Abstract
Poisoning by long acting anti-coagulant rodenticides (LAARs) requires long-term treatment with oral vitamin K1 (VK1). However, discontinuing treatment based on normalization of INR, may leave some patients with serum LAAR concentrations above a level considered safe. To address this, we carried out a retrospective analysis of 21 case reports of LAAR poisoning having at least two serum LAAR concentrations quantified during treatment with oral VK1. We identified the case reports by survey of existing peer-reviewed literature in which a patient presented to emergency department exhibiting bleeding or elevated INRs, and had quantitative measurements of serum LAAR concentrations. Of 21 case reports, measurement of serum LAAR concentrations following VK1 treatment showed that over half (n=11) had serum LAAR concentrations that were above a concentration considered to be safe (10 ng/mL), despite having received higher daily and total VK1 dosing, over an equivalent treatment duration. Since residual amounts of serum and tissue LAAR could contribute to symptom recurrence and repeated hospitalization, these results indicate that normalization of INR is not a sufficient criterion to discontinue VK1 treatment and that measurements of serum LAAR concentrations should be included to help guide decisions to continue or discontinue VK treatment.
Keywords: Rodenticide, Vitamin K1, superwarfarin, brodifacoum
The consequences of accidental or intentional ingestion of long-acting anticoagulants (LAARs) include life-threatening internal hemorrhage, for which current recommended treatment consists of resuscitation with blood products followed by high-dose (up to 100 mg or more per day), long-term (weeks to months) oral vitamin K (VK1) therapy [1]. In addition to ingestion, LAAR poisoning can occur topically as well as by inhalation, as illustrated by a current nationwide outbreak of cases, in which inhalation of synthetic cannabinoids contaminated with the LAAR brodifacoum (BDF) have led to close to 300 hospitalizations and 8 deaths [2]. The high cost and prolonged treatment requirement for VK1 raise concerns about access to care and adherence to therapy. Currently, the key biomarker of response to oral VK1 therapy is INR. However, whether normalization of INR is a sufficient criterion to recommend discontinuing VK1 treatment is not clear. Moreover, VK1-independent actions of LAARs, including renal [3] and neurological damage [4, 5], may persist even though coagulation is normalized.
We carried out a retrospective analysis of 21 case reports with serum LAAR concentrations quantified before and after oral VK1 treatment (Table 1). Across all cases, the average initial serum LAAR concentration was 318±77 ng/mL; mean treatment duration was 113±16 days with a mean of 109±29 mg daily VK1. After treatment, LAAR concentrations declined to a mean of 50±16 ng/mL; however, many patients at that time had LAAR concentrations above 10 ng/mL, a level at which brodifacoum induced coagulopathy was not observed [6, 7, 8]. Although the estimated LD50 values for LAARs differ (ranging from 0.27 mg/kg to over 1 mg/kg in rodents), we used 10ng/mL as a value to stratify patients into 2 groups, In the group (n=10) with lower post-treatment concentrations, the mean starting plasma LAAR concentration was 183±68 ng/mL and treatment with 48±13 mg/day of oral VK1 lasted an average of 119±24 days (Figure 1). The cohort with higher post-treatment LAAR concentrations (n=11) had initial mean concentrations of 449±124 ng/mL and were treated with 164±50 mg/day VK1 for an average of 109±21 days. Despite similar treatment duration, and higher daily and total VK1 doses, treatment duration in the latter cohort was insufficient to reduce serum LAAR to acceptable concentrations.
Table 1:
Summary of 21 case reports organized by serum [LAAR] at discharge
| [LAAR] ng/mL |
[LAAR] ng/mL |
[LAAR] | mg VK1 | Duration | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
LAAR |
Start | Final | % Start | Daily dose | Days |
Total mg VK1 |
Ref |
|
| BDF | 1 | 0.5 | 50% | 15 | 83 | 1245 | [13] | |
| BDF | 270 | 1 | 0% | 100 | 100 | 10000 | [14] | |
| BDF | 70 | 4 | 6% | 100 | 90 | 9000 | [9] | |
| BDF | 98 | 4.2 | 4% | 15 | 102 | 1530 | [8] | |
| BDF | 170 | 5 | 3% | 100 | 180 | 18000 | [9] | |
| BDF | 93 | 5 | 5% | 60 | 135 | 8100 | [15] | |
| FLF | 61 | 5 | 8% | 10 | 48 | 480 | [16] | |
| BDF | 289 | 7.6 | 3% | 17.5 | 300 | 5250 | [14] | |
| BDF | 731 | 10 | 1% | 50 | 114 | 5700 | [17] | |
| BDL | 92 | 10 | 11% | 10 | 34 | 340 | [7] | |
| BDF | 61 | 15 | 25% | 26 | 164 | 4264 | [18] | |
| BDF | 42 | 20 | 48% | 140 | 21 | 2940 | [19] | |
| BDF | 170 | 25 | 15% | 600 | 46 | 27600 | [6] | |
| BDF | 320 | 31 | 10% | 50 | 42 | 2100 | [20] | |
| BDF | 350 | 36 | 10% | 300 | 150 | 45000 | [21] | |
| BDF | 210 | 66 | 31% | 150 | 168 | 25200 | [22] | |
| BDF | 280 | 78 | 28% | 111 | 18 | 1998 | [23] | |
| DFN | 970 | 110 | 11% | 200 | 180 | 36000 | [24] | |
| BDF | 860 | 160 | 19% | 30 | 77 | 2310 | [25] | |
| BDF | 280 | 170 | 61% | 100 | 120 | 12000 | [26] | |
| BDF | 1302 | 291 | 22% | 100 | 209 | 20900 | [10] | |
| Mean | All | 318 | 50 | 19% | 109 | 113 | 11427 | |
| <=10 ng/mL | 183 | 5 | 11% | 48 | 119 | 5965 | ||
| > 10 ng/mL | 440 | 91 | 25% | 164 | 109 | 16392 | ||
| SEM | All | 72 | 15 | 4% | 27 | 15 | 2595 | |
| <=10ng/mL | 68 | 1 | 5% | 13 | 24 | 1761 | ||
| > 10ng/mL | 124 | 26 | 5% | 50 | 21 | 4655 | ||
Data base screening was carried out by searching PubMed and Google between 1989 and 2018 for existing peer-reviewed literature in which a patient presented to emergency department exhibiting bleeding or elevated INRs, and in which quantitative analysis of LAAR concentrations in serial serum samples was performed.
BDF, brodifacoum, estimated LD50 0.27 mg/kg in rats
BDL, bromadiolone, estimated LD50 1.125 mg/kg in rats
DFN, difenacoum, estimated LD50 >1 mg/kg in rats.
FLF, flocoumafen, estimated LD50 1 mg/kg in rats.
Figure 1.
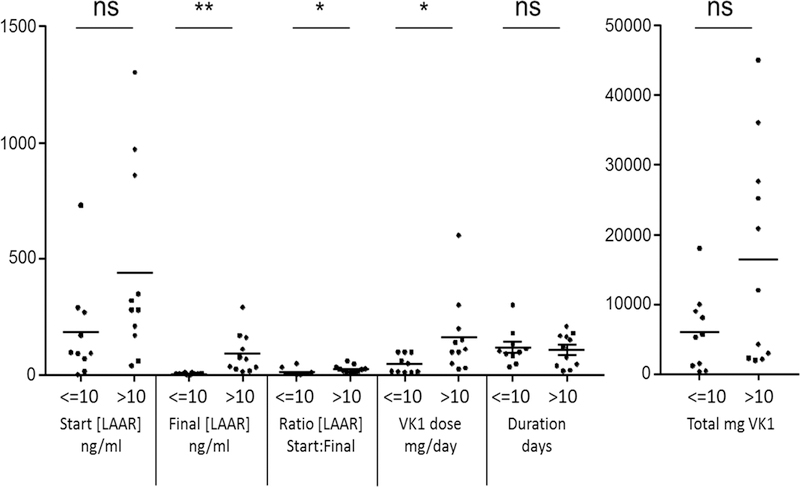
Values for the indicated parameters in patients whose initial serum LAAR concentrations were <= 10 ng/mL (n=10) or > 10 ng/mL (n=11). After testing revealed non-normal distribution, groups were compared by Mann Whitney non-parametric test. *, P <0.05; **, P<0.005. Bars indicate means.
Since higher serum LAAR concentrations are typically associated with longer prothrombin times and INRs [7, 9, 10], these data suggest that discontinuing VK1 treatment based on normalization of INR poses a risk since over half the patients retained elevated serum LAAR concentrations. Protracted tissue LAAR content can potentially lead to recurrence of life-threatening bleeding requiring hospitalization and intensive treatment [11]. These findings suggest a need to establish a system to monitor and study the relationship of blood LAAR concentrations and clinical outcomes of survivors of LAAR poisoning for prolonged periods. Consistent with this, current recommendations from the American Society of Hematology include weekly quantitative serum LAAR determinations [12], to help guide dose and duration of oral VK1 therapy.
Acknowledgments:
This work was supported by grant 1U01NS083457 (DLF)
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest:
GW is officer, shareholder and paid consultant to ResQ Pharma, Inc.
DLF is a paid consultant for ResQ Pharma, Inc.
IR and DLF are cofounders of EnSol Therapeutics, LLC.
References
- 1.King N, Tran MH. Long-Acting Anticoagulant Rodenticide (Superwarfarin) Poisoning: A Review of Its Historical Development, Epidemiology, and Clinical Management. Transfusion medicine reviews 2015; 29(4):250–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.IDPH. Illinois Department of Public Health 2018; http://www.dph.illinois.gov/search/site/synthetic%20cannabinoids.
- 3.Ware KM, Feinstein DL, Rubinstein I, et al. Brodifacoum induces early hemoglobinuria and late hematuria in rats: novel rapid biomarkers of poisoning. American journal of nephrology 2015; 41(4–5):392–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kalinin S, Marangoni N, Kowal K, et al. The Long-Lasting Rodenticide Brodifacoum Induces Neuropathology in Adult Male Rats. Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2017; 159(1):224–237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Marangoni MN, Martynowycz MW, Kuzmenko I, et al. Membrane Cholesterol Modulates Superwarfarin Toxicity. Biophysical journal 2016; 110(8):1777–1788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bruno GR, Howland MA, McMeeking A, et al. Long-acting anticoagulant overdose: brodifacoum kinetics and optimal vitamin K dosing. Annals of emergency medicine 2000; 36(3):262–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Hollinger BR, Pastoor TP. Case management and plasma half-life in a case of brodifacoum poisoning. Archives of internal medicine 1993; 153(16):1925–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Travis SF, Warfield W, Greenbaum BH, et al. Spontaneous hemorrhage associated with accidental brodifacoum poisoning in a child. The Journal of pediatrics 1993; 122(6):982–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gunja N, Coggins A, Bidny S. Management of intentional superwarfarin poisoning with long-term vitamin K and brodifacoum levels. Clinical toxicology (Philadelphia, Pa.) 2011; 49(5):385–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Olmos V, Lopez CM. Brodifacoum poisoning with toxicokinetic data. Clinical toxicology (Philadelphia, Pa.) 2007; 45(5):487–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Underwood EL, Sutton J, Ellis IK, et al. Prolonged coagulopathy after brodifacoum exposure. American journal of health-system pharmacy : AJHP : official journal of the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists 2014; 71(8):639–42. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.DeLoughery TG, Shatzel J. The Superwarfarin Chronicles. American Society of Hematology Clinical News 2018; https://www.ashclinicalnews.org/perspectives/the-superwarfarin-chronicles/.
- 13.Babcock J, Hartman K, Pedersen A, et al. Rodenticide-induced coagulopathy in a young child. A case of Munchausen syndrome by proxy. The American journal of pediatric hematology/oncology 1993; 15(1):126–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Weitzel JN, Sadowski JA, Furie BC, et al. Surreptitious ingestion of a long-acting vitamin K antagonist/rodenticide, brodifacoum: clinical and metabolic studies of three cases. Blood 1990; 76(12):2555–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Boettcher S, Wacker A, Moerike K, et al. Acquired coagulopathy caused by intoxication with the superwarfarin-type anticoagulant rodenticide flocoumafen. European journal of haematology 2011; 86(2):173–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Laposata M, Van Cott EM, Lev MH. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Case 1–2007. A 40-year-old woman with epistaxis, hematemesis, and altered mental status. The New England journal of medicine 2007; 356(2):174–82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lo VM, Ching CK, Chan AY, et al. Bromadiolone toxicokinetics: diagnosis and treatment implications. Clinical toxicology (Philadelphia, Pa.) 2008; 46(8):703–10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Altay S, Cakmak HA, Boz GC, et al. Prolonged coagulopathy related to coumarin rodenticide in a young patient: superwarfarin poisoning. Cardiovascular journal of Africa 2012; 23(9):e9–e11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Spahr JE, Maul JS, Rodgers GM. Superwarfarin poisoning: a report of two cases and review of the literature. American journal of hematology 2007; 82(7):656–60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kapadia P, Bona R. Acquired deficiency of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors due to brodifacoum ingestion. Connecticut medicine 2008; 72(4):207–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Tsutaoka BT, Miller M, Fung SM, et al. Superwarfarin and glass ingestion with prolonged coagulopathy requiring high-dose vitamin K1 therapy. Pharmacotherapy 2003; 23(9):1186–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Morgan BW, Tomaszewski C, Rotker I. Spontaneous hemoperitoneum from brodifacoum overdose. The American journal of emergency medicine 1996; 14(7):656–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Miller MA, Levy PD, Hile D. Rapid identification of surreptitious brodifacoum poisoning by analysis of vitamin K-dependent factor activity. The American journal of emergency medicine 2006; 24(3):383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.McCarthy PT, Cox AD, Harrington DJ, et al. Covert poisoning with difenacoum: clinical and toxicological observations. Human & experimental toxicology 1997; 16(3):166–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pavlu J, Harrington DJ, Voong K, et al. Superwarfarin poisoning. Lancet (London, England) 2005; 365(9459):628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Watts RG, Castleberry RP, Sadowski JA. Accidental poisoning with a superwarfarin compound (brodifacoum) in a child. Pediatrics 1990; 86(6):883–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


