile men: A double-blind, placebo controlled, randomized study. J. Urol. 2009;181:741–751. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2008.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Omu AE, Dashti H, Al-Othman S. Treatment of asthenozoospermia with zinc sulphate: Andrological, immunological and obstetric outcome. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 1998;79:179–184. doi: 10.1016/S0301-2115(97)00262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Scott R, et al. The effect of oral selenium supplementation on human sperm motility. Br. J. Urol. 1998;82:76–80. doi: 10.1046/j.1464-410x.1998.00683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Suleiman S, Eamin Ali M, Zaki Z, El-Malik E, Nasr M. Lipid peroxidation and human sperm motility: Protective role of vitamin E. J. Androl. 1996;17:530–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Gaskins AJ, et al. Physical activity and television watching in relation to semen quality in young men. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015;49:265–270. doi: 10.1136/bjsports-2012-091644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Salas-Huetos Albert, et al. Effect of nut consumption on semen quality and functionality in healthy men consuming a Western-style diet: a randomized controlled trial. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 2018;108:953–962. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/nqy181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fernández-Ballart JD, et al. Relative validity of a semi-quantitative food-frequency questionnaire in an elderly Mediterranean population of Spain. Br. J. Nutr. 2010;103:1808–16. doi: 10.1017/S0007114509993837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Moreiras, O. & Carvajal, A. Tablas de Composición de Alimentos (Food Composition Tables). 16th ed., (2005).
- 53.Björndahl L, Barratt CLR, Mortimer D, Jouannet P. ‘How to count sperm properly’: Checklist for acceptability of studies based on human semen analysis. Hum. Reprod. 2016;31:227–232. doi: 10.1093/humrep/dev305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.