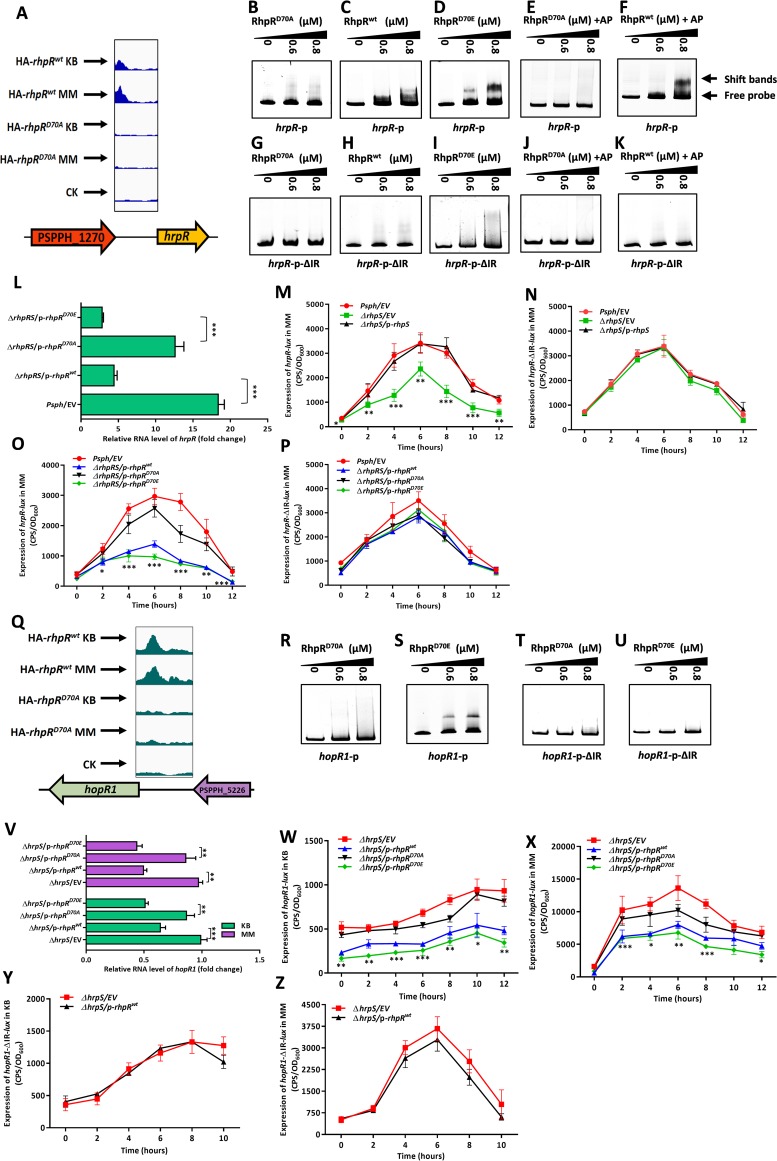
FIG 4.
RhpR binds to hrpR and hopR1 promoter regions by targeting the IR element and represses the induction of T3SS. RhpR directly inhibits hrpR and hopR1 by targeting the IR element. (A) RhpR binds to the promoter region of hrpR. (B to F) Validation of binding of RhpR to hrpR promoter regions by EMSA. The full-length hrpR promoter was subjected to EMSA with RhpR, RhpR pretreated with 20 mM acetyl phosphate, RhpRD70A, RhpRD70A pretreated with 20 mM acetyl phosphate, and RhpRD70E. (G to K) Validation of the binding site of RhpR to the hrpR promoter regions by EMSA. The IR element in the hrpR promoter was deleted by using overlap PCR, and products were added to the EMSA reaction mixtures. (L) RT-qPCR reveals that RhpR suppresses the expression of hrpR. pHM1-RhpR, pHM1-RhpRD70A, pHM1-RhpRD70E, or pHM1 empty vector was transformed into the P. savastanoi pv. phaseolicola 1448A ΔrhpRS strain. RT-qPCR was performed to measure the transcription level of hrpR in all strains. (M and N) Regulation of hrpR and hrpR-ΔIR promoters by RhpR in vivo. Activities of hrpR-lux or hrpR-ΔIR-lux were introduced into the wild-type 1448A strain, ΔrhpS strain, and ΔrhpS strain carrying the pHM1-rhpS plasmid. The bacteria were grown in KB and induced in MM before measurement of luciferase (lux) activities. (O and P) Regulation of hrpR and hrpR-ΔIR promoters by RhpR in the ΔrhpRS strain. Activities of hrpR-lux or hrpR-ΔIR-lux were introduced into the ΔrhpRS strain, ΔrhpRS strain carrying the pHM1-rhpR plasmid, ΔrhpRS strain carrying the pHM1-rhpRD70A plasmid, and ΔrhpRS strain carrying the pHM1-rhpRD70E plasmid. (Q) Original sequence peaks show the RhpR binding regions in the hopR1 promoter. The binding peaks diminished in RhpRD70A background strains. (R and S) EMSA shows that RhpR directly binds to the hopR1 promoter region. The full-length hopR1 promoter was subjected to EMSA with RhpR or RhpRD70E. (T and U) The hrpR promoter lacking the IR element was used in the EMSA reaction. The hopR1-ΔIR promoter was subjected to EMSA with RhpR or RhpRD70E. (V) RT-qPCR shows that RhpR independently suppresses the expression of hopR1. pHM1-RhpR, pHM1-RhpRD70A, pHM1-RhpRD70E, or pHM1 empty vector was transformed into the ΔhrpS strain. RT-qPCR was performed to measure the transcription level of hopR1 in both strains. (W to Z) Regulation of hopR1 promoters and hopR1-ΔIR promoters by RhpR in the ΔhrpS strain. Activities of hopR1-lux and hopR1-ΔIR-lux were introduced into the ΔhrpS strain, ΔhrpS strain carrying the pHM1-rhpR plasmid, ΔhrpS strain carrying the pHM1-rhpRD70A plasmid, and ΔhrpS strain carrying the pHM1-rhpRD70E plasmid. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01, and ***, P < 0.001, compared to the ΔrhpS, ΔrhpRS/p-rhpRD70A, or ΔhrpS strain by Student's t test. Each experiment was performed three times. Error bars represent standard error.