Abstract
Human CLCN7 encodes voltage-gated chloride channel 7 (ClC-7); mutations of CLCN7 lead to osteopetrosis which is characterized by increased bone mass and impaired osteoclast function. In our previous clinical practice, we noticed that osteopetrosis patients with CLCN7 mutations had some special deformities in craniofacial morphology and tooth dysplasia. It is unclear whether these phenotypes are the typical features of CLCN7 involved osteopetrosis and whether ClC-7 could regulate the development of craniofacial bone and tooth in some signaling pathways.
Methods: First, we collected 80 osteopetrosis cases from the literature and compared their craniofacial and dental phenotypes. Second, four osteopetrosis pedigrees with CLCN7 mutations were recruited from our clinic for gene testing and clinical analysis of their craniofacial and dental phenotypes. Third, we used a zebrafish model with clcn7 morpholino treatment to detect the effects of ClC-7 deficiency on the development of craniofacial and dental phenotypes. General observation, whole mount alcian blue and alizarin red staining, whole mount in situ hybridization, scanning electron microscope observation, lysoSensor staining, Q-PCR and western blotting were performed to observe the in vivo characteristics of craniofacial bone and tooth changes. Fourth, mouse marrow stromal cells were further primarily cultured to detect ClC-7 related mRNA and protein changes using siRNA, Q-PCR and western blotting.
Results: Over 84% of osteopetrosis patients in the literature had some typical craniofacial and tooth phenotypes, including macrocephaly, frontal bossing, and changes in shape and proportions of facial skeleton, and these unique features are more severe and frequent in autosomal recessive osteopetrosis than in autosomal dominant osteopetrosis patients. Our four pedigrees with CLCN7 mutations confirmed the aforementioned clinical features. clcn7 knockdown in zebrafish reproduced the craniofacial cartilage defects and various dental malformations combined the decreased levels of col10a1, sp7, dlx2b, eve1, and cx43. Loss of clcn7 function resulted in lysosomal storage in the brain and jaw as well as downregulated cathepsin K (CTSK). The craniofacial phenotype severity also presented a dose-dependent relationship with the levels of ClC-7 and CTSK. ClC-7/CTSK further altered the balance of TGF-β/BMP signaling pathway, causing elevated TGF-β-like Smad2 signals and reduced BMP-like Smad1/5/8 signals in clcn7 morphants. SB431542 inhibitor of TGF-β pathway partially rescued the aforementioned craniofacial bone and tooth defects of clcn7 morphants. The ClC-7 involved CTSK/BMP and SMAD changes were also confirmed in mouse bone marrow stromal cells.
Conclusion: These findings highlighted the vital role of clcn7 in zebrafish craniofacial bone and tooth development and mineralization, revealing novel insights for the causation of osteopetrosis with CLCN7 mutations. The mechanism chain of ClC-7/CTSK/ TGF-β/BMP/SMAD might explain the typical craniofacial bone and tooth changes in osteopetrosis as well as pycnodysostosis patients.
Keywords: osteopetrosis, ClC-7, craniofacial bone, tooth, SB431542
Introduction
Osteopetrosis is a group of genetic disorders characterized by increased bone mass and density due to defective bone resorption 1. Currently, the candidate genes of osteopetrosis include IKBKG, CLCN7, OSTM1, TCIRG1, PLEKHM1, CAII, RANK, and RANKL 1,2. Human CLCN7 encoding voltage-gated chloride channel 7 (ClC-7) is one of the key molecules involved in osteopetrosis 2-5. In our previous study, we reported two osteopetrosis patients with CLCN7 mutations, who had impacted teeth, enamel dysplasia, malformed teeth, altered tooth eruption and root dysplasia 6-8. A few years later, our group and other groups showed that Clcn7 deficiency displayed dental defects in tooth eruption or root formation 7,9-11. All of these findings provided new insights to further understand the pathological mechanisms of CLCN7-related osteopetrosis.
According to our previous clinical observations and some other references 12, craniofacial bone dysplasia is quite common in osteopetrosis patients. It is unclear whether these phenotypes are the typical features of CLCN7 involved osteopetrosis and whether or how these phenotypes were caused by ClC-7 deficiency.
Some signaling molecules, including BMP, TGF-β1, FGF, Hedgehog, and Wnt, are involved in the regulation of craniofacial pattern 13-17. The balance between BMP2 and TGF-β1 signaling pathway could be affected by cathepsin K (CTSK), which is one of the important factors for osteoclastic function and development 18. Several studies reported that ClC-7 deficiencies in humans and mice disrupted osteoclastic function and bone resorption 19-22, and resulted in decreased lysosome luminal Cl- concentration 23,24. Hence, in this study, we wondered if ClC-7 could influence CTSK by changing the local luminal condition, which affects the downstream balance between BMP2 and TGF-β1. This remains to be a key mechanism by which ClC-7 affects craniofacial bone and tooth development.
Methods
Literature review of craniofacial and dental phenotypes in osteopetrosis
Related osteopetrosis references were searched to summarize the general craniofacial and dental phenotypes in osteopetrosis patients. The following keywords were used to search the references (1965 to present) from PubMed: osteopetrosis, osteomyelitis, mandible, maxilla, tooth, craniofacial, skull, and calvarium. The 58 papers in PubMed matched the searching criteria and only those references showing detailed clinical craniofacial and dental phenotypes were included in our analysis. Finally, 80 osteopetrosis cases from 41 references were included to summarize the general characteristics of abnormal craniofacial and dental phenotypes. The genetic background for most of the cases was not mentioned (Supplementary references).
Pedigree analysis and DNA sequencing
Five osteopetrosis patients with CLCN7 mutations from four families were recruited in the Clinic of Oral Rare Diseases and Genetic Diseases, School of Stomatology at the Fourth Military Medical University (Xi'an, China). The patients were clinically examined and detected using different X-ray techniques including panoramic radiograph, CT, or RVG dental film as previously described 6. The patients diagnosed with osteopetrosis demonstrated increased bone mass and frequent fractures. This study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the School of Stomatology, Fourth Military Medical University (Approval No. 2012-2-8). Informed consent was obtained from the patients and their family members. Total genomic DNA of patients and their family members was obtained from whole blood 25. The CLCN7 gene was amplified using polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for sequencing as described previously 26. Sequence maps were analyzed using Sequencher software (version 5.0, Gene Codes Corporation, Ann Arbor, MI, USA). The new finding variants were identified in at least fifty healthy controls.
Zebrafish husbandry
Embryos and adult AB strain zebrafish were raised and maintained 27. Embryos were incubated with 0.004% 1-phenyl 2-thiourea (PTU) to avoid pigmentation. Euthanasia and handling of zebrafish in the experiments were performed according to the policies of Institutional Animal Care of the School of Stomatology, the Fourth Military Medical University.
Morpholino injection and rescue experiments
The standard control morpholino oligonucleotide (MO) (5' - CCTCTTACCTCAGTTACAATTTATA-3') and a translation blocking MO (tbMO) by the sequence (5'-CCTGCTAAGCAGAGAACTACTGCGT-3') targeting -31 to -55 in exon 1 of zebrafish clcn7 were obtained from Gene Tools, LLC (Philomath, OR). A 1 nL of 0.25 nM clcn7 MO was injected into the embryos of zebrafish at one-cell stage using a gas-driven microinjector. The efficiency of MO was evaluated by measuring the expression of clcn7 as assessed by Q-PCR and phenotypic penetrance. The injected embryos were cultured in the embryo medium and harvested at 3 dpf (days post-fertilization) or 5 dpf for the following experiments 28.
Full-length human CLCN7 cDNA was amplified and subcloned into vector pCS2-EGFP. Sequencing confirmed that all the amplified sequences synthesized a complete open reading frame with EGFP sequence. The constructed vectors were digested using Not I, and the mRNAs were synthesized in vitro using mMESSAGE Sp6 transcription kit (Ambion, Austin, Texas, USA). MO and mRNA were co-injected into zebrafish embryos of one-cell stage. Emission fluorescence of EGFP and phenotype was observed under a fluorescence microscope (Leica M165 FC, Heidelberger, Germany).
Qualitative transcript analysis
Total RNA was extracted from pooled 0.75 hpf (hours post-fertilization), 4 hpf, 6 hpf, 12 hpf, 1 dpf, 2 dpf, 3 dpf and 4 dpf larvae (n = 50) using Trizol reagent (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, USA). The qualities of the isolated RNA were tested as described previously 29. cDNA was reverse-transcribed using PrimeScriptTM RT Master Mix according to the manufacturer's protocol (TaKaRa, Dalian, China). Q-PCR was performed as described 30 using specific primers listed in Table S1. The relative expression levels were calculated using the comparative threshold cycle (∆∆CT) method.
Whole-mount alcian blue and alizarin red staining
To detect the morphological changes of tooth and craniofacial structures, 5 dpf zebrafish embryos were collected and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight. The cartilages and mineralized tissues were stained using alcian blue and alizarin red as previously described 26. Then, the embryos were imaged using a Leica M205 FC Stereomicroscope (Leica Microsystems Nussloch GmbH, Heidelberger, Germany). Phenotypes were quantitatively analyzed by evaluating the length of body, head, ceratohyal and palatoquadrat, the width of head and Meckel´s cartilage, the distance between Meckel's cartilage and ceratohyal, and the ceratohyal angle. The amount of calcification was determined according to the intensity of red staining from the attachment point of 4V1 tooth in the fifth ceratobranchial arches (cb5) of 5 dpf larvae using the NIH ImageJ software (Wayne Rasband, NIH, USA).
In situ hybridization
Embryos were collected and fixed in fresh 4% paraformaldehyde, dehydrated in methanol and stored at -20 °C until use. In situ probe primers targeting Sp7 transcription factor (sp7) (also known as osterix), α1 chain of collagen type X (col10a1), connexin 43 (cx43), distal-less homeobox 2b (dlx2b), and even-skipped-like1 (eve1) were synthesized and listed in Table S2. All probes were amplified from cDNA derived from 2 dpf embryos and subcloned into pEASY-T3 (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China). In situ probe synthesis was performed using Digoxigenin RNA Labeling Kit (SP6/T7, Roche Diagnostics, Mannheim, Germany). Whole-mount in situ hybridization (WISH) was performed using the standard procedure 31. Embryos were mounted into glycerin, and imaged using Leica M205 FC Stereomicroscope (Leica Microsystems Nussloch GmbH, Heidelberger, Germany).
Scanning electron microscope observation
Zebrafish larvae at 5 dpf were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight and stained by alcian blue and alizarin red. After that, the tooth and cb5 were isolated and incubated with 2% sodium hypochlorite for 2 min. The ultrastructure of zebrafish teeth was observed by scanning electron microscope (HITACHI S-4800, Tokyo, Japan) 27.
Western blot
A total of 50 embryos from each group were collected at 3dpf. A 15 μg of protein per sample was loaded into 10% SDS-PAGE gel. The following primary antibodies were used: rabbit anti-phospho-SMAD2 (Ser465/467) (138D4) monoclonal antibody (1/500, Cell Signaling, Boston, USA), rabbit anti-SMAD2 (D43B4) monoclonal antibody (1:500, Cell Signaling, Boston, USA), rabbit anti-phospho-SMAD1 (Ser463/465)/SMAD5 (Ser463/465)/SMAD9 (Ser465/ 467) (D5B10) monoclonal antibody (1:1000, Cell Signaling, Boston, USA), rabbit anti-SMAD1/5/9 (ab66737) polyclonal antibody (1:500, Abcam, Cambridge, England), rabbit anti-CTSK polyclonal antibody (1:500, Proteintech, Chicago, USA ), and mouse anti-GAPDH monoclonal antibody (1:1000, Sigma, St. Louis, Missouri, USA). Secondary antibodies included horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated goat anti-mouse and goat anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (Cowbio, Beijing, China). Chemiluminescence signals were detected by ChemiDoc MP (Bio RAD, California, USA). Signals were quantified with ImageJ (Wayne Rasband, NIH, USA).
LysoSensor staining
Live 3 dpf embryos were incubated with 1 μM LysoGreen (KeyGen Biotech, Nanjing, China) in embryo media for 30 min at 28.5 °C in dark. Embryos were then rinsed three times using fresh embryo media, and observed by using fluorescence microscopy (Leica M165 FC, Heidelberger, Germany).
Primary culture of mouse bone marrow stromal cells (BMSCs) and Clcn7 siRNA transfection
Six-week-old male Balb/c mice were scarified by cervical dislocation. BMSCs were flushed from the femur and tibia, and then were cultured with α-MEM (Gibico, Grand Island, NY, USA) medium containing 20% FBS (Hyclone, logan, Utah, USA). The protocol has been described in our previous studies 32.
The small interfering RNA (siRNA) duplexes targeting the mouse Clcn7 gene was designed and synthesized by GenePharma (Shanghai, China) according to GenBank™ (NM_011930.3). The sequences of Clcn7 siRNA were as follows: sense, 5'-GAGGAGGAAAGACGAAUCATT-3'; antisense, 5'- UGAUUCGUCUUUCCUCCUCTT-3'. The control siRNA was used as the following: sense, 5'-UUCUCCGAACGUGUCACGUTT-3'; antisense, 5'-ACGUGACACGUUCGGAGAATT-3'.
The 2nd passage BMSCs that reached up to 80% confluence were transfected with Clcn7 siRNA or control siRNA using lipofectin 2000 (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, USA). After 48 h, the cells were collected for Q-PCR and western blot analysis. The primers were listed in Table S1.
Drug Treatments
SB431542 (Selleck, Houston, USA), an effective inhibitor of the canonical TGF-β pathway, was dissolved at a concentration of 10 µM in DMSO. Control MO or clcn7 MO was injected into zebrafish embryos at one-cell stage. Then, 10 µM SB431542 was added at 14- to 15-somites stage and equal amount of DMSO was used as control. The culture medium was changed every 48 h and 5 dpf embryos were used for whole-mount alcian blue and alizarin red staining.
Results
Clinical craniofacial and dental characteristics of osteopetrosis patients
Among the 80 reviewed osteopetrosis cases, there were 51 autosomal recessive osteopetrosis (ARO) and 29 autosomal dominant osteopetrosis (ADO) patients, respectively. The typical craniofacial features of these osteopetrosis patients included macrocephaly, trapezoidal shape of head, frontal bossing, changes in the shape and proportions of facial skeletons and abnormal lateral and superior orbital walls. X-ray of calvarium showed thickened and three-layer calvarium, or hair-on-end appearance. Absence or poor pneumatization of sinuses, nasal obstruction and hypertelorism were commonly observed in the middle of the face and sinuses. Mandibular malformation was characterized by mandibular hypoplasia, widened and deepened mandible with increased gonial angle and short mandibular body. The abnormalities associated with tooth included malformed roots and crowns, missing teeth, poorly calcified teeth, abnormal pulp spaces, absence of tooth buds, caries, and enamel dysplasia. All of the above changes were more frequently observed in ARO than in ADO (Table 1). Other craniofacial abnormalities included osteomyelitis, necrotic bone and fistulae. The ratios of osteomyelitis in ARO and ADO were 47% and 34%, respectively.
Table 1.
Summary of craniofacial and tooth abnormalities in osteopetrosis patients from literature review.
| Abnormalities | ARO (cases, %) |
ADO (cases, %) |
Total (cases, %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tooth | 45/51 (88%) | 22/29 (76%) | 67/80 (84%) |
| Mandible | 33/51 (65%) | 9/29 (31%) | 42/80 (53%) |
| Middle of face and sinuses | 28/51 (55%) | 8/29 (28%) | 36/80 (45%) |
| Osteomyelitis | 24/51 (47%) | 10/29 (34%) | 34/80 (43%) |
| Fistulae | 13/51 (26%) | 6/29 (21%) | 19/80 (24%) |
| Calvarium | 32/51 (63%) | 9/29 (31%) | 41/80 (51%) |
| Frontal bossing | 28/51 (55%) | 6/29 (21%) | 34/80 (43%) |
| Shape and proportion of the facial skeleton | 38/51 (75%) | 13/29 (45%) | 51/80 (64%) |
| Hearing | 18/51 (35%) | 5/29 (17%) | 23/80 (29%) |
ARO: autosomal recessive osteopetrosis, ADO: autosomal dominant osteopetrosis.
Craniofacial and dental characteristics of osteopetrosis patients with CLCN7 mutations
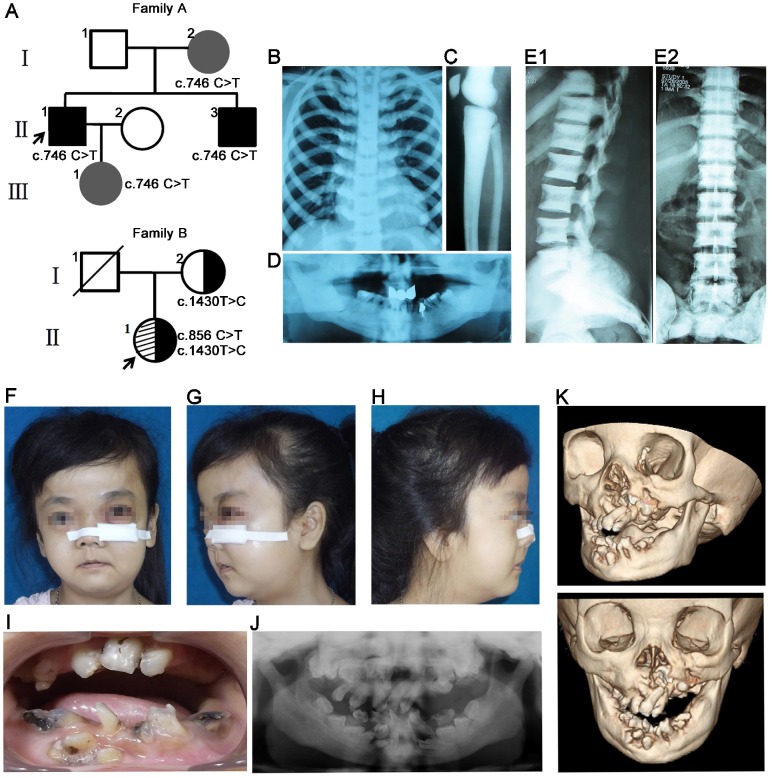
Family A presented an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance (Figure 1A). The proband II1 was diagnosed with osteopetrosis at the age of four. His major clinical symptoms included multiple fractures, anemia and interventricular septal defect, malocclusion (Figure 1D), mandibular osteomyelitis, facial bone dysplasia, and increased bone mineral density (Figure 1B-C). The proband carried c.746C>T (p. Pro477Leu) mutation in CLCN7 gene. His brother (II3) showed increased bone mineral density of the spine without other obvious symptoms and craniofacial malformations (Figure 1E1, E2). His mother (I2) and daughter (III1) carried the same mutation, but showed no obvious clinical symptoms.
Figure 1.
Pedigree and clinical examinations. (A) Pedigree maps. Family A presented an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance with c.746C>T mutation in CLCN7 gene. Black and grey represented severe phenotypes and no complaint of symptoms, respectively. The proband (II1) in family B carried compound heterozygous mutations in CLCN7 gene (c.856C>T; c.1430T>C) and the variant c.1430T>C in exon 16 was inherited from her mother. (B-D) Radiographic images of II1 in family A. Increased bone density in chest (B) and long bones (C). Malformation of craniofacial bones and tooth abnormalities in orthopantomography of II1 (D). (E1-E2) Radiographic images of II3 in family A. Sandwich vertebral changes. (F-K) Clinical images of individual II1 in family B. (F-H) Typical craniofacial deformities including macrocephaly, frontal bossing, and changes in shape and proportions of facial skeleton. Osteomyelitis and fistulae in the left facial bones. (I-J) Intraoral photography and orthopantomography showed malocclusion and tooth malformation. (K) Hypoplasia of facial skeletons from CT images.
The proband (II1) in family B was 29 years old. Her radiographs revealed a general increase of bone density in the jaws, clavicle and ribs. Her major symptoms included delayed growth rate, short stature, multiple bone fractures and severe anemia. The main craniofacial features included recurrent osteomyelitis in the facial region, malocclusion, maxillofacial and mandiblular dysplasia, macrocephaly and frontal bossing (Figure 1F-K). The proband presented compound heterozygous mutations in CLCN7 gene (c.856C>T, p. Arg286Trp; c.1430T>C, p. Leu 477 Pro) and the variant c.1430T>C in exon 16 was inherited from her mother (Figure 1A). Her mother reported no obvious clinical symptoms. Detailed information about family C and family D was reported previously 6, and the two probands have typical craniofacial and tooth features including osteomyelitis and unerupted teeth with root dysplasia.
To sum up, the craniofacial and dental features in the four pedigrees with CLCN7 mutations, three cases (II1 in family A, family B and family C, respectively) presented typical craniofacial features of osteopetrosis such as macrocephaly, frontal bossing, and changes in shape and proportions of facial skeleton. The cases belonged to intermediate autosomal osteopetrosis (IRO) or severe ADO type II (ADO II), and their craniofacial features matched the general osteopetrosis analysis results. Meanwhile, clinical variations, even in a pedigree with the same CLCN7 mutation, were observed, which were consistent with the previous report 33. More details of craniofacial and dental features in the four pedigrees were presented in Table 2.
Table 2.
Information of individuals with CLCN7 mutations.
| Family | No. | DNA Nucleotide Change (NM_001287.5) |
Predicted Protein Change (NP_001278.1) | Genotype | Subtype | Radiographic changes | Anemia | Craniofacial Phenotypes | Dental Phenotypes | Age at diagnosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | I2 | c.746C>T | p.Pro249>Leu | heterozygous | asymptomatic | mild | absent | absent | absent | N/A |
| II1 | c.746C>T | p.Pro249>Leu | heterozygous | ADO II | serve | moderate | moderate | moderate | 4 years old | |
| II3 | c.746C>T | p.Pro249>Leu | heterozygous | ADO II | serve | absent | mild | mild | 7 years old | |
| III1 | c.746C>T | p.Pro249>Leu | heterozygous | asymptomatic* | mild | absent | absent | absent | N/A | |
| B | I2 | c.1430T>C | p.Leu477Pro | heterozygous | asymptomatic | N/A | absent | absent | N/A | N/A |
| II1 | c.856C>T; c.1430T>C | p.Arg286Trp; p.Leu477Pro | compound heterozygous | IRO | severe | severe | severe | severe | 3-4 years old | |
| C | I2 | c.1409C>T | p.Pro470Leu | heterozygous | asymptomatic | N/A | absent | absent | N/A | N/A |
| II1 | c.1409C>T | p.Pro470Leu | homozygous | IRO | severe | severe | severe | severe | 6-7 years old | |
| D | II1 | c.856C>T | p.Arg286Trp | heterozygous | ADO II | moderate | absent | moderate | moderate | 6 years old |
N/A: not available; * polydactyly; IRO: intermediate autosomal osteopetrosis; ADO II: autosomal dominant osteopetrosis, type II.
Spatial and temporal expression of clcn7 in early zebrafish development
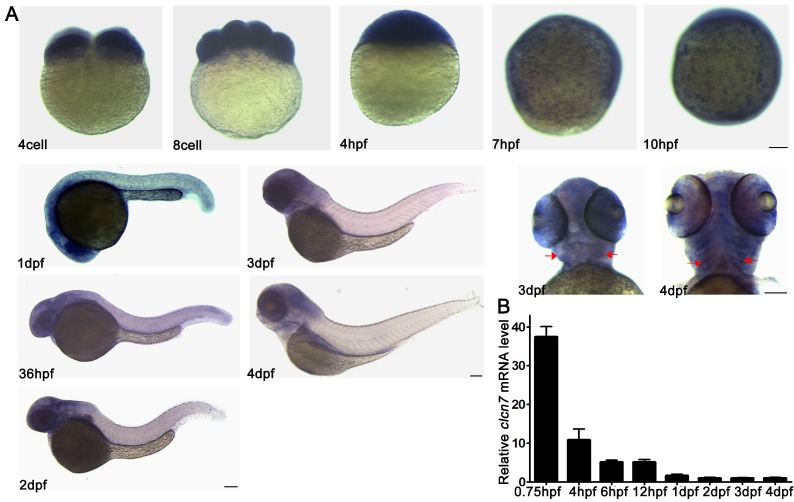
As shown in Figure 2A, the maternal mRNA signals of clcn7 were detected during the cleavage stage of the embryos (4 cell, 8 cell), and then ubiquitously expressed during the blastula period (4 hpf). Expression of clcn7 was confined to the enveloping layer (EVL) surrounding the embryo during the gastrula and bud stages (7 hpf, 10 hpf). The positive expression location of clcn7 was present in the head including brain, eye and jaw from 1 dpf to 4 dpf. An intensive expression was also found in the ceratobranchial arches at 4 dpf. The consistent transcript level of clcn7 was confirmed by Q-PCR (Figure 2B). This expression pattern suggested that clcn7 might be involved in the development of brain, eye or craniofacial bone.
Figure 2.
Spatial and temporal expression patterns of clcn7 during zebrafish early development. (A) WISH results. clcn7 was detected during cleavage stage (4 cell, 8 cell) in whole cells at blastula stage (4 hpf), especially in the enveloping layer at gastrula and bud stages (7 hpf, 10 hpf) in the head of embryos from 1dpf to 4dpf. Strong signaling appeared in pharyngeal arches from the ventral portion (3 dpf, 4 dpf). (B) Q-PCR results of clcn7. The red arrow indicates pharyngeal arches. dpf: days post-fertilization. hpf: hours post-fertilization. Error bars represent standard deviation. Each experiment was repeated at least three times. Scale bars: 100 μm.
ClC-7 deficiency causes zebrafish craniofacial defects
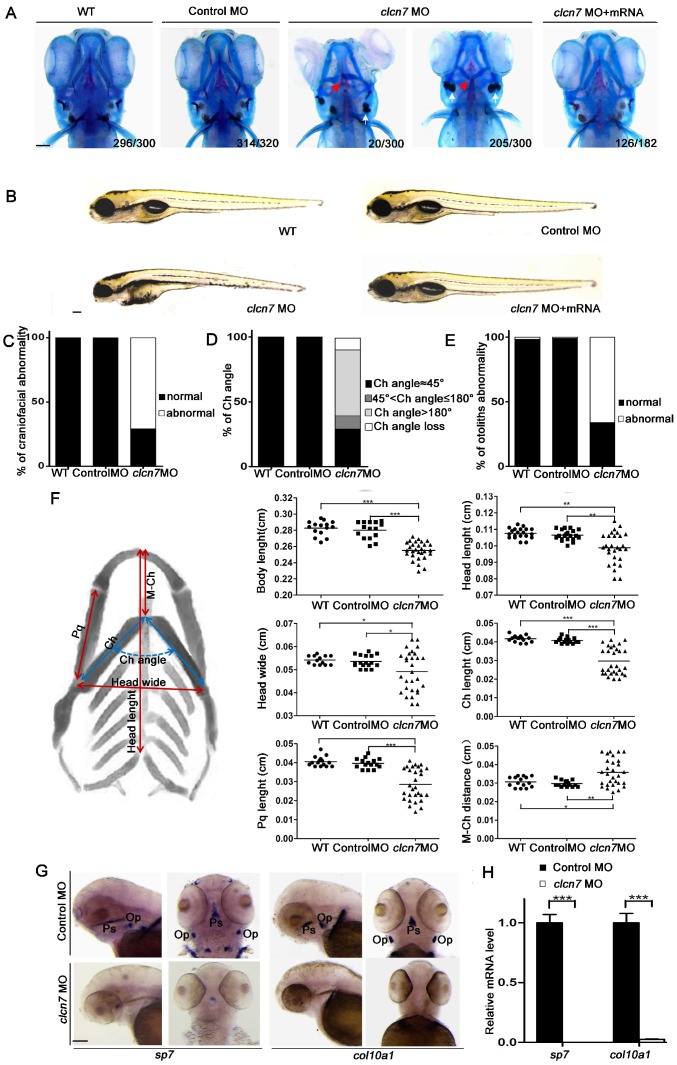
According to our clinical data analysis, ARO and ADO II cases with CLCN7 mutations showed specific malformations of craniofacial bones and mandibles. Consistently, knockdown of clcn7 by morpholino in zebrafish embryos resulted in shorter body, smaller head and craniofacial abnormalities when compared with control, MO-injected embryos (Figure 3A-B). To evaluate the efficiency of MO, CLCN7 mRNA containing clcn7 MO target sequence were co-injected into embryos, and the results showed rescuing of craniofacial phenotypes (Figure 3A-B). These data indicated that clcn7 was required for patterning of zebrafish craniofacial skeleton.
Figure 3.
Craniofacial bone and cartilage abnormalities in clcn7 morphants. (A) Craniofacial phenotype comparison between control and clcn7 morphants. Cranial cartilages (blue) and mineralized bones (red) were stained with alcian blue and alizarin red in control and clcn7 morphants at 5 dpf, respectively. (A-C) Compared to WT and Control embryos, clcn7 morphants showed more malformed craniofacial skeletons, and clcn7 mRNA rescued the abnormalities in craniofacial region. (D, E) Abnormal ceratohyal (Ch) angle and altered location of otolith in clcn7 morphants. (F) Quantitative analysis of a series of changes of phenotypic indexes. clcn7 morphants showed obvious changes in the pattern of craniofacial structure. (G) WISH analysis showed the abolished expression of sp7 and col10a1 in cranial skeleton, most notably in the parasphenoid (Ps) and opercle (Op) bones in clcn7 morphants at 3 dpf. (H) Q-PCR analysis confirmed the reduced level of sp7 and col10a1. For A-E, WT n=300, Control MO n=320, clcn7 MO n=300, clcn7 MO + mRNA n=182. For H: Control MO n=50, clcn7 MO n=50. The red arrow indicates abnormal Ch angle, and the white arrow points to abnormal otolith. Ch: ceratohyal. M: Meckel's. Op: opercle. Pq: palatoquadrate. Ps: parasphenoid. WT: wide type. Error bar represents the SD. The experiment was repeated at least thrice with the same conditions. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm.
There were a series of craniofacial cartilage defects in clcn7 morphants, including altered ceratohyal (Ch) angle (Figure 3A, C-D), increased distance from Meckel's cartilage (M) to Ch and shorter length of Ch and palatoquadrate (Pq) (Figure 3F), which may contribute to shorter head. In contrast to control morphants, clcn7 morphants displayed the defects or even loss of ceratobranchial arches (Figure 3A), and enlarged or inversed Ch angle (Figure 3A, D). Interestingly, the position of otolith was also changed in clcn7 morphants with comparable calcification degree (Figure 3A, E).
clcn7 morphants demonstrated hypocalcification of most of the bones with weak red alizarin red staining (Figure 3A). WISH and Q-PCR analysis confirmed significant decrease in the expression levels of sp7 and col10a1 (Figure 3G-H) in clcn7 morphants. Thus, these evidences confirmed that clcn7 was crucial for craniofacial development and mineralization in zebrafish, explaining the craniofacial abnormalities in human osteopetrosis involved CLCN7 mutations. There was a wide variety of the aforementioned craniofacial abnormalities in clcn7 MO group, which mimicked the variable phenotypic changes in osteopetrosis cases with CLCN7 mutations.
Loss of clcn7 function leads to zebrafish tooth defects
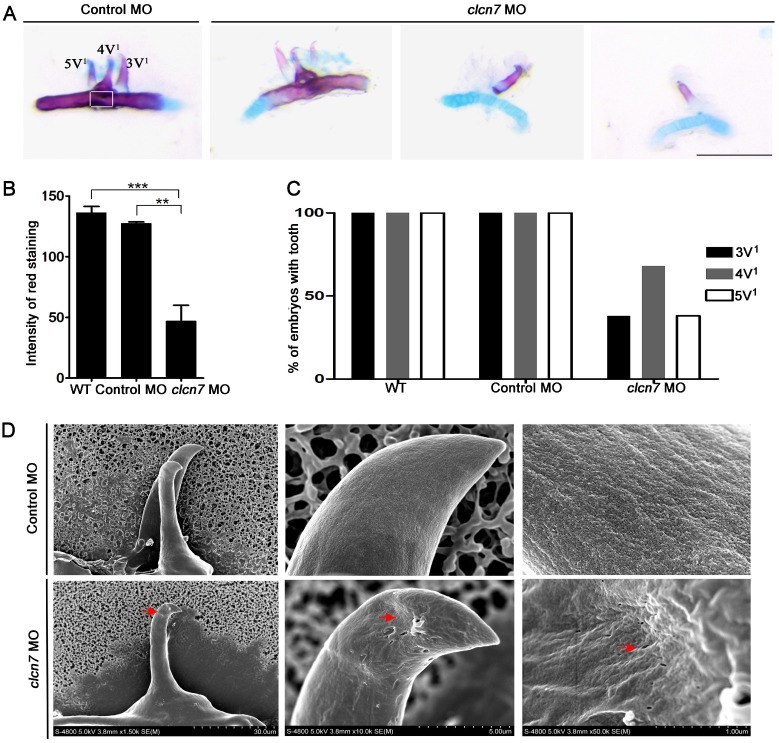
According to the aforementioned clinical analysis, osteopetrosis patients with/without CLCN7 mutations showed a higher rate of defective teeth. Consistent with these findings, we also observed significant changes in tooth shape and number of clcn7 morphants. Histological staining revealed that teeth 3V1, 4V1 and 5V1 with regular morphology were conspicuously found in the control morphants at 5dpf (Figure 4A). In contrast, only 70% clcn7 morphants had 4V1 tooth and 30% of them had 3V1 and 5V1 tooth (Figure 4A, C). The configuration of teeth was also malformed and exhibited decreased calcium deposition in clcn7 morphants (Figure 4A-B). SEM observation demonstrated that the control tooth 4V1 presented smooth and coherent surface, whereas rough and porous surface was visible in the teeth of clcn7 morphants (Figure 4D).
Figure 4.
Defective tooth phenotypes in clcn7-deficient zebrafish. (A) Alcian blue and alizarin red staining results of 5th ceratobranchial arch and teeth in control and clcn7 morphants at 5dpf. The malformed teeth were fewer with weak red staining clcn7 morphants. (B) Quantitative comparison of the extent of calcification among WT embryos, control and clcn7 morphants. (C) Comparison of embryonic tooth number. WT and control embryos had 3V1, 4V1 and 5V1 teeth, while clcn7 morphants showed 3V1, 4V1 and 5V1 fewer teeth. (D) Ultrastructure of tooth 4V1 in control and clcn7 morphants. clcn7 morphants had malformed tooth and enameloid dysplasia. Red arrows point to the pits on the enameloid surface. For A, B, D: WT n=50, Control MO n=50, clcn7 MO n=50. The white square in the first image of figure A is the region for measuring calcified content in panel B. Error bar represents the SD. The experiment was repeated thrice with the same conditions. The data in image C was one of the representative experimental results. WT n=300, Control MO n=320, clcn7 MO n=300. ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm.
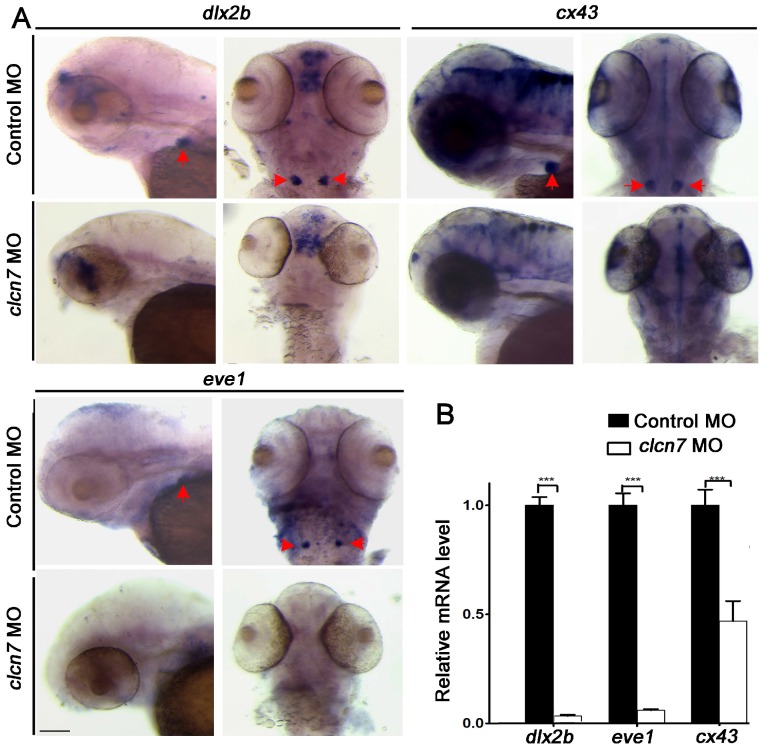
To better understand the involvement of ClC-7 mechanisms of tooth defects, several markers of tooth development were assessed including dlx2b, a tooth epithelium and mesenchymal marker 34, cx43, expressed in odontoblasts and ameloblasts 34, eve1, expressed in ameloblasts of 4V1 35, and sp7, a marker for tooth and osteoblast differentiation 36. WISH analysis showed that all dlx2b, cx43, eve1 and sp7 genes were prominently abolished in clcn7 morphants (Figure 5A and Figure 3G), and Q-PCR confirmed the downregulation of dlx2b, cx43, eve1 and sp7 with clcn7 deficiency (Figure 5B and Figure 3H). These results illustrate that knockdown of clcn7 affected tooth development and calcification including enameloid changes in zebrafish.
Figure 5.
Molecular changes in the teeth of clcn7-deficient zebrafish. (A-B) WISH and Q-PCR analysis results. The fair expression of dlx2b, cx43, and eve1 in the teeth of clcn7 morphants at 3 dpf were diminished compared to that in control morphants. The data in image B was one of the representative experimental results. Error bar represents the SD. Control MO n=50, clcn7 MO n=50. The experiment was repeated thrice with the same conditions. *** p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm.
Lysosomal abnormalities and reduced CTSK expression in clcn7 deficient zebrafish
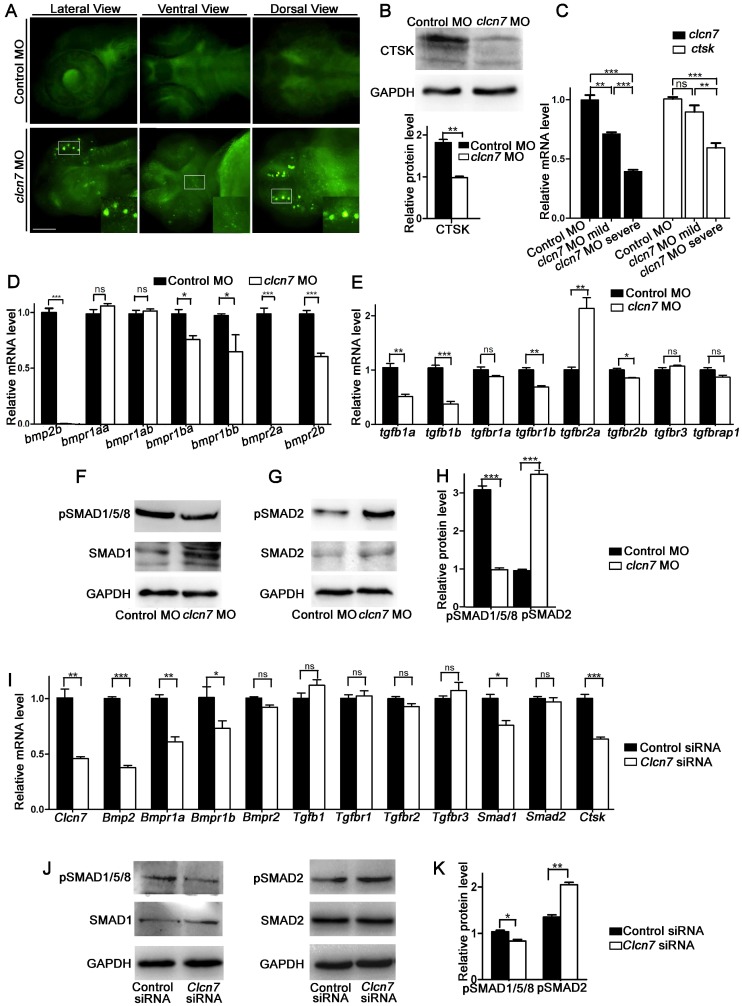
ClC-7 is localized in late endosomes and lysosomes, and its deficiencies led to defective lysosome in mammals 23. There was a pronounced increase of LysoTracker intensity in the head of clcn7 morphants, especially in the brain and jaw, whereas no noticeable signals were detected in the control morphants (Figure 6A). This implied that clcn7 deficiency also led to impaired lysosomal function in zebrafish.
Figure 6.
clcn7 deficiency led to lysosomal storage, reduced Cathepsin K expression and imbalanced TGF-β/BMP signaling pathway. (A) LysoTracker staining revealed lysosomal storage in the brain and jaw in clcn7 morphants at 3dpf compared to control morphants. The insets showed higher magnification of the white boxed areas in clcn7 morphants. (B) Western blot and quantification analysis showed that CTSK protein was markedly decreased in clcn7 morphants at 3dpf. (C) Comparison of clcn7 and ctsk level using Q-PCR detection. The mRNA level of clcn7 and ctsk showed a dose-dependent parallel downregulation with severe craniofacial changes. (D, E) Q-PCR analysis results. Transcript levels of bmp2b and bmpr1ba, bmpr1bb, bmpr2a, bmpr2b were decreased, the levels of tgfb1a, tgfb1b were declined and that of tgfbr2a was increased in clcn7 morphants compared to controls at 3dpf. (F, G and H) Western blots results. The protein levels of pSMAD1/5/8 proteins were significantly reduced, while pSMAD2 levels were increased compared to control. (I) Q-PCR results of BMSCs. Compared to controls, the transcript levels of Bmp2 and Bmpr1a, Bmpr1b, Smad1 and Ctsk were decreased in Clcn7 siRNA group. (J, K) Western blot analysis showed that Clcn7 siRNA increased the protein levels of pSMAD2, while pSMAD1/5/8 levels were reduced compared to controls. For B-H: Control MO n=50, clcn7 MO n=50, clcn7 MO mild n=50, clcn7 MO severe n=50. All data represent mean ±SD. The experiment was repeated at least thrice with the same conditions. ns: not significant difference. * p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001. Scale bars: 100 μm.
It has been reported that perturbation of lysosomal function leads to alterations in the activity of cathepsin proteases such as CTSK. Not surprisinggly, we detected a remarkable decrease of CTSK in clcn7 morphants (Figure 6B), which was consistent with the previous report regarding the reduced expression of CTSK mRNA in ADO II patient 37.
As varied craniofacial changes of clcn7 morphants were found, we wondered whether the clcn7 expression level showed a dose-dependent effect on the phenotypes of craniofacial bones. clcn7 morphants were divided into severe and mild groups according to the major changes in Ch angle and severe group had the reversal Ch angle (Ch angle >180º). The expression level of clcn7 was lower in the severe group than in the mild group. The ctsk mRNA level was parallelly down-regulated in the clcn7 morphants with severe craniofacial changes (Figure 6C). These findings manifested new insights into the role of CTSK in CLCN7-related osteopetrosis.
ClC-7 deficiency disrupted the balance between BMP signaling and TGF-β signaling
The transcript levels of bmp2b, bmpr1ba, bmpr1bb, bmpr2a, and bmpr2b (Figure 6D) as well as BMP downstream signaling phosphorylated SMAD1/5/8 (pSMAD1/5/8) showed significant reduction in clcn7 morphants (Figure 6F). TGF-β-propagated Smad2/3 signals usually balanced the changes of BMP-regulated Smad1/5/8 signals in matured chondrocytes 38. Unsurprisingly, the levels of phosphorylated SMAD2 (pSMAD2) and tgfbr2a were prominently higher in clcn7 morphants compared to controls (Figure 6E, G). These data demonstrated that knockdown of clcn7 led to unbalance between TGF-β and BMP signaling, which, therefore, changed the pattern and development of craniofacial bone and tooth in zebrafish.
ClC-7 deficiency caused similar CTSK/BMP changes in mouse BMSCs
After Clcn7 siRNA transfection, the expression of Clcn7 in BMSCs was downregulated. Subsequently, the mRNA expression levels of Ctsk were decreased in BMSCs, and so did the expression levels of Bmp2, Bmpr1a, Bmpr1b and Smad1 (Figure 6I). The protein level of pSMAD1/5/8 was reduced and that of pSMAD2 was increased in Clcn7 deficiency BMSCs, respectively (Figure 6J, K).
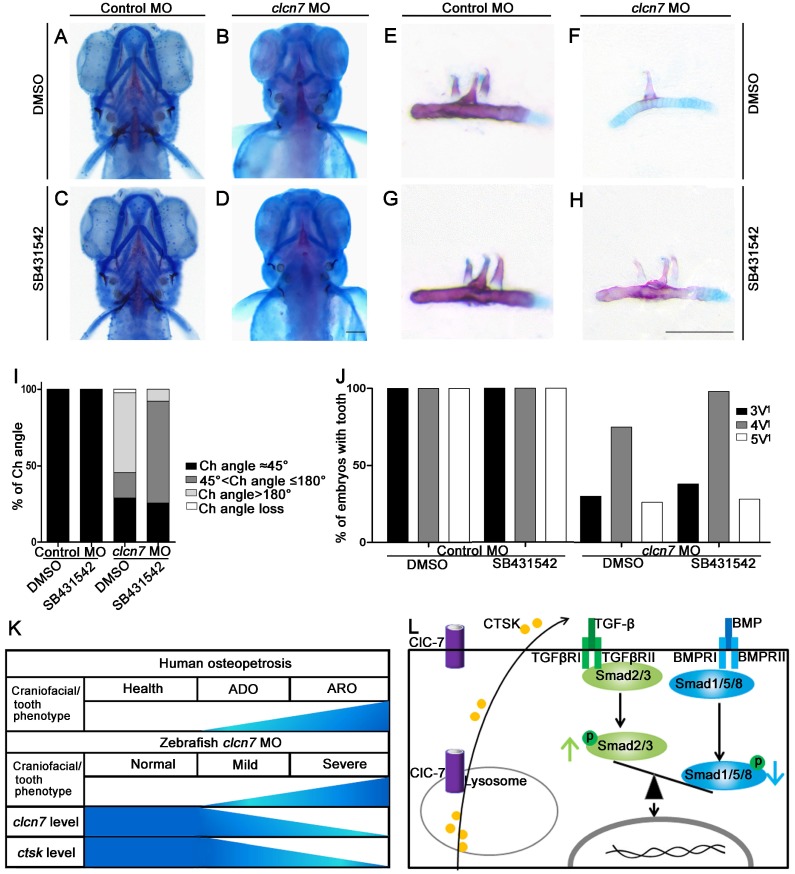
SB431542 inhibitor of TGF-β pathway rescued the craniofacial defects of clcn7 morphants
Imbalance in TGF-β/BMP signaling contributes to craniofacial phenotypes of clcn7 morphants, while the disruption of this imbalance might rescue some other phenotypes. As the level of TGF-β- propagated Smad2/3 signals was relatively increased, SB431542, a selective small molecule inhibitor of the activin receptor-like kinase (ALK)-4, ALK-5, and ALK-7, has been shown to selectively block TGF-β1 signaling by preventing phosphorylation of SMAD2 without affecting BMP signaling 39-41. To avoid perturbations in the early developmental roles of TGF-β family signaling, embryos were treated with 10 μM SB431542 during 14- to 15-somite stages. Compared to the controls (Figure 7A), most clcn7 MO embryos exhibited enlarged or inversed Ch angle (Figure 7B). SB431542-treated clcn7 morphants exhibited partial restoration of Ch angle (Figure 7D). Quantitation of changes in phenotypic severity revealed a significant shift in the number of mutants from severe to mild phenotypes. Under DMSO treatment, the clcn7 deficient embryos with enlarged Ch angle and inversed Ch angle were 16.67% and 52.22%, respectively (Figure 7I). Under SB431542 treatment, the clcn7 deficient embryos with enlarged Ch angle and inversed Ch angle were switched to 66.67% and 7.78%, respectively (Figure 7I). Consistent with these findings, we found significant rescued tooth phenotypes in SB431542-treated clcn7 morphants (Figure 7E-H). 98% of SB431542-treated clcn7 morphants had 4V1 tooth compared to 70% of clcn7 deficient embryos under DMSO treatment (Figure 7J). Thus, SB431542 treatment prevented the severity of craniofacial bone and tooth defects to some extent.
Figure 7.
Inhibition of TGF-β signaling partially rescues craniofacial abnormalities in clcn7 deficient zebrafish. (A-D) Ventral views of 5dpf zebrafish with alcian blue and alizarin red staining. Control zebrafish treated with DMSO (A) or 10 μM SB431542 (C) showed no obvious changes of Ch angle. (B) clcn7 knockdown zebrafish treated with DMSO showed abnormal Ch angle, and 10 μM SB431542 partially rescued Ch angle, showing significant differences (D, I). (E-H) Comparison of embryonic tooth number among controls and clcn7 morphants treated with DMSO or 10 μM SB431542. (J) clcn7 morphants treated with 10 μM SB431542 showed the higher eruption rate of 4V1 tooth. (K) Schematic correlation between the amount of ClC-7 and craniofacial/tooth phenotypes in humans and zebrafish. ARO showed more and severe craniofacial/tooth phenotypes than ADO. The more severe the craniofacial phenotypes in clcn7 morphants, the lower level of clcn7 and ctsk, which further results in the imbalance between TGF-β and BMP signals, affecting the craniofacial and tooth development. (L) Schematic representation of ClC-7- and CTSK-mediated TGF-β/BMP pathway in zebrafish. clcn7 deficiency led to impaired lysosomal function and reduced CTSK expression. TGF-β-like Smad2 signals are elevated and BMP-like Smad1/5/8 signals are reduced in clcn7 knockdown zebrafish, which may contribute to the imbalance in TGF-β/BMP signaling during craniofacial and tooth development. The experiment was repeated thrice with the same conditions. The data in image J was one of the representative experimental results. For A-J: Control MO DMSO n=210, Control MO SB431542 n=198, clcn7 MO DMSO n=158, clcn7 MO SB431542 n=134. Scale bars: 100 μm.
Discussion
Craniofacial and tooth characteristics have been reported in osteopetrosis since 1965 42 and were summarized during early 1992 43. Review of the literatures and our own clinical data showed that ARO and severe ADO II osteopetrosis more likely cause craniofacial and tooth changes, which also occurred in osteopetrosis cases with CLCN7 mutations. The typical craniofacial features in osteopetrosis with CLCN7 mutations and in Clcn7 mutant mice 11 suggested that ClC-7 might affect the formation pattern of craniofacial structures.
Our zebrafish results demonstrated that reduced clcn7 signaling led to aberrations in craniofacial chondrogenesis and osteogenesis, including shorter Ch and Pq, defective Ch, abnormal Ch angle, and poorly mineralized bones. The above pharyngeal arch loss or reversal and neurocranial abnormalities mimicked the craniofacial changes in osteopetrosis patients and clcn7-/- mice 44,11, suggesting that the regulation of ClC-7 on the craniofacial development and pattern of craniofacial structures were conservative.
Type X collagen is expressed by hypertrophic chondrocytes during endochondral ossification. As a bone-specific transcription factor 45, SP7 is required for the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and osteoblasts as well as bone formation 46. Diseases associated with SP7, which include osteogenesis imperfecta and zebrafish sp7 mutants, cause poor differentiation of teeth 47. Both the intensity of alizarin red staining in craniofacial bones and teeth as well as the expression of col10a1 and sp7 were reduced in clcn7 morphants, indicating that ClC-7 deficiency impaired the calcification of craniofacial bones and teeth. Clinical osteopetrosis reports and our pedigree analysis demonstrated that craniofacial bones, such as mandibles or maxilla, showed hypodysplasia or malformation, and were more liable to osteomyelitis; our study data on zebrafish are consistent with the above clinical manifestation of craniofacial bones.
Pycnodysostosis is another bone genetic disorder with increased radiographic bone density. As reported previously, the characteristics of head and craniofacial bones in pycnodysostosis patient, 48 including macrocephaly, frontal bossing, changes in the shape and proportions of facial skeleton, were similar to those of osteopetrosis patients summarized in this report. CTSK is the causative gene of pycnodysostosis 49. In situ hybridization showed strong staining of ctsk in craniofacial regions, pharyngeal arch and Meckels cartilage of zebrafish 50. ClC-7 locates lysosomes in most cell types 10,51. clcn7 knockdown in zebrafish showed lysosomal storage, which is consistent with previous studies in Clcn7/ Ostm1 gene knockout mice 10,23,24, and the cells lacking either ClC-7 or OSTM123,48. The protease activity of CTSK relies much on intracellular conditions such as lysosomal pH. Therefore, lysosomal storage of clcn7 knockdown of zebrafish is probably the key for the impairment of the expression and activity of CTSK.
The clinical variations of osteopetrosis with CLCN7 mutations have been previously reported 52,53 and noticed in our patients as well. Here, we also found that the variable phenotypes of craniofacial bones were related to the amount of ClC-7 and CSTK. The connection between ClC-7 and CSTK was the key influential factor for craniofacial bone development and pattern formation (Figure 6C and Figure 7K).
The impact of BMPs on zebrafish development has been explored in the past decades 54-56. BMP signals, such as bmp2a, bmp2b, and bmp4, existed in zebrafish pharyngeal teeth during initiation and morphogenesis stages. BMP signaling is required for cranial development, including lower jaw, ventral arch and palate 17,57,58, and tooth formation 59,60. In addition to BMP signaling pathway, TGF-β signaling pathway also contributes to the development of craniofacial bone and tooth as well as several patterning events during early embryonic development, including proper craniofacial development 61, neurocranial and pharyngeal arch chondrogenesis 62. Imbalance between TGF-β and BMP signaling causes secondary craniofacial malformations in mucolipidosis II 63, which was also found in our clcn7 morphants. BMSCs were the major cells involved in bone development, and we further confirmed that ClC-7 deficiency also resulted in the imbalance between TGF-β and BMP signaling pathways at the cellular level of BMSCs. Together, ClC-7 deficiency impaired lysosomal condition- dependent CTSK, which may in turn modulate TGF-β/BMP signaling to regulate early craniofacial bone development and pattern formation (Figure 7L).
Of the 80 osteopetrosis cases, 84% presented tooth abnormalities. Our clinical and mice data also confirmed that ClC-7 deficiency resulted in tooth abnormalities such as tooth dysplasia, impacted teeth, and root dysplasia. We further demonstrated the conservative function of ClC-7 in the regulation of tooth formation. dlx2b belongs to distal-less (Dlx) family and plays a role in the development of forebrain, craniofacial and tooth 64 as well as split-hand/foot formation 65. The reduced dlx2b mRNA level might explain tooth malformation and tooth agenesis in clcn7 morphants, as well as tooth problems of osteopetrosis with CLCN7 mutations.
Another striking feature was that enameloid dysplasia and hypocalcification in clcn7 morphants matched the high ratio of enamel dysplasia in osteopetrosis cases. eve1 is required for the differentiation of ameloblasts and for the initiation and morphogenesis of the first tooth in zebrafish 35. cx43 encodes connexin 43 in zebrafish, and reduced levels of Cx43 resulted in ameloblast dysregulation, enamel hypoplasia, and secondary tissue responses 66. The reduced mRNA levels of eve1, cx43, and mineralization-related molecule sp7 might explain the morphological and calcification changes of enamel.
Conclusion
In conclusion, clcn7 acts as a key factor for the regulation of craniofacial bone and tooth formation by targeting lysosomes, CTSK and downstream TGF-β/BMP signaling pathway. Our study provided new insights into the regulatory mechanisms of clcn7 in zebrafish craniofacial embryonic bone and tooth development, and put forward a mechanism chain of ClC-7/CTSK/TGF-β/BMP/SMAD to explain the typical craniofacial bone and tooth changes in osteopetrosis or even pycnodysostosis patients. Meanwhile, we found that the inhibitors of TGF-β signaling pathway could rescue the craniofacial bone and tooth phenotypes in clcn7-deficient zebrafish. These data suggest a new idea for the future treatment of craniofacial pathologies associated with osteopetrosis as well as pycnodysostosis.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC Nos. 81771052, 81271116, 81470728, 31601838). We thank for the agreement of the patients and the controls to join in this research.
Abbreviations
- ADO
autosomal dominant osteopetrosis
- ADO II
autosomal dominant osteopetrosis, type II
- ARO
autosomal recessive osteopetrosis
- BMP
bone morphogenetic protein
- BMSCs
bone marrow stromal cells
- ClC-7
voltage-gated chloride channel 7
- CLCN7
human ClC-7 gene
- Clcn7
mouse ClC-7 gene
- clcn7
zebrafish ClC-7 gene
- col10a1
α1 chain of collagen type X
- cx43
connexin 43; dlx2b: distal-less homeobox 2b
- eve1
even-skipped-like1
- IRO
intermediate autosomal osteopetrosis
- pSMAD1/5/8
phosphorylated SMAD1/5/8
- pSMAD2
phosphorylated SMAD2
- Q-PCR
quantitative real time polymerase chain reaction
- sp7
Sp7 transcription factor
- TGF-β
transforming growth factor β
- WISH
whole-mount in situ hybridization.
Supplementary Material
Supplementary tables.
References
- 1.Stark Z, Savarirayan R. Osteopetrosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009;4:5. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-4-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Campos-Xavier AB, Saraiva JM, Ribeiro LM, Munnich A, Cormier-Daire V. Chloride channel 7 (CLCN7) gene mutations in intermediate autosomal recessive osteopetrosis. Hum Genet. 2003;112:186–89. doi: 10.1007/s00439-002-0861-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhang XY, He JW, Fu WZ, Wang C, Zhang ZL. Novel mutations of TCIRG1 cause a malignant and mild phenotype of autosomal recessive osteopetrosis (ARO) in four Chinese families. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2017;38:1456–65. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Del FA, Cappariello A, Teti A. Genetics, pathogenesis and complications of osteopetrosis. Bone. 2008;42:19–29. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2007.08.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Frattini A, Pangrazio A, Susani L, Sobacchi C, Mirolo M, Abinun M. et al. Chloride channel ClCN7 mutations are responsible for severe recessive, dominant, and intermediate osteopetrosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18:1740–47. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.10.1740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Xue Y, Wang W, Mao T, Duan X. Report of two Chinese patients suffering from CLCN7-related osteopetrosis and root dysplasia. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2012;40:416–20. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2011.07.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang H, Pan M, Ni J, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Gao S. et al. ClC-7 Deficiency impairs tooth development and eruption. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19971. doi: 10.1038/srep19971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Duan X. Ion channels, channelopathies, and tooth formation. J Dent Res. 2014;93:117–25. doi: 10.1177/0022034513507066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lu X, Rios HF, Jiang B, Xing L, Kadlcek R, Greenfield EM. et al. A new osteopetrosis mutant mouse strain (ntl) with odontoma-like proliferations and lack of tooth roots. Eur J Oral Sci. 2009;117:625–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.2009.00690.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kornak U, Kasper D, Bosl MR, Kaiser E, Schweizer M, Schulz A. et al. Loss of the ClC-7 chloride channel leads to osteopetrosis in mice and man. Cell. 2001;104:205–15. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wen X, Lacruz RS, Paine ML. Dental and cranial pathologies in mice lacking the Cl(-) /H(+) -exchanger ClC-7. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2015;298:1502–08. doi: 10.1002/ar.23118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Detailleur V, Vansteenkiste G, Renard M, Verdonck A. Dental care approach in patients with osteopetrosis. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent. 2016;17:435–43. doi: 10.1007/s40368-016-0251-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Walshe J, Mason I. Fgf signalling is required for formation of cartilage in the head. Dev Biol. 2003;264:522–36. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2003.08.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wada N, Javidan Y, Nelson S, Carney TJ, Kelsh RN, Schilling TF. Hedgehog signaling is required for cranial neural crest morphogenesis and chondrogenesis at the midline in the zebrafish skull. Development. 2005;132:3977–88. doi: 10.1242/dev.01943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Brault V, Moore R, Kutsch S, Ishibashi M, Rowitch DH, McMahon AP. et al. Inactivation of the beta-catenin gene by Wnt1-Cre-mediated deletion results in dramatic brain malformation and failure of craniofacial development. Development. 2001;128:1253–64. doi: 10.1242/dev.128.8.1253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jayasena CS, Bronner ME. Rbms3 functions in craniofacial development by posttranscriptionally modulating TGF-beta signaling. J Cell Biol. 2012;199:453–66. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201204138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Alexander C, Zuniga E, Blitz IL, Wada N, Le Pabic P, Javidan Y. et al. Combinatorial roles for BMPs and Endothelin 1 in patterning the dorsal-ventral axis of the craniofacial skeleton. Development. 2011;138:5135–46. doi: 10.1242/dev.067801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Saftig P, Hunziker E, Wehmeyer O, Jones S, Boyde A, Rommerskirch W. et al. Impaired osteoclastic bone resorption leads to osteopetrosis in cathepsin-K-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:13453–58. doi: 10.1073/pnas.95.23.13453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Chen MF, Chen TY. Different fast-gate regulation by external Cl(-) and H(+) of the muscle-type ClC chloride channels. J Gen Physiol. 2001;118:23–32. doi: 10.1085/jgp.118.1.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Neutzsky-Wulff AV, Karsdal MA, Henriksen K. Characterization of the bone phenotype in ClC-7-deficient mice. Calcif Tissue Int. 2008;83:425–37. doi: 10.1007/s00223-008-9185-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sartelet A, Stauber T, Coppieters W, Ludwig CF, Fasquelle C, Druet T. et al. A missense mutation accelerating the gating of the lysosomal Cl-/H+-exchanger ClC-7/Ostm1 causes osteopetrosis with gingival hamartomas in cattle. Dis Model Mech. 2014;7:119–28. doi: 10.1242/dmm.012500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Weinert S, Jabs S, Hohensee S, Chan WL, Kornak U, Jentsch TJ. Transport activity and presence of ClC-7/Ostm1 complex account for different cellular functions. EMBO Rep. 2014;15:784–91. doi: 10.15252/embr.201438553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Kasper D, Planells-Cases R, Fuhrmann JC, Scheel O, Zeitz O, Ruether K. et al. Loss of the chloride channel ClC-7 leads to lysosomal storage disease and neurodegeneration. EMBO J. 2005;24:1079–91. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lange PF, Wartosch L, Jentsch TJ, Fuhrmann JC. ClC-7 requires Ostm1 as a beta-subunit to support bone resorption and lysosomal function. Nature. 2006;440:220–23. doi: 10.1038/nature04535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhang Y, Ke Y, Zheng X, Liu Q, Duan X. Correlation between genotype and phenotype in three families with Peutz-Jeghers Syndrome. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13:507–14. doi: 10.3892/etm.2016.3980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cleiren E, Benichou O, Van Hul E, Gram J, Bollerslev J, Singer FR. et al. Albers-Schonberg disease (autosomal dominant osteopetrosis, type II) results from mutations in the ClCN7 chloride channel gene. Hum Mol Genet. 2001;10:2861–67. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.25.2861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Zheng X, Xu R, He H, Duan X. Grading and quantification of dental fluorosis in zebrafish larva. Arch Oral Biol. 2016;70:16–23. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2016.05.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Santos-Ledo A, Garcia-Macia M, Campbell PD, Gronska M, Marlow FL. Kinesin-1 promotes chondrocyte maintenance during skeletal morphogenesis. PLoS Genet. 2017;13:e1006918. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhao W, Zhang Y, Yang S, Hao Y, Wang Z, Duan X. Analysis of two transcript isoforms of vacuolar ATPase subunit H in mouse and zebrafish. Gene. 2018;638:66–75. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2017.09.065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Duan X, Liu J, Zheng X, Wang Z, Zhang Y, Hao Y. et al. Deficiency of ATP6V1H causes bone loss by inhibiting bone resorption and bone formation through the TGF-β1 pathway. Theranostics. 2016;6:2183–95. doi: 10.7150/thno.17140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Thisse C, Thisse B. High-resolution in situ hybridization to whole-mount zebrafish embryos. Nat Protoc. 2008;3:59–69. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2007.514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Li L, Yang S, Zhang Y, Ji D, Jin Z, Duan X. ATP6V1H regulates the growth and differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;502:84–90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Waguespack SG, Hui SL, Dimeglio LA, Econs MJ. Autosomal dominant osteopetrosis: clinical severity and natural history of 94 subjects with a chloride channel 7 gene mutation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:771–78. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-1986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Jackman WR, Draper BW, Stock DW. Fgf signaling is required for zebrafish tooth development. Dev Biol. 2004;274:139–57. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.07.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Laurenti P, Thaeron C, Allizard F, Huysseune A, Sire JY. Cellular expression of eve1 suggests its requirement for the differentiation of the ameloblasts and for the initiation and morphogenesis of the first tooth in the zebrafish (Danio rerio) Dev Dyn. 2004;230:727–33. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.DeLaurier A, Eames BF, Blanco-Sanchez B, Peng G, He X, Swartz ME. et al. Zebrafish sp7:EGFP: a transgenic for studying otic vesicle formation, skeletogenesis, and bone regeneration. Genesis. 2010;48:505–11. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chen X, Zhang K, Hock J, Wang C, Yu X. Enhanced but hypofunctional osteoclastogenesis in an autosomal dominant osteopetrosis type II case carrying a c.1856C>T mutation in CLCN7. Bone Res. 2016;4:16035. doi: 10.1038/boneres.2016.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Goldring MB, Tsuchimochi K, Ijiri K. The control of chondrogenesis. J Cell Biochem. 2006;97:33–44. doi: 10.1002/jcb.20652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Inman GJ, Nicolás FJ, Callahan JF, Harling JD, Gaster LM, Reith AD. et al. SB-431542 is a potent and specific inhibitor of transforming growth factor-β superfamily type I activin receptor-like kinase (ALK) receptors ALK4, ALK5, and ALK7. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;62:65–74. doi: 10.1124/mol.62.1.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chablais F, Jazwinska A. The regenerative capacity of the zebrafish heart is dependent on TGFbeta signaling. Development. 2012;139:1921–30. doi: 10.1242/dev.078543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ho DM, Chan J, Bayliss P, Whitman M. Inhibitor-resistant type I receptors reveal specific requirements for TGF-beta signaling in vivo. Dev Biol. 2006;295:730–42. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.03.050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Francisco JV, Reichman L. Osteopetrosis with a complication osteomyelitis of the mandible. Report of a case. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1965;19:462–5. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(65)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Elster AD, Theros EG, Key LL, Chen MY. Cranial imaging in autosomal recessive osteopetrosis. Part II. Skull base and brain. Radiology. 1992;183:137–44. doi: 10.1148/radiology.183.1.1549660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kornak U, Kasper D, Bosl MR, Kaiser E, Schweizer M, Schulz A. et al. Loss of the ClC-7 chloride channel leads to osteopetrosis in mice and man. Cell. 2001;104:205–15. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00206-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.DeLaurier A, Eames BF, Blanco-Sanchez B, Peng G, He X, Swartz ME. et al. Zebrafish sp7:EGFP: a transgenic for studying otic vesicle formation, skeletogenesis, and bone regeneration. Genesis. 2010;48:505–11. doi: 10.1002/dvg.20639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kimmel CB, DeLaurier A, Ullmann B, Dowd J, McFadden M. Modes of developmental outgrowth and shaping of a craniofacial bone in zebrafish. PLoS One. 2010;5:e9475. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kague E, Witten PE, Soenens M, Campos CL, Lubiana T, Fisher S. et al. Zebrafish sp7 mutants show tooth cycling independent of attachment, eruption and poor differentiation of teeth. Dev Biol. 2018;435:176–84. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2018.01.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Xue Y, Wang L, Xia D, Li Q, Gao S, Dong M. et al. Dental abnormalities caused by novel compound heterozygous CTSK mutations. J Dent Res. 2015;94:674–81. doi: 10.1177/0022034515573964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Paznekas WA, Boyadjiev SA, Shapiro RE, Daniels O, Wollnik B, Keegan CE. et al. Connexin 43 (GJA1) mutations cause the pleiotropic phenotype of oculodentodigital dysplasia. Am J Hum Genet. 2003;72:408–18. doi: 10.1086/346090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Steinberg BE, Huynh KK, Brodovitch A, Jabs S, Stauber T, Jentsch TJ. et al. A cation counterflux supports lysosomal acidification. J Cell Biol. 2010;189:1171–86. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200911083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Weinert S, Jabs S, Supanchart C, Schweizer M, Gimber N, Richter M. et al. Lysosomal pathology and osteopetrosis upon loss of H+-driven lysosomal Cl- accumulation. Science. 2010;328:1401–03. doi: 10.1126/science.1188072. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pang Q, Chi Y, Zhao Z, Xing X, Li M, Wang O. et al. Novel mutations of CLCN7 cause autosomal dominant osteopetrosis type II (ADO-II) and intermediate autosomal recessive osteopetrosis (IARO) in Chinese patients. Osteoporos Int. 2016;27:1047–55. doi: 10.1007/s00198-015-3320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Frattini A, Pangrazio A, Susani L, Sobacchi C, Mirolo M, Abinun M. et al. Chloride channel ClCN7 mutations are responsible for severe recessive, dominant, and intermediate osteopetrosis. J Bone Miner Res. 2003;18:1740–47. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.10.1740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Nie X, Luukko K, Kettunen P. BMP signalling in craniofacial development. Int J Dev Biol. 2006;50:511–21. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.052101xn. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhang YD, Chen Z, Song YQ, Liu C, Chen YP. Making a tooth: growth factors, transcription factors, and stem cells. Cell Res. 2005;15:301–16. doi: 10.1038/sj.cr.7290299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Chen G, Deng C, Li YP. TGF-β and BMP signaling in osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Int J Biol Sci. 2012;8:272–88. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zuniga E, Rippen M, Alexander C, Schilling TF, Crump JG. Gremlin 2 regulates distinct roles of BMP and Endothelin 1 signaling in dorsoventral patterning of the facial skeleton. Development. 2011;138:5147–56. doi: 10.1242/dev.067785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Schoenebeck JJ, Hutchinson SA, Byers A, Beale HC, Carrington B, Faden DL. et al. Variation of BMP3 contributes to dog breed skull diversity. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002849. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wise SB, Stock DW. Conservation and divergence of Bmp2a, Bmp2b, and Bmp4 expression patterns within and between dentitions of teleost fishes. Evol Dev. 2006;8:511–23. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-142X.2006.00124.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Payne TL, Skobe Z, Yelick PC. Regulation of tooth development by the novel type I TGFbeta family member receptor Alk8. J Dent Res. 2001;80:1968–73. doi: 10.1177/00220345010800110401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Chai Y, Ito Y, Han J. TGF-beta signaling and its functional significance in regulating the fate of cranial neural crest cells. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 2003;14:78–88. doi: 10.1177/154411130301400202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Cheah FS, Winkler C, Jabs EW, Chong SS. Tgfbeta3 regulation of chondrogenesis and osteogenesis in zebrafish is mediated through formation and survival of a subpopulation of the cranial neural crest. Mech Dev. 2010;127:329–44. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2010.04.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Flanagan-Steet H, Aarnio M, Kwan B, Guihard P, Petrey A, Haskins M. et al. Cathepsin-mediated alterations in TGFβ-related signaling underlie disrupted cartilage and bone maturation associated with impaired lysosomal targeting. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31:535–48. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Dai J, Si J, Ouyang N, Zhang J, Wu D, Wang X. et al. Dental and periodontal phenotypes of Dlx2 overexpression in mice. Mol Med Rep. 2017;15:2443–50. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Theisen A, Rosenfeld JA, Shane K, McBride KL, Atkin JF, Gaba C. et al. Refinement of the region for split hand/foot malformation 5 on 2q31.1. Mol Syndromol. 2010;1:262–71. doi: 10.1159/000328405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Toth K, Shao Q, Lorentz R, Laird DW. Decreased levels of Cx43 gap junctions result in ameloblast dysregulation and enamel hypoplasia in Gja1Jrt/+ mice. J Cell Physiol. 2010;223:601–9. doi: 10.1002/jcp.22046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplementary tables.