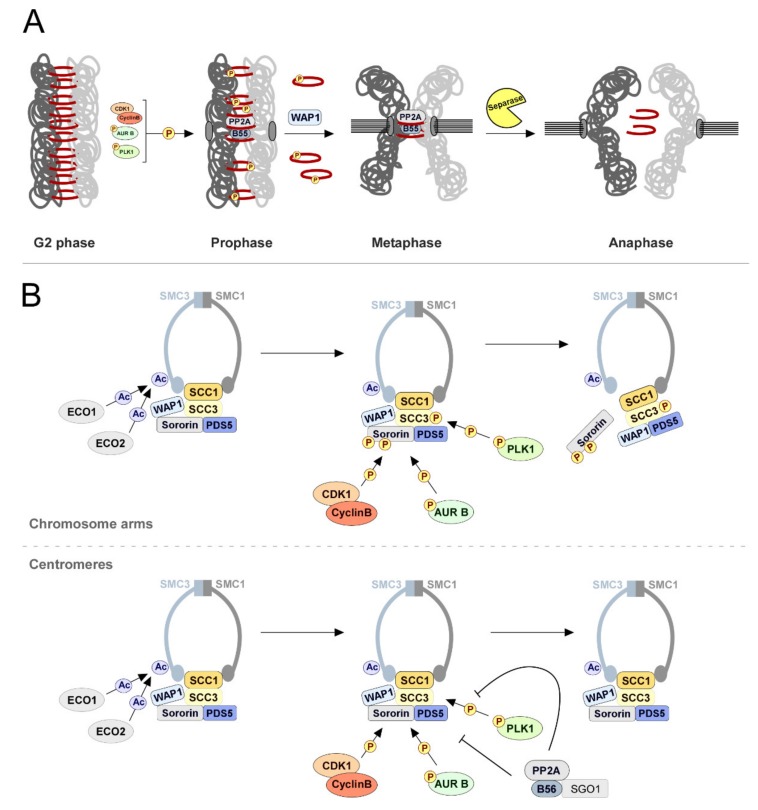
Figure 4.
PP2A-B56 maintains centromeric cohesion until anaphase onset. (A) Following DNA replication, sister chromatids are held together by cohesin-ring complexes. During prophase, CDK1, PLK1, and Aurora B trigger WAP1-mediated removal of cohesin from chromosome arms. Centromere cohesion is protected from WAP1 by the activity of PP2-B56 bound to SGO1. Centromeric PP2-B56 antagonizes the phosphorylations catalyzed by the mitotic kinases, hence maintaining cohesion at centromeres until kinetochores of all chromosomes are correctly attached to microtubules of opposite spindle poles. At this stage, Separase catalyzes the proteolytic degradation of cohesin complexes, abolishing cohesion and enabling sister chromatid separation in anaphase. (B) During G2, cohesin rings are insensitive to WAP1 by Sororin recruited to acetylated SMC3. The presence of Sororin prevents WAPl binding to PDS5. Following mitotic entry, Aurora B- and CDK1-dependent phosphorylation of Sororin causes its dissociation, thus consenting WAP1 binding to PDS5. WAP1-mediated removal of cohesin also requires phosphorylation of SCC3 by PLK1. At centromeres, PP2A-B56 in complex with SGO1 counteracts Aurora B, CDK1, and PLK1 destabilizing phosphorylations and thereby prevents the dissociation of cohesin complexes by WAP1.