Abstract
Iridium complexes modified by PhanePhos catalyze the 2-propanol-mediated reductive coupling of diverse 1,1-disubstituted allenes 1a-1u with fluoral hydrate 2a to form CF3-substituted secondary alcohols 3a-3u that incorporate acyclic quaternary carbon-containing stereodiads. By exploiting concentration-dependent stereoselectivity effects related to the interconversion of kinetic (Z)- and thermodynamic (E)-σ-allyliridium isomers, adducts 3a-3u are formed with complete levels of branched regioselectivity and high levels of anti-diastereo- and enantioselectivity. The utility of this method for construction of CF3-oxetanes and CF3-azetidines is illustrated by the formation of 4a and 6a, respectively. Studies of the reaction mechanism aimed at illuminating the singular effectiveness of PhanePhos as a supporting ligand in this and related transformations have led to the identification of a chromatographically stable cyclometallated iridium-(R)-PhanePhos complex Ir-PP-I that is catalytically competent for allene-fluoral reductive coupling and previously reported transfer hydrogenative C-C couplings of dienes or CF3-allenes with methanol. Deuterium labelling studies, reaction progress kinetic analysis (RPKA) and computational studies corroborate a catalytic mechanism involving rapid allene hydrometalation followed by turnover-limiting carbonyl addition. A computationally determined stereochemical model shows the ortho-CH2 group of the cyclometallated iridium-PhanePhos complex plays a key role in directing diastereo- and enantioselectivity. The collective data provide key insights into the structural-interactional features of allyliridium complexes required to enforce nucleophilic character, which should inform the design of related cyclometallated catalysts for umpoled allylation.
Graphical Abstract
Introduction
Diverse catalytic enantioselective methods enabling formation of quaternary carbon stereocenters that reside within cyclic frameworks have been reported.1 In contrast, catalytic enantioselective methods that deliver acyclic quaternary carbon stereocenters remain relatively uncommon.1a,g,2,3 Even more elusive are asymmetric methods that deliver (a) acyclic quaternary carbon-containing stereopolyads3 or (b) fluorinated acyclic quaternary carbon-containing structural motifs.4 In the course of developing catalytic enantioselective carbonyl reductive couplings via alcohol-mediated hydrogen transfer or hydrogen auto-transfer,5 we recently developed enantioselective methods for the formation of acyclic quaternary carbon stereocenters that operate under non-cryogenic conditions and completely atom-efficient, bypassing the use of stoichiometric metals.6 In these processes, vinyl epoxides,6a 1,3-dienes6b and CF3-allenes6c serve as pronucleophiles.
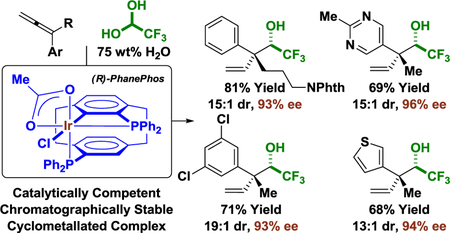
In the latter two processes, iridium complexes modified by PhanePhos7 were uniquely effective in catalyzing highly regio- and stereoselective methanol-mediated formaldehyde additions.6b,c,8 Other chelating phosphine ligands were completely inactive in these processes. The singular effectiveness of the iridium-PhanePhos catalyst prompted further exploration of its capabilities and investigations into the precise nature of the catalytically active species. Here, we report that the iridium complex derived from [Ir(cod)Cl]2 and PhanePhos catalyzes highly regio-, diastereo- and enantioselective allene-fluoral reductive couplings mediated by 2-propanol to form acyclic quaternary carbon-containing stereodiads.9,10,11,12 Of greater significance, these studies have led to the identification of a cyclometallated iridium-PhanePhos complex that is catalytically competent - not only in the present transformation, but also in previously reported iridium-PhanePhos catalyzed reactions developed in our laboratory.6b,c This complex contributes to a growing collection of cyclometallated iridium complexes that display diverse catalytic activities (Figure 1).13
Figure 1.

Diverse catalytic activities of cyclometallated iridium complexes and the identification of a catalytically competent cyclometallated iridium-PhanePhos complex.
Research Design and Methods
Reaction Optimization, Scope and Applications.
Prior work in our laboratory on enantioselective iridium-PhanePhos catalyzed C-C coupling focused on methanol-mediated formaldehyde additions.6b,c Steric issues posed by the formation of a more highly substituted quaternary carbon C-C bond prohibited reactions of higher aldehydes. It was posited that fluoral, a highly reactive carbonyl electrophile like formaldehyde, might participate in alcohol-mediated reductive coupling to provide acyclic quaternary carbon stereodiads incorporating a trifluoroethyl carbinol fragment.14 However, the feasibility of allene-fluoral reductive coupling was rendered uncertain by two issues. First, fluoral is only commercially available as the hydrate or hemiacetal, yet the vast majority of enantioselective metal-catalyzed fluoral additions require use of anhydrous fluoral.4 Secondly, high levels of stereoselectivity not only require discrimination of enantiotopic carbonyl π-faces, but intervention of a single geometrical isomer of the σ-allyliridium nucleophile. The latter issue is further complicated by the fact that hydroiridation of 1,1-disubstituted allenes occurs preferentially at the allene π-face proximal to the smaller allene substituent (Rs) to furnish the less stable (Z)-σ-allyliridium isomer. Hence, notwithstanding Curtin-Hammett effects,15 in order to form the quaternary carbon stereocenter with optimal levels of stereoselectivity, kinetic stereoselectivity favoring formation of the (Z)-σ-allyliridium isomer must either be preserved or equilibration between the (Z)- and (E)-σ-allyliridium isomers must be achieved prior to carbonyl addition with complete conversion to the latter (Figure 2). The difference in energy between (Z)- and (E)-2-phenyl-2-butenes is more than 1 Kcal/mol, and greater energetic differentiation is anticipated for the corresponding (Z)- and (E)-σ-allyliridium species.16
Figure 2.
Relative and absolute stereoselection in 2-propanolmediated reductive couplings of allenes with fluoral hydrate via concentration-dependent diastereoselectivity.a
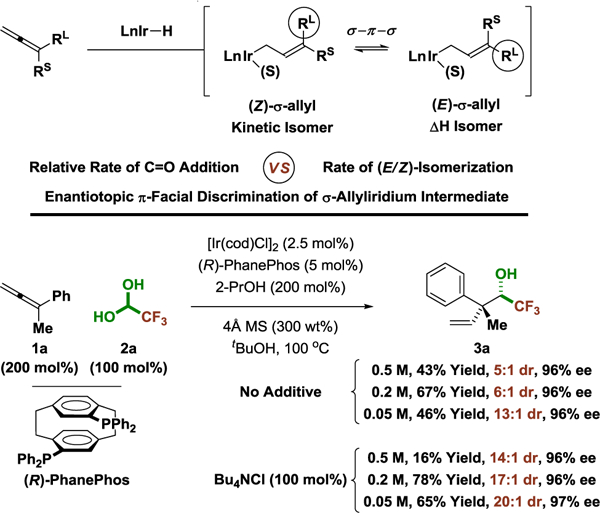
a Diastereoselectivity determined by 19F NMR of crude reaction mixtures. Enantioselectivities were determined by chiral stationary phase HPLC analysis. Yields of material isolated by silica gel chromatography. See Supporting Information for further experimental details.
With these considerations in mind, the following series of experiments was performed (Figure 2). Allene 1a (200 mol%), fluoral hydrate 2a (100 mol%, 75 wt% in water) and 2-propanol (200 mol%) were exposed to the iridium catalyst derived from [Ir(cod)Cl]2 (2.5 mol%) and (R)-PhanePhos (5 mol%) in tert-butanol (0.5 M) at 100 °C. In the absence of desiccant, only trace quantities of the targeted reductive coupling product 3a was observed. However, upon addition of 4 Å molecular sieves, compound 3a was formed in 43% yield as 5:1 mixture of diastereomers in 96% enantiomeric excess. In accord with our stereochemical analysis, it was reasoned that more dilute conditions might increase diastereoselectivity by decreasing the rate of carbonyl addition with respect to the rate of equilibration between the (Z)- and (E)-σ-allyliridium isomers.15 Indeed, in the event, diastereoselectivity was found to increase with increasing dilution and at 0.05 M a 13:1 diastereomeric ratio was observed without any erosion of enantioselectivity, although under these dilute conditions the isolated yield of 3a suffered. In the course of our optimization experiments, we also observed that more Lewis basic solvents promote higher diastereoselectivities. This fact led us to explore the effect of halide additives. To our delight, introduction of Bu4NCl (100 mol%) not only improved diastereoselectivity and but also increased the isolated yield of 3a. At 0.2 M in the presence of Bu4NCl, compound 3a was formed in 78% yield as a 17:1 mixture of diastereomers with a 96% enantiomeric excess. Diastereoselectivity remained constant at 80, 90, and 100 °C, and at lower temperatures conversion decreased precipitously so diastereoselectivity was not calculated.
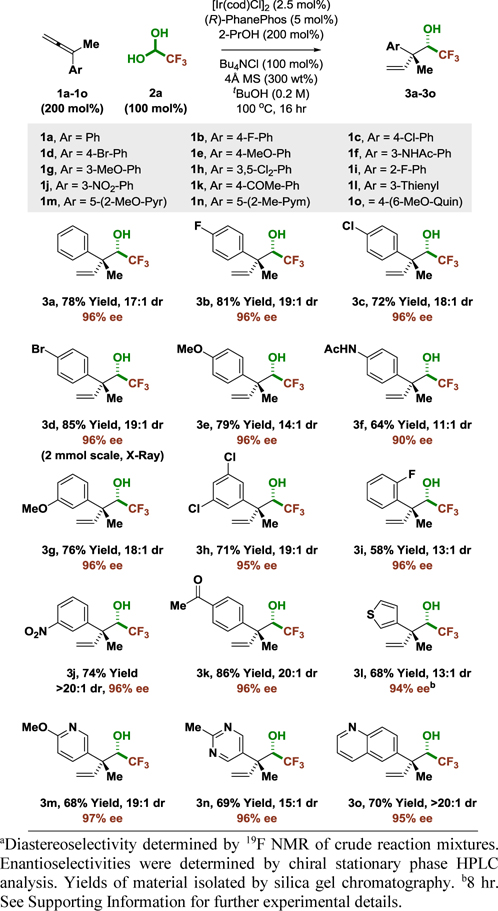
These optimized conditions were applied to the reductive coupling 1,1-disubstituted allenes 1a-1o bearing aryl and methyl groups with fluoral hydrate 2a (Table 1). Allenes 1b-1k bearing aryl moieties with diverse substitution patterns and electronic properties are converted to adducts 3b-3k in good yield with uniformly high levels of regio-, diastereo- and enantioselectivity. Notably, functional groups that are potentially susceptible to reduction, for example nitro groups (3j) and ketones (3k), remain intact. Heteroaryl-substituted allenes 1l-1o are also effective partners for reductive coupling, providing adducts 3l-3o with high levels of relative and absolute stereocontrol. For N-hetereocycles at least one ortho-substituent adjacent to nitrogen is required for high levels of conversion.
Table 1.
Variation of aryl substituent in iridium-catalyzed coupling of allenes 1a-1o with fluoral hydrate 2a to form adducts 3a-3o bearing acyclic quaternary carbon stereocenters.a
 |
To test the limits of stereoselectivity, 1,1-disubstituted allenes 1p-1u bearing higher alkyl substituents were evaluated in reductive couplings to fluoral 2a (Table 2). Remarkably, although increasing size of the alkyl moiety was anticipated to erode partitioning of the transient (E)- and (Z)-σ-allyliridium isomers, excellent levels of stereocontrol were retained in reactions of allenes 1p-1u that incorporate linear alkyl groups. In contrast, attempted reactions of allenes bearing branched alkyl groups, for example, cycloalkyl moieties, were lowyielding and non-diastereoselective. The absolute stereochemical assignment of all adducts 3a-3u is made in analogy to that established for the 3,5-dinitrobenzoate of 3d, which was determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction analysis.
Table 2.
Variation of alkyl substituent in iridium-catalyzed coupling of allenes 1p-1u with fluoral hydrate 2a to form adducts 3p-3u bearing acyclic quaternary carbon stereocenters.a
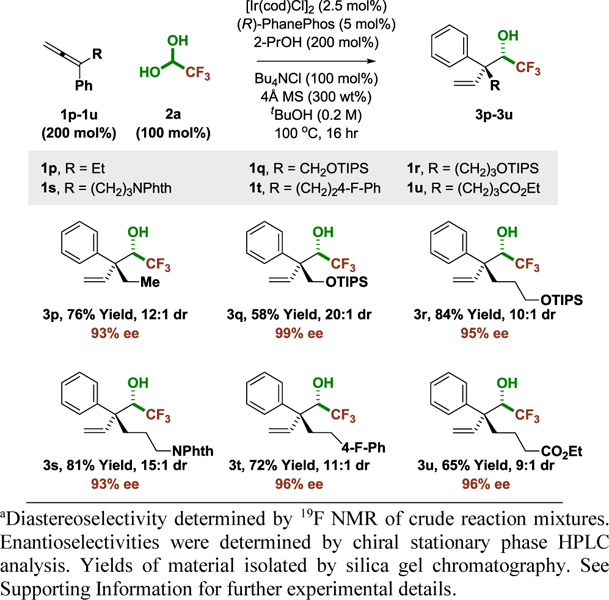 |
To briefly illustrate the utility of the reaction products, fluoral adduct 3a was converted to the CF3-oxetane 4a, which bears a quaternary carbon stereocenter (eq. 1).17 Oxetanes have emerged as useful building blocks in medicinal chemistry due to their ability to serve as carbonyl and gem-dimethyl isosteres.18 Recently, CF3-oxetanes were shown to function as a more polar tert-butyl isostere.19 To prepare CF3-oxetane 4a, fluoral adduct 3a was transformed to the mesylate and subjected to ozonolysis conditions. The resulting primary alcohol was exposed to sodium hydride to provide oxetane 4a (eq. 1). As corroborated by the conversion of primary tosylate 5a to oxetane 4a (eq. 2), the formation of 4a proceeds via secondary to primary methanesulfonate transfer. Just as trifluoroethylamines serve as amide bioisosteres,20 CF3-azetidines21 may be viewed as β-lactam mimics. To prepare CF3-azetidine 6a, fluoral adduct 3a was converted the mesylate and subjected to ozonation conditions to deliver the corresponding aldehyde. Reductive amination-cyclization provided CF3-azetidine 6a (eq. 3).
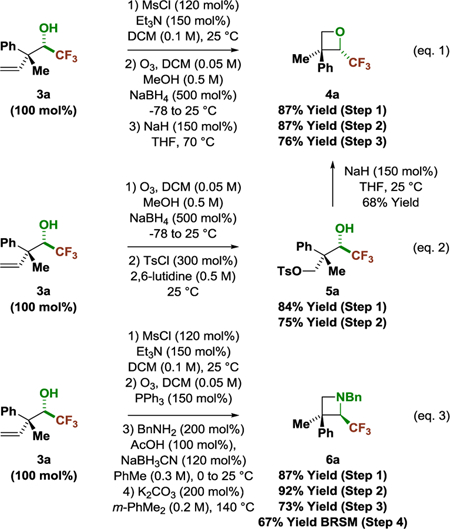
Identification of A Catalytically Competent Cyclometallated Complex.
Insight into the unusual effectiveness of the iridium-PhanePhos catalyst was essential in terms of formulating an accurate interpretation of the catalytic mechanism. Products of allene-fluoral reductive coupling were not formed upon use of other chelating phosphine ligands such as BINAP or SEGPHOS under otherwise identical conditions. The same is true for previously reported iridium-PhanePhos catalyzed couplings of methanol with 1,3-dienes6b and CF3-allenes.6c Consequently, the fact that cyclometallated π-allyliridium C,O-benzoate complexes (Figure 1)13c promote C-C coupling in the aforesaid processes (albeit with suboptimal levels of stereocontrol) was deemed significant. This observation raised the question of whether the unique topology of PhanePhos rendered this ligand susceptible to cyclometallation. Although cyclometallated complexes of PhanePhos have not been reported, a relatively short contact of 3.56 Å is found in the X-ray crystal structure of a palladium-PhanePhos complex22 between metal and the ortho-carbon atom of the cyclophane ring. For an iridium center, which has a larger atomic radius, one could easily imagine an agostic interaction or C-H oxidative addition to form a cyclometallated complex. With these thoughts in mind, an effort was made to prepare a cyclometallated iridium-PhanePhos complex and evaluate its catalytic activity.
In the event, heating a THF solution of [Ir(cod)Cl]2 (100 mol%), (R)-PhanePhos (200 mol%) and allyl acetate (400 mol%) at 100 °C for one hour gave a yellow residue, which upon flash silica gel column chromatography delivered the 4-membered metallacycle Ir-PP-I in up to 60% yield. The structural assignment of Ir-PP-I was corroborated by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis (Figure 3). The cyclometallated iridium complex is of distorted octahedral geometry with the two phosphorus atoms of PhanePhos and acetate lying in the same plane and with the chloride and aryl moieties apical to the plane. The distance between the phosphorus atoms (3.34 Å) is noticeably less than that found in the related square planar Pd(rac-PhanePhos)Cl2 complex (3.62 Å).22 Additionally, the P–Ir–P “bite angle” (95.90°) is significantly compressed compared to that found in the palladium complex (103.69°).22 The P–Ir–C bond angle of the iridacycle is 67.95° with an Ir–C bond length of 2.04 Å. The bond length of the cyclometallated Ir–P is 2.24 Å, which is slightly shorter than the other Ir–P bond, which has a bond length of 2.26 Å. The differential trans influence of these two phosphorus atoms is reflected by the disparity between the two Ir–O bond lengths of the acetate moiety. The Ir–O bond that is trans to the activated phosphorus atom has bond length of 2.19 Å, which is slightly longer than the Ir–O bond trans to the non-cyclometallated phosphorus atom, which has a bond length of 2.15 Å.
Figure 3.
Structure of the cyclometallated iridium-(R)-PhanePhos complex Ir-PP-I as determined by single crystal X-ray diffraction.a
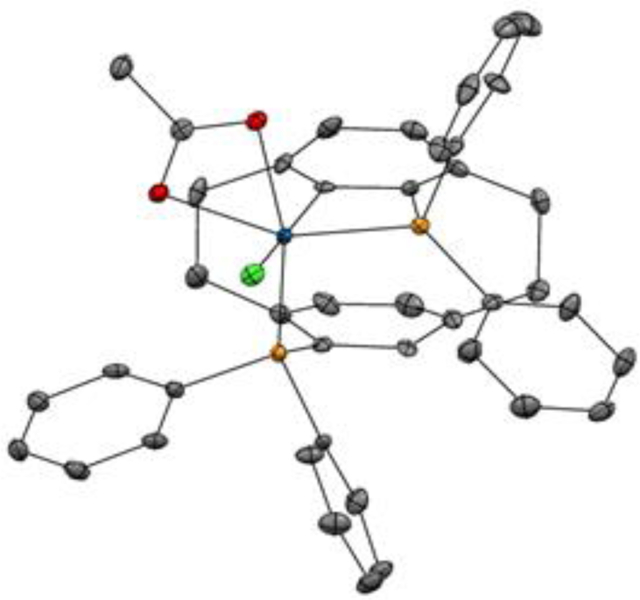
a Displacement ellipsoids are scaled to the 50% probability level. See Supporting Information for further details.
To probe the catalytic competency of the cyclometallated complex, allene 1e was exposed to fluoral hydrate 2a in the presence of Ir-PP-I (5 mol%) under otherwise standard conditions. The product of reductive coupling 3e was formed in 72% yield as a 14:1 diastereomeric ratio and 96% enantiomeric excess (eq. 4). Similarly, allene 1p was exposed to fluoral hydrate 2a in the presence of Ir-PP-I (5 mol%) under otherwise standard conditions to furnish the reductive coupling product 3p in 62% yield as a 16:1 diastereomeric ratio and 93% enantiomeric excess (eq. 5). These data are in good alignment with the yields and stereoselectivities observed in reactions in which the catalyst is generated in situ from [Ir(cod)Cl]2 (2.5 mol%) and (R)-PhanePhos (5 mol%) (Tables 1 and 2, respectively). The cyclometallated complex Ir-PP-I is also a competent catalyst in the previously reported iridium-PhanePhos catalyzed couplings of methanol with 1,3-dienes (eq. 6)6b and CF3-allenes (eq. 7).6c These data (eq. 4–7) corroborate intervention of a cyclometallated catalyst related to Ir-PP-I in the present allene-fluoral reductive coupling and the previously reported transfer hydrogenative C-C couplings of dienes6b or CF3-allenes.6c While roughly equivalent stereoselectivities are observed using the preformed complex Ir-PP-I, slightly lower yields are evident. This may be due to the fact that the catalyst generated in situ incorporates a monodentate chloride counterion, whereas Ir-PP-I contains a bidentate acetate counterion, which may inhibit catalysis.
Deuterium Labelling Studies and General Catalytic Mechanism.
To gain further insight into the catalytic mechanism, a series of deuterium labelling experiments were conducted (eq. 7 and 8). Exposure of fluoral hydrate 2a to deuterio-1a, which incorporates a fully deuterated methyl group, under standard reaction conditions delivers deuterio-3a (eq. 7). Deuterium is completely retained at the methyl group and is not redistributed to any other position. This experiment demonstrates that the reaction does not proceed by way of allene-to-diene isomerization. Indeed, the isomeric diene was prepared and subjected to standard reaction conditions and was not a competent partner for C-C coupling. The coupling of 1a and 2a mediated by d8–2-propanol under otherwise standard conditions delivers deuterio-3a′ (eq. 8). Deuterium is incorporated exclusively at the interior vinylic position (15% 2H). Exchange between iridium-hydrides and the deuterium atoms of D2O is well-documented,23 and incomplete deuterium incorporation is likely due to H-D exchange with tert-butanol or water associated with aqueous fluoral hydrate. Consistent with this hypothesis, when the reaction is conducted in d10-tert-butanol or toluene, enhanced levels of deuterium incorporation are observed (eq. 8).
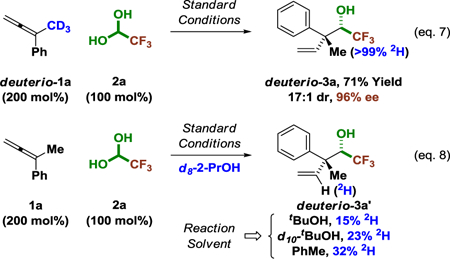
The collective data are consistent with the indicated catalytic mechanism (Scheme 1). Entry into the catalytic cycle is achieved via C-H oxidative addition of the ortho-C-H bond of PhanePhos to iridium(I). Allene hydrometallation from the resulting iridium(III) hydride I delivers the kinetic (Z)-σ-allyliridium isomer IIa. Isomerization to the thermodynamically preferred (E)-σ-allyliridium isomer IIb is followed by association of fluoral and carbonyl addition to furnish the homoallylic iridium(III) alkoxide IV. Alkoxide exchange with 2-propanol releases the product of carbonyl addition 3a. β-Hydride elimination from the 2-propoxy iridium(III) species V regenerates the iridium(III) hydride I to close the catalytic cycle. Knowing that the active catalyst is a cyclometallated halide containing iridium(III) complex, one can better understand how halides “tune” the environment at the iridium center to influence reactivity and selectivity. In the present transformation, the additive Bu4NCl may assist by preserving chloride at the iridium(III) center, while in previously reported couplings of methanol with CF3-allenes,6c Bu4NI likely substitutes the chloride at iridium(III).
Scheme 1.
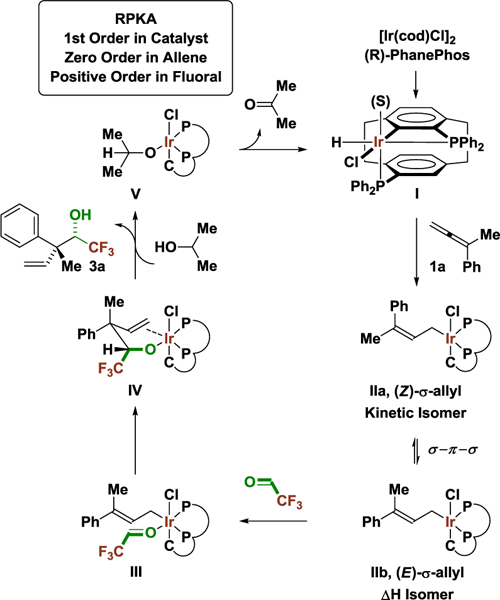
Proposed catalytic mechanism for iridium-PhanePhos catalyzed allene-fluoral reductive coupling mediated by 2-propanol.
Reaction Progress Kinetic Analysis.
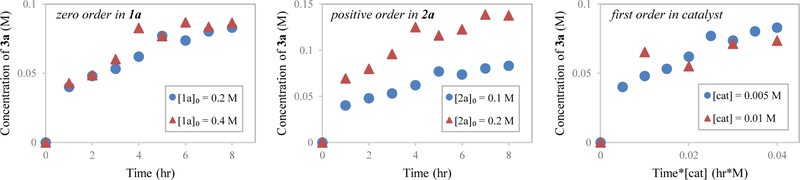
To gain further mechanistic insight, reaction progress kinetic analysis (RPKA) was applied to the coupling of allene 1a with fluoral hydrate 2a to form adduct 3a.24,25 Due to the volatile nature of the reactants and the complex equilibria between fluoral, fluoral hydrate and hemiacetals that arise upon addition of 2-propanol and tert-butanol, the progress of a single reaction could not be monitored. Therefore, a series of reactions were conducted in parallel, and for each successive time point an individual reaction was stopped and the extent of product formation was determined by GC analysis using an internal standard. As each data point derives from a separate experiment the quality of the data were not ideal, nevertheless, several significant conclusions could be drawn.
The results of experiments carried out using the “different excess” protocol elucidate the order in allene 1a and fluoral hydrate 2a (Figure 5). The observed overlap between data sets indicates zero-order kinetics in allene, since the rate of product formation is not effected by the change of initial concentration of allene (Figure 5, left). In contrast, higher concentrations of 2a result in faster rates of product formation, which suggests a positive order in fluoral (Figure 5, middle). Evaluation of the effect of increasing catalyst loading using Burés method26 suggests the reaction is first order in catalyst (Figure 5, right). Furthermore, results of a set of experiments performed using the “same excess” protocol indicate minimal catalyst deactivation occurs (see Supporting Information). These data corroborate a catalytic mechanism involving rapid allene hydrometalation followed by turnover-limiting carbonyl addition (Scheme 1). These data also implicate the π-allyliridium species, which could be detected via high resolution mass spectrometry as the catalyst resting state.
Figure 5.
Product formation as monitored by GC analysis in reactions carried out utilizing “different excess” protocol. [cat] = 0.005 M; [TBAC] = 0.1 M; [2-propanol] = 0.2 M; (a) [1a]0 = 0.2 M, [2a]0 = as noted; (b) [2a]0 = 0.1 M, [1a]0 = as noted. (c) Time adjustment of product formation in varying catalyst loading reactions as monitored by GC analysis. [1a] = 0.2 M; [2a] = 0.1 M; [TBAC] = 0.1 M; [2-propanol] = 0.2 M; [cat] = as noted.
Computational Studies.
Initial computational studies were aimed at formulating a unified stereochemical model accounting for relative and absolute stereochemistry in the present and prior6b,c iridium-(R)-PhanePhos catalyzed transfer hydrogenative carbonyl additions (eq. 4–7). Accordingly, 48 different conformations based on a Zimmerman-Traxler-type transition structure27 were thus computationally analyzed to identify the transition state with the lowest energy barrier (see Supporting Information). In the most favored transition state (Figure 6), the σ-allyl occupies a coordination site that minimizes steric repulsion with the CH2 moiety of the cyclophane ethano-linkage that resides ortho to iridium. At the same time, nonbonded interactions between the terminal aryl moiety of the σ-allyl and the cyclometallated phenyl ring are decreased. The carbonyl electrophile, floural, can then enter the coordination site trans to the PPh2 moiety of the iridacycle and syn to Ir-Cl with the CF3 pointing away from the Ir center. The orientation of the fluoral C-H bond suggests possible intervention of a formyl C-H bond with the chloride ligand.28 Addition of the σ-allyl to the Si-face of the carbonyl through a closed transition structure defines enantiotopic π-facial selectivity. This model is also applicable to iridium-(R)-PhanePhos-catalyzed couplings of methanol with 1,3-dienes6b and CF3-allenes.6c
Figure 6.
Computationally determined stereochemical model accounting for relative and absolute stereochemistry for all iridium-(R)-PhanePhos catalyzed transfer hydrogenative carbonyl additions.a
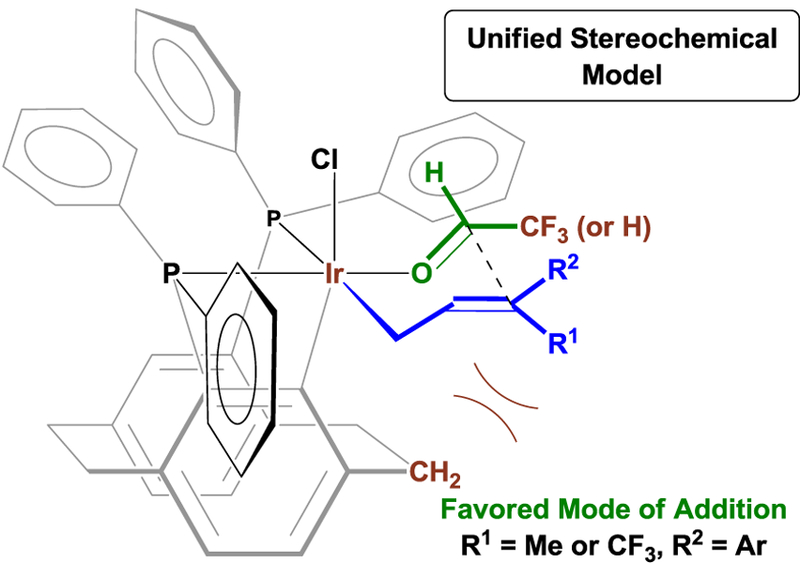
a See Supporting Information for details on computational studies.
Computational studies were used to further assess the veracity of our interpretation of the catalytic mechanism (Scheme 2). Allene hydrometallation from intermediate I, an iridium(III) hydride-allene complex, delivers the kinetic (Z)-σ-allyliridium isomer IIb, which can interconvert with the thermodynamically preferred (E)-σ-allyliridium isomer IIa. The Curtin–Hammett situation15 favors the reaction to proceed by association of fluoral to IIIa followed by carbonyl addition via TS2-E to furnish the homoallylic iridium(III) alkoxide IVa. Alkoxide exchange with 2-propanol releases the product of carbonyl addition 3a and regenerates the iridium(III) hydride coordinated with an allene after β-hydride elimination to close the catalytic cycle. Consistent with the excellent levels of diastereo- and enantioselectivity that are observed, the transition state leading to the disfavored enantiomer, TS2-E-2R3S, requires the floural carbonyl group to become anti-periplanar to Ir-Cl bond, which results in a higher energy barrier due to the increased steric interactions with the cyclometallated phenyl ring and the ortho-CH2 group of the PhanePhos ligand. Within the same core geometry at iridium, the second lowest transition state, TS2-Z-2S3S, will afford a diastereomer from the (Z)-isomer (IIb) with the same stereoselectivity for the allylation of floural. Notably, both computational studies and RPKA implicate rapid allene hydrometallation followed by turnover-limiting carbonyl addition with the allyliridium species as a potential catalyst resting state.
Scheme 2.
Computationally determined energy profiles of the proposed catalytic mechanism.a

a See Supporting Information for details on computational studies.
Conclusions
In summary, we report a highly regio- and enantioselective iridium catalyzed allene-fluoral reductive coupling mediated by 2-propanol. This method enables generation of enantiomerically enriched quaternary carbon stereocenters in the context of a CF3-bearing stereodiad. Of greater significance, we have identified a chromatographically stable cyclometallated iridium-(R)-PhanePhos complex Ir-PP-I that is catalytically competent in the present allene-fluoral reductive couplings as well as previously reported iridium-PhanePhos catalyzed C-C couplings of methanol with dienes6b or CF3-allenes.6c These findings suggest that cyclometallated iridium-PhanePhos complexes akin to Ir-PP-I may constitute a privileged catalyst class. A catalytic mechanism involving rapid allene hydrometalation followed by turnover-limiting carbonyl addition was corroborated by deuterium labelling studies, reaction progress kinetic analysis (RPKA) and DFT calculations. Computational studies also were used to formulate a unified stereochemical that accounts for the origins of enantioselectivity in the present fluoral-allene reductive couplings and previously reported iridium-PhanePhos catalyzed C-C couplings of methanol with dienes6b or CF3-allenes.6c Future studies will focus on the discovery and development of related umpoled allylations29 via alcohol-mediated carbonyl addition catalyzed by cyclometallated iridium-PhanePhos complexes.
Supplementary Material
Figure 4.
Corroboration of catalytic competency of Ir-PP-I for all iridium-(R)-PhanePhos-catalyzed transfer hydrogenative carbonyl additions.a
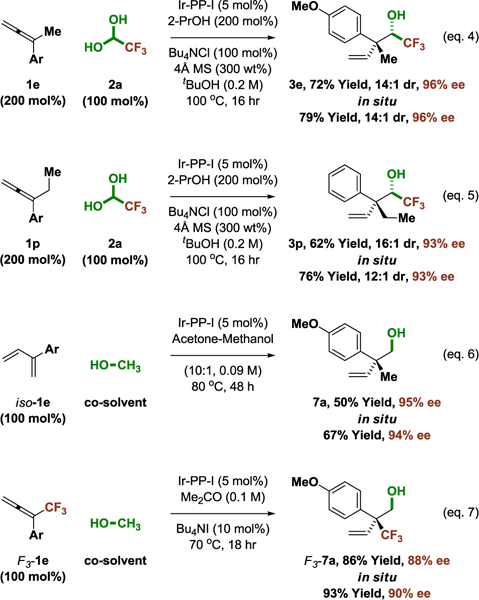
a Diastereoselectivity determined by NMR analysis of crude reaction mixtures. Enantioselectivities were determined by chiral stationary phase HPLC analysis. Yields of material isolated by silica gel chromatography. See Supporting Information for further experimental details.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
The Robert A. Welch Foundation (F-0038), the NIH (RO1-GM069445, 1 S10 OD021508–01), and King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) are acknowledged for partial support of this research. Eli Lilly and Company is acknowledged for LIFA post-doctoral fellowship funding (M.H.). Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) is acknowledged for postdoctoral fellowship support (G.B. 2017/00734–5). We thank Professor Donna G. Blackmond for assistance with RPKA. The service of Ibex, Shaheen 2 High Performance Computing Facilities was provided with financial support from KAUST.
Footnotes
ASSOCIATED CONTENT
Supporting Information. Experimental procedures and spectral data. HPLC traces of racemic and enantiomerically enriched products. Crystallographic data for the 3,5-dinitrobenzoate of 3d and the cyclometallated iridium-(R)-PhanePhos complex Ir-PP-I. Reaction progress kinetic analysis data and data pertaining to computational studies. This material is available free of charge via the internet at http://pubs.acs.org.
Notes.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
REFERENCES
- (1).For recent reviews on the enantioselective formation of quaternary carbon stereocenters, see: (a) Das JP; Marek I Enantioselective synthesis of all-carbon quaternary stereogenic centers in acyclic systems. Chem. Commun 2011, 47, 4593. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Minko Y; Marek I Stereodefined acyclic trisubstituted metal enolates towards the asymmetric formation of quaternary carbon stereocenters. Chem. Commun 2014, 50, 12597. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Marek I; Minko Y; Pasco M; Mejuch T; Gilboa N; Chechik H; Das JP All-Carbon Quaternary Stereogenic Centers in Acyclic Systems through the Creation of Several C–C Bonds per Chemical Step. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2014, 136, 2682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Quasdorf KW; Overman LE Catalytic enantioselective synthesis of quaternary carbon stereocenters. Nature 2014, 516, 181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Liu Y; Han S-J; Liu W-B; Stoltz BM Catalytic Enantioselective Construction of Quaternary Stereocenters: Assembly of Key Building Blocks for the Synthesis of Biologically Active Molecules. Acc. Chem. Res 2015, 48, 740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Zeng X-P; Cao Z-Y; Wang Y-H; Zhou F; Zhou J Catalytic Enantioselective Desymmetrization Reactions to All-Carbon Quaternary Stereocenters. Chem. Rev 2016, 116, 7330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Feng J; Holmes M; Krische MJ Acyclic Quaternary Carbon Stereocenters via Enantioselective Transition Metal Catalysis. Chem. Rev 2017, 117, 12564. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (2).For selected examples of the enantioselective metal-catalyzed formation of acyclic quaternary carbon stereocenters, see: (a) Sawamura M; Sudoh M; Ito Y An Enantioselective Two-Component Catalyst System: Rh−Pd-Catalyzed Allylic Alkylation of Activated Nitriles. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1996, 118, 3309. [Google Scholar]; (b) Zhang A; RajanBabu TV All-Carbon Quaternary Centers via Catalytic Asymmetric Hydrovinylation. New Approaches to the Exocyclic Side Chain Stereochemistry Problem. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 128, 5620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Krautwald S; Sarlah D; Schafroth MA; Carreira EM Enantio- and Diastereodivergent Dual Catalysis: α-Allylation of Branched Aldehydes. Science 2013, 340, 1065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Zhang C; Santiago CB; Crawford JM; Sigman MS Enantioselective Dehydrogenative Heck Arylations of Trisubstituted Alkenes with Indoles to Construct Quaternary Stereocenters. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 15668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Zhou Q; Cobb KM; Tan T; Watson MP Stereospecific Cross Couplings To Set Benzylic, All-Carbon Quaternary Stereocenters in High Enantiopurity. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 12057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Patel HH; Sigman MS Enantioselective Palladium-Catalyzed Alkenylation of Trisubstituted Alkenols To Form Allylic Quaternary Centers. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 14226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Ohmiya H; Zhang H; Shibata S; Harada A; Sawamura M Construction of Quaternary Stereogenic Carbon Centers through Copper‐ Catalyzed Enantioselective Allylic Alkylation of Azoles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2016, 55, 4777. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Cruz FA; Dong VM Stereo-divergent Coupling of Aldehydes and Alkynes via Synergistic Catalysis Using Rh and Jacobsen’s Amine. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2017, 139, 1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (i) Hojoh K; Ohmiya H; Sawamura M Synthesis of α-Quaternary Formimides and Aldehydes through Umpolung Asymmetric Copper Catalysis with Isocyanides. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2017, 139, 2184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (j) Starkov P; Moore JT; Duquette DC; Stoltz BM; Marek I Enantioselective Construction of Acyclic Quaternary Carbon Stereocenters: Palladium-Catalyzed Decarboxylative Allylic Alkylation of Fully Substituted Amide Enolates. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2017, 139, 9615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (k) Shockley SE; Hethcox JC; Stoltz BM Enantioselective Synthesis of Acyclic α‐Quaternary Carboxylic Acid Derivatives through Iridium‐Catalyzed Allylic Alkylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2017, 56, 11545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (l) Fujita T; Yamamoto T; Morita Y; Chen H; Shimizu Y; Kanai M Chemo- and Enantioselective Pd/B Hybrid Catalysis for the Construction of Acyclic Quaternary Carbons: Migratory Allylation of O-Allyl Esters to α-C-Allyl Carboxylic Acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 5899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (3).For a recent review on the formation of acyclic stereopolyads, see: Eppe G; Didier D; Marek I Stereocontrolled Formation of Several Carbon–Carbon Bonds in Acyclic Systems. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 9175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (4).For selected reviews on the preparation of organofluorine compounds, see: (a) Gong Y Recent Applications of Trifluoroacetaldehyde Ethyl Hemiacetal for the Synthesis of Trifluoromethylated Compounds. Curr. Org. Chem 2004, 17, 1659. [Google Scholar]; (b) Cahard D; Xu X; Couve-Bonnaire S; Pannecoucke X Fluorine & chirality: how to create a nonracemic stereogenic carbon–fluorine centre? Chem. Soc. Rev 2010, 39, 558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Nie J; Guo H-C; Cahard D; Ma J-A Asymmetric Construction of Stereogenic Carbon Centers Featuring a Trifluoromethyl Group from Prochiral Trifluoromethylated Substrates. Chem. Rev 2011, 111, 455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Furuya T; Kamlet AS; Ritter T Catalysis for fluorination and trifluoromethylation. Nature 2011, 473, 470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Besset T; Schneider C; Cahard D Tamed arene and heteroarene trifluoromethylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2012, 51, 5048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Studer AA “Renaissance” in radical trifluoromethylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2012, 51, 8950. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Liang T; Neumann CN; Ritter T Introduction of fluorine and fluorine-containing functional groups. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2013, 52, 8214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Campbell MG; Ritter T Modern Carbon–Fluorine Bond Forming Reactions for Aryl Fluoride Synthesis. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (i) Xu X-H; Matsuzaki K; Shibata N Synthetic Methods for Compounds Having CF3–S Units on Carbon by Trifluoromethylation, Trifluoromethylthiolation, Triflylation, and Related Reactions. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (j) Yang X; Wu T; Phipps RJ; Toste FD Advances in Catalytic Enantioselective Fluorination, Mono-, Di-, and Trifluoromethylation, and Trifluoromethylthiolation Reactions. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (k) Alonso C; Martinez de Marigorta E.; Rubiales G; Palacios F Carbon Trifluoromethylation Reactions of Hydrocarbon Derivatives and Heteroarenes. Chem. Rev 2015, 115, 1847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (5).For recent reviews on catalytic enantioselective alcohol-mediated carbonyl reductive coupling, see: (a) Ketcham JM; Shin I; Montgomery TP; Krische MJ Catalytic Enantioselective C-H Functionalization of Alcohols by Redox‐Triggered Carbonyl Addition: Borrowing Hydrogen, Returning Carbon. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2014, 53, 9142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Nguyen KD; Park BY; Luong T; Sato H; Garza VJ; Krische MJ Metal-catalyzed reductive coupling of olefin-derived nucleophiles: Reinventing carbonyl addition. Science 2016, 354, 300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Kim SW; Zhang W; Krische MJ Catalytic Enantioselective Carbonyl Allylation and Propargylation via Alcohol-Mediated Hydrogen Transfer: Merging the Chemistry of Grignard and Sabatier. Acc. Chem. Res 2017, 50, 2371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (6).For catalytic enantioselective formation of acyclic quaternary carbon stereocenters via alcohol-mediated carbonyl reductive coupling, see: (a) Feng J; Garza VJ; Krische MJ Redox-Triggered C–C Coupling of Alcohols and Vinyl Epoxides: Diastereo- and Enantioselective Formation of All-Carbon Quaternary Centers via tert-(Hydroxy)-Prenylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2014, 136, 8911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Nguyen KD; Herkommer D; Krische MJ Enantioselective Formation of All-Carbon Quaternary Centers via C–H Functionalization of Methanol: Iridium-Catalyzed Diene Hydrohydroxymethylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 14210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Holmes M; Nguyen KD; Schwartz LA; Luong T Krische MJ. Enantioselective Formation of CF3-Bearing All-Carbon Quaternary Stereocenters via C–H Functionalization of Methanol: Iridium Catalyzed Allene Hydrohydroxymethylation. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2017, 139, 8114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (7).Pye PJ; Rossen K; Reamer RA; Tsou NN; Volante RP; Reider PJ A New Planar Chiral Bisphosphine Ligand for Asymmetric Catalysis: Highly Enantioselective Hydrogenations under Mild Conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1997, 119, 6207. [Google Scholar]
- (8).For a review on the use of paraformaldehyde and methanol as C1-feedstocks in metal-catalyzed C-C coupling, see: Sam B; Breit B; Krische MJ Paraformaldehyde and Methanol as C1 Feedstocks in Metal‐Catalyzed C-C Couplings of π‐Unsaturated Reactants: Beyond Hydroformylation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2015, 54, 3267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (9).For late transition metal catalyzed allene-carbonyl and allene-imine reductive coupling, see: (a) Nickel: Ng S-S; Jamison TF. Highly Enantioselective and Regioselective Nickel-Catalyzed Coupling of Allenes, Aldehydes, and Silanes. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2006, 127, 7320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Ng S-S; Jamison TF Nickel-catalyzed coupling of terminal allenes, aldehydes, and silanes. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 11350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Ng S-S; Jamison TF Enantioselective and regioselective nickel-catalyzed multicomponent coupling of chiral allenes, aromatic aldehydes, and silanes. Tetrahedron 2005, 61, 11405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Ruthenium: Ngai M-Y; Skucas E; Krische MJ. Ruthenium Catalyzed C−C Bond Formation via Transfer Hydrogenation: Branch-Selective Reductive Coupling of Allenes to Paraformaldehyde and Higher Aldehydes. Org. Lett 2008, 10, 2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (e) Skucas E; Zbieg JR; Krische MJ anti-Aminoallylation of Aldehydes via Ruthenium-Catalyzed Transfer Hydrogenative Coupling of Sulfonamido Allenes: 1,2-Aminoalcohols. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131, 5054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (f) Zbieg JR; McInturff EL; Krische MJ Allenamide Hydro−Hydroxyalkylation: 1,2-Amino Alcohols via Ruthenium-Catalyzed Carbonyl anti-Aminoallylation. Org. Lett 2010, 12, 2514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (g) Zbieg JR; McInturff EL; Leung JC; Krische MJ Amplification of Anti-Diastereoselectivity via Curtin−Hammett Effects in Ruthenium-Catalyzed Hydrohydroxyalkylation of 1,1-Disubstituted Allenes: Diastereoselective Formation of All-Carbon Quaternary Centers. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2011, 133, 1141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (h) Sam B; Montgomery TP; Krische MJ Ruthenium Catalyzed Reductive Coupling of Paraformaldehyde to Trifluoromethyl Allenes: CF3-Bearing All-Carbon Quaternary Centers. Org. Lett 2013, 15, 3790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (i) Sam B; Luong T; Krische MJ Ruthenium‐Catalyzed C-C Coupling of Fluorinated Alcohols with Allenes: Dehydrogenation at the Energetic Limit of β‐Hydride Elimination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2015, 54, 5465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (j) Oda S; Sam B; Krische MJ Hydroam-inomethylation Beyond Carbonylation: Allene–Imine Reductive Coupling by Ruthenium‐Catalyzed Transfer Hydrogenation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2015, 54, 8525 and reference 6c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (k) Iridium: Skucas E; Bower JF; Krische MJ. Carbonyl Allylation in the Absence of Preformed Allyl Metal Reagents: Reverse Prenylation via Iridium-Catalyzed Hydrogenative Coupling of Dimethylallene. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 12678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (l) Bower JF; Skucas E; Patman RL; Krische MJ Catalytic C−C Coupling via Transfer Hydrogenation: Reverse Prenylation, Crotylation, and Allylation from the Alcohol or Aldehyde Oxidation Level. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2007, 129, 15134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (m) Han SB; Kim IS; Han H; Krische MJ Enantioselective Carbonyl Reverse Prenylation from the Alcohol or Aldehyde Oxidation Level Employing 1,1-Dimethylallene as the Prenyl Donor. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2009, 131, 6916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (n) Moran J; Preetz A; Mesch RA; Krische MJ Iridium-catalysed direct C– C coupling of methanol and allenes. Nature Chem 2011, 3, 287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (o) Copper: Tsai EY; Liu RY; Yang Y; Buchwald SL. A Regio- and Enantioselective CuH-Catalyzed Ketone Allylation with Terminal Allenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 1140, 2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (p) Liu RY; Yang Y; Buchwald SL Regiodivergent and Diastereoselective CuH‐Catalyzed Allylation of Imines with Terminal Allenes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2016, 55, 14077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (10).For alkynes as latent allenes in metal catalyzed allene-carbonyl reductive coupling, see: (a) Park BY; Nguyen KD; Chaulagain MR; Komanduri V; Krische MJ Alkynes as Allylmetal Equivalents in Redox-Triggered C–C Couplings to Primary Alcohols: (Z)-Homoallylic Alcohols via Ruthenium-Catalyzed Propargyl C–H Oxidative Addition. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2014, 136, 11902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Liang T; Nguyen KD; Zhang W; Krische MJ Enantioselective Ruthenium-Catalyzed Carbonyl Allylation via Alkyne–Alcohol C–C Bond-Forming Transfer Hydrogenation: Allene Hydrometalation vs Oxidative Coupling. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 3161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Zhang W Chen W; Xiao H; Krische MJ Carbonyl anti-(α-Amino)allylation via Ruthenium Catalyzed Hydrogen Autotransfer: Use of an Acetylenic Pyrrole as an Allylmetal Pronucleophile. Org. Lett 2017, 19, 4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (11).For a recent review covering allene-carbonyl and allene-imine reductive coupling, see: Holmes M; Schwartz LA; Krische MJ Intermolecular Metal-Catalyzed Reductive Coupling of Dienes, Allenes, and Enynes with Carbonyl Compounds and Imines. Chem. Rev 2018, 118, 6026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (12).For a recent review on the synthesis of allenes, see: Neff RK; Frantz DE Recent Advances in the Catalytic Syntheses of Allenes: A Critical Assessment. ACS Catalysis 2014, 4, 519. [Google Scholar]
- (13).(a)Gupta M; Hagen C; Flesher RJ; Kaska WC; Jensen CM A highly active alkane dehydrogenation catalyst: stabilization of dihydrido rhodium and iridium complexes by a P–C–P pincer ligand. Chem. Commun 1996, 2083.; (b) Kiener CA; Shu C; Incarvito C; Hartwig JF Identification of an Activated Catalyst in the Iridium-Catalyzed Allylic Amination and Etherification. Increased Rates, Scope, and Selectivity. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2003, 125, 14272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Kim IS; Ngai M-Y; Krische MJ Enantioselective Iridium-Catalyzed Carbonyl Allylation from the Alcohol or Aldehyde Oxidation Level via Transfer Hydrogenative Coupling of Allyl Acetate: Departure from Chirally Modified Allyl Metal Reagents in Carbonyl Addition. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2008, 130, 14891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (d) Chen L-A; Xu W; Huang B; Ma J; Wang L; Xi J; Harms K; Gong L; Meggers E Asymmetric Catalysis with an Inert Chiral-at-Metal Iridium Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2013, 135, 10598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (14).A cyclometalated π-allyliridium C,O-benzoate complex modified by (S)-Cl,MeO-BIPHEP catalyzes highly enantioselective 2-propanol-mediated reductive couplings of branched aryl-substituted allylic acetates with fluoral hydrate: Cabrera JM; Tauber J; Zhang W; Xiang M; Krische MJ Selection between Diastereomeric Kinetic vs Thermodynamic Carbonyl Binding Modes Enables Enantioselective Iridium-Catalyzed anti-(α-Aryl)allylation of Aqueous Fluoral Hydrate and Difluoroacetaldehyde Ethyl Hemiacetal. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2018, 140, 9392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (15). For Curtin-Hammett effects in ruthenium-catalyzed alcohol-mediated allene-carbonyl reductive coupling, see reference 9g.
- (16).Schwartz RS; Yokokawa H; Graham EW Kinetics of the acidcatalyzed isomerization of phenylbutenes in glacial acetic acid. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1972, 94, 1247. [Google Scholar]
- (17).For diastereo- and enantioselective synthesis of oxetanes bearing quaternary carbon stereocenters, see: Guo Y-A; Lee W; Krische MJ Enantioselective Synthesis of Oxetanes Bearing All‐Carbon Quaternary Stereocenters via Iridium‐Catalyzed C−C Bond‐Forming Transfer Hydrogenation. Chem. Eur. J 2017, 23, 2557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (18).For an authoritative review on the use of oxetanes in medicinal chemistry, see: Bull JA; Croft RA; Davis OA; Doran R; Morgan KF Oxetanes: Recent Advances in Synthesis, Reactivity, and Medicinal Chemistry. Chem. Rev 2016, 116, 12150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (19).Mukherjee P; Pettersson M; Dutra JK; Xie L; am Ende CW Trifluoromethyl Oxetanes: Synthesis and Evaluation as a tert‐Butyl Isostere. Chem. Med. Chem 2017, 12, 1574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (20).For a review covering the use of trifluoroethylamines serve as amide bioisosteres, see: Meanwell NA Synopsis of Some Recent Tactical Application of Bioisosteres in Drug Design. J. Med. Chem 2011, 54, 2529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (21).For a review covering the synthesis of CF3-azetidines, see: Meyer F Trifluoromethyl nitrogen heterocycles: synthetic aspects and potential biological targets. Chem. Commun 2016, 52, 3077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (22).Dyer PW; Dyson PJ; James SL; Martin CM; Suman P The First Structural Characterization of a [2.2]PHANEPHOS−Transition-Metal Complex: Structure of rac-[Pd(4,12-bis(diphenylphosphino)[2.2]paracyclophane)Cl2]. Organometallics 1998, 17, 4344. [Google Scholar]
- (23).Klei SR; Golden JT; Tilley TD; Bergman RG Iridium-Catalyzed H/D Exchange into Organic Compounds in Water. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2002, 124, 2092 and references cited therein. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (24).For a review on reaction progress kinetic analysis, see: Blackmond DG Reaction Progress Kinetic Analysis: A Powerful Methodology for Mechanistic Studies of Complex Catalytic Reactions. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2005, 44, 4302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (25).For selected applications of reaction progress kinetic analysis, see: (a) Ji Y; Plata RE; Regens CS; Hay M; Schmidt M; Razler T; Qiu T; Geng P; Hsiao Y; Rosner T; Eastgate MD; Blackmond DG Mono-Oxidation of Bidentate Bis-phosphines in Catalyst Activation: Kinetic and Mechanistic Studies of a Pd/Xantphos-Catalyzed C-H Functionalization. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 13272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Ruiz-Castillo P; Blackmond DG; Buchwald SL Rational Ligand Design for the Arylation of Hindered Primary Amines Guided by Reaction Progress Kinetic Analysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Whitaker D; Burés J; Larrosa I Ag(I)-Catalyzed C-H Activation: The Role of the Ag(I) Salt in Pd/Ag-Mediated C-H Arylation of Electron-Deficient Arenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2016, 138, 8384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (26).For the use of Burés plots to determine reaction order, see: (a) Burés J Variable Time Normalization Analysis: General Graphical Elucidation of Reaction Orders from Concentration Profiles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2016, 55, 16084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (b) Burés J A Simple Graphical Method to Determine the Order in Catalyst. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed 2016, 55, 2028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; (c) Nielsen CD-T; Burés J Visual kinetic analysis. Chem. Sci 2019, 10, 348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (27).Zimmerman HE; Traxler MD The Stereochemistry of the Ivanov and Reformatsky Reactions. I. J. Am. Chem. Soc 1957, 79, 1920. [Google Scholar]
- (28).Grayson MN; Krische MJ; Houk KN Ruthenium-Catalyzed Asymmetric Hydrohydroxyalkylation of Butadiene: The Role of the Formyl Hydrogen Bond in Stereochemical Control. J. Am. Chem. Soc 2015, 137, 8838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- (29).For a review on umpoled carbonyl allylation, see: Spielmann K; Niel G; de Figueiredoa RM; Campagne JM Catalytic nucleophilic ‘umpoled’ π-allyl reagents. Chem. Soc. Rev 2018, 47, 1159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.