Abstract
Malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumors (GNETs) are rare aggressive malignant neoplasms that exclusively occur within the wall of the gastrointestinal tract. The GNET was first described as an ‘osteoclast-rich tumor of the gastrointestinal tract with features resembling clear cell sarcoma (CCS) of soft parts’ in 2003. Although the GNET shares certain histological features with CCS, it is characterized by a lack of melanocytic differentiation and the presence of non-tumoral osteoclast-like giant cells (OLGCs). The present study reports a case of a GNET of the ileum with intra-abdominal granulomatous nodules, an uncommon accompanying finding, and summarizes the current literature. A 30-year-old woman presented with the symptoms of intestinal obstruction, and a mass was found within the ileum wall. Multiple grey-white nodules were found adhering to the omentum and serosa of the ileum. Histologically, the tumor was located in the muscularis propria and infiltrated the mucosa and the serosa. Tumor cells presented with oval or polygonal nuclei and prominent nucleoli, and were predominantly arranged in nested and pseudopapillary patterns, with the presence of cluster of differentiation (CD)68-positive, scattered OLGC. Immunohistochemically, it was determined that the tumor cells expressed Vimentin, CD56, S-100 and transcription factor SOX-10, while being negative for pan-cytokeratin, cytokeratin (CK)7, CK20, synaptophysin, chromogranin-A, CD117, anoctamin-1, CD34, human melanoma black-45, Melan-A, smooth muscle actin, CD3 and CD20 expression. Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 gene rearrangement was identified by fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis. Ultrastructurally, no typical melanosomes were identified. In addition, the intra-abdominal grey-white nodules were microscopically identified as chronic granulomatous inflammation. The patient received four cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy following routine tumor resection. Due to its rarity and histological similarity with other neoplasms, unfamiliarity with the features of GNETs by surgical pathologists can easily lead to a misdiagnosis. Therefore, comprehensive assessments, including morphology and ancillary studies, are required for an accurate diagnosis of GNET.
Keywords: malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor, clear cell sarcoma-like tumor of the gastrointestinal tract, fluorescence in situ hybridization, transcription factor SOX-10, EWSR1
Introduction
Clear cell sarcoma-like tumor of the gastrointestinal tract (CCSLTGT), also known as an ‘osteoclast-rich tumor of the gastrointestinal tract with features resembling clear cell sarcoma (CCS) of soft parts’, is a rare and malignant tumor entity that occurs exclusively within the wall of the gastrointestinal tract (1). In contrast to CCS of the soft tissue (previously known as melanoma of the soft tissue), CCSLTGT was initially described as a distinct entity by Zambrano et al (2) in 2003 from a series of 6 cases that were characterized histologically by the presence of osteoclast-like giant cells (OLGCs) and immunohistochemically by the absence of melanocyte-specific markers. An increasing number of cases support that CCSLTGT is a distinctive tumor entity, and not a variant of CCS of the soft tissue (3–10). However, the pathological nature of CCSLTGT is distinguishable from CCS of the soft tissue in that it always arises in tendons and aponeuroses, and shows melanocytic differentiation at the light microscopic, ultrastructural and protein levels (1,10). In 2012, Stockman et al (6) proposed to re-designate this tumor entity as a ‘malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor’ (GNET) instead of a CCSLTGT, and this term has been increasingly accepted by pathologists (7–9,11–13). Based on recent studies, cases that were previously reported as soft tissue-type CCS of the gastrointestinal tract (CCS-GI) lacking melanocytic differentiation may be appropriately categorized as CCSLTGT or GNET, although a GNET remains a controversial tumor entity (1–4,6–11,13). To the best of our knowledge, only 47 cases that may represent a GNET have been reported in the English or Chinese languages, including 31 of which appear to be reported as a CCSLTGT or GNET and 16 that correspond to CCS-GI lacking melanocytic differentiation. Table I summarizes the clinicopathological and cytogenetic features of all 47 previous cases (2–9,11–24). Due to its rarity and histological similarity, a GNET may be easily misdiagnosed as a variety of neoplasms, including adenocarcinoma, a gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), a neuroendocrine tumor, CCS and a malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) (1). The present study reports a case of a GNET of the ileum with intra-abdominal granulomatous nodules in a 30-year-old woman who was initially misdiagnosed with a poorly differentiated carcinoma by intra-operative frozen section diagnosis.
Table I.
Summary of clinicopathological features of 47 cases that were previously reported as CCSLTGT, GNET or CCS-GI lacking melanocytic differentiation.
| Authors (publication) | CCSLTGT or GNET case | Age, years | Sex | Location | S100 | SOX-10 | HMB-45/Melan-A | EM findings | Genetic findings | Follow-up | Additional findings | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zambrano et al (2003) | Yes | 15 | F | Jejunum | + | ND | − | No melanosomes | t(12;22) (q13;q12) | DOD at 16 months | OLGC | (2) |
| Yes | 21 | F | Jejunum | + | ND | − | ND | ND | DOD at 12 months | OLGC/LN met. | ||
| Yes | 35 | F | Ileum | + | ND | − | No melanosomes | ND | Liver met. at 12 months | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 37 | F | Ileum | + | ND | − | ND | ND | Lost | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 13 | M | Stomach | + | ND | − | No melanosomes | ND | Recurrence at 8 months | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 32 | M | Ileum | + | ND | − | ND | ND | NA | OLGC/LN met. | ||
| Huang et al (2006) | Yes | 40 | M | Stomach | + | ND | − | ND | ND | NA | OLGC | (4) |
| Antonescu et al (2006) | No | 81 | F | Colon | + | ND | − | No melanosomes | EWSR1-CREB1 | Intra-abdominal and Liver met. at 60 months | LN met. | (14) |
| No | 42 | F | Ileum | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1-CREB1 | NA | OLGC | ||
| No | 42 | F | Ileum | + | ND | − | No melanosomes | EWSR1-CREB1 | NA | Mesenteric met. | ||
| Friedrichs et al (2005) | Yes | 41 | M | Jejunum | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1-ATF1 | Liver met. at 6 months | OLGC | (3) |
| Venkataraman et al (2005) | No | 21 | F | Ileum | + | ND | − | No melanosomes | EWSR1 rearrangement | NA | (15) | |
| Granville et al (2006) | No | 16 | M | Ileum | + | ND | − | Rare pre-melanosomes | EWSR1-ATF1 | DOD at 11 months | OLGC | (16) |
| Comin et al (2007) | No | 31 | F | Ileum | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1 rearrangement | NA | LN met. | (17) |
| Joo et al (2009) | No | 60 | M | Ileum | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1 rearrangement | NA | OLGC/LN and Liver met. | (18) |
| No | 46 | M | Jejunum | + | ND | − | ND | No EWSR1 rearrangement | NA | LN met./Ig-G4-scle.dis | ||
| Lagmay et al (2009) | No | 10 | F | Stomach | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1-ATF1 | NED at 4 months | LN and liver met. | (19) |
| Terazawa et al (2009) | No | 20+ | F | Ileum | + | ND | ND | ND | EWSR1-ATF1 | AWD at 24 months | OLGC | (20) |
| Shenjere et al (2012) | No | 53 | F | Ileum | + | ND | − | No melanosomes | EWSR1-ATF1 | NA | OLGC/LN met. | (21) |
| No | 26 | F | Small and large bowel | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1-CREB1 | NA | Mesenteric met. | ||
| No | 66 | M | Small bowel | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1-CREB1 | NA | LN met. | ||
| Stockman et al (2012) | Yes | 30 | F | Jejunum | + | + | − | Dense-core granules | EWSR1-ATF | AWD at 21 months | (6) | |
| Yes | 35 | M | Jejunum | + | + | − | Dense-core granules | EWSR1-ATF1 | DOD at 18 months | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 33 | M | Ileum | + | + | − | Dense-core granules | EWSR1-CREB1 | AWD at 1.5 months | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 50 | F | Stomach | + | + | − | Dense-core granules | EWSR1-ATF1 | AWD at 20 months | |||
| Yes | 20 | F | Small bowel | + | + | − | Dense-core granules | EWSR1 rearrangement | NED at 20 months | |||
| Yes | 52 | M | Ileum | + | + | − | ND | EWSR1 and FUS-negative | DOD at 22 months | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 46 | M | Stomach | + | + | − | ND | EWSR1 rearrangement | NA | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 34 | F | Stomach | + | + | − | ND | EWSR1-ATF1 | DOD at 19 months | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 37 | F | Ileum | + | + | ND | ND | ND | NA | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 77 | F | Colon | + | + | − | ND | EWSR1-ATF1 | DOD at 106 months | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 31 | M | Colon | + | + | − | ND | ND | DOD at 3 months | OLGC | ||
| Yes | 17 | M | Small bowel | + | + | − | ND | EWSR1 rearrangement | NA | |||
| Yes | 60 | M | Ileum | + | + | − | ND | EWSR1-ATF1 | AWD at 36 months | |||
| Yes | 60 | F | Jejunum | + | + | − | ND | EWSR1-CREB1 | NED at 41 months | |||
| Yes | 56 | M | Stomach | + | + | − | ND | EWSR1-CREB1 | NA | |||
| Yes | 28 | F | Small bowel | + | + | − | ND | EWSR1 rearrangement | DOD at 23 months | |||
| Lasithiotakis et al (2013) | No | 49 | F | Jejunum | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1 rearrangement | NED at 20 months | (22) | |
| Kong et al (2014) | Yes | 17 | M | Stomach | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1 rearrangement | NED at 10 months | OLGC | (7) |
| Thway et al (2014) | Yes | 33 | M | Small bowel | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1-CREB1 | DOD at 7 months | LN met./hepatoblastoma history | (5) |
| Zhao et al (2014) | Yes | 33 | F | Ileum | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1 rearrangement | NED at 12 months | (8) | |
| Insabato et al (2015) | Yes | 29 | M | Stomach | + | ND | − | No melanosomes | EWSR1 rearrangement | AWD at 74 months | Ewing's Sarcoma history | (11) |
| Boland et al (2016) | Yes | 46 | F | Stomach | + | + | − | ND | EWSR1-ATF1 | NA | Oncocytic variant | (12) |
| Alyousef et al (2017) | Yes | 18 | M | Jejunum | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1 rearrangement | DOD at 48 months | OLGC | (13) |
| Li et al (2005) | No | 40 | M | Stomach | + | ND | − | No melanosomes | ND | NED at 9 months | OLGC/LN met. | (23) |
| Huang et al (2014) | No | 45 | F | Colon | + | ND | − | ND | EWSR1 rearrangement | Liver met. at 16 months | OLGC/LN met. | (24) |
| Kansal et al (2017) | Yes | 55 | F | Jejunum | + | ND | − | ND | ND | NA | Neurofilament(+) | (9) |
20+ indicates early twenties. IgG4-scle. Dis, immunoglobulin 4-related sclerosing disease; EM, electron microscopy; AWD, alive with disease; DOD, succumbed to disease; NED, no evidence of disease; ND, not done; NA, not available; met., metastasis; LN, lymph node; OLGC, osteoclast-like giant cell; EWSR1, Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1; CREB1, cyclic responsive element binding protein 1; ATF1, activating transcription factor 1; M, male; F, female.
Case report
A 30-year-old woman presenting with acute abdominal pain and occasional vomiting was admitted to the Department of General Surgery, 924th (181st) Hospital of the Chinese People's Liberation Army (Guilin, Guangxi, China) in November 2017. The patient had a history of 10 kg of weight loss over the past 6 months and an appendectomy 6 months previously.
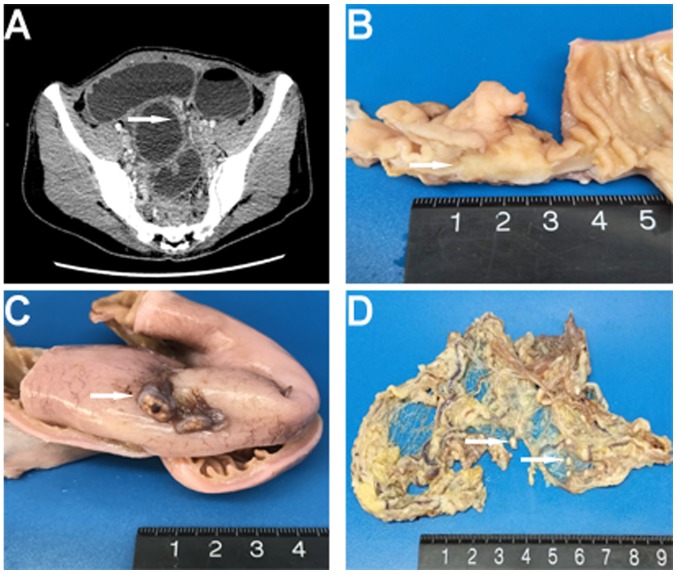
Physical examination revealed a mid-abdominal bulge with visible intestinal peristalsis. A computed tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis showed a segmental wall thickening and dilatation of the distal ileum, evidence of intestinal obstruction (Fig. 1A). The patient underwent an exploratory laparotomy, and a mass located in the distal ileum, as well as multiple gray-white nodules adhering to the omentum majus and ileal serosa, were identified. An excision of the segmental ileum and partial omentum majus was performed.
Figure 1.
(A) Enhanced computed tomography revealed a dilatation and wall thickening of the distal small intestine (arrowhead). (B) Macroscopically, a mass within the intestinal wall that was well-circumscribed and gray-white was identified (arrowhead). (C and D) Multiple gray-white nodules were found adhering to the serosa surface of the intestine and the omentum majus (arrowhead).
As the patient was in an unstable condition, further imaging examinations besides the CT scan, including magnetic resonance imaging and position emission tomography-computed tomography, were not performed. The patient presented with symptoms of acute intestinal obstruction and was subjected to an immediate exploratory laparotomy. The mass in the ileum was initially misdiagnosed as a poorly differentiated carcinoma based on an intra-operative frozen section diagnosis; the growth pattern of the tumor was nested and sheet-like with the presence of intra-abdominal small nodules.
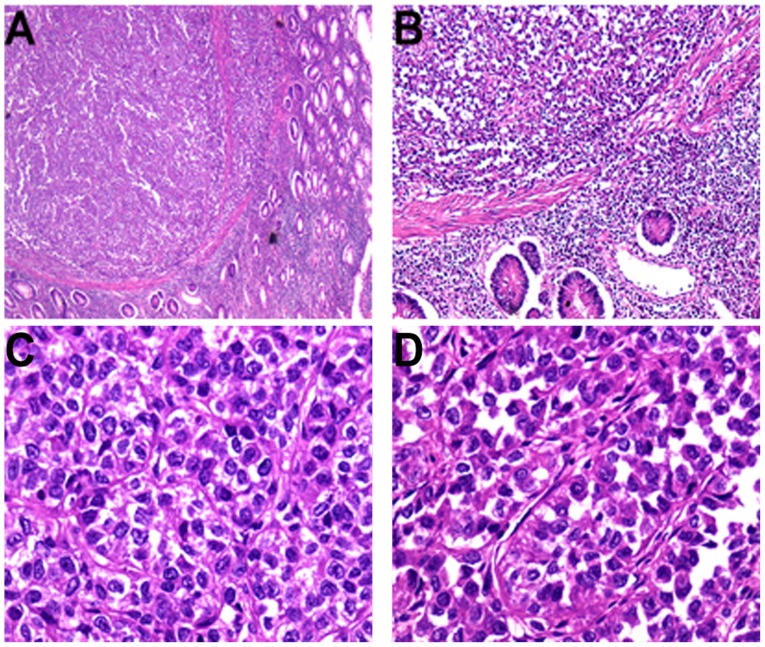
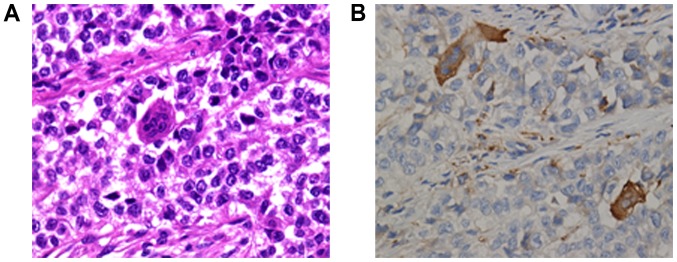
Macroscopic examination revealed a 3.5×2×1.8-cm annular mass within the ileum wall; the cut surface was gray-white and well-circumscribed (Fig. 1B). Multiple gray-white nodules were adhered to the ileal serosa and omentum that appear similar in nature to metastatic carcinoma nodules (Fig. 1C and D). For the microscopic examination, surgical specimens were fixed in neutral buffered 10% formalin overnight at room temperature and paraffin-embedded. Subsequently, 3-µm sections were stained with hematoxylin for 5 min and eosin for 40 sec at room temperature. Under light microscopy (DM3000; Leica Microsystems GmbH, Wetzlar, Germany), the tumor was situated in the muscularis propria and extended into the mucosa and serosa (Fig. 2A and B). Tumor cells were predominantly arranged in nested and pseudopapillary patterns with eosinophilic cytoplasm, oval or polygonal vesicular nuclei and prominent nucleoli (Fig. 2C and D). Cluster of differentiation (CD)68-positive, scattered OLGCs were identified (Fig. 3A and B). Necrosis and mitotic figures (in 8/10 high-powered fields) were also noted. There was no tumor involvement in the surgical margin, regional lymph nodes or liver. The gray-white nodules that adhered to the omentum and ileal serosa were identified as a chronic granulomatous inflammation.
Figure 2.
(A) Microscopically, the tumor was located in the muscularis propria and had disrupted the muscularis mucosae (H&E staining; original magnification, ×25). (B) The muscularis mucosae were interrupted and tumor cells invaded the mucosa (H&E staining; original magnification, ×100). Histologically, (C) nested and (D) pseudopapillary architectural patterns were present, and tumor cells presented with vesicular nuclei and eosinophilic cytoplasm (H&E staining; original magnification, ×400). H&E, hematoxylin and eosin staining.
Figure 3.
(A) A characteristic feature of malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumors, multinucleated OLGCs, was identified (H&E staining, original magnification ×400). (B) Scattered OLGCs were positive for cluster of differentiation 68 immunostaining, but tumor cells were negative, indicating that the OLGCs were not tumor-derived, in contrast to the tumor-derived giant cells of conventional clear cell sarcomas (immunohistochemistry; original magnification, ×400). OLGC, osteoclast-like giant cell.
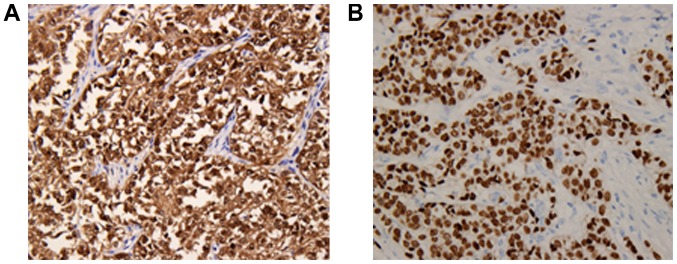
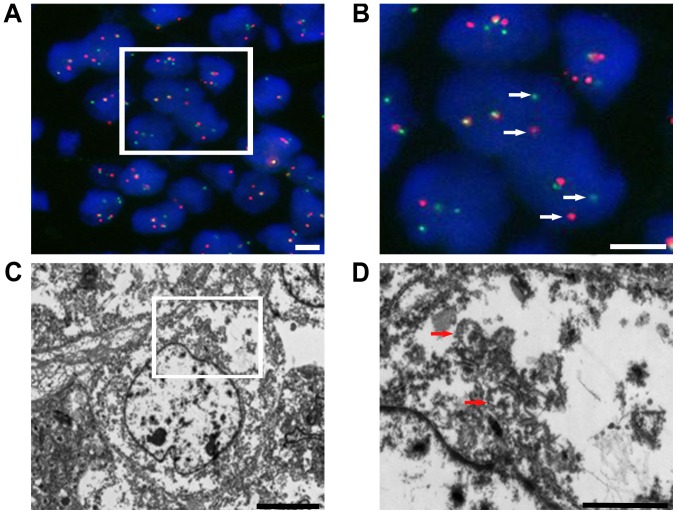
The differential diagnosis included a variety of epithelial and mesenchymal tumors, and tests using a panel of immunohistochemical markers were performed. The immunohistochemical assay was performed as previously described (8). Images were acquired using a light microscope DM3000 (Leica Microsystems GmbH) and the antibodies used in this case study were listed in Table II. The neoplastic cells showed strong diffuse expression of S-100 and SOX-10 protein (Fig. 4A and B), and positive staining for Vimentin and CD56, but no staining for pan-cytokeratin AE1/AE3, cytokeratin (CK)7, CK20, homeobox protein CDX-2 (CDX-2), synaptophysin, chromogranin-A, CD117, anoctamin-1 (DOG-1), CD34, human melanoma black-45 (HMB-45), Melan-A, smooth muscle actin, CD3 and CD20. Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) analysis was performed as previously described (5) with an Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1 (EWSR1) break-apart probe that revealed the splitting signal in 164 out of 200 nuclei, i.e., a significant separation of the red and green signals, indicating the presence of EWSR1 gene rearrangement (Fig. 5A and B). Ultrastructurally, no typical melanosomes were identified, but there were isolated dense-core secretory granules in the tumor cell cytoplasm. The nuclei were irregularly shaped, and the nucleoli were dense and occasionally prominent (Fig. 5C and D).
Table II.
Antibodies used in the immunohistochemical analysis.
| Antibodies | Catalogue number | Supplier | Dilution |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pan-cytokeratin | M351529-2 | Dako | 1:500 |
| Cytokeratin 7 | M701829-2 | Dako | 1:400 |
| Cytokeratin 20 | M701929-2 | Dako | 1:400 |
| S-100 | ab4066 | Abcam | 1:600 |
| SOX-10 | ab212843 | Abcam | 1:600 |
| Vimentin | M072501-2 | Dako | 1:800 |
| CD56 | M730401-2 | Dako | 1:500 |
| Synaptophysin | M731529-2 | Dako | 1:300 |
| Chromogranin-A | M086929-2 | Dako | 1:300 |
| CD117 | M3260 | Spring Bioscience; Roche | 1:200 |
| DOG-1 | ab53212 | Abcam | 1:300 |
| CDX-2 | 06970940001 | Roche | 1:300 |
| CD34 | M716529-2 | Dako | 1:200 |
| CD3 | 05493315001 | Roche | 1:200 |
| CD20 | 05493234001 | Roche | 1:200 |
| HMB-45 | M063429-2 | Dako | 1:500 |
| Melan-A | M719629-2 | Dako | 1:200 |
| Smooth muscle actin | 06770886001 | Roche | 1:200 |
| Secondary antibodies | P044701-2 & P044801-2 | Dako | 1:1,000 |
Abcam, Cambridge, UK; Dako; Agilent Technologies, Inc., Santa Clara, CA, USA; Roche Diagnostics GmbH, Mannheim, Germany.
Figure 4.
(A) Nuclear and cytoplasmic immunostaining for S-100 was strongly and diffusely positive in the tumor cells. (B) Nuclear immunostaining for transcription factor SOX-10 was diffusely positive in the tumor cells (immunohistochemistry; original magnification, ×200).
Figure 5.
(A and B) Representative image of EWSR1 gene rearrangements. Fluorescence in situ hybridization analysis with a dual-color EWSR1 break-apart probe showed that the analyzed tumor cell presented with at least one fusion signal, and the separated red and green signals (arrowhead), indicative of a rearrangement of one copy of EWSR1. Scale bars, 5 µm. (C and D) Ultrastructural features, including some isolated dense-core secretory granules (arrowhead), irregularly shaped nuclei and prominent nucleoli, were identified. Scale bars, (C) 5 µm and (D) 2 µm. EWSR1, Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1.
The patient received 4 cycles of adjuvant chemotherapy with ifosfamide (400 mg/day for 5 days) plus epirubicin (40 mg/day for 1 day) following the intestinal segment resection, as described previously (8,11). The patient remained alive without tumor recurrence or metastasis during the 6-month follow-up period from December 2017 to May 2018. The patient received imaging examinations every 6 months and to determine her prognosis an intensive follow-up schedule was required.
Discussion
Since CCSLTGT was first described by Zambrano et al (2) in 2003, it has remained a controversial entity. In 1985, Alpers and Beckstead (25) reported a case of a malignant neuroendocrine tumor of the jejunum with OLGCs, which particularly resembled CCSLTGT histologically. However, an increasing number of cases support CCSLTGT as an independent tumor entity that lacks melanocytic differentiation at the light microscopic, ultrastructural and protein levels (3–10). In 2012, Stockman et al (6) proposed that this tumor entity should be re-designated as a GNET, a term which has achieved increasing acceptance (7–9,11–13). GNETs are rare and aggressive malignant neoplasms that predominantly occur in younger and middle-aged adults (median age, 35 years) without sex predominance (Table I). In a review of the literature, all reported cases of GNET arose within the abdominal cavity, frequently involving the small intestine, stomach or colon (2–9,11–24). GNETs appear to progress aggressively with preferential metastases to the liver and/or mesenteric lymph nodes (2,5,14,17–19,21,23,24). Patients often present with abdominal pain, intestinal obstruction or incidental image findings of an abdominal mass. Occasionally non-specific symptoms, including weight loss and anemia, are associated (1).
The etiology of GNETs is unknown. A total of 2 cases of GNETs document a patient history of hepatoblastoma or Ewing's sarcoma in early childhood, suggesting that genetic aberration in the embryonic stage could be regarded as a risk for the oncogenesis of this tumor (5,11). A single case occurred as a secondary malignancy following irradiation for neuroblastoma in infancy, suggesting that radiotherapy may also be regarded as a risk factor for the development of this tumor later in life (26). Intra-abdominal granulomatous inflammation in the present case, and immunoglobulin-4-related sclerosing inflammation in another case have been reported with this tumor, suggesting that immune factors may participate in its progression (18). Furthermore, it was found that the granulomatous nodules in the current case were formed of abundant CD68-positive macrophages, indicating that immune cells, particularly macrophages, may be associated with the development of this tumor. Due to the absence of melanocyte-specific markers and the significant expression of SOX-10 protein, an important transcriptional factor responsible for the development of the neural crest, GNETs are hypothesized to originate from gastrointestinal neuroectodermal precursor cells that are unable to differentiate into the melanocytic lineage through uncertain etiology (6).
Macroscopically, GNETs typically arise within the muscularis propria of the gastrointestinal tract, and often extend into the submucosa and subserosa with a well-circumscribed and pushing border (1,6). Certain tumors manifest as a polypoid mass (2). These growth patterns frequently lead to an ulcerated mucosa, or a thickening or stenosing gastrointestinal wall (1,2,6). Histologically, tumor cells frequently present with a solid, nested, pseudoalveolar or fascicular growth pattern, occasionally forming an uncommon pseudopapillary, microcystic or rosette-like architecture (1,2,6–8). The majority of tumor cells are composed of medium and large-sized ovoid, epithelioid or spindle cells with eosinophilic or clear cytoplasm, occasionally with an oncocytic cytoplasm (1,6,12). The nuclei are often located centrally and are polygonal. The nucleoli are not usually prominent, while the nuclei occasionally display numerous macronucleoli (1,2,6). The presence of OLGCs and the absence of melanin pigment detected by Fontana stain are characteristic features distinguishing GNETs from other mesenchymal tumors of the gastrointestinal tract, particularly soft tissue-type CCS involvement of the gastrointestinal tract (1,4,6,14). CCS may also feature multinucleated tumor-derived giant cells, but the OLGCs in GNETs are not tumor-derived, and invariably appear to be CD68-positive (2). As presented in Table I, the OLGC feature was not observed in a number of the cases of GNETs (5,6,8,9,11,12,14,17–19,21,22).
Immunohistochemically, S-100 protein positivity has been found in all reported cases. Melanocyte-specific markers (HMB-45, Melan-A and tyrosinase) are negative in the majority of cases, indicating a deficiency in melanocytic differentiation. At least one of the neuroendocrine markers (including chromogranin-A, synaptophysin, neuron-specific enolase and CD56) is positive in the majority of cases. A 100% positivity rate for SOX-10 protein expression was found in all cases where SOX-10 immunostaining was performed, further supporting the hypothesis that GNET arises from a primitive neural crest cell lineage (6,12). GIST markers, including CD117, DOG-1 and CD34, were negative in all cases. The GNETs were also negative for desmin, smooth muscle actin and pan-cytokeratin AE1/AE3, and just 1 case was reported to be focally positive CAM5.2 (6). Ultrastructurally, no melanosomes or melanosome-like structures were generally identified, although rare pre-melanosomes (stage I) were observed in 1 case (16). The neoplastic cells commonly showed clear secretory vesicles, dense-core secretory granules or multiple interdigitating cell processes (6,14).
Genetically, GNETs are characterized by EWSR1 (22q12.2) gene rearrangement in the majority of investigated cases; common fusion partners are the cAMP responsive element binding protein 1 or activating transcription factor 1 CREB1 or ATF1 genes (5,6,12,19–21). However, Stockman et al (6) and Joo et al (18) reported that EWSR1 gene rearrangement was not detected by FISH in their cases, indicating that other genetic events may also be associated with GNET tumorigenesis. Fused in sarcoma (FUS; 16p11.2), a gene that shares extensive nucleotide sequence homology with EWSR1, was proposed by Stockman et al (6) as an alternative gene, but FUS had no signal for gene rearrangement detection in all cases analyzed. EWSR1 gene rearrangement has been identified in other distinctive tumors, including Ewing sarcoma, hyalinizing clear cell carcinoma of the salivary gland, myoepithelial carcinoma, extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma, myxoid liposarcoma, angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma and desmoplastic small round cell tumors (27–30). Therefore, EWSR1 gene rearrangement is not a specific criterion for GNETs, but can aid in confirming the diagnosis of a GNET.
In the patients with follow-up data, regional lymph nodes and liver metastases were common (2,3,6,23). As GNET cases are rare, no 5-year survival rate is available. The reported cases include survival periods ranging from 3 to 106 months (6). The consensus treatment for a GNET is a surgical resection of the involved bowel segment followed by regular image monitoring for recurrence and metastasis (1). Although 2 patients received chemotherapy in previously reported cases, chemotherapy is not regarded as an evidence-based practice for this tumor entity (8,11).
The differential diagnosis of a CCSLTGT or GNET includes adenocarcinoma, a GIST, a neuroendocrine tumor, CCS involving the gastrointestinal tract, metastatic melanoma, an MPNST, a malignant granular cell tumor and synovial sarcoma. Microscopically, a poorly differentiated carcinoma usually has a nested and sheet pattern composed of epithelial tumor cells, potentially leading to a misdiagnosis. A panel of epithelial markers of the gastrointestinal tract, including pan-cytokeratin AE1/AE3, CK20 and CDX-2, will be useful for distinguishing poorly differentiated carcinomas from GNETs. Although GISTs can display a variety of morphologies, occasionally mimicking the structure and morphology of GNETs, routine immunohistochemistry can exclude the diagnosis of a GIST. GISTs usually express at least one marker from CD117, DOG-1 and CD34, whereas GNETs are negative for all these markers (31). Although the expression of neuroendocrine markers is often found in GNETs, the OLGCs and genetic translocation features are useful for excluding neuroendocrine tumors (6). Metastatic melanoma usually presents with a history of previous skin melanoma and generally expresses HMB-45, Melan-A or tyrosinase, and lacks EWSR1 rearrangement (1,6). Soft tissue-type CCS typically occurs at tendons and aponeuroses, and CCS involving the gastrointestinal tract is extremely rare (13). CCS commonly displays tumor-derived giant cells rather than non-tumor OLGCs, is positive for HMB-45 and/or Melan-A, and contains melanin pigment, as detected by Fontana stain (1,10). SOX-10 is also positive in certain cases of CCS, so SOX-10 immunoreactivity is less useful (32). Genetic analysis is also not beneficial for distinguishing CCS from GNETs due to the presence of similar genetic hallmarks, whereas electron microscopy analysis presenting numerous melanosomes in varying developmental stages is of value in diagnosing CCS (33). The mass of an MPNST may be connected to a nerve, and typically occurs in a patient with a history of neurofibroma or schwannoma. The epithelioid MPNST may show a similar histology to a GNET, while it often shows a strong and diffuse immunostaining for S-100 protein when compared with GNETs. Malignant granular cell tumors are exceedingly rare and may display similar immunophenotypes to GNETs. It is occasionally difficult to make a definitive diagnosis based on morphology, but genetic analysis is valuable in distinguishing GNETs from malignant granular cell tumors (12). Although synovial sarcomas focally express S-100 protein in up to 40% of cases, potentially confusing the diagnosis, epithelial markers, including EMA and cytokeratins, are commonly focally detectable in various types of synovial sarcoma (34). This tumor is characterized by the t(X;18)(p11;q11) translocation that results in the SS18 nBAF chromatin remodeling complex subunit-SSX family member 2 gene fusion, which is found exclusively in synovial sarcoma (35). Transducin-like enhancer of split 1 was also recently identified as a robust diagnostic biomarker for synovial sarcoma and correlates with t(X;18) (36).
In conclusion, the present study reports a case of a GNET of the ileum with intra-abdominal granulomatous nodules, an uncommon accompanying finding. A GNET is a rare tumor that shares some features with certain other neoplasms. Unfamiliarity with the features of GNETs by surgical pathologists can easily lead to a misdiagnosis. Therefore, it is necessary to comprehensively assess the clinical, gross, morphological, immunohistochemical, genetic and even ultrastructural characteristics for a definitive diagnosis of a GNET.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Glossary
Abbreviations
- CCSLTGT
clear cell sarcoma-like tumor of the gastrointestinal tract
- CCS
clear cell sarcoma
- OLGC
osteoclast-like giant cells
- GNET
malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor
- CCS-GI
soft tissue-type CCS of the gastrointestinal tract
- GIST
gastrointestinal stromal tumor
- MPNST
malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor
- FISH
fluorescence in situ hybridization
- EWSR1
Ewing sarcoma breakpoint region 1
- FUS
fused in sarcoma
Funding
The collection of data from FISH analysis and electron microscopy in this study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant no. 81360320) and the Scientific Research and Technology Development Program of Guilin (grant nos. 20180107-12 and 2016012702-3).
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Authors' contributions
GXH made substantial contributions to acquisition of the patient data and drafting the manuscript. QYC contributed to the interpretation of the patient data. LLZ performed the FISH and electron microscopy, and contributed to the data analysis. HC contributed to the histological assessment and case diagnosis. HPZ performed the histological examination. XFL performed the immunochemical analysis. FT designed the study and reviewed the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of clinical details was obtained from the patient.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
References
- 1.Wang J, Thway K. Clear cell sarcoma-like tumor of the gastrointestinal tract: An evolving entity. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2015;139:407–412. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2013-0547-RS. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Zambrano E, Reyes-Mugica M, Franchi A, Rosai J. An osteoclast-rich tumor of the gastrointestinal tract with features resembling clear cell sarcoma of soft parts: Reports of 6 cases of a GIST simulator. Int J Surg Pathol. 2003;11:75–81. doi: 10.1177/106689690301100202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Friedrichs N, Testi MA, Moiraghi L, Modena P, Paggen E, Plötner A, Wiechmann V, Mantovani-Löffler L, Merkelbach-Bruse S, Buettner R, Wardelmann E. Clear cell sarcoma-like tumor with osteoclast-like giant cells in the small bowel: Further evidence for a new tumor entity. Int J Surg Pathol. 2005;13:313–318. doi: 10.1177/106689690501300402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Huang W, Zhang X, Li D, Chen J, Meng K, Wang Y, Lu Z, Zhou X. Osteoclast-rich tumor of the gastrointestinal tract with features resembling those of clear cell sarcoma of soft parts. Virchows Arch. 2006;448:200–203. doi: 10.1007/s00428-005-0051-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Thway K, Judson I, Fisher C. Clear cell sarcoma-like tumor of the gastrointestinal tract, presenting as a second malignancy after childhood hepatoblastoma. Case Rep Med. 2014;2014:984369. doi: 10.1155/2014/984369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Stockman DL, Miettinen M, Suster S, Spagnolo D, Dominguez-Malagon H, Hornick JL, Adsay V, Chou PM, Amanuel B, Vantuinen P, Zambrano EV. Malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor: Clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, and molecular analysis of 16 cases with a reappraisal of clear cell sarcoma-like tumors of the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:857–868. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31824644ac. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kong J, Li N, Wu S, Guo X, Gu C, Feng Z. Malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor: A case report and review of the literature. Oncol Lett. 2014;8:2687–2690. doi: 10.3892/ol.2014.2524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhao Z, Zhang D, Li W, Zhang L, Li Z, Zhou J. Primary malignant neuroectodermal tumor of the ileum with predominantly uncommon pseudopapillary architecture. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7:8967–8971. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kansal S, Rao S. Malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor: A unique rare neoplasm. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2017;8:630–633. doi: 10.1007/s13193-017-0654-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kosemehmetoglu K, Folpe AL. Clear cell sarcoma of tendons and aponeuroses, and osteoclast-rich tumour of the gastrointestinal tract with features resembling clear cell sarcoma of soft parts: A review and update. J Clin Pathol. 2010;63:416–423. doi: 10.1136/jcp.2008.057471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Insabato L, Guadagno E, Natella V, Somma A, Bihl M, Pizzolorusso A, Mainenti PP, Apice G, Tornillo L. An unusual association of malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor (clear cell sarcoma-like) and Ewing sarcoma. Pathol Res Pract. 2015;211:688–692. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2015.06.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Boland JM, Folpe AL. Oncocytic variant of malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor: A potential diagnostic pitfall. Hum Pathol. 2016;57:13–16. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2016.05.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Alyousef MJ, Alratroot JA, ElSharkawy T, Shawarby MA, Al Hamad MA, Hashem TM, Alsayyah A. Malignant gastrointestinal neuroectodermal tumor: A case report and review of the literature. Diagn Pathol. 2017;12:29. doi: 10.1186/s13000-017-0620-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Antonescu CR, Nafa K, Segal NH, Dal Cin P, Ladanyi M. EWS-CREB1: A recurrent variant fusion in clear cell sarcoma-association with gastrointestinal location and absence of melanocytic differentiation. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:5356–5362. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-2811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Venkataraman G, Quinn AM, Williams J, Hammadeh R. Clear cell sarcoma of the small bowel: A potential pitfall. Case report. APMIS. 2005;113:716–719. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0463.2005.apm_243.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Granville L, Hicks J, Popek E, Dishop M, Tatevian N, Lopez-Terrada D. Visceral clear cell sarcoma of soft tissue with confirmation by EWS-ATF1 fusion detection. Ultrastruct Pathol. 2006;30:111–118. doi: 10.1080/01913120500406400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Comin CE, Novelli L, Tornaboni D, Messerini L. Clear cell sarcoma of the ileum: Report of a case and review of literature. Virchows Arch. 2007;451:839–845. doi: 10.1007/s00428-007-0454-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Joo M, Chang SH, Kim H, Gardner JM, Ro JY. Primary gastrointestinal clear cell sarcoma: Report of 2 cases, one case associated with IgG4-related sclerosing disease, and review of literature. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2009;13:30–35. doi: 10.1016/j.anndiagpath.2008.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lagmay JP, Ranalli M, Arcila M, Baker P. Clear cell sarcoma of the stomach. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2009;53:214–216. doi: 10.1002/pbc.22014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Terazawa K, Otsuka H, Morita N, Yamashita K, Nishitani H. Clear-cell sarcoma of the small intestine detected by FDG-PET/CT during comprehensive examination of an inflammatory reaction. J Med Invest. 2009;56:70–75. doi: 10.2152/jmi.56.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shenjere P, Salman WD, Singh M, Mangham DC, Williams A, Eyden BP, Howard N, Knight B, Banerjee SS. Intra-abdominal clear-cell sarcoma: a report of 3 cases, including 1 case with unusual morphological features, and review of the literature. Int J Surg Pathol. 2012;20:378–385. doi: 10.1177/1066896911425485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Lasithiotakis K, Protonotarios A, Lazarou V, Tzardi M, Chalkiadakis G. Clear cell sarcoma of the jejunum: A case report. World J Surg Oncol. 2013;11:17. doi: 10.1186/1477-7819-11-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Li DJ, Zhang XH, Huang WB, Meng K, Zhou XJ. An osteoclast-rich tumor of the gastrointestinal tract with features resembling clear cell sarcoma of soft parts: A case report and review of the literature. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2005;34:757–758. (In Chinese) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Huang HF, L Q, Bu H, Chen M, Chen HJ, Lin YY, Zhang HY. Clear cell sarcoma of gastrointestinal tract: Clinicopathologic analyses and review of literatures. J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;30:383–388. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Alpers CE, Beckstead JH. Malignant neuroendocrine tumor of the jejunum with osteoclast-like giant cells. Enzyme histochemistry distinguishes tumor cells from giant cells. Am J Surg Pathol. 1985;9:57–64. doi: 10.1097/00000478-198501000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Yang JC, Chou AJ, Oeffinger KC, La Quaglia MP, Wolden SL. Clear cell sarcoma of the gastrointestinal tract after very low-dose therapeutic radiation therapy: A case report. J Pediatr Surg. 2012;47:1943–1945. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2012.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Thway K, Fisher C. Tumors with EWSR1-CREB1 and EWSR1-ATF1 fusions: The current status. Am J Surg Pathol. 2012;36:e1–e11. doi: 10.1097/PAS.0b013e31824b1ee0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Antonescu CR, Katabi N, Zhang L, Sung YS, Seethala RR, Jordan RC, Perez-Ordoñez B, Have C, Asa SL, Leong IT, et al. EWSR1-ATF1 fusion is a novel and consistent finding in hyalinizing clear-cell carcinoma of salivary gland. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2011;50:559–570. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Antonescu CR, Dal Cin P, Nafa K, Teot LA, Surti U, Fletcher CD, Ladanyi M. EWSR1-CREB1 is the predominant gene fusion in angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 2007;46:1051–1060. doi: 10.1002/gcc.20491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tanas MR, Rubin BP, Tubbs RR, Billings SD, Downs-Kelly E, Goldblum JR. Utilization of fluorescence in situ hybridization in the diagnosis of 230 mesenchymal neoplasms: An institutional experience. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134:1797–1803. doi: 10.5858/2009-0571-OAR.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.West RB, Corless CL, Chen X, Rubin BP, Subramanian S, Montgomery K, Zhu S, Ball CA, Nielsen TO, Patel R, et al. The novel marker, DOG1, is expressed ubiquitously in gastrointestinal stromal tumors irrespective of KIT or PDGFRA mutation status. Am J Pathol. 2004;165:107–113. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63279-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Karamchandani JR, Nielsen TO, van de Rijn M, West RB. Sox10 and S100 in the diagnosis of soft-tissue neoplasms. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2012;20:445–450. doi: 10.1097/PAI.0b013e318244ff4b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mukai M, Torikata C, Iri H, Mikata A, Kawai T, Hanaoka H, Yakumaru K, Kageyama K. Histogenesis of clear cell sarcoma of tendons and aponeuroses. An electron-microscopic, biochemical, enzyme histochemical, and immunohistochemical study. Am J Pathol. 1984;114:264–272. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Pelmus M, Guillou L, Hostein I, Sierankowski G, Lussan C, Coindre JM. Monophasic fibrous and poorly differentiated synovial sarcoma: immunohistochemical reassessment of 60 t(X;18)(SYT-SSX)-positive cases. Am J Surg Pathol. 2002;26:1434–1440. doi: 10.1097/00000478-200211000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ladanyi M, Antonescu CR, Leung DH, Woodruff JM, Kawai A, Healey JH, Brennan MF, Bridge JA, Neff JR, Barr FG, et al. Impact of SYT-SSX fusion type on the clinical behavior of synovial sarcoma: A multi-institutional retrospective study of 243 patients. Cancer Res. 2002;62:135–140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Knosel T, Heretsch S, Altendorf-Hofmann A, Richter P, Katenkamp K, Katenkamp D, Berndt A, Petersen I. TLE1 is a robust diagnostic biomarker for synovial sarcomas and correlates with t(X;18): Analysis of 319 cases. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:1170–1176. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2010.01.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.