Abstract
Background
BK polyomavirus (BKPyV)–associated nephropathy (BKPyVAN) is a major threat for kidney transplant recipients (KTRs). The role of specific BKPyV genotypes/serotypes in development of BKPyVAN is poorly understood. Pretransplantation serotyping of kidney donors and recipients and posttransplantation genotyping of viremic recipients, could reveal the clinical relevance of specific BKPyV variants.
Methods
A retrospective cohort of 386 living kidney donor-recipient pairs was serotyped before transplantation against BKPyV genotype I–IV viral capsid protein 1 antigen, using a novel BKPyV serotyping assay. Replicating BKPyV isolates in viremic KTRs after transplantation were genotyped using real-time polymerase chain reaction and confirmed by means of sequencing. BKPyV serotype and genotype data were used to determine the source of infection and analyze the risk of viremia and BKPyVAN.
Results
Donor and recipient BKPyV genotype and serotype distribution was dominated by genotype I (>80%), especially Ib, over II, III and IV. Donor serotype was significantly correlated with the replicating genotype in viremic KTRs (P < .001). Individual donor and recipient serotype, serotype (mis)matching and the recipient replicating BKPyV genotype were not associated with development of viremia or BKPyVAN after transplantation.
Conclusions
BKPyV donor and recipient serotyping and genotyping indicates the donor origin of replicating BKPyV in viremic KTRs but provides no evidence for BKPyV genotype–specific virulence.
Keywords: BK polyomavirus, BK virus, genotype, genotyping, kidney transplantation, serotype, serotyping
BK polyomavirus (BKPyV) causes asymptomatic infection early in life [1, 2], reaching a seroprevalence of approximately 90% in adults [3, 4]. Thereafter, BKPyV latently persists in the urothelium and renal tubular cells [5, 6]. In immunocompromised patients, BKPyV infections can cause manifest disease, such as BKPyV-associated nephropathy (BKPyVAN) in kidney transplant recipients (KTRs) [1, 2]. BKPyVAN represents a major problem for KTRs [7–9], causing graft dysfunction and graft loss in 1%–10% of them [10–13]. Currently, reduction of immunosuppressive therapy is the only effective evidence-based treatment with the disadvantage of increasing the risk of allograft rejection [13, 14].
BKPyV is classified into 4 genotypes, I–IV [15–18], and several subtypes, including Ia, Ib1, Ib2, Ic, IVa1, IVa2, IVb1, IVb2, IVc1, and IVc2 [19–22]. The various genotypes and respective subtypes show a different geographic distribution [19, 21–24]. Genotype I is the most prevalent and widespread worldwide (approximately 80%), followed by genotype IV (approximately 15%), mainly found in Europe and East Asia. Genotypes II and III are rare in all geographic regions (approximately 5%) [19, 21–27]. Reported prevalence percentages are generally based on BKPyV isolates from viruric and viremic (immunocompromised) individuals, and therefore may not represent the BKPyV genotype distribution in the general (immunocompetent) population. Coinfection of a dominant genotype with other BKPyV genotypes/subtypes (quasispecies) is common [24, 28, 29].
Little is known about the association between specific BKPyV genotypes and the risk, course and severity of BKPyV-associated infection after kidney transplantation (KTx). It has been shown that genotype I replicates more efficient than genotype IV in human renal epithelial cells in vitro [30], possibly suggesting more efficient infection in vivo. Some studies reported associations between BKPyVAN and genotypes I and IV in particular [16, 31–34]. However, these studies were all performed in regions where I and IV are the most prevalent genotypes, thereby introducing a potential bias [16, 31–35]. A recent report investigating BKPyV genotype–specific neutralizing antibody profiles of KTRs, showed that the absence of antibodies specifically neutralizing the replicating genotype rather than the genotype itself increased the risk of BKPyV viremia [36].
Taken together, these studies provide conflicting evidence for BKPyV genotype–specific associations with BKPyV-associated disease. To solve a number of these issues, we recently developed a BKPyV serotyping assay based on Luminex technology [37]. This assay enables simultaneous detection of seroresponses against the major viral capsid protein 1 (VP1) of BKPyV genotypes I, II, III and IV, and its main subtypes. With the help of this assay, by calling the genotype that elicits the strongest seroresponse the serotype, each seropositive individual can be BKPyV serotyped. Based on validation of this approach by mutual comparison of measured seroreactivity against individual BKPyV genotypes, we found this assay to reliably serotype infections with the common BKPyV genotypes I and IV, whereas infections with genotypes II and III were hard to detect and distinguish serologically [37].
In the current study, with the help of this new method, we serotyped a large retrospective cohort of KTRs and their donors before KTx [37]. These data were mutually compared and compared with the replicating BKPyV genotype identified in KTRs who developed viremia and BKPyVAN after KTx. In this way we could determine the origin (donor or recipient) of the replicating BKPyV strain, the presence of genotype-specific associations with development of viremia and BKPyVAN, and the relevance of donor-recipient pair BKPyV genotype (mis)matching for developing viremia and BKPyVAN.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study Population and Sample Collection
The study cohort was extensively described elsewhere [38] and initially included 407 living donor-recipient pairs transplanted at Leiden University Medical Center between 2003 and 2013. For the current study, 21 pairs were excluded, because not enough serum was available from either donor or recipient for determination of BKPyV genotype immunoglobulin G levels. The remaining 386 donor-recipient pairs were included in the study (Supplementary Figure 1). Donor and recipient serum samples were collected a median of 125 and 6 days before KTx, respectively, and recipient blood plasma samples were collected after KTx at 5 regular time points, during 1 year of follow-up with a mean follow-up of 9.1 months. The study protocol was submitted to Leiden University Medical Center’s medical ethical committee, which decided that formal approval was not needed, owing to the retrospective study design and the use of previously collected anonymized samples.
BKPyV Serotyping
Serum samples were analyzed by means of a laboratory-developed Luminex immunoassay detecting immunoglobulin G reactivity against VP1 of BKPyV Ia/Ib1, Ib2, Ic, II, III, and IVb1, as described elsewhere [37]. Because BKPyV variants Ia and Ib1 have 100% VP1 amino acid sequence similarity, they represent a single serotype [37, 39]. Because BKPyV genotype IV subtypes belong to a single serotype [39], IVb1 included in this analysis accounts for all IV subtypes.
BKPyV serotype immunoassay cutoff values were based on immunocompetent children aged 7–24 months (n = 36), as described elsewhere [4, 37]. The following serotype-specific mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) cutoff values were obtained: Ib1, 478; Ib2, 1013; Ic, 1451; II, 792; III, 758; and IV, 356. The geometric mean titers (GMTs) of all BKPyV serotypes were determined for donors and recipients, as described elsewhere [37], by testing serum dilution series of 1:100; 1:1000; 1:10 000, and 1:100 000.
Detection of BKPyV Viremia and Assessment of BKPyVAN
Viremia was detected by means of quantitative BKPyV polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis of blood plasma, as described elsewhere [38, 40]. All BKPyVAN cases included in our analysis were biopsy confirmed. A kidney biopsy was performed if indicated in the view of the treating physician, and BKPyVAN was diagnosed based on the criteria described elsewhere [38].
BKPyV Genotyping
Total nucleic acid extracted from recipient BKPyV DNA-containing plasma samples was analyzed to determine the infecting genotype, with the help of a BKPyV genotype–specific real-time PCR assay and VP1 sequencing. The BKPyV genotype–specific real-time PCR assay was performed according to a published protocol [28]. In brief, this assay consists of BKPyV genotype–specific real-time PCRs targeted to the most conserved region of the VP1 gene for each of the 4 genotypes.Primers and probes were designed in a region of the VP1 gene with low variability between the subtypes of a genotype, but with high variability between the genotypes.
For VP1 sequencing, serum samples with a BKPyV load ≥10 000 copies/mL were selected. Primers (sense primer 5′-CCTCAATGGATGTTGCCTTT-3′, antisense primer 5′-ACC ACCCCCAAAATAACACA-3′) were chosen just outside the VP1 gene (BKPyV Dunlop strain; Genbank V01108) with the help of Primer3 software (http://primer3.sourceforge.net/). The BKPyV genotype was determined through Sanger sequencing of the generated PCR products, using the selected and 4 additional PCR primers (sense primer 5′-CTAACCTGTGGAAATCTACT-3′, antisense primer 5′-TACWGTYACAGCCTCCCACA-3′, sense primer 5′-CAGCTACCACAGTGTTGCT-3′, antisense primer 5′-CCCCACACCCTGTTCATC-3′).
Statistical Analyses
Data were analyzed with IBM SPSS Statistics software, version 21. Differences between viremic and nonviremic KTRs and viremic KTRs with or without BKPyVAN were assessed using χ2 test or Fisher exact tests. The GMT and MFI values of the Luminex immunoassay were compared and assessed using Cohen κ agreement analysis. For all performed tests, differences were considered statistically significant at P < .05 (2-sided test).
RESULTS
BKPyV Serotyping of Donors and Recipients
To serotype all donors and recipients, seroreactivity against 6 common BKPyV genotypes/subtypes (Ia/Ib1, Ib2, Ic, II, III, and IVb1) was determined in the serum samples collected before KTx. Both the MFI value measured at 1:100 serum dilution and the calculated GMT based on a 10-fold serum dilution series (1:100 to 1:100 000) were recorded. Comparable with what our group reported elsewhere [37], among both donors and recipients strong agreement was observed between the BKPyV genotype with the highest seroreactivity expressed as MFI value or expressed as GMT (κ > 0.8; Supplementary Tables 1A and 1B). In the rest of this article, we will use the MFI values obtained with the 1:100 serum dilution for further analyses.
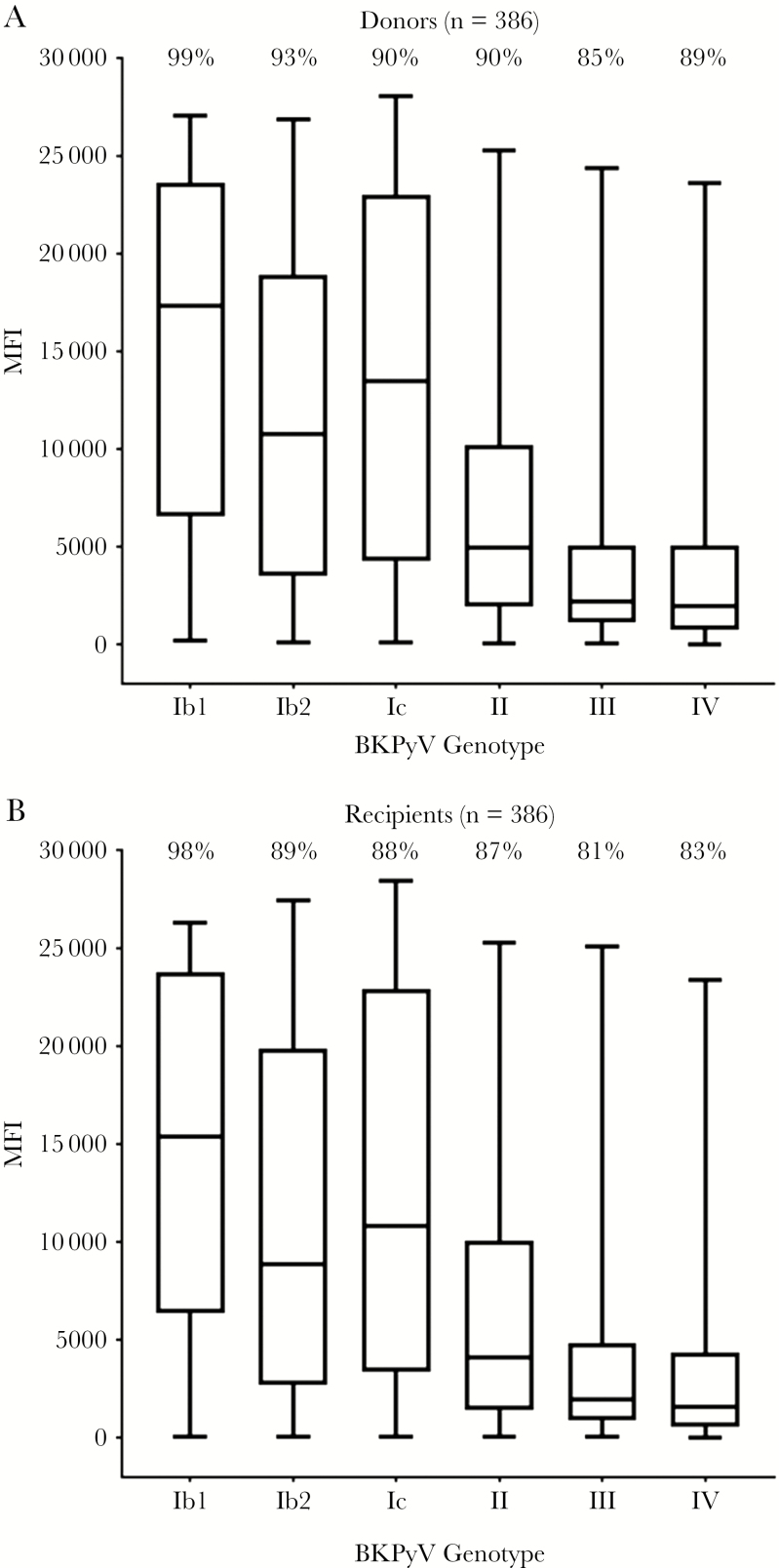
Overall, seroresponses were observed against all of the analyzed genotypes, and measured MFI values did not differ between donors and recipients (Figure 1). The seropositivity rate of all BKPyV variants in donors and recipients was high (>80%). The highest mean seroreactivity was measured for BKPyV genotype I subtypes, followed by genotypes II, III, and IV. Ranking of seroresponses according to the BKPyV genotype VP1 antigen that obtained the highest MFI value within a subject indicated that most donors and recipients were seroresponsive to BKPyV belonging to genotype I, primarily Ib1, followed by II, IV, and III (Table 1), suggesting that most subjects were primarily infected with genotype I.
Figure 1.
Seroreactivity against BK polyomavirus (BKPyV) genotype–specific viral capsid protein 1 (VP1) antigens in kidney transplant donors and recipients. Seroreactivity against BKPyV genotype–specific VP1 antigens was measured in serum samples collected before transplantation from donors (A) and recipients (B). Results are given as the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) obtained at a 1:100 serum dilution. For each genotype, the box represents the interquartile range; the line within the box, the median; and the whiskers, the minimum and maximum recorded seroreactivities. The percentage above each box represents the seroprevalence of each BKPyV genotype or subtype.
Table 1.
Pretransplantation BKPyV Serotype Distribution Among 386 Kidney Transplant Donors and Recipients
| BKPyV Serotype, No. (%) of Donors or Recipients | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| I | Ib1 | Ib2 | Ic | II | III | IV | |
| Donors | 331 (86) | 223 (58) | 19 (5) |
89 (23) |
45 (12) | 3 (1) | 7 (2) |
| Recipients | 331 (86) | 223 (58) | 22 (6) | 86 (22) | 38 (10) | 11 (3) | 6 (2) |
Abbreviation: BKPyV, BK polyomavirus.
BKPyV Genotyping of Viremic KTRs
In total, viremia developed in 103 of the 386 KTRs (27%) during 1 year of follow-up after KTx. To identify the replicating BKPyV genotype, DNA isolated from each KTR with a viral load >103 genome copies/mL (n = 92) was analyzed by means of genotype-specific real-time PCR. This analysis revealed 76 replicating infections with BKPyV genotype I (87%), 6 with genotype IV (7%), 5 with genotype II (6%), and none with genotype III (Table 2). In 5 recipients genotyping failed, probably because the DNA load was too close to the detection limit. VP1 sequencing and subsequent genotyping, which required a higher concentration of input DNA of ≥105 genome copies/mL, succeeded in 45 of the 92 recipients. The obtained sequences showed complete agreement with the genotype-specific PCR results (Supplementary Table 2).
Table 2.
Association Between Kidney Transplant Donor and Recipient BKPyV Serotype Determined Before Transplantation and the BKPyV Genotype Replicating After Transplantation
| No. (%) of Donors or Recipients by Genotype of Replicating BKPyV Strain in Viremic Recipients (n = 87) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BKPyV Serotype | I (n = 76) | II (n = 5) | III (n = 0) | IV (n = 6) | P Valuea |
| Donors | |||||
| I (n = 79) | 75 (95) | 1 (1) | 0 (0) | 3 (4) | <.001 |
| II (n = 6) | 1 (17) | 4 (67) | 0 (0) | 1 (17) | |
| III (n = 0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| IV (n = 2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 2 (100) | |
| Recipient | |||||
| I (n = 77) | 69 (90) | 4 (5) | 0 (0) | 4 (5) | .08 |
| II (n = 8) | 6 (75) | 1 (13) | 0 (0) | 1 (13) | |
| III (n = 1) | 1 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | |
| IV (n = 1) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (100) | |
Abbreviation: BKPyV, BK polyomavirus
a P values were calculated with the Fisher exact test, with results considered statistically significant at P < .05.
Correlation Between Replicating BKPyV Genotype and Donor Serotype
The BKPyV serotype distribution among donors and recipients was comparable to the distribution of replicating genotypes among viremic recipients, with a predominance of serotype/genotype I in all groups (Table 2). We compared the BKPyV genotyping results obtained from viremic recipients after KTx with the donor and recipient BKPyV serotyping results obtained before KTx, to assess the source of the replicating virus in the recipient. A strong association was observed between the recipient replicating genotype and the donor serotype (P < .001) (Table 2), suggesting similarity between the donor BKPyV and the virus replicating in the recipient.
Lack of Association Between Viremia and BKPyVAN Development and BKPyV Serotype
Next we looked for associations between the donor and recipient BKPyV serotype and development of viremia and BKPyVAN after KTx. In this regard, no significant differences were observed between viremic and nonviremic recipients, and between viremic recipients with or without BKPyVAN (Table 3). Moreover, donor-recipient pair BKPyV serotype (mis)matching showed no difference in the incidence of viremia or BKPyVAN (Tables 3 and Supplementary Table 3).
Table 3.
Association of Donor and Recipient BKPyV Serotype With Development of Viremia and BKPyVAN in Recipients During Follow-up
| All Recipients, No. (%) (n = 386) | Viremic Recipients, No. (%) (n = 103) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BKPyV Serotype | No BKPyV Viremia (n = 283) | BKPyV Viremia (n = 103) | P Valuea | No BKPyVAN (n = 92) |
BKPyVAN (n = 11) |
P Valuea |
| Donors | ||||||
| I | 238 (72) | 93 (28) | .42 | 82 (88) | 11 (12) | .68 |
| II | 37 (82) | 8 (18) | 8 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| III | 3 (100) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | ||
| IV | 5 (71) | 2 (29) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| Recipients | >.99 | |||||
| I | 243 (73) | 88 (27) | .88 | 78 (89) | 10 (11) | |
| II | 27 (71) | 11 (29) | 10 (91) | 1 (9) | ||
| III | 9 (82) | 2 (18) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| IV | 4 (67) | 2 (33) | 2 (100) | 0 (0) | ||
| Donor-recipient pair | ||||||
| Matched | 205 (72) | 79 (28) | .40 | 71 (90) | 8 (10) | .72 |
| Mismatched | 78 (76) | 24 (24) | 21 (88) | 3 (13) | ||
Abbreviations: BKPyV, BK polyomavirus; BKPyVAN, BKPyV-associated nephropathy.
a P values were calculated using χ2 or Fisher exact tests, with results considered statistically significant at P < .05.
DISCUSSION
By serotyping and genotyping a retrospective cohort of KTx donor-recipient pairs, we aimed to determine the source (donor or recipient) of the replicating BKPyV strain, evaluate BKPyV genotype–specific associations with BKPyV infection after KTx, and determine the role of donor-recipient BKPyV genotype matching in the development of viremia and BKPyVAN.
The observed seropositivity rate of all analyzed BKPyV variants in both donors and recipients was high (>80%). The rates were higher than expected for BKPyV genotypes II, III, and IV, which could mean that genotypes II, III, and IV circulate more often in the general population than expected based on BKPyV-viremic KTR screening only [36, 41], and that mixed infection with different BKPyV variants is common. Three previous studies also reported the occurrence and detection of mixed BKPyV infections in healthy and immunocompromised patients [24, 28, 29]. Although we believe that BKPyV genotyping generally underestimates the prevalence of different BKPyV genotypes among study populations, we think the seropositivity rates of genotypes II and III are generally overrated, because of a substantial amount of cross-reactivity, especially with genotype IV [37].
To determine the main infecting BKPyV genotype by serotyping, we ranked the genotype-specific seroresponses according to the BKPyV genotype VP1 antigen that obtained the highest MFI and GMT values. Our group recently showed good agreement between these measures and the presence of neutralizing antibodies against the relevant BKPyV genotype [37]. Our serotyping results suggest that most subjects, donors as well as recipients, are primarily infected with BKPyV genotypes belonging to serotype I (86%), especially Ib1 (58%), whereas some seem primarily infected with II (10%–12%), IV (2%), or III (1%–3%). This serotype distribution is somewhat different from what has been reported elsewhere in Europe, with genotype Ib2 as the most prevalent subtype (approximately 75%), and genotype IV accounting for most of the remaining subjects (15%), respectively [22, 26]. Geographic differences in genotype distribution may account for these differences, but it should be kept in mind that both serotyping and genotyping have their limitations, and their data may be difficult to compare.
Overall, the distribution of BKPyV genotypes among viremic KTRs in our cohort was comparable to the serotype distribution obtained from donors and recipients before KTx, probably representing the distribution of the BKPyV genotypes present in the general population [19, 22, 26]. The observed agreement between the genotype and serotype distributions suggests that serotyping represents a useful surrogate method for genotyping, especially in immunocompetent populations that do not shed sufficient amounts of BKPyV for genotyping.
Because BKPyV infection in KTRs is thought to originate from the kidney allograft [38, 42–45], we analyzed whether the serotype of donors and recipients, determined before KTx, was correlated with the BKPyV genotype found in viremic KTRs. The replicating BKPyV genotype in viremic KTRs was significantly correlated with the serotype of the donor and not the recipient, indicating that BKPyV infection after KTx is indeed donor derived.
For some viruses, for example hepatitis C virus, it is known that the different genotypes influence the course, treatment response, and outcome of disease [46]. For BKPyV, we found no indication that the genotype is relevant to any of the analyzed aspects of BKPyV infection. Furthermore, we observed no differences in virological and clinical outcome between BKPyV genotype–matched and mismatched donor-recipient pairs. We did no confirm specific associations between BKPyVAN development and genotype I and IV infection, as described in other studies [16, 31–34].
To conclude, donor and recipient serotyping shows that BKPyV genotype I infections dominate the picture and that replicating BKPyV strains in KTRs are donor derived. Furthermore, our study showed no direct effect of specific BKPyV genotypes or genotype (mis)matching was shown for development of viremia or BKPyVAN.
Supplementary Data
Supplementary materials are available at Open Forum Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the posted materials are not copyedited and are the sole responsibility of the authors, so questions or comments should be addressed to the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
Author contributions. H. F. W. and M. C. W. F. initiated and designed the study. A. C. M. K. provided the infrastructure. C. S. d. B. and L. G. performed the experiments and gathered the experimental data. H. F. W. analyzed the data. H. F. W., J. W. d. F., J. I. R., and M. C. W. F. interpreted the data. H. F. W. and M. C. W. F. drafted the manuscript, including figures and tables. All authors reviewed and approved the final report.
Financial support. This study was supported by the Dutch Kidney Foundation (grant 13A1D302).
Potential conflicts of interest. All authors: No reported conflicts of interest. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Presented in part: 21st European Society of Clinical Virology annual meeting, Athens, Greece, 23 September 2018; abstract O10.
References
- 1. Hirsch HH, Steiger J. Polyomavirus BK. Lancet Infect Dis 2003; 3:611–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Rinaldo CH, Tylden GD, Sharma BN. The human polyomavirus BK (BKPyV): virological background and clinical implications. APMIS 2013; 121:728–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Kean JM, Rao S, Wang M, Garcea RL. Seroepidemiology of human polyomaviruses. PLoS Pathog 2009; 5:e1000363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. van der Meijden E, Bialasiewicz S, Rockett RJ, et al. Different serologic behavior of MCPyV, TSPyV, HPyV6, HPyV7 and HPyV9 polyomaviruses found on the skin. PLoS One 2013; 8:e81078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Boldorini R, Veggiani C, Barco D, Monga G. Kidney and urinary tract polyomavirus infection and distribution: molecular biology investigation of 10 consecutive autopsies. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005; 129:69–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Chesters PM, Heritage J, McCance DJ. Persistence of DNA sequences of BK virus and JC virus in normal human tissues and in diseased tissues. J Infect Dis 1983; 147:676–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Chand S, Atkinson D, Collins C, et al. the spectrum of renal allograft failure. PLoS One 2016; 11:e0162278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. El-Zoghby ZM, Stegall MD, Lager DJ, et al. Identifying specific causes of kidney allograft loss. Am J Transplant 2009; 9:527–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Kuypers DR. Management of polyomavirus-associated nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Nat Rev Nephrol 2012; 8:390–402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Hirsch HH, Drachenberg CB, Steiger J, Ramos E. Polyomavirus-associated nephropathy in renal transplantation: critical issues of screening and management. Adv Exp Med Biol 2006; 577:160–73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Hirsch HH, Knowles W, Dickenmann M, et al. Prospective study of polyomavirus type BK replication and nephropathy in renal-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med 2002; 347:488–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Huang G, Zhang L, Liang X, et al. Risk factors for BK virus infection and BK virus-associated nephropathy under the impact of intensive monitoring and pre-emptive immunosuppression reduction. Transplant Proc 2014; 46:3448–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Sood P, Senanayake S, Sujeet K, et al. Management and outcome of BK viremia in renal transplant recipients: a prospective single-center study. Transplantation 2012; 94:814–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Hardinger KL, Koch MJ, Bohl DJ, et al. BK-virus and the impact of pre-emptive immunosuppression reduction: 5-year results. Am J Transplant 2010; 10:407–15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Luo C, Bueno M, Kant J, et al. Genotyping schemes for polyomavirus BK, using gene-specific phylogenetic trees and single nucleotide polymorphism analysis. J Virol 2009; 83:2285–97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Varella RB, Zalona ACJ, Diaz NC, et al. BK polyomavirus genotypes Ia and Ib1 exhibit different biological properties in renal transplant recipients. Virus Res 2018; 243:65–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Jin L, Gibson PE, Booth JC, Clewley JP. Genomic typing of BK virus in clinical specimens by direct sequencing of polymerase chain reaction products. J Med Virol 1993; 41:11–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Knowles WA, Gibson PE, Gardner SD. Serological typing scheme for BK-like isolates of human polyomavirus. J Med Virol 1989; 28:118–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Ikegaya H, Saukko PJ, Tertti R, et al. Identification of a genomic subgroup of BK polyomavirus spread in European populations. J Gen Virol 2006; 87:3201–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Stoner GL, Alappan R, Jobes DV, et al. BK virus regulatory region rearrangements in brain and cerebrospinal fluid from a leukemia patient with tubulointerstitial nephritis and meningoencephalitis. Am J Kidney Dis 2002; 39:1102–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Takasaka T, Goya N, Tokumoto T, et al. Subtypes of BK virus prevalent in Japan and variation in their transcriptional control region. J Gen Virol 2004; 85:2821–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Zheng HY, Nishimoto Y, Chen Q, et al. Relationships between BK virus lineages and human populations. Microbes Infect 2007; 9:204–13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Nishimoto Y, Zheng HY, Zhong S, et al. An Asian origin for subtype IV BK virus based on phylogenetic analysis. J Mol Evol 2007; 65:103–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Luo C, Hirsch HH, Kant J, Randhawa P. VP-1 quasispecies in human infection with polyomavirus BK. J Med Virol 2012; 84:152–61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Morel V, Martin E, François C, et al. A simple and reliable strategy for BK virus subtyping and subgrouping. J Clin Microbiol 2017; 55:1177–85. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Zhong S, Randhawa PS, Ikegaya H, et al. Distribution patterns of BK polyomavirus (BKV) subtypes and subgroups in American, European and Asian populations suggest co-migration of BKV and the human race. J Gen Virol 2009; 90:144–52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Fishman JA. infection in organ transplantation. Am J Transplant 2017; 17:856–79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Gard L, Niesters HG, Riezebos-Brilman A. A real time genotyping PCR assay for polyomavirus BK. J Virol Methods 2015; 221:51–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Jin L, Pietropaolo V, Booth JC, et al. Prevalence and distribution of BK virus subtypes in healthy people and immunocompromised patients detected by PCR-restriction enzyme analysis. Clin Diagn Virol 1995; 3:285–95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Nukuzuma S, Takasaka T, Zheng HY, et al. Subtype I BK polyomavirus strains grow more efficiently in human renal epithelial cells than subtype IV strains. J Gen Virol 2006; 87:1893–901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Baksh FK, Finkelstein SD, Swalsky PA, et al. Molecular genotyping of BK and JC viruses in human polyomavirus-associated interstitial nephritis after renal transplantation. Am J Kidney Dis 2001; 38:354–65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Boukoum H, Nahdi I, Sahtout W, et al. BK polyomavirus genotypes and nephropathy: is there a relationship? Transpl Infect Dis 2016; 18:309–11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Gosert R, Rinaldo CH, Funk GA, et al. Polyomavirus BK with rearranged noncoding control region emerge in vivo in renal transplant patients and increase viral replication and cytopathology. J Exp Med 2008; 205:841–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Yogo Y, Sugimoto C, Zhong S, Homma Y. Evolution of the BK polyomavirus: epidemiological, anthropological and clinical implications. Rev Med Virol 2009; 19:185–99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Schwarz A, Linnenweber-Held S, Heim A, et al. Viral origin, clinical course, and renal outcomes in patients with BK virus infection after living-donor renal transplantation. Transplantation 2016; 100:844–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Solis M, Velay A, Porcher R, et al. Neutralizing antibody-mediated response and risk of BK virus-associated nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 2018; 29:326–34. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Wunderink HF, de Brouwer CS, van der Meijden E, et al. Development and evaluation of a BK polyomavirus serotyping assay using Luminex technology. J Clin Virol 2019; 110:22–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Wunderink HF, van der Meijden E, van der Blij-de Brouwer CS, et al. pretransplantation donor-recipient pair seroreactivity against BK polyomavirus predicts viremia and nephropathy after kidney transplantation. Am J Transplant 2017; 17:161–72. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. Pastrana DV, Ray U, Magaldi TG, et al. BK polyomavirus genotypes represent distinct serotypes with distinct entry tropism. J Virol 2013; 87:10105–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Wunderink HF, Haasnoot GW, de Brouwer CS, et al. Reduced risk of BK polyomavirus infection in HLA-B51 positive kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2019;103:604–12. doi:10.1097/TP.0000000000002376 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Randhawa P, Pastrana DV, Zeng G, et al. Commercially available immunoglobulins contain virus neutralizing antibodies against all major genotypes of polyomavirus BK. Am J Transplant 2015; 15:1014–20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. Bohl DL, Storch GA, Ryschkewitsch C, et al. Donor origin of BK virus in renal transplantation and role of HLA C7 in susceptibility to sustained BK viremia. Am J Transplant 2005; 5:2213–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43. Schmitt C, Raggub L, Linnenweber-Held S, et al. Donor origin of BKV replication after kidney transplantation. J Clin Virol 2014; 59:120–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Funk GA, Steiger J, Hirsch HH. Rapid dynamics of polyomavirus type BK in renal transplant recipients. J Infect Dis 2006; 193:80–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Abend JR, Changala M, Sathe A, et al. Correlation of BK virus neutralizing serostatus with the incidence of BK viremia in kidney transplant recipients. Transplantation 2017; 101:1495–505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46. Kohli A, Shaffer A, Sherman A, Kottilil S. Treatment of hepatitis C: a systematic review. JAMA 2014; 312:631–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.