Abstract
Background
Yaws is targeted for eradication by 2020 in the WHA66.12 resolution of the World Health Assembly. The objective of this study was to describe the occurrence of yaws in the Americas and to contribute to the compilation of evidence based on published data to undertake the certification of yaws eradication.
Methodology
A systematic review of the epidemiological situation of yaws in the Americas was performed by searching in MEDLINE, Embase, LILACS, SCOPUS, Web of Science, DARE and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Experts on the topic were consulted, and institutional WHO/PAHO library databases were reviewed.
Principal findings
Seventy-five full-text articles published between 1839 and 2012 met the inclusion criteria. Haiti and Jamaica were the two countries with the highest number of papers (14.7% and 12.0%, respectively). Three-quarters of the studies were conducted before 1970. Thirty-three countries reported yaws case count or prevalence data. The largest foci in the history were described in Brazil and Haiti. The most recent cases reported were recorded in eight countries: Suriname, Guyana, Colombia, Haiti, Martinique, Dominica, Trinidad and Tobago, and Brazil. Gaps in information and heterogeneity were detected in the methodologies used and outcome reporting, making cross-national and chronological comparisons difficult.
Conclusions
The lack of recent yaws publications may reflect, in the best-case scenario, the interruption of yaws transmission. It should be possible to reach the eradication goal in the region of the Americas, but it is necessary to collect more information. We suggest updating the epidemiological status of yaws, especially in two countries that need to assess ongoing transmission. Twenty-four countries need to demonstrate the interruption of transmission and declare its status of yaws endemicity, and sixteen countries should declare if they are yaws-free. It is necessary to formally verify the achievement of this goal in Ecuador.
Author summary
Yaws is a contagious non-venereal treponematosis caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum subspecies pertenue, transmitted by skin contact. It is a poverty-related chronic disease characterized by primary and secondary skin lesions, with latent infection and a chronic stage, which could include a destructive process of bones and joints. Early detection and treatment can avoid gross disfigurement and the associated stigma. Currently, the treatment with a single dose of oral azithromycin has proven effective. This systematic review shows that in the Americas there is a need to update the epidemiological situation of yaws and if needed, to implement and optimize the best public health recommended interventions to interrupt transmission and then verify elimination of transmission. Current WHO guidelines define the methodology for monitoring and evaluating yaws control programs. Yearly surveys of pre-school children, though logistically complex, are needed in the post-zero case surveillance.
Introduction
Yaws is a poverty-related chronic disease characterized by a primary skin lesion (“mother yaws”) followed by a secondary skin lesion, latent infection, and a chronic stage which may include a destructive process of bones and joints. [1,2]
The disease is a contagious non-venereal treponematosis caused by the bacterium Treponema pallidum subspecies pertenue, transmitted by skin contact. The incubation period is 9–90 days, with an average of 21 days. Humans are the only source of infection. There is no natural immunity to yaws, and there is no vaccine to prevent it. [1,2] Yaws affects mainly children below 15 years of age (with a peak between 6 and 10 years) and sex differences were not described.[3]
Early detection and treatment can avoid gross disfigurement, which occurs in about 10% of the cases.[1] Nevertheless, yaws remains a cause of disability and associated stigma in much of the developing world, primarily affecting those who reside in tropical regions, in rural and overcrowded communities, living in substandard hygiene conditions, with lack of knowledge of the risk factors for infection, and limited access to healthcare. [4]
Diagnosis should include patient examination and laboratory confirmation with a combination of treponemal and non-treponemal serological tests as the serological tests are indispensable for diagnosing latent disease. It is however also necessary to take into consideration the epidemiological context because the serological tests cannot differentiate between yaws and other treponematoses. [5]
In 1950 the World Health Organization (WHO) estimated that 50 million people were infected with yaws. [6] A review of historical documents from the 1950s shows that over 85 countries and territories were endemic for this disease. The WHO and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) provided technical assistance to 46 of these countries between 1952 and 1964, with the consequent drastic decline of yaws prevalence in the endemic areas. [7] Since then, disease control activities were reduced in most countries, and a surveillance phase began, but yaws has not been eradicated.[6,8] Reporting of yaws to the WHO has not been mandatory since 1990 and therefore the availability of up-to-date data on yaws infection is limited.[7] According to WHO, in the Americas, 26 countries were previously considered endemic, and their current status is unknown, seven countries do not have previous history of yaws, and one country–Ecuador–has claimed the interruption of the transmission but it is still necessary to formally verify this achievement. [9,10]
Treatment with a single dose of oral azithromycin has proven effective [11] and has renewed optimism that eradication can be achieved through a new treatment policy, the so-called “Morges Strategy.”[2] This should be implemented along with efforts to facilitate access to clean water, improve sanitation, and promote health education within the community.
Yaws is targeted for eradication, defined as the complete interruption of transmission (absence of new cases of yaws) globally, by 2020 in the WHA66.12 resolution of the World Health Assembly (2013)[12] and by the WHO roadmap on Neglected Tropical Diseases (2012).[13] The Directing Council of the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) adopted the eradication goal in the CD55.R9 resolution and the plan of action for the elimination of neglected infectious diseases and post-elimination actions 2016–2022.[14,15] WHO details the procedures for verification and certification of interruption of yaws transmission.[3]
To guide the process towards successful eradication, a better knowledge of the historical and current epidemiological status of yaws in the Americas is needed. This review shall allow formulating recommendations and methodological suggestions to move forward on the certification process in the Region.
The objective of this study was to describe the occurrence of yaws in the Americas by age group and by country and to contribute to the compilation of evidence based on published data to undertake the certification of the yaws eradication.
Methods
A systematic review of the epidemiological situation of yaws in the Americas was performed. An electronic search of the scientific literature published until June 1, 2017, was conducted in the following databases: MEDLINE (PubMed), Embase, LILACS (including SciELO), SCOPUS, Web of Science, Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE) and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Experts on the topic were consulted, and institutional PAHO/WHO library databases were reviewed.
The search terms used in DARE, Pubmed and EMBASE were “yaws” and “endemic treponematoses”, introduced as MeSH terms or text terms (all fields) or as major terms in EMBASE, together with a combination of the names of all countries, capitals, and main cities of the Region of the Americas introduced as text terms. In LILACS the keywords were also entered in Spanish, Portuguese, and French. Search was limited to studies in humans.
Details of the search strategy are provided in a supplementary file online.
The review was elaborated following the PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) Statement criteria for reporting systematic reviews.[16] The review protocol was registered in the PROSPERO database (Reg. N° CRD42017067449) before conducting the study.
The studies included in this review had to fulfill the following criteria: (a) Participants: Persons who have been evaluated clinically or serologically for a diagnosis of yaws. (b) Intervention: Clinical evaluation or serological test for yaws. (c) Outcomes: Number of suspected or confirmed cases (according to the WHO case definition)[2] and/or prevalence of yaws. (d) Study Design: Clinical trials, systematic reviews and meta-analyses, cross-sectional studies, observational studies, and reports of cases. The exclusion criteria were: (1) Studies conducted outside of the Region of the Americas. (2) Studies published in languages other than the official languages of the PAHO Region (English, Spanish, Portuguese, or French). (3) Studies presenting data that had already been included in the review due to their previous publication in another article (duplication).
Prevalence data were only recorded for studies conducted in the community or studies that reported statistical data from epidemiological surveillance.
Two reviewers (ACZ and VBN) carried out the study selection independently, with any disagreements resolved by discussion and consensus. Full-text articles of potentially relevant studies selected through title and abstract screening were analyzed.
For studies that met the inclusion criteria, data were extracted and entered into a Microsoft Excel database. The following information was collected: number of cases (per age group if available), location, year of sample, and setting. For studies not reporting the year in which the survey was carried out, the year of publication was recorded instead.
For studies describing the number of cases or prevalence results by geographical area within several areas of a country or municipality, these data was treated separately rather than as a single data set. Thus, one study may have yielded more than one outcome record.
For studies that did not report results by age group, data were recorded for the total of the population. Results were analyzed separately for children (0–16 years old) and for the general population (includes information from studies that did not report the age of the cases or were conducted in people over 16 years of age).
Mapping was undertaking using Tableau 10.4.
Results
Characteristics of the included studies
The initial search identified a total of 679 references. After removing the duplicates, 472 unique references (titles and abstracts) were screened, and 223 papers were selected for full-text reading. Of these, 148 were excluded mainly because they did not report cases. Agreement between the two reviewers was unanimous for the excluded citations. The PRISMA flow diagram of the search strategy is presented in a supplementary file online. Seventy-five full-text articles published between 1839 and 2012 met the inclusion criteria (Table 1). Three-quarters of the studies were conducted before 1970.
Table 1. Main characteristics of the studies included in the systematic review (n = 75).
|
Author (publication date) |
Countries or territories | Study design | Setting | Age group | Type of diagnosis | Serological test | Sub-area | Cases (number or range) | Prevalence (%) | Enrollment (year/s or period) | Total population, 1st July 1950 (thousands)* |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rat (1904)[17] | Anguilla | Case series | Health facility | 5 | 1 | ND | 8 | 1902 | 5 | ||
| Pons (1963)[18] | Argentina | Case report | Health facility | 4 | 3 | 2 | Mendoza; Capital | 1 | 1963 | 17,150 | |
| Jorg (1974)[19] | Argentina | Case report | Health facility | 4 | 4/3 | ND | Chaco; Pilcomayo/ Formosa; Mg L.J Fontana | 2 | 1939/ 1960 | ||
| Guimaraes (1953)[20] | Brazil | Case series | Health facility | 1 | 3 | 2 | Rio de Janeiro; 2° adm: 5 | 1,086 | 1945–1950 | 53,975 | |
| Guimaraes (1961)[21] | Brazil | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 3 | ND | 1° adm: 13, 2° adm: 450 | 515,637 | 7.1 | 1956–1959 | |
| Pinotti (1968)[22] | Brazil | Case series | Community | 5 | ND | Para | 18,201 | 28.4 | 1956 | ||
| Muniz (2012)[23] | Brazil | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 1 | 1° adm: 9–11; 2° adm: 78–197 | 583,515 | 7.2 | 1958–1960 | ||
| Prussia (1985)[24] | Barbados | Case series | Health facility | 4 | 3 | 3 | ND | 1 | 1982 | 211 | |
| Vargas-Cuellar (1949)[25] | Colombia | Case series | Health facility | 1 | 3 | 2 | Valle Del Cauca | 1,281 | 1938–1939 | 12,341 | |
| Lopez-Narvaez (1956)[26] | Colombia | Cross sectional | Community | 6 (0-7/ 8-14/ total) | 3 | 2 | Pacific coast and Chocó | 111,144 | 1950–1953 | ||
| Hopkins et al. (1977)[27] | Colombia | Case series | Community | 5 | 3 | 3 | Pacific Coast | 23,682 | 1947–1974 | ||
| Uribe (1985)[28] | Colombia | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 1 | Pacific Coast; 1° adm: 22 | 10,747 | 0.2 | 1973–1983 | ||
| Restrepo et al. (2001)[29] | Colombia | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 3 | 3 | Pacific Coast; Narino, Cauca, Choco | 0 | 1995 | ||
| Pardo-Castello (1939)[30] | Cuba | Cross sectional | Community | 6 (0-15/ 16-50/ >50) | 3 | 2 | Santiago de Cuba | 500 | 0.0 | 1937 |
5,920 |
| Gener (1945)[31] | Cuba | Case series | Health facility | 5 | 3 | ND | Sierra Maestra | 189 | 1945 | ||
| Moss (1929)[32] | Dominican Republic | Case series | Health facility | 5 | 3 | 2 | Santo Domingo | 1,046 | 1920 | 2 365 | |
| Guderian et al. (1995)[33] | Ecuador | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 3 | 3 | Esmeraldas; Eloy Alfaro, Santiago Basin; Localities: 87 | 333 | 11.2 | 1988 | 3,470 |
| Anselmi et al. (1995)[34] | Ecuador | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 3 | 3 | Esmeraldas; Eloy Alfaro, Santiago Basin; Localities: 87 | 16 | 0.6 | 1993 | |
| Anselmi et al. (2003)[10] | Ecuador | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 3 | 3 | Esmeraldas; Eloy Alfaro, Santiago Basin; Localities: 87 | 0 | 0.0 | 1998 | |
| Cockin (1913)[35] | Grenada | Case series | Health facility | 5 | ND | Saint George | 360 | 1912 | 77 | ||
| Hartley (1935)[36] | Grenada | Case report | Health facility | 3 | ND | Saint George | 1 | 1934 | |||
| Padilla-Bolaños et al. (1934)[37] | Guatemala | Case report | Health facility | 5 | 4 | Suchitepequez; San Pablo Jocopilas | 6 | 1931–1932 | 3,115 | ||
| Floch (1945)[38] | French Guyana | Case report | Health facility | 4 | 4 | ND and Cayenne | 2 | 1943 | 25 | ||
| Sausse (1951)[39] | French Guyana | Case series | ND | 5 | 1 | St Lorent du Maroni | 17 | 1951 | |||
| Scolnik et al. (2003)[40] | Guyana | Cross sectional | School | 6 (1-13/ 15–53) | 3 | 3 | Cuyuni/Mazaruni; Mazaruni/Left Bank Essequibo River; Localities: 7 | 60 | 4 | 2000–2001 | 407 |
| Wilson et al. (1930)[41] | Haiti | Case series | Health facility | 6 (0-5/6-10/11-20/≥21)/5 | 1 | Ouest; Port-au-Prince | 4,712 |
1929 |
3,221 |
||
| Dwinelle et al. (1947)[42] | Haiti | Case series | Health facility | 6 (0-5/6-12/13-16/≥17) | 3 | 2 | Ouest; Port-au-Prince and Leogane | 500 | 1944–1945 | ||
| Guthe et al. (1951)[43] | Haiti | Case series | Community | 5 | 3 | 2 | Localities: 336 | 500,000 | 17.0 | 1950 | |
| Petrus et al. (1953)[44] | Haiti | Cross sectional | Community | 6 (0-16/≥17) | 4 | Sud and Grand Anse; 2° adm: 5; rural sections/localities: 12 | 38 | 0.6 | 1952 | ||
| Hume et al. (1956)[45] | Haiti | Case series | Health facility | 1 | 3 | 2 | Sud-Est; Bainet | 1,049 | 1951–1952 | ||
| Samame (1956)[46] | Haiti | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 4 | 1° adm: 7; 2° adm: 4 | 518 | 0.6 | 1954–1955 | ||
| Petrus et al. (1957)[47] | Haiti | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 1 | 1° adm: 7; 2° adm: 5 | 560 | 0.5 | 1952–1955 | ||
| Rao (1960)[48] | Haiti | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 4 | 1° adm: 5 | 271 | 0.3 | 1958 | ||
| La Pommeray et al. (1962)[49] | Haiti | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 4 | 1° adm: 4 | 2 | 1.1 | 1960 | ||
| PAHO (1962)[50] | Haiti | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 1/4 | National | 1,297,868 | 35.8 | 1950–56 | ||
| ND | 1,368 | 0.0 | 1959–62 | ||||||||
| Gentilini et al. (1964)[51] | Haiti | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | ND | National | 70.0 | 1948 | |||
| ND | 1.0 | 1960 | |||||||||
| 33 | 1961 | ||||||||||
| 0 | 1963 | ||||||||||
| Maxwell (1839)[52] | Jamaica | Case report | Health facility | 5 | 1 | ND | 19 | 1824–1839 |
1,403 |
||
| Turner et al. (1935)[53] | Jamaica | Cross sectional | Community | 1 | 3 | 2 | St Thomas; Bath and Seaforth | 2,426 | 53.5 | 1932 | |
| Saunders et al. (1936)[54] | Jamaica | Cross sectional | Community/ School |
3/ 6 (5–14 yr) |
3 | 2 | 1° adm: 14; Localities: 48 | 0–84.0 | 1932–36 | ||
| 12,942 | 15.1 | 1936 | |||||||||
| Hill (1953)[55] | Jamaica | Case series | Health facility | 5 | 3 | 2 | ND | 200 | 1951–1953 | ||
| Ashcroft et al. (1965)[56] | Jamaica | Cross sectional | School | 6 (7–15 yr) | 3 | 2 | St Mary, Kingston and St Catherine | 80 | 9.2 | 1963 | |
| Gentle (1965)[57] | Jamaica | Cross sectional | Health facility | 1 | 3 | 2 | 1° adm: 12 | 673 | 1963 | ||
| Gourlay et al. (1965)[58] | Jamaica | Case series | Community | 5 | 3 | 2 | Kingston; Hermitage and August Town (suburban) | 4 | 0.1 | 1964 | |
| Cummins (1972)[59] | Jamaica | Case series | Health facility | 5 | 3 | 3 | Kingston and Clarendon | 20 | 1972 | ||
| Ashcroft et al. (1978)[60] | Jamaica | Cross sectional | School | 6 (6–14 yr) | 3 | 3 | St Andrews and St Mary | 0.6 |
1976 |
||
| Lee et al. (1963)[61] | Saint Lucia | Cross sectional/ Case series |
School/ Community |
6 (4–15 yr)/ 5 |
1/ 3 |
ND | Region 4 and 6 | 41 | 3.1 | 1957 | 83 |
| 1° adm: 7 | 3,450 | 1954–62 | |||||||||
| Lee (1967)[62] | Saint Lucia | Cross sectional/ Case series |
School/ Community |
6 (<15 yr)/ 5 |
3 | ND | Dennery District; Dennery Village and Richfond Valley | 294 | 8.6 | 1964 | |
| 3 | 1965–1966 | ||||||||||
| Montestruc (1953)[63] | Martinique | Case series | Health facility | 5 | 3 | 2 | National | 6 | 1949–1952 | 222 | |
| Maier et al. (2001)[64] | Martinique | Case series | Community | 5 | 2 | 3 | National | 13 | 20.7 | 1995–1999 | |
| Espinosa et al. (1952)[65] | Panama | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | ND | Darien; Chepigana and Pinogana; Villages: 16 | 355 | 8.7 |
1949 |
860 | |
| Kooy (1970)[66] | Suriname | Case series | Health facility | 5 | ND | National | 73 | 1966 |
215 |
||
| Niemel et al. (1979)[67] | Suriname | Cross sectional | School | 6 (4–16 yr) | 3 | 2 | Saramacca | 212 | 21.9 | 1976 | |
| Niemel et al. (1985)[68] | Suriname | Cross sectional/ Case series |
School/ Community/ Health facility |
6 (4–16 yr)/ 5 |
3 | 3 | 1° adm: 6 | 652 | 7.5 | 1976–1981 | |
| National | 8,094 | 1949–1962 | |||||||||
| Paramaribo | 71 | 1973–1981 | |||||||||
| Fawkes (1957)[69] | Trinidad and Tobago |
Case series |
Health facility/ Community |
5 | 3/1 | 2 | 1° adm: 15; Localities: 27 | 11,350 | 1945–1953 | 646 | |
| ND | 18,825 | 1888–1920 | |||||||||
| 7–13 | 1924 | ||||||||||
| 9–11 | 1932 | ||||||||||
| Fox (1922)[70] | USA | Case report | Health facility | 4 | 3 | 2 | New York; New York | 1 | 1921 | 158,804 | |
| Alderson et al. (1923)[71] | USA | Case report | Health facility | 4 | 3 | 2 | California; San Francisco | 1 | 1922 | ||
| Cady et al. (1924)[72] | USA | Case report | Health facility | 4 | 3 | 2 | Missouri; St. Louis | 1 | 1923 | ||
| Downing (1948)[73] | USA | Case report | Health facility | 2 | 3 | 2 | Massachusetts; Suffolk; Boston | 2 | 1947 | ||
| Post (1948)[74] | USA | Case report | Health facility | 3 | 3 | 2 | New York; New York | 1 | 1947 | ||
| Abreu et al. (1951) | Venezuela | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | 1 | Miranda; Paez; Cupira | 62 | 1.2 | 1949 | 5,482 | |
| ND | 9 | 0.2 | 1950 | ||||||||
| Medina et al. (1954) | Venezuela | Cross sectional | Community | 5 | ND | 1° adm: 16 | 18,560 | 2.4 | 1943–1950 | ||
| Smith et al. (1971)[75] | Venezuela | Case series | Health facility | 5 | 3 | 3 | Distrito Federal; Libertador (Caracas) | 71 | 1969 | ||
| PAHO (1933)[76] | 5 | Case series | Health facility /ND | 6 (0–13)/5 | ND | 1° adm: 5 | 3–61,931 | 1918–1933 | |||
| PAHO (1935)[77] | Colombia/ Jamaica/ Panama |
Case series | ND/ Health facility / Community |
5 | ND | Choco | 4,000 | 1930–1934 | |||
| National/ Subnational, Localities: 5 |
9–61 |
0.6–16.4 | 1935 | ||||||||
| PAHO (1936)[78] | 5 | Case series | ND | 6 (0–15)/5 | ND | National and subnational | 1–651 | 1936 | |||
| PAHO (1937)[79] | 7 | Case series | School/ ND | 6 (children)/5 | ND | National and subnational | 0–95,779 | 1937 | |||
| PAHO (1939)[80] | 3 | Case series | ND | 6(0-5/5-10/10-20)/5 | 3/ND | ND | National and subnational | 260–4,690 | 1939 | ||
| Samame (1952)[81] | 15 | Case series | ND | 5 | ND | National and subnational | 0–4.9 | 1952 | |||
| Bica et al. (1957)[82] | 40 | Case series | ND | 5 | ND | National | 0–528,243 | 1937–1956 | |||
| Hopkins (1977)[83] | 5 | Case series | ND | 5 | ND | National and subnational | 4–61,353 | 1950–1975 | |||
| WHO (1981)[84] | 18 | Case series | ND | 5 | ND | National | 0–4,742 | 1971–1979 | |||
| WHO (1984)[85] | 13 | Case series | ND | 5 | ND | National | 1–627 | 1977–1982 | |||
| Antal et al. (1985)[6] | 15 | Case series | ND | 5 | ND | National | 0–2,065 | 1971–1981 | |||
| St John (1985)[86] | Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | Case series | ND | 5 | ND |
National and subnational |
18 | 0.0 | 1956–1958 | 67 | |
| Suriname/Colombia | 120–215 | 1979–1983 | |||||||||
| Meheus et al (1992)[8] | 7 | Case series | Community/ School/ Health facility |
6 (school-children)/5 | ND | National | 0–241 | 1977–1992 |
ND: Not documented
Subarea: Name of the 1st administrative level; number of municipalities or 2nd administrative level; number of localities (cities or villages).
Age groups: (1) WHO age range categories recommended (0–4 /5-9/ 10–14 /≥15 years); (2) 5–9 years exclusively; (3) 10–14 years exclusively; (4) ≥ 15 years exclusively; (5) when studies did not report age group differences; (6) other age group classification.
Type of diagnosis: (1) Clinical diagnosis exclusively; (2) Serological diagnosis exclusively; (3) Clinical and serological diagnosis, with or without darkfield/histology examination; (4) Clinical and darkfield/ histology examination.
Serological test: (1) treponemal test; (2) non-treponemal; (3) treponemal test +non treponemal test.
(*) United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division (2017). World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision, DVD Edition. Available at: https://population.un.org/wpp/Download/Standard/Population/
Epidemiological data were found for 43 countries (Table 2 and Fig 1). The scientific literature mainly stemmed from Haiti (n = 11, 14.7%) and Jamaica (n = 9, 12.0%). Thirteen studies (17.3%) reported cases from various countries.
Table 2. Number of cases of yaws per year (range) in general population by country or territory and sample period.
| Subregion | Country or territory | Sample periods | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Before 1970 | After 1970 | ||
| North America | Canada | 0 | |
| United States of America | 0–3 | ||
| Central American Isthmus | Belize | 0 | |
| Costa Rica | 6–40 | ||
| El Salvador | 0–1 | ||
| Guatemala | 1–6 | 0–1 | |
| Honduras | 0 | ||
| Nicaragua | 0–4 | ||
| Panama | 1–104 | 0–1 | |
| Latin Caribbean | Cuba | 189–4,000 | |
| Dominican Republic | 1,046–3,827 | 0–9 | |
| French Guiana | 0–17 | ||
| Guadeloupe | 100–501 | ||
| Haiti | 0–1,281,666 | 11–123 | |
| Martinique | 6 | 2–40 | |
| Puerto Rico | 0–94 | ||
| Andean Area* and Brazil | Colombia | 8,622–68,725 | 1–573 |
| Ecuador | 541–13,651 | 0–868 | |
| Peru | 555–2,797 | 1–23 | |
| Venezuela | 9–10,235 | 0 | |
| Brazil | 2–297,681 | 2–2,996 | |
| Southern Cone | Argentina | 0–3 | |
| Chile | 0 | ||
| Paraguay | 0 | ||
| Uruguay | 0 | ||
| Non-Latin Caribbean* | Anguilla | 8 | |
| Antigua and Barbuda | 0–70 | 0–9 | |
| Aruba | 0 | ||
| Bahamas | 0 | ||
| Barbados | 0 | 1 | |
| Curacao | 0 | ||
| Dominica | 1,031–1,469 | 3–351 | |
| Grenada | 360–1,500 | 0–15 | |
| Guyana | 25–72 | 0–36 | |
| Jamaica | 4–8,500 | 0–62 | |
| Montserrat | 0 | ||
| Saint Lucia | 0–1,124 | 0–26 | |
| Saint Vincent and the Grenadines | 5–1,117 | 0–96 | |
| Suriname | 73–1,436 | 0–45 | |
| Trinidad and Tobago | 16–8,069 | 0–1,048 | |
| Virgin Islands (UK) | 1 | ||
General Population includes information from studies that did not report the age of the cases or were conducted in adult population only.
*Bolivia and Saint Kitts and Nevis only reported prevalence data before 1970
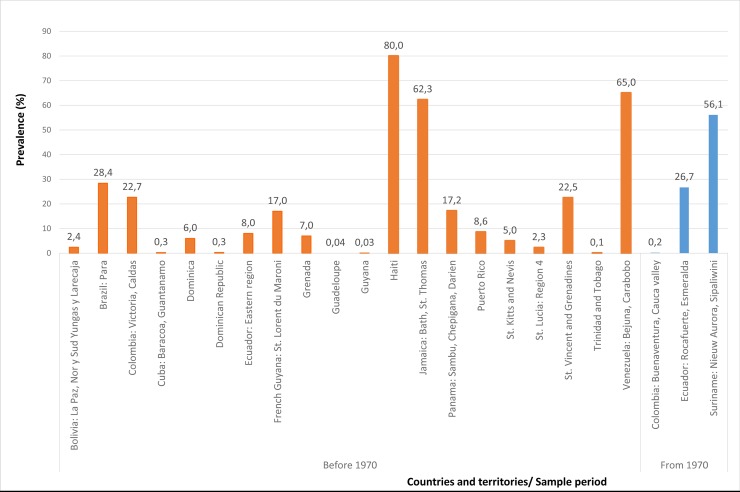
Fig 1. Prevalence of yaws (maximum) in general population by country or territory and sample period.
More than half of the studies were case series or case reports (n = 46, 61.3%) followed by cross-sectional design (n = 26, 34.7%), and three studies (4.0%) had a mixed design (both case-series and cross-sectional design).
More than half of the studies did not report the age of the cases (n = 42, 56.0%) or were conducted in adult population only (n = 7, 9.3%). Twenty-six studies reported cases in children up to 16 years old (34.7%). Categorization into four categories according to age as recommended by the WHO (0–4; 5–9; 10–14; ≥15 years old) was performed in five articles (6.8%). The remaining 21 studies that reported cases in children (28.0%) either used other age categories or did not disaggregate the results into age groups.
There was a notable heterogeneity in the diagnostic method used: 48.0% of the studies (n = 36) performed both clinical and serological diagnosis in combination with or without dark-field or histology examination; 10.7% of the studies (n = 8) used solely clinical diagnosis; 8.0% of the studies (n = 6) used clinical diagnosis with dark-field or histology examination; one study in children used serological diagnosis exclusively (1.3%); and five studies reported cases identified through more than one diagnostic algorithm (6.7%). The diagnostic methods were not documented in 19 studies (25.3%).
From the 41 studies that mentioned having used a serological test, most used non-treponemal tests (n = 23, 56.1%) or combined non-treponemal/treponemal tests (n = 12, 29.3%), and six articles (14.6%) did not specify the kind of serological test used.
Countries with reports of yaws data 1839–2012
According to the filiation of countries to the PAHO, there are 35 Member States, four Associate Members, and three Participant States with 12 territories in the Region of the Americas. [87] For this study we will call them countries and territories. Information was identified for 43 countries and territories of the Americas (Table 2 and Fig 1). Yaws case counts were reported in 31 countries: one from North America, five from Central America, seven from Latin Caribbean, five from Andean Area and Brazil, one from Southern Cone, and twelve from the Non-Latin Caribbean. Yaws prevalence data were reported in 20 countries which included Bolivia and Saint Kitts and Nevis.
The absence of yaws was reported from 10 countries or territories: Aruba, Bahamas, Belize, Canada, Chile, Curacao, Honduras, Montserrat, Paraguay, and Uruguay. No data were available for seven countries or territories: Bermuda, Turks and Caicos, Bonaire, Saba, Saint Eustatius, Sint Maarten, and the Cayman Islands. Although information for Mexico was not found in this review, according to the information from the PAHO no cases of yaws have ever been reported in Mexico. [82,83]
Report of yaws in general population
The reported number of cases of yaws and the highest prevalence of yaws in general population by country or territory and sample period are summarized in Table 2 and Fig 1, respectively. Taking into account that three-quarters of the studies were conducted before 1970, the information was summarized into two groups according to the period (before 1970 and since 1970 to date).
General Population includes information from studies that did not report the age of the cases or were conducted in adult population only.
Before 1970 (32 countries or territories described at least one case in this period):
In the United States of America, three cases of yaws were reported between 1921 and 1923. In Costa Rica, a total of 40 cases were described in the province of Puntarenas in 1929, and six cases were detected at the eastern border of the country between 1951 and 1956. In El Salvador, one case was reported in 1936. Guatemala reported a maximum of six cases in San Pablo Jocopilas in 1931. Nicaragua reported four cases in 1936. In Panama, the highest case number was 104 cases (prevalence 17.2%) in Sambu in Chepigana, Darien, in 1949. In Cuba, an estimated maximum of 4,000 cases was recorded in 1953 (last data available), principally in the Eastern Province. The Dominican Republic reported a maximum of 3,827 cases in 1955–1956. Seventeen cases of yaws were observed in the villages of the Maroni Basin tropical rainforest in French Guiana in 1951, and the last national report from 1954 included eight cases. Guadeloupe had a historic maximum of 501 cases in 1932, and the last report from 1950–1953 informed of 100 cases (0.04% of the total population). Haiti reported the highest nation-wide prevalence of yaws (80.0%) in 1948 and a maximum of 1,281,666 cases in the period 1950–1954. Martinique reported six cases between 1949 and 1952. Puerto Rico reported a maximum of 94 cases in 1936; the last report from 1956 reported no new cases. A yaws prevalence of 2.4% in the general population was recorded in the La Paz department in Bolivia in 1946. Colombia reported a maximum of 68,725 cases between 1950 and 1953 on the Pacific Coast and in Chocó. Ecuador reported a maximum of 13,651 cases in the Coastal Region between 1950 and 1955. In Peru, a maximum of 2,797 cases was reported from the eastern part of the country in the period 1952–1954. Venezuela reported a maximum of 10,235 cases from 1951 to 1955, primarily from the States of Miranda, Sucre, Yaracuy, Cojedes, and Carabobo. Brazil reported a maximum of 297,681 cases from 12 states (197 municipalities) in 1957. Most of these cases were concentrated in the Northeastern Region. The highest prevalence rate reached 28.4% in Para (1956–1959). In Argentina, three cases were reported between 1939 and 1963. Anguilla reported eight cases in 1902. Antigua and Barbuda reported a historic maximum of 70 cases in 1954. Dominica reported a historic maximum of 1,469 cases in 1954. Grenada reported a maximum of 1,500 cases (7.0% of the total population) from 1950 to 1953. Guyana reported a prevalence of yaws of 0.03% in 1952 and 72 cases in 1954. Jamaica reported a maximum of 8,500 cases in 1955 and the highest prevalence (62.3%) was described in St. Thomas, Bath, in 1932. Saint Kitts and Nevis reported a national yaws prevalence of 5% in a total population of 55,000 in 1956. Saint Lucia reported a historic maximum of 1,124 cases in 1954. Saint Vincent and the Grenadines reported a maximum of 1,117 cases (22.5% of the population) in 1956. In Suriname, a historic maximum of 1,436 cases was recorded in 1950. Trinidad and Tobago reported a total of 8,069 cases from 1946 to 1953 (with a prevalence of 0.1% in 1952). For the Virgin Islands (UK), sporadic cases of yaws were described in 1956.
Since 1970 (19 countries or territories described at least one case in this period): Guatemala reported one case in 1975, and the last update from 1979 reported no cases. Panama reported one case in 1977, and the last update from 1980 reported no cases. The Dominican Republic reported nine cases in 1971, and the last update from 1979 reported no cases. In Haiti, the case count decreased from 123 in 1971 to 31 in 1979 (last data available). In Martinique, a peak of 40 cases was recorded in 1975, and the last report from 1995–1999 cited 13 cases detected in blood donors. Colombia reported 573 cases on the Pacific Coast in 1973 and a prevalence of 0.2% in Buenaventura, Cauca Valley, in 1981. In 1992, 108 cases were reported, and the last update from 1995 reported no cases. Ecuador reported a maximum of 868 cases in 1975. Three epidemiological surveys conducted in the same 87 communities from the Santiago Basin Esmeraldas revealed the highest percentage of people affected by yaws in Rocafuerte (26.7%) in 1988 and all the communities reported zero cases in 1998. The last two cases in Peru were diagnosed in 1979. In Brazil, the number of cases described ranged from two in the state of Rondõnia (1972) to 2,996 in Amazonas (1970). The last report from 1977 described 17 cases. Antigua and Barbuda reported nine cases in 1972, and the last case was reported in 1977. One case was reported in Barbados in 1982. Dominica reported 351 cases in 1971 and 28 cases in 1979 (last report identified). Grenada reported 15 cases in 1971 and the last report from 1979 identified no cases. Guyana reported 36 cases in the period 1979–1984. The last report from 2002 from Mazaruni/Left Bank Essequibo River did not report any new cases. Jamaica reported 62 cases in 1972, and the last report with no new cases dates from 1979. Saint Lucia reported 26 cases in 1971 and the last case was reported in 1979. Saint Vincent and the Grenadines reported 96 cases in 1972 and the last case was reported in 1979. In Suriname, 45 and 21 cases were reported in 1982 and 1983, respectively (last data available). Trinidad and Tobago reported a maximum of 1,048 cases in 1974 and the last report identified included 123 cases in 1979.
Report of yaws in children
Given the heterogeneity of the age group reporting in children, results were analysed without disaggregating into subgroups of age.
Yaws infection in children was described in 12 of the 43 countries or territories in which data were recorded (Table 3). In the entire study period, the highest case count reported in the community setting was of 42,419 children on the Pacific Coast and in Chocó, Colombia (1950–1953). The highest prevalence (90%) was found in Brandon Hill, Saint James, Jamaica, in 1932.
Table 3. Number of cases and prevalence of yaws (range) in children (0–16 years old) by country or territory, setting and sample period.
| Country or territory | Setting | Sample periods | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before 1970 | After 1970 | ||||
| Cases (n) | Prevalence (%) | Cases (n) | Prevalence (%) | ||
| Brazil | Health facility | 521 | |||
| ND | 272 | ||||
| Colombia | Community | 42,419 | |||
| School | 824 | 70.1 | |||
| Health facility | 579 | ||||
| Cuba | Community | 224 | |||
| Grenada | Health facility | 1 | |||
| Guyana | School | 8–52 | 1.5–5.1 | ||
| Haiti | Community | 0–718 | 0–2.6 | ||
| Health facility | 114–1,053* | ||||
| Jamaica | Community | 228–496 | 0–90.0 | ||
| School | 24–2,354 | 0.15–38.6 | 2–3 | 0.29–1.5 | |
| Health facility | 369 | ||||
| Panama | Health facility | 3 | |||
| Saint Lucia | School | 9–237 | 1.3–13.2 | ||
| Suriname | School | 2–398 | 0.2–42.1 | ||
| United States of America | Health facility | 3 | |||
| Venezuela | ND | 77* | |||
* Includes children from 0 to 20 years old; ND: Not documented
In the school setting, the highest case number recorded was 2,354 cases from 64 schools in Saint Catherine, Jamaica, in 1932. The highest prevalence rate reached 70.1% (824 children) reported from 29 schools in Cauca, Colombia, in 1937.
The highest number of cases identified in a health facility setting was reported from Port-au-Prince, Haiti, in 1929 (1,053 children).
Discussion
This systematic review compiles epidemiological information (occurrence of yaws) for 43 countries and territories of the Americas. Included studies originated primarily from two countries in the Caribbean (Haiti and Jamaica) and were published between 1839 and 2012.
Data show that before 1970, the yaws infection was well established in many countries or territories of the Americas, with cases described in 32 countries. Several large foci of the disease were observed in the first half of the 20th century. For example, 61,931 cases were reported in Colombia (1918–1927)[76] and 25,186 cases in Brazil (Teofilo Otoni, Minas Gerais; 1934–1941).[20] The efforts of some of the countries such as Colombia, Suriname or Jamaica to control yaws with arsenical or bismuth treatment in the pre-antibiotic era appear not to have had a large impact on public health as the prevalence of the yaws infection remained high in the subsequent decades in these countries.
In the fifties and sixties, yaws infection continued to afflict the Region. The largest foci described in the history were located in Brazil and Haiti, with both countries reporting more than 500,000 cases.[23,50] The large number of studies and cases identified for these two decades probably reflects the greater political commitment fostered internationally by the WHO and UNICEF [7] and increased provision of economic and human resources for surveying extensive areas, undertaking population treatment campaigns, establishing surveillance systems, and publishing research papers and evaluation reports, rather than an actual spread of the disease.
The information encountered suggests that the yaws spread got under control during the following two decades on this continent: the number of countries or territories with yaws cases decreased down to 19, with less than 1,000 cases reported from each one of them except for Brazil [83] and Trinidad and Tobago.[84] This decline seems to be related to the success of the above-mentioned mass penicillin treatment campaigns in the 1950s.[8] In the 1970s, the yaws programs were integrated into primary health care systems in some countries, but in many others, they became weak or almost non-existent. [7]
Since 1990, when mandatory reporting of yaws cases to the WHO was rescinded, the data have been scarce: information has been available for six countries only, and low-level transmission of yaws was reported from Colombia,[8] Martinique,[64] and Guyana.[40] In Venezuela and Panama, no yaws cases have been identified since 1977 and 1980, respectively.[8] After two well-conducted epidemiological surveys in 1993 and 1998 that reported an absence of clinical and serological cases, Ecuador may be considered a yaws-free country, but formal WHO verification of the interruption of transmission is needed.[10] Yaws information from other countries has become outdated. [7] The last update on the status of endemicity of yaws of the Global Health Observatory data repository of the WHO did not report cases from any country of the Americas for the period 2008 to 2013.[9]
According to the information provided by the PAHO’s Regional Neglected Infectious Diseases Program, from 21 countries that responded to a survey in 2017 (initiative of the WHO to compile information globally for yaws eradication purposes), only Bermuda, Jamaica, and Nicaragua have included yaws in their current surveillance system. No country reported having national guidelines or a policy document for yaws except Nicaragua, which has included yaws in its notifiable diseases reporting system. No country in the Region of the Americas has identified any yaws cases between 2014 and 2017 except for Colombia and Haiti. Colombia identified less than 100 yaws cases (without diagnostic confirmation) based on data retrieved from the health information system using the yaws codes of the 10th revision of the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10); the monitoring of the events and the anti-yaws campaign were dismantled in 2001. Haiti reported seven cases detected in the Department of Grand’Anse in 2015.
The reduction of the number of countries and territories with reports of cases or prevalence of yaws published before 1970 (n = 32) and after 1970 (n = 19) by almost 60% is remarkable. The lack of recent yaws publications may reflect, in the worst-case scenario, a) that the countries face difficulties in publishing yaws data in indexed journals; b) a lack of capacities, interest or funding to conduct epidemiological surveys; and/ or c) a lack of political interest for undertaking further surveys as the issue of yaws is not considered a priority due to more pressing public health problems or the increasing relevance of other infectious diseases (e.g., chikungunya or zika). In the best-case scenario, it may be indicative of the interruption of the yaws transmission which could be related to the impact of the disease eradication interventions and improvements in the socioeconomic status in many countries. However, in many countries, the epidemiological surveillance, which is key to detecting and responding to a possible resurgence of the disease and to certifying the interruption of the transmission, stopped after 1970. The criterion proposed by the WHO for confirming that transmission of yaws in an area has ceased is the absence of new cases for a continuous period of three years of clinical and serological (in children under five years of age) surveillance. [2]
Given that this is a review without date limits and with flexibility in the type of studies included, we detected gaps in information and considerable heterogeneity in the methodologies used and outcome reporting. Thus, the comparison between countries must be carried out with caution: (a) In spite of the fact that cases were registered by the smallest geographic unit identified whenever possible, information was frequently found at the national level only. (b) In many studies, the prevalence reported had to be calculated over the total number of persons examined instead of over the total population ascertained by a census. (c) Several studies, especially those that included data reported to the WHO by national health authorities, did not specify whether the cases reported were active only or also latent,[84] when it is known that the ratio of clinical to latent cases is around 1:6.[88] Moreover, half of the studies either did not use serology in the diagnostic protocol or did not mention its use, not allowing distinguishing between suspected or confirmed cases, yet only surveys with clinical and serological diagnosis can provide data on the actual level of endemicity in a population.[4] Therefore, the information identified in this review can mainly indicate the mere existence of cases or foci of yaws in a determined country in a specified period. [84]
There was a large variation in the age of the cases reported and in the age range categorization. More than half of the studies did not report the age of the cases, 26 studies reported cases in children, and only five studies grouped participants by age into four categories as recommended by the WHO.[2] The separate analysis of children and adult data is essential because on one hand, it is known that children under 15 years of age are the main reservoir of the infection;[88] and on the other hand, it detects the occurrence of new infections and avoids the complexity of dealing with adult population that was successfully treated but remains seropositive. [4] Yearly surveys of pre-school children, though logistically complex, are needed in the post-zero case surveillance.
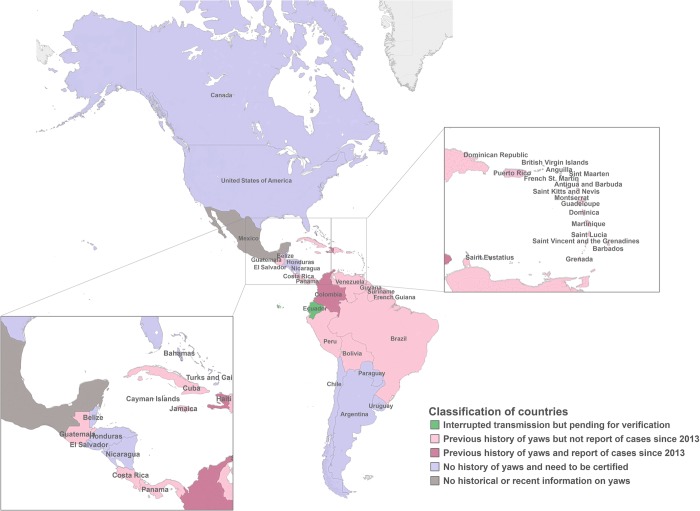
Based on this review, and by combining the results to the classification of countries for verification of interruption of yaws transmission proposed by WHO [3], we suggest the following actions be carried out in the countries of the Americas (Fig 2):
Fig 2. Classification of countries for certification of interruption of yaws transmission in the Americas.
Countries that have interrupted transmission and need to be verified
Ecuador has claimed the achievement of the goal. It would be recommendable to reassess the interruption of transmission in children aged 1–5 years in areas were yaws was historically endemic. The epidemiological and historical information supporting the achievement of the interruption of transmission of yaws in the country should be compiled in a dossier and submitted to the WHO for the verification process. Ecuador may be the first country in the Americas to apply the PAHO/WHO procedures for verification and certification of interruption of transmission of yaws.
Countries with no history of autochthhonous infectious cases of yaws that need to be certified
Six countries reported less than ten imported cases before 1970 (Argentina, 1963; Nicaragua, 1957; Virgin Island (UK) 1956; the United States of America, 1947; El Salvador, 1936; and Anguilla, 1902). Also, ten countries reported zero cases before 1970 (Canada, Belize, Honduras, Chile, Paraguay, Uruguay, Aruba, Bahamas, Curacao, and Monserrat). We did not find reports of yaws cases after 1970 in all these countries. Documentation to support that autochthhonous cases of yaws have ever occurred should be compiled and submitted to PAHO/WHO in all these countries along with the evidence that its health and surveillance systems are sufficient to detect any imported yaws case.
Countries with history of yaws but no report of cases since 2013
Cuba, Guadeloupe, Puerto Rico, Costa Rica and French Guiana reported cases, and Bolivia and Saint Kitts and Nevis reported prevalence before 1970. Peru, Antigua and Barbuda, Barbados, Saint Lucia, and Saint Vincent and the Grenadines have reports of one or two cases of yaws after 1970, most of them before 1980. Guyana, Suriname, Dominica, Trinidad and Tobago, Brazil and Martinique reported cases after 1970, most of them before 1990. Guatemala, Panama, Dominican Republic, Grenada, Jamaica, and Venezuela have reports of zero cases in studies carried out after 1978. These countries should review in depth the information at local level, mainly in the municipalities with a history of yaws. These countries should provide comprehensive evidence to support the elimination in a dossier, and declare the status of yaws endemicity indicating whether there is evidence of the interruption of transmission or whether additional assessment needs to be carried out.
Countries with history of yaws and report of cases since 2013
Although Colombia had the latest publication of yaws in 1992, the country reported suspected cases between 2014 and 2017 to PAHO/WHO. Haiti also reported cases in 2015 to PAHO/WHO. In these countries, it would be necessary to carry out an assessment including the collection of information to support the absence of the disease, review past and existing records, and conduct clinical and serological surveys in children in previously endemic areas. Countries with confirmed cases should implement the Morges Strategy.
Countries with no historical or recent information on yaws
For seven countries there was no data available on the occurrence of yaws: Bermuda, Turks and Caicos, Bonaire, Saba, Saint Eustatius, Sint Maarten, and the Cayman Islands. A more in-depth search of information, studies or data published locally should be carried out in each one to decide on next steps. Although Mexico reported no cases of yaws since 2013 to PAHO/WHO, the country should compile all the information to support its current epidemiological status.
The proposed classification of countries is intended to encourage countries in the Americas to start reviewing and documenting the current epidemiological situation of yaws. In conclusion, it should be possible to reach the eradication goal in the region of the Americas, but it is necessary to update the epidemiological status and evidence must be compiled to confirm whether the interruption of yaws transmission has occurred in most of the countries.
Supporting information
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
Acknowledgments
The authors, which are staff members of the Pan American Health Organization, alone are responsible for the views expressed in this publication, and they do not necessarily represent the decisions or policies of the Pan American Health Organization.
Data Availability
It is a systematic review, all the included papers are published online and can be found in the references of the paper.
Funding Statement
This work was developed as part of the work plan products of the PAHO/WHO Regional Program for Neglected Infectious Diseases. The institutional funders supporting the work of the regional program had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Giacani L, Lukehart SA. The endemic treponematoses. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2014;27: 89–115. 10.1128/CMR.00070-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.WHO. Summary report of a consultation on the eradication of yaws, 5–7 March 2012, Morges, Switzerland [Internet]. Morges: World Health Organization; 2012. Available: http://files/3664/Estrategia Morges 2012_SUMMARY.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 3.WHO. Eradication of yaws: procedures for verification and certification of interruption of transmission. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Marks M, Mitja O, Vestergaard LS, Pillay A, Knauf S, Chen C-Y, et al. Challenges and key research questions for yaws eradication. Lancet Infect Dis. 2015;15: 1220–1225. 10.1016/S1473-3099(15)00136-X [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mitjà O, Šmajs D, Bassat Q. Advances in the Diagnosis of Endemic Treponematoses: Yaws, Bejel, and Pinta. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2013;7 10.1371/journal.pntd.0002283 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Antal GM, Causse G. The control of endemic treponematoses. Rev Infect Dis. 1985;7 Suppl 2: S220—226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Asiedu K, Fitzpatrick C, Jannin J. Eradication of Yaws: Historical Efforts and Achieving WHO’s 2020 Target. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014;8 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Meheus A, Antal GM. The endemic treponematoses: not yet eradicated. World Health Stat Q. Switzerland; 1992;45: 228–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.WHO. Global Health Observatory data repository Status of endemicity for yaws. Data by country. In: World Health Organization; [Internet]. 2013 [cited 11 Nov 2017]. Available: http://apps.who.int/gho/data/node.main.NTDYAWSEND?lang=en [Google Scholar]
- 10.Anselmi M, Moreira J-M, Caicedo C, Guderian R, Tognoni G. Community participation eliminates yaws in Ecuador. Trop Med Int Heal. 2003;8: 634–638. 10.1046/j.1365-3156.2003.01073.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Mitjà O, Hays R, Ipai A, Penias M, Paru R, Fagaho D, et al. Single-dose azithromycin versus benzathine benzylpenicillin for treatment of yaws in children in Papua New Guinea: an open-label, non-inferiority, randomised trial. Lancet. 2012;379: 342–347. 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)61624-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.WHO. World Health Assembly 66.12 Neglected tropical diseases [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013. Available: http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/150163 [Google Scholar]
- 13.WHO. Accelerating work to overcome the global impact of neglected tropical diseases: a roadmap for implementation Executive summary [Internet]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012. Available: http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/70809 [Google Scholar]
- 14.PAHO. 55th Directing Council. 68th Session of the Regional Committee of WHO for the Americas. Plan of action for the elimination of Neglected Infectious Diseases and post-elimination actions 2016–2022 [Internet]. Washington DC.: Panamerican Health Organization; 2016. Available: http://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_download&gid=35741&Itemid=270&lang=en
- 15.PAHO. 55th Directing Council. 68th Session of the Regional Committee of WHO for the Americas. Resolution CD55.R9 [Internet]. Washington DC.: Panamerican Health Organization; 2016. Available: http://www.paho.org/hq/index.php?option=com_docman&task=doc_download&gid=36408&Itemid=270&lang=en
- 16.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Group P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6: e1000097 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rat JN. Yaws: its introduction into Anguilla in 1902. J Trop Med. 1904; 86–87. Available: http://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/es/med-7225 [Google Scholar]
- 18.PONS S. [Yaws in Mendoza (Non-autochthonous case)]. Arch Argent Dermatol. 1963;13: 259–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jorg ME. 2 non-autochtonous cases of yaws seen in Argentina. Prensa Med Argent. 1974;61: 625–634. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Guimaràes FN. Yaws in Brazil. Bull World Health Organ. 1953;8: 225–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Guimaràes FN. Actual situation of the campaign to erradicate yaws in Brazil. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1961;50: 241–245. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v50n3p241.pdf [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pinotti M. [Improved perspectives in the fight against rural endemics]. Rev Assoc Med Bras. 1958;4: 199–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Muniz ES. “Is a shot alone enough?”: concepts of health, hygiene, and nutrition and the Program to Eradicate Yaws in Brazil, 1956–1961. Hist Ciencias Saude-Manguinhos. 2012;19: 197–216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Prussia PR, Dasilva PA. Yaws in Barbados. West Indian Med J. 1985;34: 63–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vargas Cuellar P. Yaws in the Department of Cauca Valley. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1949;20: 897–914. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lopez Narvaez G. Yaws and the anti-yaws campaign in Colombia. Rev Fac Med Univ Nac Colomb. 1956;24: 294–342. Available: http://revistas.unal.edu.co/index.php/revfacmed/article/view/23022/23804 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hopkins DR, Florez D. Pinta, yaws and venereal syphilis in Colombia. Int J Epidemiol. 1977;6: 349–355. 10.1093/ije/6.4.349 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Uribe WR. Yaws in Colombia. Rev Infect Dis. 1985;7: S276—S277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Restrepo Marcos; Restrepo Berta; Orozco Betariz; Padilla Julio; Cuervo Claudia; Alvarez G. Yaws seroepidemiological survey in the Pacific Coast of Colombia. Biomedica. 2001;21: 155–61. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pardo-Castello V. Yaws—Five hundred cases observed in Cuba. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1939;40: 762–775. 10.1001/archderm.1939.01490050078007 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gener G. [The two terrible enemies of the Cuban peasant are yaws and leprosy]. Rev Sifilogr Leprolog Dermatol. 1945;2: 193–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Moss AL. Yaws—An analysis of 1046 cases in the Dominican Republic. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1922;33: 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Guderian RH, Anselmi M, Calvopiña M, Cooper PJ, Mancero T. Yaws in the Province of Esmeraldas, Ecuador. Biomedica. 1995;15: 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Anselmi M, Araujo E, Narvaez A, Cooper PJ, Guderian RH. Yaws in Ecuador—Impact of control measures on the disease in the Province of Esmeraldas. Genitourin Med. 1995;71: 343–346. Available: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1196100/pdf/genitmed00018-0007.pdf [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Cockin RP. Treatment of Yaws by intramuscular injections of salvarsan. A report on a series of 45 cases treated at the Yaws Hospital, St. George’s, Grenada, BWI. Lancet. 1913;2: 1609–1610. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Hartley PHS. “Yaws” in the Island of Grenada. Br Med J. 1935;1935: 674 Available: http://www.bmj.com/content/1/3873/674.1 [Google Scholar]
- 37.Padilla Bolaños E, López Selva M. [Yaws, tropical disease of Guatemala]. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1934;13: 113–119. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v13n2p113.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 38.Floch H. [Gangosa in French Guiana; on mutilating rhinopharyngitis]. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1945;38: 198–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Sausse A. Comparative pathology of primitive Negro and Indian populations of French Guiana. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1951;44: 455–460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Scolnik D, Aronson L, Lovinsky R, Toledano K, Glazier R, Eisenstadt J, et al. Efficacy of a targeted, oral penicillin-based yaws control program among children living in rural South America. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;36: 1232–1238. 10.1086/374338 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Wilson PW, Mathis MS. Epidemiology and pathology of yaws—A report based on a study of one thousand four hundred and twenty-three consecutive cases in Haiti. J Am Med Assoc. 1930;94: 1289–1292. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Dwinelle JH, Sheldon AJ, Rein CR, Sternberg TH. Evaluation of penicillin in the treatment of yaws—final report. Am J Trop Med. 1947;27: 633–641. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Guthe T, Reynolds F. World health and treponematoses. Br J Vener Dis. 1951;27: 1–19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Petrus E, Levitan S, Paoliello A, Nicol R. The anti-yaws campaign in Haiti. Bull World Health Organ. 1953;8: 261–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Hume JC, Facio G. An analysis of the results of the treatment of yaws with a single injection of procaine penicillin with 2{%} aluminium monostearate. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;15: 1057–1085. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Samame GE. Treponematosis eradication, with special reference to yaws eradication in Haiti. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;15: 897–910. Available: %7B%25%7D3CGo [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Petrus E, Velarde Thome J. Five years of anti-yaws campaings in Haiti. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1957;42: 22–30. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v42n1p22.pdf [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rao T. Statistical surveys: Their importance in yaws eradication program in Haiti. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1960;49: 355–363. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v49n4p355.pdf [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.La Pommeray HB, Reyes S, Delva H. Research on ulcers and their relation to yaws in Haiti. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1962;53: 313–316. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v53n4p313.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 50.PAHO. Final report on the yaws eradication campaign in Haiti: budgetary report on the yaws eradication campaign in Haiti [Internet]. Minneapolis: Panamerican Health Organization; 1962. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/English/GOV/CSP/16%7B_%7D76.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gentilini M, Laroche V, Degremont A. Aspects of parasitic and infectious tropical pathology in the Republic of Haiti. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1964;57: 565–570. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Maxwell J. Observations on yaws and its influence in originating leprosy; also observations on acute traumatic tetanus, and tetanus infantum [Internet]. 1839. Available: http://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/es/med-2961
- 53.Turner TB, Saunders GM, Johnston HM. Yaws in Jamaica II A plan of control based upon treatment. Am J Hyg. 1935;21: 522–539. [Google Scholar]
- 54.Saunders GM, Kumm HW, Rerrie JI. The relationship of certain environmental factors to the distribution of yaws in Jamaica. Am J Hyg. 1936;23: 558–579. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a118238 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Hill KR. Antibiotics other than penicillin in the treatment of yaws. West Indian Med J. 1953;2: 43–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Ashcroft MT, Urquhart AE, Gentle GHK. Treponema serological tests in Jamaican school children. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1965;59: 649–656. 10.1016/0035-9203(65)90094-5 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gentle GH. Yaws survey—Jamaica, 1963. Br J Vener Dis. G.H. Gentle; 1965;41: 155–162. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Gourlay RJ, Marsh M. An outbreak of yaws in a suburban community in Jamaica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1965;14: 777—{&}. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Cummins AC. The significance of the V.D.R.L., R.P.C.F., and F.T.A.-ABS tests in the diagnosis of syphilis in Jamaica [Internet]. University of the West Indies; (Mona: ). 1972. Available: http://bases.bireme.br/cgi-bin/wxislind.exe/iah/online/?IsisScript=iah/iah.xis%7B&%7Dsrc=google%7B&%7Dbase=MedCarib%7B&%7Dlang=p%7B&%7DnextAction=lnk%7B&%7DexprSearch=13744%7B&%7DindexSearch=ID [Google Scholar]
- 60.Ashcroft MT, Urquhart AE. Treponemal serological tests in Jamaican school children, 1976. West Indian Med J. 1978;27: 26–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Lees REM, de Bruin AM. Review of yaws in St. Lucia five years after an eradication campaign. West Indian Med J. 1963. pp. 98–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Lees REM. Yaws control: report of a mass juvenile sweep in St. Lucia. West Indian Med J. 1967;16: 228–232. [Google Scholar]
- 63.Montestruc E. [False serological reactions in syphilis in natives of the Antilles]. Bull Soc Pathol Exot Filiales. 1953;46: 180–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Maier H, Cesaire R, Bera O, Kerob-Bauchet B, Ould Amar AK, Desbois N, et al. [The role of yaws in the serologic screening of treponematoses in blood donors in Martinique]. Transfus Clin Biol. 2001;8: 403–409. 10.1016/s1246-7820(01)00191-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Espinosa A, Amador Guevara J. Control of yaws in the Republic of Panama. Arch Med Panamenos. 1952;1: 8–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kooy P. Brucellosis, treponematosis, rickettsiosis, and psittacosis in Surinam. A serological survey. Trop Geogr Med. 1970;22: 172–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Niemel PLA, Brunings EA, Menke HE. Attenuated yaws in Surinam. Br J Vener Dis. 1979;55: 99–101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Niemel PL, Sadal S, van der Sluis JJ. Yaws in Suriname. Rev Infect Dis. P.L. Niemel; 1985;7 Suppl 2: S273—275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Fawkes MA. A short history of yaws in Trinidad. West Indian Med J. 1957;6: 189–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Fox H. The prevalence of yaws (frambesia tropica) in the United States. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1922;6: 657–674. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Alderson HE, Coe HC. Report of a case of yaws in California. Cal State J Med. 1923;21: 162–163. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Cady LD, Engman MF. A case of yaws occurring in Missouri. Arch Derm Syphilol. 1924;10: 446–452. [Google Scholar]
- 73.Downing JG. Yaws in Massachusetts. N Engl J Med. 1948;239: 17–18. 10.1056/NEJM194807012390104 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Post CF, Sheard C. A case of yaws in New-York-City. N Y State J Med. 1948;48: 1920–1926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Smith JL, David NJ, Indgin S, Israel CW, Levine BM, Justice J, et al. Neuro-ophthalmological study of late yaws and pinta .2. Caracas project. Br J Vener Dis. 1971;47: 226—{&}. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.PAHO. [Chronicles: ophidism; yaws; venereas]. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1933;12: 160–184. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v12n2p160.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 77.PAHO. [Yaws]. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1935;14: 871–873. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v14n9p871.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 78.PAHO. [Yaws]. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1936;15: 672–676. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v15n7p660a.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 79.PAHO. [Yaws]. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1937;16: 647–655. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v16n7p647.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 80.PAHO. [Yaws]. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1939;18: 163–165. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v18n2p149b.pdf [Google Scholar]
- 81.Samame G. Nature and the extend of the yaws problem in the Americas. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1952;33: 126–127. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v33n2p126.pdf [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Bica AN, Roman J. The problem of yaws in the Americas. Bull Pan Am Sanit Bur. 1957;42: 413–420. Available: http://hist.library.paho.org/Spanish/BOL/v42n5p413.pdf [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Hopkins DR. Yaws in the Americas, 1950–1975. J Infect Dis. 1977;136: 548–554. Available: http://www.jstor.org/stable/30106605 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Endemic treponematosis. Wkly Epidemiol Rec Relev épidémiologique Hebd. 1981;31: 241–244. [Google Scholar]
- 85.Surveillance of treponematoses. Wkly Epidemiol Rec Relev épidémiologique Hebd. 1984;49: 377–380. [Google Scholar]
- 86.St John RK. Yaws in the Americas. Rev Infect Dis. 1985;7 Suppl 2: S266—272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.PAHO. 29th Pan American Sanitary Conference. 69th Session of the Regional Committee of WHO for the Americas. Strategic Plan of the Pan American Health Organization 2014–2019. Washington (DC): Panamerican Health Organization; 2017.
- 88.Mitjà O, Asiedu K, Mabey D. Yaws. Lancet. 2013;381: 763–773. 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)62130-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
(DOCX)
Data Availability Statement
It is a systematic review, all the included papers are published online and can be found in the references of the paper.