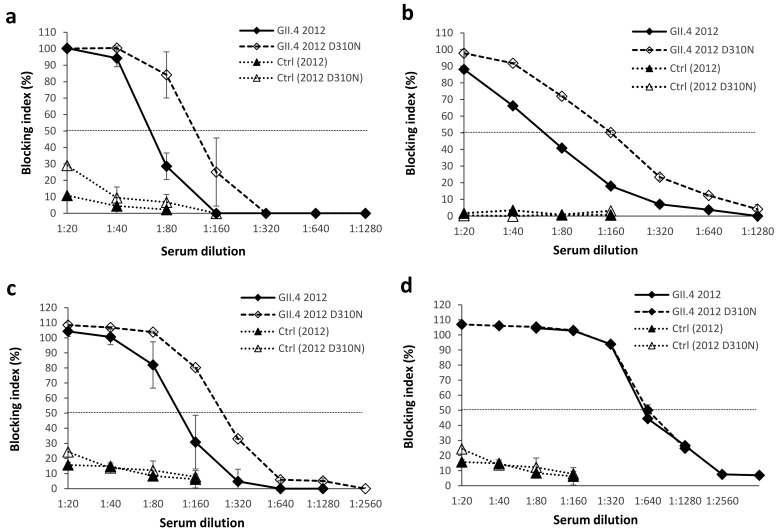
Figure 4.
The effect of amino acid (aa) 310 mutation within the NERK motif on cross-blocking activity. Residue 310 of GII.4 2012 virus-like particles (VLPs) was substituted from D (aspartic acid) to N (asparagine) to generate mutated GII.4 2012 D310N VLPs. Pooled GII.4 1999 immune serum was assayed against wild-type and mutated GII.4 2012 VLPs in blocking assays utilizing human saliva type A (a), pig gastric mucin (b), or synthetic H-type-1 (c) as the source of histo-blood group antigens (HBGAs). Pooled GII.4 2012 immune serum was used to block the binding of GII.4 2012 and GII.4 2012 D310N VLPs to synthetic H-type-1 HBGAs (d). Control (Ctrl) mice sera illustrate the non-specific blocking activity. The blocking index (percent) was calculated as follows: 100% × ((OD wells with serum/OD wells without serum, maximum binding) × 100%). The symbols represent the mean blocking indexes with standard errors between two repeated assays ((a) and (c)) or duplicate wells ((b) and (d)) and the horizontal dashed line represents the blocking titer 50% (BT50).