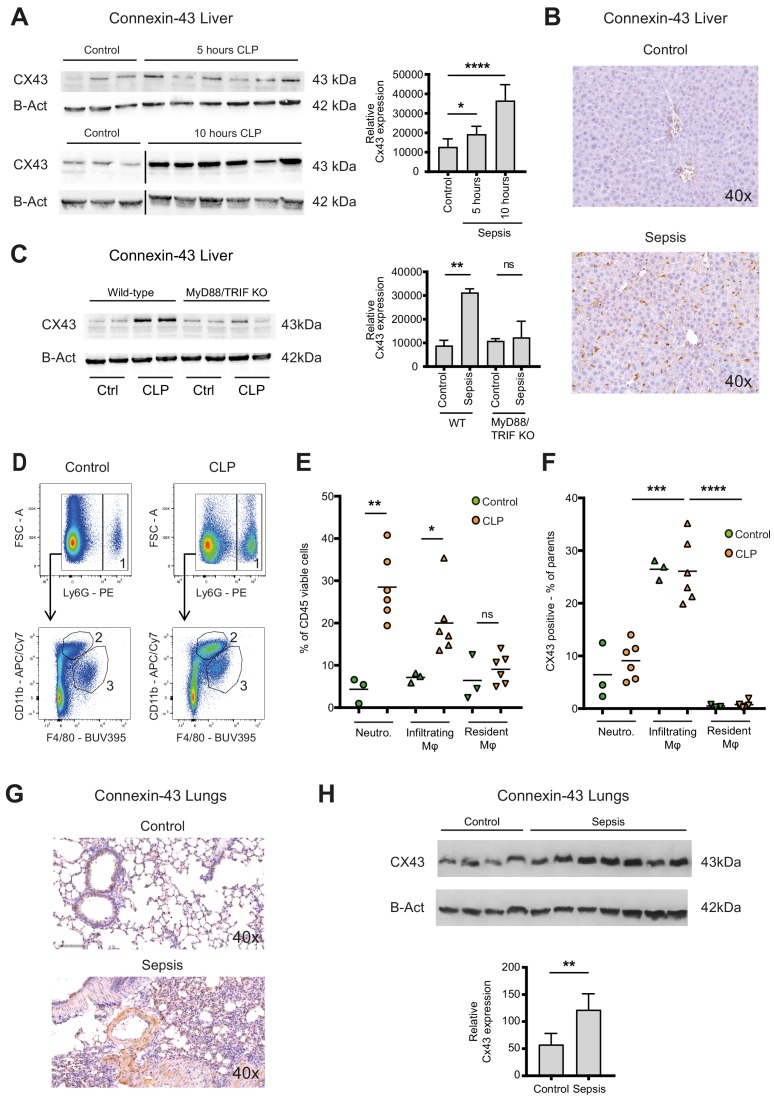
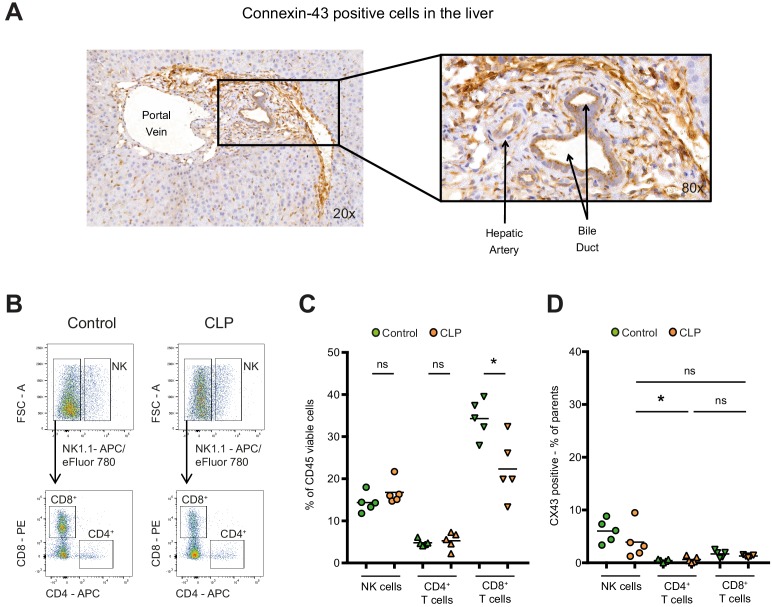
Figure 3. Connexin-43 expressing macrophages are recruited systemically during sepsis.
(A) Elevated CX43 protein expression in the liver 5 and 10 hr after CLP compared to controls (N = 3 animals in each control group from the gels at 5 hr and 10 hr, all used for the calculation of the histogram) and N = 6 animals for each time point, unpaired t-test). (B) Elevated expression of CX43 on non-parenchymal cells in the liver 10 hr after CLP compared to controls. (C) Abrogated CX43 protein expression in the liver of MyD88/TRIF double KO mice 10 hr after CLP (N = 2 mice per group, unpaired t-test). (D–E) Following CLP (orange), neutrophils (1) and infiltrating macrophages (2) increased in the liver, while resident macrophages (3) remained constant compared to controls (green). (F) Infiltrating macrophages highly expressed CX43 levels while neutrophils (1) and resident macrophages (3) were CX43 low (N = 3 animals in control group and N = 6 animals in CLP group, unpaired t-test). (G, H) Elevated expression of CX43 on non-parenchymal cells in the lungs in response to CLP compared to control mice (N = 4 animals in control group and N = 7 animals in CLP group, unpaired t-test). Full uncut western blot membranes are available in Source data 1.