Abstract
This study aimed to summarize the clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment of Chiari malformation type I- (CM-1-) associated syringobulbia. We performed a literature review of CM-1-associated syringobulbia in PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Web of Science databases. Our concerns were the clinical features, radiologic presentations, treatment therapies, and prognoses of CM-1-associated syringobulbia. This review identified 23 articles with 53 cases. Symptoms included headache, neck pain, cranial nerve palsy, limb weakness/dysesthesia, Horner syndrome, ataxia, and respiratory disorders. The most frequently involved area was the medulla. Most of the patients also had syringomyelia. Surgical procedures performed included posterior fossa decompression, foramen magnum decompression, cervical laminectomy, duraplasty, and syringobulbic cavity shunt. Most patients experienced symptom alleviation or resolution postoperatively. A syringobulbic cavity shunt provided good results in refractory cases. Physicians should be aware of the possibility of syringobulbia in CM-1 patients, especially those with symptoms of sudden-onset brain-stem involvement. The diagnosis relies on the disorder's specific symptomatology and magnetic resonance imaging. Our review suggests that the initial therapy should be posterior fossa decomposition with or without duraplasty. In refractory cases, additional syringobulbic cavity shunt is the preferred option.
1. Introduction
Syringobulbia (SB) refers to a longitudinally oriented fluid-filled cavity within the brain stem. It is intimately associated with syringomyelia (SM), which is more common [1–3]. Many conditions can cause syringobulbia, including posterior fossa or spinal cord neoplasms, inflammatory disorders (e.g., arachnoiditis and meningitis), and Chiari malformations [1, 4]. SM occurs in CM-I patients at an incidence of 80%, [5] whereas case reports of CM-1-associated SB are rare. Studies of each disorder, however, have only a limited number of patients. Menezes et al. recently reported a series of 326 pediatric CM-I patients, with only 13 (4%) identified as having secondary SB [6]. Because of the rarity of SB, its manifestations, treatment methods, and long-term prognosis are still not established. We therefore conducted a systematic review to clarify the clinical characteristics of these patients.
2. Literature Search Strategy
This systematic review was conducted according to PRISMA (Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) guidelines and recommendations. Two reviewers (J.S., K.Y.H.) independently performed a literature search. PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Web of Science databases were searched from their dates of inception to August 2018 using combinations of the following terms: “Arnold–Chiari malformation/Chiari malformation,” “type 1,” “tonsillar herniation,” “syringobulbia,” “syringomyelia,” and “syringitis/syrinx.” The reference lists of all retrieved articles were reviewed for identification of further potentially relevant studies.
2.1. Selection Criteria
Eligible case reports were systematically assessed using the following inclusion criteria: (1) diagnosis of CM-I with syringobulbia confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and (2) case reports and/or case series. Exclusion criteria were (1) presence of syringobulbia secondary to other causes (e.g., trauma, tumor, and shunt device malfunction) and (2) no syringobulbia identified on MRI. All publications were limited to those involving human subjects and those written in the English language. Editorials and expert opinions were excluded. Review articles were omitted because of potential publication bias and duplication of results.
2.2. Data Extraction and Critical Appraisal
The data were extracted from article texts, tables, and figures, with any estimates made based on the presented data and figures. If more information was needed for clarification, we attempted to contact the study's authors. Two investigators independently reviewed each retrieved article (K.Y.H., J.S.).
3. Results
3.1. Literature Search
The search strategy identified 130 studies. After removing 62 duplicate studies, our inclusion and exclusion criteria were applied to the titles of the 68 remaining articles, which yielded 49 studies that underwent full-text analysis. Finally, 23 articles with 53 cases were included in our study (Figure 1). Table 1 and the Supplementary Table (available here) detail the clinical presentations, operative therapies, and outcomes for each patient (three case series with 30 patients are presented in the Supplementary Materials) [1, 5, 6].
Figure 1.
Flow diagram of the literature review.
Table 1.
Summary of CM-I patients with syringobulbia.
| Author, year | Age, sex |
Manifestations | Examination findings | Extent of SB | Extent of SM | Operation | Outcome | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feinberg M., 2016 | 3, M | Trismus | Completely normal aside from isolated trismus | Medulla, right pontine tegmentum | C1-T8 | Suboccipital craniectomy, C-1 laminectomy | Resolved | 1yr |
| Shankar, B., 2014 | 22, M | Persistent singultus | Ataxia, dysesthesia | Medulla | Holocord | Decompression | Resolved | None |
| Massimi, L., 2011 | 38, M | Acute respiratory failure | Consciousness, normal ICP | Medulla | Hydrocephalus, holocord | ETV | Resolved | 3yrs |
| 1, M | Hemiparesis, Horner syndrome | Left flaccid hemiparesis, myosis, ptosis, Horner syndrome | Medulla, pons | Cervicothoracic | PFD, C-1 laminectomy, and duraplasty | Improved | 3yrs | |
| 2.5, M | Tetraparesis, dyspnea, neck pain | Tetraplegia, limb and trunk hypesthesia | Medulla, pons | Cervicothoracic | Not mentioned | Improved | 10m | |
| Massey, S. L., 2011 | 4, F | Eye inward deviation, neck tilting | CN VI, VII palsies, ataxia, limb spasticity | Medulla, pons | Cervicothoracic | Decompression | Alleviated | 1.5yrs |
| Viswanatha, B., 2009 | 36, F | Dysarthria, headache, neck pain | CN IX, X palsies, dysarthria | Medulla, pons | Holocord | FMD | Improved | 1yr |
| Robert E., 2009 | 16, M | Tetraparesis, headaches, urinary retention | CN VI palsies, tetraparetic, limb weakness | Medulla | Cervical | Large-volume shunt, PFD, laminectomy, duraplasty | Alleviated | Not mentioned |
| 14, M | Vomiting, facial weakness, diplopia, hoarseness, ataxia | CN VI and VII palsies | Medulla, pons | Cervicothoracic | Suboccipital craniectomy, C-1 laminectomy, fenestration, duraplasty | Improved | 4 yrs | |
| Seki, T., 2004 | 27, M | Trunk numbness, limb weakness | Hyperreflexia, dysesthesia(R) | Medulla | C2-C7 | PFD, laminectomy, duraplasty | Alleviated | 5m |
| Aryan, H, 2004 | 55, M | Dysphagia, diplopia, gait difficulty | Bulbar, sensory, motor, and coordination deficits | Medulla | C1-T8 | PFD, laminectomy, duraplasty, VP-shunt | No relief | 3m |
| Lee, J., 2001 | 16, M | Dysphagia, drowsy | Quadriparesis | Medulla, pons | C1-T11 | PFD, laminectomy, duraplasty, syringoperitoneal shunt | Remission | 6m |
| Penarrocha, M., 2001 | 45, M | Orofacial pain | Hypoesthesia | Medulla | Cervical | Decompression, shunt | Resolved | 2yrs |
| Galarza, M, 2001 | 9, M | Lethargy and respiratory arrest | Quadriparesis | Medulla | Cervical | Ventricle external drainage | Improved | Not mentioned |
| Nogues, M., 2000 | 58, F | Dysesthesia | Increased tone | Medulla | Cervicothoracic | None | None | None |
| Takahashi, Y., 1999 | 15, M | Gait disturbance, dysphagia | Horizontal nystagmus, ataxia, limb weakness | Medulla | Cervicothoracic | FMD, laminectomy | Improved | 8yrs |
| Afifi, A, 1997 | 11, F | Diplopia, snoring | CN VI, XII palsies, arm hyporeflexia, leg hyperreflexia | Medulla, pons | Cervical | PFD, laminectomy, duraplasty, 4th-V shunt | Improved | 6m |
| Anwer, U, 1996 | 47, F | Dysphagia, tough numbness | Hemiparalysis, Horner's syndrome | Medulla | Cervicothoracic | PFD | Improved | 2m |
| Kanev, P, 1994 | 13, F | Diplopia | Diplopia | Medulla, pons | Cervical | PFD, laminectomy | Improved | 2m |
| Rhoton, E. L., 1991 | 69, F | Limbs weakness and numbness | Hemiparesis, dysesthesia, hyperreflexia | Brain stem, syringocephaly | C2-C6 | craniectomy, laminectomy, 4th V shunt | Resolved | Not mentioned |
| Weissman, J., 1990 | 46, M | Arm weakness and Dysesthesia, dysarthria and dysphagia | Torsional nystagmus, vocal cord paralysis | Medulla | C2-T8 | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Not mentioned |
| Okada, S., 1989 | 10, F | Limbs weakness, dysesthesia | Hemiparesis, dysesthesia, hyperreflexia, CN V palsies | Brain stem, syringocephaly | C1-T10 | Craniectomy, laminectomy, duraplasty | Improved | 1m |
| Bresnan, M., 1987 | 17, F | limbs numbness, nausea, vomiting, diplopia, oscillopsia, dysarthria | Rotatory nystagmus, CN V-VII palsies | Medulla | C2-T4 | Decompressed, stent shunt, duraplasty | Improved | 1m |
C: cervical, CN: cranial nerve, ETV: endoscopic third ventriculostomy, F: female, FMD: foramen magnum decompression, ICP: intracranial pressure, M: male, m: month(s), PDF: posterior foramen decompression, SB: syringobulbia, SM: syringomyelia, T: thoracic, yrs: year(s), and VP: ventriculoperitoneal.
3.2. Clinical Presentation
The symptoms of syringobulbia included headache, neck pain, cranial nerve palsy, limb weakness or dysesthesia, Horner syndrome, ataxia, and respiratory disorders. Limb weakness, whether unilateral or bilateral, was the most common symptom. Cranial nerves (CNs) IX and X were most frequently involved, manifesting as bulbar palsy, dysphagia, and dysarthria. Diplopia and ptosis were also common. Neurological examinations often revealed tendon hyperreflexia, although hyporeflexia sometimes occurred. Ataxia, gait disturbance, eye nystagmus, and other signs of cerebellum involvement were also common. Dyspnea and respiratory arrest, with an incidence of 9.4% (5/53), were unique presentations of medulla involvement. Other rare presentations included trismus, persistent singultus, and oscillopsia.
3.3. Imaging Findings
Syringobulbia was identified on MRI in all but one patient [7]. The medulla was involved in all patients, and solo medulla syringobulbia was most common. Pons involvement was also frequent, whereas the cerebrum was involved in only three patients. Syringobulbia usually presents on MRI as a silt-like lesion in one side of the medulla. Most patients had combined syringomyelia, which could be cervical, cervicothoracic, or holochord. Only five patients did not have syringomyelia (9.4%).
3.4. Surgical Treatment and Outcomes
Surgical procedures included posterior fossa (or suboccipital) decompression, foramen magnum decompression, cervical laminectomy, duraplasty, and syringobulbic cavity shunt. SB was alleviated in most cases. In refractory cases, a syringobulbic cavity shunt to the subarachnoid space was mostly successful. The ratio of complete resolution of symptoms increased among patients who underwent the shunt (Figure 2), although this result lacks statistical support because of the quality of the data.
Figure 2.
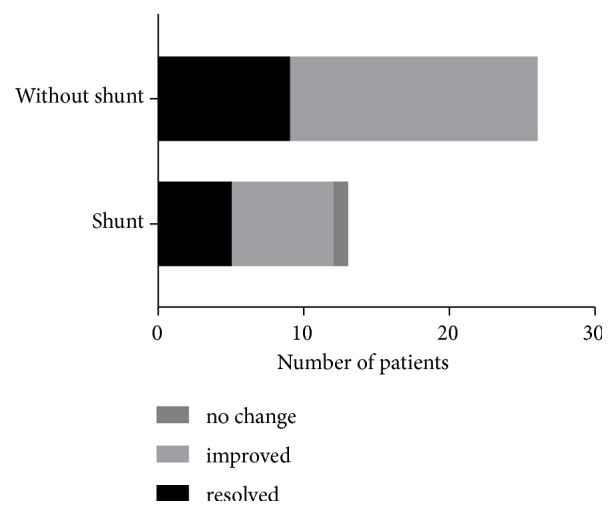
Surgical outcomes with and without the syringobulbic cavity shunt to the subarachnoid space.
4. Discussion
CM-1 is a common neurosurgical condition in both pediatric and adult populations. According to the literature, the rate of accompanying syringomyelia could be as high as 80%, whereas accompanying syringobulbia is much rarer. Menezes et al. reported that the incidence of syringobulbia was 4% in a series of 326 pediatric patients with CM-I [6]. Our literature review identified 23 cases with 130 CM-I-associated syringobulbia patients.
Although the symptomatology of CM-I has been well described in the literature, patients with accompanying syringobulbia have more prominent symptomatology because of the brain-stem involvement. SB-related symptoms usually appear in a chronic pattern, although sudden-onset cases have occurred, especially when there is a sudden onset of CN X palsy [8–10]. Headache, gait and balance disorders, and limb weakness or dysesthesia were the most frequent complaints of CM-I patients with SB. Cranial nerve dysfunction was common [11, 12]. CNs IX and X were most frequently affected, followed by CN V [13]. Persistent singultus that lasted >48 h, oscillopsia, nystagmus, and Horner syndrome were revealing presentations of syringobulbia [13–15]. Horner syndrome was present in 18% of patients in a previous study [16–18]. Central hypoventilation syndrome also occurred in CM-I patients with syringobulbia and, in fact, is the leading cause of sudden death in patients with CM-I [19, 20].
MRI was the most useful technique for detecting syringobulbic cavities [21]. A slit-like hyperintense area in the medulla was the characteristic presentation, [3, 6, 22] although in some patients the silt-like cavity was too thin to be visualized [7]. Other studies noted that SB could appear in three locations: the floor of the fourth ventricle, the midline floor of the fourth ventricle, or areas ventral to the fourth ventricle [15, 23]. The medulla is most frequently involved and was reported in all cases of this review. Further rostral extension into the pons (syringopontia), midbrain (syringomesencephaly), or cerebrum (syringocephaly) also occurred in several cases [24]. Although the cavity of syringobulbia is usually unilateral, midline cavities also occurred in some patients, leading to bilateral neurological defects.
The mechanism of syringobulbia formation is not clear. Tubbs et al. reported that there were no morphometric peculiarities for patients with CM-I-associated syringobulbia in regard to other CM-I patients with and without isolated syringomyelia [25]. Sherman et al., [21] in an MRI study, found that there are two types of syringobulbia. One type presents with thin clefts or slits extending into the medulla, with much smaller cavities than cervical cavities. The other type presents with saccular syringobulbia, with isometric medullary cavities, unlike the cervical or spinal syrinx cavity. Most cases are of the first type. Considering the close relation of syringobulbia and syringomyelia, syringobulbia might result from upward impulsive fluid movements due to previously established syringomyelia [26]. In contrast, the second type could be congenital—that is, the syringobulbia occurred during the fetal stage. Syringobulbia clefts due to dissection of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) under pressure from the fourth ventricle should be differentiated from the ascending syringobulbia [16]. Other studies found that arachnoid veils or arachnoidal scars could cause syringobulbia or syringomyelia by partially obstructing CSF flow, which is often observed during surgery [6, 27]. Williams et al., however, thought that the most common correlation of syringobulbia was with none of the above mechanisms but with pressure differences acting downward on the hindbrain, with distortion of the cerebellum and stem, traction on the cranial nerves, and/or indentation of the brain stem by vascular loops [16]. The dramatic alleviation of SB and SM following posterior fossa decompression indicates a pathogenetic role of the tonsils or intradural pathology at the level of the egress of the fourth ventricle [6, 27].
Syringobulbia progression is usually slow [28]. The main surgical therapy is laminectomy for syringomyelia and posterior fossa or foramen magnum decompression for CM-I [6, 22]. Whether post-decompression duraplasty improves the outcome is still controversial. Recent meta-analyses supported reconstructive duraplasty in addition to compression because the overall clinical improvement is better [29–31]. In most cases, posterior fossa decompression with intradural exploration and duraplasty leads to its resolution [6]. Several reports suggested that a syringobulbia cavity–fourth ventricle shunt or syringobulbia cavity–subarachnoid space shunt benefits resolution [6, 7]. If the syringobulbia is communicating with the fourth ventricle, a fourth ventricle opening into the subarachnoid space is needed [7, 32].
5. Conclusion
Syringobulbia, a rare entity closely associated with CM-I, is characterized by an abrupt onset of symptoms due to the brain-stem involvement. The diagnosis mainly relies on the unique symptomatology of syringobulbia and MRI. Treatment is posterior fossa decomposition with or without duraplasty. An additional syringobulbic cavity shunt may improve the rate of total resolution of symptoms, especially in refractory cases.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no.81501065), Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation (no.LY16H090004), and International Cooperation Project of Science Technology Department of Zhejiang Province (no.2015C34007). The authors thank Nancy Schatken BS, MT(ASCP), from Liwen Bianji, Edanz Group China (http://www.liwenbianji.cn/ac), for editing the English text of a draft of this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Authors' Contributions
Jian Shen, Jie Shen, and Kaiyuan Huang contribute equally.
Supplementary Materials
The supplementary material is complementary to Table 1. It is a summary of three case series of CM-I patients with syringobulbia [1, 5, 6].
References
- 1.Greenlee J. D. W., Menezes A. H., Bertoglio B. A., Donovan K. A. Syringobulbia in a pediatric population. Neurosurgery. 2005;57(6):1147–1152. doi: 10.1227/01.NEU.0000188282.72429.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Sharafuddin M. J. Syringomyelia extending to basal ganglia. Journal of Neurosurgery. 1990;73(4):p. 645. doi: 10.3171/jns.1990.73.4.0645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Okada S., Nakagawa Y., Hirakawa K. Syringomyelia extending to the basal ganglia. Case report. Journal of Neurosurgery. 1989;71(4):616–617. doi: 10.3171/jns.1989.71.4.0616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Weese-Mayer D. E., Brouillette R. T., Naidich T. P., McLone D. G., Hunt C. E. Magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography in central hypoventilation. American Review of Respiratory Disease. 1988;137(2):393–398. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/137.2.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Botelho R. V., Bittencourt L. R. A., Rotta J. M., Tufik S. Polysomnographic respiratory findings in patients with Arnold-Chiari type I malformation and basilar invagination, with or without syringomyelia: Preliminary report of a series of cases. Neurosurgical Review. 2000;23(3):151–155. doi: 10.1007/PL00011947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Menezes A. H., Greenlee J. D. W., Dlouhy B. J. Syringobulbia in pediatric patients with Chiari malformation type i. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. 2018;22(1):52–60. doi: 10.3171/2018.1.PEDS17472. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bresnan M. J., Chiappa K. H., Hedleywhyte E. T., et al. A 17-year-old girl with numbness of the right leg and the recent onset of vertigo and right-sided weakness - syringomyelia, with syringobulbia - chiari malformation of hindbrain, type-i. The New England Journal of Medicine. 1987;316(3):150–157. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198701153160307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jha S., Das A., Gupta S., Banerji D. Syringomyelia with syringobulbia presenting only with paralysis of 9th and 10th cranial nerves. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. 2002;105(4):341–343. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0404.2002.1c232.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Heidel K. M., Benarroch E. E., Gené R., et al. Cardiovascular and respiratory consequences of bilateral involvement of the medullary intermediate reticular formation in syringobulbia. Clinical autonomic research: Official Journal of The Clinical Autonomic Research Society. 2002;12(6):450–456. doi: 10.1007/s10286-002-0075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kanev P. M., Getch C. C., Jallo J., Faerber E. N. Cerebral syrinx with chiari i malformation. Pediatric Neurosurgery. 1994;20(3):214–216. doi: 10.1159/000120791. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Massey S. L., Buland J., Hauber S., et al. Acute VI nerve palsy in a 4 year-old girl with Chiari I malformation and pontomedullary extension of syringomyelia: Case report and review of the literature. European Journal of Paediatric Neurology. 2011;15(4):303–309. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpn.2011.04.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Viswanatha B. Syringomyelia with syringobulbia presenting as vocal fold paralysis. Ear, Nose & Throat Journal. 2009;88(7):p. E20. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Shankar B., Narayanan R., Paruthikunnan S. M., Kulkarni C. D. Persistent singultus as presenting symptom of syringobulbia. BMJ Case Reports. 2014;2014 doi: 10.1136/bcr-2014-205314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Weissman J. D., Seidman S. H., Dell'osso L. F., Naheedy M. H., Leigh R. J. Torsional, see-saw, 'bow-tie' nystagmus in association with brain stem anomalies. Neuro-Ophthalmology. 1990;10(6):315–318. doi: 10.3109/01658109009009629. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Nogués M., López L., Meli F. Neuro-ophthalmologic complications of syringobulbia. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports. 2010;10(6):459–466. doi: 10.1007/s11910-010-0139-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Williams B. Hindbrain-related syringomyelia clinic and treatment - syringobulbia: a surgical review. Acta Neurochirurgica. 1993;123(3-4):190–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Trobe J. D. The evaluation of horner syndrome. Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology. 2010;30(1):1–2. doi: 10.1097/WNO.0b013e3181ce8145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Morgan D., Williams B. Syringobulbia: A surgical appraisal. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 1992;55(12):1132–1141. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.12.1132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nogues M. A., Gene R., Encabo H. Risk of sudden death during sleep in syringomyelia and syringobulbia. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 1992;55(7):585–589. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.55.7.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Massimi L., Della Pepa G. M., Tamburrini G., Di Rocco C. Sudden onset of chiari malformation type i in previously asymptomatic patients: report of 3 cases. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. 2011;8(5):438–442. doi: 10.3171/2011.8.PEDS11160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sherman J. L., Citrin C. M., Barkovich A. J. MR imaging of syringobulbia. Journal of Computer Assisted Tomography. 1987;11(3):407–411. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198705000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Feinberg M., Babington P., Sood S., Keating R. Isolated unilateral trismus as a presentation of Chiari malformation: Case report. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. 2016;17(5):533–536. doi: 10.3171/2015.7.PEDS1592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nogués M. A., Benarroch E. Abnormalities of respiratory control and the respiratory motor unit. The Neurologist. 2008;14(5):273–288. doi: 10.1097/NRL.0b013e318173e830. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Menezes A. H., Greenlee J. D. W., Longmuir R. A., Hansen D. R., Abode-Iyamah K. Syringohydromyelia in association with syringobulbia and syringocephaly: Case report. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. 2015;15(6):657–661. doi: 10.3171/2014.11.PEDS14189. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tubbs R. S., Bailey M., Barrow W. C., Loukas M., Shoja M. M., Oakes W. J. Morphometric analysis of the craniocervical juncture in children with Chiari i malformation and concomitant syringobulbia. Child's Nervous System. 2009;25(6):689–692. doi: 10.1007/s00381-009-0810-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Heidel K. M., Benarroch E. E., Gené R., et al. Cardiovascular and respiratory consequences of bilateral involvement of the medullary intermediate reticular formation in syringobulbia. Clinical Autonomic Research. 2002;12(6):450–456. doi: 10.1007/s10286-002-0075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Dlouhy B. J., Dawson J. D., Menezes A. H. Intradural pathology and pathophysiology associated with chiari i malformation in children and adults with and without syringomyelia. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. 2017;20(6):526–541. doi: 10.3171/2017.7.PEDS17224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Elliott R., Kalhorn S., Pacione D., Weiner H., Wisoff J., Harter D. Shunt malfunction causing acute neurological deterioration in 2 patients with previously asymptomatic chiari malformation type i: report of 2 cases. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. 2009;4(2):170–175. doi: 10.3171/2009.4.PEDS0936. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lu V. M. Erratum. The addition of duraplasty to posterior fossa decompression in the surgical treatment of pediatric Chiari malformation Type I: a systematic review and meta-analysis of surgical and performance outcomes. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. 2018;21(2):p. 197. doi: 10.3171/2017.10.PEDS16367a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Xu H., Chu L., He R., Ge C., Lei T. Posterior fossa decompression with and without duraplasty for the treatment of Chiari malformation type I—a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurgical Review. 2017;40(2):213–221. doi: 10.1007/s10143-016-0731-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Lu V. M., Phan K., Crowley S. P., Daniels D. J. The addition of duraplasty to posterior fossa decompression in the surgical treatment of pediatric Chiari malformation Type I: A systematic review and meta-analysis of surgical and performance outcomes. Journal of Neurosurgery: Pediatrics. 2017;20(5):439–449. doi: 10.3171/2017.6.PEDS16367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Peñarrocha M., Okeson J. P., Peñarrocha M. S., Cervelló M. A. Orofacial pain as the sole manifestation of syringobulbia-syringomyelia associated with arnold-chiari malformation. Journal of Orofacial Pain. 2001;15(2):170–173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The supplementary material is complementary to Table 1. It is a summary of three case series of CM-I patients with syringobulbia [1, 5, 6].