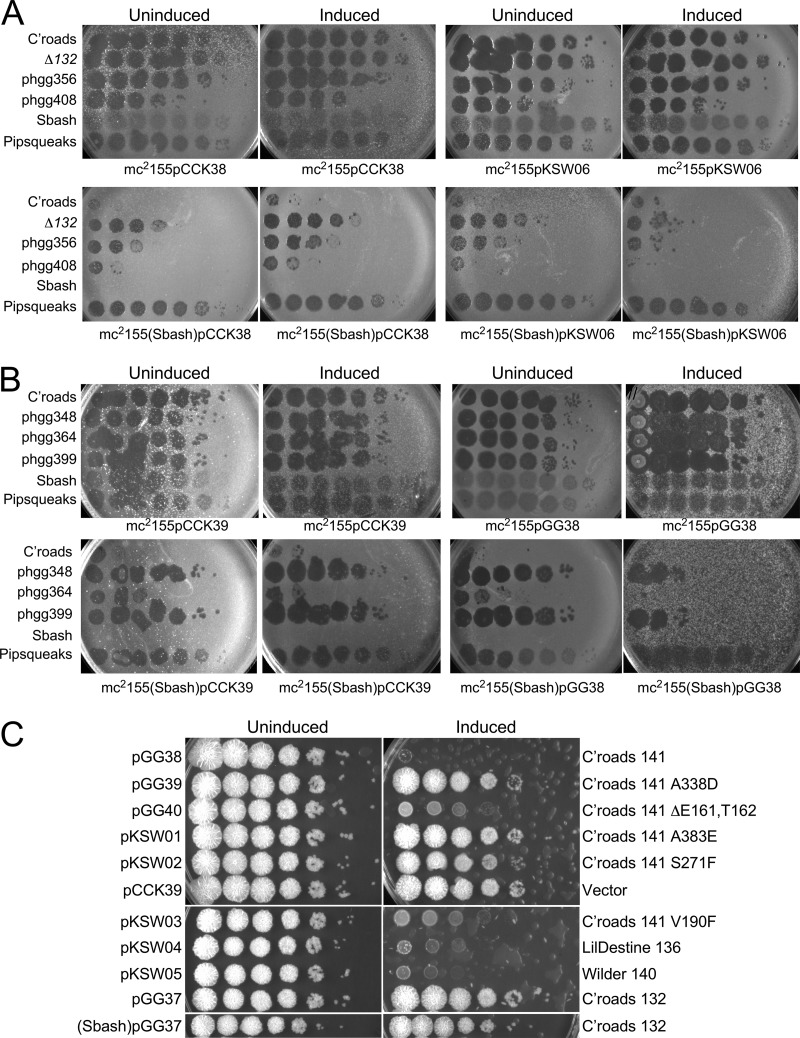
FIG 6.
Expression of Crossroads gp132 and gp141. (A) Strains were constructed carrying extrachromosomal expression vector pCCK38 or plasmid pKSW06, in which Crossroads 132 expression can be induced by addition of ATc, in either M. smegmatis mc2155 (top row) or a Sbash lysogen (bottom row). Lawns were prepared on solid media with (Induced) or without (Uninduced) ATc, and 10-fold serial dilutions (from left to right) of phages were spotted. Phages tested were Crossroads, Crossroads Δ132, DEM mutants phgg356 and phgg408, Sbash, and Pipsqueaks. Expression of gp132 in mc2155(Sbash) results in an approximately 100-fold reduction in EOP of strain Δ132 and the DEMs relative to the uninduced control. It is unclear why some of these phages have reduced plating efficiencies on M. smegmatis (Sbash) pCCK38 relative to M. smegmatis mc2155pCCK38. (B) Strains containing integration-proficient vector pCCK39 or plasmid pGG38 in which Crossroads 141 can be induced with ATc were plated as described in the panel A legend, except the ATc concentration was reduced to 5 ng/ml and the plates were incubated for 3 days (all others were incubated for 1.5 days). Phages Crossroads, phgg348, phgg364, phgg399, Sbash, and Pipsqueaks were spotted as described in the panel A legend. Expression of gene 141 substantially reduced the plating efficiencies of DEM mutants in a Sbash lysogen. (C) Liquid cultures of strains containing the plasmids indicated on the left were grown to an OD600 of 0.5, serially diluted 10-fold, and spotted onto solid media with (Induced) or without (Uninduced) ATc. The genes/mutants in each plasmid are noted at the right. Plasmids pGG37 and pKSW06 are integrating and extrachromosomal plasmids, respectively, containing Crossroads 132, and neither displayed toxicity in either a Sbash lysogen or a nonlysogen.