Abstract
Background
Research has shown that some individuals can develop problematic patterns of online gaming, leading to significant psychological and interpersonal problems. Psychiatric distress and impulsivity have been suggested to contribute to problematic online gaming (POG).
Objective
This study aimed to investigate the potential mediating or moderating mechanisms of impulsivity and gender-related differences in possible associations between psychiatric distress and POG.
Methods
A total of 596 matched female and male participants, ranging in age from 14 to 38 years (mean 21.4, SD 4.5), were chosen from a large cross-sectional, nationwide Hungarian online gaming sample. Participants completed online questionnaires about self-reported impulsivity, psychiatric distress, and POG.
Results
Psychiatric distress directly predicted POG, and impulsivity partially mediated the relationship between psychiatric distress and POG. However, this mediation effect was found only for the impatience factor of impulsivity. Impulsivity did not moderate the relationship between psychiatric distress and POG. A moderating effect of gender was not found in the direct relationship between psychiatric distress and POG. However, a moderated mediation analysis revealed that impatience mediated the association between psychiatric distress and POG in males, whereas the indirect effect of impatience was not significant in females.
Conclusions
The results of this work highlight gender-related difference among online gamers in the mediation effect of impulsivity between psychiatric distress and POG and provide novel insights regarding clinical implications for preventing or treating POG.
Keywords: internet, video games, addictive behavior, psychopathology, impulsivity, gender
Introduction
Background
Problematic online gaming (POG) may be defined as the persistent and recurrent use of the internet to play video games, leading to clinically significant impairment or distress. Internet gaming disorder was included as a “condition for further study” in the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, Fifth Edition, section 3 [1]. Furthermore, gaming disorder, including online gaming, has been formally included along with gambling disorder as a disorder because of addictive behaviors in the recently released listing of conditions in the International Classification of Diseases 11th Revision [2]. Some have considered POG to be a global public health problem because of its relevant high prevalence and significant negative outcomes in worldwide populations, particularly among adolescents [3,4]. A recent review suggested that the overall prevalence of POG ranged from 0.7% to 15.6% in studies of naturalistic populations, with an average percentage of 4.7% [5].
Psychiatric symptoms such as depression have been associated more broadly with POG and problematic internet use [6,7]. POG has been positively correlated with psychiatric symptom dimensions including depressed mood, loneliness, social anxiety, and negative self-esteem [8-11]. Individuals (particularly females) may engage in potentially addictive behaviors to escape from negative mood states or other psychiatric distress (negative reinforcement motivations), and this may lead to problematic or addictive engagement. Although previous research has focused primarily on the direct association between psychiatric distress and POG, fewer studies have examined how specific factors may moderate relationships between psychiatric distress and POG or how the relationships between psychiatric distress and POG may operate through intervening variables via mediation effects. To address these gaps, this study constructed a moderated mediation model to test the mediating role of impulsivity and the moderating role of gender in the relation between psychiatric distress and POG. Such studies could advance our understanding of how and when psychiatric distress might lead to greater POG and may have implications for the prevention and treatment of POG.
Impulsivity as a Mediator or Moderator
Impulsivity has been described as being characterized by “actions that are poorly conceived, prematurely expressed, unduly risky, or inappropriate to the situation and that often result in undesirable outcomes” [12]. Although impulsivity is a multidimensional construct, impatience is an important component of impulsiveness that may result from relative disregard of future outcomes and oversensitivity to immediate rewards [13]. Impulsivity has been related to substance use, gambling, and gaming [14]. Impulsivity has been proposed to contribute significantly to the development and/or maintenance of addictions [3,15]. It has also been linked to poor addiction treatment outcomes [16]. Furthermore, impulsivity has been associated with problematic internet use and POG. For instance, adolescents with internet addiction exhibited more impulsivity than those without [17], and the severity of internet addiction was positively correlated with the level of impulsivity in individuals with internet addiction [18]. Greater impulsivity among internet users was associated with poorer control over the use of the internet [19]. Similarly, individuals with POG have been found to score high on measures of impulsivity [20].
Psychiatric symptoms may relate to impulsivity. Negative emotional states may lead individuals to focus more on their feelings, which may trigger poor self-control [21]. Semple et al [22] found that depression scores could best discriminate between substance users with high and low impulsivity. Depression and loneliness scores have also correlated with low self-control and problematic internet use [6].
Previous studies have shown that impulsivity may mediate the relation between psychiatric distress and addictive behaviors. For example, impulsivity has been shown to mediate the influence of life stress on pathological gambling [23] and the relationship between depression and problematic gambling [24]. However, mixed findings have been reported in moderation analyses. Although a moderating effect of impulsivity was also observed in a study by Tang and Wu [23], in which a positive association between life stress and pathological gambling was significant among those with low impulsivity only, and pathological gambling remained high regardless of the stress level among those with high impulsivity, this moderating effect was not supported in the study by Clarke [24]. Although studies have examined the relationship between impulsivity and problematic internet use [17,18], and the mediating and/or moderating effects of impulsivity on psychiatric distress and pathological gambling [23,24], few studies have examined a role for impulsivity in relationships between psychiatric distress and POG. Internet addiction has been reported to have comparable levels of impulsivity compared with pathological gambling [18], and POG may be characterized by high impulsivity such as other addictive disorders including gambling disorder [20]. Therefore, previous studies of pathological gambling may shed light on mechanisms of how psychiatric distress may relate to POG. Thus, this study investigated the extent to which impulsivity would mediate and/or moderate a hypothesized relationship between psychiatric distress and POG. On the basis of the findings above, we proposed the following hypotheses (denoted H#):
H1: POG would correlate positively with impulsivity with a moderate effect size (H1a) and psychiatric distress with a large effect size (H1b).
H2: According to the mediation model, impulsivity would mediate the relationship between psychiatric distress and POG. Psychiatric distress would relate to POG directly as well as indirectly through impulsivity.
H3: According to the moderation model, impulsivity would moderate the relation between psychiatric distress and POG, with the relationship being stronger for individuals with lower impulsivity.
Gender as a Moderator
Although psychiatric distress may relate to impulsivity and POG, it is possible that not all individuals are equally influenced. This study examined whether the direct effect of psychiatric distress on POG and the indirect effect of impulsivity would be moderated by gender.
Gender may relate importantly to internet gaming behaviors. First, boys have been found to be more likely than girls to report having played video games [25-27] and to report more problematic gaming than girls [28]. Second, being male was a strong predictor of problematic game use [26], and POG was strongly associated with being male [29]. Third, gender-related differences may extend to gaming motivation. Female gamers scored significantly higher on fantasy, escape, social, and recreation motives, whereas male gamers reported significantly higher scores on competition motives [9]. Male players also reported a greater need for gaming-related friendships than did females [30].
Gender-related differences may also exist in impulsivity’s relationship to addictive behaviors. Gender was found to moderate the relationship between sensation seeking/impulsivity and alcohol use; in particular, males and females were found to have comparable alcohol use frequencies under conditions of low sensation seeking/impulsivity, and males were found to have a higher frequency of alcohol use than females under conditions of high sensation seeking/impulsivity [31]. A moderating effect of gender on the association between impulsivity and alcohol-use problems was also found in the study by Stoltenberg et al [32]. Similarly, impulsivity was found only to associate with levels of alcohol use in males [33]. Given that urges/cravings in POG and substance-use disorders may share similar neurobiological mechanisms [34], gender-related differences in previous studies of alcohol use may extend to POG, and this possibility should be tested directly.
Together, both the association between psychiatric distress and POG and the association between impulsivity and POG may be moderated by gender. Furthermore, if impulsivity were to mediate the relation between psychiatric distress and POG, and gender were to moderate the association between impulsivity and POG simultaneously, the mediating effect of impulsivity would be moderated by gender. In other words, there would be a moderated-mediation model involving impulsivity and gender in the relation between psychiatric distress and POG. We sought to test this model. Thus, we put forward the following hypotheses (see Figure 1).
Figure 1.
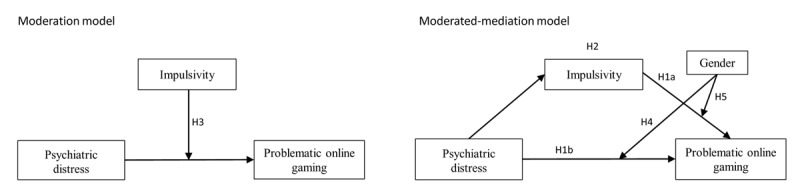
Conceptual model of hypotheses. H1a: Hypothesis 1a; H1b: Hypothesis 1b; H2: Hypothesis 2; H3: Hypothesis 3; H4: Hypothesis 4; H5: Hypothesis 5.
H4: Gender would moderate the relationship between psychiatric distress and POG, with the relation being stronger for males.
H5: Gender would moderate the mediating effect of impulsivity in the relationship between psychiatric distress and POG, with the mediating effect only being significant among males.
Methods
Participants and Procedure
We used data from a nationwide Hungarian online gaming sample. Participants were recruited via gaming-related websites and Facebook pages. A total of 3 calls containing the link to the questionnaire were posted on a popular gaming magazine’s (ie, GameStar) website and Facebook page in August and September 2014. The magazine’s Facebook page had approximately 65,000 followers at the time of the data collection. The post was liked more than 800 times and shared more than 130 times during this period, reaching a wide circle of Hungarian gamers. A shopping voucher of approximately 300 Euro was drawn and offered to 1 study participant as an incentive to boost participation. For more details of the data collection process, see the study by Király O et al [35]. Participants were informed about the aim of the study, the time necessary for completion, and confidentiality of the data. Every participant included in this analysis provided informed consent by ticking a checkbox indicating agreement before starting the questionnaire. Participants aged between 14 and 17 years needed to indicate the approval of their parents with an affirmative response from the parent to the question stating, “I allow my child to participate: parent.” This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Eötvös Loránd University, Budapest, Hungary. The Institutional Review Board of Yale University approved the use of deidentified data in these analyses. This study was performed in line with the Helsinki Declaration. We used the larger sample in 2 previous studies, which did not include data analysis findings reported in this study [35,36].
A total of 7757 gamers started the survey. To verify unique entries (ie, emanating from different individuals), email addresses were checked for uniqueness, and cases having the same email address were removed from the dataset. Furthermore, we checked for invalid answer patterns (eg, the impulsivity scale had several reversed items—if a person gave the same values for all items, the answers were considered as invalid). We deleted responses from individuals with invalid answer patterns. After excluding cases reflecting duplicate submissions, severe incompleteness or inconsistencies on the variables from this study, 5222 online gamers remained in the sample from this study (4830 males and 384 females). Due to the overrepresentation of males that is frequent in specific video gamer samples, we identified a matched sample of males based on the female participants (298 males and 298 females) for further analysis. The matching method is described in the Statistical Analysis section. In the sample from this study, the mean age was 21.4 years (SD 4.5, age range 14-38). Most participants were either single (41.6%, 248/596) or in a relationship but living separately (39.3%, 234/596), and most were students (68.9%, 409/594). For further details on sample demographics, see Table 1.
Table 1.
Demographics and weekly gaming time of sample participants.
| Demographics | Male (n=298) | Female (n=298) | |
| Age in years, mean (SD) | 21.4 (4.5) | 21.4 (4.5) | |
| Education (years completed), mean (SD) | 13.0 (2.6) | 13.0 (2.6) | |
| Marital status, n (%) | |||
|
|
Single | 124 (41.6) | 124 (41.6) |
|
|
In a relationship but living separately | 117 (39.3) | 117 (39.3) |
|
|
Living in a partnership | 51 (17.1) | 51 (17.1) |
|
|
Married | 6 (2.0) | 6 (2.0) |
|
|
Divorced | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
|
|
Widowed | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) |
| Currently a studenta, n (%) | 203 (68.6) | 206 (69.1) | |
| Working status, n (%) | |||
|
|
Does not work | 165 (55.4) | 165 (55.4) |
|
|
Has a part-time job | 58 (19.5) | 58 (19.5) |
|
|
Has a full-time job | 75 (25.2) | 75 (25.2) |
| Weekly gaming timeb, n (%) | |||
|
|
Less than 7 hours | 48 (16.2) | 57 (19.2) |
|
|
7-14 hours | 52 (17.5) | 78 (26.3) |
|
|
15-28 hours | 109 (36.7) | 100 (33.7) |
|
|
29-42 hours | 57 (19.2) | 49 (16.5) |
|
|
More than 42 hours | 31 (10.4) | 13 (4.4) |
a2 missing values in males.
b2 missing values (1 male and 1 female, respectively).
Measures
Problematic Online Gaming Questionnaire
The Problematic Online Gaming Questionnaire (POGQ) is an 18-item scale assessing POG [37], showing good psychometric properties in both adult and adolescent samples (Pápay et al). The scale comprises 6 factors: social isolation, interpersonal conflicts, overuse, withdrawal, immersion, and preoccupation. Participants responded on a 5-point Likert scale (1=“never” and 5=“almost always/always”) to each item (eg, “How often do you get irritable or upset when you cannot play?” and “How often do you neglect other activities because you would rather be gaming?”), with higher scores indicating greater POG. The scale was originally developed in the Hungarian context and showed good psychometric properties in other cultures as well, for example, the study by Ballabio et al [10]. The internal consistency of this scale was 0.89 in this study.
Brief Symptom Inventory
The Brief Symptom Inventory assesses psychiatric distress with 53 items on 9 self-reported clinically relevant psychological symptoms: somatization, obsession-compulsion, interpersonal sensitivity, depression, anxiety, hostility, phobic anxiety, paranoid ideation, and psychoticism [38]. Respondents rank the distress level of each item (eg, “Having to check and double check what you do,” “Feeling fearful,” and “Trouble falling asleep”) on a 5-point Likert scale (0=“not at all” and 4=“extremely”) during the past 7 days. Rankings characterize the intensity of distress during the past 7 days. In this study, a global index of Global Severity Index (GSI), namely the mean for all 53 items, was used to assess the level of general distress. Higher GSI scores indicate stronger psychiatric distress. The scale was previously adapted to the local (Hungarian) culture and showed good psychometric properties [39]. The internal consistency of this scale was 0.96.
Barratt Impulsiveness Scale
The Barratt Impulsiveness Scale (BIS)-21, revised from the original BIS [40], has been tested in 3 different Hungarian adult samples, including a representative one, and assesses impulsivity with 21 items comprising 3 components of impulsivity: self-control, impulsive behavior, and impatience [41]. Participants indicated their responses on a 4-point Likert scale (1=“rarely/never” and 4=“almost always/always”) to each item (eg, “I am future oriented,” “I do things without thinking,” and “I am restless at the theater or lectures,”), with higher scores indicating greater impulsivity. The internal consistency (Cronbach alpha) was .74 for the self-control subscale, .78 for the impulsive behavior subscale, and .63 for the impatience subscale, whereas it was .80 for the whole scale.
Statistical Analysis
We used the case-control matching tools in Medcalc v17.8 (MedCalc Software bvba) to obtain matched data from the sample pool (N=5222). Female status was set to be the matching target group, and male cases were chosen from the pool to match each female case by case. The matching condition was set to include a maximal allowable difference in age of 1 year and required both paired individuals to be the same on measures of education, marital relationship, and work status. This approach generated 298 pairs of cases satisfying the matching conditions.
Description analysis, correlation analysis, and t tests were performed with SPSS 19. Internal consistencies were assessed by Cronbach alpha coefficient. Cohen d was used to measure the effect size.
Mediation and moderation effects were tested using SPSS PROCESS (v3.0) for bootstrapping as described by Hayes [42]. PROCESS is a computational tool for path analysis–based moderation and mediation analysis as well as for their combination [42]. We first tested a mediation model (model number 4 in PROCESS) for H2 using the total score of the BIS-21; we then tested a moderation model (model number 1 in PROCESS) for H3. If positive mediation and/or moderation effects of impulsivity were observed, then a series of post hoc analyses were used to examine specific subscales of the BIS-21 separately. We further tested the moderated mediation model (model number 15 in PROCESS) for H4 and H5. Values of variables were standardized before calculating the models in PROCESS for the purpose of obtaining the standardized regression coefficient. Age, education, and working status were included as covariates in all models. Significant interactions in the moderated-mediation model were followed-up with simple slopes analysis at high (+1 SD) and low (−1 SD) values of the moderator variable [42]. Indirect mediating effects were evaluated with 95% CIs using the percentile method based on 5000 bootstrap samples. If the CI did not contain zero, then the indirect effect was considered statistically significant [42]. If the presence of such an indirect effect depended on the value of a moderating variable, then it was considered an indication of moderated mediation.
Results
Sample Description
Given the matching process, males and females in the subsample had precisely the same demographic characteristics with respect to age, education, marital status, and working status. Student status was also largely similar. Chi-square testing revealed that a higher percentage of males played games for more than 14 hours per week compared with females (χ24=14.3; P=.006, odds ratio=1.64).
The descriptive statistics and zero-order correlations for demographic variables and psychological measures are presented in Table 2. GSI was positively and strongly correlated with POG (r=0.52, P<.001), whereas impulsivity was moderately related to POG (r=0.33, P<.001); thus, H1 was confirmed.
Table 2.
Mean, SD, and Spearman’s correlation matrix with P values of overall variables.
| Variables | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| 1. Age | 1.00 | —a | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 2. Education | 0.66 (<.001) | 1.00 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 3. Working statusb | .64 (<.001) | .42 (<.001) | 1.00 | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| 4. Problematic online gaming | −0.18 (<.001) | −0.16 (<.001) | −0.18 (<.001) | 1.00 | — | — | — | — | — |
| 5. Global Severity Index | −0.20 (<.001) | −0.21 (<.001) | −0.15 (<.001) | 0.52 (<.001) | 1.00 | — | — | — | — |
| 6. BISc self-control | −0.06 (=.17) | −0.06 (=.18) | −0.08 (=.07) | 0.19 (<.001) | 0.16 (<.001) | 1.00 | — | — | — |
| 7. BIS impulsive behavior | −0.09 (=.03) | −0.12 (=.006) | −0.04 (=.38) | 0.25 (<.001) | 0.13 (<.001) | 0.37 (<.001) | 1.00 | — | — |
| 8. BIS impatience | −0.06 (=.14) | −0.03 (=.43) | −0.03 (=.44) | 0.36 (<.001) | 0.33 (<.001) | 0.22 (<.001) | 0.43 (<.001) | 1.00 | — |
| 9. BIS total score | −0.09 (=.04) | −0.09 (=.047) | −0.06 (=.15) | 0.33 (<.001) | 0.27 (<.001) | 0.78 (<.001) | 0.76 (<.001) | 0.70 (<.001) | 1.00 |
| Mean (SD) | 21.38 (4.48) | 13.00 (2.55) | 1.70 (0.85) | 0.74 (0.66) | 12.8 (3.76) | 17.37 (4.40) | 9.96 (3.06) | 12.56 (3.43) | 39.70 (8.02) |
aThe correlation coefficient was not shown as it was shown in the asymmetrically diagonal position of the table.
bWorking status: it was coded as 1=“does not work,” 2=“has a part-time job,” and 3=“has a full job.”
cBIS: Barratt Impulsiveness Scale (version 21).
Gender-Related Differences
We examined gender-related differences using t tests (see Table 3). Statistically significant gender-related differences were not observed in impulsivity. Females scored higher in immersion (t565=−3.52; P<.001, Cohen d=0.30) but lower in overuse (t563=2.10; P=.04, Cohen d=−0.18) than males on subscales of the POGQ. GSI scores were higher in females than males (t491=−5.40; P<.001, Cohen d=0.49), but males spent more weekly time gaming than did females (t592=3.14; P=.002, Cohen d=−0.26).
Table 3.
Gender differences in overall variables.
| Variables | Male, mean (SD) | Female, mean (SD) | t test(df) | P value | Cohen d | |
| Impulsivity | ||||||
|
|
Self-control | 17.15 (4.34) | 17.60 (4.46) | −1.18(539) | .24 | 0.10 |
|
|
Impulsive behavior | 9.82 (3.11) | 10.09 (3.00) | −1.03(547) | .30 | 0.09 |
|
|
Impatience | 12.42 (3.43) | 12.69 (2.43) | −0.89(545) | .37 | 0.08 |
|
|
Total score | 39.22 (7.99) | 40.18 (8.04) | −1.38(526) | .17 | 0.12 |
| Problematic online gaming | ||||||
|
|
Preoccupation | 5.24 (1.83) | 5.33 (2.03) | −0.56(572) | .57 | 0.05 |
|
|
Immersion | 11.87 (3.51) | 12.93 (3.65) | −3.52(565) | <.001 | 0.30 |
|
|
Withdrawal | 6.89 (3.24) | 6.85 (3.44) | 0.16(566) | .87 | −0.01 |
|
|
Overuse | 6.05 (2.67) | 5.58 (2.72) | 2.10(563) | .04 | −0.18 |
|
|
Social isolation | 5.08 (2.40) | 5.09 (2.70) | −0.03(570) | .98 | 0.00 |
|
|
Total score | 39.22 (11.15) | 39.73 (11.74) | −0.53(540) | .60 | 0.04 |
|
|
Global Severity Index | 0.58 (0.55) | 0.89 (0.73) | −5.40(491) | <.001 | 0.49 |
|
|
Weekly game timea | 2.90 (1.19) | 2.61 (1.10) | 3.14(592) | .002 | −0.26 |
a6-point scale: 0=“none,” 1=“less than 7 hours,” 2=“7-14 hours,” 3=“15-28 hours,” 4=“29-42 hours,” and 5=“more than 42 hours.”
Impulsivity
To test the hypothesis regarding a mediating role for impulsivity (H2), the mediating effect of impulsivity as well as indirect effects and direct effects of psychiatric distress on POG was calculated with 5000 bootstrap samples. Age, education, and working status were controlled as covariates. The bootstrap results showed that impulsivity partially mediated the effect of GSI on POG. In particular, the total (nonmediated) effect of GSI was significant and strong (beta=.54, SE 0.04, t465 =13.95, P<.001). After controlling for impulsivity, the direct effect of psychiatric distress was weakened but remained significant and strong (beta=.51, SE 0.04, t464 =12.50, P<.001). The indirect effect of GSI through impulsivity was significant, with a small effect size estimate (0.04 with a 95% bootstrap CI of 0.01 to 0.06; see model a in Figure 2).
Figure 2.
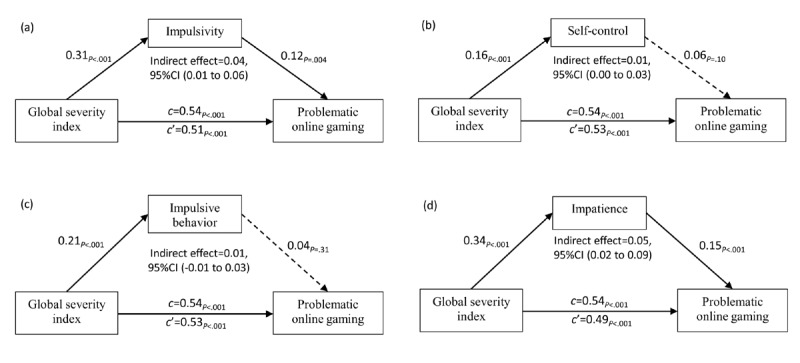
Results of models testing for mediating effects of impulsivity and its dimensions in the relationship between measures of global severity index and problematic online gaming (N=5000 bootstrapping resamples). Path c=total (nonmediated) effect; Path c'=direct (controlling mediator) effect; all paths are quantified with standardized regression coefficients.
In post hoc analyses, we examined the specific subscales of the BIS-21 in mediation analyses. In the model of self-control and impulsive behavior (see model b and c in Figure 2), the 95% bootstrap CI of the indirect effect included zero, so the mediation effect was not significant. However, the mediation effect of impatience was significant with an effect size estimate of 0.05 with a 95% bootstrap CI of 0.02 to 0.09 (see model d in Figure 2).
To test the moderation effect of impulsivity (H3), a multiple regression analysis was conducted to determine main and interaction effects of impulsivity and GSI on POG. As shown in Table 4, main effects of GSI (beta=.53, P<.001) and impulsivity (beta=.12, P=.003) were both significant, but their interaction term (GSI×Impulsivity) was not significant (P=.10). Thus, the moderation effect of impulsivity was not supported in the study.
Table 4.
Summary of multiple regression analyses for the moderated analysis.
| Predictorsa | Beta | SE | t test(df) | P value | 95% bootstrap CI |
| Ageb | −.06 | 0.06 | −1.04(492) | .30 | −0.18 to 0.06 |
| Educationb | −.06 | 0.05 | −1.25(492) | .21 | −0.16 to 0.04 |
| Work statusb | .03 | 0.05 | 0.60(492) | .55 | −0.07 to 0.13 |
| GSIc | .53 | 0.04 | 12.52(492) | <.001 | 0.44 to 0.61 |
| Impulsivity | .12 | 0.04 | 3.02(492) | .003 | 0.04 to 0.20 |
| GSI×Impulsivity | −.06 | 0.04 | −1.64(492) | .10 | −0.13 to 0.01 |
aDependent variable is POG (problematic online gaming).
bCovariate variables; N=5000 bootstrapping resamples.
cGSI: Global Severity Index.
Test of Moderated Mediation
As only the impatience subscale of BIS-21 was significant in the mediation model, we further tested H4 and H5 with respect to impatience by adding gender as a moderator into the model. The result revealed that gender significantly moderated the relationship between impatience and POG (beta=.19, P=.02), but its moderation effect in the direct path between GSI and POG was not significant (beta=.08, P=.34; see Table 5).
Table 5.
Summary of multiple regression analyses for the moderated mediation analysis.
| Dependent variables | Beta | SE | t test(df) | P value | 95% bootstrap CI | |
| Impatience | ||||||
|
|
Agea | −.02 | 0.07 | −0.23(464) | .82 | −0.15 to 0.12 |
|
|
Educationa | .02 | 0.06 | 0.27(464) | .79 | −0.10 to 0.13 |
|
|
Work statusa | .04 | 0.06 | 0.69(464) | .49 | −0.07 to 0.15 |
|
|
GSIb | .34 | 0.04 | 7.52(464) | <.001 | 0.25 to 0.42 |
| Problematic online gaming | ||||||
|
|
Agea | −.04 | 0.06 | −0.73(460) | .47 | −0.16 to 0.07 |
|
|
Educationa | −.07 | 0.05 | −1.50(460) | .14 | −0.17 to 0.02 |
|
|
Work statusa | .02 | 0.05 | 0.32(460) | .75 | −0.08 to 0.11 |
|
|
GSI | .53 | 0.04 | 12.32(460) | <.001 | 0.44 to 0.61 |
|
|
Impatience | .14 | 0.04 | 3.64(460) | <.001 | 0.07 to 0.22 |
|
|
Gender | .17 | 0.08 | 2.25(460) | .03 | 0.02 to 0.32 |
|
|
Gender×GSI | .08 | 0.08 | 0.96(460) | .34 | −0.08 to 0.25 |
|
|
Gender×Impatience | .19 | 0.08 | 2.35(460) | .02 | 0.03 to 0.34 |
aCovariate variables; N=5000 bootstrapping resamples.
bGSI: Global Severity Index.
Graphs of the interaction (Gender×Impatience) are presented in Figure 3 with simple slopes, derived from the regression equations, where high and low values of impatience were specified as 1 SD above and below the mean. Results indicate a significant positive association between impatience and POG for males (beta=.24, P<.001) but not for females (beta=.05, P=.36). In females, impatience and POG were not associated. Testing the indirect effect of psychiatric distress on POG via impulsivity revealed that impatience scores mediated the association between GSI and POG but only in males and not in females (see Table 6).
Figure 3.
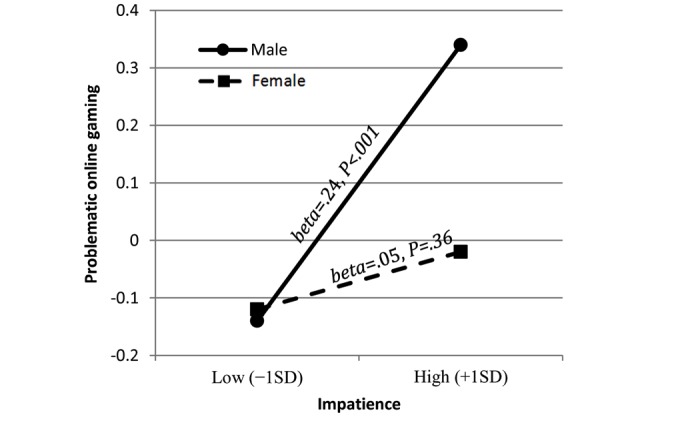
Simple slopes probing the interaction between gender and impatience in the prediction of problematic online gaming (Z score).
Table 6.
Conditional direct and indirect effects of Global Severity Index (independent variable) on Problematic Online Gaming (outcome variable) via impatience (mediator) and gender (moderator).
| Values of the moderator | Direct effects | Indirect effects | |||||
| Beta | SE | t test(df) | P value | Effect (bootstrap estimate) | SE (bootstrap estimate) | 95% bootstrap CI | |
| Male | .57 | 0.07 | 8.41(496) | <.001 | 0.08 | 0.02 | 0.04 to 0.13 |
| Female | .49 | 0.05 | 9.42(496) | <.001 | 0.02 | 0.02 | −0.02 to 0.06 |
Discussion
Principal Findings
Although several studies have examined links between psychiatric distress and POG [8-11], this study is the first to provide empirical evidence investigating the extent to which impulsivity and facets thereof may mediate and/or moderate this relationship in a gender-sensitive fashion. Our a priori hypotheses were partially supported in which impulsivity mediated the relationship between psychiatric distress and POG. However, this relationship seemed most relevant for impatience and was moderated by gender such that the mediating relationship was evident in males but not females. These findings provide insight into possible mechanisms by which psychiatric distress may influence POG.
The finding that POG was related to psychiatric distress supported H1 and is consistent with previous findings in POG [8-10,43], as well as findings in other behavioral addictions [44,45]. The findings from this study expand upon previous ones through exploration of a role for impulsivity. As hypothesized (H2), the relationship between psychological distress and POG was mediated partially through impulsivity, consistent with studies of problematic gambling [23,24]. However, the hypothesized moderation effect of impulsivity was not observed, consistent with findings from the study by Clarke [24] but not from the study by Tang et al [23]. For POG, psychological distress and impulsivity did not interact to account for POG beyond the main effects. As distress increased, the likelihood of experiencing POG symptoms increased, partially through impulsivity. The results resonate with the pathways model of problematic gambling described by Blaszczynski et al [46]. According to the third path in the model, the effect of impulsivity may be increased when experiencing negative emotions or when feeling pressured or stressed, and impulsivity is proposed to mediate the effects of emotional disturbances on problem and pathological gambling symptoms through an interactive process [46]. Further analysis revealed that this mediation effect only appeared in the dimension of impatience. Previous studies have found that impatience is related to increased substance use [47], pathological gambling [48], and POG [49]. The findings from this study suggest an important role of psychiatric distress that may influence POG indirectly through impatience; therefore, helping to develop skills in specific impatience-related domains (emotion regulation and behavioral control) may be important when treating patients with POG.
Earlier studies have reported that boys were more likely to play online games than girls and also more likely to be problematic players [11,28]. Our results indicate that males did spend more time online playing games compared with females; however, there was no gender-related difference in overall POG (as assessed by POGQ total scores) in the sample from this study. Possible reasons may be related to the sample from this study, which was recruited from gaming-related websites and Facebook pages; therefore, both gender groups may have comprised highly engaged gamers [50]. In this study, females had higher psychological distress than males, but the groups did not differ in levels of impulsivity. Moreover, results provided some support for gender as a moderator among the association between impatience and POG in the mediation model. Specifically, as predicted in H5, the indirect effect of impatience was significant in males but not in females. The result is consistent with previous findings in alcohol-use behaviors, in which impulsivity was correlated with alcohol use in males but not in females [33]. The findings from this study suggest that males may be more vulnerable to POG triggered by impulsivity. However, gender did not moderate the direct effect of psychological distress and POG as hypothesized in H4, which suggests both males and females may exhibit POG symptoms in relation to psychiatric distress.
Limitations and Implications
This research should be viewed in light of several limitations. First, male players are overrepresented (92.5%) in the original sample of gamers (N=5222) recruited online. Therefore, a new matched sample based on the female cohort was used for this study, and the results may not extend to the general population. Second, this study involved cross-sectional survey data. Thus, it does not permit identification of cause-and-effect associations. For example, we could not determine whether psychiatric distress increased POG or whether POG led to distress. It is also possible that there was a reciprocal influence between distress and POG. Future studies should utilize longitudinal methods to examine the directionality of relationships among POG, psychiatric distress, and impulsivity. Third, despite the advantage of a larger sample size, the self-selected data collected online from a Hungarian sample are derived from a convenience sample, thus limiting the generalizability of our findings. The sample likely overrepresents active and highly engaged gamers, as suggested elsewhere [50]. Nevertheless, data from this sample have both limitations and strengths and may be particularly suitable for examining potential roles of impulsivity and psychiatric distress in problematic gaming. The use of different anchor points for Likert scales across instruments in the study also has both strengths and limitations, with strengths including the use of values employed in the originally described and validated instruments and weaknesses including potential complexities in comparing findings internally across instruments. Finally, the self-report nature of the data may introduce certain biases (eg, memory recall bias and social desirability bias) that should be considered.
Despite the above limitations, the results have significant clinical implications. Cooccurring features of POG (eg, depression and impulsivity) should be considered in its treatment [51]. The findings in this investigation suggest that because distress affects impulsivity, it may thus be appropriate to treat emotional distress experienced by problematic gamers in addition to treating impulsivity, as suggested by Clarke [24]. Moreover, targeting impulsivity, and particularly impatience, may be helpful to weaken the link between psychiatric distress and POG, especially for males. Cognitive-behavioral therapy, by itself or in conjunction with medication, might be helpful in treating associated impatience/restlessness and emotional distress [52]. As video games are attractive to and accepted by those at risk of POG, they may be considered in novel approaches to help control impulsivity and improve emotion regulation. For example, in other disorders, some video games (eg, PlayMancer) may be effective as additional therapy tools to help improve emotional regulation and impulse control in cases with bulimia nervosa [53] and gambling disorder [54]. The potential therapeutic effect of video games in POG may be worth exploring in future studies. However, one should also consider the potential triggering effects of exposing individuals with POG to online games, especially if abstinence is being targeted. As males with high impulsivity may be more vulnerable to POG than females, future interventions for POG should consider gender-related differences in this domain. Furthermore, given that attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) has been linked to online gaming [55] and greater impatience/restlessness during abstinence from gaming [56], medications that reduce impulsive behaviors (eg, stimulants like methylphenidate or nonstimulants like atomoxetine) may be helpful in reducing POG, particularly in males. As relationships between ADHD and problematic internet use, more broadly, have been observed, especially in young adults [57], the extent to which the findings and corresponding intervention-related considerations are relevant to a broader range of problematic online behaviors (gambling, shopping, and pornography viewing) warrants direct investigation. Among females, the higher GSI scores suggest that psychopathology may be a greater consideration related to POG in females as compared with males. Given that females exhibit anxiety more frequently than males, they receive more mental health treatment and engage in addictive behaviors like gambling for negative reinforcement motivations [58-60]. Future studies should assess these domains as they relate to POG, particularly in females.
Conclusions
In conclusion, this study provides some of the first empirical data investigating the extent to which impulsivity and its dimensions may mediate and/or moderate relationships between psychiatric distress and POG in a gender-sensitive fashion. The study suggests that impulsivity (specifically impatience) acts as a mediator rather than a moderator in the relationship between psychiatric distress and POG. A moderating effect of gender was not found in the direct relationship between psychiatric distress and POG. However, a moderated mediation analysis suggested that impatience mediated the association between psychiatric distress and POG in males, whereas the indirect effect of impatience was not significant in females. The findings suggest important implications for preventing or treating POG in online gamers. Future studies should examine other individual differences (eg, with respect to age or race/ethnicity) that may also help understand different populations and potentially advance prevention and treatment efforts.
Acknowledgments
Wenliang Su was supported by the China Scholarship Council (Grant No. 201706655002) and Fujian Educational Science Project (Grant No. FJJKCG17-199). Marc Potenza was supported by a Center of Excellence grant from the National Center for Responsible Gaming. This study was supported by the Hungarian National Research, Development and Innovation Office (Grant No. K111938, KKP126835) and the COST Action (Grant No. CA16207) funded by the Horizon 2020 Framework Program of the European Union. The study was also supported by the Hungarian Ministry of Human Capacities (ELTE Institutional Excellence Program, 783-3/2018/FEKUTSRAT).
Abbreviations
- ADHD
attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder
- BIS
Barratt Impulsiveness Scale
- GSI
Global Severity Index
- POG
problematic online gaming
- POGQ
Problematic Online Gaming Questionnaire
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
References
- 1.American Psychiatric Association . Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (5th-ed) Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 2013. p. 947. [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization (WHO) 2018. [2018-10-19]. ICD-11: Gaming Disorder https://icd.who.int/dev11/f/en .
- 3.Petry NM, Rehbein F, Ko C, O'Brien CP. Internet gaming disorder in the DSM-5. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 2015 Sep;17(9):72. doi: 10.1007/s11920-015-0610-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Saunders JB, Hao W, Long J, King DL, Mann K, Fauth-Bühler M, Rumpf H, Bowden-Jones H, Rahimi-Movaghar A, Chung T, Chan E, Bahar N, Achab S, Lee HK, Potenza M, Petry N, Spritzer D, Ambekar A, Derevensky J, Griffiths MD, Pontes HM, Kuss D, Higuchi S, Mihara S, Assangangkornchai S, Sharma M, Kashef AE, Ip P, Farrell M, Scafato E, Carragher N, Poznyak V. Gaming disorder: its delineation as an important condition for diagnosis, management, and prevention. J Behav Addict. 2017 Sep 1;6(3):271–9. doi: 10.1556/2006.6.2017.039. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/28816494 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Feng W, Ramo DE, Chan SR, Bourgeois JA. Internet gaming disorder: trends in prevalence 1998-2016. Addict Behav. 2017 Dec;75:17–24. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2017.06.010.S0306-4603(17)30232-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Özdemir Y, Kuzucu Y, Ak S. Depression, loneliness and internet addiction: how important is low self-control? Comput Human Behav. 2014 May;34:284–90. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2014.02.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yau YH, Potenza MN, White MA. Problematic internet use, mental health and impulse control in an online survey of adults. J Behav Addict. 2013;2(2):72. doi: 10.1556/jba.1.2012.015. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/24294501 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Kim NR, Hwang SS, Choi JS, Kim DJ, Demetrovics Z, Király O, Nagygyörgy K, Griffiths MD, Hyun SY, Youn HC, Choi SW. Characteristics and psychiatric symptoms of internet gaming disorder among adults using self-reported DSM-5 criteria. Psychiatry Investig. 2016 Jan;13(1):58–66. doi: 10.4306/pi.2016.13.1.58. http://psychiatryinvestigation.org/journal/view.php?doi=10.4306/pi.2016.13.1.58 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Király O, Urbán R, Griffiths MD, Ágoston C, Nagygyörgy K, Kökönyei G, Demetrovics Z. The mediating effect of gaming motivation between psychiatric symptoms and problematic online gaming: an online survey. J Med Internet Res. 2015 Apr 7;17(4):e88. doi: 10.2196/jmir.3515. http://www.jmir.org/2015/4/e88/ v17i4e88 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ballabio M, Griffiths MD, Urbán R, Quartiroli A, Demetrovics Z, Király O. Do gaming motives mediate between psychiatric symptoms and problematic gaming? An empirical survey study. Addict Res Theory. 2017 Mar 27;25(5):397–408. doi: 10.1080/16066359.2017.1305360. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.van Rooij AJ, Kuss DJ, Griffiths MD, Shorter GW, Schoenmakers TM, van de Mheen D. The (co-)occurrence of problematic video gaming, substance use, and psychosocial problems in adolescents. J Behav Addict. 2014 Sep;3(3):157–65. doi: 10.1556/JBA.3.2014.013. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/25317339 .jba.3.2014.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Evenden JL. Varieties of impulsivity. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 1999 Oct;146(4):348–61. doi: 10.1007/pl00005481.91460348.213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.van den Bos W, Rodriguez CA, Schweitzer JB, McClure SM. Adolescent impatience decreases with increased frontostriatal connectivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jul 21;112(29):E3765–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1423095112. http://www.pnas.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=26100897 .1423095112 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Walther B, Morgenstern M, Hanewinkel R. Co-occurrence of addictive behaviours: personality factors related to substance use, gambling and computer gaming. Eur Addict Res. 2012;18(4):167–74. doi: 10.1159/000335662. http://www.karger.com?DOI=10.1159/000335662 .000335662 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Gullo MJ, Dawe S. Impulsivity and adolescent substance use: rashly dismissed as "all-bad"? Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2008 Oct;32(8):1507–18. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.06.003.S0149-7634(08)00097-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Stevens L, Verdejo-García A, Goudriaan AE, Roeyers H, Dom G, Vanderplasschen W. Impulsivity as a vulnerability factor for poor addiction treatment outcomes: a review of neurocognitive findings among individuals with substance use disorders. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2014 Jul;47(1):58–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2014.01.008.S0740-5472(14)00026-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Cao F, Su L, Liu T, Gao X. The relationship between impulsivity and internet addiction in a sample of Chinese adolescents. Eur Psychiatry. 2007 Oct;22(7):466–71. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpsy.2007.05.004.S0924-9338(07)01331-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lee HW, Choi JS, Shin YC, Lee JY, Jung HY, Kwon JS. Impulsivity in internet addiction: a comparison with pathological gambling. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2012 Jul;15(7):373–7. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2012.0063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Meerkerk GJ, van den Eijnden RJ, Franken IH, Garretsen HF. Is compulsive internet use related to sensitivity to reward and punishment, and impulsivity? Comput Human Behav. 2010 Jul;26(4):729–35. doi: 10.1016/j.chb.2010.01.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Choi SW, Kim HS, Kim GY, Jeon Y, Park SM, Lee JY, Jung HY, Sohn BK, Choi JS, Kim DJ. Similarities and differences among Internet gaming disorder, gambling disorder and alcohol use disorder: a focus on impulsivity and compulsivity. J Behav Addict. 2014 Dec;3(4):246–53. doi: 10.1556/JBA.3.2014.4.6. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/25592310 .34Q0583483LU2141 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ward A, Mann T. Don't mind if I do: disinhibited eating under cognitive load. J Pers Soc Psychol. 2000 Apr;78(4):753–63. doi: 10.1037//0022-3514.78.4.753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Semple SJ, Zians J, Grant I, Patterson TL. Impulsivity and methamphetamine use. J Subst Abuse Treat. 2005 Sep;29(2):85–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jsat.2005.05.001.S0740-5472(05)00098-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Tang CS, Wu AM. Impulsivity as a moderator and mediator between life stress and pathological gambling among chinese treatment-seeking gamblers. Int J Ment Health Addict. 2011 Aug;10(4):573–84. doi: 10.1007/s11469-011-9355-0. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Clarke D. Impulsivity as a mediator in the relationship between depression and problem gambling. Pers Individ Dif. 2006 Jan;40(1):5–15. doi: 10.1016/j.paid.2005.05.008. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Sampasa-Kanyinga H, Lewis RF. Frequent use of social networking sites is associated with poor psychological functioning among children and adolescents. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2015 Jul;18(7):380–5. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2015.0055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mentzoni RA, Brunborg GS, Molde H, Myrseth H, Skouverøe KJ, Hetland J, Pallesen S. Problematic video game use: estimated prevalence and associations with mental and physical health. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2011 Oct;14(10):591–6. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2010.0260. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mottram AJ, Fleming MJ. Extraversion, impulsivity, and online group membership as predictors of problematic internet use. Cyberpsychol Behav. 2009 Jun;12(3):319–21. doi: 10.1089/cpb.2007.0170. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Desai RA, Krishnan-Sarin S, Cavallo D, Potenza MN. Video-gaming among high school students: health correlates, gender differences, and problematic gaming. Pediatrics. 2010 Dec;126(6):e1414–24. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-2706. http://pediatrics.aappublications.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=21078729 .peds.2009-2706 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Király O, Griffiths MD, Urbán R, Farkas J, Kökönyei G, Elekes Z, Tamás D, Demetrovics Z. Problematic internet use and problematic online gaming are not the same: findings from a large nationally representative adolescent sample. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2014 Dec;17(12):749–54. doi: 10.1089/cyber.2014.0475. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/25415659 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Huang CL, Yang SC, Chen AS. Motivations and gratification in an online game: relationships among players' self-esteem, self-concept, and interpersonal relationships. Soc Behav Personal. 2015 Mar 21;43(2):193–203. doi: 10.2224/sbp.2015.43.2.193. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Baker JR, Yardley JK. Moderating effect of gender on the relationship between sensation seeking-impulsivity and substance use in adolescents. J Child Adoles Subst. 2002 Dec;12(1):27–43. doi: 10.1300/J029v12n01_02. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Stoltenberg SF, Batien BD, Birgenheir DG. Does gender moderate associations among impulsivity and health-risk behaviors? Addict Behav. 2008 Feb;33(2):252–65. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2007.09.004. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/17913380 .S0306-4603(07)00238-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Nagoshi CT, Wilson JR, Rodriguez LA. Impulsivity, sensation seeking, and behavioral and emotional responses to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1991 Aug;15(4):661–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1991.tb00575.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Ko CH, Liu GC, Hsiao S, Yen JY, Yang MJ, Lin WC, Yen CF, Chen CS. Brain activities associated with gaming urge of online gaming addiction. J Psychiatr Res. 2009 Apr;43(7):739–47. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2008.09.012.S0022-3956(08)00229-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Király O, Tóth D, Urbán R, Demetrovics Z, Maraz A. Intense video gaming is not essentially problematic. Psychol Addict Behav. 2017 Nov;31(7):807–17. doi: 10.1037/adb0000316.2017-43593-001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Király O, Sleczka P, Pontes HM, Urbán R, Griffiths MD, Demetrovics Z. Validation of the Ten-Item Internet Gaming Disorder Test (IGDT-10) and evaluation of the nine DSM-5 internet gaming disorder criteria. Addict Behav. 2017 Jan;64:253–60. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2015.11.005.S0306-4603(15)30056-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Demetrovics Z, Urbán R, Nagygyörgy K, Farkas J, Griffiths MD, Pápay O, Kökönyei G, Felvinczi K, Oláh A. The development of the Problematic Online Gaming Questionnaire (POGQ) PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e36417. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0036417. http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0036417 .PONE-D-12-02935 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Derogatis LR. Clinical Psychometric Research. Baltimore: 1993. [2019-02-01]. Brief Symptom Inventory https://www.pearsonclinical.com/psychology/products/100000450/brief-symptom-inventory-bsi.html . [Google Scholar]
- 39.Urbán R, Kun B, Farkas J, Paksi B, Kökönyei G, Unoka Z, Felvinczi K, Oláh A, Demetrovics Z. Bifactor structural model of symptom checklists: SCL-90-R and Brief Symptom Inventory (BSI) in a non-clinical community sample. Psychiatry Res. 2014 Apr 30;216(1):146–54. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2014.01.027.S0165-1781(14)00068-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Patton JH, Stanford MS, Barratt ES. Factor structure of the Barratt impulsiveness scale. J Clin Psychol. 1995 Nov;51(6):768–74. doi: 10.1002/1097-4679(199511)51:6<768::aid-jclp2270510607>3.0.co;2-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kapitány-Fövény M, Urbán R, Varga G, Potenza M, Griffiths M, Szekely A. The 21-item Barratt Impulsiveness Scale Revised (BIS-R-21): An alternative three-factor model. Manuscript in preparation. 2019 doi: 10.1556/2006.2020.00030. (forthcoming) [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hayes A.F. Introduction to Mediation, Moderation, and Conditional Process Analysis. 2nd ed A Regression-Based Approach. New York: Guilford Press; 2017. Dec 13, p. 692. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Starcevic V, Berle D, Porter G, Fenech P. Problem video game use and dimensions of psychopathology. Int J Ment Health Addict. 2010 Jul 7;9(3):248–56. doi: 10.1007/s11469-010-9282-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Jiménez-Murcia S, Granero R, Wolz I, Baño M, Mestre-Bach G, Steward T, Agüera Z, Hinney A, Diéguez C, Casanueva FF, Gearhardt AN, Hakansson A, Menchón JM, Fernández-Aranda F. Food addiction in gambling disorder: frequency and clinical outcomes. Front Psychol. 2017 Apr;8:473. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00473. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Maraz A, Urbán R, Griffiths MD, Demetrovics Z. An empirical investigation of dance addiction. PLoS One. 2015 May;10(5):e0125988. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125988. http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0125988 .PONE-D-15-04485 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Blaszczynski A, Nower L. A pathways model of problem and pathological gambling. Addiction. 2002;97(5):487–99. doi: 10.1046/j.1360-0443.2002.00015.x.15 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Reynolds B, Fields S. Delay discounting by adolescents experimenting with cigarette smoking. Addiction. 2012;107(2):417–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2011.03644.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wiehler A, Peters J. Reward-based decision making in pathological gambling: the roles of risk and delay. Neurosci Res. 2015 Jan;90:3–14. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2014.09.008.S0168-0102(14)00219-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Wang Y, Wu L, Zhou H, Lin X, Zhang Y, Du X, Dong G. Impaired executive control and reward circuit in internet gaming addicts under a delay discounting task: independent component analysis. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017 Apr;267(3):245–55. doi: 10.1007/s00406-016-0721-6.10.1007/s00406-016-0721-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Khazaal Y, van Singer M, Chatton A, Achab S, Zullino D, Rothen S, Khan R, Billieux J, Thorens G. Does self-selection affect samples' representativeness in online surveys? An investigation in online video game research. J Med Internet Res. 2014;16(7):e164. doi: 10.2196/jmir.2759. http://www.jmir.org/2014/7/e164/ v16i7e164 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Han DH, Renshaw PF. Bupropion in the treatment of problematic online game play in patients with major depressive disorder. J Psychopharmacol. 2012 May;26(5):689–96. doi: 10.1177/0269881111400647. http://jop.sagepub.com/content/26/5/689.abstract .0269881111400647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Schmitz JM. The interface between impulse-control disorders and addictions: are pleasure pathway responses shared neurobiological substrates? Sex Addict Compulsivity. 2005 Apr;12(2-3):149–68. doi: 10.1080/10720160500203641. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Fagundo AB, Santamaría JJ, Forcano L, Giner-Bartolomé C, Jiménez-Murcia S, Sánchez I, Granero R, Ben-Moussa M, Magnenat-Thalmann N, Konstantas D, Lam T, Lucas M, Nielsen J, Bults RG, Tarrega S, Menchón JM, de la Torre R, Cardi V, Treasure J, Fernández-Aranda F. Video game therapy for emotional regulation and impulsivity control in a series of treated cases with bulimia nervosa. Eur Eat Disord Rev. 2013 Nov;21(6):493–9. doi: 10.1002/erv.2259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Tárrega S, Castro-Carreras L, Fernández-Aranda F, Granero R, Giner-Bartolomé C, Aymamí N, Gómez-Peña M, Santamaría JJ, Forcano L, Steward T, Menchón JM, Jiménez-Murcia S. A serious videogame as an additional therapy tool for training emotional regulation and impulsivity control in severe gambling disorder. Front Psychol. 2015 Nov 12;6:1721. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01721. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2015.01721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Stockdale L, Coyne SM. Video game addiction in emerging adulthood: cross-sectional evidence of pathology in video game addicts as compared to matched healthy controls. J Affect Disord. 2018 Jan 1;225:265–72. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.08.045.S0165-0327(17)30112-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Bidwell LC, Balestrieri SG, Colby SM, Knopik VS, Tidey JW. Abstinence-induced withdrawal severity among adolescent smokers with and without ADHD: disentangling effects of nicotine and smoking reinstatement. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2018 Jan;235(1):169–78. doi: 10.1007/s00213-017-4753-z.10.1007/s00213-017-4753-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ioannidis K, Treder MS, Chamberlain SR, Kiraly F, Redden SA, Stein DJ, Lochner C, Grant JE. Problematic internet use as an age-related multifaceted problem: evidence from a two-site survey. Addict Behav. 2018 Jun;81:157–66. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2018.02.017. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0306-4603(18)30082-0 .S0306-4603(18)30082-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Echeburúa E, González-Ortega I, de Corral P, Polo-López R. Clinical gender differences among adult pathological gamblers seeking treatment. J Gambl Stud. 2011 Jun;27(2):215–27. doi: 10.1007/s10899-010-9205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Potenza MN, Steinberg MA, McLaughlin SD, Wu R, Rounsaville BJ, O'Malley SS. Gender-related differences in the characteristics of problem gamblers using a gambling helpline. Am J Psychiatry. 2001 Sep;158(9):1500–5. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.158.9.1500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Blanco C, Hasin DS, Petry N, Stinson FS, Grant BF. Sex differences in subclinical and DSM-IV pathological gambling: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on alcohol and related conditions. Psychol Med. 2006 Jul;36(7):943–53. doi: 10.1017/S0033291706007410.S0033291706007410 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


