Abstract
Farber disease (FD) is a debilitating lysosomal storage disorder characterized by severe inflammation and neurodegeneration. FD is caused by mutations in the ASAH1 gene, resulting in deficient acid ceramidase (ACDase) activity. Patients with ACDase deficiency exhibit a broad clinical spectrum. In classic cases, patients develop hepatosplenomegaly, nervous system involvement, and childhood mortality. Ocular manifestations include decreased vision, a grayish appearance to the retina with a cherry red spot, and nystagmus. That said, the full effect of ACDase deficiency on the visual system has not been studied in detail. We previously developed a mouse model that is orthologous for a known patient mutation in Asah1 that recapitulates human FD. Herein, we report evidence of a severe ocular pathology in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Asah1P361R/P361R mice exhibit progressive retinal and optic nerve pathology. Through noninvasive ocular imaging and histopathological analyses of these Asah1P361R/P361R animals, we revealed progressive inflammation, the presence of retinal dysplasia, and significant storage pathology in various cell types in both the retina and optic nerves. Lipidomic analyses of retinal tissues revealed an abnormal accumulation of ceramides and other sphingolipids. Electroretinograms and behavioral tests showed decreased retinal and visual responses. Taken together, these data suggest that ACDase deficiency leads to sphingolipid imbalance, inflammation, dysmorphic retinal and optic nerve pathology, and severe visual impairment.
Farber disease (FD; Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man number 228000) is an autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorder caused by mutations in the ASAH1 gene, resulting in deficient acid ceramidase (ACDase) activity.1 ACDase is a key lysosomal enzyme that hydrolyzes the bioactive lipid ceramide into sphingosine (Sph) and a free fatty acid.2 Currently, there is no cure for FD, and with only 152 cases recorded in the literature to date, obtaining tissues and samples to study this disorder has been challenging.3 The clinical manifestations of FD are broad; patients with the classic variant die early in childhood.1 The cardinal features of FD are the presence of s.c. lipogranulomatous nodules, joint contractures, and aphonia.1 Patients with severe forms of FD will also develop respiratory complications, hepatosplenomegaly, and neurologic decline.4, 5 Impaired ACDase activity leads to systemic ceramide accumulation in FD patients. Ceramide and other sphingolipids are key components of membranes and play a role in a variety of cellular functions, including inflammation, cell proliferation, and apoptosis.6 The balance of ceramide and its metabolites are tightly regulated, and dysregulation results in disease and potential visual system defects.7, 8
The most frequent ophthalmic manifestation that has been described in patients with FD is a cherry red spot in the macula.3, 9, 10, 11, 12 Other reported ocular phenotypes in patients with FD include corneal opacities, xanthoma-like growths on the conjunctiva, nystagmus, and macular degeneration.13, 14, 15
Ocular manifestations are a common feature in lysosomal storage disorders in general, and corresponding rodent models of the disorders have been instrumental for characterizing their pathogenesis.16, 17, 18, 19 We previously reported the first viable model for ACDase deficiency, wherein a known human ASAH1 mutation, proline (P) 362 to arginine (R), was knocked in to the corresponding locus in murine Asah1 (P361R).20 Mice homozygous for this mutation mirror many FD patient features, including heightened inflammation and pathology in the hematopoietic, respiratory, and neuroglial systems that leads to early mortality.20, 21, 22
In this study, we investigated the consequences of ACDase deficiency by completing a comprehensive investigation of ocular manifestations in the Asah1P361R/P361R mouse model of FD. Noninvasive ocular imaging was used to monitor disease progression and highlight the abnormal sphingolipids present in the retina. Furthermore, ACDase deficiency was found to reduce visual function that is, in part, due to progressive inflammation, neurologic involvement, and abnormal storage pathology in cells of the visual system.
Materials and Methods
Animal Use, Breeding, and Genotyping
To generate homozygous Asah1P361R/P361R mice, Asah1+/P361R heterozygotes were crossed, as previously reported.20 Genotypes were confirmed by PCR using genomic DNA isolated from ear notches. To detect the wild-type Asah1 allele, the following primers were used: 5′-CAGAAGGTATGCGGCATCGTCATAC-3′ (forward) and 5′-AGGGCCATACAGAGAAACCCTGTCTC-3′ (reverse). These primers yielded a 379-bp product. For the Asah1 knock-in allele, the following primers were used: 5′-TCAAGGCTTGACTTTGGGGCAC-3′ (forward) and 5′-GCTGGACGTAAACTCCTCTTCAGACC-3′ (reverse). These primers amplify a 469-bp product from the neomycin resistance cassette. All animal procedures were approved and performed in strict adherence to the policies of the Medical College of Wisconsin Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee. Animals used for this study were maintained in controlled ambient illumination on a 12-hour light/dark cycle, with an illumination level of 2 to 3 lux. Exposure to bright light was kept to a minimum for all study animals for the duration of this study.
Slit-Lamp Analysis
Mice were anesthetized with inhaled isoflurane (3% induction, 1% to 2% maintenance) in 0.6 L/minute oxygen flow. The cornea and the lens were evaluated and imaged with the Topcon SL-D81 slit-lamp biomicroscope (Topcon Medical Systems Inc., Oakland, NJ) with a digital camera (Nikon D810 36.3MP DSLR Camera; Nikon Inc., Melville, NY). The eye was then dilated and cyclopleged with one eye drop each of 2.5% phenylephrine hydrochloride and 1% tropicamide (Akron, Inc., Lake Forest, IL). The lens was then reevaluated and imaged after dilation. All examinations were performed by a board-certified ophthalmologist (I.S.K.) with experience in animal models of ocular disease.
Fundus Imaging and Confocal Scanning Laser Ophthalmoscopy
Mice were anesthetized and prepared for imaging as described above. Fundus images were taken with the Phoenix Micron IV (Phoenix Research Labs, Pleasanton, CA). Near-infrared (810-nm) reflectance imaging and blue autofluorescence (excitation, 486 nm; emission filter, 525/50 nm) imaging were performed with a customized Heidelberg Spectralis (Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany) confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope (cSLO). The automatic real-time composite mode in the Spectralis software version 6.6.2.0 (Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany) was used to average 40 and 100 frames of the near-infrared and blue autofluorescence images, respectively.
Optical Coherence Tomography
To perform optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging, mice were anesthetized and prepared for imaging as described above. Imaging was performed with a Bioptigen Envisu R2200 spectral domain–OCT system (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) equipped with a Superlum Broadlighter T870 light source centered at 878.4 nm with a 186.3-nm bandwidth (Superlum, Cork, Ireland). InVivoVue control software version 2.4.33 (Leica Microsystems, Wetzlar, Germany) and the Bioptigen mouse objective were used for retinal imaging. A customized Bioptigen mouse stage was used to aim the imaging beam to the desired retinal location. GenTeal lubricant eye gel and Systane Ultra lubricating eye drops (Alcon, Fort Worth, TX) were used as needed to maintain corneal hydration. Dispersion, reference arm position, and light power of the sample arm were optimized iteratively for each animal at each time point. During acquisition, all scans were displayed and acquired in logarithmic intensity mode. Horizontal line scans (1 mm, 1000 A-scans/B-scan; 100 repeated scans) of the retina were acquired with the optic nerve head (ONH) centered for each scan. With our system and these scan parameters, the pixel size was calculated to be 1.00 × 1.61 μm (xz axes, respectively). B-scans (20 to 50) were registered to a manually selected template frame and averaged using custom software described previously.23 The registration was limited to a displacement of approximately 10 μm to exclude scans acquired at different retinal locations. The Duke OCT Retinal Analysis Program version 63.6 (Duke University, Durham, NC) was used to segment the inner limiting membrane and the retinal pigmented epithelium,24 which were clearly visible in all animals. Total retinal thickness was defined as the optical path length between these boundaries, assuming a group refractive index of 1.38. The order of the images was randomized, the boundaries were manually corrected, and thickness was analyzed by an observer (A.E.S.) masked to the genotype.
ERG
Before testing herein, mice were dark adapted overnight. Apparatus setup and animal preparations were conducted under dim red illumination. Mice were anesthetized and prepared as they were for imaging. Mice were placed on a heated platform (38°C). A silver-coated nylon contact lens with a custom-made active electrode was positioned on the eye. To maintain electrical conductivity, two subdermal platinum needle electrodes were positioned in the scruff (reference) and base of the leg (ground). Prepared animals were then positioned inside the Ganzfeld dome of the Espion E2 system (Diagnosys LLC, Cambridge, UK). All recordings were completed in a custom-made Faraday cage. Signals from the electroretinogram (ERG) were differentially amplified and digitized at a rate of 5 kHz (bandpass filtered 0 to 100 Hz). Recording sessions started with the dark-adapted flash ERG, which consisted of a six-log intensity series (−4 to 1 log cd·second/m2). Twenty responses were collected and averaged for the −4 and −3 log cd·second/m2 stimulus with an interstimulus internal of 5 seconds, 10 responses were collected and averaged for the −2 and −1 log cd·second/m2 stimuli with an interstimulus interval of 10 seconds, and five responses were collected and averaged for the 0 and 1 log cd·second/m2 stimuli with an interstimulus interval of 20 seconds. For the light-adapted series, mice were first exposed to a 30 cd·second/m2 white light background for 10 minutes for rod saturation, then progressed to a light-adapted flash ERG over a two-log intensity series (0 to 1 log cd·second/m2). Twenty responses were collected and averaged for each condition. Recordings concluded with two flicker ERG tests performed with continuous 5- and 15-Hz flicker (30 cd·second/m2). Thirty responses were collected and averaged for each flicker condition.
Visual Cliff Behavioral Test
To evaluate visual perception, a mouse open-field setup was modified to replicate the presence of a visual cliff.25 In brief, a gray circular structure with a diameter of 49.5 cm was placed on top of a clear 60 × 60-cm plexiglass surface, half of which was hanging off a table. To enhance the edge effect, the portion of the plexiglass surface on the support table was covered with a checkered pattern. Lamps directed at the floor, which also had a checkered pattern, were used to enhance depth and add illumination. Mice were placed near the middle of the visual cliff and monitored for 5 minutes with a camera linked to the Any-Maze behavior tracking software version 3.9.6 (Any-Maze, Stoelting, IL). For data analysis, three zones were created: ground, air, and cliff zones. The cliff zone measured 3 cm in depth from the edge of both the ground and air side. This 3-cm area was excluded from data collection because normal animals frequently stretched their body over the cliff edge to assess the area. For data collection, total distance traveled and total movement time were used to measure activity. To reduce variability, circadian rhythms were taken into account and all experiments were performed between 7 and 11 am. All tests were performed on the same apparatus, in the same room, and by the same individual.
Histopathology and Eye Measurements
For these studies, mice were euthanized via carbon dioxide inhalation and immediately perfused with ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline via cardiac puncture with a 24-gauge needle. Globes were enucleated with the optic nerve intact and fixed in 10% phosphate-buffered formalin or Davidson's fixative for 24 to 48 hours. Whole-eye globes and separated optic nerves were dehydrated and embedded in paraffin. Globes were sectioned sagittally at the midline through the optic nerve (ON) and stained for hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Luxol fast blue. Histology slides were scanned on the Aperio AT2 histology slide scanner (Leica Biosystems, Buffalo Grove, IL) or NanoZoomer 2.0-HT histology slide scanner (Hamamatsu Photonics, Ichinocho, Japan). All analyses and measurements were performed using Aperio ImageScope analysis software version 12.3.3 (Leica Biosystems, Buffalo Grove, IL). Morphometric analyses of the retinal layers were obtained approximately two- to three-disc diameters away from the optic nerve. Samples that contained retinal folding two- to three-disc diameters from the optic nerve were excluded from measurements. The anterior-to-posterior globe measurements were taken from the midline of the cornea to the base of the retinal epithelium (Bruch membrane). The remainder of the globe, lens, and corneal measurements were obtained at the anterior/posterior or dorsal/ventral midlines.
Retinal Dysplasia Scoring
H&E-stained retinal sections from Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice at 3 to 4 and 8 to 9 weeks of age were evaluated for retinal dysplasia severity. Our retinal dysplasia scoring system contained three categories: normal, intermediate, and severe. Samples categorized as normal contained no overt folding but may have had minor ridges within the retina. The height of each ridge was ≤20 μm, and no more than two retinal layers were affected. Samples in the intermediate category consisted of one to two folds/whorls. Each fold/whorl affected up to three retinal layers, and the peak height of each fold/whorl was between 20 and 100 μm. Last, for the severe category, samples displayed more than two folds/whorls. The folds/whorls there also affected more than three retinal layers, and the peak height of each fold/whorl was >100 μm. Some cases of severe folding also showed signs of retinal detachment.
Immunohistochemistry and Immunofluorescence
Eyes were fixed in 10% formalin overnight for retinal sectioning, as described above. For immunohistochemistry (IHC), the following primary antibodies, secondary antibodies, and staining reagents were used: rat anti-mouse Mac-2 at 1:8000 (galectin-3 clone M3/38; Cedarlane, Burlington, ON, Canada); goat anti-mouse cathepsin D at 1:3000 (Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX); biotinylated rabbit anti-rat IgG antibody at 1:5000 (Vector Laboratories, Burlingame, CA); biotinylated donkey anti-rabbit IgG antibody at 1:500 (Vector Laboratories); avidin-biotin/horseradish peroxidase (Vector Laboratories); 3,3′-diaminobenzidine kit (Vector Laboratories); and Vectastain ABC Elite Standard kit (Vector Laboratories). For immunofluorescence staining, the following primary antibodies were used: rabbit anti-ionized, calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1) at 1:2000 (Wako Chemicals USA, Cambridge, MA) and chicken anti–glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) at 1:2000 (Aves Lab Inc., Tigard, OR). DAPI at 1:7000 (Sigma Aldrich, St. Louis, MO) was used for nuclear staining. The following secondary antibodies were used to detect the primary antibodies: goat anti-chicken fluorescein isothiocyanate 1:500 (Aves Lab Inc.) and donkey anti-rabbit Cy3 1:500 (Jackson ImmunoResearch USA, West Grove, PA). Immunofluorescence microscopy was performed on the Carl Zeiss LSM510 confocal microscope (Carl Zeiss Microscopy, LLC, Thornwood, NY) using the Zeiss Aim software version 4.2 (Carl Zeiss Microscopy, LLC).
Electron Microscopy
After euthanasia, mice were perfused with 4% paraformaldehyde. Eye globes with intact ONs were removed and placed in 4% paraformaldehyde for 24 to 48 hours. ONs were from the posterior pole of the eye globe; approximately 2-mm transverse sections were cut for transmission electron microscope processing. For analysis of the posterior chamber, the cornea was gently cut to expose and remove the lens. The remaining posterior segment structures were used for transmission electron microscope processing. In brief, samples were post-fixed in 3% glutaraldehyde, washed, and placed in 2% OsO4 in phosphate buffer overnight for contrasting. After dehydration, samples were embedded in Durcupan Epon (Fluka, Hatfield, PA) for polymerization. Ultrathin sections (60 nm thick) were cut from tissue blocks of ON and posterior eye samples and placed on copper grids. Ultrathin sections were further stained with uranyl acetate and lead citrate. Samples were analyzed with the JEOL 1400+ (JEOL, Tokyo, Japan) transmission electron microscope equipped with an Olympus Veleta charge-coupled device camera (Olympus Soft Imaging Solutions GMBH, Münster Germany) and Radius software version 1.3 (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan).
To assess myelin sheath thickness, the G-ratio (axon diameter/total outer myelin sheath diameter) was measured on electron micrographs of ON cross sections from 8- to 9-week–old mice. Images of the ON were obtained at a magnification of ×2500 (xy axes image sampling density, 27.9 nm). The G-ratio was determined from 300 to 400 randomly chosen fibers per nerve cross section. Images were analyzed using ImageJ software version 1.51 (NIH, Bethesda, MD; https://imagej.nih.gov/ij/index.html), and G-ratio measurements were performed with the G-ratio plugin and online source code (http://gratio.efil.de, last accessed June 12, 2018).
Sphingolipid Mass Spectrometry
After mice were euthanized and perfused as described above, globes were enucleated. Retinas were then carefully separated from the globes under a dissection microscope. Retinal tissue was homogenized in 300 μL phosphate-buffered saline with the Omni Bead Raptor 24 tissue homogenizer (Omni International, Inc., Kennesaw, GA) using 2.8-mm ceramic beads. Lipids were extracted from 100 μL of retinal tissue lysate with 400 μL of methanol. The supernatant was reconstituted with 300 μL of water for mass spectrometry analyses, as previously described.26 The following internal standards were spiked in to each retina homogenate before extraction: 50 ng each of deuterated ceramide-1-phosphate [d18:1/16:0 or d18:1/24:0 (Matreya Inc., Pleasant Gap, PA) and d18:1/24:1 (Avanti Polar Lipids Inc., Alabaster, AL)]; 50 ng of deuterated ceramide (d18:1/22:0; Medical University of South Carolina Lipidomics Core, Charleston, SC); 50 ng of C17 analog of monohexosylceramide (d:18:1/17:0; Avanti Polar Lipids Inc.); 500 ng of C17 analog of sphingomyelin (d18:1/17:0; Avanti Polar Lipids Inc.); 100 ng of d7-Sph (Avanti Polar Lipids Inc.); and 100 ng of d7-sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P; Avanti Polar Lipids Inc.).
The samples were analyzed on the Shimadzu 20AD high-performance liquid chromatography system using reverse-phase C18 high-performance liquid chromatography columns (Agilent Co, Santa Clara, CA) and a Leap PAL autosampler coupled to a triple quadrupole mass spectrometer (API-4000; Applied Biosystems, Carlsbad, CA) operated in multiple reaction mode at the Medical University of South Carolina Lipidomics Core. Positive-ion electrospray ionization mode was used to detect all sphingolipids. Retinal extraction samples were injected in duplicate for data averaging. The Analyst software version 1.5.1 was used for data analysis (Applied Biosystems). Sphingolipid measurements were normalized for individual protein concentrations obtained via a bicinchoninic acid assay (Thermo Scientific Pierce, Waltham, MA) and expressed as fold-change over results from Asah1+/+ mice. Lipidomic analyses were conducted separately on retinal tissue from the two different age groups. Ceramide-1-phosphate (C1P) was analyzed in retinal samples from 8- to 9-week–old mice but could not be analyzed in 3- to 4-week–old mice because of insufficient tissue lysate and lipid standards. S1P levels were lower than the limit of detection in retinal samples from both 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old mice.
Statistical Analysis
Data are expressed as means ± SEM and analyzed with a t-test unless otherwise stated. Statistics were performed using GraphPad Prism software version 5.0 (GraphPad Software Inc., La Jolla, CA) and MATLAB (MathWorks, Inc., Natick, MA). P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Noninvasive Imaging Reveals Ocular Pathology
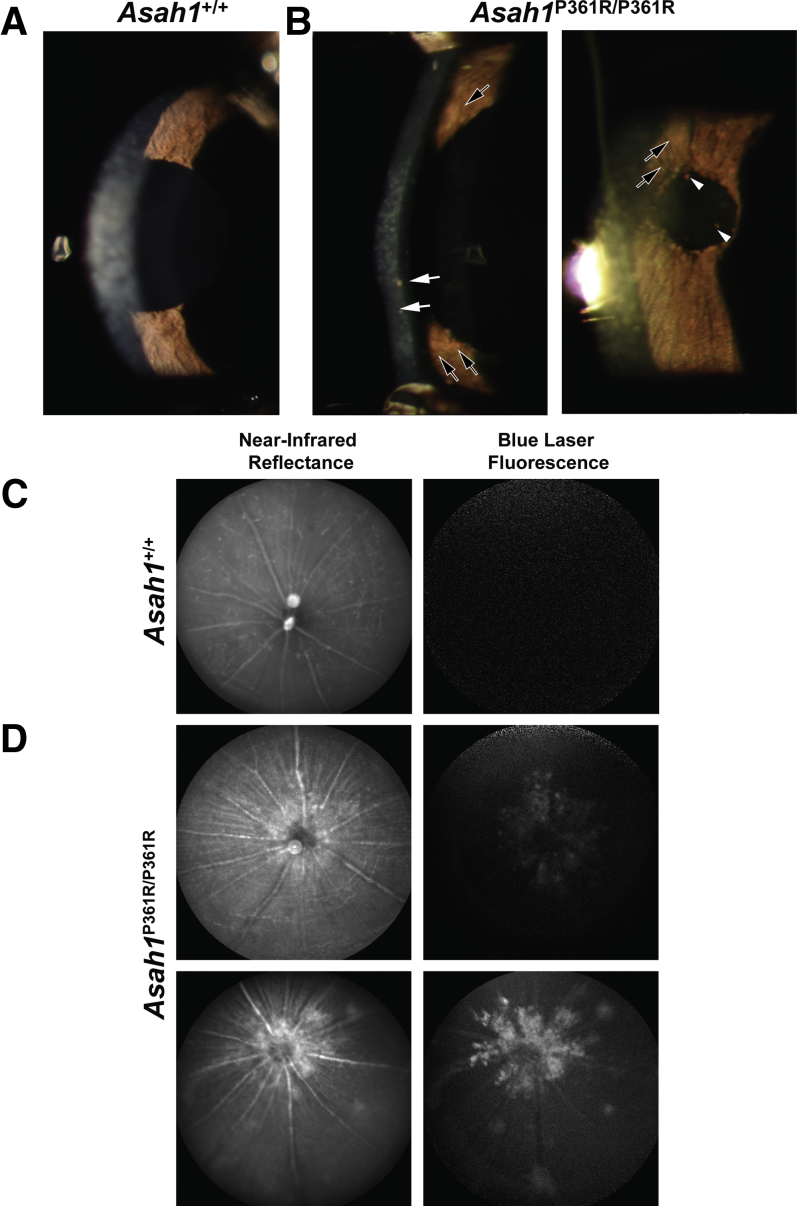
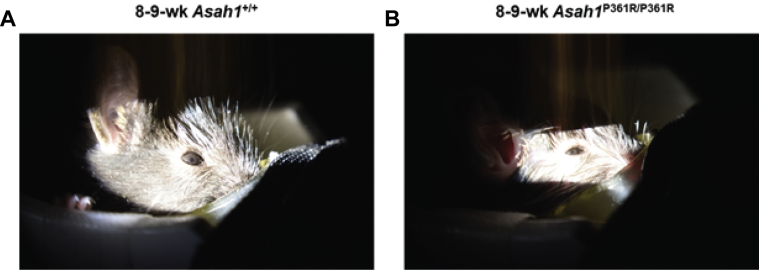
In comparison to control 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ mice (Figure 1A), slit-lamp examination of the anterior chamber revealed signs of uveitis in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mouse eyes (Figure 1B). These included corneal endothelial granulomatous keratic precipitates, Busacca and Koeppe nodules on the iris, and occasional pigmented deposits along the anterior lens capsule (Figure 1B). No corneal epithelial or stromal defects were observed in the slit-lamp examination.
Figure 1.
Anterior uveitis and optic nerve pathology in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A and B: Slit-lamp images of the anterior section of 8- to 9-week–old control Asah1+/+ (A) and Asah1P361R/P361R (B) mice. Granulomatous keratic precipitates (white arrows) and Busacca and Koeppe nodules (black arrows) indicate inflammation of the anterior segment of the Asah1P361R/P361R eye with clusters of pigment on anterior lens capsule (white arrowheads). C and D: Confocal scanning laser ophthalmoscope imaging was performed on 8- to 9-week–old control Asah1+/+ (C) and Asah1P361R/P361R (D) mice for near-infrared reflectance (IR; 810 nm) and blue light autofluorescence (BAF; 486 nm; emission filter, 525/50 nm). Representative IR and BAF images of healthy retinas from Asah1+/+ mice showing no autofluorescence (C). Representative IR and BAF images from two Asah1P361R/P361R mice each with varying levels of reflectivity and autofluorescence permeating from the optic nerve (D).
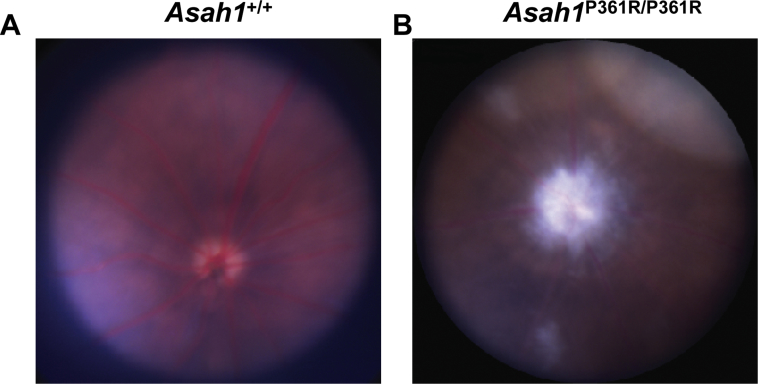
En face infrared and blue autofluorescence cSLO images revealed significant hyperreflectivity and autofluorescence surrounding the periphery of the ONH in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice in comparison to control Asah1+/+ mice (Figure 1, C and D). Variable patches of hyperreflective and autofluorescent lesions were also observed in the fundus of Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 1D). Examination of 3- to 4-week–old mice using infrared and blue autofluorescence cSLO revealed no abnormal reflectivity in either Asah1+/+ or Asah1P361R/P361R mice at that age (data not shown). Colored fundus images captured from 8- to 9-week–old mice appeared to correspond with cSLO images (Supplemental Figure S1). The 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice had significant accumulation of white deposits near the ONH, with occasional spots along the periphery of the fundus (Supplemental Figure S1).
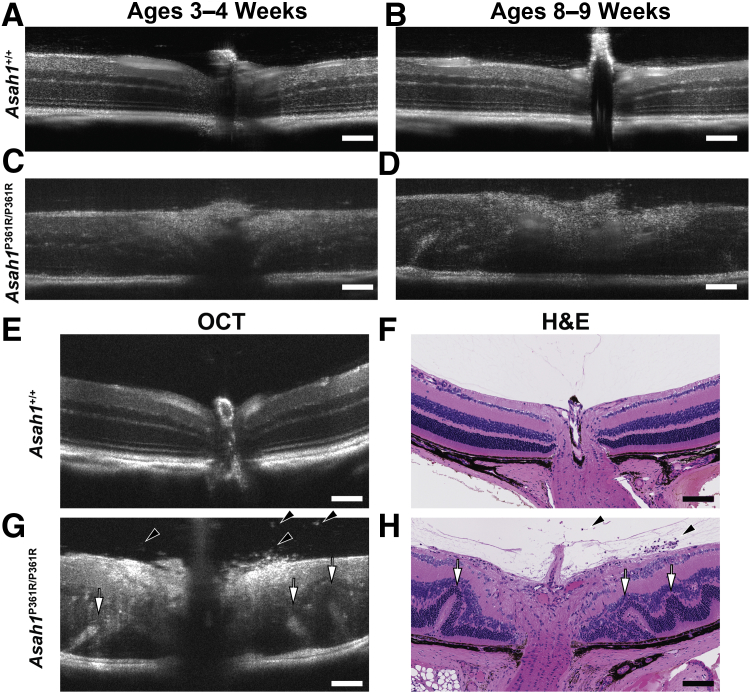
To further investigate retinal involvement in Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice, OCT imaging was performed at two time points. The first time point was at 3 to 4 weeks of age (Figure 2, A and C); the second time point was at 8 to 9 weeks of age (Figure 2, B and D). Most OCT images obtained from 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice appeared phenotypically to have normal retinal development (Figure 2C). However, some mice displayed less contrast within the individual retinal layers and on occasion there were hyperreflective spots within the vitreous (Figure 2C). This was most notable in the regions proximal to the ONH. OCT at the later time point revealed more pronounced impairment in the retinal layers (Figure 2, D and G), in comparison with control Asah1+/+ mice (Figure 2, B and E). Increased hyperreflectivity was most pronounced along the nerve fiber layer/retinal ganglion cell (RGC) layer, and the presence of hyperreflective specks was observed within the vitreous body of eyes from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 2G and Supplemental Video S1). After OCT imaging, H&E staining of the corresponding globe confirmed retinal dysmorphia in the 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 2H), in comparison with control Asah1+/+ mice (Figure 2F).
Figure 2.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) highlights retinal pathology in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A–D: Representative OCT scans from the same eyes at 3 to 4 weeks of age and then again at 8 to 9 weeks of age from control Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. C and D: Longitudinal OCT scans of eyes from Asah1P361R/P361R mice at 3 to 4 and 8 to 9 weeks of age show increasing disorganization of retinal morphology as the animals age. E–H: OCT scans with corresponding hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) micrographs of the same eyes from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. G and H: Inflammatory cells in the vitreal space (black arrowheads) and retinal folding (white arrows) are present in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Scale bar = 100 μm.
Impaired Retinal and Visual Function
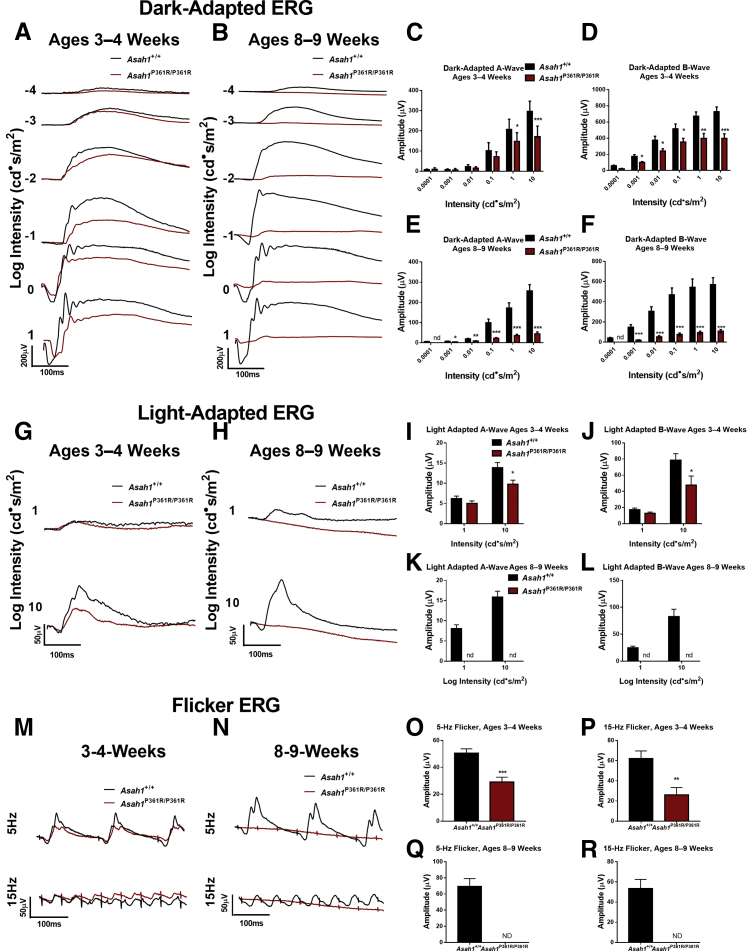
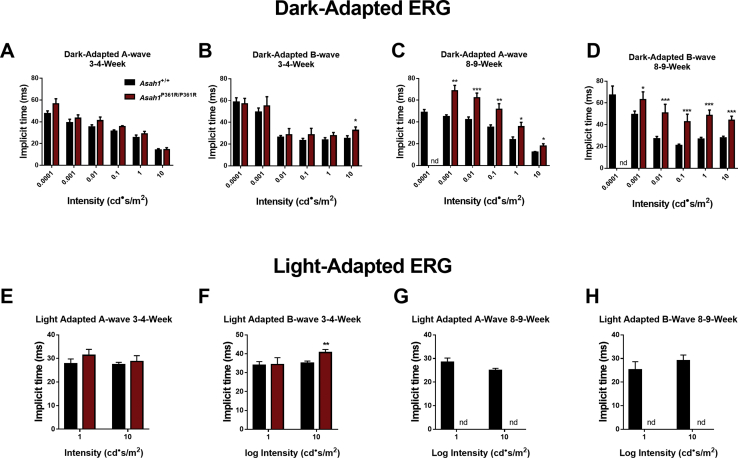
To test retinal function, dark-adapted, light-adapted, and flicker ERGs were performed on cohorts of both 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old mice. A-waves, which in the dark-adapted condition measure rod photoreceptor function, were unchanged at lower intensities, but decreased starting at the 0 log cd·second/m2 flash intensity in 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 3, A and C). B-waves, which assess rod and bipolar cell function in the inner retina, were found decreased by the −3 log cd·second/m2 intensity in 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 3, A and D). Dark-adapted, 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice also displayed no changes to A-wave implicit time compared with age-matched controls (Supplemental Figure S1). That said, 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice displayed an increase in the B-wave implicit time at the highest flash intensity (Supplemental Figure S2, A and B). Dark-adapted ERGs were repeated on the same cohorts of mice at 8 to 9 weeks of age. There was a significant reduction in signal from the Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 3B). A reduction in A- and B-wave amplitudes was detected at the −3 log cd·second/m2 flash intensity, as well as increased implicit times, and a negligible response was observed at the −4 log cd·second/m2 flash intensity (Figure 3, B, E, and F, and Supplemental Figure S2, C and D).
Figure 3.
Electroretinogram (ERG) demonstrates progressive impairment in rod and cone function in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A and B: Dark-adapted ERG response waveforms from studies on 3- to 4-week–old (A) and 8- to 9-week–old (B) Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. C–F: A- and B-wave amplitudes. C and D: Waveforms were unrecordable for the −4 log cd·second/m2 stimulus in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice. G and H: Light-adapted ERG response waveforms from 3- to 4-week–old (G) and 8- to 9-week–old (H) Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. I–L: A- and B-wave amplitudes. M and N: Flicker ERG response waveforms from 3- to 4-week–old (M) and 8- to 9-week–old (N) Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. O–R: Flicker amplitudes. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 10 animals for each genotype. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. ND, no data because of an absence of a recordable waveform.
In the light-adapted ERG, which is an inference of cone function, a decrease in both A- and B-wave amplitudes as well as an increase in B-wave implicit time at the higher flash intensity in 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 3, G, I, and J, and Supplemental Figure S2, E and F) was detected. Flicker ERG, another indicator of cone function, revealed a decreased signal in both 5- and 15-Hz rates of flicker in 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 3, M, O, and P). Repeating light-adapted ERGs and flicker ERG on the same mice at 8 to 9 weeks of age demonstrated a lack of response from the Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 3, H, K, L, N, Q, and R, and Supplemental Figures S2, G and H).
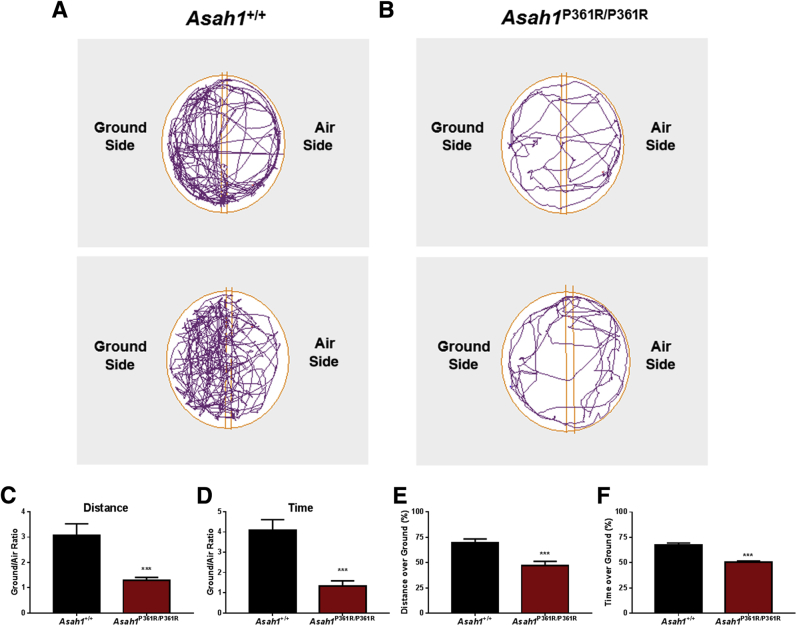
To further validate visual impairment in this model, a modified visual cliff test was performed on 8- to 9-week–old mice. Control Asah1+/+ mice spent most of their time within the ground side of the apparatus (Figure 4, A and C–F). They also traveled a greater distance. In contrast, Asah1P361R/P361R mice demonstrated no preference for ground or air zones, spending roughly equal time in both sectors. They also traveled an equal total distance within the ground and air side (Figure 4, B–F). Although other behavioral deficits have been previously demonstrated in Asah1P361R/P361R mice,21 the results from this modified visual cliff test and the ERG data together suggest significant visual impairment in these animals.
Figure 4.
Visual cliff test reveals perturbed depth perception in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A and B: Representative movement traces of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ (A) and Asah1P361R/P361R (B) mice during the visual cliff test. Distance traveled in each zone expressed as ground/air ratio. C:Asah1P361R/P361R mice spend equal amounts of time in both the ground side and the air side. D: Duration spent in each zone expressed as ground/air ratio. E and F: Percentage of the distance traveled (E) and the time spent (F) on the ground side. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 15 animals for each genotype. ∗∗∗P < 0.001.
Increased Retinal Thickness
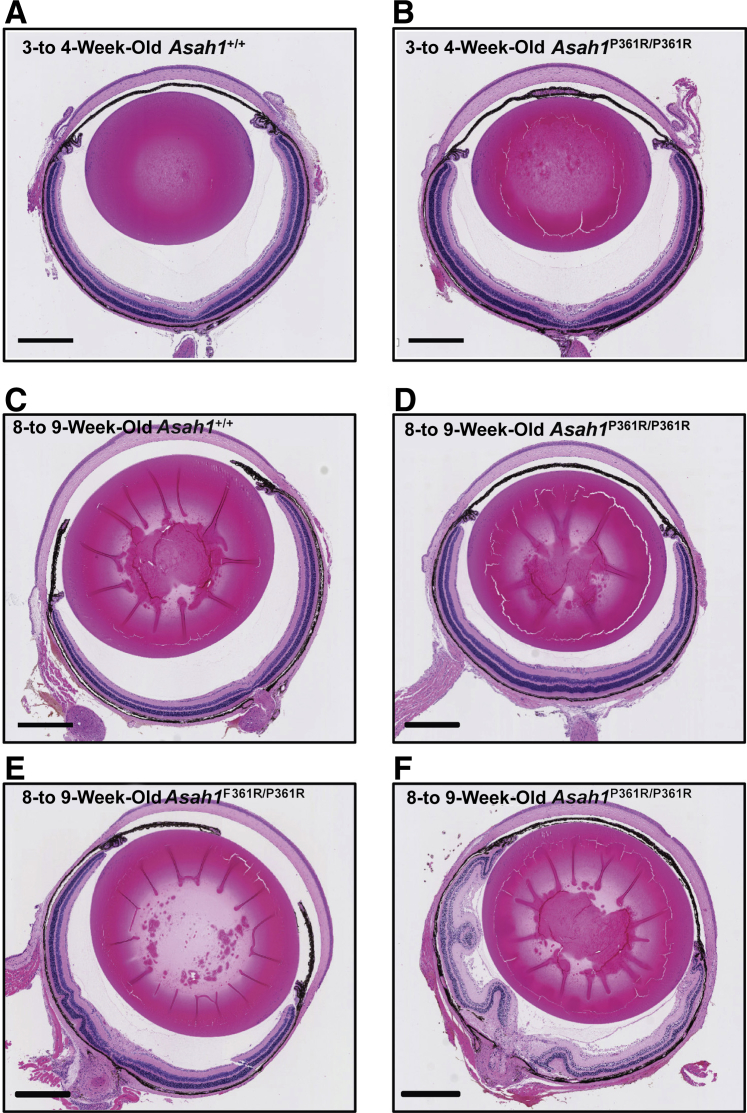
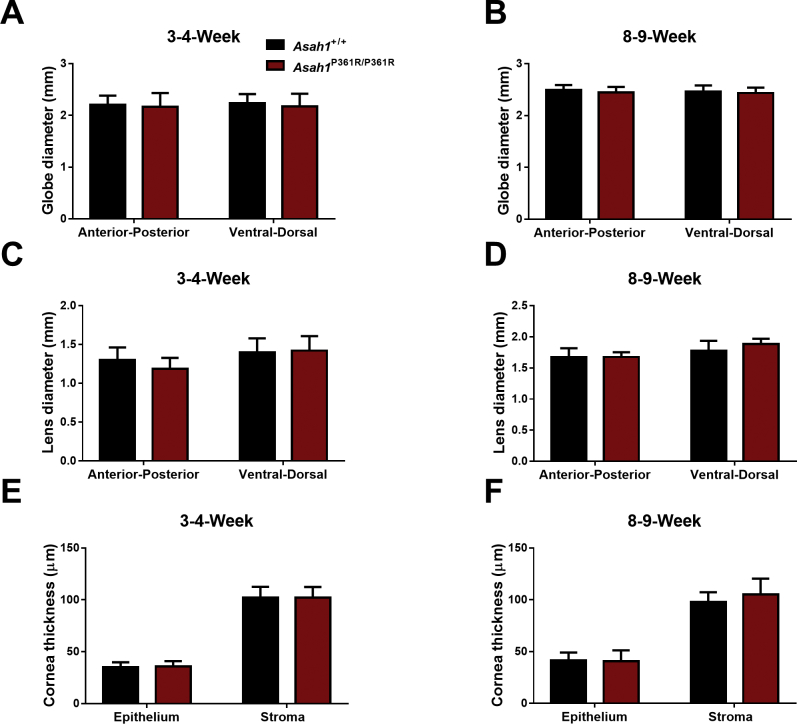
Asah1P361R/P361R mice are smaller than age-matched controls. By 4 to 5 weeks of age, they also start to progressively lose weight until they succumb to the disorder.20 During examination of the eyes, Asah1P361R/P361R mice had smaller interpalpebral fissures compared with age-matched controls (Supplemental Figure S3). To assess whether eye development was affected, gross measurements were performed on micrographs obtained from H&E-stained globe sections. Measurements revealed no significant differences in globe or lens diameter in 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice, respectively (Supplemental Figure S4, A–D). Measurements of the anterior chamber also revealed no differences in the thickness of the corneal epithelium and stroma between Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice at both 3 to 4 and 8 to 9 weeks of age (Supplemental Figure S4, E and F). This phenotype may be the clinical equivalent of ptosis or blepharophimosis, which has not been described in FD.
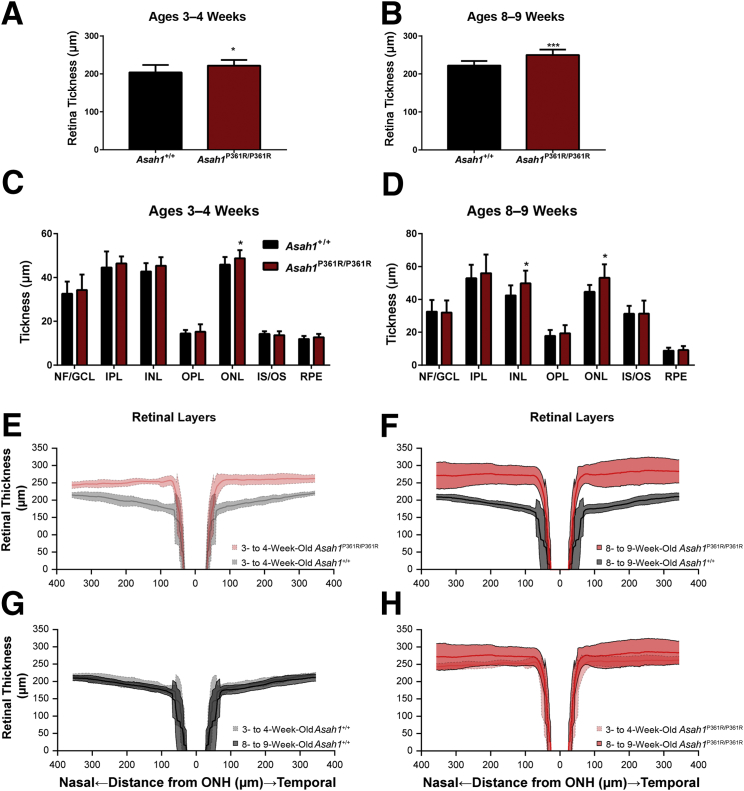
Surprisingly, Asah1P361R/P361R mice displayed increased retinal thickness as early as 3 to 4 weeks of age when compared with age-matched Asah1+/+ mice (Figure 5, A and B). Specifically, by 3 to 4 weeks of age, the outer nuclear layer was significantly thicker (Figure 5C). By 8 to 9 weeks of age, increased thickness was observed in both the inner nuclear layer and outer nuclear layer (Figure 5D). To validate our histology measurements, retinal thickness was analyzed from our previous OCT images with OCT retinal analysis software.23 Analyses of OCT images revealed that 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice exhibited increased nasal and temporal retinal thickness in comparison to age-matched Asah1+/+ mice (Figure 5E). This increased thickness became more progressive by 8 to 9 weeks (Figure 5, F and H). No changes in thickness were seen between 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ mice (Figure 5G).
Figure 5.
Increased retinal thickness in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A–D: Morphometric analyses of retinas from 3- to 4-week–old (A and C) and 8- to 9-week–old (B and D) control Asah1+/+ mice and test Asah1P361R/P361R mice from hematoxylin and eosin–stained sections. E–H: Retinal thickness plot generated from optical coherence tomography B-scans on samples from 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ mice and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Retinal thickness is significantly increased in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice when an n-way analysis of variance is performed for factors that included genotype, age, and retinal location. E and F:P < 0.0001. Data are expressed as means ± SEM (A–D) and means ± SD (E–H). n = 10 animals per group (A–D); n = 6 to 10 animals per group (E–H). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗P < 0.001. GCL, ganglion cell layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; IS, inner segment; NF, nerve fiber; ONH, optic nerve head; ONL, outer nuclear layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer; OS, outer segment; RPE, retinal pigment epithelium.
Variable Penetrance of Retinal Dysplasia
To examine the presence of retinal dysplasia, H&E-stained retinas were examined to evaluate their morphology. All of the retinas from 3- to 4-week–old control Asah1+/+ and 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice showed no dysplasia (Figure 6, A and B). Examination of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice, however, revealed a range in retinal dysplasia (Figure 6, C–F). Approximately 25% of globes from Asah1P361R/P361R mice were within normal limits, 45% developed an intermediate degree of dysplasia, and 30% had severe retinal folding. Retinal dysplasia was most pronounced in regions closest to the ONH. Mice that developed severe retinal disturbances often had involvement of multiple layers, with folds even reaching into the vitreous body (Figure 6F).
Figure 6.
Varying degree of retinal dysplasia in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A–F: Light micrographs of hematoxylin and eosin–stained globe cross sections from 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. D–F: A varying degree of retinal dysplasia is observed in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Retinal morphology is within normal limits for all 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ mice and 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice globes that were scored. In 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice, morphology scoring reveals 30% of globes with severe dysplasia, 45% of globes with intermediate dysplasia, and 25% of globes within normal limits. n = 20 retinal samples per group. Scale bar = 500 μm.
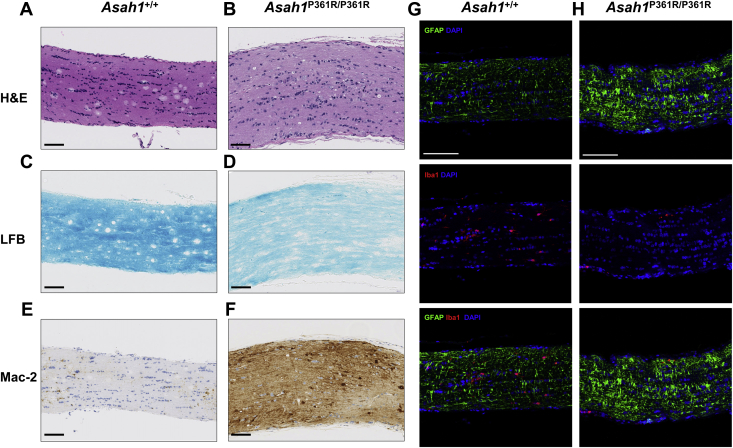
Inflammation, Astrogliosis, and Storage Pathology in the Retina, ONH, and Unmyelinated Optic Nerve
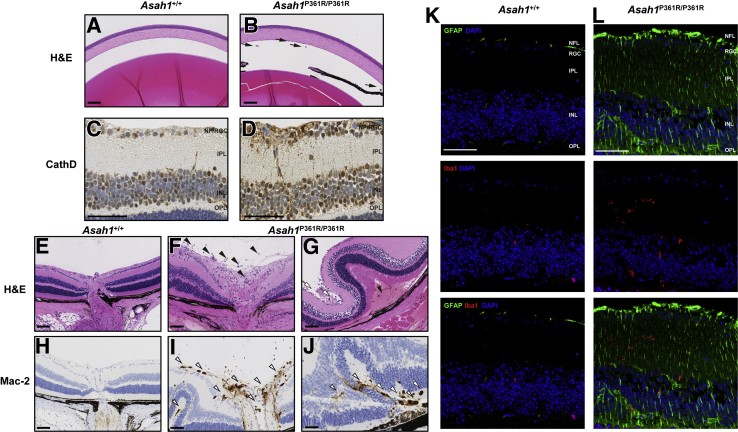
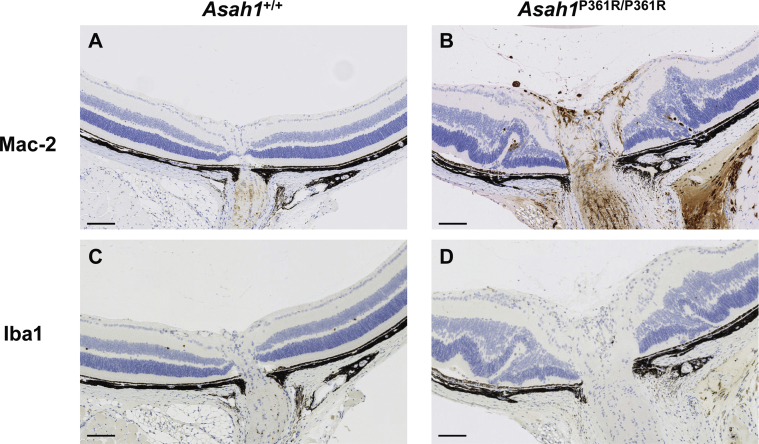
Inflammatory cells were observed in the eyes of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 7, B, E, G, I, and J). Control Asah1+/+ mice did not display such cellular recruitment (Figure 7, A, E, and H). Infiltrating inflammatory cells were observed in both the anterior chamber and vitreous humor of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 7B). An increased abundance of inflammatory cells was most notable in the vitreal region above the ONH, presumably where the central retinal vein and artery are located (Figure 7, F and G).
Figure 7.
Retinal pathology in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A: Light micrograph of the anterior chamber of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ mouse. B: Presence of inflammatory cells in anterior chamber (black arrows) in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mouse. C and D: Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining for cathepsin D (CathD) featuring the various retinal layers in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ (C) and Asah1P361R/P361R (D) mice. Asah1P361R/P361R mice display increased and more intense staining for CathD. E: Light micrograph of the retina and optic nerve head (ONH) from an 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ mouse. F: Numerous inflammatory cells (black arrowheads) can be seen along the ONH in sections from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice. G: In Asah1P361R/P361R mice that exhibit significant retinal dysplasia, loss/sloughing of the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) layer is observed (white arrows), as well as retinal detachment leading to the presence of a hemorrhage (black arrowhead). H–J: IHC staining for Mac-2 on sections from Asah1+/+ mice and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. I: Many of the invading inflammatory cells near the RGC and optic nerve vessels are macrophages (white arrowheads). J: Invading cells (white arrowheads) can also be detected in the choroid layers, where there are retinal folds. K and L: Immunofluorescence staining for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1), and DAPI on retinal sections from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. GFAP is a marker for astrocytes and Müller cells, and Iba1 is a marker for microglia and macrophages. Scale bar = 50 μm. H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; INL, inner nuclear layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; NFL, nerve fiber layer; OPL, outer plexiform layer.
Next, IHC staining was performed for Mac-2 (a macrophage marker) on globes from 8- to 9-week–old mice. Many of these inflammatory cells were observed in Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 7, H–J). Although they were commonly localized around the ONH, macrophages were also observed within the vessels of the RGC layer and along the choroid/pigment epithelium layer in regions where retinal folding occurred (Figure 7, I and J). In the 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice that developed significant retinal folding, detachment of the retina often occurred, as well as subretinal hemorrhages (Figure 7G).
IHC staining for cathepsin D revealed an increase in lysosomal staining, particularly in RGC and inner nuclear retinal layers of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice compared with controls (Figure 7, C and D). Examination of the nerve fiber/RGC layers of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice revealed increased vacuolation and a more intense granular cathepsin D staining (Figure 7D). Of the 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice that had severe retinal dysplasia, the nerve fiber/RGC layer showed degeneration and sloughing (Figure 7G).
To further characterize neuroinflammation, retinal sections were assessed from 8- to 9-week–old mice by immunofluorescence staining for GFAP, a label for glial cells such as astrocytes and Müller cells. Staining was also performed for Iba1, a marker for activated microglia (Figure 7, K and L). The retina of Asah1P361R/P361R mice did not contain many cells that were positive for Iba1. On occasion, some microglia-like cells that had branching projections in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice were observed; however, such occurrences were infrequent, and those cells were not found to be localized to one particular region. Furthermore, IHC on serial retinal sections revealed areas where Mac-2 staining was positive and Iba1 was negative (Supplemental Figure S5). This suggests that these recruited cells are predominantly macrophages.
Increased GFAP staining was found on multiple retinal layers, but most intense in the nerve fiber/RGC layer of retinal sections from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 7L). GFAP staining was also positive along the inner plexiform layer, the inner nuclear layer, and the outer plexiform layer of retinal sections from mutant mice. This observation suggests astrocytosis and Müller cell activation in the retina of the ACDase-deficient mice. To assess whether activation of microglia was present in the visual system, retinal tissue was stained for Iba1. On occasion, we observed an increased number of Iba1-positive cells; however, phenotypically, these labeled cells appeared similar to those from wild-type animals (Figure 7L).
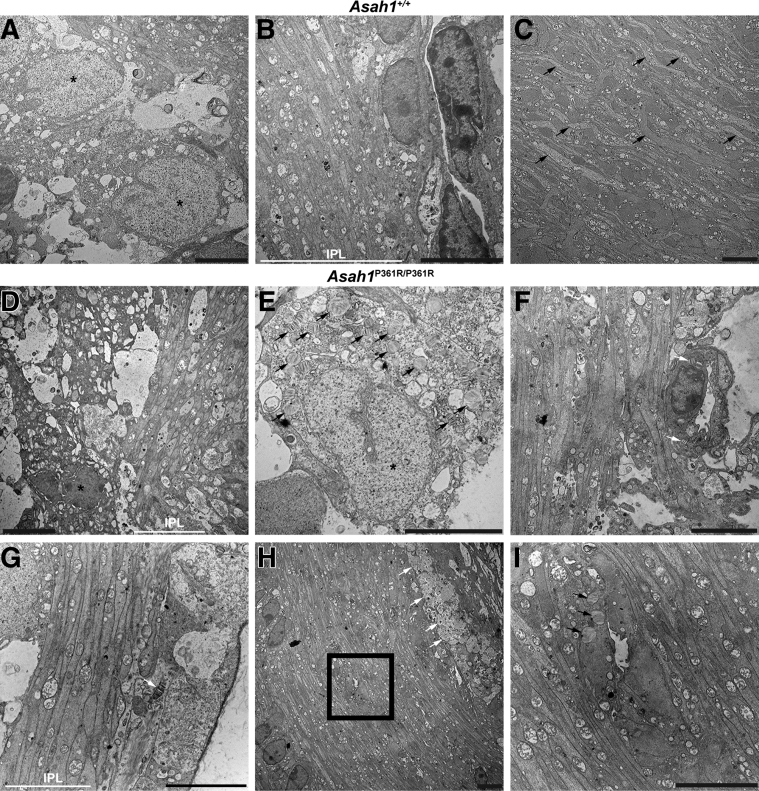
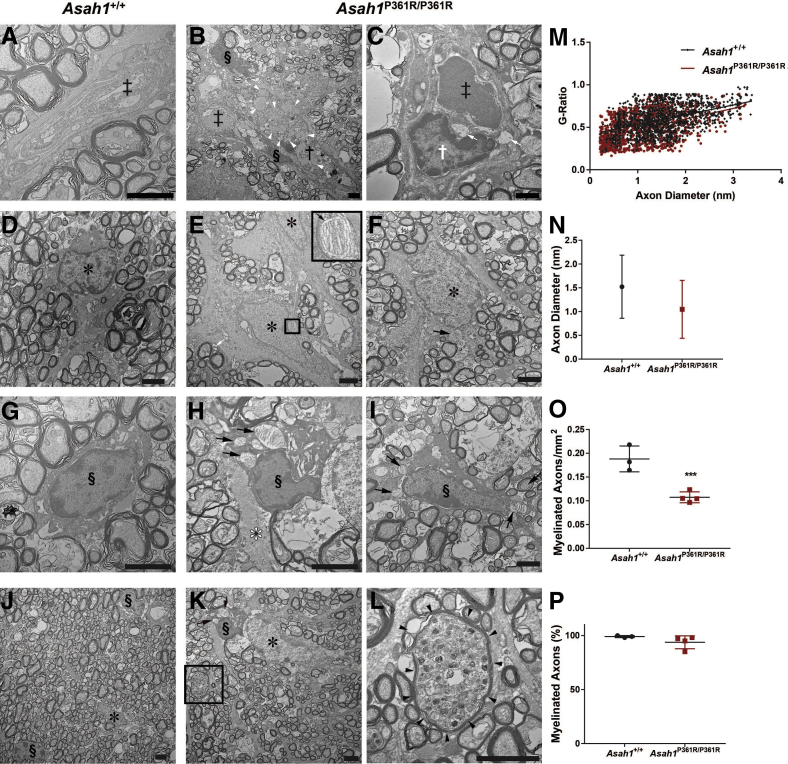
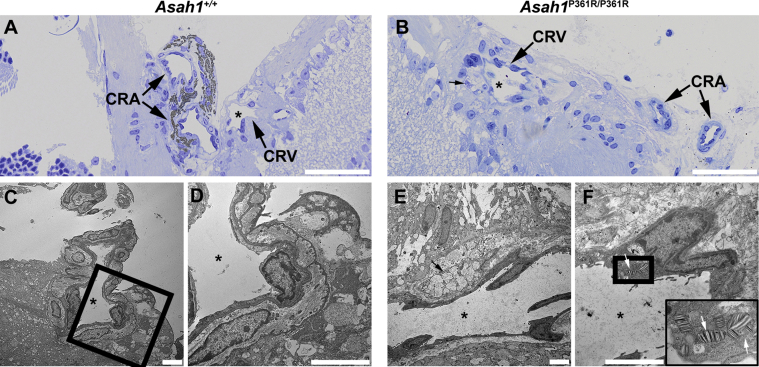
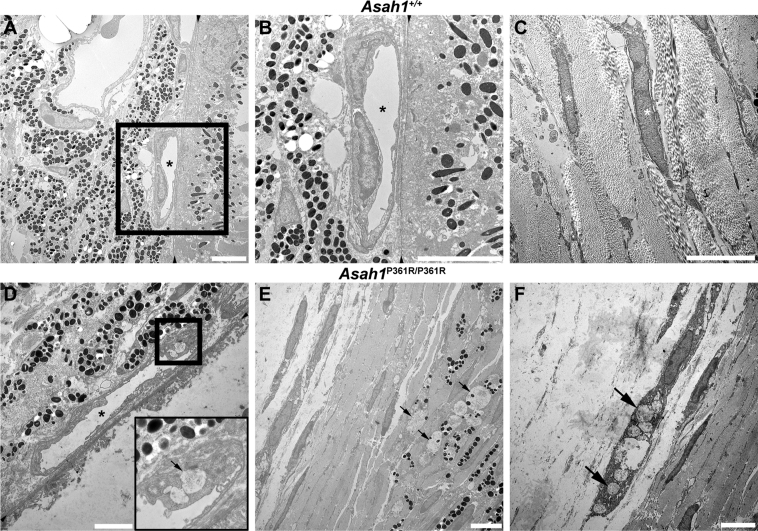
Ultrastructural analyses of the retina and unmyelinated portion of the ON in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice revealed extensive storage pathology in a range of cell types that was absent in samples from 8- to 9-week–old control mice (Figure 8, A–C). Ganglion cells in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice contained an excess of zebra-like storage bodies (Figure 8, D and E). Zebra bodies were also present in endothelial cells of the vessels of the inner plexiform layer (Figure 8F). The inner plexiform layer also contained abnormal storage vacuoles in the abundant astrocytic processes (Figure 8, G–I) and abnormal macrophage-like cells with an excess of curved-linear tubular body–like profiles in the vicinity of capillaries (Figure 8H) and zebra body–like storage vacuoles in the astrocytic processes (Figure 8I). In addition, storage vacuoles were observed within endothelial cells on the central retinal vessels of the ONH (Figure 8F). Similar to the rest of the retina and central nervous system,21 the perivascular space of the ONH contained storage-laden, macrophage-like abnormal cells (Supplemental Figure S6). Curved-linear tubular body–like storage vacuoles were also observed within endothelial cells of the choroid capillaries and inside melanosome-containing cells along the outer choroid (Supplemental Figure S7). Last, zebra bodies (indicating storage) were also present within scleral fibroblasts (Supplemental Figure S7).
Figure 8.
Retinal and unmyelinated on ultrastructure pathology in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A: Electron micrographs highlighting the ganglion cells (nuclei; black asterisks) in the Asah1+/+ mouse. B: Inner plexiform layer (IPL) in the Asah1+/+ mouse. C: Optic nerve disk/unmyelinated part of the ON (astrocytic processes; black arrows) in the Asah1+/+ mouse. D and E: Ganglion cells (nuclei hallmarked by black asterisks) in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice are with numerous zebra-like storage vacuoles in their cytoplasm (black arrows). F–I: White arrows highlight zebra body–like storage profiles in the endothelial cell (F); zebra body–like storage vacuole (white arrow) in the astrocytic process (G); macrophage-like cells (white arrows) laden with curved-linear tubular body–like storage bodies (H); and zebra body–like storage vacuoles (black arrows) in the astrocytic processes (I; image corresponds to the boxed area in H). Scale bar = 5 μm.
Pathology of the Myelinated Optic Nerve
Representative light micrographs of H&E-stained ON tissue from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice are shown in Figure 9, A and B. Asah1P361R/P361R mice displayed a thickening of the ON pial sheath (Figure 9B). H&E staining of ON tissue from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice also revealed the presence of mononuclear cellular infiltrates with abundant vacuolated cytoplasm and/or cytoplasm distended with granular material that preferentially accumulated in the vicinity of the optic vein (Figure 9B). When the corresponding ON tissue from 8- to 9-week–old mice was stained with Luxol fast blue, the staining on Asah1P361R/P361R mice ON tissue appeared less intense (Figure 9, C and D).
Figure 9.
Optic nerve pathology in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A–F: Light micrograph of hematoxylin and eosin (H&E), Luxol fast blue (LFB), and Mac-2–stained optic nerve sections from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. G and H: Immunofluorescence staining for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1), and DAPI on optic nerves of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Scale bars: 100 μm (A–F); 50 μm (G and H).
IHC staining for Mac-2 confirmed the presence of infiltrating macrophages along the ON track in samples from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice but not in samples from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ mice (Figure 9, E and F). Sections of ON tissue from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice displayed greater GFAP staining than controls (Figure 9, G and H). This suggests that astrocytosis is also affecting the ON tissue of Asah1P361R/P361R mice.
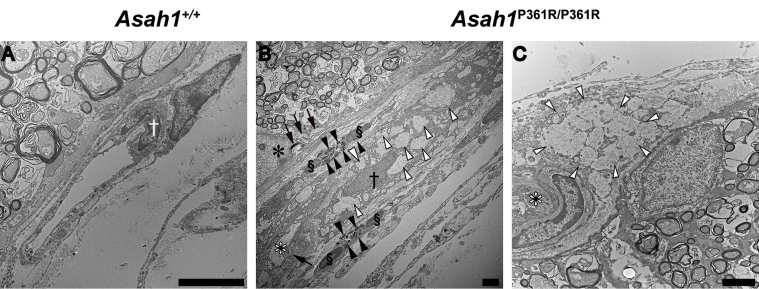
Ultrastructure analysis of ON sections from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice revealed abnormal storage in macrophages accumulating in the intraneuronal perivascular spaces (Figure 10, A–C). These macrophage- and fibroblast-like cells contained curved-linear tubular body storage in vacuoles. ON from Asah1P361R/P361R mice also showed discernible storage vacuoles in astrocytes and zebra-like storage vacuoles within the cytoplasm of oligodendrocytes (Figure 10, D–I). Abnormal storage vacuoles were also present in the endothelial cells of vessels (both pial and intraneuronal) and in capillaries (Supplemental Figure S8).
Figure 10.
Optic nerve ultrastructure pathology in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A: Representative micrograph of a normal intraneuronal capillary in the Asah1+/+ mouse. B and C: Electron micrograph of endothelial cells and pericapillary macrophages with storage vacuoles in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. D: An astrocyte from an Asah1+/+ mouse with finely structured cytoplasmic extensions. E and F: Hyperplastic astrocytes from Asah1P361R/P361R mice with zebra body–like and curved-linear tubular body CTB containing storage vacuoles. Boxed area in E is shown in higher magnification in the inset: Zebra body–like material is presented at higher magnification. G: Normal structured oligodendrocyte from an Asah1+/+ mouse. H and I: Oligodendrocytes containing zebra body–like storage bodies in cytoplasm. J: Micrograph displaying ON axon diameters and axonal density in Asah1+/+ mice. Asah1P361R/P361R mice appear to show less density in ON axons. K and L: Presence of neuronal axonal dystrophy (axonal spheroid) containing accumulated axonal cargo (K; highlighted by black boxed area and enlarged in L). Double dagger denotes capillary lumina; white asterisk, astrocyte; black asterisk, astrocyte nucleus; white dagger, endothelial cell nucleus; black dagger, macrophage nucleus; section symbol, oligodendrocyte nucleus; black arrows, zebra body–like storage bodies; white arrow, storage vacuole with curvilinear tubular (Farber) bodies; white arrowheads, partly cleared macrophage storage vacuoles with curvilinear tubular (Farber) bodies; black arrowheads, outline of the axonal spheroid. The G-ratio (axon diameter/fiber diameter) was plotted against axon diameter. M: In samples from 8- to 9-week–old animals, Asah1P361R/P361R mice (1350 axons) show a difference in myelination compared with Asah1+/+ mice (1333 axons) (P < 0.001 from clustered rank sum test). N: Comparison of axon diameters. O and P: Quantification of myelinated axon density and percentage of myelinated axons. n = 3 (M). ∗∗∗P < 0.001. Scale bar = 2 μm (A–L).
Neuroaxonal Dystrophy and Reduced Axonal Density
Ultrastructure analyses of tissue (interior and periphery) from 8- to 9-week–old animals revealed that the ON of mutant mice had a qualitative reduction in axon density compared with controls (Figure 10, J–L). Signs of neuroaxonal dystrophy in some axons via the formation of axonal spheroids were also observed in the ON of Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 10, K and L).
To assess myelination, the G-ratio (axon diameter/fiber diameter; where fiber diameter = axon diameter + myelin sheath thickness) of the ON from 8- to 9-week–old mice was measured. The analysis revealed a significant reduction in the G-ratio in samples from Asah1P361R/P361R mice in comparison to those from control Asah1+/+ mice (Figure 10M). However, no differences were detected in the ON axon diameter between 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 10N). Further evaluation revealed a reduction in the density of myelinated axons in Asah1P361R/P361R ONs; however, of the axons that were assessed, no changes in the percentage of myelinated axons were observed (Figure 10, O and P).
Altered Sphingolipid Profile in the Retina
Ceramide, sphingomyelin (SM), monohexosylceramide (MHC), Sph, and S1P were measured via liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry in retinal lipid extracts from both 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. C1P was measured via liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry in retinal lipid extracts from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice.
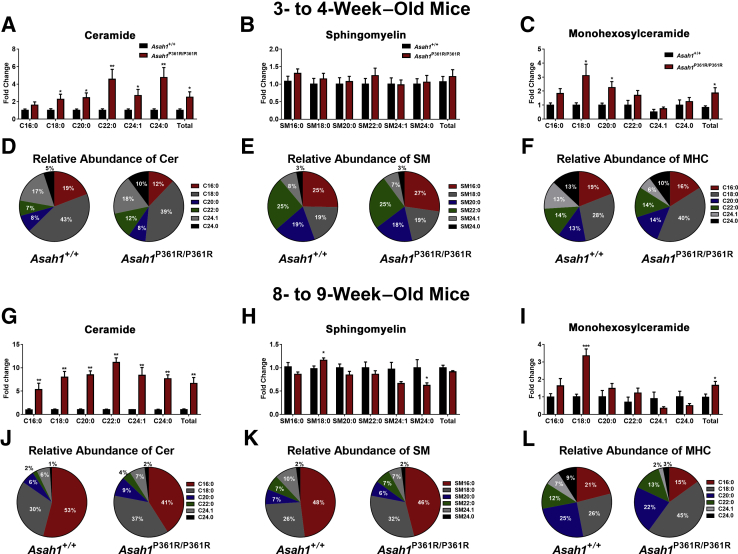
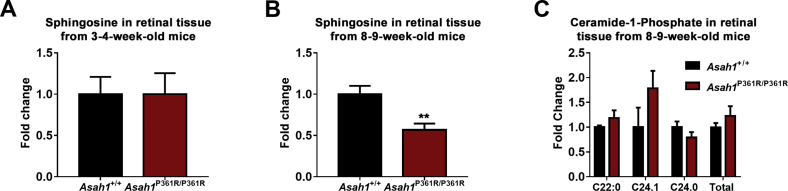
Analyses of the individual species of each sphingolipid class revealed an accumulation of many ceramide species by 3 to 4 weeks of age and all ceramide species studied in retinal samples from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 11, A and G). SM was unchanged in retinal samples from both 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 11B). SM 18:0 was increased, and SM 24:0 was decreased, in retinal samples from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 11H). Total MHC was elevated in retinal samples from both 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 11, C and I). The C18:0 MHC species displayed the highest fold-change in retinal samples from both the 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 11, C and I). Sph levels were unchanged in retinal samples from 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice but were significantly decreased in retinal samples from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Supplemental Figure S9, A and B). S1P was also measured in retinal samples from both age groups; however, readings were lower than the limit of detection (data not shown). Although C1P was not measured in retinal samples from the 3- to 4-week–old mice because of insufficient sample and lipid standards, no alterations in C1P levels were observed in retinal samples from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Supplemental Figure S9C).
Figure 11.
Altered sphingolipid species in the retina of Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Sphingolipids were quantified in retinal tissue from Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice by liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry. Quantification of ceramide (Cer; A), sphingomyelin (SM; B), and monohexosylceramide (MHC; C) species in retinal tissue from 3- to 4-week–old Asah1+/+ mice and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. The relative abundance of Cer (D), SM (E), and MHC (F) species in retinal tissue from 3- to 4-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Quantification of Cer (G), SM (H), and MHC (I) species in retinal tissue from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. The relative abundance of Cer (J), SM (K), and MHC (L) species in retinal tissue from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 5 to 6 animals for each genotype and age group. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001.
Alterations in the relative abundance of sphingolipids were also detected in retinal samples from both the 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. The relative abundance of C16:0 ceramide decreased, whereas the relative abundance of several other ceramides increased, in retinal samples from 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 11D). The relative abundance of C16:0 ceramide also decreased in retinal samples from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice, whereas the relative abundance of all of the other ceramides measured increased (Figure 11J). Although the relative abundance of SM was almost unchanged in retinal samples from 3- to 4-week–old Asah1+/+ mice and 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 11E), an increase in the SM18:0 species and a slight decrease in many of the other SM species were observed in retinal samples from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 11K). The largest change in MHC relative abundance was an increase in the C18:0 species, which coincided with decreased C16:0, C20:0, C24:1, and C24:0 species in retinal samples from both the 3- to 4- and the 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice (Figure 11, F and L). Because the quantification of sphingolipids in retinal samples from the 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old mice was performed independently, no comparisons were made between the two age groups.
Discussion
ACDase deficiency is an ultrarare orphan disease that can manifest along a wide broad clinical spectrum. The cardinal phenotypes include painful joints, formation of lipogranulomatous nodules, and aphonia.1 In classic and more severe variants, neurologic involvement is common and is often associated with functional and behavioral deficits.4, 27 Ocular manifestations are commonly seen in patients who also display neurologic dysfunction, with the most common phenotype being a cherry red spot in the macula.3, 9, 10, 11, 12 Herein, we have provided an analysis of the ocular pathology present in the ACDase-deficient mouse. The results demonstrate that a deficiency in ACDase leads to a broad range of ophthalmic abnormalities. We highlight findings from noninvasive ocular imaging, characterize the affected cell types, and demonstrate visual impairment.
Although ocular disease is often present in FD, reports of an eye phenotype have thus far been restricted to superficial/observational descriptions. In the literature, there are only two studies on the visual aspects of FD that were located. The first was published in 1966 and applied light microscopy and histologic techniques to reveal the presence of lipid granules within the RGCs of an FD patient who died at 11 months of age.9 The second report, published in 1985, described the retinal ultrastructure of an FD patient who died before the age of 3 years.28 Five types of cytoplasmic inclusions were identified in the second patient, with the most abundant being described as flattened stacks of osmophilic lamellae.28 The RGCs, glia, and phagocytic cells all showed significant inclusions.28 The findings from these reports are recapitulated in our murine model. The H&E retinal tissue staining revealed a disorganized and vacuolated RGC layer in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Ultrastructural analyses of the retina also revealed significant storage pathology in various cell types—much like those reported by Zarbin and colleagues in 1985.28 Similar retinal pathology has also been noted in RGCs in other lysosomal storage disorders, such as Niemann-Pick disease type A, Pompe disease, and Tay-Sachs disease.29, 30, 31 Herein, significant storage pathology was further observed in endothelial cells, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and macrophage-like cells in the retina and optic nerves from Asah1P361R/P361R mice.
A heightened state of inflammation is characteristic of FD. An increased prevalence of inflammatory cells has been previously reported in the lungs, brain, and hematopoietic organs in this mouse model of FD.21, 22, 32 Thus, finding that a deficiency in ACDase activity also leads to inflammation in the eye and optic nerve could be expected. Through the use of noninvasive ocular imaging, the formation of granulomas and nodules was noted in the anterior chambers. In addition, deposits close to the ONH of the fundus were seen with cSLO, and hyperreflectivity was noted along the ONH and vitreous body by OCT. These observations can be explained by the presence of inflammatory cells. IHC staining for Mac-2 and ultrastructure analyses further demonstrated a significant presence of abnormal macrophage morphologies primarily around the choroid and other vessels along the retina and optic nerve.
We previously reported increased vascular permeability in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice.22 Although that study was primarily focused on lung pathology, one experiment involved a tail vein injection of Evans Blue Dye. Evans Blue Dye accumulation was measured in various organs in Asah1P361R/P361R mice.22 Although not reported in that study, qualitatively, Asah1P361R/P361R mouse eyes were more intensely stained than controls. Inflammatory cytokines, such as monocyte chemoattractant proteins 1, 3, and 5, increase in serum and organs from Asah1P361R/P361R animals.22, 26, 33 Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 also increases in the plasma of FD patients.33 Although cytokines were not measured in the retina, it is possible the combination of vascular leakage and altered cytokine production previously reported contributes to the macrophage and neutrophil recruitment described herein.22, 26
The microglial and astroglial pathology was further characterized via Iba1 and GFAP immunofluorescence staining of retinal and optic nerve tissue. Asah1P361R/P361R mice showed a progressive accumulation of GFAP in the retina and optic nerve, suggesting activation of astrocytes and Müller cells. Although significant macrophage infiltration was observed, Iba1 staining was largely unchanged, suggesting limited microglia involvement and that most infiltrated macrophages did not express Iba1.21, 26
Retinal dysplasia was also a prevalent feature in Asah1P361R/P361R mouse globes. Over 75% of globes analyzed had intermediate to severe retinal folding. Within the retinal folds, inflammatory cells were often discernible. Retinal folding was most prevalent in the regions near the ONH. This may be because of the proximity of the central optic vein and artery, the region where increased macrophage infiltration was also observed. The phenotype seen in the eyes of Asah1P361R/P361R mice shares some similarities with the rodent models of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis.34 During the early phase after experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis induction, cellular infiltrates can be observed in the vitreous and optic nerve head of mice eyes.35 As mice transition into the acute phase of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis, inflammation is more severe, and retinal folding and edema might occur.36, 37, 38 Although edema within the retina was directly assessed, it may be occurring in the visual system of Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Specifically, hyperreflective deposits were observed from SLO imaging, and an increased retinal thickness and inflammation was seen in Asah1P361R/P361R mice, which is associated with edema. In addition, the lung and brain of Asah1P361R/P361R mice show signs of edema.21, 22 Of interest, within the brain, approximately 70% of Asah1P361R/P361R mice at 9 weeks of age develop hydrocephalus.21 Although retinal pathology was not assessed previously, there may be a correlation between the development of hydrocephalus and retinal dysplasia because the retina is a part of the central nervous system.
The association between inflammation and retinal dysplasia has been reported in other models, such as cats infected with feline leukemia virus, dogs that were inoculated with canine herpes virus, and mice that were infected with Sindbis virus.39, 40, 41 The range of retinal dysplasia seen in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice may be because of varying rates of inflammation between individuals.
Sphingolipid metabolites have been shown to regulate both the function and the trafficking of inflammatory cells.42 This has been shown in the eye, where cases of acute uveitis can change both lipid and sphingolipid profiles.43 Conversely, there is evidence demonstrating that sphingolipid metabolism can be altered because of inflammation.44, 45, 46 Direct intravitreal injection of bioactive sphingolipids, such as C8:0 in mice, can induce a dose-dependent effect in recruiting inflammatory cells.47 From these studies, targeting the sphingolipid pathway has been suggested as an approach to treat uveitis.48 One of the most promising agents is FTY720 or fingolimod, an approved drug for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. FTY720 has shown significant anti-inflammatory effects in experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis rodent models.36, 49, 50 FTY720 is an analog of Sph that is derived from myriocin, a potent inhibitor of the de novo ceramide synthesis pathway.51 FTY720 is phosphorylated by sphingosine kinase-2 in a similar manner to the modification of Sph to S1P.51 In addition to anti-inflammatory properties via S1P binding, FTY720 has also been shown to inhibit ceramide synthase, the class of enzyme that regulates ceramide acyl chain length during synthesis.52 Because of its anti-inflammatory effects, and potential decrease in ceramides, it is possible that treatment with FTY720 in conjunction with other anti-inflammatory compounds may impede pathogenesis of FD.
We characterized the sphingolipid profiles of retinal lysates from 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Ceramide accumulation is progressive and present as early as 3 to 4 weeks of age in the retina of Asah1P361R/P361R mice. It is possible that this early accumulation of ceramide in the retinas of Asah1P361R/P361R mice contributes to the abnormal ERG activity recorded in these animals. Retinal ceramide levels were significantly higher in the 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice. These older Asah1P361R/P361R mice display progressive retinal inflammation, dysmorphic retinal pathology, and severe visual impairment. Thus, our data suggest that increasing retinal ceramide accumulation over time is associated with the retinal dysfunction and pathology reported herein.
The downstream metabolites of ceramide were measured, and it was found that only MHC was elevated in retinal lysate from Asah1P361R/P361R mice. SM was unchanged in both age groups of Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Sph was unchanged in 3- to 4-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice and decreased in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice. These findings appear specific to the retina because previous studies characterizing other organ systems in the ACDase-deficient mouse have noted accumulation of both ceramide and downstream ceramide metabolites.21, 22, 26 Within the liver and lungs of Asah1P361R/P361R mice, SM, C1P, and MHC were significantly elevated.22, 26 In the brain of Asah1P361R/P361R mice, Sph and MHC were significantly elevated.21, 26 Future in-depth studies that investigate upstream and downstream metabolites of ceramide at various time points in different cells and tissues from the ACDase-deficient mouse may provide further insight into the complex biochemistry of this disorder.
Maintaining sphingolipid equilibrium is essential for proper health and vision. Ocular manifestations are commonly reported in lysosomal storage disorders, and animal models have been instrumental in understanding disease progression. Studies on the acid sphingomyelinase–deficient mouse, the model for Niemann-Pick A/B disease, have revealed progressive retinal degeneration and inflammation.17, 18 In the context of Sandhoff disease, work on the β-hexosaminidase mutant mouse showed robust storage pathology preferentially in the RGC and impaired neurite outgrowth from cultured retinal explants.16, 53 Decreased ERG amplitude has also been documented in mice deficient in acid sphingomyelinase, hexosaminidase, and ceramide synthases 1, 2, and 4.17, 18, 54 The similarities in disease manifestations seen in these reports and our current study suggest that insults to sphingolipid metabolism lead to comparable pathologies because homeostatic control of sphingolipids is tightly regulated.
Ceramide is a central signaling lipid in the sphingolipid pathway. In more common retinal diseases, such as retinitis pigmentosa, increases in ceramide can lead to downstream effects, such as photoreceptor cell death.55 One study in the retinal degeneration 10 mouse model showed that ceramides are increased with progressive photoreceptor degeneration and that treatment with the inhibitor myriocin could protect photoreceptors from apoptosis.56 Another study in a rat model of light-induced retinal degeneration showed a neuroprotective effect of FTY720 that acted independent of its immunosuppressive action.57 Together, these reports demonstrate the deleterious effects of ceramide in the retina. In the case of chronic ceramide accumulation, such as in FD, alternative pathways may be switched on in response to sphingolipid buildup. Further work will be required to fully understand the role of ceramide signaling in FD and visual biology.
This study has provided the first in-depth analysis of the ocular manifestations and optic nerve pathology in the ACDase-deficient mouse. It has highlighted parallels between human cases and our model, particularly in terms of inflammation, storage pathology, and central nervous system decline. Given the lack of patients with FD and the dearth of available human tissue to study, this mouse model has aimed to fill the gap. Our results demonstrate a progressive decline in retinal function in Farber mice that coincides with severe retinal and optic nerve pathology and sphingolipid accumulation. These findings, although exploratory, may provide insight into the possible ocular pathology present in classic and severe variants of human FD.
Currently, there is an ongoing clinical trial (ID NCT03233841) to understand the natural history of FD. We have demonstrated the feasibility of noninvasive ocular imaging to assess and follow ocular pathology over time with serial testing in a mouse model of FD. Use of noninvasive ocular imaging may not only aid in diagnosis but serve as a screening modality to assess the inflammatory and neurologic status of patients with FD. In addition, recombinant enzyme therapy is currently being developed for the treatment of FD, and our laboratory has an ongoing interest in pursuing gene therapy to ameliorate this disorder.20, 58, 59 Noninvasive monitoring of the ocular conditions may also be a modality to assess the efficacy of these and future therapies.
Acknowledgments
We thank the staff at the Children's Hospital of Wisconsin Children's Research Institute Histology Core for technical assistance with histology and immunohistochemistry services; Christine Duris and Chris Skumatz for technical assistance; Dr. Suresh Kumar for microscopy assistance; and Dr. William M. Mckillop for critical review of the manuscript.
J.A.M. and F.P.S.Y. conceived and designed research; F.P.S.Y., B.S.S., J.S., A.E.S., M.S.N., J.G., I.S.K., and D.M.L. performed experiments; J.A.M., F.P.S.Y., B.S.S., J.S., A.E.S., M.S.N, and I.S.K. analyzed data; J.A.M, F.P.S.Y., J.S., I.S.K., D.M.L., and J.C. interpreted results; J.A.M. and F.P.S.Y. wrote the manuscript; J.A.M., F.P.S.Y., B.S.S., J.S., A.E.S., I.S.K., D.M.L., and J.C. edited and revised the manuscript; and J.A.M. and F.P.S.Y. approved the final version of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Supported by the Midwest Athletes Against Childhood Cancer Fund Professorship (J.A.M.). Ocular imaging analyses were supported by NIH grants P30EY001931 (B.S.S., A.E.S., I.S.K., D.M.L., and J.C.) and T32EY014537 (B.S.S. and A.E.S.). The electron microscopic analyses were supported by Operační program Praha konkurenceschopnost grant CZ.2.16/3.1.00/24509, National Center for Medical Genomics grant LM2015091, the Charles University Institutional Research and Development scheme, and Progres Q26 (J.S.).
Disclosures: None declared.
Supplemental material for this article can be found at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2018.10.018.
Supplemental Data
Supplemental Figure S1.
Pathology in fundus of Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A and B: Representative fundus images of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ (A) and Asah1P361R/P361R (B) mice. B: A white reflective substance is present around the optic nerve head region of Asah1P361R/P361R mice.
Supplemental Figure S2.
Abnormal electroretinogram (ERG) implicit times. A–D: Dark-adapted ERG implicit times from 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ mice and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. E–H: Light-adapted ERG implicit times from 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ mice and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 10 animals for each genotype. ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, and ∗∗∗P < 0.001. ND, no data because of an absence of a recordable waveform.
Supplemental Figure S3.
Reduced eye opening in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A and B: Representative images of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ mice and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice taken during slit-lamp analysis. B:Asah1P361R/P361R mice display a smaller interpalpebral fissure.
Supplemental Figure S4.
No changes in globe diameter, lens diameter, or corneal thickness in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Measurements of globe diameter, lens diameter, and cornea thickness analyzed in hematoxylin and eosin micrographs of 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A and B: Anterior to posterior and ventral to dorsal globe diameters are similar in Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. C and D: Anterior to posterior and ventral to dorsal lens diameter measurements are similar in Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. E and F: Corneal thickness (epithelium and stroma) is similar in Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 10 animals per group.
Supplemental Figure S5.
Infiltration of Mac-2–positive macrophages in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A–D: Light micrograph of retinal sections stained for Mac-2 and ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1 (Iba1) from 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Staining on serial sections suggests that the population of Mac-2–positive macrophages are negative for Iba1. Scale bar = 50 μm.
Supplemental Figure S6.
Central retinal artery (CRA) and central retinal vein (CRV) pathologies in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Electron micrograph of a normal CRA and CRV in an Asah1+/+ mouse. A, C, and D: The black asterisks highlight the same vessel. Electron micrograph featuring storage pathology in the CRA, the CRV, and the optic disk in the Asah1P361R/P361R mouse. Boxed area in C is shown at higher magnification in D. B, E, and F: The black asterisks highlight the same vessel. Perivascular macrophages with curved-linear tubular body–like storage bodies (black arrow) or zebra-like storage vacuoles (white arrow) are seen within endothelial cells. F: Thick boxed area highlighting zebra-like storage vacuoles is presented at higher magnification in the inset. Scale bars: 25 μm (A and B); 5 μm (C–F).
Supplemental Figure S7.
Choroid and scleral pathology in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Retinal pigment epithelium, choroid, and choroid capillary (black asterisks) in the Asah1+/+ mice. A and B: Bruch membrane (black arrowheads). Boxed area in A is shown at a higher magnification in B. C: Scleral fibroblasts (nuclei; white asterisks) are spindle shaped and surrounded by a collagen-rich extracellular matrix. D: Bruch membrane (black arrowheads) in the Asah1P361R/P361R mouse and endothelial cells within the choroid capillary (lumen highlighted by the black asterisk) shown containing curved-linear tubular body (CTB)–like storage vacuoles (black arrow and the higher-magnification inset). E and F: CTB-like storage bodies can be found in melanosome-containing cells of the outer choroid (small black arrows; E) and scleral fibroblasts (large black arrows; F). Scale bar = 5 μm.
Supplemental Figure S8.
Pial vessel pathology in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Representative electron micrograph featuring vascular cells in the ON of 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A: Normal structured pial vessel in an Asah1+/+ mouse. B and C: Pial vessel in an Asah1P361R/P361R mouse that is thickened by accumulation of vacuolated cells with macrophage and fibroblast morphology. B and C: Storage pathology is also present in the endothelial cells that line the optic vein. White dagger, endothelial cell nucleus; black dagger, macrophage nucleus; section sign, eosinophil granulocyte nucleus; white asterisk, smooth muscle cell nucleus; black asterisk, astrocyte nucleus; black arrows, zebra body–like storage bodies; black arrowheads, eosinophil granulocytes; white arrowheads, partly cleared storage vacuoles with curvilinear tubular (Farber) bodies. Scale bar = 2 μm.
Supplemental Figure S9.
Reduced sphingosine in the Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Additional sphingolipids were measured in retinal lysates of both 3- to 4- and 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. A and B: Quantification of sphingosine in retinal lysates from 3- to 4-week–old (A) and 8- to 9-week–old (B) mice. C: Quantification of ceramide-1-phosphate in retinal lysates from 8- to 9-week–old mice. Sphingosine-1-phosphate was measured in retinal lysates from both age groups but was lower than the limit of detection. Data are expressed as means ± SEM. n = 5 to 6 animals for each genotype and age group. ∗∗P < 0.01.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) reveals retinal pathology in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Representative OCT horizontal volume scans of B-scans moving from inferior to superior retina in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Video speed recorded at 16 frames per second.
References
- 1.Levade T., Sandhoff K., Schulze H., Medin J.A. In: Acid Ceramidase Deficiency: Farber Lipogranulomatosis. Scriver's OMMBID (Online Metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Diseases) Valle D., Beaudet A.L., Vogelstein B., Kinzler K.W., Antonarakis S.E., Ballabio A., editors. McGraw-Hill; New York, NY: 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Schuchman E.H. Acid ceramidase and the treatment of ceramide diseases: the expanding role of enzyme replacement therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1862:1459–1471. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.05.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zielonka M., Garbade S.F., Kölker S., Hoffmann G.F., Ries M. A cross-sectional quantitative analysis of the natural history of Farber disease: an ultra-orphan condition with rheumatologic and neurological cardinal disease features. Genet Med. 2017;20:524–530. doi: 10.1038/gim.2017.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ehlert K., Frosch M., Fehse N., Zander A., Roth J., Vormoor J. Farber disease: clinical presentation, pathogenesis and a new approach to treatment. Pediatr Rheumatol. 2007;5:15–22. doi: 10.1186/1546-0096-5-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bao X.H., Tian J.M., Ji T.Y., Chang X.Z. A case report of childhood Farber's disease and literature review. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi. 2017;55:54–58. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.0578-1310.2017.01.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Arana L., Gangoiti P., Ouro A., Trueba M., Gómez-Muñoz A. Ceramide and ceramide 1-phosphate in health and disease. Lipids Health Dis. 2010;9:15. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-9-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Chen H., Tran J.A., Brush R.S., Saadi A., Rahman A.K., Yu M., Yasumura D., Matthes M.T., Ahern K., Yang H. Ceramide signaling in retinal degeneration. Retin Degenerative Dis. 2012;723:553–558. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0631-0_70. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hannun Y.A., Obeid L.M. Sphingolipids and their metabolism in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2017;19:175–191. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2017.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Cogan D.G., Kuwabara T., Moser H., Hazard G.W. Retinopathy in a case of Farber's lipogranulomatosis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1966;75:752–757. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1966.00970050754007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moser H.W., Prensky A.L., Wolfe H.J., Rosman N.P. Farber's lipogranulomatosis: report of a case and demonstration of an excess of free ceramide and ganglioside. Am J Med. 1969;47:869–890. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(69)90202-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zarbin M.A., Green W.R., Moser A.B., Tiffany C. Increased levels of ceramide in the retina of a patient with Farber's disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 1988;106:1163. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1988.01060140323008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cvitanovic-Sojat L., Juraski R.G., Sabourdy F., Fensom A.H., Fumic K., Paschke E., Levade T. Farber lipogranulomatosis type 1–late presentation and early death in a Croatian boy with a novel homozygous ASAH1 mutation. Eur J Paediatr Neurol. 2011;15:171–173. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2010.06.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zetterström R. Disseminated lipogranulomatosis (Farber's disease) Acta Paediatr. 1958;47:501–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1958.tb07665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tanaka T., Takahashi K., Hakozaki H., Kimoto H., Suzuki Y. Farber's disease (disseminated lipogranulomatosis) a pathological, histochemical and ultrastructural study. Pathol Int. 1979;29:135–155. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1979.tb01298.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chandwani R., Kuwar A.S. Farber's disease. Indian Pediatr. 2002;39:502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sango K., Takano M., Ajiki K., Tokashiki A., Arai N., Kawano H., Horie H., Yamanaka S. Impaired neurite outgrowth in the retina of a murine model of Sandhoff disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2005;46:3420–3425. doi: 10.1167/iovs.05-0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Dannhausen K., Karlstetter M., Caramoy A., Volz C., Jägle H., Liebisch G., Utermöhlen O., Langmann T. Acid sphingomyelinase (aSMase) deficiency leads to abnormal microglia behavior and disturbed retinal function. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464:434–440. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wu B.X., Fan J., Boyer N.P., Jenkins R.W., Koutalos Y., Hannun Y.A., Crosson C.E. Lack of acid sphingomyelinase induces age-related retinal degeneration. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0133032. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Grishchuk Y., Stember K.G., Matsunaga A., Olivares A.M., Cruz N.M., King V.E., Humphrey D.M., Wang S.L., Muzikansky A., Betensky R.A. Retinal dystrophy and optic nerve pathology in the mouse model of mucolipidosis IV. Am J Pathol. 2016;186:199–209. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.09.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Alayoubi A.M., Wang J.C., Au B.C., Carpentier S., Garcia V., Dworski S., El-Ghamrasni S., Kirouac K.N., Exertier M.J., Xiong Z.J., Prive G.G., Simonaro C.M., Casas J., Fabrias G., Schuchman E.H., Turner P.V., Hakem R., Levade T., Medin J.A. Systemic ceramide accumulation leads to severe and varied pathological consequences. EMBO Mol Med. 2013;5:827–842. doi: 10.1002/emmm.201202301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sikora J., Dworski S., Jones E.E., Kamani M.A., Micsenyi M.C., Sawada T., Le Faouder P., Bertrand-Michel J., Dupuy A., Dunn C.K., Yang Xuan Ingrid C., Casas J., Fabrias G., Hampson D.R., Levade T., Drake Richard R., Medin J.A., Walkley S.U. Acid ceramidase deficiency in mice results in a broad range of central nervous system abnormalities. Am J Pathol. 2017;187:864–883. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2016.12.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yu F.P., Islam D., Sikora J., Dworski S., Gurka' J., Lopez-Vasquez L., Liu M., Kuebler W.M., Levade T., Zhang H., Medin J.A. Chronic lung injury and impaired pulmonary function in a mouse model of acid ceramidase deficiency. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017;314:406–420. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00223.2017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dubra A., Harvey Z. Registration of 2D images from fast scanning ophthalmic instruments. Biomed Image Registration. 2010;6204:60–71. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Chiu S.J., Li X.T., Nicholas P., Toth C.A., Izatt J.A., Farsiu S. Automatic segmentation of seven retinal layers in SDOCT images congruent with expert manual segmentation. Opt Express. 2010;18:19413–19428. doi: 10.1364/OE.18.019413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Fox M.W. The visual cliff test for the study of visual depth perception in the mouse. Anim Behav. 1965;13:232–233. doi: 10.1016/0003-3472(65)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yu F.P.S., Dworski S., Medin J.A. Deletion of MCP-1 impedes pathogenesis of acid ceramidase deficiency. Sci Rep. 2018;8:1808. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-20052-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Eviatar L., Sklower S.L., Wisniewski K., Feldman R.S., Gochoco A. Farber lipogranulomatosis: an unusual presentation in a black child. Pediatr Neurol. 1986;2:371–374. doi: 10.1016/0887-8994(86)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Zarbin M.A., Green W.R., Moser H.W., Morton S.J. Farber's disease: light and electron microscopic study of the eye. Arch Ophthalmol. 1985;103:73–80. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1985.01050010077025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cogan D.G., Kuwabara T. The sphingolipidoses and the eye. Arch Ophthalmol. 1968;79:437–452. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1968.03850040439013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Brownstein S., Carpenter S., Polomeno R.C., Little J.M. Sandhoff's disease (Gm2 gangliosidosis type 2): histopathology and ultrastructure of the eye. Arch Ophthalmol. 1980;98:1089–1097. doi: 10.1001/archopht.1980.01020031079014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Yanovitch T.L., Banugaria S.G., Proia A.D., Kishnani P.S. Clinical and histologic ocular findings in pompe disease. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2010;47:34–40. doi: 10.3928/01913913-20100106-08. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dworski S., Berger A., Furlonger C., Moreau J.M., Yoshimitsu M., Trentadue J., Au B.C., Paige C.J., Medin J.A. Markedly perturbed hematopoiesis in acid ceramidase deficient mice. Haematologica. 2015;100:162–165. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2014.108530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Dworski S., Lu P., Khan A., Maranda B., Mitchell J.J., Parini R., Di Rocco M., Hugle B., Yoshimitsu M., Magnusson B., Makay B., Arslan N., Guelbert N., Ehlert K., Jarisch A., Gardner-Medwin J., Dagher R., Terreri M.T., Marques Lorenco C., Barillas-Arias L., Tanpaiboon P., Solyom A., Norris J.S., He X., Schuchman E.H., Levade T., Medin J.A. Acid ceramidase deficiency is characterized by a unique plasma cytokine and ceramide profile that is altered by therapy. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Biol Lipids. 2017;1863:386–394. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.11.031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gasparin F., Takahashi B.S., Scolari M.R., Gasparin F., Pedral L.S., Damico F.M. Experimental models of autoimmune inflammatory ocular diseases. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2012;75:143–147. doi: 10.1590/s0004-27492012000200016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chen J., Qian H., Horai R., Chan C., Caspi R.R. Use of optical coherence tomography and electroretinography to evaluate retinal pathology in a mouse model of autoimmune uveitis. PLoS One. 2013;8:e63904. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0063904. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Commodaro A.G., Peron J.P.S., Lopes C.T., Arslanian C., Belfort R., Rizzo L.V., Bueno V. Evaluation of experimental autoimmune uveitis in mice treated with FTY720. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2010;51:2568–2574. doi: 10.1167/iovs.09-4769. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chan C., Caspi R.R., Ni M., Leake W.C., Wiggert B., Chader G.J., Nussenblatt R.B. Pathology of experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in mice. J Autoimmun. 1990;3:247–255. doi: 10.1016/0896-8411(90)90144-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Caspi R.R., Silver P.B., Luger D., Tang J., Cortes L.M., Pennesi G., Mattapallil M.J., Chan C. Mouse models of experimental autoimmune uveitis. Ophthalmic Res. 2008;40:169–174. doi: 10.1159/000119871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Albert D.M., Lahav M., Carmichael L.E., Percy D.H. Canine herpes-induced retinal dysplasia and associated ocular anomalies. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1976;15:267–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Albert D.M., Lahav M., Colby E.D., Shadduck J.A., Sang D.N. Retinal neoplasia and dysplasia, I: induction by feline leukemia virus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1977;16:325–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Carreras B., Griffin D.E., Silverstein A.M. Sindbis virus-induced ocular immunopathology. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1982;22:571–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.El Alwani M., Wu B.X., Obeid L.M., Hannun Y.A. Bioactive sphingolipids in the modulation of the inflammatory response. Pharmacol Ther. 2006;112:171–183. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2006.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Wang H. Crosslink between lipids and uveitis: a lipidomic analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58:5758. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rivera J., Proia R.L., Olivera A. The alliance of sphingosine-1-phosphate and its receptors in immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 2008;8:753–763. doi: 10.1038/nri2400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Cyster J.G., Schwab S.R. Sphingosine-1-phosphate and lymphocyte egress from lymphoid organs. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;30:69–94. doi: 10.1146/annurev-immunol-020711-075011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Maceyka M., Spiegel S. Sphingolipid metabolites in inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;510:58–67. doi: 10.1038/nature13475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chan A.Y., Chen R., Stone D.S., Eckerd A., Mandal N. Bioactive sphingolipids as mediators of ocular inflammation: observations in an animal model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2012;53:1239. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Copland D.A., Liu J., Schewitz-Bowers L.P., Brinkmann V., Anderson K., Nicholson L.B., Dick A.D. Therapeutic dosing of fingolimod (FTY720) prevents cell infiltration, rapidly suppresses ocular inflammation, and maintains the blood-ocular barrier. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:672–681. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.10.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kurose S., Ikeda E., Tokiwa M., Hikita N., Mochizuki M. Effects of FTY720, a novel immunosuppressant, on experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis in rats. Exp Eye Res. 2000;70:7–15. doi: 10.1006/exer.1999.0777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Raveney B.J., Copland D.A., Nicholson L.B., Dick A.D. Fingolimod (FTY720) as an acute rescue therapy for intraocular inflammatory disease. Arch Ophthalmol. 2008;126:1390–1395. doi: 10.1001/archopht.126.10.1390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chueh S.J., Kahan B.D. Update on FTY720: review of mechanisms and clinical results. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. 2003;8:288–298. [Google Scholar]
- 52.Berdyshev E.V., Gorshkova I., Skobeleva A., Bittman R., Lu X., Dudek S.M., Mirzapoiazova T., Garcia J.G., Natarajan V. FTY720 inhibits ceramide synthases and up-regulates dihydrosphingosine 1-phosphate formation in human lung endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:5467–5477. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M805186200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Denny C.A., Alroy J., Pawlyk B.S., Sandberg M.A., D'Azzo A., Seyfried T.N. Neurochemical, morphological, and neurophysiological abnormalities in retinas of Sandhoff and GM1 gangliosidosis mice. J Neurochem. 2007;101:1294–1302. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04525.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Brüggen B., Kremser C., Bickert A., Ebel P., Dorp K., Schultz K., Dörmann P., Willecke K., Dedek K. Defective ceramide synthases in mice cause reduced amplitudes in electroretinograms and altered sphingolipid composition in retina and cornea. Eur J Neurosci. 2016;44:1700–1713. doi: 10.1111/ejn.13260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sanvicens N., Cotter T.G. Ceramide is the key mediator of oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in retinal photoreceptor cells. J Neurochem. 2006;98:1432–1444. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2006.03977.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Strettoi E., Gargini C., Novelli E., Sala G., Piano I., Gasco P., Ghidoni R. Inhibition of ceramide biosynthesis preserves photoreceptor structure and function in a mouse model of retinitis pigmentosa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:18706–18711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1007644107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Chen H., Tran J.T., Eckerd A., Huynh T.P., Elliott M.H., Brush R.S., Mandal N.A. Inhibition of de novo ceramide biosynthesis by FTY720 protects rat retina from light-induced degeneration. J Lipid Res. 2013;54:1616–1629. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M035048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.He X., Dworski S., Zhu C., DeAngelis V., Solyom A., Medin J.A., Simonaro C.M., Schuchman E.H. Enzyme replacement therapy for Farber disease: proof-of-concept studies in cells and mice. BBA Clin. 2017;7:85–96. doi: 10.1016/j.bbacli.2017.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ramsubir S., Nonaka T., Girbés C.B., Carpentier S., Levade T., Medin J.A. In vivo delivery of human acid ceramidase via cord blood transplantation and direct injection of lentivirus as novel treatment approaches for Farber disease. Mol Genet Metab. 2008;95:133–141. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgme.2008.08.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) reveals retinal pathology in Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Representative OCT horizontal volume scans of B-scans moving from inferior to superior retina in 8- to 9-week–old Asah1+/+ and Asah1P361R/P361R mice. Video speed recorded at 16 frames per second.