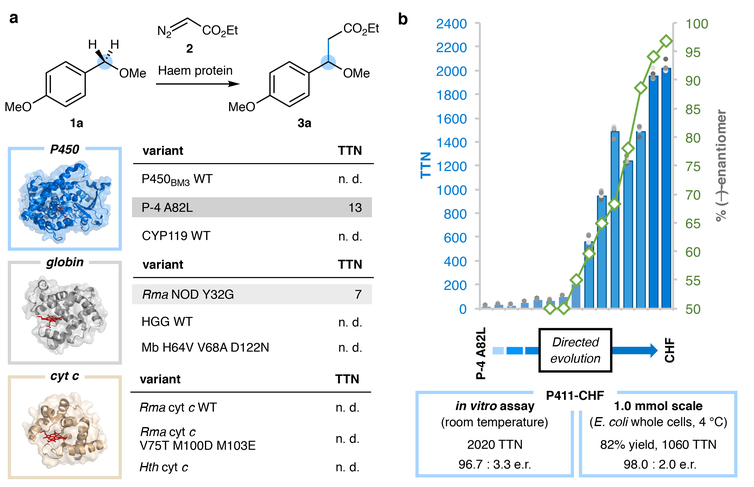
Figure 2 |. Haem protein-catalysed sp3 C–H alkylation.
a, Select subset of haem proteins tested for promiscuous C–H alkylation activity. Structural illustrations are of representative superfamily members with the haem cofactor shown as red sticks: cytochrome P450BM3 (PDB 2IJ2), sperm whale myoglobin (PDB 1A6K), and Rma cytochrome c (PDB 3CP5). TTN, total turnover number; n. d., not detected; WT, wild type; Mb, sperm whale myoglobin, HGG, Hell’s Gate globin; cyt c, cytochrome c; Hth, Hydrogenobacter thermophilus. b, Directed evolution of a cytochrome P411 for enantioselective C–H alkylation (reaction shown in (a)). Bars represent average TTNs from reactions performed in quadruplicate; each TTN data point is shown as a grey dot. Enantioselectivity results are represented by green diamonds. Unless otherwise indicated, reaction conditions were haem protein in E. coli whole cells (OD600 = 30, (a)) or in clarified E. coli lysate (b), 10 mM substrate 1a, 10 mM ethyl diazoacetate, 5 vol% EtOH in M9-N buffer at room temperature under anaerobic conditions for 18 hours. Reactions performed with lysate contain 1 mM Na2S2O4. TTN is defined as the amount of indicated product divided by total haem protein as measured by the hemochrome assay. See Supplementary Information for the complete list of haem proteins tested and detailed experimental procedures.