Abstract
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDP-GlcNAc) acyltransferase (LpxA) catalyzes the first step of lipid A biosynthesis, the transfer of an R-3-hydroxyacyl chain from its acyl carrier protein (ACP) to the 3-OH group of UDP-GlcNAc. Essential in the growth of Gram-negative bacteria, LpxA is a logical target for antibiotics design. A pentadecapeptide (Peptide 920) with high affinity towards LpxA was previously identified in a phage display library. Here we created a small library of systematically designed peptides with the length of four to thirteen amino acids using Peptide 920 as a scaffold. The concentrations of these peptides at which 50% of LpxA is inhibited (IC50) range from 50 nM to >100 μM. We determined the crystal structure of E. coli LpxA in a complex with a potent inhibitor. LpxA-inhibitor interaction, solvent model and all contributing factors to inhibitor efficacy were well resolved. The peptide primarily occludes the ACP binding site of LpxA. Interactions between LpxA and the inhibitor are different from those in the structure of Peptide 920. The inhibitory peptide library and the crystal structure of inhibitor-bound LpxA described here may further assist in the rational design of inhibitors with antimicrobial activity that target LpxA and potentially other acyltransferases.
Introduction
Lipid A is the hydrophobic anchor that secures the sugar components (core and O-groups) of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) to the external surface of the outer membrane1,2. The lipid A component of LPS also elicits an immune response in animal systems2–4. The minimal structure required for the viability of Gram-negative bacteria is lipid IVA5. Because lipid A is essential for the viability of Gram-negative bacteria, all the enzymes involved in its biosynthesis represent potential targets for inhibitory compounds with antibacterial activities6.
UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase (LpxA) catalyzes the first step of lipid A biosynthesis2,3. LpxA catalyzes the transfer of an R-3-hydroxymyristoyl chain from ACP to the 3-OH glucosamine group of UDP-GlcNAc. The acylation of UDP-GlcNAc is a thermodynamically unfavorable reaction with an equilibrium constant of ~0.017,8. Consequently, the second step of lipid A biosynthesis, catalyzed by the deacetylase LpxC, is the committed and first irreversible step of this pathway. Lipid A synthesized by most Gram-negative bacteria is similar to that of E. coli. Structural differences observed in the lengths of the acyl chain in the lipid A of various Gram-negative bacteria at the 3 and 3′ positions of the disaccharide glucosamine ring can be attributed to the differences in acyl chain specificity of the various LpxA orthologs. LpxA shows specificity for acyl chain containing a 3-OH moiety and only utilizes ACP as its donor substrate7. For example, E. coli LpxA is unable to substitute myristoyl-ACP for R-3-hydroxymyristoyl-ACP7. However, myristoyl-ACP appears to be an inhibitor of LpxA. Interestingly, Chlamydia trachomatis LpxA is unique in its ability to utilize myristoyl-ACP instead of R-3-hydroxymyristoyl-ACP9. Though highly specific for a R-3-hydroxymyristoyl-ACP, E. coli LpxA is capable of utilizing a shorter R-3-hydroxydecanoyl-ACP and R-3-hydroxylauroyl-ACP, albeit far less efficiently7,10. A single amino acid change in E. coli LxpA appears to be responsible for acyl chain specificity. A G173M mutation reverses the acyl chain specificity of E. coli LpxA from a 14-carbon acyl chain dependent enzyme to a 10-carbon acyl chain dependent enzyme11. The reverse mutation (M169G) in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, LpxA converts the acyl chain preference from a 10-carbon acyl chain to a 14-carbon acyl chain11,12.
The crystal structure of LpxA reveals a homotrimer that possesses a left-handed parallel β-helix. Each monomeric subunit of the trimer contains two domains, an NH2-terminal β-helical domain (residues 1–186), and a COOH-terminal α-helical domain (residues 187–262)13–15. The active site is located in a deep cleft between adjacent subunits where there are multiple conserved histidines and other basic residues. Each active site is related by symmetry, and therefore LpxA has three identical active sites. Previous crystallographic and mutagenesis studies demonstrated that LpxA’s likely proceed through a general base catalytic mechanism using an absolutely conserved catalytic histidine (H125)13,14,16. Other conserved basic residues such as H122, H144, H160, and R208 were proposed to be involved in substrate binding based on mutagenesis studies that revealed a significant reduction in the enzymes’ activities as well as a shift in the apparent Kms13,14,16.
Previously, we described Peptide 920, a 15 amino acid long potent inhibitor of E. coli LpxA with an IC50 of 60 nM13. Using Peptide 920 as a scaffold, a small peptide library was created and screened. Our goal was to search for a smaller efficacious peptide with an enhanced inhibitory potential, as well as to identify the essential residues that contribute to inhibitor potency (Table 1). The most potent inhibitor was structurally characterized to visualize carefully those interactions that contributes to inhibitor efficacy.
Table 1.
A small library of the truncated Peptide 920 and their IC50.
| Peptide identity | Peptide sequence | IC50 |
|---|---|---|
| Peptide 920 | SSGWMLDPIAGKWSR | 60 ± 9 nM* |
| Truncation of Peptide 920 N-terminus | ||
| CR19 | GWMLDPIAGKWSR | 77 ± 3 nM |
| CR20 | WMLDPIAGKWSR | 50 ± 6 nM |
| Truncation of Peptide 920 C-terminus | ||
| CR21 | SSGWMLDPIAGKWS | 12 ± 1.4 μM |
| CR22 | SSGWMLDPIAGKW | 9 ± 2.2 μM |
| Truncation of Peptide 920 N and C- terminus | ||
| CR23 | GWMLDPIAGKW | 10 ± 0.3 μM |
| CR24 | GWMLDPIA | >100 μM |
| CR25 | WMLDPI | >100 μM |
| CR26 | WMLD | >100 μM |
*IC50 value taken from previous publication13. Error bars show standard deviations of triplicates.
Here we report the successful crystallization of E. coli LpxA complexed with peptide CR20 (WMLDPIAGKWSR) at a resolution of 1.60 Å. Peptide CR20 is a potent inhibitor of E. coli LpxA with an IC50 of ~50 nM. The peptide is located at the interface of each adjacent subunit and interacts with residues from both sides. It occupies part of the ACP binding site that was inferred from previous structural and mutagenesis studies13,17. All the residues of the peptide CR20 were well resolved. The design and characterization of our small library of peptides complemented with the structural characterization of LpxA-peptide CR20 complex sheds light on the key residues in LpxA that are important inhibitory targets. It also shed light on the residues of the peptide that contributes to inhibitor efficacy. For example, removing a single amino acid from the C-terminus of the peptide results in a three orders of magnitude loss in the efficacy of peptide CR20. Additionally, a higher resolution the crystal structure of peptide CR20 bound to LpxA may assist in the rational design of inhibitors with antibiotic activity.
Results
A small library of truncated peptides
Peptide 920 was identified in phage display library, and when expressed fused to glutathione sepharose (GST) in E. coli, it inhibited bacterial growth and showed high specificity for its target, LpxA18. Here we systematically designed and synthesized a small library of peptides using Peptide 920 as the scaffold. The peptides were assayed for acyl transferase inhibitory activity under conditions where the concentrations of UDP-GlcNAc and R-3-hydroxymyristoyl-ACP were 1 µM each. The data revealed that truncations at the N-terminus of Peptide 920 were tolerated more so than truncations at the C-terminus (Table 1). Removal of three residues at the N-terminal of Peptide 920 created an efficacious peptide (CR20) with an IC50 ~ 50 nM. Conversely, removal of the arginine from the C-terminus (Peptide CR21) resulted in a two orders magnitude shift in the IC50 (10 μM). Peptide CR21 and CR23 still have good inhibitory potential of 10 μM albeit lower than peptide CR20. This data suggests the contacts made by the C-terminus of the peptide are crucial for inhibitor efficacy and probably stability in the active site of LpxA.
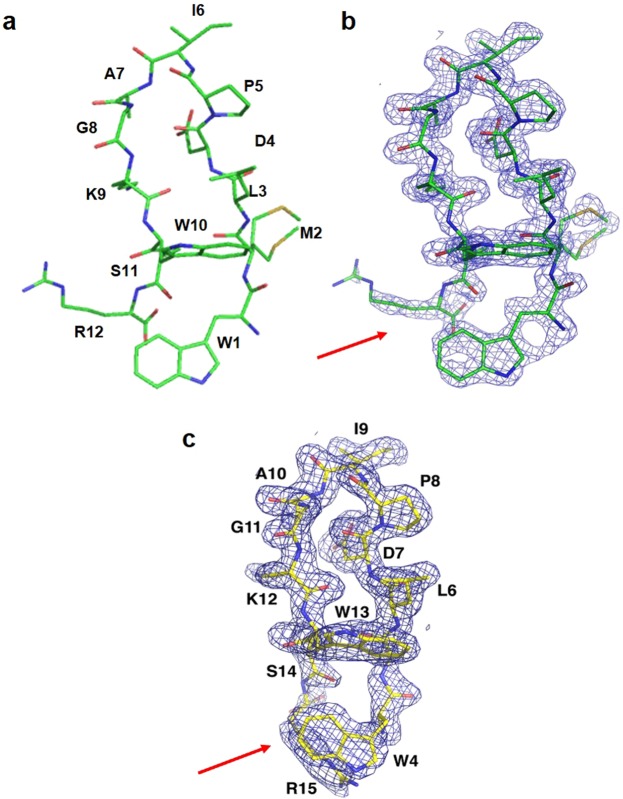
To structurally assess the specific interactions of peptide CR20 with LpxA, this complex was crystallized. LpxA was crystallized in the presence of 25 molar excess of peptide CR20. The crystals diffracted to a resolution of 1.60 Å and the complex solved by molecular replacement using the coordinates of the free enzyme (PDB ID: 1LXA) as a model. There is a single LpxA molecule in the asymmetric unit, and three asymmetric units associate around a crystallographic three-fold axis to form the homotrimer of LpxA (Fig. 1). The refinement converged Rwork and Rfree to 0.191 and 0.218 respectively, (Table 2) with a low all-atom clash score and good geometry. All 262 residues of E. coli LpxA were visible, with the exception of the methionine side chain at position one. All 12 residues of the peptide were clear and well defined with multiple conformations of the side chain of the methionine at position 2 (Fig. 2).
Figure 1.
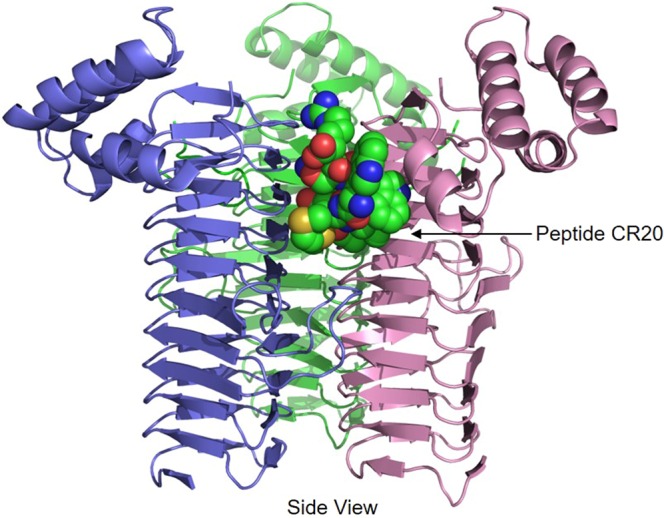
Crystal Structure of LpxA-peptide CR20 complex at 1.60 Å. The individual subunits are colored pink, green, and blue. The LpxA N termini is located at the bottom, and displays the start of the β-helix domain of each subunit. The peptide (green) is in a β-hairpin conformation with the N and C termini exposed to solvent. In the peptide, the carbons are colored green, the nitrogens blue, and the oxygens red. The free enzyme (LpxA)and LpxA-peptide CR20 reveal that there were not much global movements in the side chains except for minor perturbations of those interacting directly with the peptide. LpxA appears to be a rigid structure where bound ligands are more likely to adopt different conformations, as noted previously13.
Table 2.
Data-collection and refinement statistics. Values in parentheses are for the outer shell.
| Data Collection | LpxA |
|---|---|
| Ligand added | Peptide CR20 |
| Data collection | |
| Wavelength (Å) | 1.5415 |
| Resolution range (Å) | 21.65–1.60 (1.69–1.60) |
| Space group | P213 |
| a = b = c (Å) | 96.73 |
| CC1/2 (%) | 94.80 (76.70) |
| Unique reflections | 34668 (2647) |
| Completeness (%) | 99.84 (100) |
| Mean I/σ(I) | 14.2(3.9) |
| Wilson B factor (Å2) | 23.684 |
| R merge a | 0.078 (0.085) |
| Refinement | |
| R factor b | 0.1910 (0.453) |
| R free c | 0.2260 (0.3850) |
| No. of atoms | 2500 |
| No. of waters | 400 |
| No. of protein residues | 274 |
| R.m.s.d., bonds (Å) | 0.007 |
| R.m.s.d., angles (°) | 1.091 |
| Ramachandran favored (%) | 98.5 |
| Ramachandran outliers (%) | 0 |
| B factors (Å 2 ) | |
| Protein | 23.68 |
| Ligand | 25.68 |
| Solvent | 38.90 |
| All-atom clash score | 2.85 |
| Molprobity score | 1.07 (99th percentile) |
Resolution limit was defined as the highest resolution shell where the average I/σ(I) was 2.
aRmerge = ΣhklΣi|Ii(hkl) − <I(hkl)>|/ΣhklΣiI(hkl).
bRfactor = Σ|Fo − Fc|/ΣFo. Five percent of the reflections was used to calculate cRfree.
Figure 2.
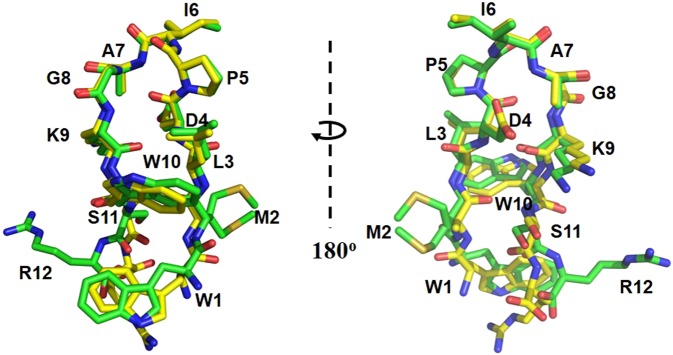
Alignment of Peptide 920 and peptide CR20. The two peptides fold slightly different. Peptide 920 (PDB ID: 2AQ9) carbons are colored in yellow, oxygens in red and nitrogens in blue. Peptide CR20 carbons are colored in green, oxygens in red and nitrogens in blue. The model on the right is rotated 180°, showing the rear view of the model on the left.
Peptide CR20 residues bind between adjacent subunits in the active site region. The left-handed β-helix fold of LpxA is not perturbed upon peptide binding (Fig. 1). An overlay of LpxA-Peptide 92013 and LpxA-peptide CR20 gave a root-mean-square distance of 0.074 for all Cα pairs of the backbone. A comparison of the side chains from the free enzyme (LpxA), and LpxA-peptide CR20 reveal that there were not much global movements in the side chains or backbone of LpxA except for minor perturbations of those interacting directly with the peptide15. LpxA is a rigid structure where bound ligands are more likely to adopt different conformations.
Interactions between peptide CR20 and LpxA
LpxA-bound peptide CR20 is folded into a β-hairpin conformation. The hairpin inserts into the active site of LpxA and the N and C termini of the peptide is solvent exposed. Peptide CR20 makes extensive contacts with LpxA. An overlay of Peptide 920 and peptide CR20 reveals similarity between the buried portions of the peptide; however, there were differences observed in the residues at the end of the C and N termini (Fig. 2)13. In LpxA- Peptide 920 there appears to be a cation-π interaction between the arginine (R15) at the C-terminus of the peptide and the tryptophan (W4) at the N-terminus. In contrast, the R15 in peptide CR20, is flipped 180°, (Fig. 2) while, the tryptophan is interacting with R204 via a water-mediated interaction instead of a cation-π interaction (Fig. 2). This observation suggests that these bulky residues are indeed flexible and they could be manipulated for peptidomimetics.
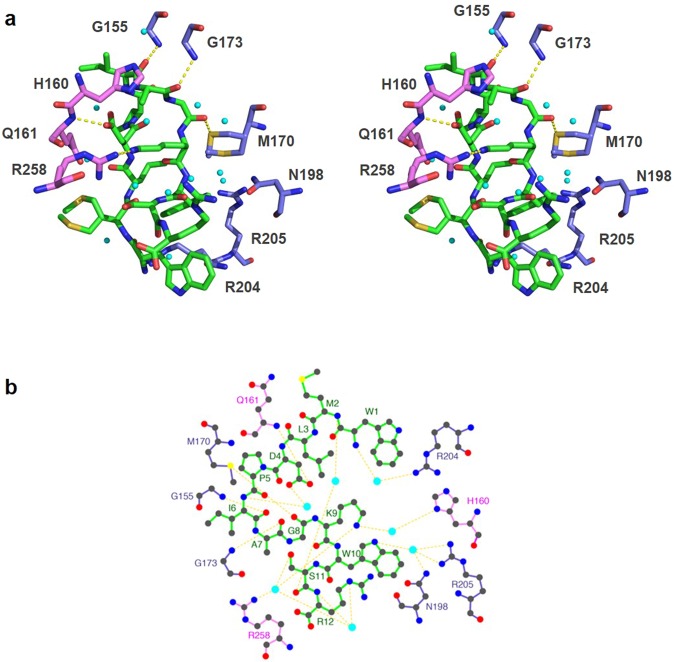
The overall density of the peptide CR20 (all 12 residues) and the surrounding residues from LpxA was clear and continuous (Fig. 3). Peptide CR20 does not disrupt any contacts between the individual monomers of LpxA, but instead forms a bridge between the adjacent subunits. The significant interaction of peptide CR20 with LpxA is sustained by hydrogen bonds, some of which are mediated by water molecules. There is indeed an intricate hydrogen-bonding network with at least thirteen water molecules that are directly hydrogen-bonded to peptide CR20 (Fig. 4). Residues of LpxA involved in direct hydrogen bonds with the peptide are Q161 (backbone N) and R258 from one protomer and G155, G173, and M170 from the adjacent protomer (Fig. 4). These direct hydrogen bonds are also present in the LpxA-Peptide 920 complex13. However, there were differences, in the partners they engage with for hydrogen bond interactions. For example, R258 is directly hydrogen bonded to K9 of peptide CR20 instead of S11, and M170 is hydrogen bonded to the backbone carbonyl of G8 in peptide CR20 instead of W10 (Fig. 4). Residues that interact with peptide CR20 via water-mediated interactions are R204, R205, N198, and Q161 (side chain) from the blue chain and H160 from the pink chain. Only, Q161 water mediated interaction was previously observed in the LpxA-Peptide 920 complex13 (Fig. 4). It appears that there are localized deviations in the way the peptide is supported in the active site of LpxA, although peptide-binding region remains the same. There are four additional hydrogen bonds that are formed within peptide CR20. The peptide β-hairpin conformation may be supported by these intra-peptide hydrogen bonds.
Figure 3.
Electron density maps of peptide CR20 and Peptide 920. (a) Peptide CR20 is shown as a stick model with carbons in green. (b) The 2fo-fc electron density map is contoured at 1σ around peptide CR20. There are multiple conformations of the methionine side chain. (c) The 2fo-fc electron density map contoured at 1σ around Peptide 920 (PDB ID: 2AQ9). The density for the methionine side chain was missing in this model. Red arrows point to the different orientations in residues at the N and C termini of the two peptides.
Figure 4.
A close-up of peptide CR20 interactions with LpxA. (a) Stereo-view of polar interactions made by LpxA-peptide CR20. Peptide CR20 is colored in green and the LpxA subunit is colored in blue or pink, consistent with the color scheme of Fig. 1. All the N and O atoms are blue and red, respectively. Hydrogen bonds are yellow dashed lines. Water molecules are cyan spheres. Hydrogen bonds involving water are not included for clarity. (b) Key interactions between peptide CR20 and LpxA in 2D. Hydrogen bonds are shown as yellow dashes. Water molecules are cyan circles. The 2D interaction diagram was created by LigPlot + software29.
The importance of residues implicated in peptide binding
Peptide CR20 is interacting with residues implicated in substrate binding as revealed by previous mutagenesis studies (H160, G173 and R204) (Fig. 5)19. G173 involved in acyl chain binding is not interacting with the proposed catalytic residue (H125) but could potentially block or partially occlude access to this residue. The peptide interacts with H160 via a water-mediated interaction (Fig. 4). The H160A mutant has significantly less activity than the wild-type19 however this residual activity was resistant to inhibition by peptide CR20 (IC50 ~10,000 µM) (data not shown). This was surprising at first, however, H160 is interacting with K9 of the C-terminus of the peptide CR20, which is essential to the efficacy of the peptide interaction with LpxA.
Figure 5.
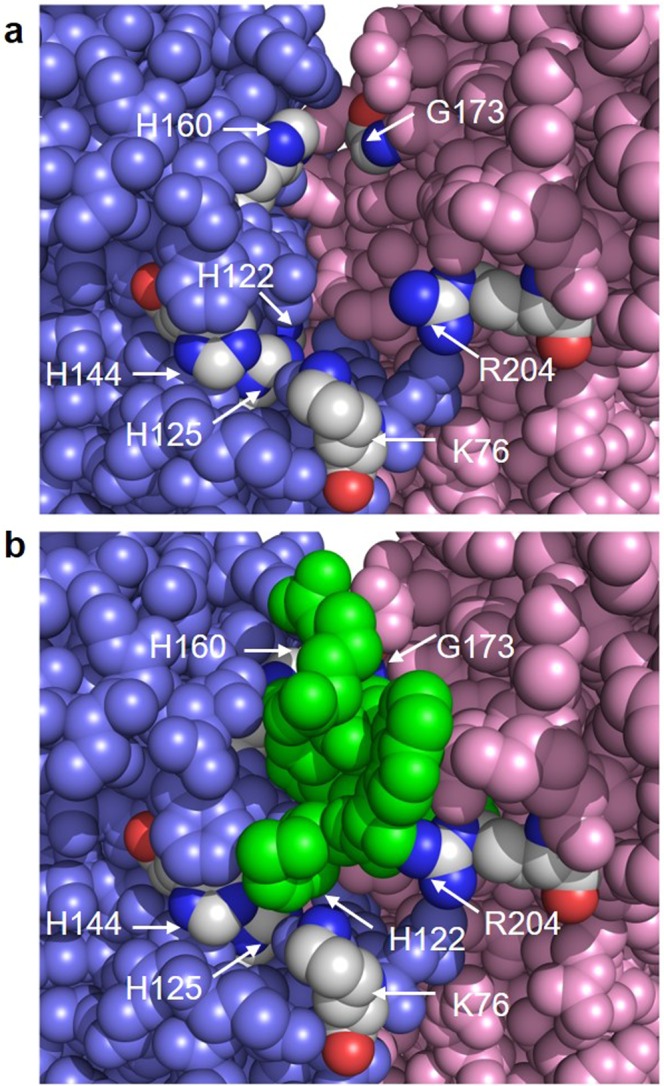
Location of peptide CR20 and conserved residues implicated in catalysis. (a) View into one of the three peptide-binding cavities of the LpxA trimer with the peptide CR20 hidden. LpxA subunits are colored pink, slate, or green (not visible) as in Fig. 1. Key residues implicated in catalysis or substrate binding by mutagenesis are colored according to element with carbons in grey. (b) Same view as above but with peptide CR20 present in green. Conserved LpxA residues are labeled in white. There is some space between peptide CR20 and the conserved residues H125, H144, H122 and K76. Peptide CR20 is interacting with G173 and H160, these residues are largely hidden from view. In the complete model, a few water molecules are located in the space beneath peptide CR20 (not shown).
Discussion
Lipid A (endotoxin) plays an important role in bacterial growth, outer membrane integrity, and stimulation of the mammalian immune system1,2,20. All the enzymes in the lipid A pathway are potential targets for inhibitors and some may be effective antibiotics. LpxA catalyzes the first step of lipid A biosynthesis and is essential for viability in most Gram-negative pathogens2.
The E. coli LxpA-peptide CR20 complex solved at high resolution (1.60 Å) facilitated the identification of a dedicated space in the essential LpxA enzyme that can be targeted for inhibitors. LpxA has two substrates: UDP-GlcNAc and acyl-ACP. The binding site of both substrates have been identified in previous structural studies13,14,16,17. Peptides CR19-CR22 represent potential starting points for the design of potent more efficacious inhibitor that target LpxA (Table 1). The most efficacious peptide CR20 binds in a region that would mainly occlude the binding site of acyl-ACP. The superposition of the CR20-bound LpxA to the UDP-3-O-(R-hydroxymyristoyl)-GlcNAc product bound structure shows that peptide CR20 overlaps with the UDP-3-O-(R-hydroxymyristoyl)-GlcNAc product in active site of LpxA (Fig. 6a–c). Peptide CR20 is a potent inhibitor of LpxA with an IC50 of approximately 50 nM (Table 1).
Figure 6.
Superpositions of LpxA and LpxD. (a) The structure of LpxA with the bound product, UDP-3-O-(R-hydroxymyristoyl)-GlcNAc (PDB ID: 2QIA). LpxA is shown in grey and UDP-3-O-(R-hydroxymyristoyl)-GlcNAc is shown in pink. (b) LpxA-peptide CR20 superposed with the product bound structure of LpxA. (c) A close-up view to the product binding site. Peptide CR20 overlaps with UDP-3-O-(R-hydroxymyristoyl)-GlcNAc product. (d) The structure of LpxD in complex with the intact R-3-hydroxymyristoy-ACP (PDB ID: 4IHF). LpxD is shown in orange. ACP and the pantetheine arm are shown in cyan and magenta, respectively. (e) LpxA-peptide CR20 superposed with LpxD and intact R-3-hydroxymyristoy-ACP. (f) A close-up view to the acyl-ACP binding site. Peptide CR20 occludes the binding site of acyl-ACP at the pantetheine arm.
Peptide CR20 is more ordered in the active site of LpxA than Peptide 920. The electron densities of all 12 residues of peptide CR20 was clear and well defined. Notably, the interaction of peptide CR20 with LpxA is secured by a majority of polar interactions some of which are mediated by water molecules. There are approximately 13 water molecules involved in water-mediated interactions or supporting the peptide in the LpxA active site by hydrogen bonding (Fig. 4), suggesting that in the absence of substrate the active site is highly solvated. Delivery of the acyl chain by ACP would displace the solvent in the active site of LpxA.
Acyl carrier protein is an important component in fatty acid and polyketide biosynthesis. Recently, crystal structures of LpxD, the second acyltransferase in the Lipid A pathway, in complex with intact acyl-ACP gave an unprecedented view of how ACP delivers acyl chain linked to prosthetic 4′-phosphopantethiene group among acyl transferases in the lipid A pathway15. LpxA and LpxD share significant structural homology (Fig. 6d,e). A superposition of LpxA-peptide CR20 with LpxD-acyl-ACP reveal conservation of the acyl-ACP binding site (Fig. 6d–f). In support of previous enzymatic evidence that revealed Peptide 920 is largely competitive with respect to ACP11, it appears that Peptide 920 would block access of ACP to its binding site on LpxA. Perhaps, these basic residues (H160, R258, Q161 R204, R205, N198) (Fig. 3) play a role in ACP binding. ACP is a highly acidic protein with an isoelectric point of 4.1 and a pH solubility of roughly 3.921. It is likely that the charge complementarity between the LpxA and ACP interacting regions would be disrupted by inhibitory peptides. The binding site of CR20 and the other peptides presented herein could be targeted for rational design of antibiotics that could block acyl chain delivery by ACP.
Because small peptides do not cross membranes and are subjected to protease degradation, the use of peptide CR20 or the other inhibitory peptides as drugs, targeting cytoplasmic LpxA is unrealistic. However, we have mapped the space and location of important residues of LpxA, that if engage by small molecules could contribute efficiently to the inhibition of LpxA. Therefore, all the structural and biochemical information garnered from this study are promising starting points for the development of antimicrobials using structure-based drug design. The results of this study should provide useful information for the further development of molecules that target the essential lipid A enzyme, LpxA.
Materials and Methods
Sample Preparation for crystallization
LpxA was overexpressed and purified as previously described11,19. Briefly, LpxA was purified from BL21(DE3)/pLysE/pTO1. The construct pTO1 is a pET23c (Novagen) vector that contains the wild type lpxA gene. Cells were lysed by one passage through a French pressure cell at 18,000 psi and centrifuged at 10,000 xg for 20 min to remove cell debris. The supernatants were further centrifuged at 100,000 xg for 90 min to obtain soluble proteins. The purification scheme consists of Green19-Agarose (Sigma) affinity chromatography (pH 7.4), followed by Source Q ion-exchange chromatography (pH 8) and Superdex 200 gel filtration chromatography in 10 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7, containing 250 mM NaCl8,19,22. The purity of LpxA was evaluated by SDS-PAGE, LpxA activity assays, and electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Mass spectra analyses were performed on a QSTAR XL quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometer (ABI/MDS-Sciex, Toronto, Canada) equipped with an electrospray source23. Peptide CR20 (NH2-WMLDPIAGKWSR-COOH) and other truncated peptides described in this work were prepared at the University of North Carolina Peptide Synthesis Facility (Table 1). Each synthesized peptide was evaluated by MALDI mass spectrometry and was confirmed to have greater than 90% purity.
Protein crystallization
Co-crystals of LpxA- peptide CR20 complex were obtained by combining a concentrated LpxA solution (20 mg/ml) with a 25-fold molar excess of peptide CR20 (12.5 mM). Crystals of LpxA- peptide CR20 were obtained by hanging drop vapor diffusion method from a 1:1 mixture of peptide and protein. Individual droplets contained 2 μl of the LpxA- peptide CR20 mixture and 2 μl of 0.8–1.8 M phosphate buffer, pH 6.3–6.9. Crystals appeared after 24 hrs and grew to approximately 1.0 mm after 2 weeks.
Data Collection, Structure Determination and Refinement
Crystals of the LpxA-peptide CR20 complex were cryo-protected in 1.0 M Na/K phosphate, pH 6.9, and 35% DMSO, and then were flash cooled in liquid nitrogen. Diffraction data were collected on an R-Axis IV image plate detector. Diffraction images were processed and scaled using HKL2000. Crystals diffract to 1.60 Å and belong to the cubic space group P213 (a = b = c = 96.73 Å, Table 2). Phases were calculated using molecular replacement with the program MolRep in the CCP4i suite24. Previously published structure of LpxA monomer was used as the search model (PDB code 1LXA). Iterative rounds of model building were performed using O and COOT, with rounds of refinement in REFMAC24–26. The quality of the final model was evaluated using MolProbity and PROCHECK (PDB ID: 6HY2)27,28. The figures were drawn using PyMOL (DeLano Scientific, San Carlos, CA). Data collection and refinement statistics are presented in Table 2.
Inhibition of LpxA activity by Peptide 920
The LpxA enzymatic reaction monitors the conversion of [α-32P]UDP-GlcNAc to [α-32P]UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxymyristoyl)- GlcNAc. The assay components consist of 40 mM HEPES buffer, pH 8, 1 mg/ml BSA, 1 μM R-3-hydroxymyristoyl-ACP, and 1 μM [α-32P]UDP-GlcNAc (2 × 106 cpm/nmol). Truncated peptides (Table 1) was dissolved in DMSO and pre-incubated with the reaction mixture at 30 °C for 3 minutes in the absence of enzyme at concentrations ranging from 1 nM to 10 µM. The final concentration of DMSO was adjusted to 10% to match the peptide solvent in all enzymatic assays.
The reactions were started by the addition of 1 nM of LpxA and incubated at 30 °C for a maximum of 10 min. Three or four time points were collected during this time. Termination of the reaction was accomplished by the addition of 1 μl portions onto a silica thin layer chromatography (TLC) plate. The TLC plates were air dried for 10 min before developing in chloroform/methanol/water/acetic acid (25:15:4:2, v/v). Plates were exposed to PhosphorImager screens overnight, and the data were evaluated with Molecular Dynamics PhosphorImager equipped with ImageQuant software. Inhibition of LpxA by Peptide 920 and truncated peptides was analyzed by plotting the initial velocities as a function of the inhibitor concentration. To determine the IC50 at 30 °C, the data were fit to the following equations,
| 1 |
or
| 1a |
vi represents the initial rate, at given concentrations of inhibitor, vc represents the initial velocity of the control reaction without inhibitor, and I represents the inhibitor concentration. The IC50 determination represents the concentration of inhibitor needed to inhibit 50% of the enzyme activity.
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge James Phillips the manager of the Duke University x-ray crystallography facility, for his technical assistance and his thorough grasp of the knowledge of data collection and processing. This research was supported by NIH Grant GM-51310 to CRH Raetz and in part by the CMB training grant (GM-07184) to AHW. We thank Dr. Evelyne Richet for helpful comments on this manuscript.
Author Contributions
A.H.W. and C.R.H.R. designed research. M.D. and A.H.W. conducted experiments, collected and analyzed data. A.H.W. wrote the manuscript. M.D. prepared figures. C.R.H.R. and A.H.W. supervised the work.
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Raetz CR. Biochemistry of endotoxins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:129–170. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.001021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Raetz CR, Whitfield C. Lipopolysaccharide endotoxins. Annual review of biochemistry. 2002;71:635–700. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.71.110601.135414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Raetz CR, Dowhan W. Biosynthesis and function of phospholipids in Escherichia coli. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1990;265:1235–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Loppnow H, et al. IL-1 induction-capacity of defined lipopolysaccharide partial structures. J Immunol. 1989;142:3229–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Klein G, Lindner B, Brabetz W, Brade H, Raina S. Escherichia coli K-12 Suppressor-free Mutants Lacking Early Glycosyltransferases and Late Acyltransferases: minimal lipopolysaccharide structure and induction of envelope stress response. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:15369–15389. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M900490200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wyckoff TJ, Raetz CR, Jackman JE. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory agents that target endotoxin. Trends in microbiology. 1998;6:154–159. doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(98)01230-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Anderson MS, Raetz CR. Biosynthesis of lipid A precursors in Escherichia coli. A cytoplasmic acyltransferase that converts UDP-N-acetylglucosamine to UDP-3-O-(R-3-hydroxymyristoyl)-N-acetylglucosamine. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1987;262:5159–5169. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Anderson MS, et al. UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase of Escherichia coli. The first step of endotoxin biosynthesis is thermodynamically unfavorable. The Journal of biological chemistry. 1993;268:19858–19865. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Sweet CR, Lin S, Cotter RJ, Raetz CR. A Chlamydia trachomatis UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase selective for myristoyl-acyl carrier protein. Expression in Escherichia coli and formation of hybrid lipid A species. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2001;276:19565–19574. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M101868200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Williamson JM, Anderson MS, Raetz CR. Acyl-acyl carrier protein specificity of UDP-GlcNAc acyltransferases from gram-negative bacteria: relationship to lipid A structure. Journal of bacteriology. 1991;173:3591–3596. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3591-3596.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wyckoff TJ, Lin S, Cotter RJ, Dotson GD, Raetz CR. Hydrocarbon rulers in UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:32369–32372. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.49.32369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dotson GD, Kaltashov IA, Cotter RJ, Raetz CR. Expression cloning of a Pseudomonas gene encoding a hydroxydecanoyl-acyl carrier protein-dependent UDP-GlcNAc acyltransferase. Journal of bacteriology. 1998;180:330–337. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.2.330-337.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Williams AH, Immormino RM, Gewirth DT, Raetz CR. Structure of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase with a bound antibacterial pentadecapeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2006;103:10877–10882. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0604465103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Williams AH, Raetz CR. Structural basis for the acyl chain selectivity and mechanism of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2007;104:13543–13550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0705833104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Raetz CR, Roderick SL. A left-handed parallel beta helix in the structure of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase. Science. 1995;270:997–1000. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5238.997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Robins LI, Williams AH, Raetz CR. Structural basis for the sugar nucleotide and acyl-chain selectivity of Leptospira interrogans LpxA. Biochemistry. 2009;48:6191–6201. doi: 10.1021/bi900629e. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Masoudi A, Raetz CR, Zhou P, Pemble CWT. Chasing acyl carrier protein through a catalytic cycle of lipid A production. Nature. 2014;505:422–426. doi: 10.1038/nature12679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Benson RE, Gottlin EB, Christensen DJ, Hamilton PT. Intracellular expression of peptide fusions for demonstration of protein essentiality in bacteria. Antimicrob Agents Ch. 2003;47:2875–2881. doi: 10.1128/Aac.47.9.2875-2881.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wyckoff TJ, Raetz CR. The active site of Escherichia coli UDP-N-acetylglucosamine acyltransferase. Chemical modification and site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:27047–27055. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.38.27047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nikaido H. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003;67:593–656. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.4.593-656.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Rock CO, Cronan JE., Jr. Re-evaluation of the solution structure of acyl carrier protein. J Biol Chem. 1979;254:9778–9785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pfitzner U, Raetz CR, Roderick SL. Crystallization of UDP-N-acetylglucosamine O-acyltransferase from Escherichia coli. Proteins. 1995;22:191–192. doi: 10.1002/prot.340220212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.McClerren AL, Zhou P, Guan Z, Raetz CR, Rudolph J. Kinetic analysis of the zinc-dependent deacetylase in the lipid A biosynthetic pathway. Biochemistry. 2005;44:1106–1113. doi: 10.1021/bi048001h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Murshudov GN, Vagin AA, Dodson EJ. Refinement of macromolecular structures by the maximum-likelihood method. Acta crystallographica. Section D, Biological crystallography. 1997;53:240–255. doi: 10.1107/S0907444996012255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jones TA, Zou JY, Cowan SW, Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta crystallographica. Section A, Foundations of crystallography. 1991;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/S0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Emsley P, Cowtan K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004;60:2126–2132. doi: 10.1107/S0907444904019158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Davis IW, Murray LW, Richardson JS, Richardson DC. MOLPROBITY: structure validation and all-atom contact analysis for nucleic acids and their complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004;32:W615–619. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkh398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lovell SC, et al. Structure validation by Calpha geometry: phi,psi and Cbeta deviation. Proteins. 2003;50:437–450. doi: 10.1002/prot.10286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Laskowski RA, Swindells MB. LigPlot+: multiple ligand-protein interaction diagrams for drug discovery. J Chem Inf Model. 2011;51:2778–2786. doi: 10.1021/ci200227u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]