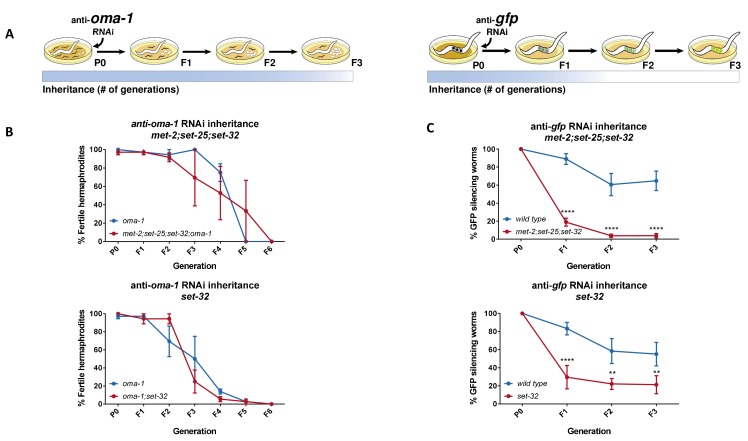
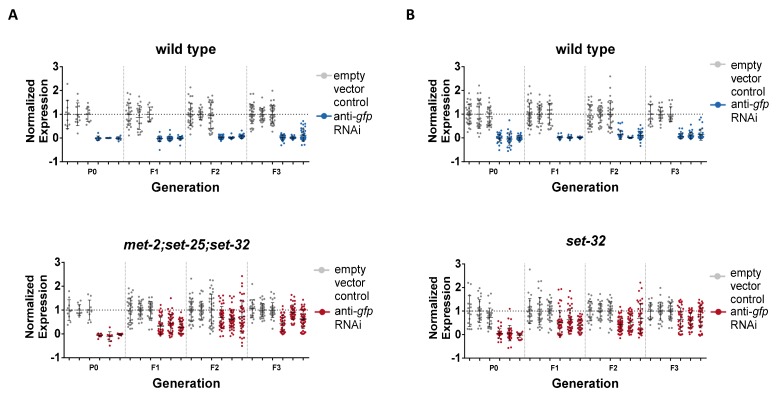
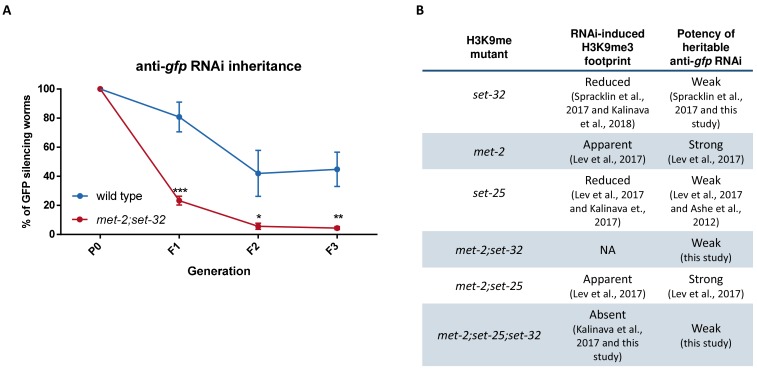
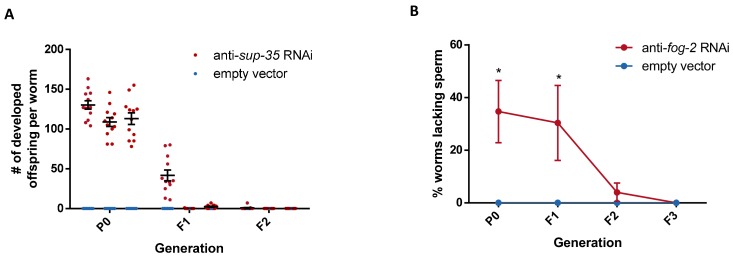
Figure 1. Heritable RNAi responses against the oma-1 and gfp genes have different requirements for H3K9me3 methyltransferases.
(A) Scheme depicting the different requirements for H3K9 methyltransferases in RNAi inheritance responses aimed at different genes. In the parental generation, worms are exposed to RNAi by growing on plates seeded with dsRNA-producing bacteria. Next, worms are transferred to plates seeded with control bacteria (that do not express dsRNA) to lay the eggs the next generation. (left) Only worms that inherit small RNAs that silence the temperature-sensitive dominant allele of oma-1 can hatch. Heritable RNAi responses aimed against the endogenous oma-1 gene do not require H3K9me3 methyltransferases. (right) Inheritance of anti-gfp small RNAs lead to heritable silencing of the gfp transgene (Pmex-5::gfp::h2b transgene). Heritable RNAi responses aimed against the foreign gfp gene strongly depends on H3K9me3 methyltransferases. (B) Inheritance of anti-oma-1 RNAi response in H3K9me3 methyltransferase mutants. The percentage of fertile worms per replicate and generation is presented (N = 12, three biological replicates). (upper panel) RNAi inheritance dynamics in met-2;set-25;set-32;oma-1 mutants compared to oma-1 mutants. (lower panel) RNAi inheritance dynamics in set-32;oma-1 mutants compared to oma-1 mutants. (C) Inheritance of anti-gfp RNAi response in H3K9me3 methyltransferase mutants. In each generation the percentage of worms silencing a germline expressed GFP transgene is presented (N > 60, five replicates). (upper panel) RNAi inheritance dynamics in met-2;set-25;set-32 triple mutants. (lower panel) RNAi inheritance dynamics in set-32 single mutants. Error bars represent standard error of mean. *p-value<0.05, **p-value<0.005, ***p-value<0.001, ****p-value<0.0001, Two-way ANOVA, Sidak's multiple comparisons test.