Abstract
Background
There is a dearth of accurate information about patterns of mortality of lymphoid neoplasms and temporal trends in China. In this nationwide mortality study, we aimed to assess the mortality of lymphoma and myeloma in 2017 and the changes in the trend from 2004 to 2016.
Methods
Death certificate data obtained from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s disease surveillance points system (CDC-DSP) and population data from the National Bureau of Statistics of China were used in this study. We described the mortality of lymphoma and myeloma in 2017 by age group, sex, residence, and region and evaluated the temporal trend from 2004 to 2016 using joinpoint regression.
Results
An estimated 52,000 deaths associated with lymphoma and myeloma occurred in 2017. The age-standardized mortality rate China (ASMRC) and age-standardized mortality rate worldwide (ASMRW) per 100,000 were 3.74 and 2.60, respectively. Males had higher ASMRC than females (4.54 vs. 2.91 per 100,000). The ASMRC in urban areas was significantly higher than that in rural areas (4.35 vs. 3.47 per 100,000). The age-specific mortality rate showed an upward trend with age and reached a maximum in the age group of over 85 years. In terms of regional variation, Eastern China had the highest mortality rate (3.43/100,000), followed by Central China (3.10/100,000) and Western China (3.02/100,000). The mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma increased annually by 4.5% during the period 2004–2016, with a significant rapid upward trend in rural areas since 2007.
Conclusions
The mortality of lymphoma and myeloma increased in China from 2004 to 2017. The rapid increase in disease burden in rural areas highlights new challenges for disease prevention and control strategies.
Keywords: Lymphoma, Multiple myeloma, Mortality, Epidemiology
Background
Lymphoid neoplasms, historically called lymphoid malignancies, comprise 5 major categories: Hodgkin lymphoma (HL), non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), myeloma, acute lymphoid leukemia, and chronic lymphoid leukemia [1]. Lymphoid neoplasms are a common leading cause of death worldwide. A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016 demonstrated that the numbers of estimated all-age deaths due to lymphoid neoplasms were as follows: HL, 28,700; NHL, 239,600; multiple myeloma, 98,400; acute lymphoid leukemia, 50,900; and chronic lymphoid leukemia, 35,400 [2].
Different geographic distributions are observed between eastern and western countries. For example, in the USA, lymphoid neoplasms were the fourth most common cancer, with an expected 136,960 new cases in 2016 [3], and the mortality rate of lymphoid neoplasms per 100,000 population was 21.6 in 2014 (0.4 due to HL, 8.3 due to NHL, 3.9 due to multiple myeloma, 9.0 due to leukemia) [4]. A nationwide statistical analysis in Korea [5] showed a total of 6638 lymphoid malignancies in 2012, and the age-standardized incidence rates of all lymphoid malignancies increased from 6.9 to 9.9 per 100,000 persons during the period 1999–2012.
However, a comprehensive mortality description of these lymphoid neoplasms based on the national population, including differences in mortality according to sex, age group, residence, and region, has not yet been conducted in China. Ultimately, an understanding of mortality trends will help to direct future studies of disease control and prevention strategies. Therefore, this analysis sought to determine the mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma in 2017, as defined by the World Health Organization classification [1], in mainland China. In addition, this study reports trends in mortality rates for lymphoma and myeloma from 2004 to 2016.
Methods
Data sources
Mortality data on patients with lymphoma and myeloma (International Classification of Diseases, 10 codes: C81–85, C88, C90, C96) between 2004 and 2017 were collected from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s disease surveillance points system (CDC-DSP). ICD-10 codes for each subtype of lymphoma and myeloma are listed in Table 1. The variables extracted were sex, age, year of diagnosis, residence (urban and rural areas), and region (Eastern China, Central China, and Western China).
Table 1.
ICD-10 codes for each subtype of lymphoma and myeloma
| Subtype | ICD-10 |
|---|---|
| Hodgkin lymphoma | C81 |
| Nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin lymphoma | C81.0 |
| Nodular sclerosis (classical) Hodgkin lymphoma | C81.1 |
| Mixed cellularity (classical) Hodgkin lymphoma | C81.2 |
| Lymphocyte-depleted (classical) Hodgkin lymphoma | C81.3 |
| Lymphocyte-rich (classical) Hodgkin lymphoma | C81.4 |
| Other (classical) Hodgkin lymphoma | C81.7 |
| Hodgkin lymphoma, unspecified | C81.9 |
| Follicular lymphoma | C82 |
| Follicular lymphoma grade I | C82.0 |
| Follicular lymphoma grade II | C82.1 |
| Follicular lymphoma grade III, unspecified | C82.2 |
| Follicular lymphoma grade IIIa | C82.3 |
| Follicular lymphoma grade IIIb | C82.4 |
| Diffuse follicle center lymphoma | C82.5 |
| Cutaneous follicle center lymphoma | C82.6 |
| Other types of follicular lymphoma | C82.7 |
| Follicular lymphoma, unspecified | C82.9 |
| Non-follicular lymphoma | C83 |
| Small cell B cell lymphoma | C83.0 |
| Mantle cell lymphoma | C83.1 |
| Diffuse large B cell lymphoma | C83.3 |
| Lymphoblastic (diffuse) lymphoma | C83.5 |
| Burkitt lymphoma | C83.7 |
| Other non-follicular lymphoma | C83.8 |
| Non-follicular (diffuse) lymphoma, unspecified | C83.9 |
| Mature T/NK cell lymphomas | C84 |
| Mycosis fungoides | C84.0 |
| Sézary disease | C84.1 |
| Peripheral T cell lymphoma, not elsewhere classified | C84.4 |
| Other mature T/NK cell lymphomas | C84.5 |
| Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-positive | C84.6 |
| Anaplastic large cell lymphoma, ALK-negative | C84.7 |
| Cutaneous T cell lymphoma, unspecified | C84.8 |
| Mature T/NK cell lymphoma, unspecified | C84.9 |
| Other and unspecified types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma | C85 |
| B cell lymphoma, unspecified | C85.1 |
| Mediastinal (thymic) large B cell lymphoma | C85.2 |
| Other specified types of non-Hodgkin lymphoma | C85.7 |
| Non-Hodgkin lymphoma, unspecified | C85.9 |
| Other specified types of T/NK cell lymphoma | C86 |
| Extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type | C86.0 |
| Hepatosplenic T cell lymphoma | C86.1 |
| Enteropathy-type (intestinal) T cell lymphoma | C86.2 |
| Subcutaneous panniculitis-like T cell lymphoma | C86.3 |
| Blastic NK cell lymphoma | C86.4 |
| Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma | C86.5 |
| Primary cutaneous CD30-positive T cell proliferations | C86.6 |
| Malignant immunoproliferative diseases | C88 |
| Waldenström macroglobulinemia | C88.0 |
| Other heavy chain diseases | C88.2 |
| Immunoproliferative small intestinal disease | C88.3 |
| Extranodal marginal zone B cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue [MALT lymphoma] | C88.4 |
| Other malignant immunoproliferative diseases | C88.7 |
| Malignant immunoproliferative disease, unspecified | C88.9 |
| Multiple myeloma and malignant plasma cell neoplasms | C90 |
| Multiple myeloma | C90.0 |
| Plasma cell leukemia | C90.1 |
| Extramedullary plasmacytoma | C90.2 |
| Solitary plasmacytoma | C90.3 |
| Other and unspecified malignant neoplasms of lymphoid, hematopoietic, and related tissue | C96 |
| Multifocal and multisystemic (disseminated) Langerhans cell histiocytosis [Letterer-Siwe disease] | C96.0 |
| Malignant mast cell tumor | C96.2 |
| Sarcoma of dendritic cells (accessory cells) | C96.4 |
| Multifocal and unisystemic Langerhans cell histiocytosis | C96.5 |
| Unifocal Langerhans cell histiocytosis | C96.6 |
| Other specified malignant neoplasms of lymphoid, hematopoietic, and related tissue | C96.7 |
| Histiocytic sarcoma | C96.8 |
| Malignant neoplasm of lymphoid, hematopoietic, and related tissue, unspecified | C96.9 |
A total of 161 surveillance points across 31 provinces were included in this population-based death registration system from 2004 to 2012, providing a population coverage of approximately 73 million people (approximately 6% of the total Chinese population). This system consists of 605 surveillance points and covers a population of 323.8 million (24.3% of the total population of the country) since 2013. Good national and regional representativeness of the system have been determined in previous studies [6–8], and detailed information about this database has been published elsewhere [9]. Multiple strategies for addressing variations in data quality are routinely implemented, including regular checking, supervision, feedback, and verification. In addition, two underreporting surveys that aimed to evaluate the data completeness of the CDC-DSP system were conducted during 2006–2008 and 2009–2011 [10, 11]. The mortality rates were adjusted by underreporting rates in each corresponding year according to the following formula: estimated mortality rates = reported mortality rates/(1—underreporting rates).
National age-specific population data were obtained from the National Bureau of Statistics of China (http://data.stats.gov.cn). At the end of 2017, there were 1,390,080,000 persons, including 711,370,000 males and 678,710,000 females, in mainland China, of which 813,470,000 resided in urban areas and 576,610,000 resided in rural areas. The products of the age-specific mortality rates and corresponding population in each stratum were added up to calculate the estimated deaths due to lymphoma and myeloma in 2017. The whole-population data were divided by age group (0–1, 1–84 in 5-year intervals and 85+ years). The 2010 census population of China and Segi’s population were used to determine the age-standardized mortality rate China (ASMRC) and the age-standardized mortality rate world (ASMRW), respectively.
Statistical analysis
The numbers of deaths and mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma in 2017 were estimated using the CDC-DSP database. Temporal trends in mortality rates from 2004 to 2017 were examined by IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows (version 21.0; IBM Corp.) and fitting joinpoint models (version 4.6.0.0; National Cancer Institute). The trends were expressed as annual percentage changes (APCs), and Z tests were used to assess whether the APCs were significantly different from zero. In describing trends, the terms “increase” and “decrease” were used when the slope of the trend was statistically significant; otherwise, the term “stable” was used. Statistical significance was assessed at the 0.05 level, and all hypothesis tests were two-sided.
Results
Expected deaths and mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma in 2017
An estimated 52,000 deaths associated with lymphoma and myeloma occurred, and the crude mortality rate was 3.83 per 100,000 in 2017. The ASMRC and ASMRW per 100,000 were 3.74 and 2.60, respectively (Table 2). Males had higher mortality rates than females. The mortality rates in urban areas were significantly higher than those in rural areas.
Table 2.
Mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma in 2017
| Sex | Deaths (× 103) |
Crude rate (1/105) |
ASMRC (1/105) |
ASMRW (1/105) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All | Both | 52 | 3.83 | 3.74 | 2.60 |
| Male | 32 | 4.67 | 4.54 | 3.30 | |
| Female | 20 | 2.97 | 2.91 | 1.93 | |
| Urban | Both | 29 | 4.43 | 4.35 | 2.97 |
| Male | 18 | 5.28 | 4.53 | 3.73 | |
| Female | 11 | 3.57 | 2.91 | 2.25 | |
| Rural | Both | 23 | 3.52 | 3.74 | 2.42 |
| Male | 14 | 4.35 | 4.53 | 3.09 | |
| Female | 9 | 2.66 | 2.91 | 1.77 |
ASMRC, age-standardized mortality rate adjusted by the Chinese standard population; ASMRW, age-standardized mortality rate adjusted by the world standard population
Age-specific mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma stratified by residence and sex
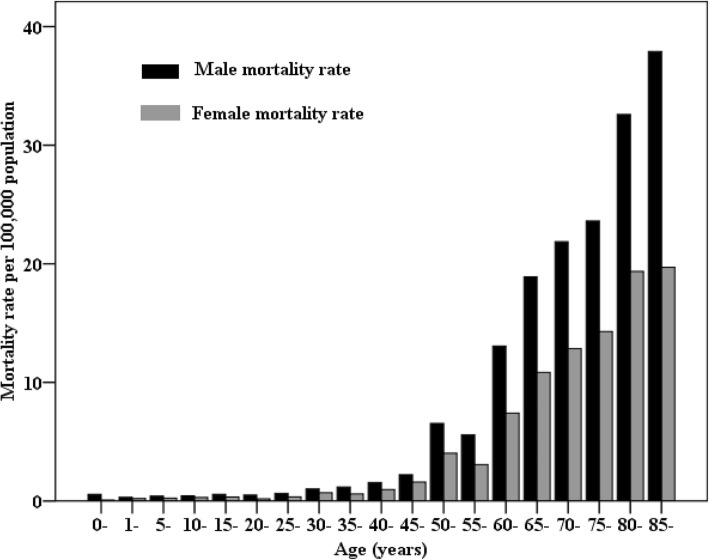
Higher mortality rates were observed in older individuals. Age-specific mortality rates showed an upward trend with age and reached a maximum in the age group of over 85 years (Table 3). Males had higher mortality rates than females in all age groups (Fig. 1). In terms of residence variation, age-specific mortality rates in urban areas were higher than those in rural areas after the age of 55 years. Males over 85 years of age in urban areas had the highest mortality rates.
Table 3.
Age-specific mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma, stratified by residence, 2017 (1/105)
| Age group | All areas | Urban areas | Rural areas | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Both | Male | Female | Both | Male | Female | Both | Male | Female | |
| 0–1 | 0.34 | 0.56 | 0.08 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.46 | 0.74 | 0.11 |
| 1–4 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 0.20 | 0.17 | 0.19 | 0.15 | 0.29 | 0.3 | 0.22 |
| 5–9 | 0.33 | 0.41 | 0.24 | 0.32 | 0.40 | 0.22 | 0.34 | 0.42 | 0.25 |
| 10–14 | 0.37 | 0.44 | 0.30 | 0.37 | 0.51 | 0.20 | 0.38 | 0.41 | 0.34 |
| 15–19 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.33 | 0.40 | 0.53 | 0.26 | 0.47 | 0.57 | 0.37 |
| 20–24 | 0.34 | 0.49 | 0.18 | 0.21 | 0.26 | 0.16 | 0.41 | 0.62 | 0.19 |
| 25–29 | 0.49 | 0.65 | 0.34 | 0.46 | 0.60 | 0.32 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.35 |
| 30–34 | 0.86 | 1.02 | 0.70 | 0.86 | 1.12 | 0.60 | 0.86 | 0.96 | 0.76 |
| 35–39 | 0.89 | 1.17 | 0.59 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.65 | 0.95 | 1.32 | 0.56 |
| 40–44 | 1.26 | 1.55 | 0.96 | 1.13 | 1.13 | 1.13 | 1.33 | 1.77 | 0.87 |
| 45–49 | 1.90 | 2.22 | 1.59 | 1.80 | 1.91 | 1.70 | 1.96 | 2.38 | 1.54 |
| 50–54 | 5.31 | 6.53 | 4.03 | 5.29 | 6.82 | 3.66 | 5.32 | 6.38 | 4.22 |
| 55–59 | 4.33 | 5.57 | 3.07 | 4.67 | 6.13 | 3.20 | 4.14 | 5.27 | 3.00 |
| 60–64 | 10.27 | 13.06 | 7.41 | 12.24 | 15.30 | 9.12 | 9.35 | 12.01 | 6.61 |
| 65–69 | 14.85 | 18.90 | 10.83 | 17.31 | 21.82 | 12.86 | 13.73 | 17.57 | 9.91 |
| 70–74 | 17.28 | 21.86 | 12.85 | 20.07 | 24.42 | 16.06 | 15.86 | 20.61 | 11.14 |
| 75–79 | 18.67 | 23.61 | 14.29 | 23.94 | 31.02 | 17.77 | 15.89 | 19.75 | 12.43 |
| 80–84 | 25.23 | 32.59 | 19.35 | 37.29 | 44.39 | 31.39 | 19.45 | 26.73 | 13.76 |
| 85+ | 26.69 | 37.90 | 19.70 | 43.76 | 60.33 | 32.72 | 18.64 | 26.66 | 13.81 |
Fig. 1.
Age-specific mortality of lymphoma and myeloma by sex in China, 2017
Age-specific mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma stratified by region
In total, Eastern China had the highest mortality rate (3.43/100,000), followed by Central China (3.10/100,000) and Western China (3.02/100,000). Upward trends with age were observed in all regions (Table 4). Western China had higher mortality rates in the age group of 0–1 years than Eastern China and Central China. Males over 85 years of age in Eastern China had the highest mortality rates.
Table 4.
Age-specific mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma by region, 2017 (1/105)
| Age group | Eastern China | Central China | Western China | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Both | Male | Female | Both | Male | Female | Both | Male | Female | |
| 0–1 | 0.30 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 0.31 | 0.57 | 0.00 | 0.43 | 0.54 | 0.31 |
| 1–4 | 0.20 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.25 | 0.36 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 0.33 | 0.38 |
| 5–9 | 0.32 | 0.34 | 0.29 | 0.27 | 0.33 | 0.20 | 0.43 | 0.63 | 0.23 |
| 10–14 | 0.31 | 0.28 | 0.34 | 0.44 | 0.60 | 0.24 | 0.38 | 0.45 | 0.31 |
| 15–19 | 0.32 | 0.36 | 0.28 | 0.51 | 0.67 | 0.33 | 0.53 | 0.65 | 0.40 |
| 20–24 | 0.27 | 0.35 | 0.17 | 0.34 | 0.47 | 0.21 | 0.45 | 0.74 | 0.16 |
| 25–29 | 0.49 | 0.72 | 0.26 | 0.52 | 0.67 | 0.38 | 0.46 | 0.48 | 0.44 |
| 30–34 | 0.84 | 0.94 | 0.73 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 0.65 | 1.00 | 1.27 | 0.72 |
| 35–39 | 0.97 | 1.28 | 0.65 | 0.97 | 1.35 | 0.59 | 0.68 | 0.84 | 0.52 |
| 40–44 | 1.27 | 1.35 | 1.19 | 1.06 | 1.39 | 0.73 | 1.52 | 2.06 | 0.95 |
| 45–49 | 1.81 | 1.99 | 1.63 | 1.77 | 2.05 | 1.50 | 2.23 | 2.77 | 1.68 |
| 50–54 | 4.64 | 5.79 | 3.43 | 5.69 | 6.98 | 4.36 | 6.08 | 7.34 | 4.74 |
| 55–59 | 4.87 | 6.13 | 3.59 | 4.16 | 5.55 | 2.76 | 3.61 | 4.62 | 2.60 |
| 60–64 | 11.56 | 14.54 | 8.54 | 9.36 | 12.14 | 6.51 | 9.33 | 11.84 | 6.72 |
| 65–69 | 16.78 | 21.57 | 12.12 | 14.72 | 18.99 | 10.44 | 11.87 | 14.49 | 9.23 |
| 70–74 | 18.94 | 24.18 | 14.00 | 15.99 | 21.21 | 10.81 | 16.24 | 18.95 | 13.59 |
| 75–79 | 20.16 | 25.38 | 15.69 | 18.15 | 22.14 | 14.47 | 16.53 | 22.42 | 11.21 |
| 80–84 | 28.52 | 36.38 | 22.69 | 23.92 | 30.54 | 18.29 | 19.95 | 27.91 | 13.17 |
| 85+ | 30.27 | 43.30 | 22.53 | 24.14 | 34.85 | 17.31 | 22.45 | 31.00 | 16.74 |
Trends in mortality of lymphoma and myeloma
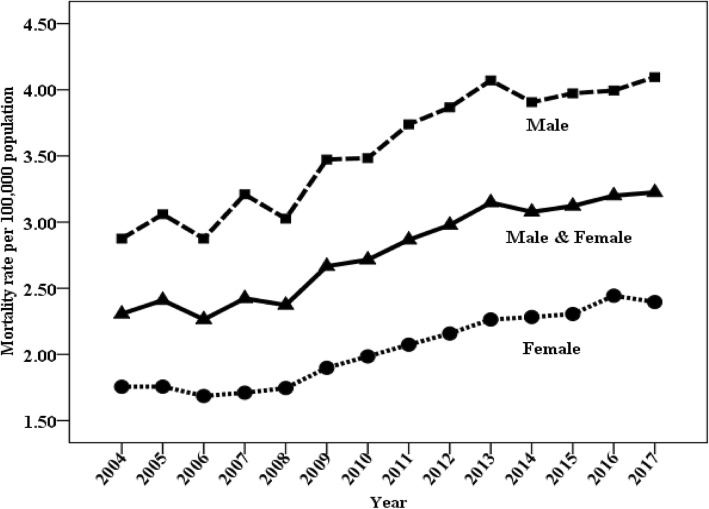
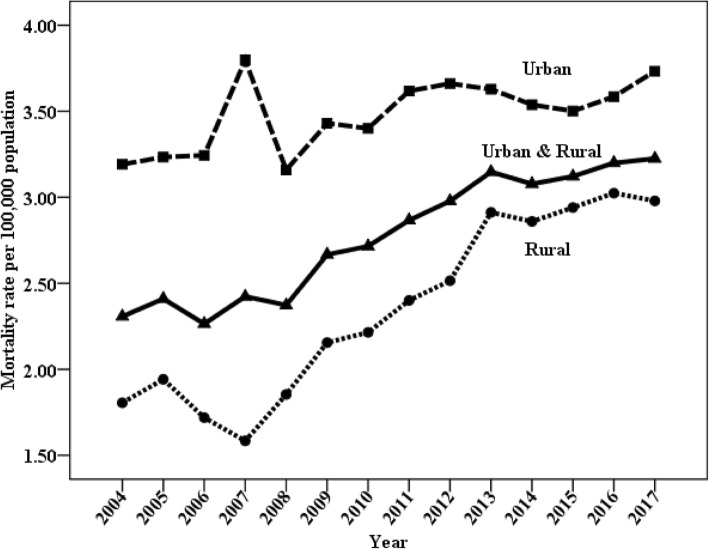
The temporal trends in mortality of lymphoma and myeloma by sex and residence over the study period (2004–2016) are illustrated in Figs. 2 and 3 and Table 5. The age-standardized mortality rates increased for both males and females (Fig. 2). Significant upward trends were observed in both urban and rural areas. Notably, the mortality rates in rural areas increased rapidly starting in 2007 (Fig. 3).
Fig. 2.
Trends in mortality of lymphoma and myeloma (age-standardized to the Chinese standard population) by sex: China, 2004 to 2017
Fig. 3.
Trends in mortality of lymphoma and myeloma (age-standardized to the Chinese standard population) by residence: China, 2004 to 2017
Table 5.
Trends in mortality of lymphoma and myeloma (age-standardized to the Chinese standard population) by sex and residence in China, 2004 to 2016
| Sex | Trend 1# | Trend 2# | Trend 3# | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | APC | Year | APC | Year | APC | ||
| All | Both | 2004–2016 | 4.5* | ||||
| Male | 2004–2016 | 4.4* | |||||
| Female | 2004–2006 | − 1.2 | 2006–2016 | 5.5* | |||
| Urban | Both | 2004–2016 | 2.3* | ||||
| Male | 2004–2016 | 1.9* | |||||
| Female | 2004–2016 | 2.9* | |||||
| Rural | Both | 2004–2016 | 6.8* | ||||
| Male | 2004–2016 | 6.7* | |||||
| Female | 2004–2007 | − 2.3 | 2007–2016 | 9.1* | |||
*The annual percentage change is significantly different from zero
#Each change in magnitude and/or direction of trend is listed separately with the years for which that trend was constant. Therefore, if only one trend is listed for 2004 through 2017, that trend was constant during the entire time period
Discussion
According to the statistics of GLOBOCAN 2018, produced by the International Agency for Research on Cancer, lymphoid neoplasms accounted for 7.2% of the 9.6 million cancer deaths worldwide in 2018, including 0.3% of deaths due to HL, 2.6% due to NHL, 1.1% due to multiple myeloma, and 3.2% due to leukemia [12]. Compared with the statistics of GLOBOCAN 2012 [13], both new cases and deaths associated with lymphoid neoplasms increased. For example, the estimated number of new NHL cases increased from 385,700 in 2012 to 509,590 in 2018, while deaths increased from 199,700 in 2012 to 248,724 in 2018. A report [14] from the National Central Cancer Registry of China (NCCRC) estimated that lymphoid neoplasms accounted for 2.1% (88,200 new cases) of all new cancer cases and 1.9% (52,100 deaths) of all cancer deaths in 2015. In our study, the estimated number of deaths associated with lymphoma and myeloma reached 52,000 in 2017 due to the growth and aging of the population, meaning that approximately 7.5% of deaths associated with lymphoid neoplasms worldwide occurred in China.
Combined factors such as age and sex may have an important impact on variations in mortality rate. As with many other cancers, the likelihood of an individual being diagnosed with lymphoma increases markedly with age [15], and adolescent and young adult patients have better survival rates [16], all of which result in higher mortality rates in older individuals. Moreover, males have higher mortality rates than females, with some explained risk factors, such as smoking and infections [17]. A study from the USA [3] demonstrated that the overall incidence rates of lymphoid neoplasms were 51% higher in males than in females, and black men had the lowest survival across lymphoid neoplasm subtypes. Similarly, a study from China [18] indicated that males had higher age-standardized incidence rates (4.89 vs. 3.49 per 100,000) and mortality rates (2.84 vs. 1.75 per 100,000) of lymphoid neoplasms using the world standard population. Consistent with previous reports, higher mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma were observed in males and older individuals in our study. In addition, geographical differences in mortality rates were observed, especially a higher mortality rate in the 0–1 year age group, which was observed in Western China due to an imbalance in socioeconomic development. Based on these disparities in disease burden in different specific populations, different strategies for disease prevention and control should be employed.
Compared with western countries, China had a lower disease burden of lymphoid neoplasms. In the European standard population, the age-standardized incidence and mortality rates of lymphoid neoplasms per 100,000 population in 2018 were 30.5 and 12.6, respectively [19]. In China, lower age-standardized incidence rates (4.18 per 100,000) and mortality rates (2.28 per 100,000) using the world standard population were estimated in 2015 [14]. However, the disease burden of lymphoid neoplasms has been rising in China over the last decade. In our study, the mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma increased annually by 4.5% during the period of 2004–2016, with increasing trends in both sexes across all areas. These upward trends may be explained partly by improvements in diagnostic procedures and changes in the classification of lymphoid neoplasms [1], but much of these trends may reflect an increase in deaths due to poor survival [20]. The prognosis of patients with lymphoid neoplasms was poor in China, with a 5-year relative survival rate of 38.3%, while it improved markedly, with a survival rate of 70% or higher, in European countries during the same period [21]. Similarly, the 5-year survival of adults with lymphoid neoplasms and children with lymphoma improved from 61.2% and 88.5% in 2000–2004 to 68.1% and 94.3% in 2010–2014 in the USA, respectively [21]. A study from the NCCRC [22] demonstrated that the age-standardized 5-year relative survival rates of lymphoid neoplasms increased by less than 5% in China (changing from 32.6% during 2003–2005 to 37.2% during 2012–2015). Therefore, further studies focused on critical factors affecting mortality, such as lifestyle and treatment models among different countries, should be executed.
Several factors contributed to the urban-rural discordance of mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma in China. Urban areas had higher incidence rates of lymphoid neoplasms than rural areas in China (4.7 per 100,000 vs. 3.4 per 100,000) [18]. Poor availability of medical services [23] and insufficient protection by healthcare insurance [24] also played important roles. There were substantial social and health inequalities between urban and rural areas in China [25]. Compared to urban residents, both rich and poor village residents were less likely to use outpatient services, with odds ratios (ORs) of 0.728 and 0.778, and were less likely to use inpatient health care, with ORs of 0.609 and 0.752, respectively [26]. Patients in rural areas had lower survival rates due to difficulty in diagnosis and delayed or reduced access to appropriate therapies, regardless of health service improvements [27]. Furthermore, rural migrants (approximately 220 million) living and working in urban areas but without gaining formal urban medical insurance created additional challenges for the provision of optimum health care [28]. Remarkable progress has been made by the Chinese government toward upgrading the health-care system. The insurance coverage increased from 29.7% in 2003 to 95.7% in 2011, while the average share of inpatient costs reimbursed from insurance increased from 14.4 to 46.9 [29]. However, there were still large challenges on the way to eliminating the disparities between urban and rural areas due to the vast population, large geographical span, and diverse cultures and socioeconomic groups [30]. These findings highlighted the need to increase medical service accessibility and affordability to modern diagnosis and treatment, particularly for rural areas of China.
Of note was an increase in mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma, especially a rapid increase since 2007 in rural areas. Between 2004 and 2016, the mortality rates increased by 4.5% for all areas, 2.3% for urban areas, and 6.8% for rural areas, respectively. Similar to our findings, a subnational analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2013 showed that the age-standardized mortality rates increased with changes of 1.3% for NHL and 7.3% for multiple myeloma from 1990 to 2013 in China [6]. These results could mainly be attributable to the increase of incidence. From 2006 to 2016, the age-standardized years lived with disability rates in China increased by 4.9% for HL, 59.4% for NHL, and 48.6% for multiple myeloma, respectively [2]. Moreover, the increase in mortality rates during the period of 2013–2017 may be interpreted partly by improvements in the CDC-DSP system. Since 2013, the number of surveillance points increased from 161 to 605, and the surveillance population increased from 6 to 24% of the Chinese population, which strengthened both nationally and regionally (i.e., eastern, central, and western; urban and rural), representative of the CDC-DSP system since 2013 [9].
The interpretation of our study has several limitations. First, the accuracy of the cause of death was not assessed when the mortality counts were extracted from the CDC-DSP database. Because of the difficulty in diagnosing lymphoid neoplasms, the rates in the present study may be underestimated, especially in rural areas. Second, the changes in CDC-DSP surveillance points and population coverage since 2013 should also be considered in a cautious interpretation of the mortality trends. Third, there was still room for improvement in the quality of the CDC-DSP data; such an improvement would modify our estimates but not bias our main findings.
Conclusions
This is the first study to present spatiotemporal variation in the mortality of lymphoma and myeloma in China using national data routinely collected from death certificates. Because the CDC-DSP system had a good national representativeness, with a coverage of 24.3% of the total Chinese population, our data determined the pattern of mortality rates of lymphoma and myeloma in China. Higher mortality rates were observed in males and in older individuals residing in urban areas. A rapid increase in mortality rates in rural areas was noted. The study results provided information on the disease burden of lymphoma and myeloma and allowed the monitoring of temporal trends in mortality in the Chinese population, which will be useful for policy-making with respect to the development of management strategies under circumstances of limited prevention measures.
Acknowledgements
We thank Lan Mi for statistical method support.
Funding
This research was supported by the Capital’s Funds for Health Improvement and Research (Grant No. 2018-1-2151). The funders of the study had no role in study design, data collection, data analysis, data interpretation, or writing of the report.
Availability of data and materials
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and, thus, are not publicly available. However, data are available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Abbreviations
- APC
Annual percentage change
- ASMRC
Age-standardized mortality rate China
- ASMRW
Age-standardized mortality rate world
- CDC-DSP
Center for Disease Control and Prevention’s Disease Surveillance Points System
- HL
Hodgkin lymphoma
- NCCRC
National Central Cancer Registry of China
- NHL
Non-Hodgkin lymphoma
Authors’ contributions
WL conceived and designed the study, analyzed the data, and drafted and revised the paper. JL prepared and analyzed the data. XW, YS, JM, and MZ drafted and revised the paper. LW and JZ designed the study, interpreted the results, and drafted and revised the paper. All authors provided critical comments on the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Weiping Liu, Email: dreaming2217@126.com.
Jiangmei Liu, Email: liujiangmei@ncncd.chinacdc.cn.
Yuqin Song, Email: songyuqin622@163.com.
Xiaopei Wang, Email: wangxiaopei@pkuih.edu.cn.
Maigeng Zhou, Email: maigengzhou@126.com.
Lijun Wang, Phone: 86 10 63040442, Email: wanglijun@ncncd.chinacdc.cn.
Jun Ma, Phone: 86 0451 84694406, Email: majun0322@126.com.
Jun Zhu, Phone: 86 10 88196596, Email: zhu-jun2017@outlook.com.
References
- 1.Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Pileri SA, et al. The 2016 revision of the World Health Organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood. 2016;127:2375–2390. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-01-643569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Global Burden of Disease Cancer Collaboration. Fitzmaurice C, Akinyemiju TF, et al. Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2016: a systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol. 2018;4(11):1553–1568. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.2706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Teras LR, DeSantis CE, Cerhan JR, Morton LM, Jemal A, Flowers CR. 2016 US lymphoid malignancy statistics by World Health Organization subtypes. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:443–459. doi: 10.3322/caac.21357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mokdad AH, Dwyer-Lindgren L, Fitzmaurice C, et al. Trends and patterns of disparities in cancer mortality among US counties, 1980-2014. JAMA. 2017;317(4):388–406. doi: 10.1001/jama.2016.20324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lee H, Park HJ, Park EH, et al. Nationwide statistical analysis of lymphoid malignancies in Korea. Cancer Res Treat. 2018;50:222–238. doi: 10.4143/crt.2017.093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhou M, Wang H, Zhu J, et al. Cause-specific mortality for 240 causes in China during 1990-2013: a systematic subnational analysis for the global burden of disease study 2013. Lancet. 2016;387:251–272. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00551-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhou M, Wang H. National and regional under-5 mortality in China in the past two decades. Lancet Glob Health. 2017;5:e121–e122. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(16)30360-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wang Y, Li X, Zhou M, et al. Under-5 mortality in 2851 Chinese counties, 1996-2012: a subnational assessment of achieving MDG 4 goals in China. Lancet. 2016;387(10015):273–283. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00554-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Liu S, Wu X, Lopez AD, et al. An integrated national mortality surveillance system for death registration and mortality surveillance, China. Bull World Health Organ. 2016;94:46–57. doi: 10.2471/BLT.15.153148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wang L, Wang LJ, Cai Y, Ma LM, Zhou MG. Analysis of under-reporting of mortality surveillance from 2006 to 2008 in China. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2011;45(12):1061–1064. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Guo K, Yin P, Wang L, et al. Propensity score weighting for addressing under-reporting in mortality surveillance: a proof-of-concept study using the nationally representative mortality data in China. Popul Health Metrics. 2015;13:16. doi: 10.1186/s12963-015-0051-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. doi: 10.3322/caac.21492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65(2):87–108. doi: 10.3322/caac.21262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen W, Zheng R, Baade PD, et al. Cancer statistics in China, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66:115–132. doi: 10.3322/caac.21338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Smith A, Crouch S, Lax S, et al. Lymphoma incidence, survival and prevalence 2004-2014: sub-type analyses from the UK’s Haematological Malignancy Research Network. Br J Cancer. 2015;112(9):1575–1584. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2015.94. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Blum KA, Keller FG, Castellino S, Phan A, Flowers CR. Incidence and outcomes of lymphoid malignancies in adolescent and young adult patients in the United States. Br J Haematol. 2018;183(3):385–399. doi: 10.1111/bjh.15532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Islami F, Chen W, Yu XQ, et al. Cancer deaths and cases attributable to lifestyle factors and infections in China, 2013. Ann Oncol. 2017;28:2567–2574. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdx342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Chen W, Sun K, Zheng R, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality in China, 2014. Chin J Cancer Res. 2018;30:1–12. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2018.01.01. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ferlay J, Colombet M, Soerjomataram I, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers in 2018. Eur J Cancer. 2018;103:356–387. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2018.07.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.GBD 2016 Causes of Death Collaborators Global, regional, and national age-sex specific mortality for 264 causes of death, 1980-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. 2017;390:1151–1210. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32152-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Allemani C, Matsuda T, Di Carlo V, et al. Global surveillance of trends in cancer survival 2000-14 (CONCORD-3): analysis of individual records for 37 513 025 patients diagnosed with one of 18 cancers from 322 population-based registries in 71 countries. Lancet. 2018;391:1023–1075. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)33326-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Zeng H, Chen W, Zheng R, et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003-15: a pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries. Lancet Glob Health. 2018;6:e555–e567. doi: 10.1016/S2214-109X(18)30127-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Huang C, Liu CJ, Pan XF, et al. Correlates of unequal access to preventive care in China: a multilevel analysis of national data from the 2011 China Health and Nutrition Survey. BMC Health Serv Res. 2016;16:177. doi: 10.1186/s12913-016-1426-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang J, Chen L, Ye T, et al. Financial protection effects of modification of China’s new cooperative medical scheme on rural households with chronic diseases. BMC Health Serv Res. 2014;14:305. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-14-305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jian W, Chan KY, Reidpath DD, et al. China's rural-urban care gap shrank for chronic disease patients, but inequities persist. Health Aff (Millwood) 2010;29(12):2189–2196. doi: 10.1377/hlthaff.2009.0989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhu D, Guo N, Wang J, et al. Socioeconomic inequalities of outpatient and inpatient service utilization in China: personal and regional perspectives. Int J Equity Health. 2017;16(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12939-017-0706-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zeng H, Zheng R, Guo Y, et al. Cancer survival in China, 2003-2005: a population-based study. Int J Cancer. 2015;136(8):1921–1930. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Peng X. China's demographic history and future challenges. Science. 2011;333(6042):581–587. doi: 10.1126/science.1209396. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Meng Q, Xu L, Zhang Y, et al. Trends in access to health services and financial protection in China between 2003 and 2011: a cross-sectional study. Lancet. 2012;379(9818):805–814. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)60278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Goss PE, Strasser-Weippl K, Lee-Bychkovsky BL, et al. Challenges to effective cancer control in China, India, and Russia. Lancet Oncol. 2014;15(5):489–538. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(14)70029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and, thus, are not publicly available. However, data are available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention.