Abstract
Background
Aflatoxin contamination caused by Aspergillus flavus is a major constraint to peanut industry worldwide due to its toxicological effects to human and animals. Developing peanut varieties with resistance to seed infection and/or aflatoxin accumulation is the most effective and economic strategy for reducing aflatoxin risk in food chain. Breeding for resistance to aflatoxin in peanut is a challenging task for breeders because the genetic basis is still poorly understood. To identify the quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for resistance to aflatoxin contamination in peanut, a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population was developed from crossing Zhonghua 10 (susceptible) with ICG 12625 (resistant). The percent seed infection index (PSII), the contents of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and aflatoxin B2 (AFB2) of RILs were evaluated by a laboratory kernel inoculation assay.
Results
Two QTLs were identified for PSII including one major QTL with 11.32–13.00% phenotypic variance explained (PVE). A total of 12 QTLs for aflatoxin accumulation were detected by unconditional analysis, and four of them (qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 for AFB1, qAFB2A07 and qAFB2B06 for AFB2) exhibited major and stable effects across multiple environments with 9.32–21.02% PVE. Furthermore, not only qAFB1A07 and qAFB2A07 were co-localized in the same genetic interval on LG A07, but qAFB1B06.1 was also co-localized with qAFB2B06 on LG B06. Conditional QTL mapping also confirmed that there was a strong interaction between resistance to AFB1 and AFB2 accumulation. Genotyping of RILs revealed that qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 interacted additively to improve the resistance to both AFB1 and AFB2 accumulation. Additionally, validation of the two markers was performed in diversified germplasm collection and four accessions with resistance to aflatoxin accumulation were identified.
Conclusions
Single major QTL for resistance to PSII and two important co-localized intervals associated with major QTLs for resistance to AFB1 and AFB2. Combination of these intervals could improve the resistance to aflatoxin accumulation in peanut. SSR markers linked to these intervals were identified and validated. The identified QTLs and associated markers exhibit potential to be applied in improvement of resistance to aflatoxin contamination.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12863-019-0734-z) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Peanut, Resistance, Aflatoxin, Aspergillus flavus, QTL, Diagnostic marker
Background
Peanut or groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) is an oilseed crop with global importance, grown in more than 100 countries with a global production of 47.53 Mt. from an area of 20.46 Mha [1]. As an excellent and cheap source of nutrition, peanuts supply abundant nutrients to the human such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, vitamins, minerals and fiber [2]. However, aflatoxin contamination caused by Aspergillus flavus and/or Aspergillus parasiticus is an enormous threat to peanut industry and food safety. Aflatoxins including aflatoxin B1, B2, G1 and G2 (AFB1, AFB2, AFG1 and AFG2) are highly toxic and carcinogenic substances and hard to be eliminated from contaminated materials [3–5]. Peanut tend to be infected by A. flavus covering the whole industrial chain including pre-harvest, during harvest, post-harvest drying, in storage and during transport [6–8]. A lot of prevention strategies for aflatoxin contamination have been implemented, including using bio-control agents, taking good agricultural practices and planting resistant varieties [9–12]. Development of peanut varieties with suitable resistance to A. flavus infection and/or aflatoxin production is considered to be the most effective and economical approach. However, breeding for resistance to aflatoxin is still a challenging task for breeders due to poor unavailability of highly resistance germplasm and understanding the genetics. Furthermore, the trait phenotyping faces high environmental influence and variable soil microbiome across environments and locations.
Quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping is a conventional method to investigate the genetic basis of complex traits. In recent years, numerous QTLs have been identified in peanut for several important traits such as plant height [13], pod shape, seed shape [14, 15], drought tolerance [16] and resistances to late leaf spot [17], bacterial wilt [18] and rust [19]. Molecular markers closely linked to QTLs can be identified, validated and deployed in marker-assisted breeding. The rust resistance was successfully improved in three early maturing elite varieties using four markers linked to a major QTL [19]. However, limited efforts have been made in identifying QTLs for complex traits in peanut such as aflatoxin contamination. Six QTLs for resistance to A. flavus invasion were detected in three independent recombinant inbred line (RIL) populations with 6.2–22.7% phenotypic variation explained (PVE) [20], but so far, no QTL for aflatoxin accumulation has been reported in peanut. Therefore, it is necessary to identify QTLs for resistance to both A. flavus infection and/or aflatoxin accumulation in order to accelerate the process of peanut breeding by bringing together favorable alleles.
Aflatoxin contamination is a result of interactions among host plant, toxicogenic fungi and environment, but these factors are always inconsistent and unpredictable in field. Additionally, there is a significant G × E interaction for aflatoxin contamination, which increased the difficulties of revealing the resistance mechanism [12]. Considering minimization of environmental impact, artificial inoculation of seeds with toxicogenic A. flavus in laboratory is more suitable for QTL analysis comparing with field inoculation.
In our previous study, a RIL population was developed from a cross involving a susceptible peanut variety, Zhonghua10 and a resistant germplasm line, ICG 12625, and a high-density linkage map was constructed. This genetic linkage map contains 1219 loci (1175 SSR markers and 42 transposon markers) covering A and B sub-genome and all 20 chromosomes of peanut genome with map length of 2038.75 cM. The A sub-genome contains 583 loci with map length of 1010.95 cM, while the B sub-genome contains 636 loci with map length of 1027.80 cM [13]. In present study, the phenotypic data including the percent seed infection index (PSII), aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) and aflatoxin B2 (AFB2) contents of 140 individuals were collected in three consecutive years via inoculation with A. flavus in laboratory. QTLs for PSII, AFB1 and AFB2 contents were identified, and the genetic relationship between resistance to AFB1 and AFB2 contents was investigated by conditional QTL analysis. The obtained information would get insights on the genetic basis of resistance to aflatoxin contamination in peanut.
Methods
Plant materials
A mapping population consisting of 140 RIL lines was developed form a cross between Zhonghua 10 and ICG 12625 using single seed decent method. The female parent Zhonghua 10 (A. hypogaea var. vulgaris) is a susceptible variety to aflatoxin contamination developed by Oil Crops Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Science (OCRI-CAAS), Wuhan, China. The male parent ICG 12625 (PI 497597, A. hypogaea var. aequatoriana) is a resistant germplasm line received from the International Crop Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT), Hyderabad, India. The RIL population (F4-F6) and the two parents were planted in experimental field of OCRI-CAAS in Wuhan, China, using a random block design with three replications in consecutive years from 2013 to 2015. Each plot contained one row, with 10–12 plants in each row, 10 cm between plants within each row and 30 cm between the rows. Field management followed the standard agricultural practices.
Phenotyping for A. flavus infection and aflatoxin accumulation
The toxicogenic A. flavus strain (AF2202) isolated from peanut was maintained in 20% glycerol (− 80 °C) at CAAS-OCRI, China. Conidia of AF2202 were taken from the stored sample and cultured on fresh potato dextrose agar medium at 29 ± 1 °C for 7 days. Conidia were then collected and suspended in sterile water containing 0.05% Tween-80. The concentration of conidia in the suspension was determined using a haemocytometer.
About 20 g healthy and mature peanut seeds from each line were selected and surface sterilized with 75% ethanol for 1 min followed by three washes with sterile distilled water. Then, 1 ml conidial suspension (2 × 106 conidia/ml) of A. flavus was added to peanut seeds in a sterile Petri plate. The plates were incubated at 29 ± 1 °C in dark.
The external seed infection was measured by visual inspection using the percent seed infection index (PSII), which was investigated at 7 days after inoculation. Based on previous studies [21], the invasion level of A. flavus was defined and classified with minor modifications as Level 0 when no conidium observed on the seed surface; Level 1 when less than 1/3 of the seed surface covered by conidia; Level 2 when 1/3–2/3 of the seed surface covered by conidia; Level 3 when more than 2/3 of the seed surface covered by conidia. The formula was used to calculate the PSII, where n, n1, n2 and n3 are the number of seeds in total, level 1, level 2 and level 3, respectively.
After investigation of PSII, the peanut seeds were rinsed with 75% ethanol to remove conidia of A. flavus on the seed surface, and then dried at 110 °C for 60 min. Aflatoxin in these seeds were extracted by 55% ethanol solution and analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography to detect the contents of AFB1 and AFB2 as described by Wang et al. [22].
Statistical analysis and QTL mapping
Statistical analyses for the phenotypic data of PSII, contents of AFB1 and AFB2 were performed with SPSS Statistics 22.0 statistical software [23]. The broad-sense heritability for each trait was calculated as: H2 = σ2 g/(σ2 g + σ2 ge/n + σ2 e/rn), where σ2 g is genetic variance, σ2 ge is the interaction variance between genotype and environment, σ2 e is the residual (error) variance, r is the number of replications in each environment and n is the number of environments. The variance of each component was estimated by restricted maximum likelihood (REML) method as previous study described [13]. Correlation coefficients were estimated between each pair of the three traits. Genotype data was collected and the linkage map was constructed in previous study [13].
QTL mapping was conducted by composite interval mapping method in the Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5 software using mean value of each trait in each environment [24]. The default model (model 6) was selected in the software. The number of control markers, window size and walk speed were set as 5, 10 and 2 cM, respectively. The threshold of LOD for declaring the presence of a QTL was determined by 1000 permutation tests.
Conditional analysis was also performed by Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5 software based on conditional phenotypic values y(AFB1|AFB2) and y(AFB2|AFB1), which were calculated by the mixed-model method using QGA Station 1.0 software [25].
Results
Phenotypic evaluation of resistance to aflatoxin contamination
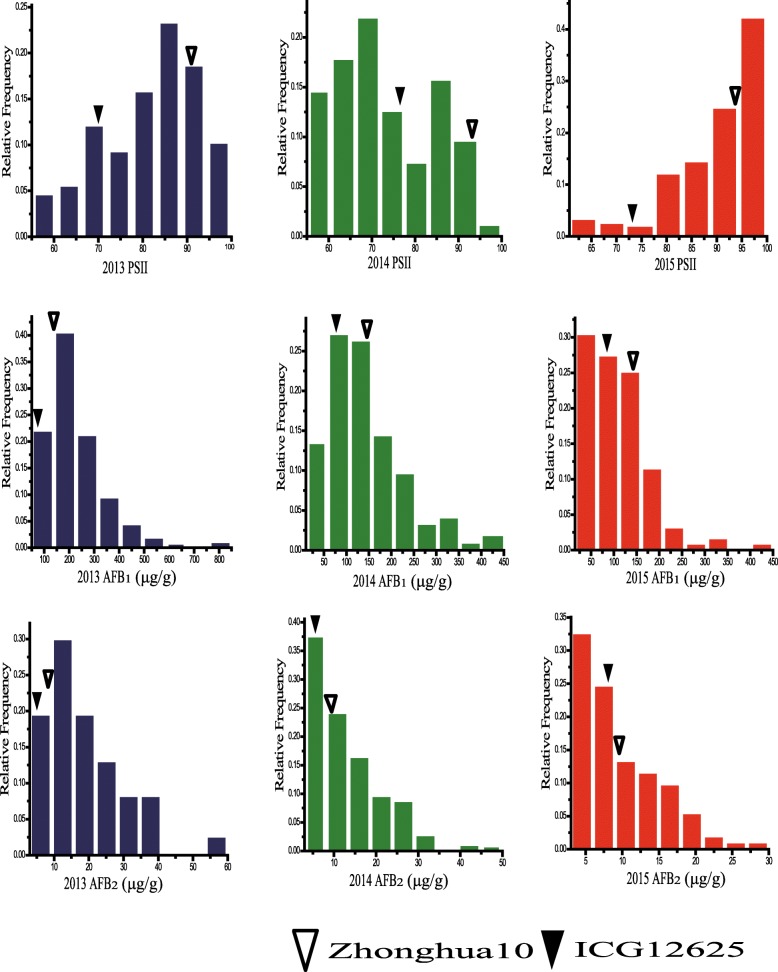
The resistance performance of two parents and the RIL population was investigated by artificial inoculation with toxicogenic A. flavus in laboratory across three environments. Significant differences of PSII and aflatoxin content between Zhonghua 10 and ICG 12625 were observed (Table 1 and Fig. 1). ICG 12625 exhibited desirable resistance with lower infection rate and less aflatoxin accumulation (Table 1). Transgressive segregation and continuous distribution in the RIL population for both PSII and aflatoxin contents were observed in all the environments (Table 1 and Fig. 1), suggesting that both the parents had favorable alleles for resistance to aflatoxin contamination. Broad-sense heritability was estimated to be 0.64 for PSII, 0.78 for AFB1 content and 0.75 for AFB2 content (Table 1), indicating these traits were controlled by genetic factors. Variance analysis across the three trials also revealed that the genetic, environmental effects and genotype by environment interaction significantly affected PSII and aflatoxin contents (see Additional file 1).
Table 1.
Phenotypic variations of PSII, AFB1 and AFB2 of two parents and RILs in three trials
| Trait | Env | Parents | RIL Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zhonghua10 | ICG 12625 | Range | Mean ± SD | CV | H 2 | ||
| PSII (%) | 2013 | 92.33 ± 1.89 | 70.00 ± 3.74** | 25.00–100.00 | 95.28 ± 15.01 | 0.16 | 0.64 |
| 2014 | 93.00 ± 2.16 | 77.67 ± 0.47** | 40.00–97.50 | 67.08 ± 14.14 | 0.21 | ||
| 2015 | 93.00 ± 1.41 | 73.33 ± 2.49** | 53.33–100.00 | 90.35 ± 8.99 | 0.10 | ||
| AFB1 (μg/g) | 2013 | 144.10 ± 35.10 | 85.39 ± 9.77 | 29.04–812.94 | 211.09 ± 124.76 | 0.59 | 0.78 |
| 2014 | 143.06 ± 17.07 | 77.56 ± 4.43** | 10.34–443.47 | 144.59 ± 83.37 | 0.58 | ||
| 2015 | 133.58 ± 14.14 | 86.52 ± 16.99* | 15.68–409.87 | 108.96 ± 66.94 | 0.61 | ||
| AFB2 (μg/g) | 2013 | 7.60 ± 0.48 | 6.40 ± 1.48 | 2.54–56.17 | 18.64 ± 11.15 | 0.60 | 0.75 |
| 2014 | 8.33 ± 0.35 | 6.59 ± 0.59* | 1.59–46.49 | 12.13 ± 8.59 | 0.71 | ||
| 2015 | 7.63 ± 0.60 | 6.12 ± 0.93 | 0.68–27.18 | 8.54 ± 5.70 | 0.67 | ||
PSII percent seed infection index, AFB1 aflatoxin B1 content, AFB2 aflatoxin B2 content, Env environment, SD standard deviation, CV coefficient of variation, H2 broad-sense heritability; *Difference is significant at p < 0.05 level, **Difference is significant at p < 0.01 level
Fig. 1.
Phenotypic observation and distribution of PSII, AFB1 and AFB2 in parents and RIL population. Phenotypic distribution of PSII, AFB1 and AFB2 in RIL population across three environments. The y-axis represented frequency, while x-axis represented values of each trait. PSII percent seed infection index, AFB1 aflatoxin B1 content, AFB2 aflatoxin B2 content
Pairwise correlation analyses on PSII, AFB1 and AFB2 contents across three environments showed significant positive correlation (R2, 0.81–0.91) (P ≤ 0.001) between AFB1 and AFB2 contents across environments (Table 2). But neither AFB1 nor AFB2 content was correlated with PSII (Table 2), suggesting that resistance to Aspergillus infection and aflatoxin accumulation were independently regulated in peanut.
Table 2.
Correlation analysis of PSII and aflatoxins contents in RIL population
| Environment | Trait | PSII | AFB1 | AFB2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | PSII | 1 | ||
| AFB1 | 0.17 | 1 | ||
| AFB2 | 0.08 | 0.81** | 1 | |
| 2014 | PSII | 1 | ||
| AFB1 | 0.11 | 1 | ||
| AFB2 | 0.11 | 0.85** | 1 | |
| 2015 | PSII | 1 | ||
| AFB1 | 0.13 | 1 | ||
| AFB2 | 0.11 | 0.91** | 1 |
Abbreviations see Table 1, **Correlation is significant at the p < 0.01 level
Detection of QTLs for resistance to aflatoxin contamination
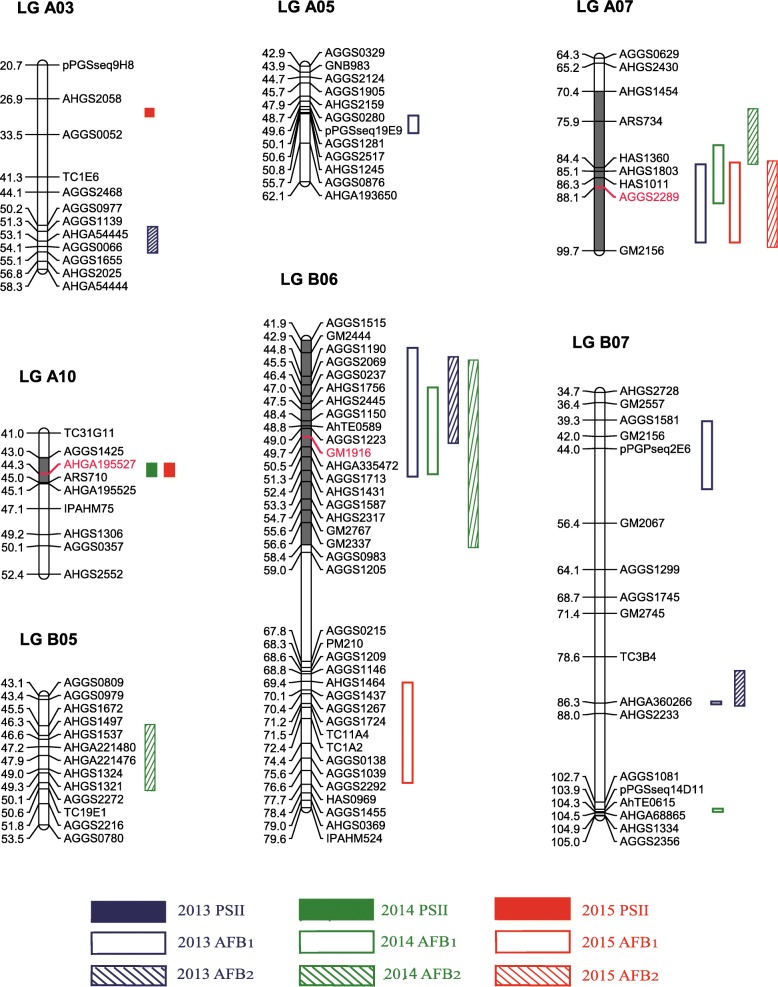
Genome-wide QTL analysis was conducted using the high-density genetic map [13] and the phenotypic data of PSII, AFB1 and AFB2 contents obtained from the RILs during 3 years (2013, 2014 and 2015) in Wuhan. For resistance to aflatoxin contamination, a total of 20 QTLs were identified in three environments that explained 7.30–21.02% PVE (Fig. 2, Table 3). If QTLs for a particular trait were detected on the same genomic region in two or more than two environments, they were considered as one consistent QTL and designated with the same name. Therefore, the 20 QTLs were designated as two for PSII, seven for AFB1 and five for AFB2 (Table 3). These QTLs were mapped onto seven LGs, comprising four LGs of the A sub-genome and three LGs of the B sub-genome (Fig. 2, Table 3). A maximum of four QTLs were identified onto LG B07, followed by three QTLs onto LG B06 (Fig. 2, Table 3). Two QTLs each were mapped onto LG A03 and A07, as well as one QTL each onto LG A05, A10 and B05.
Fig. 2.
Distribution of QTLs for traits of resistance to aflatoxin contamination on the genetic map. PSII percent seed infection index, AFB1 aflatoxin B1 content, AFB2 aflatoxin B2 content. SSR markers in red color are markers closest to the peak of QTL confidence intervals
Table 3.
QTLs identified for resistance to aflatoxin contamination in the RIL populations across three environments
| Trait | QTLa | LGb | Envc | CId | Marker Interval | LOD | PVE (%)e | Additivef |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PSII | qPSIIA03 | A03 | 2015 | 28.50–30.20 | AHGS2058 - AGGS0052 | 3.06 | 7.96 | −2.62 |
| qPSIIA10 | A10 | 2014 | 43.50–44.70 | AGGS1425 – ARS710 | 5.00 | 13.00 | 5.27 | |
| 2015 | 43.70–44.30 | AGGS1425 – ARS710 | 4.40 | 11.32 | 3.08 | |||
| AFB1 | qAFB1A05 | A05 | 2013 | 51.10–55.70 | AHGS1245 - AGGS0876 | 3.17 | 7.98 | 36.02 |
| qAFB1A07 | A07 | 2013 | 83.40–99.20 | ARS734 - GM2156 | 5.50 | 14.57 | 49.00 | |
| 2014 | 80.30–91.00 | ARS734 - GM2156 | 5.98 | 17.87 | 35.96 | |||
| 2015 | 83.80–98.20 | ARS734 - GM2156 | 4.70 | 10.62 | 25.68 | |||
| qAFB1B06.1 | B06 | 2013 | 42.50–52.90 | AGGS1515 - AGGS1587 | 6.40 | 16.33 | −52.07 | |
| 2014 | 45.70–52.70 | AGGS2069 - AGGS1587 | 3.90 | 9.52 | −26.31 | |||
| qAFB1B06.2 | B06 | 2015 | 69.50–77.60 | AHGS1464 - HAS0969 | 3.11 | 7.78 | −19.13 | |
| qAFB1B07.1 | B07 | 2013 | 39.20–51.70 | AGGS1581 - GM2067 | 3.60 | 8.48 | −40.35 | |
| qAFB1B07.2 | B07 | 2013 | 86.00–86.50 | TC3B4 - AHGS2233 | 3.10 | 7.30 | −36.16 | |
| qAFB1B07.3 | B07 | 2014 | 103.70–104.30 | AGGS1081 - AhTE0615 | 3.20 | 7.46 | −22.55 | |
| AFB2 | qAFB2A03 | A03 | 2013 | 50.19–55.08 | AGGS1139 - AHGS2025 | 3.45 | 8.32 | 3.44 |
| qAFB2A07 | A07 | 2014 | 74.30–84.40 | AHGS1454 - HAS1360 | 3.96 | 10.84 | 2.95 | |
| 2015 | 83.50–98.20 | ARS734 - GM2156 | 5.10 | 12.19 | 2.20 | |||
| qAFB2B05 | B05 | 2014 | 45.40–50.40 | AGGS0979 - TC19E1 | 4.90 | 11.05 | −3.49 | |
| qAFB2B06 | B06 | 2013 | 43.10–50.10 | GM2444 - AHGA335472 | 3.80 | 9.32 | − 3.53 | |
| 2014 | 43.20–58.30 | GM2444 - AGGS0983 | 8.80 | 21.02 | −4.11 | |||
| qAFB2B07 | B07 | 2013 | 80.80–86.50 | TC3B4 - AHGS2233 | 5.30 | 14.45 | −4.48 |
Abbreviations see Table 1, a QTLs identified in more than one environment were highlighted in bold, b Linkage group, c Environment, d Confidence interval of QTLs, e The percentage of the phenotypic variation explained, f Additive value
There were two QTLs for PSII across three environments (Table 3). Major QTL qPSIIA10 was identified as a consistent QTL with 11.32–13.00% PVE, because it was repeatedly detected in two environments (2014 and 2015). Minor QTL qPSIIA3c was only detected in 2014 (Table 3).
For AFB1 content, a total of seven QTLs were detected comprising two major QTLs and five minor QTLs, with PVE ranging from 7.30 to 17.87% (Table 3). Major QTL qAFB1A07 was identified across all the three environments and explained 10.62–17.87% PVE (Table 3). The other major QTL qAFB1B06.1 was detected in two environments with 9.52–16.33% PVE. Minor QTLs namely qAFB1A05, qAFB1B06.2, qAFB1B07.1, qAFB1B07.2 and qAFB1B07.3 were only detected in single environment (Table 3).
For AFB2 content, five QTLs were detected with a range of 8.32 to 21.02% PVE, including four major QTLs and one minor QTL (Table 3). Major QTLs namely qAFB2A07 and qAFB2B06 were consistently detected in two environments and showed 10.84–12.19% and 9.32–21.02% PVE, respectively. But other two major QTLs, qAFB2B05 and qAFB2B07, were only detected in single environment with 11.05–14.45% PVE in addition to minor QTL qAFB2A03 (Table 3).
Notably, QTLs qAFB1A07 and qAFB2A07 were co-localized into the same genetic interval (CI: 74.30–99.20) on LG A07. Similarly, qAFB1B06.1 was also co-localized with qAFB2B06 on LG B06 (CI: 43.10–58.30) (Fig. 2, Table 3). These results indicated that each of the two co-localized intervals may simultaneously regulate the resistance to AFB1 and AFB2 accumulation.
Conditional QTL mapping
For the purpose of investigating the relationship between QTLs for AFB1 and AFB2, conditional QTL analyses were performed with conditional phenotypic values y(AFB1|AFB2) and y(AFB2|AFB1). Seven QTLs for AFB1 were identified in unconditional analysis, whereas six of them failed to be detected when AFB1 content was conditioned on AFB2 content (Table 4). Major QTL qAFB1A07 was only detected in 2015, while it was not found in 2013 and 2014 in conditional mapping. Three additional QTLs (qAFB1A08, qAFB1B01, qAFB1B08) were identified with 12.62–15.19% PVE in conditional QTL analysis, but they were only detected in single environment. Of the five QTLs for AFB2 identified in unconditional mapping, three were not detected when AFB2 content was conditioned on AFB1 content (Table 4). Major QTL qAFB2B06 was detected in 2014 with decreased additive effects (16.74% PVE) compared to its corresponding unconditional QTL (21.02% PVE), however it was not detected in 2013. Minor QTL qAFB2A03 exhibited slightly enhanced additive effect (9.42% PVE) compared to that of the unconditional QTL (8.32% PVE). Overall, major QTLs for AFB1 qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 were severely affected by AFB2 content. Similarly, major QTLs for AFB2 qAFB2A07 and qAFB2B06 were strongly influenced by AFB1 content. These results indicated a strong interaction between resistance to AFB1 and AFB2 accumulation.
Table 4.
Unconditional and conditional QTLs for aflatoxin accumulation in the RIL population
| Condition | QTL | Environment | Marker interval | Unconditional QTL PVE (%)a | Conditional QTL PVE (%)b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1|AFB2c | qAFB1A05 | 2013 | AHGS1245 - AGGS0876 | 7.98e | |
| qAFB1A07 | 2013 | ARS734 - GM2156 | 14.57e | ||
| 2014 | ARS734 - GM2156 | 17.87e | |||
| 2015 | ARS734 - GM2156 | 10.62 | 9.14f | ||
| qAFB1B06.1 | 2013 | AGGS1515 - AGGS1587 | 16.33e | ||
| 2014 | AGGS2069 - AGGS1587 | 9.52e | |||
| qAFB1B06.2 | 2015 | AHGS1464 - HAS0969 | 7.78e | ||
| qAFB1B07.1 | 2013 | AGGS1581 - GM2067 | 8.48e | ||
| qAFB1B07.2 | 2013 | TC3B4 - AHGS2233 | 7.30e | ||
| qAFB1B07.3 | 2014 | AGGS1081 - AhTE0615 | 7.46e | ||
| qAFB1A08 | 2014 | TC9B8 - AHGA316376 | 12.62g | ||
| qAFB1B01 | 2014 | AGGS2497 - AHGA159068 | 13.44g | ||
| qAFB1B08 | 2015 | AGGS1664 - AGGS0189 | 15.19g | ||
| AFB2|AFB1d | qAFB2A03 | 2013 | AGGS1139 - AHGS2025 | 8.32 | 9.42f |
| qAFB2A07 | 2014 | AHGS1454 - HAS1360 | 10.84e | ||
| 2015 | ARS734 - GM2156 | 12.19e | |||
| qAFB2B05 | 2014 | AGGS0979 - TC19E1 | 11.05e | ||
| qAFB2B06 | 2013 | GM2444 - AHGA335472 | 9.32e | ||
| 2014 | GM2444 - AGGS0983 | 21.02 | 16.74f | ||
| qAFB2B07 | 2013 | TC3B4 - AHGS2233 | 14.45e |
Abbreviations see Table 1, a The percentage of the phenotypic variation explained by additive effect of unconditional QTL, b The percentage of the phenotypic variation explained by additive effect of conditional QTL, c AFB1 conditioned on AFB2, dAFB2 conditioned on AFB1, e The unconditional QTL could not be detected in conditional analysis, f The conditional QTL with increased or decreased PVE% to the unconditional QTL, g The additional QTL identified in conditional analysis
Identification of markers and recombination of QTLs
To evaluate the effect of combined effect of major QTLs qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1, co-dominant SSR markers AGGS2289 (CI: 88.14) and GM1916 (CI: 49.65) were selected as they were located closest to the peaks of QTLs qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 in multiple environments, respectively (see Additional file 2). The genotypes of AGGS2289 and GM1916 derived from Zhonghua 10 were designated as “AA” and “BB”, while the genotypes from ICG 12625 were designated as “aa” and “bb”, respectively. Genotypes of qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 in the RIL population were investigated using these two markers. As shown in Table 5, seeds with genotype AAbb accumulated significantly higher AFB1 and AFB2 than seeds with other genotypes (aabb, AABB and aaBB) after inoculation with A. flavus in all environments, indicating that introgression of any of these two QTLs could raise resistance to aflatoxin accumulation. Moreover, AFB1 content in seeds with aaBB genotype (77.97 μg/g) was significantly less than that in seeds with aabb genotype (104.31 μg/g) in 2015, which was the same genotype from resistant parent ICG 12625. Furthermore, there was significantly less AFB2 content in seeds with aaBB genotype (6.24 μg/g) compared to that in seeds with aabb genotype (12.02 μg/g) in 2014 (Table 5). Combination of resistant alleles of qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 enhanced the resistance to aflatoxin accumulation in the RIL population. Two elite RILs namely QT0393 and QT0469 exhibited superiority over parents were selected due to less AFB1 and AFB2 (Table 6). Both of them were identified as aaBB genotype, which means that the elite lines simultaneously possessed the resistant alleles of qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 (Table 6). All the results suggested that SSR markers, AGGS2289 and GM1916, could be applied in genotyping of qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1, and the resistance to aflatoxin accumulation could be improved via combining resistant alleles of these two QTLs.
Table 5.
Phenotypic effect of QTLs qAFB1A07, qAFB1B06.1 and qPSIIA10 in the RIL population
| Trait | Genotype | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AFB1 (μg/g) | AAbb | 298.83 ± 77.38a | 196.24 ± 86.95a | 156.56 ± 57.84a |
| aabb | 181.64 ± 76.88b | 134.69 ± 46.89b | 104.31 ± 52.32b | |
| AABB | 180.15 ± 77.38b | 119.60 ± 59.92b | 84.87 ± 40.91bc | |
| aaBB | 147.67 ± 75.99b | 102.16 ± 55.41b | 77.97 ± 40.91c | |
| AFB2 (μg/g) | AAbb | 26.10 ± 12.79a | 19.63 ± 9.19a | 13.23 ± 5.34a |
| aabb | 17.98 ± 9.05b | 12.02 ± 6.06b | 7.78 ± 5.12b | |
| AABB | 16.44 ± 8.62b | 8.91 ± 5.28bc | 7.75 ± 5.33b | |
| aaBB | 14.04 ± 7.73b | 6.24 ± 3.97c | 5.56 ± 3.15b | |
| PSII (%) | DD | 81.79 ± 12.96a | 70.97 ± 14.98a | 92.85 ± 6.79a |
| dd | 77.73 ± 27.11a | 62.86 ± 12.71b | 87.73 ± 10.19b |
Abbreviations see Table 1, Genotype the genotype of RIL lines, AA genotype of SSR marker AGGS2289 from Zhonghua 10, aa genotype of SSR marker AGGS2289 from ICG12625, BB genotype of SSR marker GM1916 from Zhonghua 10, bb genotype of SSR marker GM1916 from ICG 12625, DD genotype of SSR marker AHGA195525 from Zhonghua 10, dd genotype of SSR marker AHGA195527 from ICG 12625; a,b,c and d means followed by different letter are statistically different at p < 0.05 based on ANOVA and Tamhane’s T2 multiple-comparison
Table 6.
Resistance to aflatoxin contamination of best RIL lines in three environments
| Code | Genotype | AFB1 (μg/g) | AFB2 (μg/g) | PSII (%) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||
| Zhonghua 10 | AABBDD | 144.10 ± 35.10 | 143.06 ± 17.07 | 133.58 ± 14.14 | 7.60 ± 0.48 | 8.33 ± 0.35 | 7.63 ± 0.60 | 92.33 ± 1.89 | 93.00 ± 2.16 | 93.00 ± 1.41 |
| ICG 12625 | aabbdd | 85.39 ± 9.77 | 77.56 ± 4.43 | 86.52 ± 16.99 | 6.40 ± 1.48 | 6.59 ± 0.59 | 6.12 ± 0.93 | 70.00 ± 3.74 | 77.67 ± 0.47 | 73.33 ± 2.49 |
| QT0393 | aaBB | 55.50 ± 4.95* | 56.56 ± 4.06 | 76.51 ± 5.87 | 4.72 | 2.66 ± 0.31** | 4.32 ± 0.32 | |||
| QT0469 | aaBB | 82.87 ± 1.69 | 77.31 ± 0.76 | 37.25 ± 2.91* | 5.84 | 4.53 ± 0.76 | 1.58 ± 0.28** | |||
| QT0351 | dd | 70.00 ± 16.33 | 49.72 ± 4.30** | 65.55 ± 2.07* | ||||||
| QT0451 | dd | 55.83 ± 2.04** | 48.33 ± 0.47** | 66.11 ± 2.83 | ||||||
SSR marker AHGA195527 (CI: 44.25) was selected for genotyping of qPSIIA10, as it was closest marker to the peak of this QTL (see Additional file 2). The genotype derived from Zhonghua 10 was designated as “DD”, and that from ICG 12625 was designated as “dd”. After genotyping of qPSIIA10 in the RIL population, it was found that PSII of seeds with dd genotype was significantly lower than that of seeds with DD genotype across all the environments (Table 5). Similarly, two RIL lines namely QT0351 and QT0451 with higher resistance to fungal invasion also harbored the dd genotype of qPSIIA10 (Table 6). These results indicated that introgression of the QTL qPSIIA10 could enhance the resistance to PSII in peanut.
Validation of markers
In order to estimate the precision of SSR markers, AGGS2289 and GM1916, these markers were used to profile the Chinese mini-mini core collection of peanut germplasm. A total of 99 accessions were genotyped with AGGS2289 and GM1916 markers. As a result, six accessions were found to possess AAbb genotype and four accessions with aaBB (Table 7). These ten accessions were inoculated with A. flavus in laboratory, and aflatoxins contents were detected after 7 days incubation. Both AFB1 and AFB2 contents in lines with aaBB genotype (68.97 μg/g of AFB1 and 8.23 μg/g of AFB2) were significantly less than those with AAbb genotype (239.95 μg/g of AFB1 and 20.48 μg/g of AFB2) (Table 7). In particular, the accession Zh.h1498 only accumulated 26.35 μg/g of AFB1 and 1.88 μg/g of AFB2), which might be an excellent resource for improving the resistance to aflatoxin accumulation. Therefore, these two validated markers would be potentially very useful in identifying breeding lines with resistance to aflatoxin accumulation.
Table 7.
Accessions identified by markers AGGS2289 and GM1916 in Chinese mini-mini core collection of peanut germplasm
| Genotype | Code | AFB1 (μg/g) | AFB2 (μg/g) |
|---|---|---|---|
| AAbb | Zh.h1507 | 459.69 ± 27.17 | 38.64 ± 1.39 |
| Zh.h4809 | 264.78 ± 7.21 | 20.52 ± 2.43 | |
| Zh.h3364 | 210.92 ± 32.26 | 15.16 ± 0.55 | |
| Zh.h3216 | 184.12 ± 31.32 | 19.12 ± 0.46 | |
| Zh.h6275 | 166.66 ± 8.53 | 14.54 ± 2.95 | |
| Zh.h3689 | 153.51 ± 26.28 | 14.94 ± 3.62 | |
| Mean | 239.95 ± 104.65* | 20.48 ± 8.43* | |
| aaBB | Zh.h1498 | 26.35 ± 1.43 | 1.88 ± 0.60 |
| Zh.h2193 | 86.37 ± 12.32 | 11.56 ± 4.70 | |
| Zh.h2888 | 80.32 ± 4.43 | 10.64 ± 4.90 | |
| Zh.h6070 | 82.86 ± 1.47 | 11.21 ± 5.62 | |
| Mean | 68.97 ± 24.70 | 8.23 ± 4.02 |
Discussion
Aflatoxin contamination is a global challenge for peanut industry and consumers. Genetic enhancement for resistance to aflatoxin is regarded as the most cost-effective approach to reduce contamination risk in this crop. There are several reports on peanut resistance to aflatoxin contamination, but most of them are using transcriptome and proteome analysis to reveal the mechanism of resistance [26–31]. This study is the first systematic report using linkage analysis to reveal the QTLs for two types of resistance i.e., resistance to A. flavus infection and aflatoxin accumulation in peanut based on multi-environment phenotyping. Although there was only one previous study on QTL mapping for resistance to fungal invasion which was conducted using the phenotyping data generated for single environment [20]. Six QTLs related to Aspergillus flavus invasion were identified in their study, but the specific position information of these QTLs was not provided. We still mapped our markers of resistance to A. flavus infection on A10 to their QTLs, but none of them was located in QTLs they identified. Realizing the complexity of the trait, the current study was designed for generating multi-environment phenotyping data which, upon analysis, detected two QTLs for fungal invasion and 12 QTLs for aflatoxin accumulation were identified. The multi-environment phenotyping data allowed to identify one major QTL for PSII which was consistently detected on LG A10 in two environments. Coincidentally, in RNA-seq analysis of peanut seeds infected by A. flavus, relative abundance of expression of genes was significantly higher in pseudomolecule A10 [29]. Two consistent and major QTLs for AFB1 were identified on LG A07 and LG B06. Similarly, two consistent and major QTLs were also detected for AFB2 onto the same genetic intervals of LG A07 and LG B06. Identification of these QTLs started to lift the veil of genetic mechanism controlling resistance to aflatoxin contamination in peanut.
Resistance to fungal infection and aflatoxin accumulation found independent to each other
So far, there were very few reports on the relationship between resistances to A. flavus infection and aflatoxin accumulation in peanut. A previous report stated no significant relationship between these two resistance mechanisms and inherited independently [32]. Another report observed very low correlation and indicated to be governed by different genes [33]. Recently, an A. flavus strain with green fluorescent protein (GFP)-expression was used to monitor fungal growth by infection of ten peanut lines. No direct correlation was found between fungal infection and aflatoxin accumulation, which revealed that aflatoxin accumulation depended on genotypes of seeds but not A. flavus fungal growth [34]. In present study, no significant correlation was observed between resistance to fungal infection and to aflatoxin accumulation by inoculation in laboratory (Table 2). Furthermore, the major QTL for PSII was mapped on LG A10, while the major QTLs for AFB1 and AFB2 were identified on LG A07 and LG B06 (Fig. 2). Major QTLs for resistance to fungal invasion and to aflatoxin accumulation were distributed on different chromosomes. Although one minor QTL for PSII and one minor QTL for AFB2 were identified on LG A03, they were located at the different genetic intervals (Table 3). These results further confirmed that resistance to fungal infection and to aflatoxin accumulation in peanut were independent of each other. The similar phenomenon was also observed in other studies [32, 33]. As mycotoxins are produced by complex secondary metabolic pathways of fungal, and fungal infections could be affected by carbon sources, nitrogen sources and secondary metabolites of host plants. For example, ethylene in host plant could affects the colonization and infection of Aspergillus flavus but not aflatoxin production in maize [35]. Peanut seeds which are resistant to fungal infection but still accumulate large amounts of aflatoxins may because that their host environments are more conducive to toxin production.
Strong interaction detected between two major QTLs for AFB1 and AFB2
Significant positive correlation was detected between AFB1 and AFB2 contents (Table 2). It was interesting to note that the one major QTL each for AFB1 (qAFB1A07) and AFB2 (qAFB2A07) were found co-localized on LG A07. Similarly, the QTL, qAFB1B06.1 for AFB1 was also found co-localized with the QTL qAFB2B06 for AFB2 on LG B06 (Fig. 2, Table 3). Additionally, conditional QTL analysis indicated that when AFB1 content was conditioned on AFB2 content, qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 failed to be detected in 2013 and 2014 (Table 4). Even in 2015, qAFB1A07 was detected but with decreased additive effects compared to its corresponding unconditional QTL (Table 4). When AFB2 content was conditioned on AFB1 content, qAFB2A07 was unable to be detected in all environments (Table 4). The QTL, qAFB2B06, was absent in 2013, but present in 2014 with reduced PVE (Table 4). These results indicated strong interaction between AFB1 and AFB2 contents in peanut, and resistance to AFB1 and AFB2 may be controlled by the same genomic regions/genes. Hence, it is possible to simultaneously improve the peanut resistance to AFB1 and AFB2 accumulation.
Combination of major QTLs qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 provides effective strategy for improving resistance to aflatoxin contamination
Major QTLs qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 were additively interacted with each other. In the RIL population, introgression of any resistant allele could improve the resistance to aflatoxin accumulation (Table 5). When resistant alleles of these two QTLs were combined together, RILs accumulated less aflatoxin compared to those with single resistant allele of qAFB1A07 (Table 5). Moreover, RIL lines, QT0393 and QT0469, which accumulated less aflatoxin compared to resistant parent ICG 12525, had both the resistant alleles from these two QTLs (Table 6). Additionally, in the Chinese mini-mini core collection, accessions with both resistant alleles accumulated significantly less aflatoxins compared to accessions without any of them (Table 7). The above results suggest that combination of the resistant alleles of qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 is an effective strategy for improving resistance to aflatoxin contamination in peanut.
It is worth mentioning that no significant difference was observed between aflatoxin contents in RILs with both resistant alleles and those with single resistant allele of qAFB1B06.1 (Table 5), because aflatoxin accumulation could be easily affected by multiple factors, even in controlled laboratory conditions [36, 37]. There was also no significant difference between aflatoxin contents in RILs with qAFB1A07 and them in RILs with qAFB1B06.1 (Table 5). But the resistant parent ICG 12625, which only possessed resistant allele of qAFB1A07, accumulated significantly less aflatoxin compared to the susceptible parent Zhonghua 10 which only had resistant allele of qAFB1B06.1 (Table 1), implying that there must be additional genes responsible for the resistance in ICG 12625.
Linked SSR markers, AGGS2289 and GM1916, exhibited potential deployment in molecular breeding for improving aflatoxin resistance
Linked SSR markers namely AGGS2289 and GM1916 were used to genotype qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1, from which, four peanut resistant accessions were successfully identified in the Chinese mini-mini core collection (Table 7). SSR markers, AGGS2289 and GM1916, identified in this study could be used in improving aflatoxin resistance breeding. In addition, more breeder-friendly markers linked to QTLs qAFB1A07 and qAFB1B06.1 would be developed in the future to facilitate breeding for resistance to aflatoxin contamination.
Conclusions
The present study identified one major QTL for resistance to PSII and two important co-localized intervals associated with major QTLs for resistance to AFB1 and AFB2. Combination of these intervals could improve the resistance to aflatoxin accumulation in peanut. SSR markers linked to these intervals were identified and validated. The major QTLs, co-localized intervals and SSR markers identified in this study showed great value for improvement of resistance to aflatoxin contamination in peanut. Additionally, this study laid the foundation for revealing genetic basis of resistance to aflatoxin contamination and further research on fine mapping and candidate gene discovery.
Additional files
Analysis of variance for PSII, AFB1 and AFB2 in the RIL population across three environments. (XLSX 10 kb)
Position and sequences of diagnostic markers. (XLSX 8 kb)
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31371662 and 31461143022), Fundamental Research Funds for Central Non-profit Scientific Institution (Y2018PT59) and China Agriculture Research System (CARS-14). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files.
Abbreviations
- AFB1
Contents of aflatoxin B1
- AFB2
Contents of aflatoxin B2
- LGs
Linkage groups
- PSII
Percent seed infection index
- PVE
Phenotypic variance explained
- QTL
Quantitative trait loci
- RILs
Recombinant inbred lines
Authors’ contributions
BY, DH, LH, YK, MK, HS, RK, BL and HJ conceived and designed the experiments. XR, YC, XZ, HL, NL, WC and YL developed the RIL population. BY, DH and YK performed the phenotype data collection and QTL analysis. BY, DH, BL and HJ wrote the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study has not directly involved humans, animals or plants.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Bolun Yu, Email: yubolun1990@163.com.
Dongxin Huai, Email: dxhuai@caas.cn.
Li Huang, Email: huangli01@caas.cn.
Yanping Kang, Email: kangyanping@caas.cn.
Xiaoping Ren, Email: renxp1972@hotmail.com.
Yuning Chen, Email: chenyuning@caas.cn.
Xiaojing Zhou, Email: zhouxiaojing@caas.cn.
Huaiyong Luo, Email: huaiyongluo@caas.cn.
Nian Liu, Email: lnian0531@caas.cn.
Weigang Chen, Email: wgchen@caas.cn.
Yong Lei, Email: leiyong@caas.cn.
Manish K. Pandey, Email: m.pandey@cgiar.org
Hari Sudini, Email: h.sudini@cgiar.org.
Rajeev K. Varshney, Email: r.k.varshney@cgiar.org
Boshou Liao, Email: lboshou@hotmail.com.
Huifang Jiang, Email: peanutlab@oilcrops.cn.
References
- 1.Food and agriculture organization of the united nations (FAO): Production/Yield quantities of groundnuts, with shell in world. http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/QC/visualize (2016). Accessed 28 May 2018.
- 2.Settaluri VS, Kandala CVK, Puppala N, Sundaram J. Peanuts and their nutritional aspects-a review. Food Nutr Sci. 2012;3(12):1644–1650. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kew MC. Aflatoxins as a cause of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2013;22(3):305–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Khlangwiset P, Wu F. Costs and efficacy of public health interventions to reduce aflatoxin-induced human disease. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2010;27(7):998. doi: 10.1080/19440041003677475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Patten RC. Aflatoxins and disease. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1981;30(2):422–425. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1981.30.422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sugri I, Osiru M, Abudulai M, Abubakari M, Asieku Y, Lamini S, Zakaria M. Integrated peanut aflatoxin management for increase income and nutrition in northern Ghana. Cogent Food Agriculture. 2017;3(1):1312046. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Al-Saad L. Riga: Noor publishing. 2017. Biotic and abiotic control of aflatoxin b1 synthesis. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Torres AM, Barros GG, Palacios SA, Chulze SN, Battilani P. Review on pre- and post-harvest management of peanuts to minimize aflatoxin contamination. Food Res Int. 2014;62(8):11–19. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dorner JW. Management and prevention of mycotoxins in peanuts. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess. 2008;25(2):203–208. doi: 10.1080/02652030701658357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Horn BW, Dorner JW. Soil populations of Aspergillus species from section Flavi along a transect through peanut-growing regions of the United States. Mycologia. 1998;90(5):767–776. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chulze S, Palazzini JM, Torres AM, Barros G, Ponsone ML, Geisen R, et al. Biological control as a strategy to reduce the impact of mycotoxins in peanuts, grapes and cereals in Argentina. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2015;32(4):471–479. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2014.984245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bhatnagarmathur P, Sunkara S, Bhatnagarpanwar M, Waliyar F, Sharma KK. Biotechnological advances for combating Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin contamination in crops. Plant Sci. 2015;234:119–132. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2015.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Huang L, Ren X, Wu B, Li X, Chen W, Zhou X, et al. Development and deployment of a high-density linkage map identified quantitative trait loci for plant height in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Sci Rep. 2016;6:39478. doi: 10.1038/srep39478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen Y, Ren X, Zheng Y, Zhou X, Huang L, Yan L, et al. Genetic mapping of yield traits using RIL population derived from Fuchuan Dahuasheng and ICG6375 of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Mol Breed. 2017;37(2):17. doi: 10.1007/s11032-016-0587-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Luo H, Guo J, Ren X, Chen W, Huang L, Zhou X, et al. Chromosomes A07 and A05 associated with stable and major QTLs for pod weight and size in cultivated peanut ( Arachis hypogaea L.) Theor Appl Genet. 2017;131(2):276–282. doi: 10.1007/s00122-017-3000-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ravi K, Vadez V, Isobe S, Mir RR, Guo Y, Nigam SN, et al. Identification of several small main-effect QTLs and a large number of epistatic QTLs for drought tolerance related traits in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Theor Appl Genet. 2011;122(6):1119–1132. doi: 10.1007/s00122-010-1517-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zongo A, Khera P, Sawadogo M, Shasidhar Y, Sriswathi M, Vishwakarma MK, et al. SSR markers associated to early leaf spot disease resistance through selective genotyping and single marker analysis in groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Biotechnol Rep (Amst) 2017;15:132–137. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2017.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Zhao Y, Zhang C, Chen H, Yuan M, Nipper R, Prakash CS, et al. QTL mapping for bacterial wilt resistance in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Mol Breed. 2016;36:13. doi: 10.1007/s11032-015-0432-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Varshney RK, Pandey MK, Janila P, Nigam SN, Sudini H, Gowda MVC, et al. Marker-assisted introgression of a QTL region to improve rust resistance in three elite and popular varieties of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) Theor Appl Genet. 2014;127(8):1771–1781. doi: 10.1007/s00122-014-2338-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liang X, Zhou G, Hong Y, Chen X, Liu H, Li S. Overview of research progress on peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) host resistance to aflatoxin contamination and genomics at the Guangdong academy of agricultural sciences. Peanut Science. 2009;36(1):29–34. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Asis R, Muller V, Barrionuevo DL, Araujo SA, Aldao MA. Analysis of protease activity in Aspergillus flavus and A. parasiticus on peanut seed infection and aflatoxin contamination. Eur J Plant Pathol. 2009;124(3):391–403. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wang H, Huang J, Lei Y, Yan L, Wang S, Jiang H, et al. Relationship of resveratrol content and resistance to aflatoxin accumulation caused by Aspergillus flavus in peanut seeds. Acta Agron Sin. 2013;38(10):1875–1883. [Google Scholar]
- 23.IBM Corp. Statistical package for social scineces (IBM SPSS) 22.0 version. Armonk: IBM United States; 2013. https://www.ibm.com/analytics/data-science/predictive-analytics/spss-statistical-software. Accessed 25 May 2018.
- 24.Wang S, Basten C. Windows QTL Cartographer 2.5. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC. 2012. http://statgen.ncsu.edu/qtlcart/WQTLCart.htm. Accessed 01 May 2018.
- 25.Zhu J. Analysis of conditional genetic effects and variance components in developmental genetics. Genetics. 1995;141(4):1633–1639. doi: 10.1093/genetics/141.4.1633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Korani W, Chu Y, Holbrook CC, Oziasakins P. Insight into genes regulating post-harvest aflatoxin contamination of tetraploid peanut from transcriptional profiling. Genetics. 2018;209(1):143–156. doi: 10.1534/genetics.118.300478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Fountain JC, Jin K, Yang L, Pandey MK, Nayak SN, Bajaj P, et al. Proteome analysis of Aspergillus flavus isolate-specific responses to oxidative stress in relationship to aflatoxin production capability. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):3430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28.Fountain JC, Yang ML, Pandey MK, Nayak S, Kumar V, Jayale A, et al. RNAseq analysis reveals oxidative stress responses of Aspergillus flavus are related to stress tolerance and aflatoxin production. In: American Phytopathological society annual meeting. American Phytopathological Society. 2016. https://www.apsnet.org/meetings/Documents/2016_meeting_abstracts/aps2016_74.htm. Accessed 25 May 2018.
- 29.Nayak SN, Agarwal G, Pandey MK, Sudini HK, Jayale AS, Purohit S, et al. Aspergillus flavus infection triggered immune responses and host-pathogen cross-talks in groundnut during in vitro seed colonization. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):9659. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09260-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wang H, Lei Y, Wan L, Yan L, Lv J, Dai X, et al. Comparative transcript profiling of resistant and susceptible peanut post-harvest seeds in response to aflatoxin production by Aspergillus flavus. BMC Plant Biol. 2016;16:54. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0738-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang H, Lei Y, Yan L, Wan L, Ren X, Chen S, et al. Functional genomic analysis of Aspergillus flavus interacting with resistant and susceptible peanut. Toxins. 2016;8(2):46. doi: 10.3390/toxins8020046. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Utomo SD, Anderson WF, Wynne JC, Beute MK, Hagler WM, Payne GA. American Peanut Research and Education Society Meeting. 1990. Estimates of heritability and correlation among three mechanisms of resistance to Asperaillus parasiticus in peanut. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Upadhyaya HD, Nigam SN, Thakur RP. Genetic enhancement for resistance to aflatoxin contamination in groundnut. In: The seventh ICRISAT regional groundnut meeting for Western and Central Africa: International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics, Haderabad, India; 2002.
- 34.Korani WA, Chu Y, Holbrook C, Clevenger J, Ozias-Akins P. Genotypic regulation of aflatoxin accumulation but not Aspergillus fungal growth upon post-harvest infection of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) seeds. Toxins. 2017;9(7):218. doi: 10.3390/toxins9070218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Wang S, Park Y-S, Yang Y, Borrego EJ, Isakeit T, Gao X, Kolomiets MV. Seed-derived ethylene facilitates colonization but not aflatoxin production by Aspergillus flavus in maize. Front Plant Sci. 2017;8:415. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.00415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Payne GA, Brown MP. Genetics and physiology of aflatoxin biosynthesis. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 1998;36(36):329–362. doi: 10.1146/annurev.phyto.36.1.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Guo B, Chen Z, Dewey LR, Brian TS. Drought stress and preharvest aflatoxin contamination in agricultural commodity: genetics, genomics and proteomics. J Integr Plant Biol. 2008;50(10):1281–1291. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00739.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Analysis of variance for PSII, AFB1 and AFB2 in the RIL population across three environments. (XLSX 10 kb)
Position and sequences of diagnostic markers. (XLSX 8 kb)
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files.