Summary:
Cells often utilize multiple pathways to repair the same DNA lesion, and pathway choice has profound implications for the fidelity of genome maintenance. DNA interstrand cross-links (ICLs) block DNA replication and transcription by covalently linking the two strands of DNA, and the cytotoxicity of ICLs is exploited for chemotherapy. In Xenopus egg extracts, replication fork collision with ICLs initiates two distinct repair pathways. The NEIL3 glycosylase can cleave the cross-link1, but if this fails, the Fanconi anemia (FA) proteins incise the phosphodiester backbone surrounding the ICL, generating a double-strand break (DSB) intermediate that is repaired by homologous recombination2. How the simpler NEIL3 pathway is prioritized over the FA pathway, which can cause genomic rearrangements, is unknown. Here, we show that the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAIP regulates both pathways. TRAIP appears to associate with the leading edge of the replisome, ubiquitylating any protein in the replisome’s path, including the replicative DNA helicase CMG (CDC45-MCM2-7-GINS) when two replisomes converge at an ICL. In this setting, short ubiquitin chains recruit NEIL3 through direct binding, whereas longer chains are required for CMG unloading by the p97 ATPase, enabling the FA pathway. Our results identify TRAIP as a master regulator of replisome stability and ICL repair pathway choice.
ICLs are formed by chemotherapeutics and endogenous aldehydes3,4. The classic ICL repair pathway involves twenty-two “FANC” proteins, defects in which cause the human bone marrow failure and cancer predisposition syndrome, FA4. We previously showed that in Xenopus egg extracts, the FA pathway is initiated by convergence of two replication forks on an ICL, which triggers CMG helicase unloading by p971,2,5,6. CMG unloading involves polyubiquitylation of CMG’s MCM7 subunit6, allowing fork reversal and ICL unhooking via nucleolytic incisions that convert the ICL into a DSB2,7,8 (Fig. 1a, left branch). A second unhooking mechanism acts on a subset of ICLs1 (Fig. 1a, right branch). In this pathway, the NEIL3 DNA glycosylase cleaves one of the two N-glycosyl bonds comprising the ICL, avoiding DSB formation but creating an abasic site that is bypassed by translesion synthesis polymerases. While both pathways are triggered by fork convergence, only the FA pathway requires CMG unloading1. In mammals, FANC gene mutations cause stronger phenotypes than NEIL3 mutations9–12. Therefore, cells may first attempt the simpler NEIL3 pathway, but appear to rely more heavily on the versatile FA pathway for survival. Given the different mutagenic potentials of these two mechanisms, it is crucial to understand how the choice between them is governed.
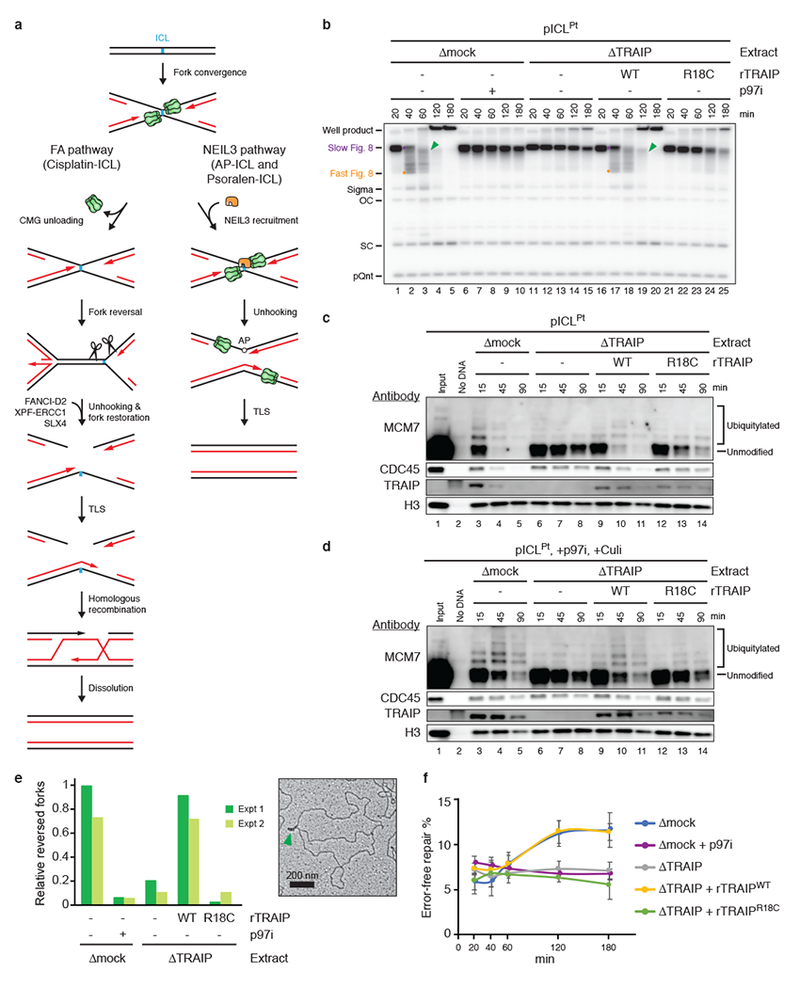
Fig. 1 |. CMG unloading at ICLs requires the E3 ubiquitin ligase TRAIP.
a, Models of ICL repair by the FA (left branch) and NEIL3 (right branch) pathways. TLS, translesion DNA synthesis; AP, abasic site.
b, pICLPt was replicated in egg extracts containing [α-32P]dATP. Replication intermediates were resolved by native agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by autoradiography. Recombinant TRAIPWT, rTRAIPR18C, and p97 inhibitor NMS-873 (p97i) were added as indicated. OC, open circular; SC, supercoiled; pQnt, undamaged control plasmid; Purple dot, Slow Figure 8; Orange dot, Fast Figure 8; Green arrowhead, reversed fork (see Extended Data Fig. 1b for discussion). For TRAIP levels in extracts, see Extended Data Fig. 2d.
c and d, Analysis of proteins associated with pICLPt during replication in the indicated extracts in the absence (c) or presence (d) of p97i and Cullin RING ubiquitin ligase inhibitor MLN4924 (Culi). Culi was added to eliminate ubiquitylation by CRL2LRR1 (see Extended Data Fig. 4d). For TRAIP levels in extracts, see Extended Data Fig. 2i. Residual MCM7 ubiquitylation in the presence of R18C was observed in eight independent experiments (e.g. Fig. 3c). Histone H3, recovery control.
e, Left, pICLPt was replicated for 90 min in the indicated extracts, and the relative abundance of reversed forks, as determined by electron microscopy, was quantified. Values were normalized to the mock-depleted extract. Error bars, range from two independent experiments. Right, representative electron micrograph of a reversed fork (green arrowhead) from TRAIP-depleted extract supplemented with rTRAIPWT. For TRAIP levels in extracts, see Extended Data Fig. 3g.
f, Error-free repair as measured by regeneration of a SapI restriction site coinciding with the ICL. The ~7% basal SapI cutting is due to contaminating undamaged plasmid8. Error bars, standard error of the mean from three independent experiments. For TRAIP levels in extracts, see Extended Data Fig. 3h.
A critical gap in our knowledge is the identity of the E3 ubiquitin ligase that ubiquitylates CMG at ICLs to activate CMG unloading and entry into the FA pathway. The RING E3 ligase TRAIP (TRAF-interacting protein) is essential for cell proliferation13, and hypomorphic TRAIP mutations cause microcephalic primordial dwarfism14. Because TRAIP associates with ICL-containing chromatin15 and its knock-down sensitizes cells to mitomycin C (MMC)16, we asked whether TRAIP promotes CMG unloading at ICLs. To this end, we used Xenopus egg extracts to replicate a plasmid containing a site-specific cisplatin-ICL (pICLPt) (Extended Data Fig. 1a). In mock-depleted extract, forks converged on the ICL and stalled, generating a discrete “Slow Figure 8” intermediate that was converted to a “Fast Figure 8” species due to CMG unloading7 (Fig. 1b, lanes 1-3, Extended Data Fig. 1b, for gel source data, see Supplementary Fig. 1). Strikingly, depletion of TRAIP (Extended Data Fig. 2a) caused an accumulation of Slow Figure 8s (Fig. 1b, lanes 11-15), the same defect observed when CMG unloading was blocked with p97 inhibitor1 (p97i; Fig. 1b, lanes 6-10). Wild-type recombinant Xenopus TRAIP (rTRAIPWT) purified from bacteria or insect cells (Extended Data Fig. 2b, c) restored Fast Figure 8 formation (Fig. 1b, Extended Data Fig. 2d-h).
Our results suggested that TRAIP promotes CMG ubiquitylation and unloading. Consistent with this idea, TRAIP was required for dissociation of CDC45 and MCM7, two CMG subunits, from pICLPt (Fig. 1c), and for efficient loss of the CMG footprint at ICLs (Extended Data Fig. 3a, b). Loss of the CMG footprint did not require FANCM or ATR signaling (Extended Data Fig. 3c-f), two factors that mediate fork traverse at ICLs17,18. In addition, MCM7 ubiquitylation was dependent on TRAIP (Fig. 1c). This effect was more evident when CMG unloading was blocked with p97i (Fig. 1d). Consistent with CMG unloading being required for fork reversal and incisions at an ICL7, TRAIP was also required for fork reversal and error-free repair of the lesion (Fig. 1e, f). rTRAIPR18C, which harbors a primordial dwarfism-associated RING-domain mutation14, was defective for Fast Figure 8 formation, MCM7 ubiquitylation and unloading, fork reversal, and ICL repair (Fig. 1b-f, Extended Data Fig. 2b-h). The low activity of rTRAIPR18C probably results from a combination of modest defects in chromatin recruitment (Fig. 1c, d) and E3 ubiquitin ligase activity (see below). Our previous conclusion that BRCA1 is required for CMG unloading19 was due to inadvertent depletion of TRAIP with BRCA1 antiserum (Extended Data Fig. 3i-n). We conclude that TRAIP is required for MCM7 ubiquitylation and CMG unloading in the FA ICL repair pathway.
Consistent with CMG unloading at ICLs requiring fork convergence5, MCM7 ubiquitylation also depended on convergence (Fig. 2a). Thus, either TRAIP is recruited de novo when CMGs converge on an ICL, or it travels with the replisome but only ubiquitylates CMG upon fork convergence. In agreement with the latter scenario, TRAIP associated with undamaged pCTRL at levels similar to those seen on pICL (Fig. 2b, compare lanes 2 and 5), and in mammalian cells, TRAIP localizes to DNA replication forks in the absence of exogenous insults14,16. Both replication licensing and initiation were essential to recruit TRAIP to chromatin (Extended Data Fig. 4a, b). TRAIP contains a conserved, C-terminal PIP box16, suggesting PCNA might recruit TRAIP to replication forks. However, TRAIP lacking its PIP box (TRAIPΔPIP) still suppresses MMC hypersensitivity16. Accordingly, recombinant Xenopus TRAIPΔPIP suppressed the accumulation of Slow Figure 8s (Extended Data Fig. 2b, g, h). TRAIP therefore travels with the replisome but ubiquitylates CMG only after fork convergence at an ICL, independently of its PIP box.
Fig. 2 |. TRAIP ubiquitylates CMGs that have converged at ICLs.
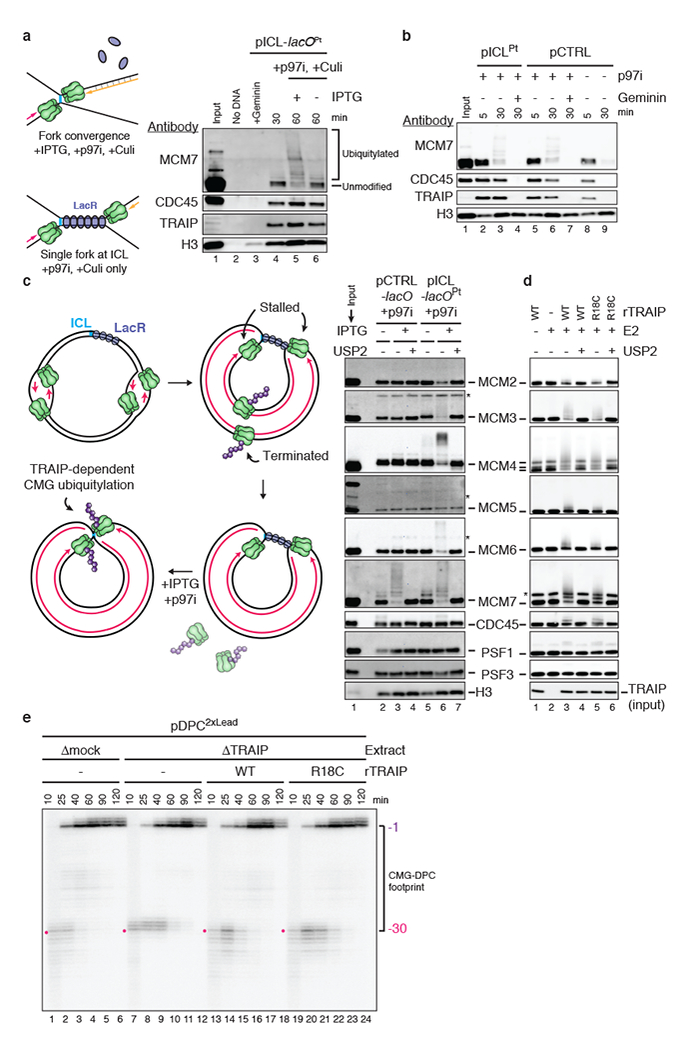
a, Left, experimental scheme. Plasmid containing an ICL flanked by 48 copies of the lac operator (lacO) (pICL-lacOPt) was incubated with Lac repressor (LacR) prior to replication in undepleted egg extract. After 30 min, IPTG addition dissociated LacR and allowed fork convergence. Right, pICL-lacOPt was recovered and blotted for the indicated proteins. Culi suppressed CRL2LRR1-dependent ubiquitylation.
b, Chromatin-associated proteins during replication of pICLPt or pCTRL in undepleted extract in the presence or absence of the licensing inhibitor Geminin and p97i.
c, Left, following CRL2LRR1-dependent unloading of CMGs that underwent termination on plasmids with multiple initiation events (see Extended Data Fig. 4d), release of the LacR array with IPTG leads to convergence of forks at the ICL, allowing analysis of TRAIP-specific ubiquitylation. Right, analysis of proteins associated with pICL-lacOPt during replication in the presence of p97i. MCM2 ubiquitylation was inferred from the increase in unmodified MCM2 upon USP2 treatment, which was used to remove all ubiquitin modifications. Asterisks, non-specifically detected proteins.
d, Analysis of rCMG subunits incubated with rTRAIP in the presence of ubiquitin, E1, E2s UbcH5a/b/c, and ATP. MCM4 was present as full-length and degradation products. Asterisk, non-specifically detected protein.
e, Nascent strand analysis of pDPC2×Lead replicated in the indicated extracts. Red dot, combined footprint of CMG and the DPC in the presence of TRAIP. For TRAIP levels in extracts, see Extended Data Fig. 4c.
CMG unloading during replication termination involves polyubiquitylation of MCM7 by CRL2LRR1 (Ref. 20,21), and this process did not require TRAIP (Extended Data Fig. 4d, e). Conversely, MCM7 ubiquitylation at ICLs did not require CRL2LRR1 (Extended Data Fig. 4f-h). Remarkably, unlike termination, ICL repair involved TRAIP-dependent ubiquitylation of MCM2, 3, 4, 6, and 7, partial ubiquitylation of CDC45, but almost no detectable ubiquitylation of PSF1 and PSF3 (Fig. 2c, Extended Data Fig. 5a, b) or other replisome-associated factors (Extended Data Fig. 5c). rTRAIPWT produced a generally similar ubiquitylation pattern on purified recombinant CMG (Fig. 2d, Extended Data Fig. 5d), consistent with direct ubiquitylation of CMG by TRAIP in extracts. rTRAIPR18C was partially compromised for in vitro ubiquitylation (Fig. 2d, Extended Data Fig. 5e). TRAIP-dependent ubiquitin chains on CMG were largely insensitive to treatment with chain-specific deubiquitylating enzymes and addition of ubiquitin lysine mutants that restrict formation of specific chain types (Extended Data Fig. 5f-h). Thus, in contrast to CRL2LRR1, which deposits K48-linked ubiquitin chains during termination20, TRAIP can deposit ubiquitin chains that appear to be heterotypically linked and/or branched.
We recently found that collision of a replication fork with a DNA-protein cross-link (DPC) leads to TRAIP-dependent ubiquitylation of the DPC22. Interestingly, upon TRAIP depletion, the leading strand advanced 2 nucleotides closer to a DPC, and both rTRAIPWT and rTRAIPR18C restored the original footprint (Fig. 2e). In contrast, no such effect was seen at ICLs (Extended Data Fig. 3a), indicating TRAIP clashes only with bulky obstacles. Thus, TRAIP appears to associate with the leading edge of the replisome, where it non-specifically ubiquitylates lysine residues on proteinaceous obstacles encountered ahead of the fork, including on ubiquitin itself, resulting in complex ubiquitin chains that are not dominated by a single linkage type.
Unlike cisplatin-ICLs, psoralen-ICLs and AP-ICLs (formed between an abasic site in one strand and an adenosine in the other strand) are unhooked by NEIL3 independently of CMG unloading1. However, MCM7 was ubiquitylated with similar kinetics at AP-ICLs and cisplatin-ICLs (Extended Data Fig. 6a). We therefore asked whether AP-ICL repair requires TRAIP. In mock-depleted extract, Figure 8s generated when forks converged on an AP-ICL were converted directly into open circular and supercoiled products by NEIL3-dependent unhooking1 (Fig. 3a; Extended Data Fig. 1c for schematic of pICLAP repair intermediates). Strikingly, unlike p97 inhibition, which had no effect on AP-ICL replication (Extended Data Fig. 6b, lanes 26-30)1, TRAIP immunodepletion caused a marked accumulation of Slow Figure 8s and a strong reduction in open circular and supercoiled plasmids (Fig. 3a). Furthermore, TRAIP depletion greatly reduced AP-ICL repair (Fig. 3b). Addition of rTRAIPWT purified from bacteria or insect cells fully reversed these defects (Fig. 3a, b; Extended Data Fig. 6e, f). Surprisingly, rTRAIPR18C also mostly reversed these defects, suggesting that lower levels of ubiquitylation are needed to support AP-ICL repair than cisplatin-ICL repair (Fig. 3a, b; Extended Data Fig. 6e). Thus, TRAIP promotes AP-ICL repair independently of CMG unloading.
Fig. 3 |. TRAIP promotes NEIL3-dependent ICL repair.
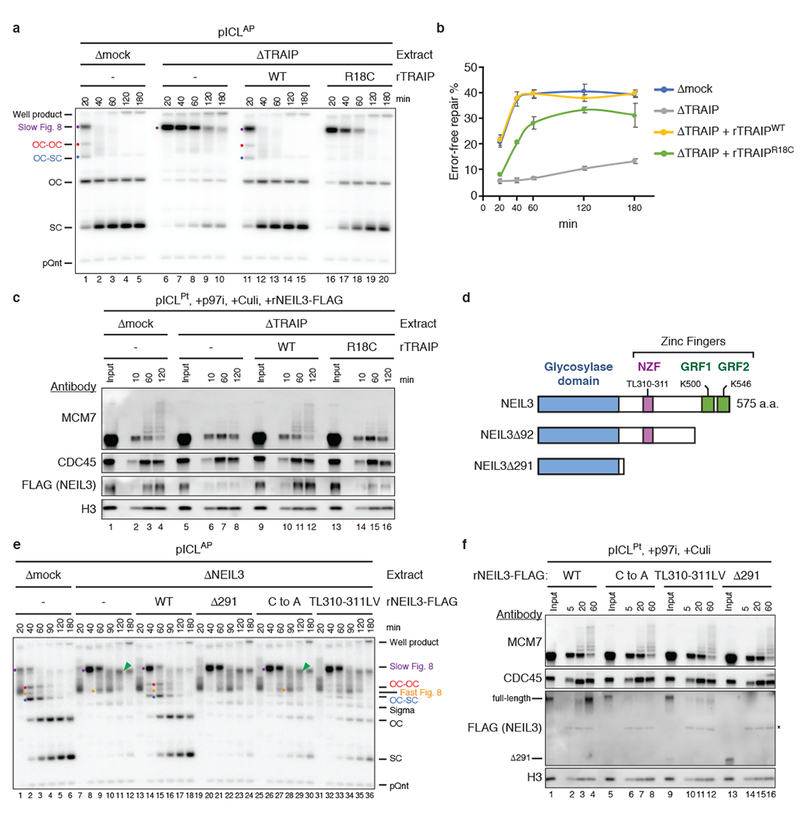
a, pICLAP was replicated in the indicated extracts and analyzed as in Fig. 1b. Red dot, OC-OC catenane; Blue dot, OC-SC catenane. For TRAIP levels in extracts, see Extended Data Fig. 6c.
b, Error-free repair of pICLAP was quantified as in Fig. 1f. Error bars, standard error of the mean from three independent experiments. For TRAIP levels in extracts, see Extended Data Fig. 6d.
c and f, Analysis of proteins associated with pICLPt during replication in the indicated extracts (c) or undepleted extract (f) in the presence of p97i and Culi. Asterisk, non-specifically detected protein.
d, Schematic of Xenopus NEIL3 proteins.
e, pICLAP was replicated in the indicated extracts and analyzed as in Fig. 1b. ICL unhooking was estimated by quantifying OC and SC signal normalized to pQnt. For NEIL3 levels in extracts, see Extended Data Fig. 8c.
We postulated that TRAIP-dependent CMG ubiquitylation recruits NEIL3 to converged forks. Because endogenous NEIL3 on chromatin was undetectable by immunoblotting, we supplemented extract with FLAG-tagged recombinant NEIL3 (rNEIL3) and examined its chromatin binding using FLAG antibody. rNEIL3 recovery was abolished by Geminin, demonstrating its binding was replication-dependent (Extended Data Fig. 6a). Interestingly, we detected more rNEIL3 on pICLPt than on pICLAP (Extended Data Fig. 6a), likely because NEIL3 becomes trapped on chromatin when it cannot unhook the ICL (Extended Data Fig. 7a, b). pICLPt was therefore used for subsequent NEIL3 recruitment assays. Importantly, depletion of TRAIP strongly reduced the association of rNEIL3 with pICLPt (Fig. 3c, lanes 1-8). Recombinant TRAIPWT fully rescued and rTRAIPR18C partially rescued this defect (Fig. 3c). Our data suggest that TRAIP-dependent CMG ubiquitylation is required to recruit NEIL3 for ICL unhooking. Consistent with this model, delaying CMG unloading extends the window of time during which NEIL3 can unhook an AP-ICL (Extended Data Fig. 7d, e).
NEIL3 contains three zinc finger motifs C-terminal to its glycosylase domain23 (Fig. 3d). NEIL3 lacking the entire C-terminal region (rNEIL3Δ291) retained glycosylase activity (Extended Data Fig. 8a) but failed to unhook pICLAP (Fig. 3e) or bind pICL in extract (Fig. 3f), suggesting that one or more of the zinc fingers helps recruit NEIL3 to stalled forks. We found that the NPL4-type zinc finger (NZF) of NEIL3 binds monoubiquitin dependent on a conserved TL motif (Extended Data Fig. 8b), as seen for other NZFs24. Importantly, pICLAP unhooking was reduced more than two-fold by TL motif substitution (rNEIL3TL310-311LV) and four-fold by substitutions of zinc-coordinating cysteines in the NZF (rNEIL3NZF-C to A; Fig. 3e). Consistent with this observation, rNEIL3NZF-C to A and rNEIL3TL310-311LV bound poorly to pICL (Fig. 3f). The other two NEIL3 zinc fingers resemble the “GRF” zinc finger of APE2 endonuclease, which binds single-stranded (ss)DNA25. We found that GRF1 and GRF2 each bound specifically to ssDNA (Extended Data Fig. 8d, e), and point mutations that disrupted this binding compromised NEIL3 association with chromatin and its ability to support AP-ICL unhooking (Extended Data Fig. 8f-h). Our data suggest that NEIL3 binds to converged CMGs through cooperation of its NZF, which recognizes ubiquitylated CMG, and its GRFs, which recognize ssDNA, possibly on the lagging strand template (Extended Data Fig. 8i).
In egg extracts, AP-ICLs and psoralen-ICLs are processed almost exclusively by NEIL3, but in its absence, they are unhooked by the FA pathway1. The question arises how the NEIL3 pathway is prioritized over the FA pathway. Interestingly, rTRAIPR18C, which only forms short ubiquitin chains on MCM7 (Figs. 1c, d, and 3c), had barely detectable activity in cisplatin-ICL repair (Fig. 1b, f) while promoting robust AP-ICL repair (Fig. 3a, b). These observations suggest that short ubiquitin chains might be sufficient to support the NEIL3 but not the FA pathway. Consistent with this idea, ubiquitin that lacks lysines and therefore cannot undergo polyubiquitylation (UbNoK) greatly stabilized pICLPt Slow Figure 8s (indicative of defective p97-dependent CMG unloading) while having only a modest effect on pICLAP Slow Figure 8 disappearance, which reflects NEIL3 unhooking (Fig. 4a). As expected, UbNoK reduced the length of ubiquitin chains formed on MCM7 (Fig. 4b, red bar). Consistent with its modest effect on AP-ICL unhooking, UbNoK did not affect recruitment of NEIL3 to chromatin (Fig. 4b). The data suggest that short ubiquitin chains on CMG are sufficient to recruit NEIL3. If the ICL cannot be cleaved by NEIL3, as in the case of cisplatin-ICLs, the chains continue to grow, leading to p97-dependent CMG unloading (Fig. 4c). Consistent with redundancy between the FA and NEIL3 pathways for repair of certain ICLs in mammalian cells, both had to be eliminated to observe hypersensitivity to psoralen-ICLs while removal of the FA pathway alone sensitized HAP1 cells to cisplatin (Fig. 4d, Extended Data Fig. 9a-d). A synthetic interaction between NEIL3 and FA pathways was also observed in the CH12 B cell line (Extended Data Fig. 9e-g). Whether the NEIL3 pathway is prioritized in cells, as seen in extracts, remains to be determined.
Fig 4 |. MCM7 ubiquitin chain length influences ICL repair pathway choice.
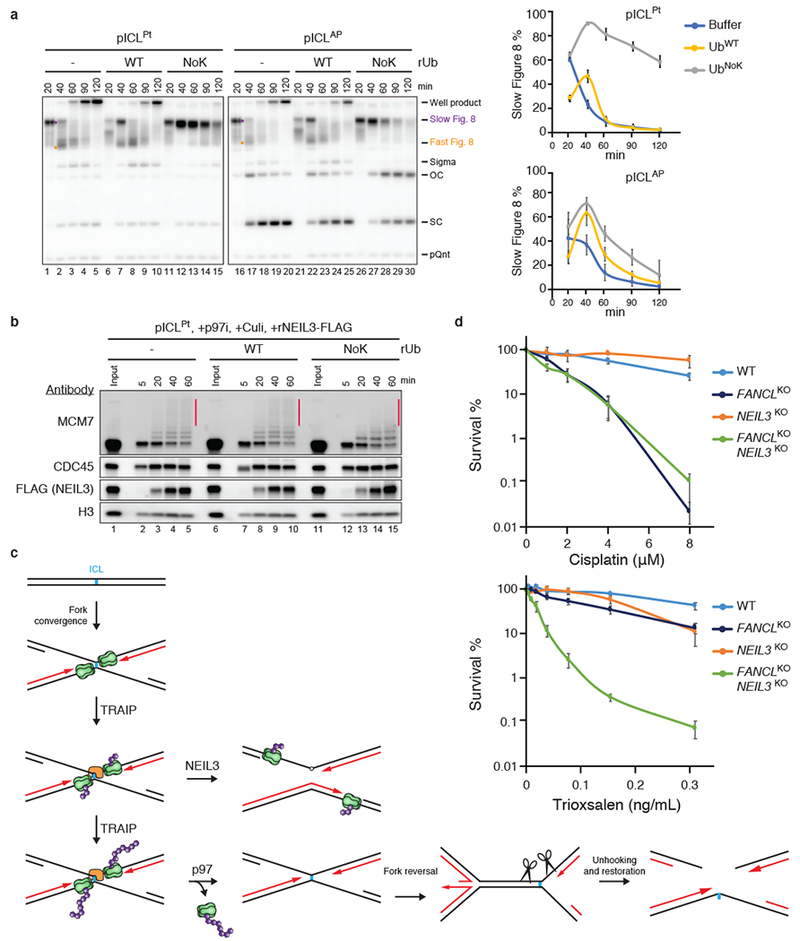
a, Left, replication of pICLPt or pICLAP in undepleted extract supplemented with buffer, UbWT, or UbNoK was analyzed as in Fig. 1b. Right, Slow Figure 8 structures quantified as a percentage of total replication products. Note that UbWT and UbNoK delayed replication by ~20 minutes. Error bars, standard error of the mean from three independent experiments.
b, Proteins associated with pICLPt during replication in undepleted extract in the presence of p97i and Culi and UbWT or UbNoK, as indicated. Black bar, longer ubiquitin chains sensitive to UbNoK addition.
c, Model for hierarchical activation of the NEIL3 and FA pathways by TRAIP. Green, CMG helicase; purple, ubiquitin; orange, NEIL3.
d, Clonogenic survival of wild-type, FANCL, NEIL3, or FANCL/NEIL3 CRISPR knockout HAP1 cells after exposure to cisplatin (top) or trioxsalen and UV-A irradiation (bottom). Error bars, standard error of the mean from at least three independent experiments.
In conclusion, we have shown that although TRAIP is a constitutive replisome component, it ubiquitylates CMG only upon fork convergence, which avoids premature CMG unloading from active replisomes (Extended Data Fig. 10a, i). Given our data, the ICL sensitivity of cells lacking TRAIP16 implies that a significant number of ICL repair events in cells require CMG convergence, even though a single fork may often trigger repair17. Interestingly, TRAIP also supports replication-coupled ubiquitylation of DNA-protein cross-links22 (Extended Data Fig. 10a, ii). Moreover, in mitosis, TRAIP ubiquitylates stalled CMGs in the absence of fork convergence, and terminated CMGs that were not unloaded by CRL2LRR1 (Deng et al., in press; Extended Data Fig. 10a, iii, iv). Collectively, our data suggest that in interphase, TRAIP only ubiquitylates proteins located ahead of the replisome. In contrast, in mitosis, TRAIP also ubiquitylates the CMG with which it associates, perhaps due to a Cyclin B1-CDK1-dependent conformational change in TRAIP. Our results establish TRAIP as a cell cycle-controlled, master regulator of DNA repair pathway choice and replisome integrity. We speculate that in humans, the significant ubiquitylation activity associated with TRAIPR18C is sufficient to support the FA pathway, albeit with slow kinetics, thereby suppressing the symptoms of FA while causing a G2 delay, reduced cell proliferation, and dwarfism. Consistent with this model, cells from both FA and TRAIP patients exhibit slow progression through G2 in the absence of exogenous crosslinking agents4,26, and FA patients often exhibit short stature4.
Methods:
All experiments were performed at least twice, with a representative result shown. All oligonucleotide sequences are listed in Supplementary Table 1.
Preparation of pICL
Preparations of the following plasmids containing site-specific crosslinks were performed as previously described: pICLPt; 2, pICL-lacOPt; 5, and pICLAP and pICL-lacOAP; 1. Briefly, purified cisplatin- or AP-crosslinked oligonucleotide duplexes comprising Pt_Top and PT_Bottom or AP_Top and AP_Bottom, respectively, were ligated into a parental plasmid linearized with BbsI, and the resulting supercoiled plasmid was isolated by cesium chloride gradient.
Preparation of pDPC2×Lead
Preparation of pDPC2×Lead was performed as previously described22,27. Briefly, oligonucleotide DPC_Fluoro_dC was ligated into a parental plasmid nicked with Nt.BbvCI and then crosslinked to recombinant Haemophilus parainfluenzae methyltransferase M.HpaII-His6.
Xenopus Egg Extracts and DNA Replication
All animal work was approved by the Harvard Medical Area Standing Committee on Animals (HMA IACUC Study ID IS00000051-3, approved 10/25/2017). The institution has an approved Animal Welfare Assurance (#A3431-01) from the Office of Laboratory Animal Welfare. Xenopus egg extracts were prepared essentially as described28. For DNA replication, plasmids were licensed by incubation in high-speed supernatant (HSS) of egg cytoplasm at room temperature for 30 min at a final concentration of 7.5 ng pICL/µl extract (for replication intermediate and nascent strand analyses) or 15 ng pICL/µl extract (for plasmid pull-down and electron microscopy analyses) and, where indicated, 0.375 ng pQnt/µl extract. For reactions using pICL-lacO plasmids with a pre-assembled LacR array, the plasmid was incubated for 1 hr at room temperature with purified biotinylated LacR29 at a final concentration of 14 µM prior to licensing as described above. To inhibit licensing, Geminin was added to HSS at a final concentration of 10 µM and incubated for 10 min at room temperature prior to addition of DNA. Replication was initiated by addition of two volumes of nucleoplasmic egg extract (NPE). In all figures except Extended Data Fig. 10b, c, the addition of NPE corresponds to the 0 min time point. For nascent strand radiolabeling, reactions were supplemented with trace amounts of [α-32P]dATP. Where indicated, reactions were supplemented with 200 µM NMS-873 p97 inhibitor (Sigma), 200 µM MLN4924 Cullin RING ligase inhibitor (Active Biochem), 111 µM RO-3306 CDK1 inhibitor (EMD Millipore), 100 µM ETP-46464 ATR inhibitor (Sigma), 50 µM PHA-767491 hydrochloride CDC7 inhibitor (Sigma), and/or 100 µM recombinant His6-tagged ubiquitin (Boston Biochem) and incubated for 5 min prior to addition of the licensing reaction, unless otherwise indicated. To generate mitotic extract, NPE was supplemented with 50 ng/µL CDK1-Cyclin B1 ((Life Technologies). Reactions were supplemented with approximately 30 to 50 nM recombinant NEIL3-FLAG and 50 nM recombinant TRAIP, with the following exceptions: extracts used in Figs. 2f and 3c and Extended Data Fig. 5a were supplemented with 600 nM rTRAIP and Extended Data Fig. 3a with 20 nM rTRAIP.
Antibodies and Immunodepletions
Rabbit polyclonal antibodies raised against the following X. laevis proteins were previously described: BRCA130; CDC45 and MCM731; CLASPIN32; CUL2, LRR1, and TRAIP21; FANCM27; MCM6 and NEIL31; MCM1033; DNA Pol ε (p60 subunit)34; and PCNA35. Rabbit polyclonal antibody against X. laevis DNA Pol ε subunit 3 was raised against the peptide MAERPEDLNLPNAVC by New England Peptide. Rabbit polyclonal antibody against X. laevis DNA Pol ε catalytic subunit was raised against the peptide MVLQNSGKFRAESRGDC by New England Peptide. Rabbit polyclonal FLAG antibody raised against FLAG peptide was prepared by New England Peptide. Rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against human FANCD2 was previously described36. Rabbit polyclonal histone H3 antibody 9715 was purchased from Cell Signaling Technology. Mouse monoclonal histidine tag antibody AD1.1.10 was purchased from Bio-Rad. Rabbit polyclonal MCM3 antibody sc-292857 was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Rabbit polyclonal MCM4 antibody A300-193A and MCM5 antibody A300-195A were purchased from Bethyl Laboratories. Rabbit polyclonal NEIL3 antibody 11621-1-AP was purchased from ProteinTech Europe. Rabbit polyclonal human phospho-CHK1 (Ser345) antibody 2341 was purchased from Cell Signaling Technology. Rabbit polyclonal antibody against X. laevis PSF1 was raised against the peptide LPRWKSEQLIRQGVLEHVLS by Bethyl Laboratories. Rabbit polyclonal antibody against X. laevis PSF3 was raised against the peptide ITASNLVQNYKKRKFNEADA by Bethyl Laboratories. Rabbit polyclonal TIMELESS antibody ab50943 was purchased from Abcam. Mouse monoclonal ubiquitin antibody sc-8017 was purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnology. Mouse monoclonal vinculin V284 antibody 05-386 was purchased from EMD Millipore. The following antibodies were generous gifts: AND1 (A. Dutta, University of Virginia), CTF18 (T. Takahashi, Kyushu University), MCM2 (J. Mendez, Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Oncológicas), and TIPIN (V. Costanzo, FIRC Institute for Molecular Oncology). Immunodepletions of BRCA119 and LRR121 were performed as previously described except in Extended Data Fig. 3l-n, where BRCA1 serum was first purified on Protein A Sepharose before use in depletion. For TRAIP depletions, 2.5 volumes of 1 mg/mL Protein A Sepharose-purified antibodies against TRAIP were gently rotated with 1 volume of Protein A Sepharose beads overnight at 4°C. Five volumes of egg extract were depleted by three rounds of gentle rotation with one volume of antibody-bound beads for 1 hr at 4°C. For NEIL3 depletions, 2.5 volumes of 1 mg/mL Protein A Sepharose-purified antibodies against NEIL3 were gently rotated with 1 volume of Protein A Sepharose beads overnight at 4°C. Five volumes of egg extract were depleted by three rounds of gentle rotation with one volume of antibody-bound beads for 20 min at room temperature. For FANCM depletions, 4 volumes of 1 mg/mL affinity-purified antibodies against FANCM were gently rotated with 1 volume of Protein A Sepharose beads overnight at 4°C. Five volumes of egg extract were depleted by three rounds of gentle rotation with one volume of antibody-bound beads for 1 hr at 4°C. For FANCD2 and NEIL3 double depletion, 3 volumes of 1 mg/mL affinity-purified antibodies against NEIL3 were gently rotated with 1 volume of Protein A Sepharose beads for 2 hr at 4°C. Three volumes FANCD2 anti-serum were then added to the Protein A Sepharose beads and incubation was continued at 4°C overnight. Five volumes of egg extract were depleted by three rounds of gentle rotation with one volume of antibody-bound beads for 20 min at room temperature.
Replication Intermediate Analysis
Replication reactions were stopped at the indicated time points with 10 volumes of Stop Solution A (5% SDS, 80 mM Tris-HCl [pH 8.0], 0.13% phosphoric acid, 10% Ficoll, and 0.5% bromophenol blue). The reactions were treated with 4 mg/ml Proteinase K (Roche) for 1 hr at 37°C and resolved by 0.8% native agarose gel electrophoresis. The gels were then dried and visualized by phosphorimaging on a Typhoon FLA 7000 (GE Healthcare). Image contrast was occasionally adjusted to improve visualization of bands.
Nascent Strand Analysis
Replication reactions were stopped at the indicated time points with 10 volumes of Stop Solution B (0.5% SDS, 50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], and 25 mM EDTA [pH 8.0]). The reactions were treated with 0.16 mg/ml RNase A for 1 hr at 37°C, followed by 0.75 mg/ml Proteinase K overnight at room temperature. The reactions were then phenol/chloroform extracted, precipitated, and digested with AflIII (for pICLPt) for 3 hr at 37°C or Nb.BsmI (for pDPC2×Lead) for 1 hr at 65°C. After addition of denaturing PAGE Gel Loading Buffer II (Life Technologies), the radiolabeled nascent strands were resolved on a 7% denaturing polyacrylamide gel, transferred to filter paper, dried, and visualized by phosphorimaging on a Typhoon FLA 7000 (GE Healthcare). To enhance visualization of bands, a logarithmic transform was applied using ImageJ to all nascent strand analyses except those presented in Fig. 2e and Extended Data Figs. 3a, e and 7e. Sequencing gel markers were generating using the Thermo Sequenase Cycle Sequencing Kit (USB Corporation) with primer pICL_Seq that anneals with the pICL plasmids 149 nucleotides upstream of the crosslink.
Plasmid Pull-down
Plasmid pull-downs were performed essentially as described37. Briefly, streptavidin-coupled magnetic beads (Invitrogen) were gently rotated with biotinylated LacR29 for 40 min at room temperature. The beads were washed three times with 20 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.7), 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 250 mM sucrose, 0.25 mg/ml BSA, and 0.02% Tween-20, then resuspended in the same buffer. Replication reactions were mixed with the beads at the indicated times and gently rotated for 30 min at 4°C. The beads were washed three times with 20 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.7), 100 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.25 mg/ml BSA, and 0.03% Tween-20, then resuspended in 2× Laemmli buffer for analysis by immunoblotting.
Ubiquitin linkage analysis
A plasmid for expression of the AMSH* deubiquitylating enzyme (pOINB-AMSH*)38 was obtained from AddGene (Plasmid #66712). AMSH* expression was induced in 1 L Rosetta 2 (DE3) pLysS cells (Novagen) with 0.4 mM IPTG for 18 hr at 18°C. Bacterial cell pellets were suspended in binding buffer (20 mM Tris-HCl [pH 8.5], 300 mM NaCl, 50 mM imidazole, 2 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and 1× Roche cOmplete protease inhibitor cocktail) and sonicated. The soluble lysate was collected following centrifugation at 25,000 rpm in a SW40.1 rotor for 1 hr and bound to TALON resin (Clonetech) for 90 min at 4°C. The bound resin was then washed with 1 L binding buffer and AMSH* was eluted with binding buffer containing 250 mM imidazole. The eluate was then concentrated and dialyzed against 20 mM Trsi-HCl (pH 8.5), 150 mM NaCl, 4 mM DTT at 4°C and 6 µM aliquots were stored at −80°C. Analysis of ubiquitin chains on MCM7 and MCM4 was performed using UbiCrest deubiquitylating enzymes (Boston Biochem). Plasmid pull downs were performed as described above, except that the beads were resuspended in 1× DUB reaction buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 50 mM NaCl, 5 mM DTT) and then incubated with 5 µM USP2CD, 8 µM Otubain1 (OTUB1), 0.6 µM AMSH*, 1× Yod1, 1× OTUD3, 1× Trabid, 1× Cezanne, or 1× Otulin for 30 min at 37°C. Reactions were quenched with an equal volume 2× Laemmli buffer and analyzed by immunoblotting.
Immunoblotting
Samples were resolved on Mini-PROTEAN or Criterion TGX precast gels (Bio-Rad) and transferred to PVDF membranes (Perkin Elmer). Membranes were blocked in 5% nonfat milk in 1× PBST for 60 min at room temperature, then incubated with antibody diluted in 1× PBST containing 1% BSA overnight at 4°C. After extensive washing in 1× PBST at room temperature, the membranes were incubated with goat anti-rabbit horseradish peroxidase-conjugated antibodies (Jackson ImmunoResearch) diluted in 5% nonfat milk in 1× PBST for 1 hr at room temperature. Membranes were washed extensively in 1× PBST, briefly incubated with HyGLO chemiluminescent HRP antibody detection reagent (Denville), and imaged using an Amersham Imager 600 (GE Healthcare). Contrast was occasionally adjusted to improve visualization of bands.
Error-Free Repair Assay
The error-free repair assay was performed as previously described39. Briefly, replication reactions were stopped at the indicated time points with 10 volumes of Stop Solution B. The reactions were treated with 0.16 mg/ml RNase A for 1 hr at 37°C, followed by 0.75 mg/ml Proteinase K overnight at room temperature. The reactions were then phenol/chloroform extracted, precipitated, and digested with HincII or HincII and SapI for 3 hr at 37°C. After addition of 0.17 volumes of DNA loading buffer (10 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 60% glycerol, and 0.5% bromophenol blue), the digestion products were resolved by 0.8% native agarose gel electrophoresis, dried, and visualized by phosphorimaging on a Typhoon FLA 7000 (GE Healthcare). Repair products were quantified using ImageJ (NIH).
Purification of Recombinant Xenopus NEIL3
X. laevis NEIL3 was purified as previously described1. Briefly, constructs for expression of rNEIL3NZF-C to A, rNEIL3TL310-311LV, rNEIL3K500E, rNEIL3K546E, rNEIL3K500E K546E, and rNEIL3∆92 were prepared by digesting Integrated DNA Technologies gene blocks encompassing the C-terminal domain of NEIL3 (with FLAG epitope tag) and containing the indicated mutations with BbvCI and XhoI and then ligating the fragments into similarly digested pFastBac1-NEIL3-FLAG1. The rNEIL3∆291 expression construct was prepared by PCR amplifying the NEIL3 glycosylase domain from a X. laevis cDNA library (a gift from T.G.W. Graham) using primers NEIL3_291_A and NEIL3_291_B. The fragment was then digested with EcoRI and XhoI and ligated into similarly digested pFastBac1 (Thermo Fisher Scientific). All mutations and truncations were confirmed by Sanger sequencing. Baculoviruses expressing rNEIL3 were then prepared using the Bac-to-Bac system (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s protocols. rNEIL3 protein was expressed in 250 ml suspension cultures of Sf9 insect cells (Expression Systems) by infection with baculovirus expressing NEIL3-FLAG for 48 to 72 hr. Sf9 cells were collected and suspended in 10 ml NEIL3 Lysis Buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 300 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, 1× Roche EDTA-free cOmplete protease inhibitor cocktail, 0.5 mM PMSF, and 0.2% Triton X-100). Cells were lysed by sonication, and the soluble fraction was collected by spinning the lysate at 25,000 rpm in a Beckman SW41 rotor for 1 hr. The soluble lysate was incubated with 200 µl anti-FLAG M2 affinity resin (Sigma) for 90 min at 4°C. The resin was washed once with 10 ml Lysis Buffer, twice with NEIL3 Wash Buffer (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 300 mM NaCl, 10% glycerol, and 0.2% Triton X-100), and three times with Buffer A (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 300 mM NaCl, and 10% glycerol). NEIL3-FLAG protein was eluted from the resin with Buffer A containing 100 μg/ml 3× FLAG peptide (Sigma). Elution fractions containing NEIL3-FLAG protein were pooled and dialyzed against 50 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.0), 300 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, and 20% glycerol at 4°C for 12 hr and then dialyzed against 50 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.0), 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, and 15% glycerol at 4°C for 3 hr. Aliquots of protein were stored at −80°C. Constructs for expression of GST-TEV-NZF fusion proteins were prepared by PCR amplifying the NEIL3 NZF from pFastBac1-NEIL3-FLAG and pFastBac1-NEIL3TL310-311LV-FLAG using primers NEIL3_NZF_A and NEIL3_NZF_B. The pGEX-6P-1 backbone (with GST-TEV tag) was PCR amplified from pGEX-6P-1-GST-TEV-FLAG-UBXN7 with primers GST_A and GST_B. The resulting fragments were then assembled using the NEBuilder HiFi DNA assembly cloning kit (New England Biolabs) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Expression of GST-TEV-NZF proteins was induced in 1 L Rosetta 2 (DE3) pLysS cells (Novagen) with 0.5 mM IPTG for 3 hr at 37°C. Bacterial cell pellets were suspended in Buffer A (10 mM sodium phosphate [pH 7.4], 150 mM NaCl, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, 10 μM ZnCl2 and 1× Roche cOmplete protease inhibitor cocktail) and sonicated. The soluble lysate was collected following centrifugation at 25,000 rpm in a SW40.1 rotor for 1 hr and bound to Glutathione Sepharose 4B (GE Healthcare) for 1.5 hr at 4°C. The bound resin was then washed five times with Buffer A and protein was eluted with Buffer B (50 mM Tris-HCl [pH 8.0], 150 mM NaCl, 10 μM ZnCl2, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and 20 mM glutathione). Fractions containing GST-TEV-NZF fusion proteins were dialyzed against 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 150 mM NaCl, 10 μM ZnCl2, 5 mM β-mercaptoethanol, and 10% glycerol at 4°C and aliquots were stored at −80°C. Constructs for expression of MBP-TEV-GRF ZF fusion proteins were prepared by amplifying the NEIL3 GRF ZF1 or GRF ZF2 from pFastBac1-NEIL3-FLAG or pFastBac1-NEIL3K500E K546E-FLAG using primers GRFZF1_A and GRFZF1_B or GRFZF2_A and GRFZF2_B, respectively. The MBP tag was PCR amplified using the primers MBP_A and MBP_B or MBP_A and MBP_C for GRF ZF1 and GRF ZF2 respectively. The pGEX-6P-1 backbone was PCR amplified from pGEX-6P-1-GST-TEV-FLAG-UBXN7 with primers pGEX_A and pGEX_B. The resulting fragments were then assembled using the NEBuilder HiFi DNA assembly cloning kit (New England Biolabs) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Expression of MBP-TEV-GRF ZF proteins was induced in 1 L Rosetta 2 (DE3) pLysS cells (Novagen) with 0.5 mM IPTG for 3 hr at 37°C. Bacterial cell pellets were suspended in Buffer C (20 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 300 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, and 1× Roche cOmplete protease inhibitor cocktail) and sonicated. The soluble lysate was collected following centrifugation at 25,000 rpm in a SW40.1 rotor for 1 hr and bound to amylose resin (New England Biolabs) for 1.5 hr at 4°C. The bound resin was then washed six times with Buffer C and protein was eluted with Buffer C containing 10 mM maltose. Fractions containing MBP-TEV-GRF ZF fusion proteins were dialyzed against 20 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 200 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, and 10% glycerol at 4°C and aliquots were stored at −80°C.
Purification of Recombinant Xenopus TRAIP
The X. laevis TRAIP open reading frame was PCR amplified from a X. laevis cDNA library (a gift from T.G.W. Graham) using primers TRAIP_A and TRAIP_B or TRAIP_C and TRAIP_D. For expression in bacteria, the product amplified with TRAIP_A and TRAIP_B was gel isolated, digested with BamHI, and ligated into pH6-SUMO40 linearized with BamHI. For expression in Sf9 insect cells, the product amplified with TRAIP_C and TRAIP_D was gel isolated, digested with BssHII and NotI, and ligated in pFastBac1 (Life Technologies) digested with BssHII and NotI. A 3×FLAG tag and 3C protease cleavage site were introduced by linearizing the resulting plasmid with BssHII and ligating a linker comprising annealed oligonucleotides 3×F_3C_Top_1, _2, _3 and 3×F_3C_Bottom_1, _2, _3, and _4. The R18C substitution was introduced by “around-the-horn” PCR41 using primers R18C_A and R18C_B. pH6-SUMO-TRAIPΔPIP (residues 1-455) was constructed by “around-the-horn” PCR using primers PIP_A and PIP_B. All mutations and truncations were confirmed by Sanger sequencing.
His6-SUMO-TRAIP was expressed in Rosetta 2 (DE3) pLysS (Novagen) by induction with 0.1 mM IPTG overnight at 16°C in growth media supplemented with 50 µM ZnSO4. Bacterial pellets were resuspended in TRAIP Lysis Buffer (20 mM HEPES-NaOH [pH 7.5], 400 mM sodium acetate, 10% glycerol, 10 µM ZnSO4, 0.1% NP-40, 1 mM DTT, and 1× Roche cOmplete protease inhibitor cocktail) supplemented with 20 mM imidazole. Following sonication, ammonium sulfate and polyethyleneimine were added to the lysate to final concentrations of 300 mM and 0.45%, respectively and incubated for 15 min at 4°C. The soluble fraction was collected after centrifugation at 40,000 g for 45 min at 4°C, and precipitated with saturating ammonium sulfate. The precipitated fraction was collected after centrifugation at 40,000 g for 45 min at 4°C, resuspended in Lysis Buffer, and then rotated with NiNTA resin (Qiagen) for 30 min at room temperature. The resin was washed three times with Wash Buffer (20 mM HEPES-NaOH [pH 7.5], 400 mM sodium acetate, 10% glycerol, 20 mM imidazole, 10 µM ZnSO4, 0.01% NP-40, 1 mM DTT, and 1× Roche cOmplete protease inhibitor cocktail). His6-SUMO-TRAIP was eluted from the resin with Elution Buffer (20 mM HEPES-NaOH [pH 7.5], 400 mM sodium acetate, 10% glycerol, 250 mM imidazole, 0.01% NP-40, and 1 mM DTT). Elution fractions containing His6-SUMO-TRAIP were pooled and dialyzed against Dialysis Buffer (20 mM HEPES-NaOH [pH 7.5], 400 mM sodium acetate, 10% glycerol, 0.01% NP-40, and 1 mM DTT) supplemented with 120 mM imidazole overnight at 4°C. With the exception of the indicated proteins used in Extended Data Figs. 2b, g, h, and 6e, the His6-SUMO was simultaneously cleaved by addition of 0.03 mg/mL Ulp1 during dialysis. Aliquots were flash frozen and stored at −80°C.
Baculoviruses expressing 3×F-3C-rTRAIPWT or 3×F-3C-rTRAIPR18C were prepared using the Bac-to-Bac system (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s protocols. rTRAIP protein was expressed in 200 ml suspension cultures of Sf9 insect cells (Life Technologies) by infection with baculovirus for 72 hr. Sf9 cells were collected and suspended in 10 ml TRAIP Lysis Buffer. Following sonication, the soluble lysate was collected following centrifugation at 30,000 rpm in a 45Ti rotor for 1 hr and bound to anti-FLAG M2 affinity agarose gel (Sigma) for 2 hr at 4°C. The bound resin was then washed five times with TRAIP Lysis Buffer and eluted with TRAIP Lysis Buffer supplemented with 100 μg/ml 3×FLAG peptide (Sigma). Elution fractions containing 3×F-3C-rTRAIP were pooled incubated overnight at 4°C in the presence of 3C protease. Aliquots were flash frozen and stored at −80°C.
Purification of Recombinant Xenopus CMG
The open reading frames encoding the eleven X. laevis CMG subunits (CDC45, MCM2-7 hetero-hexamer, and GINS hetero-tetramer) were cloned into a single plasmid (pGC187) using the MultiBac system42. MCM2-7 open reading frames were PCR amplified from X. laevis cDNA. A sequence encoding the FLAG tag was added to the N-terminus of MCM3. Codon-optimized GINS and CDC45 open reading frames were synthesized as gBlocks by IDT. The bacmid encoding the CMG complex was obtained by electroporating pGC187 into DH10EMBacY (Geneva Biotech) electro-competent cells and purified using ZR BAC DNA miniprep kit (Zymo Research).
CMG baculovirus was generated by transfecting pGC187 bacmid into Sf9 cells (Expression Systems) for 96 hr, and amplifying the virus in 2 rounds of 96 hr each. Individual subunit expression levels were monitored by immunoblotting. 500 mL of Tni (similar to HiFive) cell culture (Expression Systems) at a density of 2-3 million/mL was infected with 50 mL baculovirus (MOI>10). Cells harvested 72 hr post-infection were pelleted at 500 g for 15 min, frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C.
The frozen pellet was re-suspended to a final volume of 50 mL in CMG Lysis Buffer (CLB; 20 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 10% glycerol, 5 mM magnesium acetate, 300 mM potassium acetate, 0.1% Tween20, 1 mM PMSF, 0.2 mM ATP, and 1× Roche EDTA-free cOmplete protease inhibitor cocktail). Cells were lysed by sonication on ice or by Dounce homogenization and the insoluble fraction was pelleted via centrifugation for 1hr at 30,000 g at 4°C. The clarified lysate was incubated with 1 mL M2 anti-FLAG resin (Sigma) for 1 hr at 4°C on a rotating wheel. The resin was washed 5 times with 10 mL of CLB in a disposable column. The protein was eluted twice with 1 mL/each of CLB supplemented with 0.2 mg/mL 3×FLAG peptide (Sigma) for 1 hr at 4°C. Eluted fractions were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C until the ion exchange polishing could be performed.
The ion exchange polishing procedure was adapted from a previous study43. Ion exchange was performed on a GE AKTA FPLC using CMG Start Buffer (25 mM HEPES [pH 7.6], 10% glycerol, 0.02% Tween20, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 0 mM KCl, 0.4 mM PMSF, 1 mM DTT) and CMG Elution Buffer (25 mM HEPES [pH 7.6], 10% glycerol, 0.02% Tween20, 1 mM EDTA, 1 mM EGTA, 1000 mM KCl, 0.4 mM PMSF, 1 mM DTT). The FLAG eluate was diluted 3-fold with CMG Start Buffer to a final salt concentration of 100 mM and loaded onto two columns connected in tandem: MonoS 5/50 GL (GE Healthcare) and MonoQ 5/50 GL (GE Healthcare) such that the flowthrough from MonoS passed through MonoQ. In this scheme, MonoS trapped some contaminants whereas MonoQ bound CMG and its subcomplexes. After loading the protein, the columns were washed with 10 mL of 10% CMG Elution Buffer, then MonoS was disconnected. MonoQ was eluted with 30 mL 10-60% CMG Elution Buffer gradient and 0.5 mL fractions were collected. Stoichiometric CMG complex eluted at 450-500 mM KCl. CMG stoichiometry and purity were verified by SDS-PAGE imaged with SYPRO ruby. A preparation from 0.5 L of Tni cell culture usually yielded 0.1 mg of very pure CMG (Extended Data Fig. 5d).
Purified CMG was further concentrated by ion exchange on a MonoQ PC 1.6/5 (GE Healthcare) using an AKTA FPLC as previously described43, or by ion exchange on small volumes of NuviaQ resin (BioRad). To perform the latter, MonoQ fractions containing CMG were diluted 3-fold with CMG Start Buffer for a final KCl concentration of 150 mM and incubated for 1 hr at 4°C with 40 μL of NuviaQ resin pre-equilibrated in 15% CMG Elution Buffer. The resin was washed 3 times with 400 μL 15% CMG Elution Buffer in a small disposable column (Pierce), then 3 times with 400 μL 30% CMG Elution Buffer. Each time the flowthrough was collected via centrifugation for 30 sec at 500 g in a refrigerated tabletop centrifuge with a swing-bucket rotor. CMG was eluted by incubating the washed resin with 40 μL 60% CMG Elution Buffer for 15 min and collected via centrifugation. Any protein that remained bound to the resin was eluted with 40 μL 100% CMG Elution Buffer. 3-5 μL aliquots of concentrated CMG (0.5-1.0 μM) were frozen in liquid nitrogen and stored at −80°C.
In Vitro CMG Ubiquitylation Assay
A ubiquitylation assay using an equimolar mixture of the E2 ubiquitin conjugating enzymes UbcH5a, UbcH5b, and UbcH5c, recombinant TRAIPWT or TRAIPR18C at an approximate final concentration of 15 nM, and, where included, recombinant CMG at an approximate final concentration of 150 nM was performed using the Enzo BML-UW9920 Ubiquitinylation Kit according to manufacturer’s instructions (Enzo Life Sciences). Reaction products were then resuspended in 1× Laemmli buffer and analyzed by immunoblotting. For reactions containing rCMG, products were bound to anti-FLAG M2 affinity agarose gel (Sigma) for 30 min at room temperature. Bound beads were washed 3 times with egg lysis buffer (10 mM HEPES [pH 7.7], 50 mM KCl, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 2.5 M sucrose), and treated with USP2 for 30 min at 37°C as indicated prior to immunoblotting.
Electron Microscopy
Electron microscopy analysis of the replication intermediates was performed as previously described7. Briefly, replication reactions were stopped at 90 min with 10 volumes of Stop Solution C (100 mM Tris-HCl [pH 7.5], 6.7 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA [pH 8.0], and 1% SDS). The DNA was crosslinked with trimethylpsoralen (Sigma) and irradiation with UV light at 365 nM prior to protein extraction and DNA purification. Purified DNA was incubated with E. coli single-stranded DNA binding protein (SSB), fixed with 0.3% glutaraldehyde, then purified by size-exclusion chromatography. Eluted complexes were mounted onto grids, which were then subjected to rotary shadowing with platinum and carbon coating using a Leica Ace600 coating system. Samples were imaged using a JEOL 1200EX transmission electron microscope equipped with a 2k CCD camera (Advanced Microscopy Techniques). After blinding the scorer to the conditions, reversed forks were counted and expressed as a percentage of pre-incision structures, which was then normalized to the mock-depleted condition.
Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay
MBP-TEV-GRF ZF fusion protein was incubated with 10 nM 5′ end radiolabeled 25mer ssDNA (EMSA_Top) or dsDNA (EMSA_Top + EMSA_Bottom) in buffer containing 1 mM MgCl2, 100 µM ZnSO4, 10 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 50 mM NaCl, 0.2 mM TCEP, and 5% glycerol for 30 to 60 min at 4°C. Binding reactions were separated on native 5% acrylamide (37.5:1), 45 mM Tris, 45 mM borate, 1 mM MgCl2, 100 µM ZnSO4 gels and visualized by phosphorimaging on a Typhoon FLA 7000 (GE Healthcare).
NEIL3 Glycosylase Assay
AP-ICLs between complementary DNA and DNA/RNA chimeric oligonucleotides AP_assay_A and AP_assay_B were cross-linked, RNase H digested, and gel purified as described1. To monitor unhooking of AP-ICLs, 2.5 nM 5′ radiolabeled cross-linked substrate was incubated with 20 nM rNEIL3-FLAG in 20 mM HEPES-KOH (pH 7.0), 50 mM NaCl, 1 mM DTT, 0.1 mg/ml BSA at 37°C44. Reactions were quenched with 1 volume of 2× formamide buffer (86% formamide, 2× TBE, 20 mM EDTA [pH 8.0]), separated on a denaturing polyacrylamide and visualized by phosphorimaging on a Typhoon FLA 7000 (GE Healthcare).
Biolayer Interferometry
All measurements were obtained using an OctetRED384 instrument (Pall ForteBio). Samples in 0.2 mL BLI buffer (1× PBS, 0.1 mg/mL BSA, and 0.05% Tween 20) were dispensed into polypropylene 96-well black flat-bottom plates (Greiner Bio-One). GST-TEV-NZF or GST control protein (30 µg/mL) was captured on pre-wet anti-GST biosensors (Pall ForteBio). Biosensors were then transferred to wells containing BLI buffer to allow dissociation of non-specifically bound GST-TEV-NZF protein and establish a measurement base-line. Biosensors were next transferred to wells containing serial dilutions of monoubiquitin (Boston Biochem) to monitor association of ubiquitin with the immobilized GST-TEV-NZF protein. Finally, biosensors were transferred to wells containing BLI buffer to monitor dissociation of ubiquitin from GST-TEV-NZF protein. For each ubiquitin concentration, the steady state ubiquitin binding response (Req) was determined from a five second window at the end of the association phase. Req values were subsequently corrected for non-specific binding of ubiquitin to the GST epitope by subtracting Req values obtained for the GST control protein. Steady-state responses were plotted as a function of ubiquitin concentration ([Ub]) and Kd was determined using the Prism software suite by fitting the data to the non-linear regression equation where Rmax is the globally-constrained maximum association response.
Cell Lines
Wild-type and NEIL3KO HAP1 near-haploid human cells were purchased from Horizon Discovery and cultured at 37˚C and 5% CO2 in IMDM (Gibco) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum (Gibco) and penicillin/streptomycin (Gibco). NEIL3KO cells were confirmed by immunoblotting against NEIL3. For targeting of FANCL, WT and NEIL3KO cells were transfected with Turbofectin 8.0 (Origene) and the following plasmids: pX461, FANCL_left and FANCL_right CRISPR guides in U6 BsaI backbone, and FANCL-Puro targeting construct (Extended Data Fig. 9b). FANCL plasmids were obtained from the Wellcome Trust Sanger Institute. Two days post-transfection, 3.5 µg/mL puromycin (Gibco) was added, and two days later, cells were plated in 96-well plates with puromycin. After 14 days of incubation, individual clones were picked and analyzed for FANCL targeting using the SequalPrep Long PCR kit (Applied Biosystems) (see Supplementary Table 1 for primer sequences). Targeted clones were then plated with 100 ng/mL mitomycin C (Sigma) overnight and analyzed by immunoblotting for FANCD2. FANCL knockouts were identified by failure to ubiquitylate FANCD2 upon exposure to mitomycin C. All cell lines were tested to be mycoplasma negative using the MycoAlert Mycoplasma Detection Kit (Lonza).
CH12-F3 murine B lymphoma cells were cultured at 37˚C and 5% CO2 in RPMI (Gibco) supplemented with 10% fetal calf serum, penicillin/streptomycin, and 10 µM β-mercaptoethanol. To target Neil3 and Fancb, CH12 cells were transfected using the Lonza Nucleofection Kit V and the following plasmids: pX458 and CRISPR guides against either Neil3 exon 1 or 2 (Neil3_exon1 and Neil3_exon2) and/or a Fancb guide against exon 5 (Fancb_319). Two days following transfection, GFP positive cells were singly sorted by flow cytometry into 96-well plates, and cultured for 7-10 days to obtain single colonies that were screened by PCR fragment analysis. The target exons of Neil3 in putative clones were then amplified and cloned into the pMiniT 2.0 vector (NEB) and sequenced. Neil3 clone 1 carried deletion in each allele of exon 2 of sizes 14- and 26-bp respectively, whilst clone 2 carried a 38- and 6-bp deletion in each allele of exon 1. Fancb clone 1 carried a 359-bp deletion in exon 5 and clone 2 carried a 21-bp deletion. Neil3 clones were subsequently targeted for Fancb to generate double knockouts (DKO); DKO clone 1 had a 4-bp deletion in Fancb exon 5, clone 2 had a 10-bp deletion, and clone 3 had a 24-bp deletion. Disruption of Fancb function was tested by treating all clones with mitomycin C prior to detection for the loss of FANCD2 monoubiquitylation by immunoblotting as described above.
Colony Survival Assay
For the cisplatin colony survival assay (CSA), HAP1 cells were prepared at 2×105 cells/mL. Cells and cisplatin (diluted in culture media) were mixed in 96-well blocks (Greiner Bio-One Masterblock) and foil seals (Bio-Rad Microseal ‘F’) were applied before culturing cells at 37˚C for 2 hr. Cells were then serially diluted in PBS using a multi-channel pipette to obtain 1:10 and 1:100 dilutions, and 100 µL of each of three concentrations were plated in duplicate in 24-well plates filled with 1.5 mL of culture media per well. Cells were cultured for 6 days before being stained with crystal violet45 and colonies were quantified by a GelCount colony counter (Oxford Optronix).
For the trioxsalen CSA, cells were seeded in 24-well plates at 1.2×105 cells per well 5 hr prior to adding trioxsalen (Sigma) and cultured for 1 hr. Cells were then exposed to 6 kJ/m2 of UV-A light (365 nm, VL-6.L lamp) through the bottom of the tissue culture plate to photoactivate trioxsalen. The cells were washed twice with culture media, incubated at 37˚C for 10 min to offload unbound trioxsalen, then washed again and treated with 12 kJ/min/m2 UV-A to convert trioxsalen monoadducts into ICLs46,47. Cells were then trypsinized, diluted, plated, cultured, and stained as above.
Cell Viability Assay
CH12 cells were plated in flat-bottom 96-well plates at 5,000 cells per well and cultured with trioxsalen for 1 hour, then exposed to 12 kJ/min/m2 UV-A. Cells were then cultured for 3 days before being assayed with the CellTiter 96 AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay (Promega).
Data availability
All relevant data are available from the authors and/or are included with this Letter. Source images are available in Supplementary Fig. 1.
Extended Data
Extended Data Fig. 1 |. DNA replication and ICL repair in Xenopus egg extracts.

a, Schematic of pICL replication in the nucleus-free Xenopus egg extract system48. Incubation of the plasmid in HSS supports the recruitment of inactive MCM2-7 double hexamers (red hexamers; “Licensing”). Addition of NPE activates replication initiation, including the assembly of active CMG helicases (green hexamers), and elongation of nascent strands (red lines) leads to convergence of forks at the ICL.
b, Intermediates generated during replication-coupled repair of a cisplatin-ICL. Top, progression through the incision-dependent Fanconi anemia repair pathway generates distinct intermediates resulting from fork convergence, CMG unloading, leading strand approach to the ICL, fork reversal, incisions, and repair of the double strand break by homologous recombination. Bottom, deproteinization of the DNA intermediates depicted along the top yields DNA structures that travel with characteristic mobilities during native agarose gel electrophoresis. These structures are indicated along the side of the gel and with colored dots and/or arrowheads in Fig. 1b and other figures. The Slow Figure 8 arises upon fork convergence on the ICL (Fig. 1b, purple dot). Conversion of Slow to Fast Figure 8s results from CMG unloading and an accompanying change in plasmid topology (Fig. 1b, orange dot)7. Next, a species of intermediate mobility appears (Fig. 1b, green arrowhead), which represents reversed forks, as shown by electron microscopy7. Following XPF-dependent unhooking of the reversed structure7,49, double-strand DNA break repair generates joining products that barely enter the gel50 (Fig, 1b, Well product). Some of these species are resolved into monomeric, supercoiled plasmids that represent the final, fully repaired product (Fig. 1b, SC) that is sensitive to SapI digestion.
c, Intermediates generated during replication-coupled repair of an AP-ICL (pICLAP). Top, progression through the NEIL3 repair pathway generates intermediates resulting from fork convergence, NEIL3-dependent N-glycosyl bond cleavage, nascent strand ligation, decatenation, and translesion synthesis (TLS). Bottom, deproteinization of the DNA intermediates depicted along the top yields DNA structures that travel with characteristic mobilities during native gel electrophoresis. These structures are indicated along the side of the gel and with colored dots in Fig. 3a and other figures.
Extended Data Fig. 2 |. Recombinant TRAIP supports CMG unloading at cisplatin-ICLs.
a, NPE immunodepleted of TRAIP was loaded alongside a dilution series of mock-depleted NPE and blotted for TRAIP. A relative loading amount of 100 corresponds to 2 µl of NPE. Non-specifically detected proteins are marked with asterisks.
b, Bacterially-expressed rTRAIPWT, rTRAIPR18C, His6-SUMO-rTRAIPWT, and His6-SUMO-rTRAIPΔPIP (comprising residues 1-455) were partially purified, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and visualized with Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining. Note that His6-SUMO-rTRAIP is obscured by co-migrating, contaminating proteins. Bacterially-expressed rTRAIP was used for all subsequent experiments, unless otherwise indicated.
c, rTRAIPWT and rTRAIPR18C were expressed in Sf9 insect cells and purified using an N-terminal 3×FLAG tag. The tag was then cleaved using 3C protease. The recombinant proteins, along with a buffer sample containing 3C protease only, were resolved by SDS-PAGE and visualized with Coomassie Brilliant Blue staining.
d, Mock- and TRAIP-depleted extracts supplemented with rTRAIPWT or rTRAIPR18C used in Fig. 1b were analyzed by immunoblotting for TRAIP. The absence of the non-specific bands seen in a may be due to shorter incubation with the TRAIP antibody. The concentration of added recombinant TRAIP relative to endogenous TRAIP fluctuates among experiments (e.g. compare panel d and Extended Data Fig. 3b). We ascribe this difference to variations in non-specific removal of endogenous TRAIP from extracts during the mock-depletion procedure, and possibly also in the delivery of recombinant TRAIP into extract.
e, pICLPt was replicated in mock- or TRAIP-depleted extracts supplemented with [α-32P]dATP and Sf9-expressed rTRAIPWT, rTRAIPR18C, or 3C protease alone and analyzed as in Fig. 1b.
f, Extracts used in the replication reaction shown in e were analyzed as in d.
g, pICLPt was replicated in the indicated egg extracts with [α-32P]dATP and analyzed as in Fig. 1b.
h, Extracts used in the replication reaction shown in g were analyzed as in d. Note that deleting the C-terminal PIP box disrupts the epitope for the TRAIP antibody used for immunoblotting. Therefore, to assess the activity of TRAIPΔPIP in ICL repair relative to TRAIPWT, His6-SUMO-tagged proteins were added back to TRAIP-depleted extract and assayed in g. The relative amounts of His6-SUMO-TRAIPWT and His6-SUMO-TRAIPΔPIP were compared by detecting the histidine tag. By blotting the same extracts for TRAIP, a comparison of the relative concentrations of His6-SUMO-TRAIPΔPIP and endogenous TRAIP was made.
i, Mock- and TRAIP-depleted extracts used in the replication reactions shown in Fig. 1c and d were analyzed as in d.
Extended Data Fig. 3 |. TRAIP, but not FANCM, ATR, or BRCA1, is required for CMG unloading at cisplatin-ICLs.
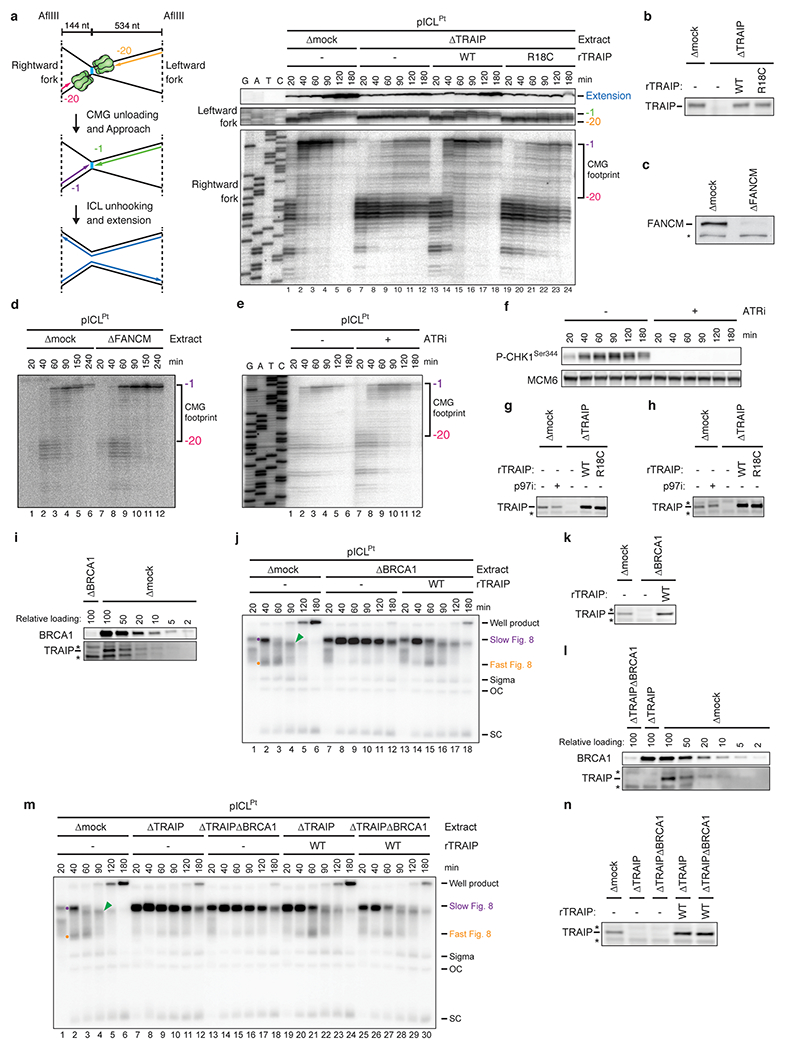
a, Left, schematic of nascent strands generated at ICLs. When forks converge on an ICL, nascent strands stall ~20 nt from the ICL on either side of the lesion due to the footprint of CMG (green hexamer). AflIII cuts 144 nt to the left and 534 nt to the right of the ICL, generating characteristic products for the leftward and rightward leading strands upon fork convergence, CMG unloading, and leading strand extension. Right, nascent strand analysis of pICLPt replication in the indicated extracts. After replication with [α-32P]dATP, nascent strands were extracted, digested with AflIII, and resolved on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel alongside a sequencing ladder and visualized by autoradiography. As seen previously2,51, when replication forks converged on the ICL in mock-depleted egg extracts, leading strands initially stalled 20-40 nucleotides (nt) from the lesion (lane 1) and then advanced to the −1 position (lanes 2-6), which depends on CMG dissociation19,51. In contrast, in TRAIP-depleted egg extracts, the −20 footprint persisted for three hours (lanes 7-12). This effect was rescued with rTRAIPWT but not rTRAIPR18C (lanes 13-24).
b, Extracts used in the replication reaction shown in a were blotted for TRAIP.
c, Mock- or FANCM-depleted extracts were blotted for FANCM. A non-specifically detected protein is marked with an asterisk.
d, Nascent strand analysis of pICLPt replicating in mock- or FANCM-depleted extracts was performed as in a. The CMG footprint disappeared at the ICL in FANCM-depleted egg extract, consistent with FANCM not being required for CMG unloading at ICLs.
e, pICLPt was replicated in the absence or presence of ATR inhibitor ETP-46464 (ATRi), and nascent strand analysis was performed as in a. ATR inhibitor was added to the reaction 2.5 min after initiation. The CMG footprint disappeared at the ICL with or without ATR inhibitor, indicating that ATR signaling is not required for CMG unloading at ICLs.
f, Extracts used in e were sampled at various time points and blotted for Xenopus CHK1 Serine-344 phosphorylation to verify ATR inhibition. MCM6 was detected as a loading control.
g and h, Mock- and TRAIP-depleted extracts used in one of the replicate reactions quantified in Fig. 1e (g) and f (h) were blotted for TRAIP.
i, We previously showed that the immunodepletion of BRCA1 from egg extracts inhibits CMG unloading at ICLs, but this defect could not be rescued with recombinant BRCA1-BARD1 complex6,19. To test whether TRAIP is co-depleted with BRCA1, NPE was immunodepleted of BRCA1 with BRCA1 antiserum, loaded alongside a dilution series of mock-depleted NPE, and blotted for BRCA1 and TRAIP. A relative loading amount of 100 corresponds to 2 µl of NPE. Non-specifically detected proteins are marked with asterisks. This analysis revealed that immunodepletion of BRCA1 also removed TRAIP from NPE. Notably, we also observed TRAIP co-depletion with antibodies against other proteins (data not shown), suggesting it interacts non-specifically with different antibodies.
j, The extracts described in i were supplemented with pICLPt, [α-32P]dATP, and rTRAIP, as indicated, and analyzed as in Fig. 1b. rTRAIPWT suppressed the stabilization of the Slow Figure 8 species seen in BRCA1-depleted extract, consistent with the restoration of CMG unloading, and indicating that the unloading defect seen in BRCA1-depleted egg extracts is due primarily to the removal of TRAIP from the extract.
k, The extracts used in j were blotted for TRAIP.
l, To determine whether BRCA1 contributes to TRAIP-dependent CMG unloading, NPE was immunodepleted of TRAIP or TRAIP and BRCA1 using Protein A Sepharose-purified antibodies purified from antiserum. A dilution series of mock-depleted NPE was loaded alongside the depleted extracts, and extracts were blotted for BRCA1 and TRAIP. A relative loading amount of 100 corresponds to 2 µl of NPE.
m, The extracts described in l were supplemented with pICLPt, [α-32P]dATP, and rTRAIP, as indicated, and analyzed as in Fig. 1b. rTRAIPWT suppressed the accumulation of Slow Figure 8s to a similar extent in TRAIP-depleted egg extracts whether or not BRCA1 was co-depleted (lanes 19-30), indicating that BRCA1 is not needed to support TRAIP function. BRCA1 depletion reproducibly resulted in a decrease in well product formation, suggesting a role for BRCA1 in recombination after a double-strand break is formed by ICL unhooking incisions.
n, The extracts used in m were blotted for TRAIP.
Extended Data Fig. 4 |. TRAIP and CRL2LRR1 promote distinct CMG unloading pathways.
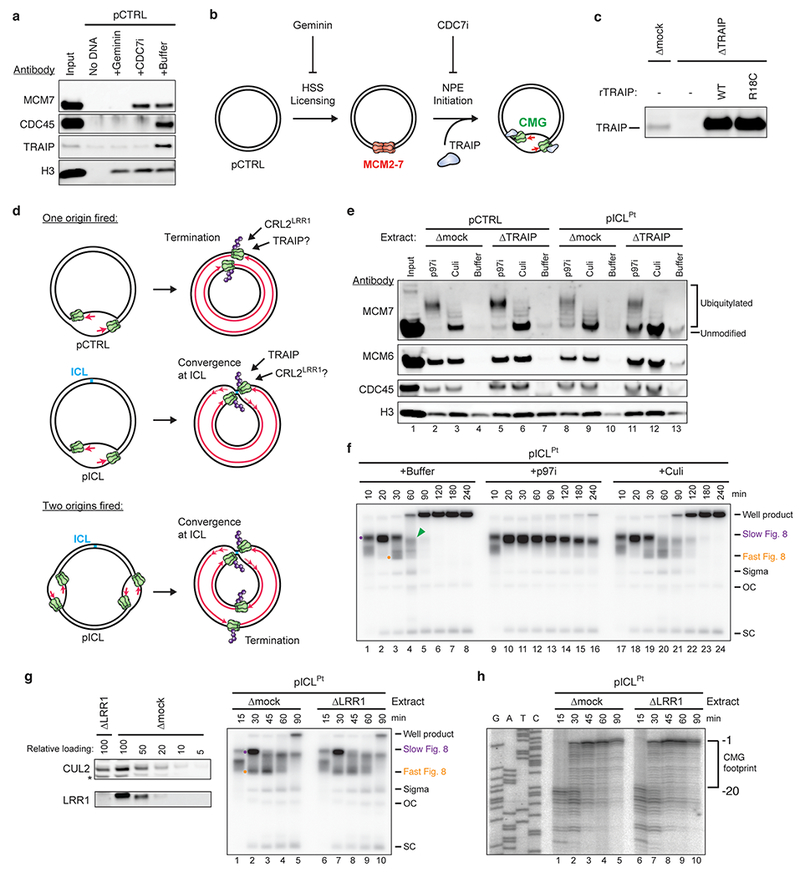
a, pCTRL was replicated in NPE in the presence of Geminin or the CDC7 inhibitor PHA-767491 (CDC7i). Eight minutes after addition of NPE, the plasmid was recovered and the indicated proteins were analyzed by immunoblot.
b, Cartoon depicting the effects of Geminin and CDC7i, and the step at which TRAIP is recruited to chromatin.
c, Extracts used in the replication reaction shown in Fig. 2e were blotted for TRAIP.
d, Top, upon termination of pCTRL replication, CMG (green) unloading depends on CRL2LRR1-mediated MCM7 ubiquitylation (purple)21,52, but it’s unknown whether unloading also requires TRAIP. Middle, CMGs that have converged at an ICL undergo TRAIP-dependent ubiquitylation (Fig. 1), but the involvement of CRL2LRR1 is unknown. Bottom, if two origins fire on a single plasmid, one pair of replication forks converges at the ICL and undergoes TRAIP-dependent CMG unloading whereas a second pair undergoes CRL2LRR1-dependent unloading. Because both pairs of CMGs should undergo ubiquitylation, in some experiments we include Culi to monitor only TRAIP-dependent ubiquitylation.
e, To determine whether TRAIP is required for CMG unloading during replication termination, we analyzed proteins associated with plasmids 60 min after replication initiation in mock- or TRAIP-depleted extracts containing p97i or Culi, as indicated. Chromatin was recovered and blotted for the indicated proteins. CMG unloading from pCTRL was unaffected by TRAIP depletion (compare lanes 4 and 7). Consistent with this, in the presence of p97i, TRAIP was not required for MCM7 ubiquitylation on pCTRL (compare lanes 2 and 5). In contrast, in the absence of TRAIP, CMG unloading from pICLPt was inhibited compared to the mock-depleted control (compare lanes 10 and 13), consistent with Fig. 1c. Similarly, TRAIP was essential for efficient MCM7 ubiquitylation on pICLPt (compare lanes 8 and 11, note the greater level of unmodified MCM7 in lane 11). The partial CMG unloading (lane 13) and residual MCM7 ubiquitylation observed on pICLPt in the absence of TRAIP (lane 11) were likely the result of termination events that occurred elsewhere on the plasmid (as described in d, bottom). Consistent with this interpretation, the combination of TRAIP depletion and Culi abolished MCM7 ubiquitylation (lane 12).
f, To determine whether CRL2LRR1 contributes to CMG unloading at ICLs, pICLPt was replicated in undepleted extract containing p97i or Culi and analyzed as in Fig. 1b. Culi had no significant effect on the accumulation of Fast Figure 8 structures, consistent with CRL2LRR1 being dispensable for CMG unloading at ICLs.
g, Left, to assess the effect of LRR1 depletion on CMG unloading at ICLs, NPE was immunodepleted of LRR1, loaded alongside a dilution series of mock-depleted NPE, and blotted for LRR1 and CUL2. A relative loading amount of 100 corresponds to 2 µl of NPE. Non-specifically detected protein is marked with an asterisk. Right, pICLPt was replicated in mock- or LRR1-depleted egg extracts and analyzed as in Fig. 1b. The absence of LRR1 had no effect on the formation of Fast Figure 8 structures, supporting the idea that CRL2LRR1 is dispensable for CMG unloading at ICLs.
h, Nascent strand analysis of pICLPt replicating in mock- or LRR1-depleted extracts was performed as in Extended Data Fig. 3a. The CMG footprint disappeared with normal kinetics at the ICL in LRR1-depleted egg extract, consistent with CRL2LRR1 not being required for CMG unloading at ICLs.
Extended Data Fig. 5 |. TRAIP ubiquitylates numerous CMG subunits with heterotypically-linked chains upon fork convergence at an ICL.

a, pICL-lacOPt was incubated with LacR prior to replication in mock- or TRAIP-depleted extracts. After 1 hr of replication (to allow for termination of replication forks that do not converge on the ICL or lacO array as depicted in Fig. 2c), 0.3 mM NMS-873 was added and the extracts were incubated for 5 min to inhibit p97. 10 mM IPTG and Sf9-expressed rTRAIPWT were then added as indicated and the extract was incubated for 2 hr to disrupt LacR DNA binding and allow fork convergence and TRAIP-dependent ubiquitylation. The plasmid was recovered and blotted for the indicated proteins.
b, The extracts described in a were blotted for TRAIP.
c, pICL-lacOPt was incubated with LacR prior to replication in undepleted egg extracts. After 30 min of replication (to allow for termination of replication forks that do not converge on the ICL or lacO array as depicted in Fig. 2c), 0.3 mM NMS-873 was added and the extracts were incubated for 5 min to inhibit p97. 10 mM IPTG was then added as indicated to disrupt LacR DNA binding and the extract was incubated for 1 hr to allow fork convergence. The plasmid was recovered and blotted for the indicated proteins.
d, Recombinant CMG was purified, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and visualized with SYPRO ruby staining.
e, rTRAIP ubiquitin ligase activity. rTRAIPWT or rTRAIPR18C was combined with ubiquitin, E1, three E2s (UbcH5a/b/c), and ATP as indicated. Polyubiquitin chain synthesis (top gel) and TRAIP autoubiquitylation (bottom gel) were detected by immunoblotting the reactions with ubiquitin and TRAIP antibody, respectively. Notably, rTRAIPR18C was much more compromised in forming free polyubiquitin chains in this assay than it was in ubiquitylating rCMG (see Fig. 2d). The data suggest that the interaction between TRAIP and CMG can suppress, to a great extent, the profound ubiquitylation defect of the R18C mutation.
f, pCTRL-lacO and pICL-lacOPt were replicated in undepleted extract as in c and recovered. Samples were treated with the indicated DUBs and blotted for the indicated proteins.
g, pCTRL-lacO and pICL-lacOPt pre-bound with LacR were replicated in undepleted extract as in c. At the time of IPTG addition to release the LacR array and allow fork convergence, 100 µM recombinant ubiquitin (wild-type or various lysine-to-arginine mutants) was added to the extract (which contains ~8 µM endogenous ubiquitin) and incubated for 1 hr. The plasmid was recovered and blotted for the indicated proteins.
h, Extracts used in g were blotted for ubiquitin. Some ubiquitin mutants contain a di-ubiquitin species (marked with asterisk). Whether this arises upon addition to extract is unclear.
Extended Data Fig. 6 |. AP-ICL repair by NEIL3 requires TRAIP.

a, Analysis of chromatin-associated proteins during replication of pICL-lacOPt or pICL-lacOAP in undepleted extract in the presence and absence of Geminin, as indicated. At different times after replication initiation, chromatin was recovered and blotted for the indicated proteins.
b, pICL-lacOPt and pICL-lacOAP were replicated in undepleted extract supplemented with Culi, Geminin, and p97i, as indicated, and analyzed as in Fig. 1b.
c, The extracts used in the replication reaction shown in Fig. 3a were blotted for TRAIP.
d, Extracts used in one of the reactions quantified in Fig. 3b were analyzed as in c.
e and f, pICLAP was replicated in the extracts shown in Extended Data Fig. 2h (e) and Extended Data Fig. 2f (f) with [α-32P]dATP and analyzed as in Fig. 1b.
Extended Data Fig. 7 |. ICL repair by NEIL3 requires CMG association with chromatin.

a, Analysis of proteins associated with pICLAP during replication with NEIL3-depleted extract supplemented with rNEIL3WT or catalytically inactive rNEIL3K60A, p97i, and Culi. At the indicated times after replication initiation, chromatin was recovered and blotted for the indicated proteins. Consistent with NEIL3 dissociating rapidly after unhooking, rNEIL3K60A was recovered more efficiently with pICLAP than rNEIL3WT.
b, pICLAP was replicated with NEIL3-depleted extract supplemented with rNEIL3WT or rNEIL3K60A, p97i, and Culi, as indicated, and analyzed as in Fig. 1b.
c, The extracts used in Fig. 3c were blotted for TRAIP. Non-specifically detected proteins are marked with asterisks.
d, If NEIL3 activity is coupled to ubiquitylated CMG, NEIL3 should only function before CMG has been unloaded. To test this prediction, we inhibited all unhooking events by depleting egg extracts of NEIL3 (to block the NEIL3 pathway) and FANCD2 (to block the FA pathway). At a late time point (90 min), we added back rNEIL3 to extract where CMG had been allowed to unload (-p97i), or extract where CMG unloading was prevented (+p97i). Our model predicts that rNEIL3 should unhook the ICL only in the latter setting. Top, schematic illustrating late addition of rNEIL3 to NEIL3- and FANCD2-depleted egg extracts in the absence (left) or presence (right) of p97i. Bottom, replication of pICLAP in mock-, NEIL3-, or NEIL3- and FANCD2-depleted extracts in the presence of [α-32P]dATP. Extracts were supplemented with p97i as indicated and rNEIL3 was added at 90 min where indicated (black arrowheads). Replication intermediates were resolved and visualized as in Fig. 1b. Depletion of NEIL3 and FANCD2 blocked all unhooking of the AP-ICL, resulting in an accumulation of reversed forks (lane 9, green arrowhead). Addition of rNEIL3 at 90 min. in the absence of p97i (after CMG unloading) failed to induce unhooking, based on the persistence of the reversed forks (lanes 21-24). In contrast, when CMG unloading was prevented with p97i (lanes 25-30; note the persistence of Slow Figure 8 intermediates), late rNEIL3 addition led to efficient ICL unhooking, as seen from the rapid conversion of Slow Figure 8s to open circular and supercoiled species (lanes 34-36). This gel image was compressed vertically to fit the page.
e, To confirm the presence or absence CMG at the AP-ICL, DNA was recovered from the reactions described in d and subjected to nascent strand analysis as in Extended Data Fig. 3a. Top, extension products and nascent strands of the leftward fork. Bottom, nascent strands of the rightward fork. Black arrowheads, rNEIL3 addition. Depletion of NEIL3 and FANCD2 did not affect loss of the CMG footprint at −20 and caused persistence of nascent DNA strands at −1 (lanes 13-24), indicative of failure to unhook the ICL. Late addition of NEIL3 failed to stimulate further nascent strand extension (lanes 21-24), indicating that unhooking did not occur. Treatment with p97i caused persistence of the CMG footprint at −20 (lanes 25-30), consistent with retention of CMG at the ICL, and late addition of NEIL3 stimulated formation of full-length nascent strand extension products (lanes 34-36), indicative of efficient unhooking. Taken together, the data in d and e strongly suggest that NEIL3 activity is coupled to the presence of CMG at the site of the ICL, although we cannot rule out that NEIL3 activity is suppressed by downstream events, such as fork reversal, that depend on CMG unloading.
Extended Data Fig. 8 |. The zinc-finger domains of NEIL3 contribute to its recruitment to the replication fork.
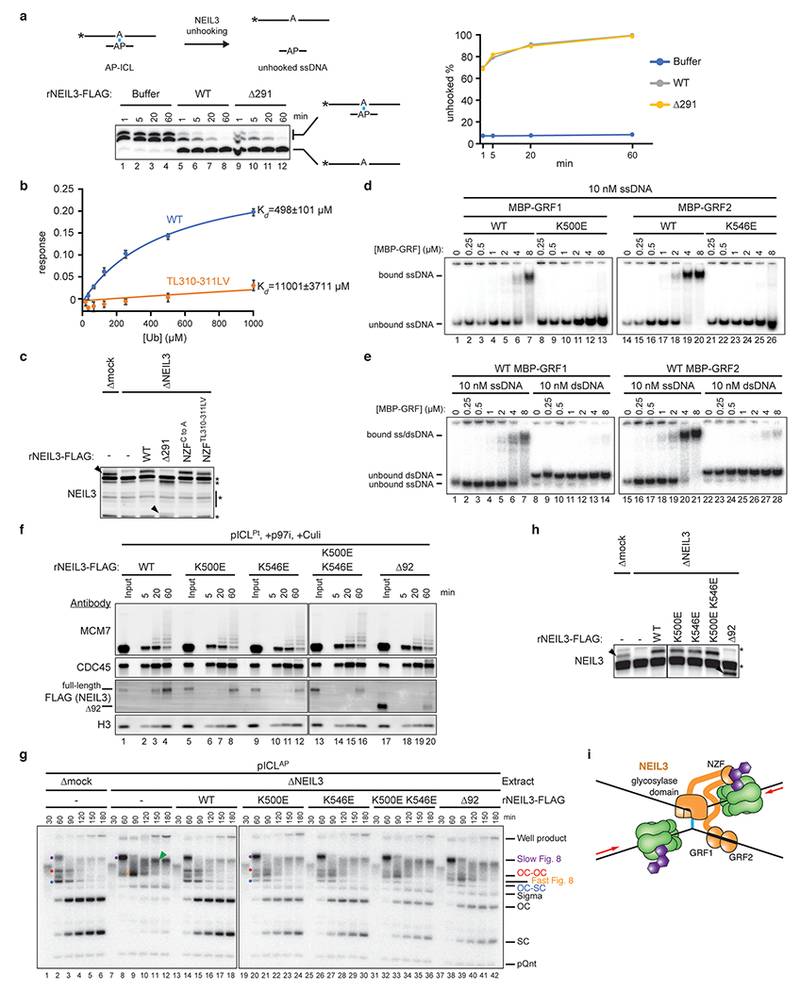
a, Left, to determine whether rNEIL3Δ291 is catalytically active, a model AP-ICL substrate comprising a synthetic 5′-radiolabeled 24mer oligonucleotide cross-linked to a ~3mer was mixed with rNEIL3Δ291 or rNEIL3WT. Cross-linked and unhooked species were resolved by denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and visualized by autoradiography. Asterisks indicate the 32P radiolabel. Note that the cross-linked species migrates as a doublet due to heterogeneity in the bottom strand following RNase digestion (see Methods for details). Right, quantification of unhooking. Equivalent results were obtained in three independent experiments, which show that rNEIL3Δ291 retains full glycosylase activity.
b, Interaction of the NEIL3 NPL4-type zinc finger (NZF; residues 300 to 328) with ubiquitin. GST-NEIL3 NZF fusion protein (WT or TL,LV substituted) was immobilized on a biosensor tip and monoubiquitin binding was measured by biolayer interferometry (BLI). The ubiquitin binding response was corrected for non-specific binding to GST and plotted as a function of ubiquitin concentration. Error bars represent standard error of the mean from three independent experiments.
c, Extracts used in Fig. 3e were blotted for NEIL3. Black arrowheads, NEIL3-specific bands. rNEIL3Δ291 is not efficiently detected by the NEIL3-specific primary antibody. Non-specifically detected proteins are marked with asterisks.
d and e, To test whether the two GRF zinc fingers in NEIL3 interact with ssDNA, we expressed each individually and performed electrophoretic mobility shift assays. rMBP-NEIL3 GRF zinc finger fusion proteins (wild-type or substituted) were incubated with 5′-radiolabeled 25-mer ssDNA or dsDNA. Bound and unbound DNAs were resolved by native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and visualized by autoradiography. This analysis reveals that both GRF domains bind specifically to ssDNA.
f, Analysis of proteins associated with pICLPt during replication in undepleted extract in the presence of p97i and Culi. Extracts were supplemented with wild-type or mutated rNEIL3. At different times, chromatin was recovered and blotted for the indicated proteins. The individual GRF substitutions modestly affected recovery of rNEIL3 upon pICL pull-down while combination of the substitutions or deletion of both GRF zinc fingers strongly reduced rNEIL3 recovery, indicating that interactions mediated by the GRF zinc fingers promote recruitment of NEIL3 to an ICL.
g, pICLAP was replicated in mock- or NEIL3-depleted extracts supplemented with wild-type or mutated NEIL3 as indicated and analyzed as in Fig. 1b. Relative to rNEIL3WT, rNEIL3 with substitutions in either GRF zinc finger that abolish ssDNA binding (K500E and K546E) exhibited modest defects in pICLAP unhooking that were exacerbated when the substitutions were combined, indicating that interactions between the GRF zinc fingers and ssDNA contribute to ICL repair.
h, Extracts used in the replication reactions shown in g, were blotted for NEIL3. Non-specifically detected proteins are marked with asterisks.
i, Model for recruitment of NEIL3 to chromatin by zinc finger-mediated interactions. Upon replication fork convergence at an ICL, TRAIP-dependent CMG ubiquitylation recruits NEIL3 through direct interactions between NEIL3’s NZF domain and ubiquitin. Association of NEIL3 with chromatin is further enhanced by interactions between the tandem GRF zinc fingers and single stranded DNA, possibly on the lagging strand template.
Extended Data Fig. 9 |. Knockout of the FA and NEIL3 pathways have additive effects on ICL sensitivity in mammalian cells.

a, Immunoblot analysis of NEIL3 expression in wild-type, NEIL3, and FANCL/NEIL3 knockout HAP1 cell lines. Histone H3 was detected as a loading control. Non-specifically detected proteins are marked with asterisks.
b, Schematic of FANCL CRISPR targeting. (i) Human FANCL exon 10, sgRNA binding sites, and homology arm targets, (ii) FANCL-Puro targeting construct with homology arms flanking exon 10, (iii) Targeted FANCL allele with integrated puromycin resistance cassette.
c, Detection of the integrated puromycin resistance cassette in HAP1 cells by FANCL long-range PCR.
d, Analysis of FANCD2 ubiquitylation in MMC-treated wild-type, FANCL, and FANCL/NEIL3 knockout HAP1 cell lines to confirm FANCL knockout. Vinculin was detected as a loading control. FANCL is the catalytic subunit of the FA core complex, which ubiquitylates FANCD2.
e, Neil3 qRT-PCR confirming gene disruption in CH12 cell lines. ND, not detected.
f, Analysis of FANCD2 ubiquitylation in mitomycin C-treated CH12 Fancb single and Neil3/Fancb double knockout cell lines to confirm Fancb knockout. Vinculin was detected as a loading control. A non-specifically detected protein is marked with an asterisk.
g, Cell viability of wild-type, Fancb, Neil3, or Fancb/Neil3 knockout CH12 cells after exposure to trioxsalen and UV-A irradiation. Two independent clones were used for the single mutants and three independent clones were used for the double mutant. Error bars, standard error of the mean. We speculate that, relative to HAP1 cells, CH12 cells may be more reliant on the FA pathway to repair trioxsalen-induced damage due to lower expression levels of NEIL3.
Extended Data Fig. 10 |. Model of TRAIP’s action in interphase and mitosis.
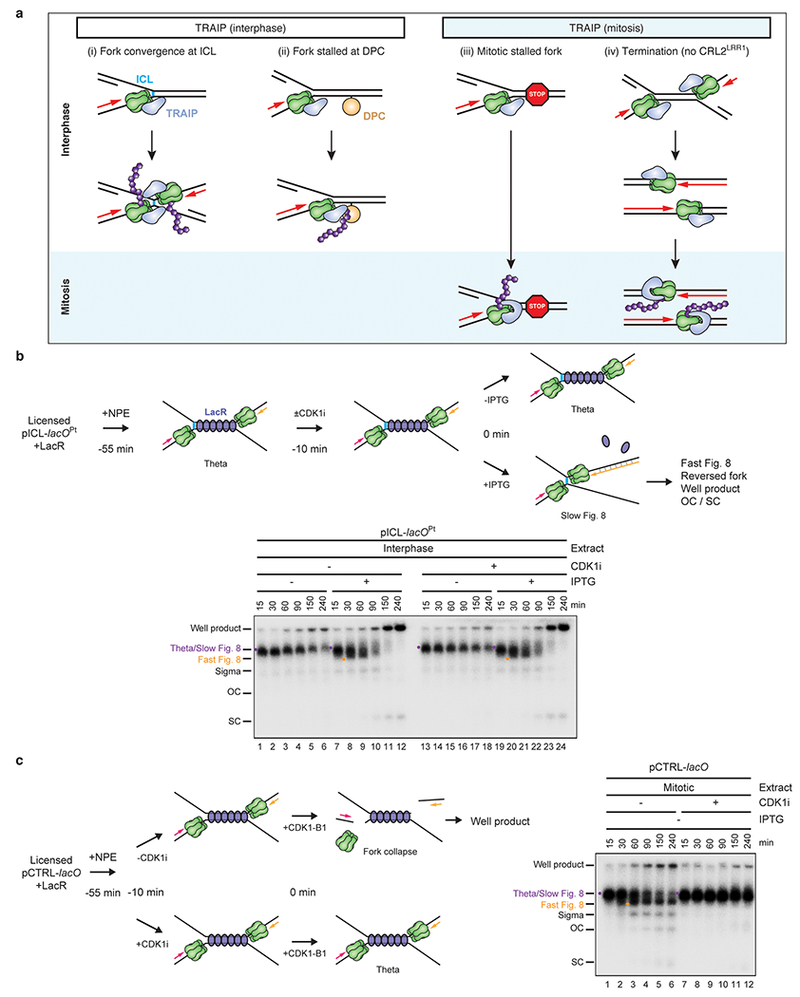
a, TRAIP (blue) travels with the replisome and associates with CMG, directly or indirectly (i-iv, top). In interphase, TRAIP is oriented such that its E2 (whose identity is unknown) points ahead of the replisome. As a result, TRAIP cannot ubiquitylate the CMG it is associated with, but it can ubiquitylate any protein that lies in the replisome’s path. TRAIP can thus ubiquitylate CMG in trans when two replisomes meet (i), and it can ubiquitylate DPCs that block the path of the replisome (ii). We speculate that TRAIP ubiquitylates any proteinaceous structure that causes extended stalling of the replisome. In mitosis, TRAIP undergoes a conformational change so that it can ubiquitylate the CMG with which it is associated in cis. As a result, in mitosis, stalled forks undergo TRAIP-dependent CMG ubiquitylation in the absence of fork convergence (iii) (Deng et al., in press). We propose that TRAIP does not ubiquitylate terminated CMGs in interphase because they rapidly move past each other29, precluding ubiquitylation by the forward-pointing TRAIP (iv, middle). However, upon mitotic entry, terminated CMGs undergo TRAIP-dependent ubiquitylation in cis (iv, bottom)(Deng et al., in press). Importantly, TRAIP-dependent CMG unloading in interphase egg extracts is not dependent on residual CDK1 activity (b and c), indicating that TRAIP is regulated differently in interphase and mitosis.
b, In interphase egg extracts, TRAIP travels with DNA replication forks but ubiquitylates CMGs only when forks converge. In the presence of Cyclin B1-CDK1, TRAIP is activated in the absence of fork convergence (Deng et al., in press)(summarized in a). We therefore wanted to know whether TRAIP-dependent CMG unloading in interphase egg extract depends on residual CDK1 activity. Top, reaction scheme to determine whether the action of TRAIP at ICLs in interphase egg extract requires residual CDK1 activity. Replication of pICL-lacOPt with a pre-assembled LacR array was initiated by addition of NPE (−55 min). Forty-five min after initiation (−10 min), reactions were supplemented with buffer or the CDK1 inhibitor RO-3306 (CDK1i) and allowed to incubate for an additional 10 min; CDK1i was added late to avoid inhibition of replication initiation. The LacR array was then released with addition of IPTG to trigger fork convergence and ICL repair (0 min). In a control, buffer instead of IPTG was added to maintain the LacR array and thereby prevent fork convergence. At the indicated times after IPTG addition, samples were collected and analyzed as in Fig. 1b to look for evidence of CMG unloading and ICL processing. Bottom, experiment described in top scheme. Fork stalling at the boundaries of the LacR array lead to a theta structure (lanes 1, 7, 13, 19). Upon addition of IPTG, theta was converted to Slow Figure 8, Fast Figure 8 (co-migrating with theta), and well product with equal efficiency in the presence and absence of CDK1i (compare lanes 7-12 and 19-24). The data suggest that CDK1 is not required for CMG unloading or ICL repair.
c, Left, reaction scheme of a control experiment to ensure that the addition of CDK1i in b blocked CDK1 activity. As recently described (Deng et al., in press), when replication forks are stalled at a LacR array, the subsequent addition of Cyclin B1-CDK1 promotes TRAIP-dependent CMG unloading and fork breakage, alternative end joining, and the formation of aberrant replication products that migrate in the well of an agarose gel. To verify that CDK1 was effectively inhibited in a, we used this CDK1-dependent well-product formation as an assay. To this end, replication of pCTRL-lacO with a pre-assembled LacR array was initiated (−55 min) by addition of NPE. Forty-five min after initiation (−10 min), reactions were supplemented with CDK1i or buffer and allowed to incubate for an additional 10 min. Cyclin B1-CDK1 was then added to activate fork breakage and well product formation (0 min). Right, experiment described in left scheme. As expected, addition of Cyclin B1-CDK1 in the absence of CDK1i led to the formation of well products (lanes 25-30) but not in the presence of CDK1i (lanes 31-36). Note that the experiments in b and c were performed in parallel; extracts were aliquoted for the various conditions described at 0 min. Therefore, the CDK1i effectively inhibited CDK1-dependent activation of TRAIP. We conclude that TRAIP activation at ICLs does not depend on residual CDK1 activity.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements:
We thank David Pellman and Walter lab members for comments on the manuscript and Kelly Arnett (Center for Macromolecular Interactions) for help with BLI experiments. J.C.W. is supported by NIH grant HL098316 and a gift from the family of Jonathan G. Wiseman. R.A.W. is supported by American Cancer Society postdoctoral fellowship 131415-PF-17-168-01-DMC, D.R.S. by NIH award K99GM129422, D.R.S. and G.C. by Jane Coffin Childs postdoctoral fellowships, J.L.S. by a Damon Runyon postdoctoral fellowship, M.W. by the Cancer Research UK Clinician Scientist Fellowship, and E.L. by NIH award F31GM122277. J.C.W is a Howard Hughes Medical Institute Investigator and an American Cancer Society Research Professor.
Footnotes
Supplementary Information:
Supplementary Table 1 is available online.
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
References:
- 1.Semlow DR, Zhang J, Budzowska M, Drohat AC & Walter JC Replication-Dependent Unhooking of DNA Interstrand Cross-Links by the NEIL3 Glycosylase. Cell 167, 498–511, doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.09.008 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Raschle M et al. Mechanism of replication-coupled DNA interstrand crosslink repair. Cell 134, 969–980 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Price NE, Catalano MJ, Liu S, Wang Y & Gates KS Chemical and structural characterization of interstrand cross-links formed between abasic sites and adenine residues in duplex DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 43, 3434–3441, doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv174 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kottemann MC & Smogorzewska A Fanconi anaemia and the repair of Watson and Crick DNA crosslinks. Nature 493, 356–363, doi: 10.1038/nature11863 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zhang J et al. DNA interstrand cross-link repair requires replication-fork convergence. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22, 242–247, doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2956 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Fullbright G, Rycenga HB, Gruber JD & Long DT p97 Promotes a Conserved Mechanism of Helicase Unloading during DNA Cross-Link Repair. Mol Cell Biol 36, 2983–2994, doi: 10.1128/MCB.00434-16 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Amunugama R et al. Replication Fork Reversal During DNA Interstrand Crosslink Repair Requires CMG Unloading. Cell Reports 23, 3419–3428 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Knipscheer P et al. The Fanconi anemia pathway promotes replication-dependent DNA interstrand cross-link repair. Science 326, 1698–1701 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Massaad MJ et al. Deficiency of base excision repair enzyme NEIL3 drives increased predisposition to autoimmunity. J Clin Invest 126, 4219–4236, doi: 10.1172/JCI85647 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Parmar K, D’Andrea A & Niedernhofer LJ Mouse models of Fanconi anemia. Mutat Res 668, 133–140, doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.03.015 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sejersted Y et al. Endonuclease VIII-like 3 (Neil3) DNA glycosylase promotes neurogenesis induced by hypoxia-ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108, 18802–18807, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106880108 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Torisu K, Tsuchimoto D, Ohnishi Y & Nakabeppu Y Hematopoietic tissue-specific expression of mouse Neil3 for endonuclease VIII-like protein. J Biochem 138, 763–772, doi: 10.1093/jb/mvi168 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chapard C, Hohl D & Huber M The role of the TRAF-interacting protein in proliferation and differentiation. Exp Dermatol 21, 321–326, doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2012.01477.x (2012). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Harley ME et al. TRAIP promotes DNA damage response during genome replication and is mutated in primordial dwarfism. Nat Genet 48, 36–43, doi: 10.1038/ng.3451 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Raschle M et al. DNA repair. Proteomics reveals dynamic assembly of repair complexes during bypass of DNA cross-links. Science 348, 1253671, doi: 10.1126/science.1253671 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hoffmann S et al. TRAIP is a PCNA-binding ubiquitin ligase that protects genome stability after replication stress. J Cell Biol 212, 63–75, doi: 10.1083/jcb.201506071 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Huang J et al. The DNA Translocase FANCM/MHF Promotes Replication Traverse of DNA Interstrand Crosslinks. Mol Cell 52, 434–446, doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2013.09.021 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mutreja K et al. ATR-Mediated Global Fork Slowing and Reversal Assist Fork Traverse and Prevent Chromosomal Breakage at DNA Interstrand Cross-Links. Cell Rep 24, 2629–2642 e2625, doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.08.019 (2018). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Long DT, Joukov V, Budzowska M & Walter JC BRCA1 promotes unloading of the CMG helicase from a stalled DNA replication fork. Mol Cell 56, 174–185, doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.08.012 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Moreno SP, Bailey R, Campion N, Herron S & Gambus A Polyubiquitylation drives replisome disassembly at the termination of DNA replication. Science 346, 477–481, doi: 10.1126/science.1253585 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dewar JM, Low E, Mann M, Raschle M & Walter JC CRL2(Lrr1) promotes unloading of the vertebrate replisome from chromatin during replication termination. Genes Dev 31, 275–290, doi: 10.1101/gad.291799.116 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Larsen NB et al. Mechanism of replication-coupled DNA-protein crosslink proteolysis by SPRTN and the proteasome Mol Cell in press, doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.11.024 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Liu M et al. Expression and purification of active mouse and human NEIL3 proteins. Protein Expr Purif 84, 130–139, doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2012.04.022 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Wang B et al. Structure and ubiquitin interactions of the conserved zinc finger domain of Npl4. J Biol Chem 278, 20225–20234, doi: 10.1074/jbc.M300459200 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wallace BD et al. APE2 Zf-GRF facilitates 3’-5’ resection of DNA damage following oxidative stress. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114, 304–309, doi: 10.1073/pnas.1610011114 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Dutrillaux B, Aurias A, Dutrillaux AM, Buriot D & Prieur M The cell cycle of lymphocytes in Fanconi anemia. Hum Genet 62, 327–332 (1982). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sparks J et al. The CMG helicase bypasses DNA protein cross-links to facilitate their repair. Cell 176, 167–181, doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2018.10.053 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lebofsky R, Takahashi T & Walter JC DNA replication in nucleus-free Xenopus egg extracts. Methods Mol Biol 521, 229–252 (2009). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Dewar JM, Budzowska M & Walter JC The mechanism of DNA replication termination in vertebrates. Nature 525, 345–350, doi: 10.1038/nature14887 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Joukov V, Chen J, Fox EA, Green JB & Livingston DM Functional communication between endogenous BRCA1 and its partner, BARD1, during Xenopus laevis development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98, 12078–12083 (2001). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Walter J & Newport J Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication: origin unwinding and sequential chromatin association of Cdc45, RPA, and DNA polymerase alpha. Mol Cell 5, 617–627 (2000). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Byun TS, Pacek M, Yee MC, Walter JC & Cimprich KA Functional uncoupling of MCM helicase and DNA polymerase activities activates the ATR-dependent checkpoint. Genes Dev 19, 1040–1052 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wohlschlegel JA, Dhar SK, Prokhorova TA, Dutta A & Walter JC Xenopus mcm10 binds to origins of DNA replication after mcm2–7 and stimulates origin binding of cdc45. Mol Cell 9, 233–240. (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pacek M, Tutter AV, Kubota Y, Takisawa H & Walter JC Localization of MCM2-7, Cdc45, and GINS to the Site of DNA Unwinding during Eukaryotic DNA Replication. Mol Cell 21, 581–587 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kochaniak AB et al. Proliferating cell nuclear antigen uses two distinct modes to move along DNA. J Biol Chem 284, 17700–17710 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Rosado IV, Langevin F, Crossan GP, Takata M & Patel KJ Formaldehyde catabolism is essential in cells deficient for the Fanconi anemia DNA-repair pathway. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol 18, 1432–1434, doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2173 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Budzowska M, Graham TG, Sobeck A, Waga S & Walter JC Regulation of the Rev1-pol zeta complex during bypass of a DNA interstrand cross-link. EMBO J 34, 1971–1985, doi: 10.15252/embj.201490878 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Michel MA et al. Assembly and specific recognition of k29- and k33-linked polyubiquitin. Mol Cell 58, 95–109, doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.042 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Knipscheer P, Raschle M, Scharer OD & Walter JC Replication-coupled DNA interstrand cross-link repair in Xenopus egg extracts. Methods Mol Biol 920, 221–243, doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-998-3_16 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Graham TG, Walter JC & Loparo JJ Two-Stage Synapsis of DNA Ends during Non-homologous End Joining. Mol Cell 61, 850–858, doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.02.010 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hemsley A, Arnheim N, Toney MD, Cortopassi G & Galas DJ A simple method for site-directed mutagenesis using the polymerase chain reaction. Nucleic Acids Res 17, 6545–6551 (1989). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Trowitzsch S, Bieniossek C, Nie Y, Garzoni F & Berger I New baculovirus expression tools for recombinant protein complex production. J Struct Biol 172, 45–54, doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2010.02.010 (2010). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ilves I, Petojevic T, Pesavento JJ & Botchan MR Activation of the MCM2–7 helicase by association with Cdc45 and GINS proteins. Mol Cell 37, 247–258 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Liu M et al. The mouse ortholog of NEIL3 is a functional DNA glycosylase in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107, 4925–4930, doi: 10.1073/pnas.0908307107 (2010). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Franken NA, Rodermond HM, Stap J, Haveman J & van Bree C Clonogenic assay of cells in vitro. Nat Protoc 1, 2315–2319, doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.339 (2006). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Vos JM & Hanawalt PC Processing of psoralen adducts in an active human gene: repair and replication of DNA containing monoadducts and interstrand cross-links. Cell 50, 789–799 (1987). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Derheimer FA, Hicks JK, Paulsen MT, Canman CE & Ljungman M Psoralen-induced DNA interstrand cross-links block transcription and induce p53 in an ataxia-telangiectasia and rad3-related-dependent manner. Mol Pharmacol 75, 599–607, doi: 10.1124/mol.108.051698 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Walter J, Sun L & Newport J Regulated chromosomal DNA replication in the absence of a nucleus. Mol Cell 1, 519–529 (1998). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Klein Douwel D et al. XPF-ERCC1 acts in Unhooking DNA interstrand crosslinks in cooperation with FANCD2 and FANCP/SLX4. Mol Cell 54, 460–471, doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.015 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Long DT, Raschle M, Joukov V & Walter JC Mechanism of RAD51-dependent DNA interstrand cross-link repair. Science 333, 84–87, doi: 10.1126/science.1204258 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Fu YV et al. Selective Bypass of a Lagging Strand Roadblock by the Eukaryotic Replicative DNA Helicase. Cell 146, 931–941, doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.045 (2011). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sonneville R et al. CUL-2LRR-1 and UBXN-3/FAF1 drive replisome disassembly during DNA replication termination and mitosis. Nat. Cell Biol 19, 468–479 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All relevant data are available from the authors and/or are included with this Letter. Source images are available in Supplementary Fig. 1.


