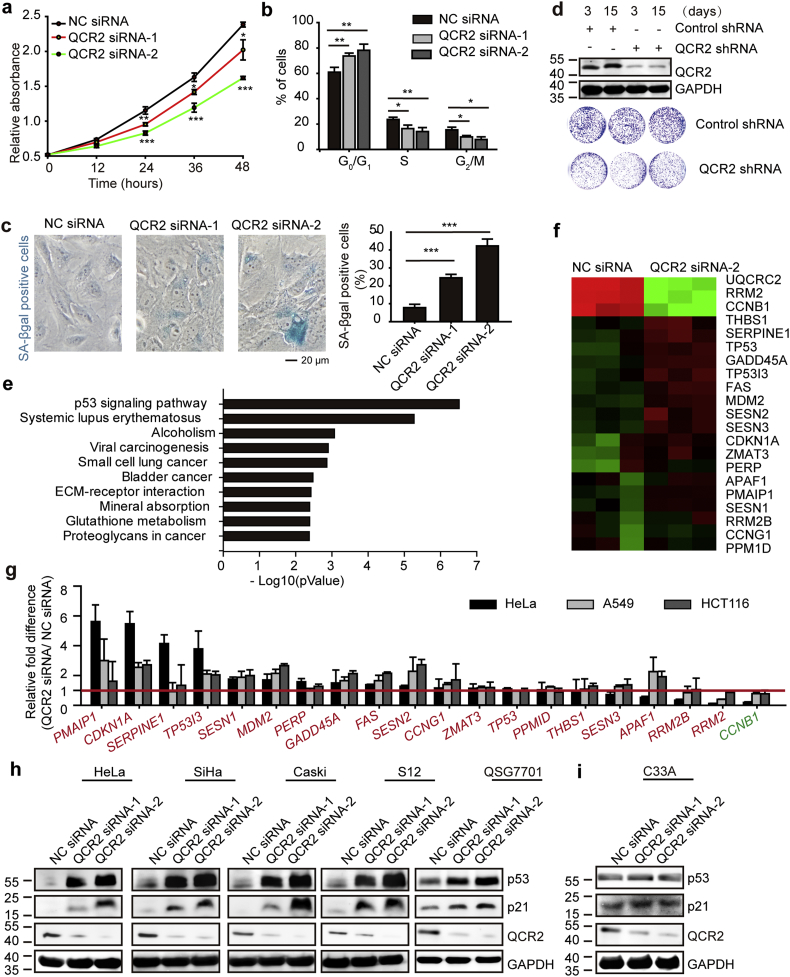
Fig. 2.
Knockdown of QCR2 inhibits cancer cell proliferation. (a–c) HeLa cells were transfected with NC siRNA, QCR2 siRNA-1, or QCR2 siRNA-2. Equal numbers of cells were plated in 96-well plates in triplicate, and viable cell proliferation was assessed using CCK-8 assays (*p < .05, **p < .01, ***p < .001, student's t-test) (a). Cell cycle distribution of asynchronous cells obtained from FACS analysis: cells were transfected with NC siRNA, QCR2 siRNA-1, or QCR2 siRNA-2, and then cultured under standard conditions. After 72 h, the cells were collected and analyzed by FACS. The bar graph represents quantification analyses of cell cycle distribution analysis (*p < .05, ***p < .001, student's t-test) (b). SA-β-gal staining of cells (scale bar = 20 μm) and the statistical result (***p < .001, student's t-test) (c). (d) Western blotting for QCR2 in HeLa cells expressing a lentiviral vector harboring QCR2 shRNA or control shRNA for 3 and 15 days (upper panels). Cells (1 × 103) with or without QCR2 knockdown were plated in 6-cm dishes (lower panels), cultured for 10 days, and stained with crystal violet. (e, f) The transcriptional profiles of A549 cells transfected with NC siRNA or QCR2 siRNA-2 were analyzed by a cDNA microarray. The bar graph represents the specific categories of genes within KEGG, for which P values were <0.005 (e). The heat map shows the representative genes belonging to the p53 signaling pathway within KEGG that were differently expressed in QCR2-knockdown cells (f). (g)The different expression of 20 genes belonging to the p53 signaling pathway within KEGG was tested by RT-qPCR. The red words were the genes activated by p53 within KEGG. The green words were the gene inhibited by p53 within KEGG, (h, i) Western blotting for p53 and p21 after transfection of cells with NC siRNA, QCR2 siRNA-1, or QCR2 siRNA-2. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)