Abstract
This study examines whether naltrexone pretreatment interferes with the antidepressant effects of ketamine.
Ketamine has rapid and robust antidepressant effects. However, there are concerns about the abuse liability of ketamine.1 This concern was heightened recently owing to a preliminary report suggesting that antidepressant effects of ketamine might be dependent on opiate receptor stimulation.2 Below, we present pilot data that indicate that the antidepressant effects of ketamine are not attenuated by naltrexone pretreatment. As a result, the combination of opiate receptor antagonism with ketamine might be a strategy to reduce addiction risk among patients with depression at risk for substance abuse.
Methods
We recruited and obtained written informed consent from 5 patients with current major depressive disorder and alcohol use disorder. In this 8-week open-label pilot study, which recieved institutional review board approval by the VA Connecticut Healthcare System Human Subjects Subcommittee, patients received injectable naltrexone (380 mg once 2-6 days prior to the first ketamine infusion) and repeated intravenous ketamine treatment (0.5 mg/kg once a week for 4 weeks; a total of 4 ketamine infusions). The study had 2 phases: (1) a 4-week ketamine treatment phase and (2) a 4-week follow-up phase. All patients were abstinent from alcohol for 5 days or longer prior to the first ketamine infusion. The primary outcome measure was clinical response defined as a 50% or higher improvement from baseline in the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale scores at 4 hours postinfusion.
Results
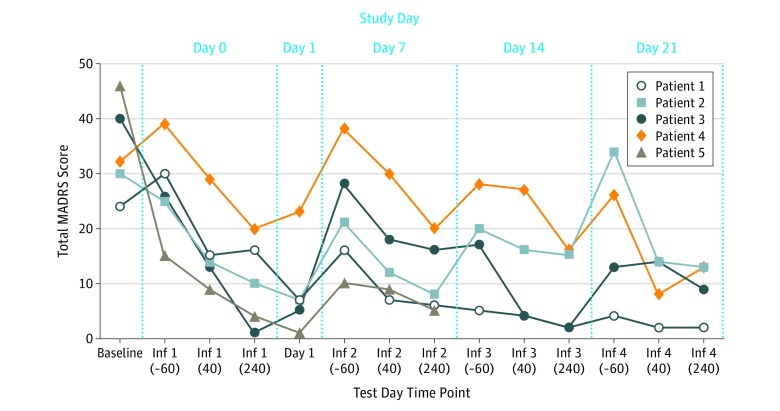
The combination of naltrexone and ketamine was associated with reduced depressive symptoms. The Figure shows that 60% (3 of 5) of patients met response criteria after their initial ketamine dose and 100% (5 of 5) met response criteria by their fourth dose, although 1 patient left the trial after receiving 2 ketamine infusions. The Table shows that depressive symptoms improved about 57% to 92%. Also, 80% (4 of 5) of patients reported improvement in alcohol craving and consumption as measured by the Obsessive Compulsive Drinking Scale. The combination treatment was safe and well tolerated in all participants. No serious adverse effects were reported in the trial.
Figure. Depressive Symptoms From Baseline to Fourth Ketamine Infusion During the Combination of Naltrexone and Ketamine Treatment.
The number in parentheses indicates the minutes before or after ketamine infusion; Inf, ketamine infusion; MADRS, Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale.
Table. Depressive Symptoms Before and After the Combination of Naltrexone and Ketamine Treatment.
| Patient No./Sex/Age, y | Race | MADRS Score | Improvement, No. (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pretreatment (Baseline) | Posttreatment (After Final Infusion) | |||
| 1/M/60 | White | 24 | 2 | 22 (92) |
| 2/M/45 | White | 30 | 13 | 17 (57) |
| 3/F/61 | White | 40 | 9 | 31 (78) |
| 4/M/48 | White | 32 | 13 | 19 (59) |
| 5/M/32 | White | 46 | 5 | 41 (89) |
Abbreviations: F, female; M, male; MADRS, Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale.
Discussion
Our pilot data suggest that naltrexone pretreatment did not interfere with the antidepressant effects of ketamine and might enhance the treatment of comorbid alcohol use disorder. This result conflicts with that reported by Williams et al2 in which pretreatment with 50 mg of naltrexone reduced the rate of clinical response to ketamine from 71% (5 of 7 individuals) to 0% (0 of 7 individuals). Their data and an editorial by George,3 although preliminary, make a case for a central role for opiate agonism in the antidepressant effects of ketamine. Although our pilot data were collected under somewhat different conditions than those of Williams et al2 (eg, different primary outcome time of 4 hours vs 1 day postinfusion, presence vs absence of alcohol use disorder, injectable vs oral naltrexone), they do not support the hypothesis that opiate receptor stimulation mediates the antidepressant effects of ketamine. Since Williams et al2 did not provide depression ratings over a 4-hour period postinfusion, we cannot examine whether 50 mg of oral naltrexone blunted ketamine response in this early 4-hour period. Our findings are consistent with an earlier study in healthy individuals showing that the behavioral effects of an antidepressant dose of ketamine were not altered by pretreatment with 25 mg of naltrexone,4 and some preclinical evidence that ketamine isomers may be weak partial agonists at μ opiate receptors.5
The initial report by Williams et al2 and our preliminary data should be interpreted with great caution. Larger randomized clinical trials are needed to better understand whether opiate receptor stimulation contributes to the antidepressant effects of ketamine. If so, then preclinical research will be needed to help us to understand this role for opiates and its implications for future rapid-acting antidepressant treatments.
References
- 1.Sanacora G, Frye MA, McDonald W, et al. ; American Psychiatric Association (APA) Council of Research Task Force on Novel Biomarkers and Treatments . A consensus statement on the use of ketamine in the treatment of mood disorders. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(4):399-405. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.0080 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Williams NR, Heifets BD, Blasey C, et al. Attenuation of antidepressant effects of ketamine by opioid receptor antagonism [published online August 29, 2018]. Am J Psychiatry. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.18020138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.George MS. Is there really nothing new under the sun? is low-dose ketamine a fast-acting antidepressant simply because it is an opioid? [published online August 29, 2018]. Am J Psychiatry. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2018.18070800 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Krystal JH, Madonick S, Perry E, et al. Potentiation of low dose ketamine effects by naltrexone: potential implications for the pharmacotherapy of alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2006;31(8):1793-1800. doi: 10.1038/sj.npp.1300994 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hirota K, Okawa H, Appadu BL, Grandy DK, Devi LA, Lambert DG. Stereoselective interaction of ketamine with recombinant mu, kappa, and delta opioid receptors expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Anesthesiology. 1999;90(1):174-182. doi: 10.1097/00000542-199901000-00023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]