SUMMARY
Propensity score matching is a common tool for adjusting for observed confounding in observational studies, but is known to have limitations in the presence of unmeasured confounding. In many settings, researchers are confronted with spatially-indexed data where the relative locations of the observational units may serve as a useful proxy for unmeasured confounding that varies according to a spatial pattern. We develop a new method, termed distance adjusted propensity score matching (DAPSm) that incorporates information on units’ spatial proximity into a propensity score matching procedure. We show that DAPSm can adjust for both observed and some forms of unobserved confounding and evaluate its performance relative to several other reasonable alternatives for incorporating spatial information into propensity score adjustment. The method is motivated by and applied to a comparative effectiveness investigation of power plant emission reduction technologies designed to reduce population exposure to ambient ozone pollution. Ultimately, DAPSm provides a framework for augmenting a “standard” propensity score analysis with information on spatial proximity and provides a transparent and principled way to assess the relative trade-offs of prioritizing observed confounding adjustment versus spatial proximity adjustment.
Keywords: Propensity score matching, Spatial confounding, Unobserved confounding
1. Introduction
Methods based on propensity score matching are widely used to estimate causal effects with observational data. Such methods rely crucially on the assumption of no unmeasured confounding. In settings of spatially-indexed data, unobserved confounders may exhibit a spatial pattern, inviting the use of spatial information to serve as proxy for similarity of units with respect to unmeasured confounding factors. Methods for confounding adjustment with spatially-indexed data have been most often considered in the context of regression adjustment, as in Paciorek (2010) and in related work that does not target confounding adjustment per se, but has been used for modeling spatially correlated residuals via spatial random effects (Hodges and Reich, 2010; Lee and Neocleous, 2010; Congdon, 2013; Chang and others, 2013; Lee and Sarran, 2015).
In this article, we unite the use of spatially-indexed data with propensity score matching while preserving the most salient benefits of using propensity scores. These benefits include the explicit comparison of treatments or policy interventions to estimate policy-relevant estimands such as the average treatment effect on the treated, as well as the oft-cited virtues of propensity score analysis related to the hypothetical “design” of a randomized study, for example, the ability to check observed covariate balance and overlap (Rubin, 2008). Augmenting such benefits with the notion that geographically closer units may exhibit similar unmeasured confounding profiles presents a methodological challenge.
The methods here are motivated by the threat of unmeasured spatial confounding that arises in studies of air pollution, where complex climatological and atmospheric processes are known to vary spatially and have strong associations with ambient air pollution, but are often unmeasured. For example, consider ambient ozone pollution, which has been previously linked to adverse health outcomes (Bell and others, 2004; Jerrett and others, 2009). A variety of regulatory strategies in the USA are designed to reduce ambient ozone pollution through incentivizing power-generating facilities (i.e. “power plants”) to reduce emissions of nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxides (NO ). When combined with sunlight and in the presence of available volatile organic compounds, NO
). When combined with sunlight and in the presence of available volatile organic compounds, NO emissions initiate atmospheric chemical reactions to form ambient ozone pollution (Allen, 2002). What’s more, regions where conditions tend to encourage the formation of ozone might be more likely to impose stricter rules on NO
emissions initiate atmospheric chemical reactions to form ambient ozone pollution (Allen, 2002). What’s more, regions where conditions tend to encourage the formation of ozone might be more likely to impose stricter rules on NO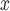 emissions. Thus, evaluating the effectiveness of emission-control strategies installed at power plants is met with the challenge that complete data on all relevant climatological, atmospheric, and regulatory confounders is almost never available but are expected to vary spatially. The goal of this article is to employ a matching procedure anchored to the propensity score to investigate whether, among coal or natural gas power plants, installation of selective catalytic or selective non-catalytic reduction (SCR/SNCR) NO
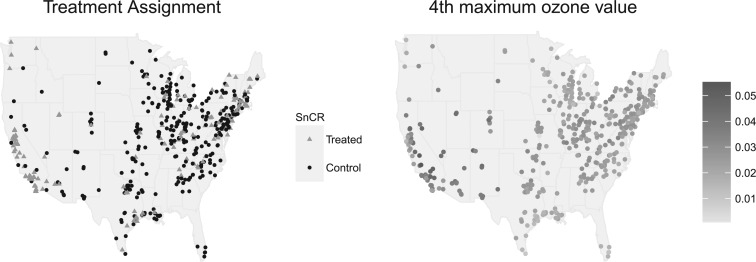
emissions. Thus, evaluating the effectiveness of emission-control strategies installed at power plants is met with the challenge that complete data on all relevant climatological, atmospheric, and regulatory confounders is almost never available but are expected to vary spatially. The goal of this article is to employ a matching procedure anchored to the propensity score to investigate whether, among coal or natural gas power plants, installation of selective catalytic or selective non-catalytic reduction (SCR/SNCR) NO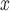 emission control technologies is more effective than alternatives for reducing ambient ozone. The treatment assignment and outcome of interest are depicted in Figure 1. Propensity scores are particularly useful for this type of policy evaluation because of the ability to adjust for confounding without strong reliance on a parametric model and the ability to empirically assess covariate balance and overlap. However, unmeasured spatial confounding presents a strong threat to the validity of a standard propensity-score analysis.
emission control technologies is more effective than alternatives for reducing ambient ozone. The treatment assignment and outcome of interest are depicted in Figure 1. Propensity scores are particularly useful for this type of policy evaluation because of the ability to adjust for confounding without strong reliance on a parametric model and the ability to empirically assess covariate balance and overlap. However, unmeasured spatial confounding presents a strong threat to the validity of a standard propensity-score analysis.
Fig. 1.
Map of facilities, colored by whether they are treated (yellow) or control (red), and map of ozone concentration surrounding power plants.
To confront these challenges, we present a new methodology, termed distance adjusted propensity score matching (DAPSm), which incorporates information from spatially-indexed data with the known virtues of propensity score matching. DAPSm incorporates observations’ spatial proximity into a matching procedure designed to adjust for observed confounders while adjusting for unmeasured spatial confounders by emphasizing, to varying degrees governed by a tuning parameter, the spatial proximity of matches. The central challenge of incorporating spatial proximity into propensity score matching is that proximity is a relative measure between two units, not a unit-specific measure like a confounder or the propensity score itself.
DAPSm shares important commonalities with the recently-proposed work of Keele and others (2015) in that both are matching methods that aim to leverage spatial proximity of units. We evaluate DAPSm relative to the method of Keele and others (2015) throughout, but note here that, despite similar conceptual goals, these methods are not directly comparable. The most salient difference has to do with reliance on the propensity score; DAPSm combines spatial proximity with propensity scores, whereas Keele and others (2015) provides an integer programing method that matches directly on covariates (i.e. not using propensity scores). Our goal here is not to investigate the relative merits of exact versus propensity score matching, but rather to isolate features related specifically to methods’ account of spatial confounding. DAPSm offers a tuning parameter governing the relative prioritization of observed covariate distances (measured through similarity of propensity score estimates) and spatial proximity. Keele and others (2015) entails a tuning parameter that governs the trade-off between spatial proximity of matches and the number of matches selected within a certain tolerance of observed covariate balance.
Both DAPSm and the method of Keele and others (2015) are evaluated in a simulation study alongside several other reasonable alternatives for incorporating spatial information into propensity score analysis. The methods are then deployed to compare the effectiveness of SCR/SNCR, relative to other strategies, for reducing NO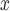 emissions and ambient ozone measured across 473 power plants and 921 air pollution monitoring locations in the USA. Ultimately, we show that incorporating spatial information in the matching can lead to substantively different conclusions when evaluating interventions on spatially-indexed observational units.
emissions and ambient ozone measured across 473 power plants and 921 air pollution monitoring locations in the USA. Ultimately, we show that incorporating spatial information in the matching can lead to substantively different conclusions when evaluating interventions on spatially-indexed observational units.
2. Notation, estimand of interest, and outline of propensity score matching
Let 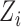 denote the indicator of whether the
denote the indicator of whether the 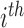 of
of 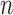 observations is subject to treatment, for example, the indicator of whether a power plant is treated with SCR/SNCR (
observations is subject to treatment, for example, the indicator of whether a power plant is treated with SCR/SNCR (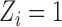 ) or not
) or not 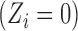 . Let
. Let 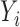 be a continuously-scaled outcome, for example, ambient ozone concentration in the area surrounding power plant
be a continuously-scaled outcome, for example, ambient ozone concentration in the area surrounding power plant 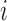 .
.
Each unit or observation is assumed to have two potential outcomes (Rubin, 1974), one under each value of the treatment. We denote 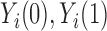 as the potential outcome of ambient ozone concentration in the area around unit
as the potential outcome of ambient ozone concentration in the area around unit 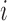 under value of
under value of 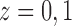 respectively. Assuming that the indexing of the observations is done at random, the index
respectively. Assuming that the indexing of the observations is done at random, the index 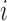 is suppressed. Interest often lies in the estimation of the average treatment effect in the treated population, defined as
is suppressed. Interest often lies in the estimation of the average treatment effect in the treated population, defined as 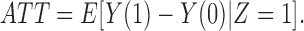
Among the assumptions required to estimate the ATT with observational data is that of “ignorable treatment assignment,” stating that observed covariates are sufficient to adjust for confounding of the treatment-outcome relationship. More formally, let 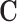 be a minimal set of confounding variables such as power plant characteristics, weather and atmospheric variables, and area-level demographics. The assumption of ignorability can be stated as:
be a minimal set of confounding variables such as power plant characteristics, weather and atmospheric variables, and area-level demographics. The assumption of ignorability can be stated as:
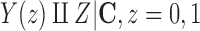 |
(2.1) |
under which the ATT can be estimated with observed-data comparisons between outcomes on treated and untreated units, conditional on 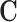 . Since
. Since 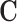 is assumed minimal, the ignorability assumption in (2.1) does not hold for any strict subset of
is assumed minimal, the ignorability assumption in (2.1) does not hold for any strict subset of 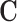 , implying that observed-data comparisons will not estimate the ATT when conditioning on a strict subset of C.
, implying that observed-data comparisons will not estimate the ATT when conditioning on a strict subset of C.
As the dimensionality of 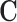 increases, investigators often use the propensity score to condense the information in C into a “balancing score” that can be used to adjust for confounding when comparing treated and untreated units. The propensity score is defined as the conditional probability of receiving treatment given the covariates,
increases, investigators often use the propensity score to condense the information in C into a “balancing score” that can be used to adjust for confounding when comparing treated and untreated units. The propensity score is defined as the conditional probability of receiving treatment given the covariates, 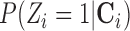 . The balancing property of the propensity score (Rosenbaum and Rubin, 1983) implies that the ignorability assumption in (2.1) can be translated to
. The balancing property of the propensity score (Rosenbaum and Rubin, 1983) implies that the ignorability assumption in (2.1) can be translated to 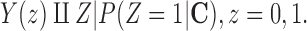
An overview of the various ways in which propensity scores can be used for confounding adjustment can be found in Stuart (2010), but we discuss methods in the context of 1:1 matching without replacement using a caliper. Such a procedure uses propensity score estimates to match one treated unit to one control unit with a similar propensity score estimate. A threshold, called a “caliper,” can be used to avoid matching observations with insufficiently similar propensity scores. For example, specifying a caliper of 0.1 prevents the matching of any two observations with propensity scores that differ by more than 0.1 standard deviations of the propensity score distribution. Matching produces a data set of matched treated and control observations with similar propensity score distributions, and thus more similar distributions of the covariates in 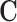 and a treatment indicator that is, under ignorability, unconfounded. The resulting matched data set can be used to estimate the ATT provided that all elements of
and a treatment indicator that is, under ignorability, unconfounded. The resulting matched data set can be used to estimate the ATT provided that all elements of 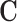 are observed and used to construct the propensity score.
are observed and used to construct the propensity score.
However, it is often the case with observational data that the vector of true confounders 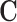 can be partitioned into two categories,
can be partitioned into two categories, 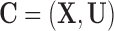 , where X denotes the confounders available in the observed data, and U denotes confounders that are unobserved. In the presence of unobserved confounders
, where X denotes the confounders available in the observed data, and U denotes confounders that are unobserved. In the presence of unobserved confounders 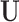 , the ignorability assumption in (2.1) cannot be satisfied by conditioning solely on the observed X, and the treatment effect is not identifiable from the data.
, the ignorability assumption in (2.1) cannot be satisfied by conditioning solely on the observed X, and the treatment effect is not identifiable from the data.
In many settings it is expected that some elements of U vary spatially so that locations that are geographically close are similar with regard to U. In this sense, the notion of prioritizing spatial proximity of matches has points of contact with the notion of a spatial “bandwidth” in a geographic regression discontinuity design (such as that in Keele and others (2015)), where only observations within the bandwidth are regarded as comparable on observed (and unobserved) factors. The method outlined below regards 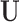 as unmeasured variables with a distribution over the whole geography of interest that is continuous as a function of space, with closer observations having more similar U.
as unmeasured variables with a distribution over the whole geography of interest that is continuous as a function of space, with closer observations having more similar U.
3. Distance adjusted propensity score matching
We propose a procedure that is anchored to the propensity score for matching on observed confounders, but augments confounding adjustment by incorporating spatial (geographical) information as a proxy for unobserved spatial variables, 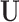 , such as weather and atmospheric conditions. In the presence of such
, such as weather and atmospheric conditions. In the presence of such 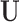 , prioritizing matched units that are geographically close to each other could yield better covariate balance on
, prioritizing matched units that are geographically close to each other could yield better covariate balance on 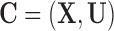 , thus (approximately) recovering the ignorability assumption and reducing bias of causal estimates. Formally, the variables
, thus (approximately) recovering the ignorability assumption and reducing bias of causal estimates. Formally, the variables 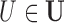 are such that
are such that 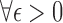 and point
and point 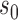 in the geography of interest
in the geography of interest 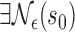 open set including
open set including 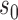 such that
such that 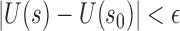 ,
, 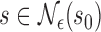 , wp1.
, wp1.
We define the distance adjusted propensity score (DAPS) as a new quantity for identifying good matches between treated and control units. In contrast to the propensity score which has a value for each unit, the DAPS is defined for every 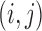 pair of treated, control observations. Specifically, for treated unit
pair of treated, control observations. Specifically, for treated unit 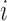 and control unit
and control unit 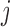 , the DAPS combines propensity score estimates and relative distances to define:
, the DAPS combines propensity score estimates and relative distances to define: 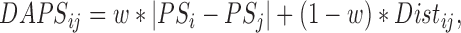 where
where 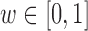 ,
, 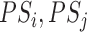 are propensity score estimates from modeling the treatment conditional on the observed confounders, and
are propensity score estimates from modeling the treatment conditional on the observed confounders, and 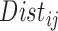 is a distance measure capturing the proximity of units i, j. DAPS is a weighted average of the propensity score difference used in “standard” propensity score matching and a measure of the distance between treated-control pairs. Therefore, it is a transparent measure of similarity between treated and control units, with an
is a distance measure capturing the proximity of units i, j. DAPS is a weighted average of the propensity score difference used in “standard” propensity score matching and a measure of the distance between treated-control pairs. Therefore, it is a transparent measure of similarity between treated and control units, with an 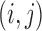 pair having small DAPS
pair having small DAPS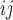 regarded as comparable on the basis of a combination of propensity score difference and spatial proximity.
regarded as comparable on the basis of a combination of propensity score difference and spatial proximity.
3.1. Choosing the weight w
Setting 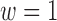 corresponds to setting DAPS equal to the absolute propensity score difference, and similarity of treated and control units is based solely on the observed confounders, without regard to spatial proximity. Setting
corresponds to setting DAPS equal to the absolute propensity score difference, and similarity of treated and control units is based solely on the observed confounders, without regard to spatial proximity. Setting 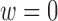 ignores
ignores 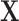 , defining similarity of units based solely on distance. In practice,
, defining similarity of units based solely on distance. In practice, 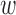 could be specified in the range
could be specified in the range 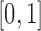 depending on contextual prioritization of observed confounding and the threats due to any suspected unobserved spatial confounding, with values closer to 0 for settings where unobserved spatial confounding is of particular concern. Data-driven procedures, such as the one described in Section 3.5 can be useful in choosing a
depending on contextual prioritization of observed confounding and the threats due to any suspected unobserved spatial confounding, with values closer to 0 for settings where unobserved spatial confounding is of particular concern. Data-driven procedures, such as the one described in Section 3.5 can be useful in choosing a 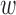 .
.
3.2. Choosing the distance measure
The quantity 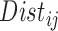 could be specified in many ways to quantify spatial proximity of units
could be specified in many ways to quantify spatial proximity of units 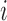 and
and 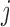 . A natural distance measure is the geographical distance between units
. A natural distance measure is the geographical distance between units 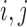 . A key consideration in choosing a distance measure is that its scale must be made comparable to that of the propensity score to ensure that one quantity does not arbitrarily dominate the calculation of DAPS. Since the absolute propensity score difference of two units can vary across the range
. A key consideration in choosing a distance measure is that its scale must be made comparable to that of the propensity score to ensure that one quantity does not arbitrarily dominate the calculation of DAPS. Since the absolute propensity score difference of two units can vary across the range 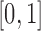 , the distance measure should also vary between 0 and 1, or on a range similar to the range of estimated propensity score differences (alternatively, instead of standardizing
, the distance measure should also vary between 0 and 1, or on a range similar to the range of estimated propensity score differences (alternatively, instead of standardizing 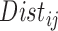 , one could scale
, one could scale 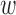 ).
).
One distance measure we consider is the standardized Euclidean distance (for simulations) or the standardized geo-distance (for the application). Specifically, if 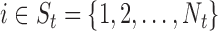 is a treated unit, and
is a treated unit, and 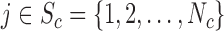 is a control unit, the standardized distance of
is a control unit, the standardized distance of 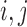 is defined as:
is defined as:
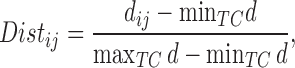 |
(3.2) |
where 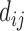 is the Euclidean (or geo) distance between
is the Euclidean (or geo) distance between 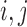 , and
, and 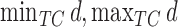 are the minimum and maximum distances of all the treated-control pairs.
are the minimum and maximum distances of all the treated-control pairs.
Other choices of distance measure can also arise in practice. For example, only permitting matches within certain boundaries (e.g. within states) corresponds to setting 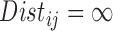 for
for 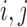 located in different states. Appendix A of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online presents an alternative definition relying on the empirical CDF of treated-control pairwise distances.
located in different states. Appendix A of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online presents an alternative definition relying on the empirical CDF of treated-control pairwise distances.
3.3. Selecting matches
We provide an R package that performs matching based on DAPS using an optimal or a greedy algorithm. The optimal algorithm uses the optmatch R package, and the greedy algorithm is described in Appendix B of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online. Gu and Rosenbaum (1993) found that optimal matching performed better than greedy matching in returning matched pairs with small Mahalanobis covariate distance, but returned similarly balanced matched data sets.
3.4. Specifying calipers
In DAPSm, a caliper can be defined as the number of DAPS standard deviations beyond which a value of DAPS is deemed too large to produce an appropriate match. In this situation, a treated-control pair cannot be matched if the corresponding DAPS of the pair is larger than the caliper. That is, the caliper is directly applied to the entire DAPS quantity.
Calipers could be alternatively defined to pertain separately to each component of DAPS. For example, one type of caliper could prevent any match with propensity score difference exceeding some threshold regardless of DAPS value, with an analogous caliper defined only for distance.
Note that when a caliper is not used, there is an equivalence between DAPSm with 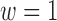 and standard 1-1 nearest neighbor propensity score matching. When a caliper is specified these procedures may not be exactly equivalent due to the definition of the caliper for the two procedures. Standard matching uses the standard deviation of propensity score estimates, while DAPSm uses the standard deviation of DAPS
and standard 1-1 nearest neighbor propensity score matching. When a caliper is specified these procedures may not be exactly equivalent due to the definition of the caliper for the two procedures. Standard matching uses the standard deviation of propensity score estimates, while DAPSm uses the standard deviation of DAPS 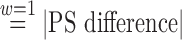 .
.
3.5. Data-driven choice of w
In DAPS, there is a transparent interplay between distance of observed covariates (as measured through the difference in the propensity score estimates) and distance of matched pairs. Automated data-driven procedures may be useful for selecting an appropriate value of 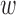 . We implement an automated procedure that re-calculates DAPS and performs matching across a range of possible
. We implement an automated procedure that re-calculates DAPS and performs matching across a range of possible 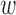 . As
. As 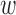 increases, balance of the observed covariates can be assessed, and the smallest value of
increases, balance of the observed covariates can be assessed, and the smallest value of 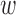 that maintains the absolute standardized difference of means (ASDM) of the observed confounders below a pre-specified cut-off is used. A different balance criterion can also be used. This choice of
that maintains the absolute standardized difference of means (ASDM) of the observed confounders below a pre-specified cut-off is used. A different balance criterion can also be used. This choice of 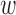 assigns the largest possible weight to proximity (and, by extension, to the unmeasured spatial confounders), while still maintaining balance of the observed confounders.
assigns the largest possible weight to proximity (and, by extension, to the unmeasured spatial confounders), while still maintaining balance of the observed confounders.
Even though this choice of 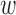 is such that it ensures observed covariate balance with respect to a specific criterion,
is such that it ensures observed covariate balance with respect to a specific criterion, 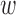 can be specified alternatively if subject-matter knowledge is available on an unmeasured spatial confounder. For example, there may be a known but unmeasured confounder (e.g. volatile organic compounds, baseline NO
can be specified alternatively if subject-matter knowledge is available on an unmeasured spatial confounder. For example, there may be a known but unmeasured confounder (e.g. volatile organic compounds, baseline NO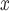 emissions in an air pollution study) that is regarded as more important than any measured variable. The value of
emissions in an air pollution study) that is regarded as more important than any measured variable. The value of 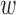 could be chosen such that DAPSm prioritizes spatial proximity of matched pairs to maximize the chance of balancing the unmeasured spatial confounder, even at the cost of balance on observed covariates. Ability to make such a judgment transparently is a key feature of DAPSm.
could be chosen such that DAPSm prioritizes spatial proximity of matched pairs to maximize the chance of balancing the unmeasured spatial confounder, even at the cost of balance on observed covariates. Ability to make such a judgment transparently is a key feature of DAPSm.
4. Simulation and comparison with alternatives
We conduct a simulation study to explore the performance of DAPSm and several reasonable alternatives for incorporating spatial information, with a focus on how different methods perform across a variety of unmeasured spatial confounding settings, as dictated by the spatial surface of simulated unmeasured confounding. We evaluate methods with respect to mean squared error (MSE) of ATT estimates, balance of observed and unobserved confounders, and number of matches. Data are simulated across the locations of 800 power generating facilities to represent a realistic spatial patterning of units reflecting that of the study of power plant emissions and ozone. Specifically, for each simulated data set, each of 800 fixed locations are simulated to have one unmeasured confounder 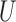 generated as a Gaussian Process with Matérn correlation function, four observed confounders
generated as a Gaussian Process with Matérn correlation function, four observed confounders 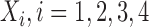 uncorrelated with
uncorrelated with 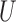 , binary treatment
, binary treatment 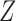 , and continuous outcome
, and continuous outcome 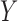 . The specifics of the data generating mechanism can be found in Appendix C of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online.
. The specifics of the data generating mechanism can be found in Appendix C of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online.
The Matérn correlation function of the spatial confounder is governed by two parameters, the smoothness, 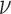 , and range,
, and range, 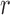 . The range,
. The range, 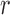 , measures how quickly the correlation of
, measures how quickly the correlation of 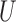 between two locations decays with distance. When
between two locations decays with distance. When 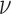 is small, the spatial process is rough, and when it is large the process is smooth. See Minasny and McBratney (2005) for a detailed description. Appendix D of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online shows four generated surfaces of a spatial variable with Matérn correlation function for combinations of small and large values of smoothness and range.
is small, the spatial process is rough, and when it is large the process is smooth. See Minasny and McBratney (2005) for a detailed description. Appendix D of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online shows four generated surfaces of a spatial variable with Matérn correlation function for combinations of small and large values of smoothness and range.
The situation presented here assumes that 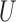 is uncorrelated with X to highlight the impact of completely unobserved spatial confounders. Situations where
is uncorrelated with X to highlight the impact of completely unobserved spatial confounders. Situations where 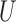 is simulated to have correlation with X produce similar results with less pronounced gains of incorporating spatial information.
is simulated to have correlation with X produce similar results with less pronounced gains of incorporating spatial information.
4.1. Methods for comparison with DAPSm
We consider alternative approaches belonging to two general strategies for incorporating spatial information with propensity scores: (i) incorporating spatial information in the matching procedure and (ii) incorporating spatial information in the propensity score estimates themselves. The former methods estimate the propensity score using 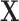 , then perform matching based in part on distance, as done in DAPSm. The latter methods estimate propensity scores that vary according to a spatial pattern by construction, then matches on these “spatial propensity scores.” After matching is performed, ATT estimates are acquired through a difference in means of the matched pairs. Further regressions adjustments could be performed in practice.
, then perform matching based in part on distance, as done in DAPSm. The latter methods estimate propensity scores that vary according to a spatial pattern by construction, then matches on these “spatial propensity scores.” After matching is performed, ATT estimates are acquired through a difference in means of the matched pairs. Further regressions adjustments could be performed in practice.
The previously described method of Keele and others (2015) is one method that incorporates spatial information in the matching. Even though Keele and others (2015) advocate for matching directly on covariates, in the simulation study this method was implemented performing exact matching on five categories of the propensity score, such that any difference in performance could be attributed solely to the methods’ ability to adjust for unmeasured spatial confounding. Simulation results for this method implemented to match directly on covariates are shown in Appendix E of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online.
We further considered another method that incorporates spatial information into the matching procedure, which we refer to as “Matching within Distance Caliper.” For this method, a distance caliper is chosen as the maximum distance of potential matched pairs. Within the distance caliper, matching is performed based solely on the propensity score estimated with 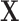 . A caliper on the propensity score can be used in addition.
. A caliper on the propensity score can be used in addition.
Methods that incorporate spatial information into the propensity score estimates include parametric and non-parametric incorporation of spatial information in the treatment assignment model. A simple approach is the introduction of fixed effects for locations’ latitude and longitude coordinates in the propensity score, in addition to the observed covariates. We refer to this as “Naïve with Coordinates”. A more flexible extension is to use gradient boosting models (GBM; Friedman, 2001) to estimate the propensity score, including the coordinates and the observed covariates 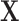 . Estimation of the model is performed using the gbm R package (Ridgeway, 2007).
. Estimation of the model is performed using the gbm R package (Ridgeway, 2007).
While the “Naïve with Coordinates” and GBM approaches are not spatial methods per se, an alternative approach is to augment the propensity score model with a spatial random effect, as implemented using the spBayes R package (Finley and others, 2007). Specifically, the propensity score is estimated by fitting 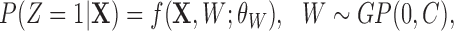 where
where 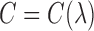 is the spatial random effect correlation matrix with parameters
is the spatial random effect correlation matrix with parameters 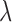 . Such approach was not pursued in detail here due to its computational intensity and its poor performance in initial investigations.
. Such approach was not pursued in detail here due to its computational intensity and its poor performance in initial investigations.
We compare the propensity-score matching with spatial information methods to the gold standard which uses the data generating outcome model, and the gold standard propensity score (“Gold PS”) which uses the true propensity score model conditional on 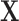 and
and 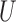 . Finally, the naïve approach performs propensity-score matching using estimates from a model solely on the observed confounders
. Finally, the naïve approach performs propensity-score matching using estimates from a model solely on the observed confounders 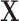 .
.
All methods are implemented with 1-1 nearest neighbor optimal matching without replacement. For DAPSm, we present results for the definition of standardized distance defined in (3.2). For GBM, we considered 3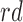 degree interactions. Results for Matching within Distance Caliper are presented with the distance caliper equal to the 10
degree interactions. Results for Matching within Distance Caliper are presented with the distance caliper equal to the 10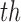 percentile of pairwise treated-control distances (the method indicated sensitivity to the choice of distance caliper, other specifications were considered, but are not shown here). The method of Keele and others (2015) was implemented across a range of values for
percentile of pairwise treated-control distances (the method indicated sensitivity to the choice of distance caliper, other specifications were considered, but are not shown here). The method of Keele and others (2015) was implemented across a range of values for 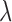 , representing different compromises between the number of returned matches and the distance between matched pairs. As Keele and others (2015) do not provide specific guidance on the selection of
, representing different compromises between the number of returned matches and the distance between matched pairs. As Keele and others (2015) do not provide specific guidance on the selection of 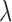 , we present results for two values meant to represent two different points in the space of compromises between distance and the number of matches:
, we present results for two values meant to represent two different points in the space of compromises between distance and the number of matches: 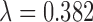 , the median pairwise distance of treated and control units (as done in Keele and others (2015)), and
, the median pairwise distance of treated and control units (as done in Keele and others (2015)), and 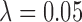 , which was determined in simulation to yield fewer matches and lower MSE for this range of simulation scenarios. For implementing DAPSm,
, which was determined in simulation to yield fewer matches and lower MSE for this range of simulation scenarios. For implementing DAPSm, 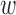 was chosen based on the algorithmic procedure described in Section 3.5.
was chosen based on the algorithmic procedure described in Section 3.5.
4.2. Simulation results
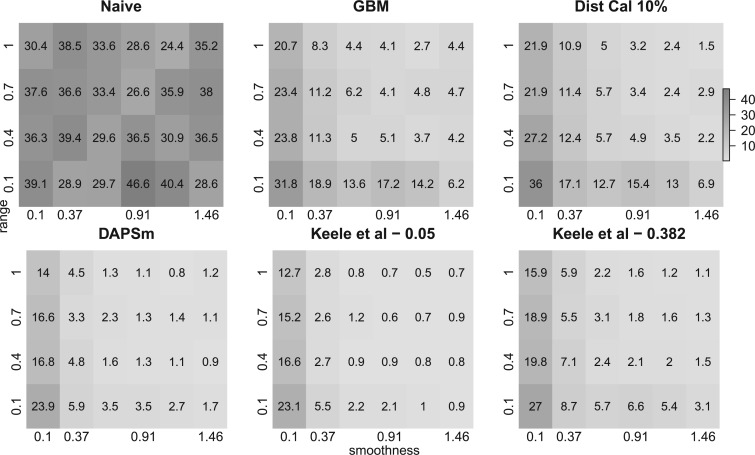
Figure 2 shows the relative MSE of the effect estimates calculated with a subset of the methods with respect to the Gold PS and for different specifications of smoothness and range of 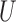 . MSE is calculated over the subset of simulated data sets for which each method returned matches. Table 1 describes the percentage of simulated data sets for which no matching was achieved for each of the methods. As expected, the naïve approach has the highest relative MSE ranging from 24.4 to 46.6. Relative MSE for the gold standard varied from 0.16 to 0.32, indicating that specifying the correct outcome model is more efficient than using the correctly specified propensity score. These approaches did not indicate patterning when varying the spatial structure. Relative MSE for the Naïve with coordinates ranged from 6 to 41.3, and indicated similar patterning as the other spatial methods with respect to the smoothness and range of
. MSE is calculated over the subset of simulated data sets for which each method returned matches. Table 1 describes the percentage of simulated data sets for which no matching was achieved for each of the methods. As expected, the naïve approach has the highest relative MSE ranging from 24.4 to 46.6. Relative MSE for the gold standard varied from 0.16 to 0.32, indicating that specifying the correct outcome model is more efficient than using the correctly specified propensity score. These approaches did not indicate patterning when varying the spatial structure. Relative MSE for the Naïve with coordinates ranged from 6 to 41.3, and indicated similar patterning as the other spatial methods with respect to the smoothness and range of 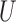 , but performed worse in terms of MSE than its more flexible form (GBM) and is emitted from Figure 2.
, but performed worse in terms of MSE than its more flexible form (GBM) and is emitted from Figure 2.
Fig. 2.
Estimates of relative mean squared error over 100 simulated data sets for each specification of smoothness 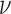 (x-axis) and range
(x-axis) and range 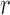 (y-axis) for the Matérn correlation function of the unobserved confounder. The baseline MSE corresponds to the Gold PS. Printed values are rounded to the first decimal.
(y-axis) for the Matérn correlation function of the unobserved confounder. The baseline MSE corresponds to the Gold PS. Printed values are rounded to the first decimal.
Table 1.
Percentage of simulated data sets that each method returned no matches (% fail), average number of treated units that were dropped when matches where returned (Dropped), the interquartile range of number of dropped treated units (IQR), and average distance of matched pairs (Distance)
| Gold PS | Naïve | N.Coords | GBM | DistCal 10% | DAPSm | Keele-0.05 | Keele-0.382 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % fail | 1.5 | 0.5 | 0.96 | 27.67 | 33.29 | 0.04 | 0 | 0 |
| Dropped | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.23 | 0 | 0 | 55.98 | 2.11 |
| IQR | (0,0) | (0,0) | (0,0) | (0,0) | (0,0) | (0,0) | (50,62) | (0,3) |
Distance (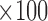 ) ) |
37.4 | 40.5 | 36.4 | 36.1 | 8.4 | 2.6 | 1.9 | 3.7 |
For all methods incorporating spatial information, relative MSE decreases as the surface gets smoother (larger values of smoothness 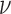 ) or the spatial correlation remains positive at longer distances (larger values of range
) or the spatial correlation remains positive at longer distances (larger values of range 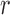 ). Similar results are observed for the absolute bias. Among the methods considered based on propensity scores, DAPSm had the lowest MSE across all specifications of range and smoothness, apart from the method of Keele and others (2015) when
). Similar results are observed for the absolute bias. Among the methods considered based on propensity scores, DAPSm had the lowest MSE across all specifications of range and smoothness, apart from the method of Keele and others (2015) when 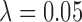 was chosen such that it reduces simulation-based MSE compared to
was chosen such that it reduces simulation-based MSE compared to 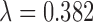 . Results for the method of Keele and others (2015) implemented to match directly on the observed covariates, instead of the propensity score, can be found in Appendix E of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online, and showed lower relative MSE than the methods presented here.
. Results for the method of Keele and others (2015) implemented to match directly on the observed covariates, instead of the propensity score, can be found in Appendix E of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online, and showed lower relative MSE than the methods presented here.
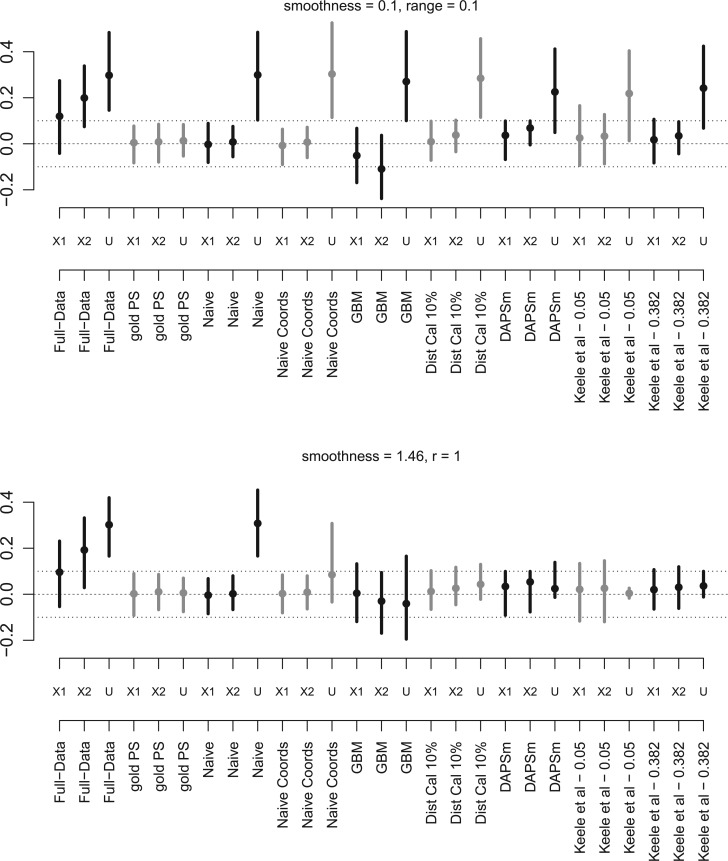
We also evaluated methods with respect to the balance of observed and unobserved covariates. Figure 3 shows the standardized difference of means of 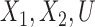 (balance of
(balance of 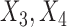 was similar to the balance of
was similar to the balance of 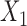 ,
, 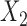 ) for the scenarios where
) for the scenarios where 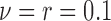 (rough uneven surface), and
(rough uneven surface), and 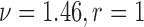 (smooth surface). First, the full data ASDM shows that all variables were imbalanced in most simulated data sets. Using the correctly specified propensity score model (Gold-PS) achieved balance of all confounders at the 0.1 cut-off. The naïve approach does not incorporate any spatial information, and the unobserved confounder remains imbalanced. Incorporating coordinates in the estimation of the propensity score improves on balancing
(smooth surface). First, the full data ASDM shows that all variables were imbalanced in most simulated data sets. Using the correctly specified propensity score model (Gold-PS) achieved balance of all confounders at the 0.1 cut-off. The naïve approach does not incorporate any spatial information, and the unobserved confounder remains imbalanced. Incorporating coordinates in the estimation of the propensity score improves on balancing 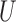 , especially in smoother surfaces. Matching within Distance Caliper performed similarly to Naïve with coordinates in the rough surface. In smooth surfaces Matching within Distance Caliper performed well in balancing both X and
, especially in smoother surfaces. Matching within Distance Caliper performed similarly to Naïve with coordinates in the rough surface. In smooth surfaces Matching within Distance Caliper performed well in balancing both X and 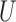 , although the balance of
, although the balance of 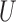 is sensitive to the choice of the distance cut-off. The GBM approach exhibited poor balance for all covariates in both scenarios. DAPSm with weight
is sensitive to the choice of the distance cut-off. The GBM approach exhibited poor balance for all covariates in both scenarios. DAPSm with weight 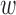 chosen as described in Section 3.5 balanced all observed covariates, while improving balance of
chosen as described in Section 3.5 balanced all observed covariates, while improving balance of 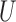 in both rough and smooth surfaces. The method of Keele and others (2015) for
in both rough and smooth surfaces. The method of Keele and others (2015) for 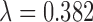 returned matches for which balance of the observed variables was better than for
returned matches for which balance of the observed variables was better than for 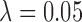 , but
, but 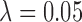 returned matched data sets with better balance on
returned matched data sets with better balance on 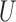 .
.
Fig. 3.
Average and (2.5%, 97.5%) intervals of standardized difference of means of 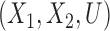 for the scenarios where
for the scenarios where 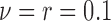 (top), and
(top), and 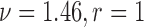 (bottom) over 100 Monte Carlo simulations.
(bottom) over 100 Monte Carlo simulations.
Lastly, the methods considered exhibited substantial variability in terms of the number of achieved matches. Optimal matching algorithms often return no matched pairs. Table 1 shows the percentage of simulated data sets that each method failed to return any matches, and the average and IQR of number of treated units that were dropped when matching was achieved. GBM and matching in distance calipers failed to return matches for a high proportion of simulated data sets, but when matching was achieved, they failed to match, on average, less than 1, or 0 treated units accordingly. DAPSm failed to return matches for 0.04% of simulated data sets, but matched all treated units otherwise. On the other hand, Keele and others (2015) returned matches with a significant amount (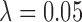 ) or a small number (
) or a small number (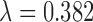 ) of dropped treated units. Differences in the number of obtained matches should be viewed in light of the fact that confining effect estimation to subsets of the available data can change the causal estimand of interest.
) of dropped treated units. Differences in the number of obtained matches should be viewed in light of the fact that confining effect estimation to subsets of the available data can change the causal estimand of interest.
5. Comparing the effectiveness of SCR/SNCR emission reduction technologies for reducing NO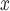 emissions and ambient ozone
emissions and ambient ozone
Regulatory strategies impacting USA power plants are predicated on the knowledge that reducing NO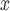 emissions reduces ambient ozone, prompting many policies that incentivize the installation of emission control technologies at power plant smokestacks. While many technologies are available, SCR, and SNCR technologies are believed to be among the most efficient for reducing NO
emissions reduces ambient ozone, prompting many policies that incentivize the installation of emission control technologies at power plant smokestacks. While many technologies are available, SCR, and SNCR technologies are believed to be among the most efficient for reducing NO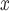 . However, no study has, to our knowledge, empirically compared the effectiveness of these strategies to evaluate whether the supposed efficiency gains of SCR/SNCR for reducing NO
. However, no study has, to our knowledge, empirically compared the effectiveness of these strategies to evaluate whether the supposed efficiency gains of SCR/SNCR for reducing NO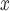 emissions actually translate to greater reductions into ambient ozone concentrations.
emissions actually translate to greater reductions into ambient ozone concentrations.
We compiled a national data source linking information on power plants, ambient pollution, population demographics, and weather. The resulting data set consists of 473 power generating facilities powered by either coal or natural gas during June, July, and August 2004, which represents the peak ozone season in a year following the institution of important NO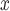 and ozone regulations. Covariate information (
and ozone regulations. Covariate information (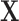 ) on each facility includes power plant operating characteristics such as operating capacity and heat input, as well as area level characteristics such as temperature and population demographics. As a measure of ozone in the area surrounding each power plant (
) on each facility includes power plant operating characteristics such as operating capacity and heat input, as well as area level characteristics such as temperature and population demographics. As a measure of ozone in the area surrounding each power plant (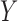 ), we use the fourth highest daily ozone concentration, averaged across all monitoring locations within a 100 km radius. This measure is chosen to mimic the National Ambient Air Quality Standard for ozone, which is based on the annual fourth-highest daily maximum 8-hour average ozone concentration. Appendix F of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online has a detailed description on the exact construction of the data set used in the final analysis, including references to publicly-available raw data sets and R scripts used for data construction and linkage.
), we use the fourth highest daily ozone concentration, averaged across all monitoring locations within a 100 km radius. This measure is chosen to mimic the National Ambient Air Quality Standard for ozone, which is based on the annual fourth-highest daily maximum 8-hour average ozone concentration. Appendix F of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online has a detailed description on the exact construction of the data set used in the final analysis, including references to publicly-available raw data sets and R scripts used for data construction and linkage.
We consider as “treated” the power plants for which at least 50% of the heat input is to facility units with at least one SCR or SNCR technology installed (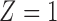 , 152 facilities), with the remaining plants regarded as untreated (
, 152 facilities), with the remaining plants regarded as untreated (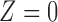 , 321 facilities). 67.7% of facilities have either 0% or 100% of their heat input used by units with installed SCR or SNCR control technologies, suggesting robustness to the 50% cut-off. Figure 1 shows maps of the power plants’ treatment assignment and ozone measurements for the surrounding area, and Appendix F of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online discusses the emission control actions of the control group
, 321 facilities). 67.7% of facilities have either 0% or 100% of their heat input used by units with installed SCR or SNCR control technologies, suggesting robustness to the 50% cut-off. Figure 1 shows maps of the power plants’ treatment assignment and ozone measurements for the surrounding area, and Appendix F of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online discusses the emission control actions of the control group  .
.
To estimate the effect of SCR/SNCR technologies relative to alternatives, we implement the “naïve” approach, Matching within Distance Caliper (distance caliper was set to 354 miles, the 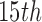 percentile of all treated-control distances), GBM, the method of Keele and others (2015), and DAPSm (with standardized geo-distance). While the method of Keele and others (2015) was implemented with the propensity score for the performance comparison in Section 4, here it is implemented in a manner more consistent with the intent of integer programming methods, matching directly on covariates. The tolerance level for Keele and others (2015) was set to 0.15 standard deviations for all continuous covariates. Multiple values were tried for the tuning parameter
percentile of all treated-control distances), GBM, the method of Keele and others (2015), and DAPSm (with standardized geo-distance). While the method of Keele and others (2015) was implemented with the propensity score for the performance comparison in Section 4, here it is implemented in a manner more consistent with the intent of integer programming methods, matching directly on covariates. The tolerance level for Keele and others (2015) was set to 0.15 standard deviations for all continuous covariates. Multiple values were tried for the tuning parameter 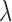 , and results are presented with
, and results are presented with 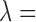 800 (
800 (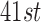 quantile of pairwise distances) such that the number of matched pairs will be similar to that of DAPSm. The caliper used for each method was decided such that methods would balance observed covariates, where “balance” is judged by an ASDM less than 0.15 (the same value used as the tolerance for the method of Keele and others (2015)).
quantile of pairwise distances) such that the number of matched pairs will be similar to that of DAPSm. The caliper used for each method was decided such that methods would balance observed covariates, where “balance” is judged by an ASDM less than 0.15 (the same value used as the tolerance for the method of Keele and others (2015)).
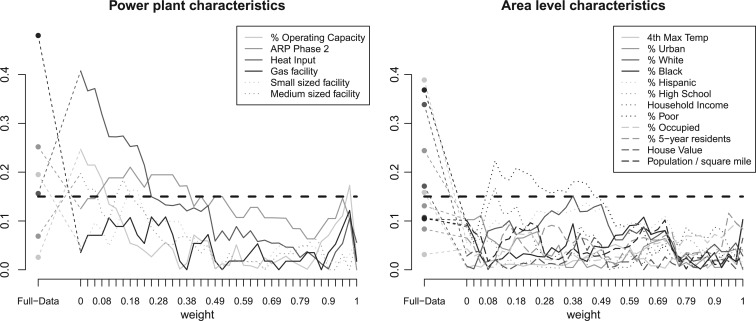
The variables that are included in the propensity score model are listed in Figure 4 and Appendix G of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online. Characteristics of the power plants (e.g. energy consumed, compliance scheme) are not expected to exhibit strong spatial patterns, but characteristics of the surrounding areas (e.g. temperature, population demographics) are.
Fig. 4.
Absolute standardized difference of means for covariates that are included in the propensity score model for the full data before any matching, and for various specification of the DAPSm weight. Balance of covariates on power plant characteristics is described on the left, and balance of area-level variables is shown on the right.
5.1. Covariate balance, number, and distance of matched pairs
Covariate balance was assessed by comparing the covariate distribution of treated and control units. Without adjustment, 10 out of 18 covariates were imbalanced between the treated and control facilities, as evidenced by the leftmost values of each panel in Figure 4. DAPSm was performed with values of 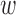 ranging from 0 to 1, with covariate balance evaluated for each
ranging from 0 to 1, with covariate balance evaluated for each 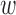 , and depicted in the remaining portions of Figure 4. Note the change in covariate balance between the unadjusted setting and the setting with DAPSm (
, and depicted in the remaining portions of Figure 4. Note the change in covariate balance between the unadjusted setting and the setting with DAPSm (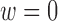 ), which matches observations based solely on proximity. Most area level characteristics achieve balance when matching only on proximity, but imbalance for power-plant level characteristics persists. Increasing values of
), which matches observations based solely on proximity. Most area level characteristics achieve balance when matching only on proximity, but imbalance for power-plant level characteristics persists. Increasing values of 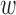 place more emphasis on observed propensity score differences, and balance for covariates representing power-plant characteristics improves, without a strong sacrifice in balance for the area-level covariates. Using the procedure described in Section 3.5,
place more emphasis on observed propensity score differences, and balance for covariates representing power-plant characteristics improves, without a strong sacrifice in balance for the area-level covariates. Using the procedure described in Section 3.5, 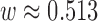 was chosen for the analysis. Table 2 summarizes the covariate balance for all methods. GBM failed to return a balanced matched sample and is excluded from the results.
was chosen for the analysis. Table 2 summarizes the covariate balance for all methods. GBM failed to return a balanced matched sample and is excluded from the results.
Table 2.
Balance of covariates assessed by the ASDM
| Naive | Distance Caliper | Keele et al. | DAPSm | Full-data | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of imbalanced variables | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| Mean ASDM | 0.067 | 0.052 | 0.065 | 0.045 | 0.189 |
| Max ASDM | 0.148 | 0.134 | 0.145 | 0.150 | 0.480 |
| Number of matches | 137 | 116 | 124 | 124 | |
| Mean distance (in miles) | 1066 | 198 | 146 | 141 |
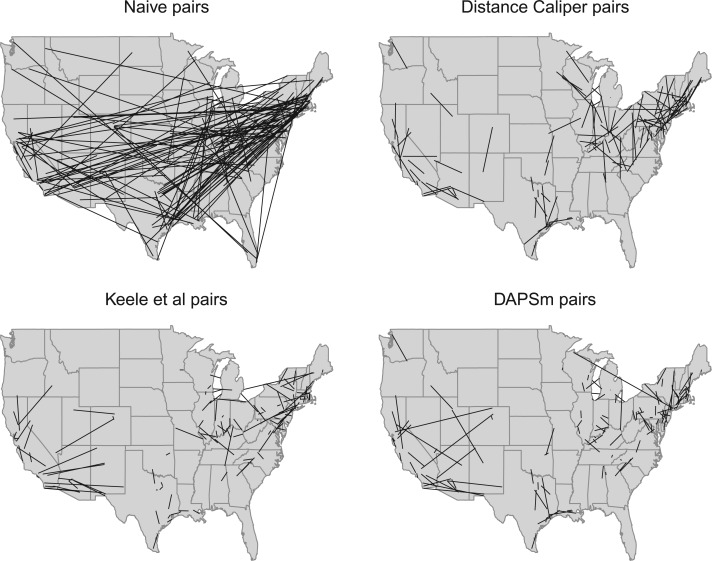
Table 2 also presents the number and mean distance of matched pairs. Number of matches ranged between 116 and 137, indicating that not all of 152 treated units were matched. Nonetheless, all methods should closely approximate the ATT in a manner that is comparable across methods, since most treated units are matched in all implementations. Characteristics of the matched population according to each method can be found in Appendix H of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online. Dropped treated units were smaller, mostly gas-operating facilities in urban areas compared to the matched treated units. Maps of the matched pairs are shown in Figure 5.
Fig. 5.
Maps of matched pairs for naïve, distance caliper, Keele and others (2015), and DAPSm approaches. Each line segment connects one treated power plant to its matched control.
5.2. Effect estimates for NO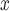 and ozone
and ozone
We evaluate the effectiveness of SCR/SNCR technology for reducing NO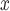 emissions and ambient ozone. Since emissions are measured at the power plant, the analysis of NO
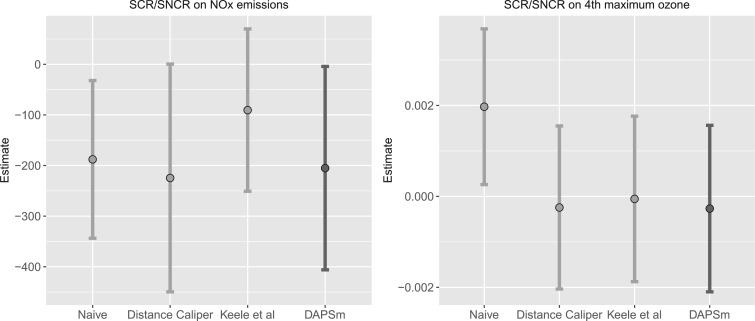
emissions and ambient ozone. Since emissions are measured at the power plant, the analysis of NO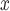 emissions is not expected to suffer from unmeasured spatial confounding. Since the formation of ambient ozone in the areas surrounding power plants is determined in part by atmospheric conditions, the analysis of ozone is expected to be susceptible to unmeasured spatial confounding. Confidence intervals (CIs) are constructed conditional linear models fit to the matched data sets (Ho and others, 2007). Results from all methods are reported in Table 3 and Figure 6.
emissions is not expected to suffer from unmeasured spatial confounding. Since the formation of ambient ozone in the areas surrounding power plants is determined in part by atmospheric conditions, the analysis of ozone is expected to be susceptible to unmeasured spatial confounding. Confidence intervals (CIs) are constructed conditional linear models fit to the matched data sets (Ho and others, 2007). Results from all methods are reported in Table 3 and Figure 6.
Table 3.
Estimates and 95% CIs for the effect of SCR/SNCR compared to alternative strategies on total NO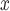 emissions (in tons) and
emissions (in tons) and 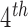 maximum ozone measurement (in parts per billion)
maximum ozone measurement (in parts per billion)
| LB | NO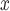 emissions Estimate emissions Estimate |
UB | LB | Ozone Estimate | UB | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naive |
 343.7 343.7 |
 187.9 187.9 |
 32.0 32.0 |
0.26 | 1.97 | 3.68 |
| Distance Caliper |
 449.6 449.6 |
 224.6 224.6 |
0.4 |
 2.04 2.04 |
 0.24 0.24 |
1.55 |
| Keele et al. |
 250.9 250.9 |
 90.5 90.5 |
70 |
 1.88 1.88 |
 0.06 0.06 |
1.76 |
| DAPSm |
 406.1 406.1 |
 205.1 205.1 |
 4.1 4.1 |
 2.1 2.1 |
 0.27 0.27 |
1.56 |
Fig. 6.
Effect estimates and 95% CIs for SCR/SNCR emission control technology installation on NO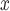 emissions and 4
emissions and 4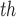 maximum ozone concentration during June–August 2004, using the naïve, Matching within Distance Caliper, Keele and others (2015), and DAPSm approaches.
maximum ozone concentration during June–August 2004, using the naïve, Matching within Distance Caliper, Keele and others (2015), and DAPSm approaches.
5.2.1. Effects of SCR/SNCR on power plant NO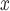 emissions.
emissions.
Point estimates for the effect of SCR/SNCR on NO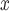 emissions were below zero across all methods, with the naïve and DAPSm returning significant results at the 95% CI level. Power plants with installed SCR/SNCR emission control technologies emitted on average 205 tons of NO
emissions were below zero across all methods, with the naïve and DAPSm returning significant results at the 95% CI level. Power plants with installed SCR/SNCR emission control technologies emitted on average 205 tons of NO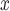 less (95% CI 4–406 tons of NO
less (95% CI 4–406 tons of NO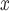 according to DAPSm) than what they would have had emitted had they adopted an alternative NO
according to DAPSm) than what they would have had emitted had they adopted an alternative NO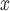 control strategy.
control strategy.
5.2.2. Effects of SCR/SNCR on ambient ozone.
In the analysis of ambient ozone concentrations, for which unmeasured spatial confounding is a concern, the naïve approach estimates a significant positive effect of SCR/SNCR installation on ambient ozone, which is inconsistent with the knowledge that SCR/SNCR reduces NO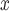 emissions and the documented relationship between NO
emissions and the documented relationship between NO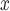 and ozone. This result corroborates suspicion of unmeasured confounding. In contrast, estimates from all methods that incorporate spatial information provide estimates very close to zero (DAPSm:
and ozone. This result corroborates suspicion of unmeasured confounding. In contrast, estimates from all methods that incorporate spatial information provide estimates very close to zero (DAPSm:  0.27 parts per billion, 95% CI
0.27 parts per billion, 95% CI  2.1 to 1.56), indicating that SCR/SNCR does not reduce ambient ozone more than alternative strategies. For reference, these effect estimates can be compared against the national ozone air quality standard of 70 parts per billion.
2.1 to 1.56), indicating that SCR/SNCR does not reduce ambient ozone more than alternative strategies. For reference, these effect estimates can be compared against the national ozone air quality standard of 70 parts per billion.
5.2.3. Comparison of effect estimates across methods.
As mentioned earlier, since NO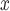 emissions are measured at the power plants’ smokestacks, we do not expect unobserved spatial predictors of the outcome for this analysis. In fact, estimates across all methods are similar.
emissions are measured at the power plants’ smokestacks, we do not expect unobserved spatial predictors of the outcome for this analysis. In fact, estimates across all methods are similar.
However, in the analysis of ozone concentrations, we see that the spatial methods return results that are inconsistent with the naïve method. In Appendix I of the supplementary material available at Biostatistics online, we provide additional evidence of the potential of unobserved spatial confounding in the analysis of ozone, by performing a sensitivity analysis of the DAPSm effect estimates as a function of 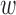 . The sensitivity analysis corroborates the existence of an unmeasured spatial confounder, with effect estimates that increase with
. The sensitivity analysis corroborates the existence of an unmeasured spatial confounder, with effect estimates that increase with 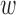 (for
(for 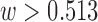 ) and approach the estimates from the naïve analysis when
) and approach the estimates from the naïve analysis when 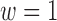 and no adjustment for spatial proximity is made. In contrast, the sensitivity analysis of the effect of SCR/SNCR on NO
and no adjustment for spatial proximity is made. In contrast, the sensitivity analysis of the effect of SCR/SNCR on NO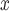 emissions indicates that spatial confounding is not an issue.
emissions indicates that spatial confounding is not an issue.
6. Discussion
Unobserved confounding is a ubiquitous issue in the analysis of observational studies. Settings with spatially-indexed data provide an opportunity to recover information on unobserved spatial confounding, but most methods have been confined to regression-based approaches. We propose a method that extends the benefits of propensity score matching procedures to settings with spatially-indexed data and provide a transparent and principled framework for assessing the relative trade-offs of prioritizing observed confounding adjustment and spatial proximity adjustment.
The simulation study showed the potential for DAPSm to recover information on unobserved spatial confounding. When deployed to evaluate the effectiveness of emission control technologies, DAPSm balanced all observed covariates in the resulting matched data set while providing protection against the existence of unobserved spatial confounders. The importance of incorporating spatial information was underscored by the ability of DAPSm (and other methods accounting for proximity) to return estimates that are more in line with subject-matter knowledge, in contrast to the naïve approach that ignores the possibility of spatial confounding. Whereas the naïve approach indicated that clear reductions in NO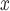 were accompanied by increases in ambient ozone, analysis with DAPSm (and other methods) provided the more credible result that SCR/SNCR do not decrease ambient ozone more than other strategies.
were accompanied by increases in ambient ozone, analysis with DAPSm (and other methods) provided the more credible result that SCR/SNCR do not decrease ambient ozone more than other strategies.
While we compare DAPSm against Keele and others (2015) for illustration, it is important to remember the important fundamental distinction between these methods: DAPSm uses the propensity score while Keele and others (2015) propose an integer programming method that matches on covariates directly. While a comparison between propensity score methods and integer programing methods is not the goal of this article, it is worth noting that the most salient operational difference of the two methods relates to their respective tuning parameters that govern the amount of emphasis placed on matching observations that are geographically close. DAPSm involves the tuning parameter (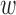 ) that offers a characterization of the price paid (in terms of observed covariate distance) by increasing emphasis on spatial proximity. This was evident in the ability to offer a practicable way to select a value of
) that offers a characterization of the price paid (in terms of observed covariate distance) by increasing emphasis on spatial proximity. This was evident in the ability to offer a practicable way to select a value of 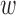 (as described in Section 3.5), and the transparent trade off between spatial proximity and observed covariate distance is an important feature of DAPSm that aligns with a scientific goal at the forefront of air pollution (and other) studies. On the other hand, the method of Keele and others (2015) entails a tuning parameter (
(as described in Section 3.5), and the transparent trade off between spatial proximity and observed covariate distance is an important feature of DAPSm that aligns with a scientific goal at the forefront of air pollution (and other) studies. On the other hand, the method of Keele and others (2015) entails a tuning parameter (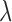 ) that balances emphasis on spatial proximity against number of obtained matches for a fixed tolerance of covariate imbalance. Keele and others (2015) provide an approach where, for a fixed tolerance,
) that balances emphasis on spatial proximity against number of obtained matches for a fixed tolerance of covariate imbalance. Keele and others (2015) provide an approach where, for a fixed tolerance, 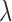 could be chosen to obtain a target number of matches. Further extensions growing from the mixed integer programing literature could give rise to alternative ways of prioritizing covariate balance, the number of matches, and the relative proximity of matches.
could be chosen to obtain a target number of matches. Further extensions growing from the mixed integer programing literature could give rise to alternative ways of prioritizing covariate balance, the number of matches, and the relative proximity of matches.
Furthermore, we evaluated the method of Keele and others (2015) in simulations and in comparison with other reasonable approaches, in addition to DAPSm. These simulations showed that, across a variety of spatial confounding surfaces, DAPSm with an appropriately chosen 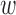 performed comparably or better than the method of Keele and others (2015) based on the propensity score, at least for some choices of
performed comparably or better than the method of Keele and others (2015) based on the propensity score, at least for some choices of 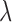 .
.
While the comparison of different methods in the analysis of power plant emission controls highlights the potential for DAPSm to adjust for unmeasured spatial confounding, there are several important limitations to the analysis. First, unmeasured (spatial or non-spatial) confounding may persist due to power plant or area level characteristics not contained in the data sources used. Second, we considered an “active control” group of power plants that did not install SCR/SNCR, but may have employed other strategies that could, in principle, be installed alongside SCR/SNCR (211 out of 311 control units employed a NO control strategy other than SCR/SNCR). Finally, the analysis relied on a simplification that linked each power plant to ambient ozone concentrations within a 100 km radius. Importantly, this does not fully capture the phenomenon of long-range pollution transport whereby emissions from a particular source travel across large distances during conversion to ambient pollution. Thus, installation of control technologies at a given power plant could affect ambient pollution concentrations around power plants located at distances greater than 100 km, a phenomenon referred to as “interference”. While interference is not expected in the analysis of NO
control strategy other than SCR/SNCR). Finally, the analysis relied on a simplification that linked each power plant to ambient ozone concentrations within a 100 km radius. Importantly, this does not fully capture the phenomenon of long-range pollution transport whereby emissions from a particular source travel across large distances during conversion to ambient pollution. Thus, installation of control technologies at a given power plant could affect ambient pollution concentrations around power plants located at distances greater than 100 km, a phenomenon referred to as “interference”. While interference is not expected in the analysis of NO emissions, ignoring interference in the analysis of ozone concentrations has potential consequences. The simplifications used here are expected to yield estimates that are closer to zero than any true effect of SCR/SNCR on ambient ozone, as installation of these technologies is likely to reduce ambient ozone even around power plants that were considered in the “control group” for this analysis. Methods for causal inference with interference have been recently considered with spatially-indexed data (Verbitsky-Savitz and Raudenbush, 2012; Zigler and others, 2012), including our own current work on methods advances to address interference in this specific setting (Papadogeorgou and others, 2017). Furthermore, the analysis relies on some extent on correct specification of the propensity score model, and King and Nielsen (2016) argue against the use of propensity score for matching altogether. For that reason, checking covariate balance in the design phase (Rubin, 2008) without evaluating outcomes, is an important component of propensity score matching.
emissions, ignoring interference in the analysis of ozone concentrations has potential consequences. The simplifications used here are expected to yield estimates that are closer to zero than any true effect of SCR/SNCR on ambient ozone, as installation of these technologies is likely to reduce ambient ozone even around power plants that were considered in the “control group” for this analysis. Methods for causal inference with interference have been recently considered with spatially-indexed data (Verbitsky-Savitz and Raudenbush, 2012; Zigler and others, 2012), including our own current work on methods advances to address interference in this specific setting (Papadogeorgou and others, 2017). Furthermore, the analysis relies on some extent on correct specification of the propensity score model, and King and Nielsen (2016) argue against the use of propensity score for matching altogether. For that reason, checking covariate balance in the design phase (Rubin, 2008) without evaluating outcomes, is an important component of propensity score matching.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
Supplementary material
Supplementary material is available at http://biostatistics.oxfordjournals.org. R Software is available at https://github.com/gpapadog/DAPSm.
Funding
Funding for this work was provided by National Institutes of Health (R01ES026217, P01CA134294, R01GM111339); USEPA (83587201-0); and Health Effects Institute (4953-RFA14-3/16-4). The contents of this work are solely the responsibility of the grantee and do not necessarily represent the official views of the USEPA. Further, USEPA does not endorse the purchase of any commercial products or services mentioned in the publication.
References
- Allen J. (2002). Chemistry in the Sunlight. Earth Observatory NASA. OnlineDoc: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/Features/ChemistrySunlight/.
- Bell M. L., McDermott A., Zeger S. L., Samet J. M. and Dominici F. (2004). Ozone and short-term mortality in 95 US urban communities, 1987-2000. JAMA 292, 2372–2378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang H. H., Reich B. J. and Miranda M. L. (2013). A spatial time-to-event approach for estimating associations between air pollution and preterm birth. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society. Series C, Applied Statistics 62, 167–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Congdon P. (2013). Assessing the impact of socioeconomic variables on small area variations in suicide outcomes in England. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 10, 158–177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finley A. O., Banerjee S. and Carlin B. P. (2007). spBayes: an R Package for univariate and multivariate hierarchical point-referenced spatial models. Journal of Statistical Software 19, 1–24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman J. H. (2001). Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. The Annals of Statistics 29, 1189–1232. [Google Scholar]
- Gu X. S. and Rosenbaum P. R. (1993). Comparison of multivariate matching methods: structures, distances, and algorithms. Source Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics 2, 405–420. [Google Scholar]
- Ho D., Imai K., King G. and Stuart E. (2007). Matching as nonparametric preprocessing for reducing model dependence in parametric causal inference. Political Analysis 15, 199–236. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges J. S. and Reich B. J. (2010). Adding spatially-correlated errors can mess up the fixed effect you love. The American Statistician 64, 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- Jerrett M., Burnett R. T., Pope C. A., Ito K., Thurston G., Krewski D., Shi Y., Calle E. and Thun M. (2009). Long-term ozone exposure and mortality. The New England Journal of Medicine 360, 1085–95. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keele L., Titiunik R. and Zubizarreta J. (2015). Enhancing a geographic regression discontinuity design through matching to estimate the effect of Ballot initiatives on voter turnout. Journal of Royal Statistical Society A 178, 223–239. [Google Scholar]
- King G. and Nielsen R. (2016). Why propensity scores should not be used for matching. Working Paper. OnlineDoc: https://gking.harvard.edu/files/gking/files/psnot.pdf.
- Lee D. and Neocleous T. (2010). Bayesian quantile regression for count data with application to environmental epidemiology. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series C, Applied Statistics 59, 905–920. [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. and Sarran C. (2015). Controlling for unmeasured confounding and spatial misalignment in long-term air pollution and health studies. Environmetrics 26, 477–487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minasny B. and McBratney A. B. (2005). The Matérn function as a general model for soil variograms. Geoderma 128, 192–207. [Google Scholar]
- Paciorek, Christopher J. (2010). The importance of scale for spatial-confounding bias and precision of spatial regression estimators. Statistical Science 25, 107–125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papadogeorgou G., Mealli F. and Zigler C. (2017). Causal inference for interfering units with cluster and population level treatment allocation programs. Working Paper. arXiv:1711.01280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ridgeway G. (2007). Generalized boosted models: a guide to the gbm package. OnlineDoc: http://www.saedsayad.com/docs/gbm2.pdf.
- Rosenbaum P. R. and Rubin D. B. (1983). The central role of the propensity score in observational studies for causal effects. Biometrika 70, 41–55. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. B. (1974). Estimating causal effects of treatments in randomized and nonrandomized studies. Journal of Educational Psychology 66, 688–701. [Google Scholar]
- Rubin D. B. (2008). For objective causal inference, design trumps analysis. Annals of Applied Statistics 2, 808–840. [Google Scholar]
- Stuart E. A. (2010). Matching methods for causal inference: a review and a look forward. Statistical Science 25, 1–21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbitsky-Savitz N. and Raudenbush S. W. (2012). Causal inference under interference in spatial settings : a case study evaluating community policing program in Chicago. Epidemiologic Methods 1, 105–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zigler C. M., Dominici F. and Wang Y. (2012). Estimating causal effects of air quality regulations using principal stratification for spatially correlated multivariate intermediate outcomes. Biostatistics 13, 289–302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.