Correction to: Zhao et al. BMC Cancer (2019) 19:201.
https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5422-x
Following publication of the original article [1], it was noticed that Fig. 3c was omitted from the final published article. The publishers apologise for the error and the inconvenience caused.
Fig. 3.
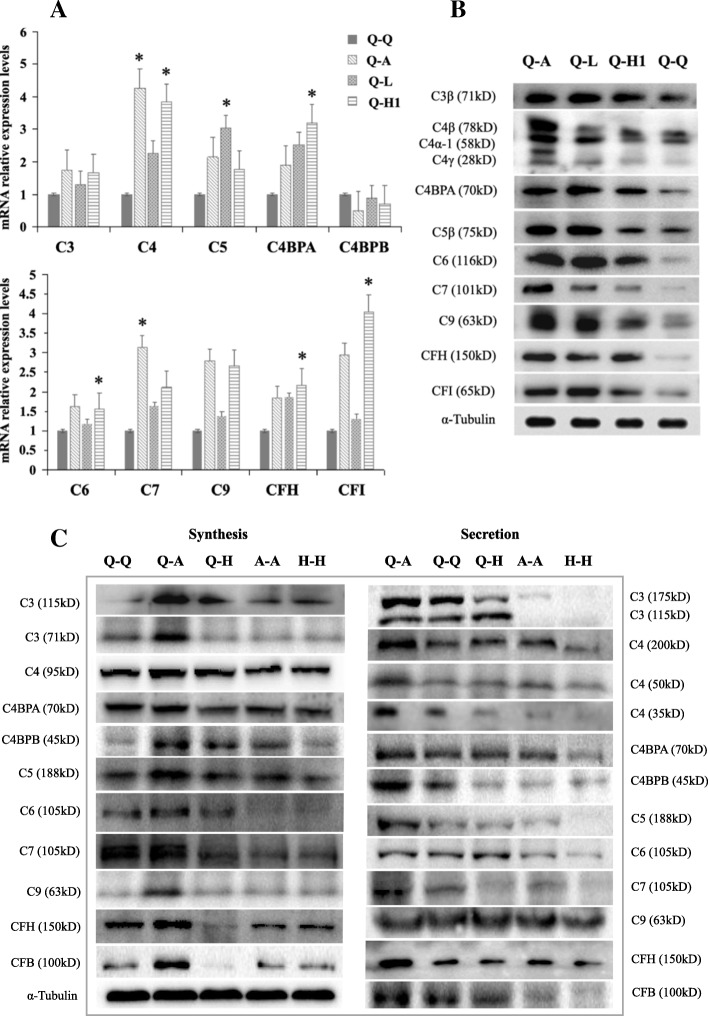
Co-culture with lung cancer cells improved hepatocyte complement synthesis and secretion. Co-culture of QSG-7701 hepatocytes with lung cancer cells (A549, LTEP-α-2 or NCI-H1703) improved complement synthesis at both the mRNA (a) and protein levels (b). c Complement protein synthesis (in QSG-7701 hepatocytes co-cultured with A549 cells) and secretion (in supernatants from co-cultures of QSG-7701 and A549 cells) were significantly increased compared to co-cultures of QSG-7701 hepatocytes and HBE cells. Q-Q, Q-A, Q-L, Q-H1, Q-H, A-A and H-H indicate paired co-cultures of both QSG-7701 hepatocytes, QSG-7701 hepatocytes and A549 cells, QSG-7701 hepatocytes and LTEP-α-2 cells, QSG-7701 hepatocytes and NCI-H1703 cells, QSG-7701 hepatocytes and HBE cells, both A549 cells or both HBE cells, respectively. α-Tubulin was used as the loading control for co-cultured QSG-7701 hepatocytes. Loading controls for co-cultured supernatants were quantitated by performing Coomassie blue staining due to the lack of proper secreted protein as control in co-cultured supernatants. For loading controls of co-cultured supernatants, please refer to Additional file 4: Fig. S4
The complete Fig. 3 is given below.
The original article [1] has been updated.
Reference
- 1.Zhao, et al. The imbalance in the complement system and its possible physiological mechanisms in patients with lung cancer. BMC Cancer. 2019;19:201. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5422-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]