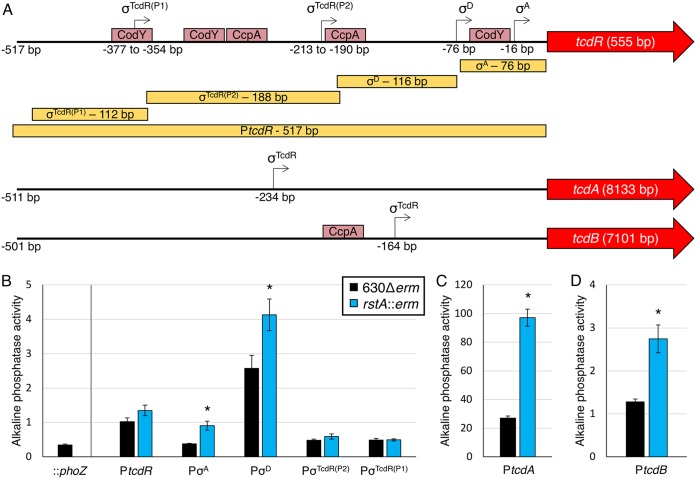
FIG 2.
RstA inhibits toxin gene expression. (A) A schematic of the promoter regions of tcdR, tcdA, and tcdB denoting the relative locations of the transcriptional start sites experimentally demonstrated (12, 32–34) and the open reading frames of all three genes (not drawn to scale). Pale red boxes approximate CodY- and CcpA-binding sites within the toxin gene promoters (8, 9, 36). The yellow boxes indicate the locations and sizes of the promoter fragments constructed for the phoZ reporter fusions in panels B to D. Alkaline phosphatase (AP) activity of the PtcdR::phoZ reporter fusions of various lengths (B) (promoterless phoZ [MC448], PtcdRσA [MC1285/MC1286], PtcdRσD [MC1145/MC1146], PtcdRσTcdR(P2) [MC1147/MC1148], and PtcdRσTcdR(P1) [MC1149/MC1150]) and the PtcdA::phoZ (C) (−511 bp to −1 bp upstream of transcriptional start; MC1249/MC1250) or PtcdB::phoZ (D) (−531 bp to −31 bp upstream of transcriptional start [MC1251/MC1252]) reporter fusions in strain 630Δerm and the rstA::erm mutant (MC391) grown in TY medium (pH 7.4) at H24. The means and standard errors of the means for four biological replicates are shown. *, P < 0.05, using Student’s t test compared to the activity observed in the 630Δerm parent strain for each promoter construct.