Abstract
Background:
Poor symptom control is common in asthma. Breathing training exercises may be an effective adjunct to medication; it is therefore important to understand facilitators and barriers to uptake of breathing training exercises.
Aims:
To gain insight into patients' perceptions of breathing training exercises designed to help control asthma symptoms.
Methods:
Semi-structured think-aloud interviews were conducted with 29 people with asthma about their views of a booklet on breathing training exercises.
Results:
Thematic analysis showed breathing training exercises were seen as acceptable in principle because they were viewed as non-pharmacological, holistic, unobtrusive, and likely to increase patient confidence in managing symptoms. Anticipated disadvantages included the time required and perceived irrelevance for those with well-controlled asthma. These views were influenced by prior experience of changing breathing, wanting to self-manage asthma, negative views of medication, and perceived asthma control/severity. Anticipated barriers to carrying out the exercises included difficulties with nose breathing, remembering to do them, and persevering with them. Anticipated facilitators included monitoring tools and social support.
Conclusions:
The idea of breathing training was viewed positively as an acceptable non-pharmacological treatment that patients can do discreetly to help them breathe more easily and reduce their reliance on medication. Uptake of breathing training may be greater among those who perceive their asthma as severe and/or have negative views of medication. To enhance uptake, it might be helpful to present breathing training exercises as holistic skills that can also benefit those with mild symptoms.
Keywords: qualitative, asthma, breathing training, perceptions
Introduction
Asthma affects over five million people in the UK.1 It is typically managed pharmacologically by β2-adrenergic agonists and inhaled corticosteroids. However, fewer than 50% of adults with asthma achieve good symptom control.2,3 Patients are often attracted to non-pharmacological management, which they feel may improve general health4 and reduce the need for pharmacological treatment.5 Up to 79% of patients have tried non-pharmacological and complementary treatments6 such as breathing training, which has recently increased in popularity due to widespread awareness of the Buteyko breathing technique, yoga, and physiotherapist-taught programmes.7–11
Breathing training involves teaching breathing techniques (e.g. advice on route of breathing, slow breathing, relaxation techniques) to modify breathing patterns and improve breathing efficiency.11 It can lead to reduced symptoms and improved quality of life (QoL) for people with asthma, it may reduce use of reliever medication,12 and it has been recommended as an evidence-based adjuvant treatment for adults whose asthma remains uncontrolled despite standard treatments.13
Breathing training may therefore be an effective adjunct to medication, particularly for patients with poor asthma control. Gaining insight into patients' views of breathing training would facilitate the understanding of factors affecting uptake and the best way to reach the maximum number of potential beneficiaries. This qualitative study was therefore designed to explore perceptions of breathing training among people with asthma.
Methods
Design
Semi-structured interviews were used to explore views of breathing training in general and reactions to a booklet “Breathing Freely: Your guide to breathing retraining for asthma”. This booklet was developed by a team of physiotherapists, health psychologists, physicians, and patient representatives for use in an ongoing clinical trial, and provides a detailed explanation and illustration of how to carry out breathing training.
Participants
Participants were recruited via study advertisements placed around a UK university, in the local community, and on the Asthma UK website. Anyone aged ≥18 years who had been diagnosed with asthma and prescribed reliever medication was eligible. Participants were purposively sampled to try to increase diversity regarding age, gender, and symptom severity. We encountered minimal refusal to participate. No further interviews were conducted once it became apparent that saturation had been reached (no new themes were emerging).
Data collection
Semi-structured interviews lasting approximately one hour were were carried out face-to-face either in the university (n=14), in the participants' homes (n=6), or by telephone (n=9) by four female research staff (EAC, ET, STC, and NP). All researchers had previous experience in conducting qualitative interviews. Participants received £6 for participation. Approval was granted by the University Ethics Committee (No 5187).
Interviews comprised two components: (1) open-ended questions exploring attitudes to breathing training exercises in the context of health beliefs and lifestyle; and (2) think-aloud methods14,15 to elicit spontaneous reactions to the booklet. Interview questions covered participants' experiences of managing their asthma. This included questions about breathing difficulties, previous experience of breathing techniques for asthma management, and perceived relevance of breathing training exercises to asthma control. Participants then read a draft booklet and said everything they thought about each page. Further open-ended questions explored impressions of the booklet, attitudes to breathing exercises, perceived attitudes of relevant others (family, healthcare professionals), barriers to carrying out breathing exercises at home, and possible ways of overcoming them. Interviews were audio recorded and transcribed verbatim. After the interview, participants provided demographic information and completed the Asthma Control Questionnaire (ACQ).16
Data analysis
Inductive thematic analysis was carried out.17,18 Two researchers (ET and EAC) read all transcripts. Through discussion, a coding manual was developed to ensure transparent and systematic coding of the data. Codes were grounded in the data, reflecting language present in participants' accounts. All transcripts were double-coded by ET and EAC, then discussed with LY to ensure good inter-rater agreement. Themes were checked for differences as a function of educational level, gender, or ethnicity. Diagramming was employed to illustrate the key themes within the data. Data analysis was assisted by NVivo Version 9.2.
Results
The 29 participants had a mean age of 38 years (range 18–69). Most were female (n=24, 82.8%) and white (n=27, 93.1%). Two identified themselves as of mixed ethnicity. The education level ranged from GCSE (the UK examinations for 16 year-olds) to degree level; (23 (79.3%) had a degree. The average age at diagnosis was 15 years (range 1–53) and the mean score on the ACQ was 1.31 (range 0.33–3.17), indicating that asthma control ranged from optimal to very poor. Most (n=27, 93%) were taking a preventer and a reliever inhaler, but two (7%) were taking a reliever only. No differences due to educational level or gender emerged.
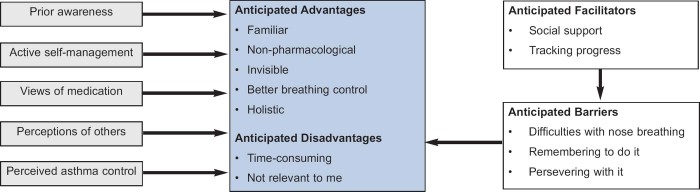
Themes are presented in terms of perceived advantages and disadvantages of breathing exercises, factors influencing these perceptions, and anticipated barriers and facilitators to uptake and commitment (see Figure 1).
Figure 1. Perceptions of breathing retraining.
Anticipated advantages
Most participants reported little awareness and no prior experience of breathing techniques for asthma management. Only two had been taught breathing techniques by a physiotherapist.
Nevertheless, the general concept of changing breathing patterns to improve outcomes was familiar. Many participants referred to experiences of changing their breathing patterns for singing, playing musical instruments, acting, and meditation.
In addition to taking medication, many participants actively self-managed their symptoms non-pharmacologically. The breathing techniques (slow breathing, diaphragmatic breathing and relaxation) were seen as familiar and acceptable as they were similar to techniques used in other methods of self-management (e.g. running, yoga).
Participants were open to exploring non-pharmacological methods of asthma management, especially if they thought it meant they would be less dependent on their medication. Most expressed negative views (frustration and concerns) about having to take their medication in the long-term, and several did not take their prescribed medication as required.
Breathing training exercises were seen as a more natural way to manage asthma and a way to help reduce reliance on medication.
Some participants viewed the breathing retraining techniques as less conspicuous to use than inhalers. This was important as some mentioned being stigmatised because of their asthma, so tried to hide it.
Breathing exercises, because viewed as invisible, were implicitly viewed positively in that perceptions of others were not considered a barrier to implementation.
Participants believed breathing techniques would give them more control over their symptoms. They thought they would feel less anxious about being exposed to triggers as they would have a management tool readily available.
Participants viewed breathing training exercises as a holistic therapy that promotes general well-being and could help anyone with managing life's demands.
Anticipated disadvantages
Some participants saw the programme as being not relevant to them due to their severity, type, or control of asthma (such as exercise-induced or well-controlled). These people considered themselves less likely to take up breathing training unless they saw it as an alternative to medication.
The time required to carry out the exercises (15 minutes twice a day for at least three weeks) was viewed as a disadvantage by almost everyone. Concerns fell into two main categories: (1) getting round to doing the breathing training; and (2) difficulties finding the time to do it twice a day initially.
Anticipated barriers
Many people mentioned often feeling ‘bunged up’, which made nose breathing more difficult. Although they were aware nose breathing would likely benefit them, they felt it would be extremely difficult to master.
Several participants thought doing the breathing training exercises twice a day would be a substantial commitment, and felt it would be hard to remember to do them and persevere with them.
Anticipated facilitators
People thought tracking progress and social support would help counteract the barriers of remembering to do breathing training and persevering with it.
Some participants thought tracking their progress would enable them to see improvements or highlight any issues they were experiencing.
Many participants felt social support would facilitate continued commitment to breathing training. They thought face-to-face support in the form of classes would facilitate mastery of the techniques and enable them to address concerns in person and overcome difficulties, thereby enhancing self-confidence and motivation for carrying out the techniques alone.
Social support from peers and family members was also seen as extremely helpful. Participants thought their partners might remind them to do it, and that doing it with others would enhance motivation due to social pressure. An online forum was suggested as a helpful way of enabling people to share their experiences, and thus persevere.
Discussion
Main findings
Breathing training exercises were viewed favourably in principle because they were seen as familiar, convenient, holistic techniques that did not involve medication and would increase confidence in managing asthma symptoms. Perceptions of breathing retraining were influenced by prior experience or awareness of changing breathing, wanting to self-manage asthma, negative views of medication, perceptions of others' views of asthma, and perceived asthma control. Anticipated disadvantages included the time required for practice, and viewing breathing retraining as irrelevant, mainly in patients who believed their asthma control was good. Anticipated barriers included remembering to do the training and persevering with it, and difficulties with nose breathing. Anticipated facilitators to counteract the first two barriers included tracking progress and social support.
Strengths and limitations of the study
This study is the first full paper and is the most detailed study of patients' views of breathing exercises as a method of asthma self-management. It provides valuable insight into how people with asthma may view breathing retraining, and therefore the factors likely to influence uptake. A limitation is that, because participants had not tried breathing training, the barriers to adherence that they anticipated may not accurately reflect factors that would influence adherence following uptake. Further research with patients undertaking breathing training is required to examine these factors. Because the booklet presented breathing training positively as a method of asthma management which reduces symptoms and improves asthma control, it is likely this influenced participants' positive impressions. Also, despite our efforts to obtain a diverse sample, men, people with lower educational levels, and those from ethnic minorities were under-represented. However, the profile of the participants is typical of people who use complementary therapies,19 so may be broadly representative of those likely to take up breathing training. Symptoms and diagnosis were not medically assessed in this study, so it was not possible to characterise the participants with clinical precision. However, subjective perceptions of asthma status were most relevant to the study aim of understanding perceptions of breathing training.
Interpretation of findings in relation to previously published work
The participants generally found the idea of breathing training appealing due to its potential to reduce reliance on medication. This is reflective of previous research, which has reported that many people with asthma adopt non-pharmacological methods of managing their symptoms, in an attempt to reduce reliance on medication.4,5 In addition, breathing training was viewed positively in principle due to its invisibility. It is known that people with asthma sometimes feel stigmatised by their illness.20 Participants saw the breathing techniques as holistic skills for everyday life, which people often prefer relative to illness-specific treatments4,21 due to non-acceptance of illness.22–24
Participants thought tracking their progress would help them persevere, which is in line with research showing that prompting self-monitoring is effective in changing behaviour.25 Participants' anticipated concerns about dealing with setbacks and remaining motivated when carrying out breathing training alone were similar to those reported by patients required to carry out unsupervised physiotherapy-based exercises for other chronic conditions.26
Implications for future research, policy and practice
Our findings suggest that uptake of breathing training will probably be greater among patients who perceive their asthma as more severe and/or wish to reduce reliance on medication. To maximise uptake, it may be helpful to present the breathing training techniques as skills for life that can benefit even those with mild/intermittent symptoms, rather than as illness management only relevant to those with severe symptoms. It may also be helpful to explain that practising in the short term can lead to lifelong automatic skills requiring little conscious effort. It will also be important to emphasise that breathing training exercises do not provide an effective substitute for preventative medication.
Breathing training programmes should provide supportive materials and allow contact with therapists — either face-to-face or online — to support setbacks and maintain motivation. It may be necessary to address co-morbidity with allergic rhinitis to facilitate nose breathing.
Conclusions
Participants viewed the idea of breathing training positively as a familiar non-pharmacological treatment which they could carry out discreetly that would help them breathe more easily and might reduce their reliance on medication. However, there were concerns about the time required to carry out the exercises. Anticipated barriers included remembering to do the exercises, persevering when alone, and difficulties with nose breathing. Breathing exercises offer a promising adjuvant therapy that is likely to be of interest to many adults with asthma if offered and supported in a convenient format.
Acknowledgments
Handling editor Dianne Goeman
Funding This project was funded by the National Institute for Health Research's Health Technology Assessment Programme HTA Project: 09/104/19.
Disclaimer The views and opinions expressed in the paper are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the HTA programme, NIHR, NHS, or the Department of Health.
Footnotes
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interest in relation to this article. MT is an Associate editor of the PCRJ, but was not involved in the editorial review of, nor the decision to publish, this article.
References
- Asthma UK. http://www.asthma.org.uk/about-asthma-uk/asthma-uk-supporter-charter.2012.
- Rabe KF, Vermeire PA, Soriano JB, Maier WC. Clinical management of asthma in 1999: the Asthma Insights and Reality in Europe (AIRE) study. Eur Respir J 2000;16(5):802–07. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00.16580200 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demoly P, Annunziata K, Gubba E, Adamek L. Repeated cross-sectional survey of patient-reported asthma control in Europe in the past 5 years. Eur Respir Rev 2012;21(123):66–74. http://dx.doi.org/10.1183/09059180.00008111 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop FL, Yardley L, Lewith GT. Treat or treatment: a qualitative study analyzing patients' use of complementary and alternative medicine. Am J Public Health 2008;98(9):1700–05. http://dx.doi.org/10.2105/AJPH.2007.110072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brien SB, Bishop FL, Riggs K, Stevenson D, Freire V, Lewith G. Integrated medicine in the management of chronic illness: a qualitative study. Br J Gen Pract 2011;61(583):e89–96. http://dx.doi.org/10.3399/bjgp11X556254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slader CA, Reddel HK, Jenkins CR, Armour CL, Bosnic-Anticevich SZ. Complementary and alternative medicine use in asthma: who is using what? Respirology 2006;11(4):373–87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1843.2006.00861.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowler SD, Green A, Mitchell CA. Buteyko breathing techniques in asthma: a blinded randomised controlled trial. Med J Aust 1998;169(11–12):575–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S, Osborne J, Newton S, et al. Effect of two breathing exercises (Buteyko and pranayama) in asthma: a randomised controlled trial. Thorax 2003;58(8):674–9. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thorax.58.8.674 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McHugh P, Aitcheson F, Duncan B, Houghton F. Buteyko breathing technique for asthma: an effective intervention. NZ Med J 2003;116(1187):U710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Opat AJ, Cohen MM, Bailey MJ, Abramson MJ. A clinical trial of the Buteyko breathing technique in asthma as taught by a video. J Asthma 2000;37(7):557–64. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/02770900009090810 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruton A, Thomas M. The role of breathing training in asthma management. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2011;11 (1):53–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/ACI.0b013e3283423085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M, McKinley RK, Mellor S, et al. Breathing exercises for asthma: a randomised controlled trial. Thorax 2009;64(1):55–61. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thx.2008.100867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott J, Blumenthal S, Buxton M, et al. Guidelines for the physiotherapy management of the adult, medical, spontaneously breathing patient. British Thoracic Society Physiotherapy Guideline Development Group. Thorax 2009;64(Suppl 1):i1–51. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thx.2008.110726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Haak MJ, de Jong MDT, Schellens PJ. Evaluation of an informational web site: three variants of the think-aloud method compared. Tech Commun 2007;54(1):58–71. [Google Scholar]
- Yardley L, Morrison LG, Andreou P, Joseph J, Little P. Understanding reactions to an internet-delivered health-care intervention: accommodating user preferences for information provision. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak 2010;10:52. http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1472-6947-10-52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juniper EF, O'Byrne PM, Guyatt GH, Ferrie PJ, King DR. Development and validation of a questionnaire to measure asthma control. Eur Respir J 1999;14(4):902–7. http://dx.doi.org/10.1034/j.1399-3003.1999.14d29.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun V, Clarke V. Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual Res Psychol 2006;3(2):77–101. http://dx.doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa [Google Scholar]
- Joffe H, Yardley L. Content and thematic analysis. In: Marks D, Yardley L. eds. Research methods for clinical and health psychology. London: Sage, 2004: pp 56–68. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop FL, Lewith GT. Who uses CAM? A narrative review of demographic characteristics and health factors associated with CAM use. eCam 2010;7(1):11–28. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ecam/nen023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolbe J, Fergusson W, Vamos M, Garrett J. Case-control study of severe life threatening asthma (SLTA) in adults: psychological factors. Thorax 2002;57(4):317–22. http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/thorax.57.4.317 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yardley L, Donovan-Hall M, Francis K, Todd C. Older people's views of advice about falls prevention: a qualitative study. Health Educ Res 2006;21(4):508–17. http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/her/cyh077 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pound P, Britten N, Morgan M, et al. Resisting medicines: a synthesis of qualitative studies of medicine taking. Soc Sci Med 2005;61(1):133–55. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2004.11.063 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherman MH, Lowhagen O. Drug compliance and identity: reasons for non-compliance. Experiences of medication from persons with asthma/allergy. Patient Educ Couns 2004;54(1):3–9. http://dx.doi.org10.1016/s0738-3991(03)00199-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams S, Pill R, Jones A. Medication, chronic illness and identity: the perspective of people with asthma. Soc Sci Med 1997;45(2):189–201. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0277-9536(96)00333-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham C, Michie S. A taxonomy of behavior change techniques used in interventions. Health Psychol 2008;27(3):379–87. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0278-6133.27.3.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jack K, Mclean SM, Moffett JK, Gardiner E. Barriers to treatment adherence in physiotherapy outpatient clinics: a systematic review. Manual Ther 2010;15(3):220–8. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2009.12.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]