Abstract
Transferrin receptor 2 (Tfr2) is mainly expressed in the liver and controls iron homeostasis. Here, we identify Tfr2 as a regulator of bone homeostasis that inhibits bone formation. Mice lacking Tfr2 display increased bone mass and mineralization independent of iron homeostasis and hepatic Tfr2. Bone marrow transplantation experiments and studies of cell-specific Tfr2 knockout mice demonstrate that Tfr2 impairs BMP-p38MAPK signaling and decreases expression of the Wnt inhibitor sclerostin specifically in osteoblasts. Reactivation of MAPK or overexpression of sclerostin rescues skeletal abnormalities in Tfr2 knockout mice. We further show that the extracellular domain of Tfr2 binds BMPs and inhibits BMP-2-induced heterotopic ossification by acting as a decoy receptor. These data indicate that Tfr2 limits bone formation by modulating BMP signaling, possibly through direct interaction with BMP either as a receptor or as a co-receptor in a complex with other BMP receptors. Finally, the Tfr2 extracellular domain may be effective in the treatment of conditions associated with pathological bone formation.
Iron is indispensable for red blood cell production, bacterial defense, and cellular respiration1, however, iron excess is cytotoxic. Therefore, systemic iron levels are maintained in a narrow range to avoid iron deficiency and anemia, or iron overload leading to multi-organ damage. Amongst other organs, bone is highly susceptible to changes in iron homeostasis. Bone mineral density is negatively associated with systemic iron concentrations2 and patients suffering from hereditary hemochromatosis, a disorder characterized by iron overload, develop premature osteoporosis3. Despite these observations, the relationship between iron homeostasis and bone turnover remains largely unexplored.
Systemic iron concentrations are maintained by balancing dietary iron absorption and iron recycling from the reticuloendothelial system1. Hepcidin is a hepatic peptide hormone and key regulator of iron homeostasis4. By binding to ferroportin, an iron exporter, hepcidin causes the internalization and degradation of ferroportin, thereby limiting iron export into the circulation. Dysregulation of this mechanism leads to iron overload. Accordingly, mutations in the gene encoding hepcidin or hepcidin-regulating genes cause hereditary hemochromatosis5.
Transferrin receptor 2 (Tfr2) is a key regulator of hepcidin. Similar to humans, mice with global or liver-specific deletion of Tfr2 accumulate iron in the liver6–9. Tfr2 is proposed to control iron homeostasis by regulating hepcidin expression and has two isoforms: Tfr2α, which represents the full-length protein and regulates iron homeostasis in the liver, and Tfr2β, which lacks the intracellular and transmembrane domains and plays an important role in iron efflux in the spleen8. To date, the mechanisms whereby Tfr2 senses and regulates systemic iron concentrations remain incompletely understood. However, holo-transferrin can bind Tfr2 and prolong its half-life10. Thus, Tfr2 has been postulated to sense circulating iron and activate hepcidin in response to elevated transferrin saturation.
Tfr2-deficient hepatocytes have reduced bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) and p38MAPK/ERK signaling11–13, implicating these pathways in its signal transduction. Although BMP signaling is mostly known for its critical role in bone development and postnatal bone homeostasis14, it has also emerged as an important regulator of iron homeostasis. Deficiency of several components of the BMP pathway (Bmpr1a, Bmpr2, Acvr1, Acvr2a, Smad4, Bmp2, Bmp6) or their pharmacological inhibition result in iron overload15–20. Moreover, hemojuvelin, another regulator of hepcidin expression, has been identified as a hepatic BMP co-receptor16, further linking BMP signaling to iron homeostasis. Importantly, activating mutations in one of the BMP receptors that controls iron homeostasis, ACVR1, cause a rare human disorder, fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP), which is characterized by excessive heterotopic ossification21. Thus, balancing BMP signaling is necessary to maintain bone and iron homeostasis in a physiological range.
Recent evidence indicates Tfr2 is not restricted to the liver, but is also expressed in erythroid progenitors to ensure their proper differentiation8,22,23. As BMP signaling has a critical role in the skeleton14,24, we hypothesized that Tfr2 may possess additional extrahepatic functions and regulate bone homeostasis. Here, we demonstrate that Tfr2 is a novel negative regulator of bone turnover. By binding BMP ligands, Tfr2 activates p38MAPK signaling in osteoblasts to induce expression of the Wnt inhibitor sclerostin and limit bone formation. Finally, by taking advantage of the BMP-binding property of the Tfr2 extracellular domain, we show that this protein fragment effectively inhibits heterotopic ossification in two preclinical models, suggesting it may also be efficacious to treat disorders of pathological bone formation.
Results
Tfr2-deficiency leads to high bone mass
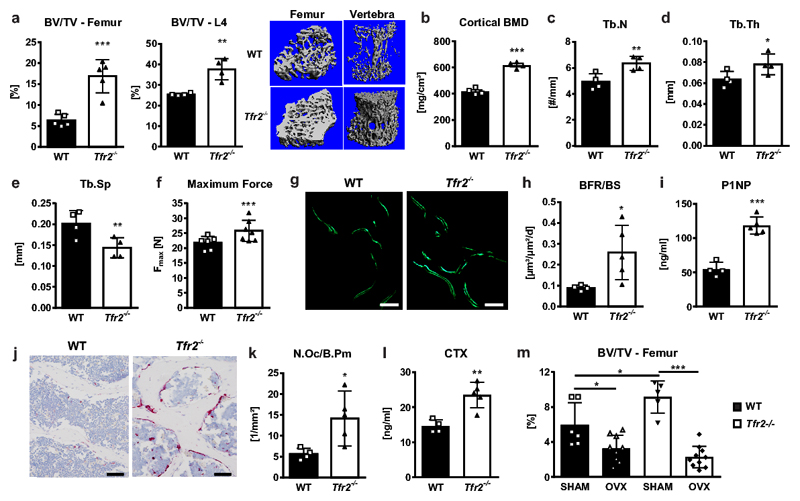
To investigate whether the iron-sensing receptor Tfr2 regulates bone homeostasis, we studied Tfr2-/- mice, which are iron overloaded. Consistent with previous reports8,25, the transferrin saturation, serum iron and ferritin concentrations, and iron content in the liver were increased in Tfr2-/- mice compared to wild-type (WT) mice (Suppl. Fig 1a-d). In addition, atomic absorptiometry revealed a higher iron content in the cortical bone of Tfr2-/- mice (Suppl. Fig. 1e). As iron overload is associated with bone loss3, we expected a decreased bone volume in Tfr2-/- mice. However, in contrast to the low bone mass phenotype of mice with diet-induced iron overload and in different mouse models of hemochromatosis, including Hfe-/- mice26 and FpnC326S mutant mice27 (Suppl. Fig. 2a-c), Tfr2-/- mice displayed a 1.5-3-fold higher trabecular bone volume in the femur and the vertebrae and a 1.5-fold higher cortical bone density compared to WT controls (Fig. 1a-b). High bone mass was independent of sex and declined with age (Suppl. Fig. 3a-b). At a structural level, Tfr2-/- vertebrae had increased trabecular number (Tb.N) and thickness (Tb.Th) and decreased separation (Tb.Sp) (Fig. 1c-e). Furthermore, Tfr2-/- mice had increased trabecular bone micro-mineralization density (Suppl. Fig. 3c), which together with the increased bone volume enhanced bone strength (Fig. 1f).
Figure 1. Tfr2 deficiency results in high bone mass.
(a-l) The bones and serum bone turnover markers of ten-week-old male WT or Tfr2-/- mice were analyzed using µCT, histology, and ELISAs. (a) 3D reconstruction and quantitation of the bone volume/total volume (BV/TV) of the distal femur and the fourth vertebral body of WT and Tfr2-/- mice. Femur, n=5 per group; vertebral body, n=4 per group. (b) Cortical bone mineral density (BMD) at the femoral mid-shaft. n=4 per group. (c-e) Quantitation of vertebral trabecular number (Tb.N), trabecular thickness (Tb.Th), and trabecular separation (Tb.Sp). n=4 per group. (f) Maximum force at the femoral shaft assessed by 3-point-bending. (WT, n=6; Tfr2-/-, n=7). (g) Representative histological sections from the third vertebral body of WT and Tfr2-/- mice showing calcein double staining. Bar indicates 100 µm. These experiments were repeated four times with similar results. (h) Quantification of the bone formation rate/bone surface (BFR/BS). (WT, n=4; Tfr2-/-, n=5). (i) Quantification of serum P1NP as a marker of bone formation. (WT, n=4; Tfr2-/-, n=5). (j) Representative histological tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase sections from the fourth vertebral body of WT and Tfr2-/- mice showing osteoclasts stained in pink. Bar indicates 100 µm. These examinations were performed four times with similar results. (k) Quantification of the number of osteoclasts/bone perimeter (N.Oc/B.Pm). (WT, n=4; Tfr2-/-, n=5). (l) Quantification of serum CTX as a marker of bone resorption. (WT, n=4; Tfr2-/-, n=5). (a-f, h-i, k-l) A two-tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis. (m) µCT analysis of femoral bone of 12-week-old sham-operated (SHAM) or ovariectomized (OVX) WT and Tfr2-/- mice. (WT Sham, n=6-10; WT OVX, n=9; Tfr2-/- Sham, n=5; Tfr2-/- OVX, n=10). Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test was used for statistical analysis. Data in all subpanels are presented as mean±SD with significances defined as *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
We performed dynamic and static histomorphometry to determine whether the high bone mass phenotype was a consequence of increased bone formation or decreased bone resorption. Tfr2 deficiency resulted in an increase in both osteoblast and osteoclast parameters. The bone formation rate and the serum concentration of the bone formation marker pro-collagen type I N-terminal peptide (P1NP) were elevated more than two-fold in Tfr2-/- mice, and the number of osteoclasts and serum concentration of the bone resorption marker C-terminal telopeptide of type I collagen (CTX) were similarly increased (Fig. 1g-l). The high bone turnover was present in both males and females at all ages studied (Suppl. Fig. 3d-e). Interestingly, Tfr2-/- mice were not protected from ovariectomy-induced bone loss, but lost even more bone than WT mice (Fig. 1m). Taken together, these data demonstrate that Tfr2 does not only control iron homeostasis, but also bone turnover.
High bone mass in Tfr2-deficient mice is independent of hepatic iron status or Tfr2 expression in the liver
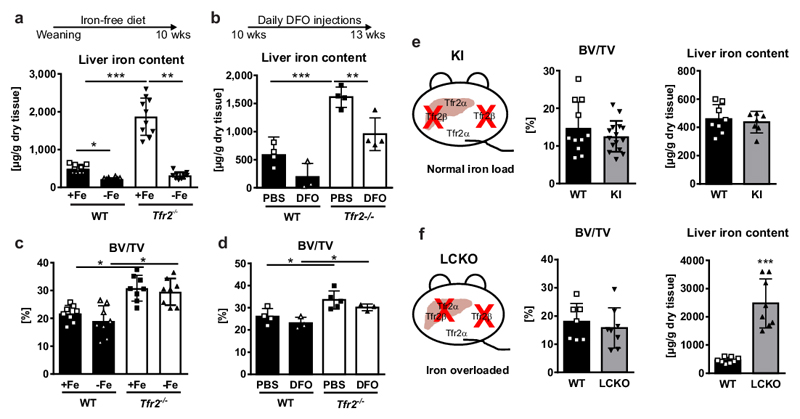
As Tfr2-/- mice have iron overload and high bone mass, whereas iron overload is commonly associated with decreased bone mass3,28, we investigated whether abnormal iron metabolism contributes to the skeletal phenotype in Tfr2-/- mice. Thus, Tfr2-/- mice received an iron-free diet for 8 weeks from weaning or were treated with the iron-chelator deferoxamine for three weeks from 10 weeks of age. Despite successful iron depletion by both regimens, bone mass remained elevated in Tfr2-/- mice (Fig. 2a-d), indicating the high bone mass phenotype in Tfr2-/- mice is independent of the hepatic iron status.
Figure 2. High bone mass in Tfr2-/- mice is independent of iron overload and the hepatic function of Tfr2.
(a, c) Male WT and Tfr2-/- mice received a purified diet without iron (-Fe) starting from weaning until the age of 10 weeks. Control mice received a standard diet with 0.2 g iron/kg food (+Fe). (a) Liver iron content was determined on dried tissue using photometry. (mean ±SD; n=10 per group). (c) Bone volume/total volume (BV/TV) was assessed using µCT. (mean±SD; WT +Fe n=9; WT –Fe, Tfr2-/- +Fe and Tfr2-/- -Fe, n=8 per group). (b, d) Ten-week-old female WT and Tfr2-/- mice received daily i.p injections of 250 mg/kg deferoxamine (DFO) or PBS for three weeks. At 13 weeks of age, mice were sacrificed to measure (b) iron liver content and (d) BV/TV. (n=3-5 per group). (a-d) Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test was used for statistical analysis. (e) Schematic representation of Tfr2 knock-in (KI) mice, which lack the Tfr2β isoform. BV/TV and iron liver content of 10-week-old male Tfr2 KI mice and control mice. (BV/TV, WT n=11, KI n=15; Liver iron, WT n=8, KI n=7). (f) Schematic representation of the Tfr2 setup of liver-specific Tfr2α knock-out (LCKO) mice on a Tfr2 KI background. BV/TV and liver iron content of 10-week-old male LCKO and WT mice. (n=8 per group). (e,f) A two-tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis. All data are presented as mean±SD. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
To corroborate these findings, we studied two distinct Tfr2 mutant mouse models, which globally lack Tfr2β but have contrasting Tfr2α expression that results in divergent abnormalities of iron homeostasis8: Tfr2 knock-in mice (KI) globally lack Tfr2β but have normal Tfr2α and thus normal iron parameters. By contrast, hepatocyte-specific Tfr2 knock-out (LCKO) mice globally lack Tfr2β, and have Tfr2α deficiency restricted to the liver, but are severely iron-overloaded. Both models had comparable bone volume fractions compared to controls (Fig. 2e-f), indicating that neither Tfr2β nor hepatic Tfr2α play a role in the control of bone homeostasis.
Tfr2-deficiency in osteoblasts drives the high bone mass phenotype
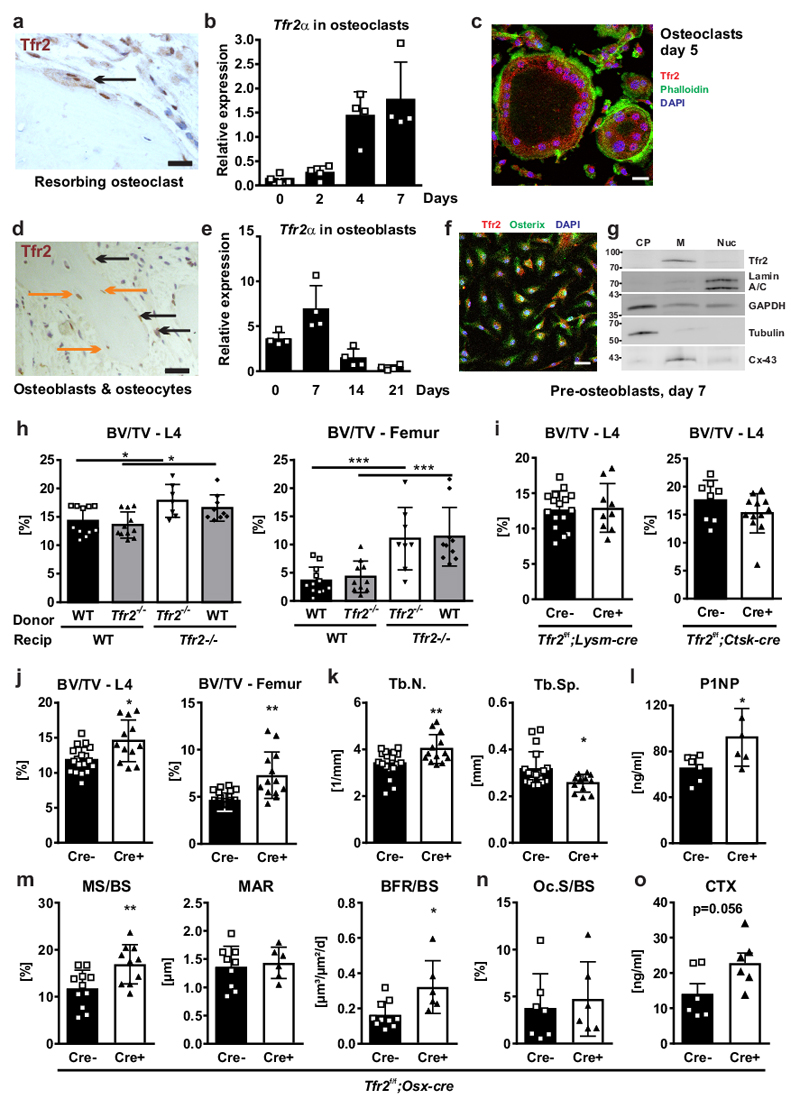
To explore whether Tfr2 regulates bone mass directly via its expression in skeletal cells, we determined expression of Tfr2α and Tfr2β in various mouse tissues. As expected, Tfr2α was predominantly expressed in the liver with the next highest expression in femoral cortical bone (Suppl. Fig. 4a). Tfr2β mRNA expression was also detected in femoral cortical bone, although at a much lower level (CT value spleen (positive control): 26, CT value bone: 32). Using an antibody that binds to the extracellular domain of Tfr2 and thus detects both Tfr2α and Tfr2β isoforms, we confirmed expression of Tfr2 in vertebral bone sections, showing Tfr2-positive osteoclasts, osteoblasts, and osteocytes (Fig. 3a, d). Staining of bone sections from Tfr2-/- mice showed no non-specific binding of the Tfr2 antibody (Suppl. Fig. 3b). Osteoclasts and osteoblasts differentiated from the bone marrow of WT mice both expressed Tfr2α and Tfr2β mRNA transcripts ex vivo but expression of Tfr2β was very low in each cell type (data for Tfr2β not shown). Tfr2α was readily detectable in osteoclasts and osteoblasts, with peak levels of expression in mature osteoclasts (day 7/7) and in immature osteoblasts (day 7/21) (Fig. 3b, e). Immunocytochemistry confirmed Tfr2 expression in osteoclasts and osterix-expressing osteoblasts that were differentiated ex vivo (Fig. 3c, f). Subcellular fractioning of osteoblasts further localized the majority of Tfr2 to the membrane fraction (Fig. 3g). A low signal was also detected in the cytoplasm.
Figure 3. Deficiency of Tfr2 in osteogenic cells increases bone mass.
(a, d) Immunohistochemical analysis of Tfr2 on vertebral bone of WT mice. One representative image is shown out of three. Arrows indicate Tfr2 expression in multinucleated osteoclasts and osteoblasts/osteocytes (osteoblasts: black arrows; osteocytes: orange arrows). Scale bar: 20 µm. (b, e) Tfr2α mRNA expression during osteoclast (b) and osteoblast (e) differentiation of WT cells (n=4). (c, f) Immunofluorescence staining for Tfr2 in mature osteoclasts (c) and immature osteoblasts (f). Scale bar: 20 µm. These staining were repeated twice with similar results. (g) Subcellular fractioning of day 7 osteoblast protein lysates from WT mice. One representative blot is shown out of three. CP: cytoplasm; M: membrane; Nuc: nuclear fraction. Cx-43: connexin-43. (h) Bone marrow was transplanted from 12-week-old male WT or Tfr2-/- mice into lethally irradiated 9-week-old male WT and Tfr2-/- recipient (recip) mice. After 16 weeks, the bone volume/total volume (BV/TV) was measured using µCT. (L4, WT-WT n=11, Tfr2-/--WT n=11, Tfr2-/--Tfr2-/- n=7, WT-Tfr2-/- n=9; Femur, WT-WT n=12, Tfr2-/--WT n=10, Tfr2-/--Tfr2-/- n=8, WT-Tfr2-/- n=10). Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test was used for statistical analysis. (i) BV/TV of the fourth lumbar vertebrae of 10-week-old male cre-positive and cre-negative Tfr2f/f;Lysm-Cre and Tfr2f/f;Ctsk-Cre mice. (Tfr2f/f; Lysm-cre, Cre- n=16, Cre+ n= 9; Tfr2f/f; CtskCre, Cre- n=8, Cre+ n=12). (j-o) Bone analysis of 10-week-old male cre-positive and cre-negative littermate control Tfr2f/f;Osx-Cre mice. (j) BV/TV (L4, Cre- n=18, Cre+ n=12; Femur, Cre- n=18, Cre+ n=13). (k) Trabecular number (Tb.N) and trabecular separation (Tb.Sp) (Tb.N., Cre- n=18, Cre+ n=13; Tb.Sp., Cre- n=19, Cre+ n=12). (l) Serum levels of P1NP. (n=6 per group). (m) Mineralizing surface per bone surface (MS/BS), mineral apposition rate (MAR), and bone formation rate per bone surface (BFR/BS) determined at the lumbar spine. (MS/BS, Cre- n=11, Cre+ n=10; MAR, Cre- n=9, Cre+ n=6; BFR, Cre- n=10, Cre+ n=6). (n) Osteoclast surface per bone surface (Oc.S/BS) analyzed at the lumbar spine. (Cre- n=7, Cre+ n=6). (o) Serum CTX levels (n=6 per group). (i-o) A two-tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis. All data are presented as mean±SD. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
To determine if Tfr2 in osteoclasts or in osteoblasts regulates bone turnover, we performed reciprocal bone marrow transplantations. In WT and Tfr2-/- mice, bone marrow transplantation had no effect on vertebral or femoral bone volume irrespective of donor genotype (Fig. 3h), suggesting that Tfr2 deficiency in the hematopoietic compartment is not responsible for the high bone mass phenotype in Tfr2-/- mice. Consistent with these findings, deletion of Tfr2 specifically in the myeloid lineage (Lysm-cre) and in mature osteoclasts (Ctsk-cre) did not affect bone volume at the spine (Fig. 3i). Femoral bone volume, however, was decreased in Tfr2f/f;Lysm-cre mice, but not in Tfr2f/f;Ctsk-cre mice (Suppl. Fig. 5a). By contrast, deletion of Tfr2 in osteoblast progenitors, in which Tfr2 expression is highest, increased bone mass at the femur and spine (Fig. 3j), increased trabecular number, and decreased trabecular separation (Fig. 3k). Bone formation was increased in Tfr2f/f;Osx-cre, as reflected by higher serum P1NP levels (Fig. 3l) and a higher bone formation rate (Fig. 3m). Finally, deletion of Tfr2 in osteoblasts did not change osteoclast numbers, but tended to increase serum levels of CTX (Fig. 3n-o). Consistent with published Tfr2f/f;Lysm-cre mice29, Tfr2f/f;Ctsk-cre and Tfr2f/f;Osx-cre mice also showed a normal liver iron content (Suppl. Fig. 5b-c). Taken together, these data indicate that Tfr2 predominantly in osteoblasts regulates bone formation, but does not contribute to systemic iron homeostasis.
Tfr2-deficiency in osteoblasts attenuates BMP-MAPK signaling and results in decreased expression of Wnt inhibitors
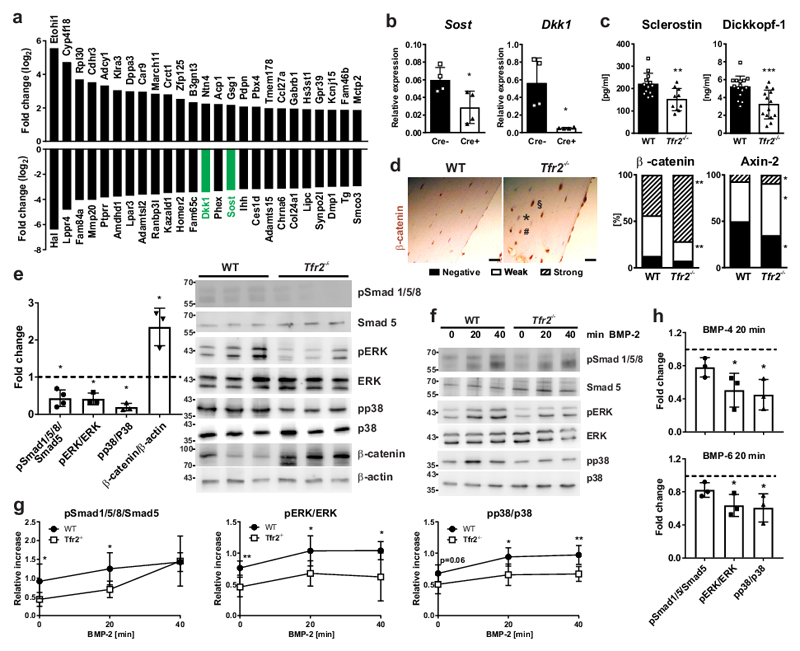
As the data indicate a direct role for Tfr2 in osteoblasts, we performed genome-wide RNA sequencing analysis using primary osteoblasts from WT and Tfr2-/- mice to identify signaling pathways affected by deletion of Tfr2. A total of 5,841 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified (Suppl. Data Set 1). We performed gene ontology analysis to determine the biological processes affected by Tfr2 deficiency (complete list in Suppl. Table 1). Genes upregulated in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts belonged to the biological processes of negative regulation of protein secretion and muscle systems. By contrast, genes involved in ossification, extracellular matrix organization, negative regulation of Wnt signaling, and Smad phosphorylation were downregulated in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts (Suppl. Fig. 6a). These data are consistent with molecular function and cellular component analyses, which revealed underrepresentation of genes involved in glycosaminoglycan and heparin binding, and BMP receptor binding as well as proteinaceous extracellular matrix and collagen formation (Suppl. Fig. 6a). Gene set enrichment analysis further demonstrated underrepresentation of genes involved in late osteoblastic differentiation and Wnt signaling, the latter associated with marked suppression of the Wnt inhibitor Dickkopf-1 (Dkk1) (Suppl. Fig. 6b-c). The complete list of significantly enriched gene sets is provided in the Suppl. Table 2.
Dkk1 and Sost (encoding the Wnt inhibitor sclerostin) were among the 25 most downregulated genes in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts ex vivo (Fig. 4a). Reduced expression of the two Wnt inhibitors was verified by qPCR and is consistent with increased expression of the Wnt target genes (Axin2, Lef1, Cd44) (Suppl. Fig 6c). Dkk1 and Sost mRNA levels were also down-regulated in osteoblasts obtained from Tfr2f/f;Osx-cre mice (Fig. 4b). Furthermore, expression of the osteocyte-associated genes Phex and Dmp1 was decreased (Suppl. Fig 6c). Importantly, impaired expression of osteocytic markers was not due to reduced osteocyte number in Tfr2-/- bone (WT: 8.73±2.74 vs Tfr2-/-: 9.77±0.85 osteocytes/bone volume fraction). Low concentrations of sclerostin and Dkk1 were further detected in the serum of Tfr2-/- mice (Fig. 4c), along with a greater proportion of osteoblasts/osteocytes with high expression of β-catenin and axin-2 (Fig. 4d). Finally, increased Wnt signaling was demonstrated in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts differentiated for 7 days using Western blot analysis of β-catenin (Fig. 4e).
Figure 4. Down-regulation of BMP signaling and Wnt inhibitors in Tfr2-deficiency.
(a) Top 25 most increased and decreased genes as identified using next generation sequencing of day 7 osteoblasts from WT and Tfr2-/- mice (n=4 per genotype). (b) Gene expression of Dkk1 and Sost in day 7 differentiated osteoblasts from Tfr2f/f;Osx-Cre mice and littermate controls. Normalized to β-actin. (n=4 per group). (c) Serum concentrations of Dickkopf-1 and sclerostin in WT and Tfr2-/- mice. (sclerostin, WT n=13, Tfr2-/- n=10; Dickkopf, WT n=15, Tfr2-/- n=14). (d) Immunohistochemical analysis of β-catenin and axin-2 on femoral bone sections from WT and Tfr2-/- mice. Scale bar: 20 µm. Cells were quantified according to their staining intensity (negative (exemplified with an asterisk), weak (hash), strong (section mark)). (n=9 per group). (e) Analysis of the status of activated Smad and MAPK signaling in ex vivo differentiated osteoblasts (day 7) from Tfr2-/- mice normalized to WT osteoblasts. Phosphorylated proteins were normalized to their unphosphorylated counterparts. Expression of β-catenin was normalized to β-actin. Quantification is the result of densitometry of 5 independent Western blot experiments. Dotted line represents the WT level. (Smad1/5/8 n=4; pERK, pp38 and ß-catenin n=3). (f-g) Ex vivo differentiated osteoblasts from WT and Tfr2-/- mice were treated with 50 ng/ml BMP-2 for 0-20-40 min. After protein extraction, phosphorylation of signaling proteins was analyzed using Western blot (f). (g) Graphs represent the quantification of 4 independent experiments. (n=4 per group). (h) Induction of Smad1/5, ERK, and p38 in WT and Tfr2-/- osteoblasts after 20 min of stimulation with 50 ng/ml BMP-4 or BMP-6. Dotted line represents the WT level. (n=3 per group). (b-e, g-h) A two-tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis. All data are presented as mean±SD (expect for (d), which shows percentages). *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001.
Deep sequencing analysis also suggested decreased BMP signaling in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts, and recent studies indicate that Sost and Dkk1 are downstream targets of BMP signaling30,31. Thus, we analyzed BMP target genes as well as the basal canonical (Smad) and non-canonical (MAPK) BMP signaling pathways in Tfr2-/- and WT osteoblasts. Smad6 and Id1 were significantly downregulated in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts, while Id2 was not different (Suppl. Fig. 6c). Both, Smad 1/5/8 phosphorylation as well as ERK and p38 activation were decreased in Tfr2-/- compared to WT osteoblasts (Fig. 4e). Moreover, activation of BMP signaling following BMP-2 treatment demonstrated that Smad activation was delayed in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts, whereas activation of p38MAPK and ERK was persistently impaired (Fig. 4f-g). The reduced activation of non-canonical BMP signaling in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts was not restricted to BMP-2, but was also observed after BMP-4 and to a lesser extent BMP-6 stimulation (Fig. 4h, Suppl. Fig. 6d). Overall, Tfr2 deficiency in osteoblasts results in impaired BMP signaling and increased activation of the Wnt pathway.
Reactivation of MAPK signaling or overexpression of sclerostin rescues high bone mass in Tfr2-deficiency
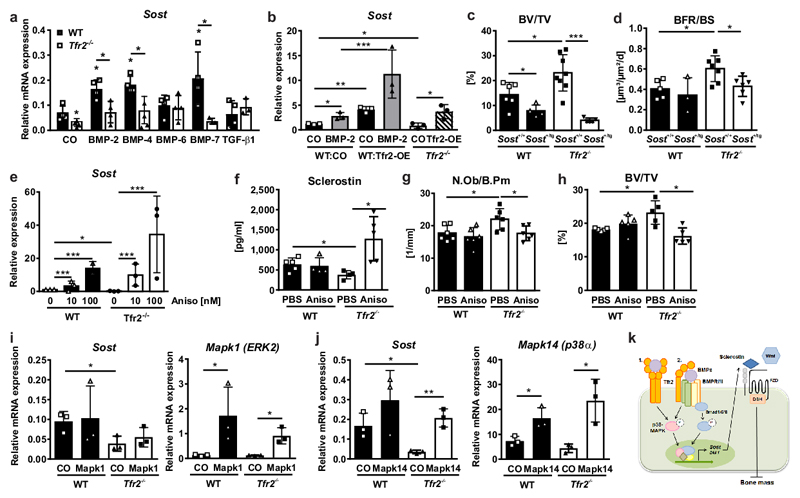
We next investigated the mechanisms underlying the Tfr2-mediated regulation of Sost expression, as this may be a major driver of the Tfr2-dependent effects on bone. Using Tfr2-/- osteoblasts in vitro, we confirmed the lack of induction of Sost expression after stimulation with BMP-2, BMP-4, and BMP-7 (Fig. 5a). Conversely, overexpression of Tfr2 in WT and Tfr2-/- osteoblasts markedly increased Sost, in particular following stimulation with BMP-2 (Fig. 5b, Suppl. Fig. 7a). To test the impact of sclerostin in producing the high bone mass in Tfr2-/- mice, we crossed Tfr2-/- mice with mice overexpressing human SOST in late osteoblasts/osteocytes (under the Dmp1-8kb-promoter). Overexpression of SOST significantly reduced the vertebral trabecular bone volume in Tfr2-/- mice (Fig. 5c) and normalized the bone formation rate (Fig. 5d). The osteoclast-covered bone surface was higher in Tfr2-/- and WT mice overexpressing SOST in osteoblasts/osteocytes compared to mice with normal Sost expression (Suppl. Fig. 7b).
Figure 5. High bone mass in Tfr2-deficiency is rescued by overexpressing SOST or reactivating MAPK signaling.
(a) WT or Tfr2-/- osteoblasts were differentiated for 7 days and stimulated with 50 ng/ml BMPs or TGF-β1 for 48 h. Sost mRNA expression was determined using qPCR. (n=4). A two-tailed t-test was used for statistical analysis. (b) Day 7 WT or Tfr2-/- osteoblasts were transfected with an empty pcDNA3.1 vector (CO) or a pcDNA3.1 vector containing the Tfr2 gene (Tfr2-OE). Cells were either treated with 50 ng/ml BMP-2 or PBS. After 48 h, mRNA expression of Sost was determined using qPCR. (n=3). (c) Bone volume/total volume (BV/TV), WT/Sost+/+ n=6, WT Sost+/tg n=4, Tfr2-/- Sost+/+ n=8, Tfr2-/- Sost+/tg n=5 and (d) bone formation rate/bone surface (BFR/BS) of 10-week-old female Tfr2-/- or WT mice containing one (SOST+/tg) or no allele (SOST+/+) of the SOST transgene. (WT/Sost+/+ n=5, WT/Sost+/tg n=3, Tfr2-/-/Sost+/+ n=7, Tfr2-/-/Sost+/tg n=6). (b-d) Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test was used for statistical analysis. (e) Sost mRNA expression in ex vivo differentiated osteoblasts from WT or Tfr2-/- mice after 24 h of anisomycin treatment (100 nM). (n=3 per group). One-way ANOVA with used for statistical analysis. (f-h) 10-week-old male WT and Tfr2-/- mice were treated with 5 mg/kg anisomycin for 3 weeks. Shown are the (f) serum levels of sclerostin (WT/PBS n=5, WT/Aniso n=4, Tfr2-/-/PBS n=4, Tfr2-/-/Aniso n=5). (g) Number of osteoblasts/bone perimeter (N.Ob/B.Pm) (n=6 per group), and (h) BV/TV of the fourth lumbar vertebrae. (n=5 per group). (i-j) Overexpression of ERK2 (pCMV6-Mapk1) and p38α (pCMV6-Mapk14) in day 7 WT and Tfr2-/- osteoblasts. Sost expression was analyzed after 48 h and normalized to β-actin. (n=3). (f-j) Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test was used for statistical analysis. All data are presented as mean±SD. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001. (k) Scheme of Tfr2 actions in osteoblasts: Tfr2 binds BMPs and either directly activates BMP/MAPK signaling (1.) or activates them via binding to BMPR (2.) to induce the transcription of Sost and Dkk1. Secreted sclerostin acts as a Wnt antagonist and inhibits bone formation and decreases bone mass.
Previous studies indicated that BMPs stimulate Sost expression via the BMP-Smad and BMP-MAPK pathways30,31. Because pERK and pp38 were most markedly reduced in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts, and neither Smad1 nor Smad4 overexpression in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts restored Sost mRNA levels (Suppl. Fig. 7c-f), we reactivated the MAPK pathways using anisomycin to rescue Sost expression. Treatment with anisomycin induced ERK and p38 phosphorylation (Suppl. Fig. 7g), and increased Sost mRNA expression in Tfr2-/- and WT osteoblasts: 19-fold in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts and 14-fold in WT osteoblasts at 100 nM anisomycin (Fig. 5e). Similarly, treatment of Tfr2-/- mice with anisomycin for 3 weeks increased serum levels of sclerostin (Fig. 5f), reduced osteoblast numbers (Fig. 5g) and decreased bone volume back to WT levels (Fig. 5h). Osteoclast numbers were not altered by anisomycin treatment (Suppl. Fig. 7h). Finally, we investigated which specific MAPK pathway, ERK or p38, regulates Sost expression. Only the overexpression of Mapk14 (encoding for p38α), but not Mapk1 (encoding for ERK2), restored reduced Sost levels in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts (Fig. 5i-j). Thus, Tfr2 controls bone mass by inducing Sost expression via the p38MAPK signaling pathway.
Tfr2 is a novel interaction partner of BMPs
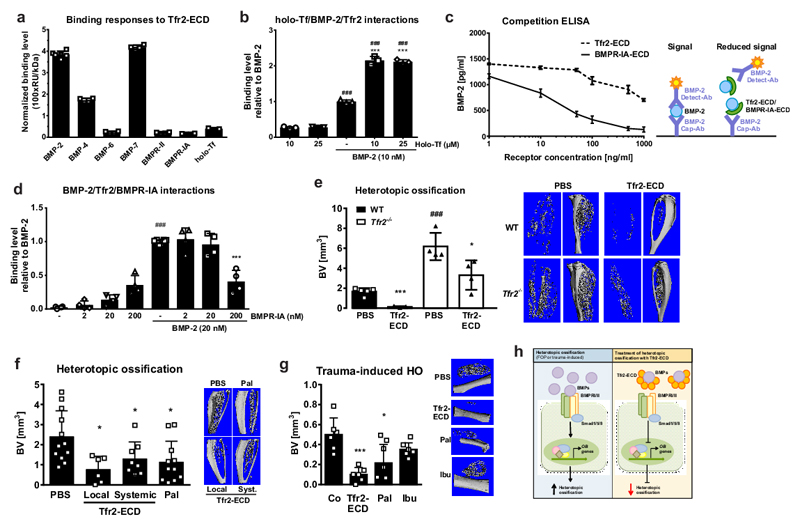
Finally, we asked how Tfr2 can lead to impaired BMP-MAPK signal transduction in osteoblasts and therefore explored whether Tfr2 can act as a BMP receptor. We generated a protein fragment containing the extracellular domain of Tfr2 (Tfr2-ECD), confirmed its presence using SDS-PAGE and Western blot (Suppl. Fig. 8a), and performed surface plasmon resonance (SPR) analysis. Tfr2-ECD immobilized on the sensor chip bound BMPs-2, 4, 6 and 7 more avidly than holo-transferrin (Tf) (Fig. 6a, Suppl. Fig. 8b), the only known Tfr2 ligand10. BMPs-2, 4, and 6 also bound to Tfr2-ECD at high salt concentrations, which were used to reduce non-specific binding, even though at a lower level (Suppl. Fig. 8c). Tfr2-BMP binding was further verified using the inverse approach using Tfr2-ECD as an analyte and BMP-2 or BMP-4 immobilized on the sensor chip (Suppl. Fig. 8d-e). Using this approach, we determined Kd values for Tfr2/BMP-2 (488.0 ± 37.0 nM) and Tfr2/BMP-4 (409.1 ± 39.0 nM) binding via steady state analysis. Holo-Tf bound to Tfr2 at micromolar concentrations suggesting a Kd value in the micromolar range (Suppl. Fig. 8f). Holo-Tf and BMP-2 did not compete for binding to Tfr2, as the sequential injection of either BMP-2 followed by holo-Tf, or holo-Tf followed by BMP-2 did not change the initial binding response (Suppl. Fig. 8g-h). Interestingly, the concomitant injection of BMP-2 and holo-Tf led to a much stronger binding response to Tfr2 than either analyte alone (Fig. 6b). As BMPs normally signal through a receptor complex consisting of the type I and type II BMP receptors, we tested whether BMPRs bind to Tfr2-ECD. Both BMPR-IA and BMPR-II had a binding response weaker than BMPs (Fig. 6a, Suppl. Fig. 8i). The physical interaction of Tfr2 and BMPR-IA was further investigated using a cell system in which they were both overexpressed. Their interaction was confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation and was not affected by the presence of BMP-2 (Suppl. Fig. 8j). BMP-2 binding to the Tfr2-ECD was further verified using a competitive sandwich ELISA with BMPR-IA as a control (Fig. 6c). Additional SPR experiments revealed that BMPR-IA competes with Tfr2 for BMP-2 binding, as adding increasing concentrations of BMPR-IA reduced the binding of BMP-2 to Tfr2-ECD (Fig. 6d). Of note, high nanomolar concentrations of BMPR-IA were required for competing with Tfr2/BMP-2.
Figure 6. Tfr2 binds BMP ligands and blocks heterotopic ossification (HO).
(a-b) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) experiments using Tfr2-ECD immobilized on the sensor chip and 1 mg/ml holo-transferrin (holo-Tf), different BMP ligands (50 nM), or 200 nM BMP receptors as analytes. All experiments were performed three independent times. (a) Quantification of the binding level normalized to the molecular weight. (BMP-2 n=6, BMP-4, 6, 7, BMPR-II and BMPR-IA n=4 per group, holo-Tf n=3). (b) Binding response of different concentrations of holo-Tf and/or BMP-2. (n=3; ###p<0.001 vs. holo-Tf alone; ***p<0.001 vs. BMP-2 alone). (c) Competitive BMP-2 sandwich ELISA was performed to test Tfr2-ECD (or BMPR-IA as a positive control) binding to BMP-2. A defined concentration of BMP-2 (1,500 pg/ml) was used with increasing concentrations of Tfr2-ECD and BMPR-IA. The principle of the assays is shown in the right schematic. (n=4). (d) SPR analyses. BMP-2 was injected either alone or with increasing concentrations of BMPR-IA. Binding response is relative to BMP-2 alone. (n=4; ###p<0.001 vs. BMPR-IA alone; ***p<0.001 vs. BMP-2 alone). (b, d) One-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis. (e) HO in 12-week-old female WT and Tfr2-/- mice after two weeks quantified by µCT (without the bone volume of the tibia). Representative images are shown at the right. (WT PBS n=5, WT Tfr2-ECD n=3, Tfr2-/- PBS n=4, Tfr2-/- Tfr2-ECD n=4; *p<0.05; ***p<0.001 to respective PBS control; ###p<0.001 vs. WT). Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc test was used for statistical analysis. (f) HO in 12-week-old female WT mice after two weeks quantified by µCT (without the bone volume of the tibia). (PBS n=12, local Tfr2-ECD n=6, systemic Tfr2-ECD n=8, Pal n=11; *p<0.05 vs. PBS control). (g) Trauma-induced HO model in 12-week-old female WT mice. HO after three weeks assessed using µCT. (n=6 per group; *p<0.05, ***p<0.001 vs. PBS control). (f, g) One-way ANOVA was used for statistical analysis. All data are presented as mean±SD. (h) Scheme of the mode of action of the Tfr2-ECD in the treatment of HO. Left: HO is induced by overactive BMP signaling, leading to the induction of osteoblastic genes and bone formation. Right: Tfr2-ECD neutralizes BMPs, preventing them from activating BMP signaling. Thus, osteoblastic bone formation is inhibited.
We validated the BMP ligand binding property of Tfr2-ECD in vivo using a heterotopic ossification model. In this model, BMP-2 is injected into the anterior tibialis muscle of mice, which leads to muscular ossification32. While BMP-2 alone led to heterotopic ossification of the muscle in WT mice, the addition of Tfr2-ECD completely abrogated this effect (Fig. 6e, Suppl. Fig 9a-b), suggesting that Tfr2 binds BMP-2 and prevents it from binding to its cognate BMPR. Similar experiments in Tfr2-/- mice demonstrated increased heterotopic ossification following BMP-2 injection as compared to WT mice, which was significantly inhibited by co-application of Tfr2-ECD (Fig. 6e, Suppl. Fig 9a-b). Thus, in addition to confirming functional BMP-binding activity of the Tfr2-ECD in vivo, these data emphasize the role of Tfr2 as a negative regulator of ossification in a BMP-dependent context.
Tfr2-ECD potently inhibits heterotopic ossification in two distinct preclinical models
Due to the robust effect of the Tfr2-ECD to diminish BMP-2-induced heterotopic ossification, we compared Tfr2-ECD with palovarotene, a selective retinoic acid receptor-γ agonist that indirectly inhibits BMP signaling33 and is currently under clinical investigation for the treatment of FOP. Tfr2-ECD was either used as a single local treatment into the muscle or as a systemic treatment (i.p. injections every other day). Both regimens reduced BMP-2-induced heterotopic ossification in WT mice after two weeks with similar efficacy to daily palovarotene administration (Fig. 6f). Investigation of the chondrogenic phase of heterotopic ossification at day 8 in WT mice revealed that both systemic Tfr2-ECD and palovarotene treatment suppressed the number of chondrocytes and the production of cartilage (Suppl. Fig. 9c-d). No adverse effects of systemic Tfr2-ECD treatment were observed on blood counts, iron parameters, bone homeostasis or the gross morphology of internal organs (Suppl. Table 3). Finally, we tested both compounds in a model of trauma-potentiated heterotopic ossification, a frequent complication after trauma, blast injuries, or hip replacement surgeries. A single dose of Tfr2-ECD inhibited new bone formation in the muscle comparable to palovarotene (Fig. 6g). Daily treatment with ibuprofen, a frequent treatment of heterotopic ossification after hip surgeries34, did not prevent trauma-induced heterotopic ossification (Fig. 6g). These data indicate that Tfr2-ECD is a potent inhibitor of heterotopic ossification and represents a potential new therapeutic strategy for treating disorders of excessive bone formation.
Discussion
Using a series of genetically modified mice and in vitro analyses, these studies identify a new role for Tfr2 as a modulator of BMP and Wnt signaling in osteoblasts. Tfr2 interacts with BMP ligands and receptors, activates p38MAPK signaling, and induces expression of the Wnt inhibitor Sost. This in turn blocks canonical Wnt signaling, thereby limiting bone formation and bone mass accrual (Fig. 5k). Further, exploiting the BMP-binding property of the Tfr2-ECD in form of a decoy receptor shows promise as a novel therapeutic strategy to prevent heterotopic ossification (Fig. 6h), which is of particular interest as there are currently no specific treatments for congenital or trauma-induced heterotopic ossification.
Besides its well-known function in the regulation of systemic iron levels6–9, Tfr2 ensures proper erythropoiesis8,22,23. Our study has now identified a novel extrahepatic role of Tfr2, control of bone mass via direct actions in osteoblasts, even though minor effects in myeloid cells including early osteoclasts cannot be excluded. This appears to be a unique property of Tfr2 among the other iron-regulating proteins, as all other investigated mouse models of hemochromatosis display low bone mass. Accordingly, others have shown low bone mass in patients with HFE-dependent hemochromatosis3 and in Hfe- and hepcidin-deficient mice35,36. In both cases, suppressed bone formation was proposed as the main underlying mechanism of low bone mass35,37. However, as both Hfe- and hepcidin-deficient mice are iron-overloaded, it is unclear whether the low bone mass is an indirect result of the negative effects of iron overload, or whether Hfe and hepcidin exert direct actions in bone cells. Importantly, the high bone mass in Tfr2-deficient mice was independent of the iron status and the hepatic function of Tfr2, indicating Tfr2 has distinct roles in osteoblasts (i.e. control of matrix production) and hepatocytes (i.e. regulation of hepcidin expression and systemic iron homeostasis).
Even though Tfr2 has been known as a regulator of iron homeostasis for over 15 years, its mechanisms of action have remained elusive. Decreased levels of Smad1/5/8 and MAPK/ERK signaling in Tfr2-deficient hepatocytes suggested that BMP signaling may be involved11,13,38, but it remained unclear how Tfr2 activates BMP signaling. Previous studies in hepatocytes suggested that Tfr2 forms a ternary complex with Hfe and hemojuvelin to activate hepcidin expression12. Our data, however, provide in vitro and in vivo evidence, which demonstrates that Tfr2 can bind BMPs directly and activate downstream signaling. Binding of BMP-2 to Tfr2 was more than 10-fold higher than that of holo-Tf, the only known ligand for Tfr210. Compared to BMP-BMPR interactions39,40, BMP-Tfr2 binding was markedly lower, suggesting that Tfr2 may act to fine-tune BMP signaling. As our studies also showed a direct interaction of Tfr2 with BMPRs, it remains to be investigated whether Tfr2 binds BMPs alone or within a multi-receptor complex with BMPRs and/or other BMP co-receptors. Despite these first indications of Tfr2 being a BMP (co)-receptor, additional experiments will be required to define accurate binding affinities that account for stoichiometry, the possibility of receptor dimerization or oligomerization, and Tfr2-ECD purity. Interestingly, the combination of holo-Tf and BMP-2 bound much more avidly to Tfr2 than either holo-Tf or BMP-2 alone, suggesting that holo-Tf may exhibit significant Tfr2 binding only in the presence of BMPs. This may be of particular importance as hepatic endothelial cells have been identified as the main producers of BMP-2 and BMP-6 that act locally on hepatocytes to control hepcidin expression and iron homeostasis41,42. While hemojuvelin has been recognized to transmit the signal of BMP-6 to modulate hepcidin expression, BMP-6 can still induce hepcidin expression in hemojuvelin knock-out mice43, suggesting that other receptors must be involved. Thus, the newly identified BMP-binding properties of Tfr2 may represent the missing link in the regulation of hepcidin via BMPs.
Our study further showed that BMP downstream signaling, in particular the BMP-p38MAPK pathway, is impaired in Tfr2-/- osteoblasts resulting in reduced expression of the canonical Wnt inhibitors Dkk1 and Sost, which are both potent negative regulators of bone formation44–46. Recent work has shown that BMP-2 stimulates expression of Dkk1 and Sost by activating BMP-dependent Smad signaling and, in the case of Dkk1, also through MAPK signaling via ERK and p3830,47. More recent studies, including our own show that Sost expression is also induced by p38MAPK signaling in osteoblasts30,48. Accordingly, anisomycin treatment, which activates all three MAPKs49, rescued Sost expression and restored bone mass in Tfr2-/- mice. Similar to the phenotype of Tfr2-/- mice and counterintuitive to the supportive actions of BMP signaling on osteoblastic bone formation, targeted disruption of Bmpr1a or Acvr1 in osteoblasts impairs expression of Sost and results in high bone mass47,50. In addition, treatment of Bmpr1a-deficient calvaria with recombinant sclerostin ex vivo restored normal bone morphology47, similarly as overexpression of SOST in Tfr2-/- mice reduced bone volume back to WT levels. However, Tfr2-deficient mice do not fully phenocopy the skeletal phenotype of Bmpr1a- or Sost-deficient mice. Considering osteoblast/osteocyte-specific knock-out strains, deletion of all three genes leads to high bone mass. However, while Bmpr1a-conditional knock-out mice have a low bone turnover30,47,51, Tfr2-conditional knock-out mice have a high bone formation rate and normal osteoclast parameters, and Sost-conditional knock-out mice have a high bone formation rate52. Osteoclast parameters have not been reported in Sost-conditional knock-out mice, but are normal in Sost-/- mice44. While an increase in bone formation appears the predominant mechanism of high bone mass in Tfr2- and Sost-conditional knock-out mice, the main driver of high bone mass in Bmpr1a-conditional knock-out mice appears to be reduced osteoclastogenesis due to a low RANKL-to-OPG ratio in osteoblasts30,47. This mechanism was reported to be independent of Wnt signaling, as overexpression of Sost did not rescue the osteoclast phenotype in Bmpr1a-conditional knock-out mice47. By contrast, Tfr2-/- mice have elevated osteoclast numbers and an increased RANKL-to-OPG ratio (WT: 0.225±0.046, Tfr2-/: 0.696±0.120, n=4, p=0.0003), but similar to Bmpr1a-conditional knock-out mice, this phenotype was not rescued by Sost overexpression. Interestingly, deficiency of Bmpr2 in osteoblasts results in high bone mass accompanied by a high bone formation rate and normal bone resorption53, suggesting that Tfr2 shares more similarities with Bmpr2 than Bmpr1a. Finally, Bmpr1a-conditional knock-out mice have disorganized bone matrix, leading to reduced bone strength54,55. This is in contrast to Tfr2-/- and Sost-/- mice, which both have normal bone matrix organization and increased bone strength44. Taken together, despite similarities, which propose Tfr2 acts in similar way or even in conjunction with BMPRs, additional pathways appear to mediate its effects on bone independent of BMP signaling. In sum, Tfr2 is clearly a critical regulator of Sost expression in osteoblasts and provides another link between BMP and Wnt signaling.
Finally, we show that the ability of the Tfr2-ECD to bind BMPs and act as a decoy receptor reduces heterotopic ossification in two distinct preclinical models. Heterotopic ossification is a serious and common medical complication after blast injuries, such as found in soldiers and civilians, burn victims, and recipients of total hip endoprostheses. Up to 30% of patients undergoing hip replacement surgery and 50% of severely wounded soldiers develop heterotopic ossification56,57. Extensive heterotopic ossification is also a hallmark of FOP, a rare human disease caused by an activating mutation in the BMP type I receptor ACVR121. Since the identification of this mutation, BMP signaling has been implicated in the pathogenesis of heterotopic ossification. To date, therapeutic options for FOP and trauma-induced heterotopic ossification are limited. Radiation and non-steroidal anti-rheumatic drugs are frequently used to inhibit surgery-induced heterotopic ossification with varying success34. In our study, ibuprofen did not significantly reduce heterotopic ossification. In FOP, glucocorticoids are used to reduce inflammation during flare-ups. However, they do not block progressive ossification. Rapamycin, anti-activin antibodies, and palovarotene have recently been shown to reduce heterotopic ossification in preclinical models of FOP via different mechanisms33,58–60. Palovarotene indirectly interferes with the BMP pathway and is currently the only drug under clinical investigation. Both, local and systemic treatment with Tfr2-ECD inhibited heterotopic ossification to a similar extent as palovarotene. Systemic treatment with Tfr2-ECD did not show adverse effects on iron or bone metabolism within the 2 week treatment period, which is of relevance as mice lacking Tfr2β, which has a similar structure as Tfr2-ECD, have increased iron levels in the spleen8 and therefore, differences in iron metabolism may have been anticipated. In the future, longer and more extensive pharmacological studies are required to conclusively address the safety profile of Tfr2-ECD.
Taken together, we have uncovered Tfr2 as a novel regulator of bone mass via modulating the BMP-p38MAPK-Wnt signaling axis and identified Tfr2-ECD as a promising therapeutic option to treat heterotopic ossification and disorders of excessive bone formation.
Methods
Mice
Generation of Tfr2-/- mice and Tfr2 knock-in (Tfr2-KI) mice, which only lack the Tfr2β isoform, were previously described8. Conditional Tfr2 knock-out mice were generated on the background of the Tfr2-KI mouse (129X1/svJ), thereby producing cell-type specific Tfr2α knock-out mice which also lack Tfr2β globally. Liver-specific Tfr2-knock-out mice (LCKO) were generated using the albumin-cre (sv129 background). To delete Tfr2α in osteoblast precursors the doxycycline-repressible osterix-cre (Osx-cre) was used61. Breeding pairs and mice up to the age of 5 weeks were kept on doxycycline (0.5 g/l). For the deletion of Tfr2α in mature osteoclasts the cathepsin K cre (Ctsk-cre) was used62. Lysozyme M (Lysm-cre) was used for deletion of Tfr2 in early osteoclasts63. Tfr2f/f;Osx-cre, Tfr2f/f;Lysm-cre, and Tfr2f/f;Ctsk-cre mice were on a mixed sv129/C57BL/6 background. Littermates were used as controls.
To obtain Tfr2-deficient mice with an overproduction of human sclerostin, Tfr2-/- mice were crossed with Dmp1-SOST transgenic mice to obtain Tfr2-/-;Dmp1-SOST+/tg mice64. The production of ferroportin knock-in mice with a point mutation (C326S) and Hfe knock-out mice were described previously26,27. All mice were routinely genotyped using standard PCR protocols.
In vivo experiments
All animal procedures were approved by the institutional animal care committee and the Landesdirektion Sachsen. All mice were fed a standard diet with water ad libitum and were kept in groups of 5 animals per cage. Mice were exposed to a 12 h light/dark cycle and an air-conditioned room at 23 °C (no specific pathogen free room). Enrichment was provided in forms of cardboard houses and bedding material. Mice were randomly assigned to treatment groups and the subsequent analyses were performed in a blinded-fashion.
Bone phenotyping
Male and female Tfr2-/- and wild-type mice at 10-12 weeks of age were used. For the characterization of Tfr2-/- mice, older mice (6 and 12 months) were also used. Male Tfr2f/f;Osx-cre and Tfr2f/f;Ctsk-cre and the corresponding cre-negative littermate controls were sacrificed at 10-12 weeks for bone phenotype analysis.
Ovariectomy
Female 11-14-week-old WT or Tfr2-/- mice were bilaterally ovariectomized or sham operated. After four weeks, mice were sacrificed for further analyses. Each group consisted of 5-10 mice.
Iron-rich diet
WT animals received a 2% iron-enriched standard diet from weaning (14 days old) until sacrifice (8 weeks of treatment). Four-five mice per group.
Iron-free diet
Male Tfr2-/- and WT mice received an iron-free diet (Envigo, Italy) from weaning until 10 weeks of age. Control mice received a standard diet containing 0.2 g iron/kg food (GLOBAL DIET 2018, Envigo, Italy). Nine mice per group.
Iron chelation
Ten-week-old male Tfr2-/- and WT mice received daily intraperitoneal injections of 250 mg/kg DFO (Sigma, Germany, dissolved in PBS) or PBS for three weeks. This experiment was performed two independent times with 3-5 mice.
Full bone marrow transplantation
Bone marrow cells were isolated from 12-week-old male Tfr2-/- mice or WT controls. Two million cells were transplanted into lethally irradiated (8 Gy) male WT or Tfr2-/- mice by retro-orbital venous plexus injection. Engraftment efficiency was monitored every four weeks using flow cytometry. After 16 weeks, mice were sacrificed for bone analyses. This experiment was performed twice with each 7-12 mice per group.
Anisomycin treatment
Female 11-week-old WT and Tfr2-/- mice were treated with 5 mg/kg anisomycin (i.p.) 3x/week for three weeks. This experiment was performed twice with each 5 mice per group.
Heterotopic ossification (HO)
The HO model was performed according to Wosczyna et al32. Briefly, 2.5 µl of 1 mg/ml recombinant BMP-2 (Thermo Fisher) or 2.5 µl of 1 mg/ml Tfr2-ECD were mixed with 47.5 µl matrigel (BD Bioscience) on ice. For the local combination treatment, 2.5 µl BMP-2 were mixed with 2.5 µl Tfr2-ECD and 45 µl matrigel. The matrigel-mixtures were injected into the midbelly of the tibialis anterior muscle of 10-week-old female WT and Tfr2-deficient mice. Some mice were treated daily with palovarotene through oral gavage using a previously published protocol58. Palovarotene (Hycultec) was dissolved in DMSO and diluted 1:4 with corn oil. Mice received palovarotene at a dose of 100 µg/mouse for the first five days and 50 µg/mouse for the remainder of the experiment (days 6-14). Two weeks after BMP-2 injection, the legs were harvested for analysis. This experiment was performed three times with 3-11 mice per group.
To analyze the chondrogenic phase of HO, we performed an experiment as described above that was terminated on day 8. This was performed once with 4-6 mice per group.
For systemic Tfr2-ECD treatment, WT mice were treated every other day with Tfr2-ECD intraperitoneally for two weeks. Mice received 250 µg Tfr2-ECD (10 mg/kg BW) per injection for the first 10 days after BMP-2/matrigel injection into the muscle and 125 µg per injection (5 mg/kg BW) for the remaining time. This experiment was performed once with 8-10 mice per group.
Drop-weight HO
This experiment was performed according to Liu et al. with minor modifications65. Female 10-12-week-old WT mice were anesthetized and placed on a ridge of a plastic container over which the right leg was bent so the femur was lying horizontally. Mice received an injection of 1 µg BMP-2 mixed in 50 µl matrigel. Afterwards, a stainless-steel ball of 16 g (16 mm diameter) was dropped from a distance of 80 cm height onto the quadriceps muscle. Mice either received a single dose of 1 µg Tfr2-ECD, which was co-injected with the BMP-2/matrigel mixture, or palovarotene (Hycultec), which was administered daily by oral gavage. Palovarotene was dissolved in DMSO and diluted 1:4 with corn oil. Mice received palovarotene at a dose of 100 µg/mouse for the first five days and 50 µg/mouse for the remainder of the experiment (days 6-21). One group of mice received ibuprofen via the drinking water at a dose of 100 mg/ml which was changed every other day66. Mice received methamizole (200 mg/kg) to reduce pain for the entire duration of the experiment. This experiment was performed twice with 6 mice per group.
Micro-CT, bone micromineralization density, and biomechanical testing
Bone microarchitecture was analyzed using the vivaCT40 (Scanco Medical, Switzerland). The femur and the fourth lumbar vertebra were imaged at a resolution of 10.5 µm with X-ray energy of 70 kVp, 114 mA, and an integration time of 200 ms. The trabecular bone in the femur was assessed in the metaphysis 20 slices below the growth plate using 150 slices. In the vertebral bone, 150 slices were measured between both growth plates. The cortical bone was determined in the femoral midshaft (150 slices). Pre-defined scripts from Scanco were used for the evaluation.
Bone micro-mineralization densities were determined by quantitative back scattered electron-scanning electron microscopy (qBSE-SEM). Neutral buffered formalin fixed fourth lumbar vertebrae (L4) from 12 week old male mice were embedded in methacrylate. Longitudinal block faces were cut through specimens, which were then polished and coated with 25 nm of carbon using a high resolution sputter coater (Agar Scientific Stanstead UK). Samples were imaged using backscattered electrons at 20 kV, 0.4 nA and a working distance of 17 mm with a Tescan VEGA3 XMU (Tescan, Brno, Czech Republic) equipped with a Deben 24 mm 4-quadrant backscatter detector (Deben, Bury St. Edmunds, UK). Bone mineralization densities were determined by comparison to halogenated dimethacrylate standards, and an eight-interval pseudocolor scheme was used to represent the graduations of micro-mineralization, as previously described67.
Three-point bending of the femur was conducted to assess bone strength. The femurs were stored in 70% ethanol and rehydrated in PBS prior to testing. Mechanical testing was performed using the zwicki-Line from Zwick, Germany. Load was applied to the anterior side of the femoral shaft to measure the maximum load at failure (Fmax, N).
Bone histomorphometry
Mice were injected with 20 mg/kg calcein (Sigma) five and two days before sacrifice. Dynamic bone histomorphometry was performed as described previously68. Briefly, the third lumbar vertebra and tibia were fixed in 4% PBS-buffered paraformaldehyde and dehydrated in an ascending ethanol series. Subsequently, bones were embedded in methacrylate and cut into 7 µm sections to assess the fluorescent calcein labels. Unstained sections were analyzed using fluorescence microscopy to determine the mineralized surface/bone surface (MS/BS), the mineral apposition rate (MAR), and the bone formation rate/bone surface (BFR/BS) as well as the bone volume/total volume (BV/TV), trabecular number (Tb.N), trabecular separation (Tb.Sp), and trabecular thickness (Tb.Th).
To determine numbers of osteoclasts, the femur and fourth lumbar vertebra were decalcified for one week using Osteosoft (Merck), dehydrated, and embedded into paraffin. Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP) staining was used to assess the osteoclast surface per bone surface (Oc.S/BS). Bone sections were analyzed using the Osteomeasure software (Osteometrics, USA) following international standards.
To assess HO using the hematoxylin/eosin staining, the calves (HO) and thighs (drop weight) were decalcified, dehydrated and embedded into paraffin. Limbs were cut into 2 µm sections and stained with hematoxylin/eosin. For von Kossa/van Giemson and Safranin O staining, legs were not decalcified, embedded into methacrylate and cut into 4 µm thick sections.
Immunohistochemistry
For immunohistochemical analysis, paraffin sections from WT and Tfr2-/- bones were dewaxed, rehydrated, and heat-retrieved of antigens. Endogenous peroxidase activity was blocked using 0.3% H2O2/PBS for 10 min at room temperature and non-specific binding sites using the blocking buffer of the VECTASTAIN Elite ABC Kit (VECTOR Laboratories) for 45 min at room temperature. Afterwards, sections were incubated with an anti-Tfr2 antibody (H-140, Santa Cruz), a β-catenin antibody (BD Bioscience) or an axin-2 antibody (#ab107613, Abcam) overnight at 4 °C. Subsequently, slides were treated with an anti-mouse secondary antibody conjugated to biotin and then developed utilizing avidin-conjugated HRP with diaminiobenzidine as substrate (DAKO). Slides were examined using a Zeiss Axio Imager M.1 microscope. Two-hundred cells were counted per slide and graded according to no staining (0), weak staining (1), and strong staining (2).
Measurement of the iron content in the liver and bone
The iron concentration in the liver was determined using 20 mg of dried liver tissue as previously published8. The iron concentration in the bone was determined using atomic absorption spectroscopy (PerkinElmer Analyst 800) of dried bone tissue (bone marrow-flushed femur and tibia) as previously published69.
Serum analysis
The bone turnover markers C-terminal telopeptide (CTX) and pro-collagen type I N-terminal peptide (P1NP) were measured in the serum using ELISAs (IDS, Germany). Serum dickkopf-1 and BMP-2 were measured using ELISAs from R&D Systems (Germany). Mouse sclerostin was measured with an ELISA from Alpco (USA). Serum ferritin and iron were measured using routine methods for clinical analyses on a Roche Modular PPE analyzer. The transferrin saturation was determined using a total iron binding capacity kit from Randox.
Primary osteoclast culture
Osteoclasts were generated from the bone marrow of WT mice and seeded at a density of 1x106 cells/cm2. Alpha-MEM (Biochrom, Germany) with 10% FCS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin, and 25 ng/ml M-CSF (all from Life Technologies) was used for the first two days of differentiation. Afterwards, medium was supplemented with 30 ng/ml RANKL (Life Technologies) for the remainder of the culture (5-7 days). RNA was isolated at various time points and mature osteoclasts were used for immunofluorescence analysis.
Primary osteoblast culture
Primary murine osteoblasts were differentiated from the bone marrow using standard osteogenic medium in DMEM with 10% FCS, 1% penicillin/streptomycin (Life Technologies, Germany). RNA was isolated at various time points and day 7 osteoblasts were used for immunofluorescence analysis of Tfr2 and for the deep sequencing analysis.
Signaling studies
day 7 differentiated cells were treated with 50 ng/ml BMP-2, BMP-4 or BMP-6 for 0, 20, and 40 min and lysed in protein lysis buffer (at least two independent experiments with 3 n each). Anisomycin was used to activate MAPK signaling on day 7 differentiated osteoblasts. Cells were treated with 100 nM anisomycin for 20 min for subsequent protein analysis. For RNA isolation and detection of gene expression, cells were treated with different doses of anisomycin for 24 h (two independent experiments with 3 n each).
Overexpression
One µg of the pcDNA3.1 vector containing the murine Tfr2 gene was transfected into 70-80% confluent cells using Fugene HD (Roche)8. An empty pcDNA3.1 vector was used as control. In addition, the overexpression vectors pCMV6-MAPK1 (ERK2), pCMV6-MAPK14 (p38α), pCMV6-Smad1, and pCMV6-Smad4 were purchased from Origene to overexpress the respective signaling proteins. The pCMV6-Entry vector was used as control. Each experiment was performed once with cells from 4 different mice.
RNA isolation, RT and real-time PCR
RNA from cell cultures was isolated with the High Pure RNA Isolation Kit (Roche) and RNA from the bones of mice was isolated by crushing flushed bones (femur and tibia) in liquid nitrogen and collecting the bone powder in Trifast (Peqlab, Germany). Other organs were homogenized directly in Trifast using an ultraturrax (IKA, Germany). Five-hundred ng RNA were reverse transcribed using Superscript II (Invitrogen, Germany) und subsequently used for SYBR green-based real-time PCRs using a standard protocol (Life Technologies). The results were calculated using the ΔΔCT method and are presented in x-fold increase relative to β-actin (or GAPDH where indicated) mRNA levels.
Protein isolation and Western blot
Cells were lysed in a buffer containing 20 mM Tris/HCl pH 7.4, 1% SDS, and a protease inhibitor (complete mini, Roche, Germany). To isolate protein from tissues, the protein fraction of the Trifast procedure was used and further processed according to the manufacturer´s protocol. The protein concentration was determined using the BCA method (Pierce, Germany). Twenty µg of heat-denatured protein was loaded onto a 10% gel, separated, and transferred onto a 0.2 μm nitrocellulose membrane (Whatman, Germany). After blocking for 1 h with 5% non-fat dry milk or 2% BSA in Tris-buffered saline with 1% Tween-20 (TBS-T), membranes were incubated with primary antibodies to signaling proteins (Cell Signaling) overnight and washed three times with TBS-T. For the detection of Tfr2, the H-140 antibody from Santa Cruz (Germany) was used, which detects an epitope corresponding to amino acids 531-670. Other antibodies used were: lamin A/C (#sc-20681, Santa Cruz), connexin-43 (#3512, Cell Signaling), tubulin (#2146, Cell Signaling), GAPDH (#5G4, Hytest). Thereafter, membranes were incubated with the appropriate HRP-conjugated secondary antibodies for 1h at RT. Finally, membranes were washed with TBS-T and incubated with an ECL substrate (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The proteins were visualized using the MF-ChemiBIS 3.2 bioimaging system (Biostep, Germany). All unprocessed Western blot images are shown in Suppl. Fig. 10 and 11.
Subcellular protein fractionation
For separation of cytoplasmic, membrane and nuclear protein extracts of osteoblasts, primary murine osteoblasts were differentiated from the bone marrow of three WT mice. At day 7, cells were harvested and the subcellular protein fractions were isolated using the subcellular protein fractionation kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to manufacturer`s recommendation.
Immunofluorescence staining
For immunofluorescence staining, cells were grown on glass slides. At the desired time point, cells were fixed with 100% methanol for 15 min, permeabilized with 0.5% Triton X-100 for 10 min and after washing for three times, blocked with 1% BSA in PBS for 30 min. Afterwards, cells were incubated with an anti-mouse Tfr2 antibody (H-140, Santa Cruz) over night at 4 °C. After washing, cells were stained with an anti-mouse osterix antibody (sc-393325, Santa Cruz) or phalloidin at RT for 1 h. Subsequently, cells were washed and incubated for 1 h with an Alexa Fluor 488 or Alexa Fluor 594-labelled secondary antibody (Life Technologies), washed, and stained with DAPI for 5 min. After washing again, glass slides were embedded in a small droplet of mounting medium (Dako). Slides were examined using a Zeiss LSM 510 confocal microscope (Zeiss EC Plan-Neofluar 40x/1.3 Oil), and photographs were taken and processed with the Zen 2009 software.
Co-immunoprecipitation
Human hepatoma cells (HuH7) were transfected with 7.5 μg of pCMV-3XFLAG-BMPR-IA and 7.5 μg pcDNA3-TFR2-HA or pcDNA3-LDLR-HA using TransIT®-LT1 Transfection Reagent (Mirus Bio LLC) following the manufacture’s protocol. Forty-eight hours after transfection cells were treated with 50 ng/ml of BMP-2 (Peprotech) for 1.5 h, where indicated. Cell lysates were incubated with pre-equilibrated anti-FLAG M2 affinity gel (Sigma Aldrich) at 4°C for 2 h. Samples were then eluted with 50 μl of lysis buffer containing 300 μg/ml 3X FLAG Peptide (Sigma Aldrich). 10% of the total lysate was used as input (In). Immunorecognition was visualized using αFLAG and αHA antibodies (1:1,000, Sigma Aldrich).
Next generation sequencing and data analysis
Total RNA was isolated from day 7 differentiated cells of Tfr2-/- and WT mice using Trifast. RNA quality was assessed using the Agilent Bioanalyzer and total RNA with an integrity number of ≥ 9 was used. mRNA was isolated from 1 µg total RNA using the NEBNext Poly(A) mRNA Magnetic Isolation Module according to the manufacturer’s instructions. After chemical fragmentation, samples were subjected to strand-specific RNA-Seq library preparation (Ultra Directional RNA Library Prep, NEB). After ligation of adaptors (Oligo1 5'-ACA CTC TTT CCC TAC ACG ACG CTC TTC CGA TCT-3', Oligo2: 5'-P-GAT CGG AAG AGC ACA CGT CTG AAC TCC AGT CAC-3') residual oligos were depleted by bead purification (XP, Beckman Coulter). During subsequent PCR enrichment (15 cycles) libraries were indexed (Primer1: Oligo_Seq AAT GAT ACG GCG ACC ACC GAG ATC TAC ACT CTT TCC CTA CAC GAC GCT CTT CCG ATC T, primer2: GTG ACT GGA GTT CAG ACG TGT GCT CTT CCG ATC T, primer3: CAA GCA GAA GAC GGC ATA CGA GAT NNNNNN GTG ACT GGA GTT. After final purification (XP beads) libraries were quantified (Qubit dsDNA HS Assay Kit, Invitrogen), equimolarly pooled and distributed on multiple lanes for 75bp single read sequencing on a Illumina HiSeq 2500 and a Illumina NextSeq 500.
After sequencing, FastQC (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/) was used for a basic quality control. Reads were then mapped onto the mouse genome (mm10) using GSNAP (version 2014-12-17) together with known splice sites (Ensembl v75) as support. Library diversity was assessed by investigating the redundancy in the mapped reads. A table with counts per gene was obtained by running featureCounts (v1.4.6) on the uniquely mapped reads using Ensembl v75 gene annotations. Normalization of the raw read counts based on the library size and testing for differential expression between the KO and WT was performed with the R package DESeq2 (v1.6.3). Genes with an adjusted (Benjamini-Hochberg) p-value of less than 0.05 were considered as differentially expressed.
Gene ontology analyses were performed with Cytoscape 3.2.1 and the ClueGO plugin. Only significantly (p<0.05) up- or down-regulated genes were fed into the analyses. Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA) was carried out using the Broad Institute GSEA software “GseaPreRanked” tool (nperm=1000, set_min=5, set_max=500, scoring_scheme=weighted) to analyze a list of 18,106 non-redundant gene symbols ranked by their log2 fold-change of expression between Tfr2-/- and WT conditions. In total 58 gene sets were used for the analysis including 50 Hallmark gene sets, three osteoblast specific gene sets from Park et al. and Zaidi et al., and five other gene sets from Sanjuan-Pla et al.70–72.
Expression of the Tfr2 extracellular domain
The coding sequence of the full-length extracellular domain (ECD, aa 103-798) of murine Tfr2 was synthesized by Genscript (Germany). Recombinant His-MBP-c3-Tfr2-ECD was expressed in Sf9 insect cells using the baculovirus expression system (pOCC211-Tfr2-ECD). Culture supernatant (5 liters) was harvested, filtered, and loaded on a HisTrap column, after extensive wash with PBS, the Tfr2-ECD protein was eluted using PBS with 250 mM imidazole. The yield in the first protein production was 40 mg and in the second 46 mg Tfr2-ECD. Presence of Tfr2 was analyzed using Coomassie staining of a SDS-PAGE with reducing conditions and Western blot.
Experiments were repeated with a commercially produced Tfr2-ECD from Cusabio. This fragment also contained the entire ECD (aa 103-798) and was dissolved in PBS only.
Surface plasmon resonance binding and kinetic analysis
Interactions of the Tfr2-ECD and holo-Tf, BMP ligands (BMP-2, -4, -6, -7, R&D Systems) and BMP receptors (BMPR-IA, BMPR-II, R&D Systems) were analyzed using a Biacore T100 instrument (GE Healthcare). Tfr2-ECD, BMP-2 and BMP-4 were immobilized onto Series S Sensor Chips C1 (GE Healthcare) via its amine groups at 25 °C. The carboxyl groups on the chip surface were activated for 7 min with a mixture containing 196 mM 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide hydrochloride and 50 mM N-hydroxysuccinimide at a flow rate of 10 µl/min. Next 5 µg/ml of Tfr2-ECD diluted in sodium acetate buffer (pH 4.5) or 2 µg/ml BMP-2 or BMP-4 were injected at 5 µl/min flow rate until an immobilization levels of approx. 200 RU in case of Tfr2-ECD or 100 RU in case of BMP-2 and BMP-4 were achieved. Unreacted groups were deactivated via injection of 1 M ethanolamine-HCl, pH 8.5 (7 min, 10 µL/min). A reference surface was created according to the same protocol but omitting the Tfr2 injection.
The binding analysis was performed at 37 °C at a flow rate of 30 µl/min. Each analyte was diluted in running buffer (HBS-P (pH 7.4), 150 mM NaCl, supplemented with 50 nM FeCl3). In some experiments, 500 mM NaCl were used to reduce potential non-specific binding. BMP ligands were used at the indicated concentrations (0-50 nM); BMP receptors at a concentration of 2-200 nM, holo-Tf at 2.5-100 µM and Tfr2-ECD at 10-5,000 nM. In some experiments, BMP-2/BMPR-IA and BMP-2/holo-Tf were injected at the same time. Concentration-dependent binding of holo-Tf was performed without intermediate regeneration.
For binding analysis, an injection of analyte for 240 s or 300 s over a Tfr2-ECD surface was followed by 1000 s dissociation. The values of the binding levels were recorded from referenced signals 10 s before the end of injection relative to baseline response. They were then emended for the respective molecular weight. After dissociation for 1000 s, the chip surface was regenerated for 60 s with 5 M NaCl, 50 mM NaOH in HBS-P, followed by a 1000 s stabilization time.
Single cycle kinetics with five sequential analyte injections were carried out with a sensitivity enhanced Biacore T200 (GE Healthcare) to determine the Kd value range of Holo-Tf/Tfr2 and the dissociation rates koff (complex stabilities) for Tfr2 binding to BMP-2 and BMP-4 surfaces. The kinetic fitting was performed by global fitting using the 1:1 Langmuir binding model (A + B = AB). Steady state analyses were conducted to determine the affinities (Kd). Therefore, a 1:1 interaction of Tfr2 with BMP-2 or BMP-4 was assumed by fitting the measured binding responses at equilibrium against the concentration. To achieve a robust fit and the typical curvature of the plot, a wide range of Tfr2 concentrations was analyzed (10-5000 nM). Binding and kinetic parameters were evaluated with Biacore™ T200 evaluation software 3.1.
BMP-2 competitive ELISA
The Duo Set BMP-2 ELISA kit from R&D Systems was used. After coating the plate with the BMP-2 capture antibody overnight, 1.5 ng/ml BMP-2 was added together with increasing concentrations of the Tfr2-ECD or the BMPR-IA (positive control, R&D Systems). After 1 h incubation at RT and extensive washing, the detection antibody was added according to the manufacturer´s protocol and the amount of BMP-2 was quantified. This experiment was performed at least three independent times.
Statistical analysis
Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation (SD). Graphs and statistics were prepared using the Graphpad Prism 6.0 software. Normality of data was determined using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test. In case data were normally distributed, statistical evaluations of two group comparisons were performed using a two-sided Student’s t-test. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used for experiments with more than two groups. Two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-hoc tests was used for analyzing genotype and treatment effects. If data were not normally distributed, the Mann-Whitney test and the Wilcoxon signed rank test were used to analyze data. Frequency distributions of micromineralization densities from qBSE-SEM gray scale images were compared using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test67.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank our technicians for their excellent work. We thank the Core Facility Cellular Imaging of the TU Dresden for their support with the confocal microscope and the acquisition of immunofluorescence images and Dr. Anja Drescher and Dr. Joachim Nickel for critical suggestions regarding SPR analyses.
This work was supported by the German Research Foundation (DFG-SFB655 to LCH and UP; TRR-67 to VH and LCH; µBONE to MR and LCH; RA1923/12-1 to MR) and MedDrive start-up grants from the Medical Faculty of the Technische Universität Dresden (MR and UB). MR was supported by the Support-the-Best Initiative of the TUD funded through the Excellence initiative of the German Federal and State Governments. JHDB and GRW received a Wellcome Trust Joint Investigator Award (110141/Z/15/Z and 110140/Z/15/Z).
Footnotes
Authorship contributions
MR, UB, AR, JSH, SR, UP, and LCH designed experiments. MR, UB, AR, RMP, JSH, HW, SR, GC, RB, AP, RL, IH, SC, DKE performed experiments and analyzed data. TB, SA, SC, MM and IT provided mouse bone samples. MR, UB, AR, JSH, HW, SR, VH, IH, TB, MM, JHDB, GRW, GS, IT, UP, and LCH interpreted the data and provided critical comments to the manuscript. MR, UB, and LCH wrote the manuscript. All authors provided critical review of the manuscript.
Competing interests
The Technische Universität Dresden holds a patent for the use of Tfr2-ECD to treat heterotopic ossification and other related bone excess diseases (PCT/EP2018/065846). Moreover, a patent application has been filed at the European Patent Office for the use of Tfr2 blockade for the treatment of bone and hematological diseases (#18 177 441.5, 19.06.2018). MR, UB, UP, and LCH are the inventors of both patents. IT is a consultant for Kymab Ltd.
The other authors declare no competing interests.
Data availability statement
All data sets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon request. A Life Science Reporting Summary is available.
References
- 1.Muckenthaler MU, Rivella S, Hentze MW, Galy B. A Red Carpet for Iron Metabolism. Cell. 2017;168:344–361. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Imel EA, et al. Serum fibroblast growth factor 23, serum iron and bone mineral density in premenopausal women. Bone. 2016;86:98–105. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2016.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Guggenbuhl P, et al. Bone mineral density in men with genetic hemochromatosis and HFE gene mutation. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA. 2005;16:1809–1814. doi: 10.1007/s00198-005-1934-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nemeth E, et al. Hepcidin regulates cellular iron efflux by binding to ferroportin and inducing its internalization. Science. 2004;306:2090–2093. doi: 10.1126/science.1104742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Powell LW, Seckington RC, Deugnier Y. Haemochromatosis. Lancet. 2016;388:706–716. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01315-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Camaschella C, et al. The gene TFR2 is mutated in a new type of haemochromatosis mapping to 7q22. Nature genetics. 2000;25:14–15. doi: 10.1038/75534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fleming RE, et al. Targeted mutagenesis of the murine transferrin receptor-2 gene produces hemochromatosis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2002;99:10653–10658. doi: 10.1073/pnas.162360699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Forejtnikova H, et al. Transferrin receptor 2 is a component of the erythropoietin receptor complex and is required for efficient erythropoiesis. Blood. 2010;116:5357–5367. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-04-281360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Wallace DF, Summerville L, Lusby PE, Subramaniam VN. First phenotypic description of transferrin receptor 2 knockout mouse, and the role of hepcidin. Gut. 2005;54:980–986. doi: 10.1136/gut.2004.062018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Johnson MB, Enns CA. Diferric transferrin regulates transferrin receptor 2 protein stability. Blood. 2004;104:4287–4293. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-06-2477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Poli M, et al. Transferrin receptor 2 and HFE regulate furin expression via mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (MAPK/Erk) signaling. Implications for transferrin-dependent hepcidin regulation. Haematologica. 2010;95:1832–1840. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2010.027003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.D'Alessio F, Hentze MW, Muckenthaler MU. The hemochromatosis proteins HFE, TfR2, and HJV form a membrane-associated protein complex for hepcidin regulation. Journal of hepatology. 2012;57:1052–1060. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.06.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Wallace DF, et al. Combined deletion of Hfe and transferrin receptor 2 in mice leads to marked dysregulation of hepcidin and iron overload. Hepatology. 2009;50:1992–2000. doi: 10.1002/hep.23198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hogan BL. Bone morphogenetic proteins: multifunctional regulators of vertebrate development. Genes & development. 1996;10:1580–1594. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.13.1580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Andriopoulos B, Jr, et al. BMP6 is a key endogenous regulator of hepcidin expression and iron metabolism. Nature genetics. 2009;41:482–487. doi: 10.1038/ng.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Babitt JL, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein signaling by hemojuvelin regulates hepcidin expression. Nature genetics. 2006;38:531–539. doi: 10.1038/ng1777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Mayeur C, Leyton PA, Kolodziej SA, Yu B, Bloch KD. BMP type II receptors have redundant roles in the regulation of hepatic hepcidin gene expression and iron metabolism. Blood. 2014;124:2116–2123. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-04-572644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Steinbicker AU, et al. Perturbation of hepcidin expression by BMP type I receptor deletion induces iron overload in mice. Blood. 2011;118:4224–4230. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-03-339952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wang RH, et al. A role of SMAD4 in iron metabolism through the positive regulation of hepcidin expression. Cell metabolism. 2005;2:399–409. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2005.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Yu PB, et al. Dorsomorphin inhibits BMP signals required for embryogenesis and iron metabolism. Nature chemical biology. 2008;4:33–41. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2007.54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shore EM, et al. A recurrent mutation in the BMP type I receptor ACVR1 causes inherited and sporadic fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Nature genetics. 2006;38:525–527. doi: 10.1038/ng1783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Wallace DF, et al. A critical role for murine transferrin receptor 2 in erythropoiesis during iron restriction. British journal of haematology. 2015;168:891–901. doi: 10.1111/bjh.13225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nai A, et al. The erythroid function of transferrin receptor 2 revealed by Tmprss6 inactivation in different models of transferrin receptor 2 knockout mice. Haematologica. 2014;99:1016–1021. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2013.103143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Urist MR. Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science. 1965;150:893–899. doi: 10.1126/science.150.3698.893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Roetto A, et al. Comparison of 3 Tfr2-deficient murine models suggests distinct functions for Tfr2-alpha and Tfr2-beta isoforms in different tissues. Blood. 2010;115:3382–3389. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-240960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Herrmann T, et al. Iron overload in adult Hfe-deficient mice independent of changes in the steady-state expression of the duodenal iron transporters DMT1 and Ireg1/ferroportin. Journal of molecular medicine. 2004;82:39–48. doi: 10.1007/s00109-003-0508-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Altamura S, et al. Resistance of ferroportin to hepcidin binding causes exocrine pancreatic failure and fatal iron overload. Cell metabolism. 2014;20:359–367. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Tsay J, et al. Bone loss caused by iron overload in a murine model: importance of oxidative stress. Blood. 2010;116:2582–2589. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-12-260083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Rishi G, Secondes ES, Wallace DF, Subramaniam VN. Normal systemic iron homeostasis in mice with macrophage-specific deletion of transferrin receptor 2. American journal of physiology. Gastrointestinal and liver physiology. 2016;310:G171–180. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00291.2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kamiya N, et al. Wnt inhibitors Dkk1 and Sost are downstream targets of BMP signaling through the type IA receptor (BMPRIA) in osteoblasts. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. 2010;25:200–210. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.090806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Simsek Kiper PO, et al. Cortical-Bone Fragility--Insights from sFRP4 Deficiency in Pyle's Disease. The New England journal of medicine. 2016;374:2553–2562. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1509342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wosczyna MN, Biswas AA, Cogswell CA, Goldhamer DJ. Multipotent progenitors resident in the skeletal muscle interstitium exhibit robust BMP-dependent osteogenic activity and mediate heterotopic ossification. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. 2012;27:1004–1017. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Shimono K, et al. Potent inhibition of heterotopic ossification by nuclear retinoic acid receptor-gamma agonists. Nature medicine. 2011;17:454–460. doi: 10.1038/nm.2334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fransen M, et al. Safety and efficacy of routine postoperative ibuprofen for pain and disability related to ectopic bone formation after hip replacement surgery (HIPAID): randomised controlled trial. Bmj. 2006;333:519. doi: 10.1136/bmj.38925.471146.4F. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Shen GS, et al. Hepcidin1 knockout mice display defects in bone microarchitecture and changes of bone formation markers. Calcified tissue international. 2014;94:632–639. doi: 10.1007/s00223-014-9845-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Guggenbuhl P, et al. Bone status in a mouse model of genetic hemochromatosis. Osteoporosis international : a journal established as result of cooperation between the European Foundation for Osteoporosis and the National Osteoporosis Foundation of the USA. 2011;22:2313–2319. doi: 10.1007/s00198-010-1456-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Doyard M, et al. Decreased Bone Formation Explains Osteoporosis in a Genetic Mouse Model of Hemochromatosiss. PloS one. 2016;11:e0148292. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0148292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Calzolari A, et al. TfR2 localizes in lipid raft domains and is released in exosomes to activate signal transduction along the MAPK pathway. Journal of cell science. 2006;119:4486–4498. doi: 10.1242/jcs.03228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Keller S, Nickel J, Zhang JL, Sebald W, Mueller TD. Molecular recognition of BMP-2 and BMP receptor IA. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2004;11:481–488. doi: 10.1038/nsmb756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Yin H, Yeh LC, Hinck AP, Lee JC. Characterization of ligand-binding properties of the human BMP type II receptor extracellular domain. Journal of molecular biology. 2008;378:191–203. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.02.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Canali S, Wang CY, Zumbrennen-Bullough KB, Bayer A, Babitt JL. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 controls iron homeostasis in mice independent of Bmp6. American journal of hematology. 2017 doi: 10.1002/ajh.24888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Koch PS, et al. Angiocrine Bmp2 signaling in murine liver controls normal iron homeostasis. Blood. 2017;129:415–419. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-07-729822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ramos E, et al. Evidence for distinct pathways of hepcidin regulation by acute and chronic iron loading in mice. Hepatology. 2011;53:1333–1341. doi: 10.1002/hep.24178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Li X, et al. Targeted deletion of the sclerostin gene in mice results in increased bone formation and bone strength. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. 2008;23:860–869. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.080216. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.MacDonald BT, et al. Bone mass is inversely proportional to Dkk1 levels in mice. Bone. 2007;41:331–339. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2007.05.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.van Bezooijen RL, et al. Sclerostin is an osteocyte-expressed negative regulator of bone formation, but not a classical BMP antagonist. The Journal of experimental medicine. 2004;199:805–814. doi: 10.1084/jem.20031454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kamiya N, et al. BMP signaling negatively regulates bone mass through sclerostin by inhibiting the canonical Wnt pathway. Development. 2008;135:3801–3811. doi: 10.1242/dev.025825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yu C, et al. Advanced oxidation protein products induce apoptosis, and upregulate sclerostin and RANKL expression, in osteocytic MLO-Y4 cells via JNK/p38 MAPK activation. Molecular medicine reports. 2017;15:543–550. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Croons V, Martinet W, Herman AG, Timmermans JP, De Meyer GR. The protein synthesis inhibitor anisomycin induces macrophage apoptosis in rabbit atherosclerotic plaques through p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics. 2009;329:856–864. doi: 10.1124/jpet.108.149948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kamiya N, Kaartinen VM, Mishina Y. Loss-of-function of ACVR1 in osteoblasts increases bone mass and activates canonical Wnt signaling through suppression of Wnt inhibitors SOST and DKK1. Biochemical and biophysical research communications. 2011;414:326–330. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.09.060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Biswas S, et al. BMPRIA is required for osteogenic differentiation and RANKL expression in adult bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells. Scientific reports. 2018;8:8475. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-26820-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Witcher PC, et al. Sclerostin neutralization unleashes the osteoanabolic effects of Dkk1 inhibition. JCI insight. 2018;3 doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.98673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Lowery JW, et al. Loss of BMPR2 leads to high bone mass due to increased osteoblast activity. Journal of cell science. 2015;128:1308–1315. doi: 10.1242/jcs.156737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Bao Q, et al. Disruption of bone morphogenetic protein type IA receptor in osteoblasts impairs bone quality and bone strength in mice. Cell and tissue research. 2018 doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2873-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhang Y, et al. Loss of BMP signaling through BMPR1A in osteoblasts leads to greater collagen cross-link maturation and material-level mechanical properties in mouse femoral trabecular compartments. Bone. 2016;88:74–84. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2016.04.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Forsberg JA, et al. Heterotopic ossification in high-energy wartime extremity injuries: prevalence and risk factors. The Journal of bone and joint surgery. American volume. 2009;91:1084–1091. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.H.00792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Regis D, Sandri A, Sambugaro E. Incidence of heterotopic ossification after surface and conventional total hip arthroplasty: a comparative study using anterolateral approach and indomethacin prophylaxis. BioMed research international. 2013;2013 doi: 10.1155/2013/293528. 293528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chakkalakal SA, et al. Palovarotene Inhibits Heterotopic Ossification and Maintains Limb Mobility and Growth in Mice With the Human ACVR1(R206H) Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP) Mutation. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. 2016;31:1666–1675. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Agarwal S, et al. mTOR inhibition and BMP signaling act synergistically to reduce muscle fibrosis and improve myofiber regeneration. JCI insight. 2016;1:e89805. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.89805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Hino K, et al. Activin-A enhances mTOR signaling to promote aberrant chondrogenesis in fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2017;127:3339–3352. doi: 10.1172/JCI93521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Rodda SJ, McMahon AP. Distinct roles for Hedgehog and canonical Wnt signaling in specification, differentiation and maintenance of osteoblast progenitors. Development. 2006;133:3231–3244. doi: 10.1242/dev.02480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Nakamura T, et al. Estrogen prevents bone loss via estrogen receptor alpha and induction of Fas ligand in osteoclasts. Cell. 2007;130:811–823. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.07.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Clausen BE, Burkhardt C, Reith W, Renkawitz R, Forster I. Conditional gene targeting in macrophages and granulocytes using LysMcre mice. Transgenic research. 1999;8:265–277. doi: 10.1023/a:1008942828960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Rhee Y, et al. PTH receptor signaling in osteocytes governs periosteal bone formation and intracortical remodeling. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. 2011;26:1035–1046. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Liu X, et al. A novel mouse model of trauma induced heterotopic ossification. Journal of orthopaedic research : official publication of the Orthopaedic Research Society. 2014;32:183–188. doi: 10.1002/jor.22500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Norden DM, et al. Ibuprofen ameliorates fatigue- and depressive-like behavior in tumor-bearing mice. Life sciences. 2015;143:65–70. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2015.10.020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Bassett JH, et al. Optimal bone strength and mineralization requires the type 2 iodothyronine deiodinase in osteoblasts. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2010;107:7604–7609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0911346107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rauner M, et al. Increased EPO Levels Are Associated With Bone Loss in Mice Lacking PHD2 in EPO-Producing Cells. Journal of bone and mineral research : the official journal of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research. 2016;31:1877–1887. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.2857. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Theurl I, et al. On-demand erythrocyte disposal and iron recycling requires transient macrophages in the liver. Nature medicine. 2016;22:945–951. doi: 10.1038/nm.4146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Sanjuan-Pla A, et al. Platelet-biased stem cells reside at the apex of the haematopoietic stem-cell hierarchy. Nature. 2013;502:232–236. doi: 10.1038/nature12495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Mootha VK, et al. PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nature genetics. 2003;34:267–273. doi: 10.1038/ng1180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Subramanian A, et al. Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2005;102:15545–15550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0506580102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.