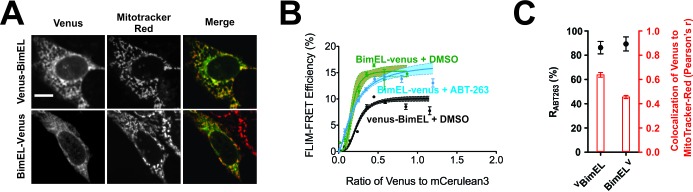
Figure 8. Bim CTS binds with non-transmembrane topology to cellular membranes.
(A) Selected images for sub-cellular localization of VBimEL and BimELV in BMK-DKO cells compared to MitoTracker. The scale bar represents 10 µm. (B) In live cells CBcl-XL binding to BimELV is resistant to ABT-263. FLIM-FRET binding curves for the interactions between CBcl-XL and BimELV in ABT-263 (blue) or DMSO (green) treated BMK-DKO cells expressing CBcl-XL. Binding of CBcl-XL to VBimEL (black) measured in the same three experiments is shown for comparison. Data from ROIs from three independent experiments were combined and used to generate binding curves with 95% confidence intervals as in Figures 1 and 2. (C) Sub-cellular localization of BimELV is impaired compared to VBimEL but ABT-263 resistant binding to CBcl-XL (RABT-263) is unchanged. Colocalization for Venus and MitoTracker-Red was measured in this experiment for manually selected regions of interest from transiently transfected cells expressing VBimEL or BimELV (Pearson’s r, red); Error bars, SEM, n > 30 cells. RABT-263 of CBcl-XL:VBimEL or CBcl-XL:BimELV complexes, black dots. Data are mean ±95% confidence intervals calculated from FLIM-FRET binding curves shown in panel b.