Abstract
In silico predictive software allows assessing the effect of amino acid substitutions on the structure or function of a protein without conducting functional studies. The accuracy of in silico pathogenicity prediction tools has not been previously assessed for variants associated with autosomal recessive deafness 1A (DFNB1A). Here, we identify in silico tools with the most accurate clinical significance predictions for missense variants of the GJB2 (Cx26), GJB6 (Cx30), and GJB3 (Cx31) connexin genes associated with DFNB1A. To evaluate accuracy of selected in silico tools (SIFT, FATHMM, MutationAssessor, PolyPhen-2, CONDEL, MutationTaster, MutPred, Align GVGD, and PROVEAN), we tested nine missense variants with previously confirmed clinical significance in a large cohort of deaf patients and control groups from the Sakha Republic (Eastern Siberia, Russia): Сх26: p.Val27Ile, p.Met34Thr, p.Val37Ile, p.Leu90Pro, p.Glu114Gly, p.Thr123Asn, and p.Val153Ile; Cx30: p.Glu101Lys; Cx31: p.Ala194Thr. We compared the performance of the in silico tools (accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity) by using the missense variants in GJB2 (Cx26), GJB6 (Cx30), and GJB3 (Cx31) genes associated with DFNB1A. The correlation coefficient (r) and coefficient of the area under the Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve as alternative quality indicators of the tested programs were used. The resulting ROC curves demonstrated that the largest coefficient of the area under the curve was provided by three programs: SIFT (AUC = 0.833, p = 0.046), PROVEAN (AUC = 0.833, p = 0.046), and MutationAssessor (AUC = 0.833, p = 0.002). The most accurate predictions were given by two tested programs: SIFT and PROVEAN (Ac = 89%, Se = 67%, Sp = 100%, r = 0.75, AUC = 0.833). The results of this study may be applicable for analysis of novel missense variants of the GJB2 (Cx26), GJB6 (Cx30), and GJB3 (Cx31) connexin genes.
1. Introduction
The most common form of hereditary nonsyndromic hearing loss is autosomal recessive deafness 1A (DFNB1A, MIM#220290) caused by pathogenic variants in the GJB2, GJB6, and GJB3 genes encoding connexin 26 (Cx26), connexin 30 (Cx30), and connexin 31 (Cx31) proteins, respectively. The estimated prevalence of DFNB1A among general human population is 14:100 000, and the main cause of DFNB1A is biallelic recessive pathogenic variants in the GJB2 gene (MIM#121011) (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1272/, 2018). Currently, about 400 different pathogenic variations of GJB2 sequence (more than 70% are missense or nonsense amino acid substitutions) are presented in the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD, http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk/ac/all.php), and this list is regularly updated by novel yet unclassified variants. The majority of nonsense variants are pathogenic since they lead to a premature termination of translation and protein synthesis, while missense variants depending on their location in the amino acid sequence can be neutral, damaging, or partially damaging to the structure and function of protein. As a consequence, pathogenicity of many missense variants is difficult to assess.
Basic information on pathogenic mutations is provided by curated databases such as Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) [1] and the Human Gene Mutation Database (HGMD) [2] collecting data on variants of all genes, mainly from the literature. Disease and gene-specific databases often contain variants that are incorrectly classified including incorrect claims published in peer-reviewed literature since different authors interpret the term “mutation pathogenicity” differently because of the increased complexity of analysis and interpretation of clinical genetic testing. Experimental study of the molecular effects of mutations is laborious, whereas useful and reliable information about the effects of amino acid substitutions can readily be obtained by theoretical methods [3]. A variety of in silico tools, both publicly and commercially available, can help in the interpretation of sequence variants without structural or functional studies. However, algorithms used by each tool may differ, but can include determination of the effect of the sequence variant at the nucleotide and amino acid as well as the potential impact of the variant on the protein. The impact of a missense substitution depends on criteria such as the evolutionary conservatism of an amino acid/nucleotide, location, and context within the protein sequence and the biochemical consequence of the amino acid substitution [4].
Different in silico tools each have their own strengths and weaknesses depending on the algorithm, and in many cases performance varies depending on the certain gene and protein [5, 6]. Performance of available prediction software is constantly being evaluated by comparing their ability to predict “known” disease-causing variants. As a result, the MutPred performed best for variants of genes associated with the RASopathy and limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD) [7]; the MAPP and the MAPP + PolyPhen-2.1 provided the best combined model for testing variants of MLH1, MSH2, MSH6, and PMS2 genes associated with Lynch syndrome, a hereditary form of colon cancer [8]; the SIFT was well suited for the analysis of variants of the UGT1A1 gene associated with Crigler-Najjar syndrome (congenital hereditary nonhemolytic unconjugated bilirubinemia) [9]; the Align GVGD in silico tool was shown as the best for testing variants of genes associated with cancer (BRCA1, BRCA2, MLH1, and MLH2) [10]; in silico test of 236 BRCA1/2 missense variants suggested that SIFT and MutationTaster2 are suitable to predict benignity of variants in these genes [11]. There is also a big class of tools for predicting splice site variations which were tested by comparing the predictions against RNA in vitro results for natural splice sites of clinically relevant genes in hereditary breast/ovarian cancer (HBOC) [12]. The analysis revealed that HSF, HSF+SSF-like, or HSF+SSF-like+MES achieved a high performance for predicting the disruption of donor sites, and SSF-like for predicting disruption of acceptor sites [12]. In general, most missense variant prediction algorithms are 65-90% accurate when examining known disease variants.
However, so far the accuracy of in silico pathogenicity prediction tools was not assessed for variants of genes associated with autosomal recessive deafness 1A. To date, the only published study was focused on the pathogenicity analysis of 211 missense variants of the GJB2 gene annotated in the Ensembl and the HGMD databases [13]. Four predictive in silico tools, SIFT, PANTHER, PolyPhen-2, and FATHMM, were used but the comparison of their performance was not performed.
The aim of this study is to compare the performance of the in silico pathogenicity prediction tools by testing the missense variants in GJB2 (Cx26), GJB6 (Cx30), and GJB3 (Cx31) genes associated with the autosomal recessive deafness 1A.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Missense Variants Selection
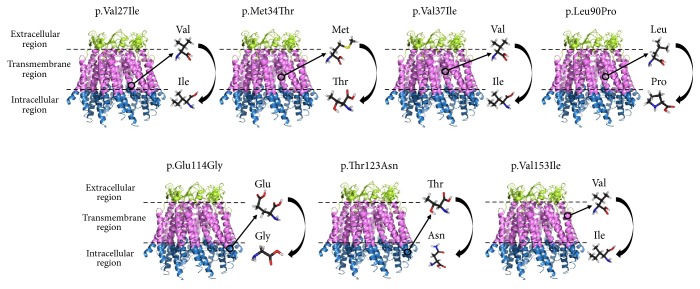
To assess accuracy of selected in silico tools, we tested nine missense variants of the GJB2 (Cx26), GJB6 (Cx30), and GJB3 (Cx31) genes found earlier in a large cohort of deaf patients and control groups from the Sakha Republic (Eastern Siberia, Russia): GJB2 (Сх26): c.79G>A (p.Val27Ile), c.101T>C (p.Met34Thr), c.109G>A (p.Val37Ile), c.269T>C (p.Leu90Pro), c.341A>G (p.Glu114Gly), c.368C>A (p.Thr123Asn), and c.457G>A (p.Val153Ile); GJB6 (Cx30): c.301G>A (p.Glu101Lys); GJB3 (Cx31): с.580G>A (p.Ala194Thr) [14–16] (Figure 1). Of these, three variants of the GJB2 gene, c.269T>C (p.Leu90Pro), c.101T>C (p.Met34Thr), and c.109G>A (p.Val37Ile), are pathogenic variants associated with hearing impairment (DFNB1A); the remaining six variants were interpreted as benign variants of no clinical significance [14, 15]. To assess the clinical relevance of the presented missense variants, we analyzed not only the results of the segregation analysis of genotype-phenotype correlation, but also the data from the databases of annotated variants: OMIM (the Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, http://www.omim.org) [1]; HGMD (the Human Gene Mutation Database, http://www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk) [2]; the ClinVar (a public archive with interpretations of clinically relevant variants, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/clinvar/) [17, 18]; ExAC (the Exome Aggregation Consortium, http://exac.broadinstitute.org) [19]; the 1000 Genomes Project (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/variation/tools/1000genomes) [20]; dbSNP (the Single Nucleotide Polymorphism database, http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/snp/) [21].
Figure 1.
Localization of the tested nonsynonymous (missense) amino acid substitutions in the structure of connexin 26. Note. The information about the structure Сx26 was obtained from the database of three-dimensional structures of proteins and nucleic acids PDB ID:2ZW3 (https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Structure/pdb/2ZW3) [22]. Localization of the studied amino acids in structure of Cx26 was obtained using the 3D-structure viewer applet with the protein structure loaded software PolyPhen-2 (http://genetics.bwh.harvard.edu/pph2/). Detailed structure models of human Cx30 and Cx31 proteins are currently not defined.
2.2. In Silico Prediction Tools
In this study, 9 predictive computer programs were used to predict pathogenicity: SIFT (Sorting Intolerant From Tolerant) [3, 24–27], FATHMM (Functional Analysis Through Hidden Markov Models) [28–30], MutationAssessor [31, 32], PolyPhen-2 (Polymorphism Phenotyping V-2) [33], CONDEL (Consensus Deleteriousness) [34], MutationTaster [35, 36], MutPred (Mutation Prediction) [37], Align GVGD (Align Grantham Variation/Grantham Deviation) [38, 39], and PROVEAN (Protein Variation Effect Analyzer) [40, 41]. Each in silico tool uses different parameters for classification of variants which are detailed according to websites listed in Supplementary Materials (see Table S1). The FASTA format and Ensembl sequence identifiers (nucleotide, amino acid, and protein) were used for query in programs (see Table S2).
2.3. Analytical Parameters of In Silico Tools
Analytical parameters of studied tools were calculated according to Fletcher & Fletcher, 2005, and Glantz, 1997 [23, 42]:
Sensitivity (Se) is a proportion of the true-positive results (correct identification of pathogenic variants), according to equation
| (1) |
where Tp denotes true-positive cases and FN denotes false negative cases.
Specificity (Sp) is a proportion of the true negative results (correct identification of benign variants), according to equation
| (2) |
where TN denotes true negative cases and Fp denotes false-positive cases.
Accuracy (Aс) is the ratio of complete correct predictions to the total number of predictions, according to the following equation.
| (3) |
Positive predictive values (PPV) are a proportion of positive results that were true-positive (the ratio of true-positive results to all positive results), according the following equation.
| (4) |
Negative predictive values (NPV) are a proportion of negative results that were true negative (the ratio of true negative results to all negative results), according to the following equation.
| (5) |
Correlation coefficient (r) is the determination of the relationship between the clinical values of missense variants and predictive evaluation of the program.
ROC curve: the way to express the relationship between sensitivity and specificity for a given test is to construct a curve, called a Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve [42]. ROC curves are frequently used in the bioinformatic analysis to evaluate classification and prediction models for supporting, diagnosis, and prognosis. To construct a ROC curve, along the Y-axis, the true-positive share (sensitivity) is plotted, along the X-axis, the false-positive share (1 − specificity). The values on the axes ran from probability of 0 to 100% [42]. The quantitative interpretation of ROC is given by AUC (area under ROC curve), the area bounded by the ROC curve and the axis of the share of false-positive cases. The bigger the area under the ROC curve, the better the model. A rough guide for classifying the accuracy of a diagnostic test is the traditional academic point system: 0.9-1.0: excellent (A); 0.8-0.9: good (B), 0.7-0.8: fair (C); 0.6-0.7: poor (D); 0.5-0.6: fail (F) (corresponds to random guessing) [43]. The ROC curves were constructed using the MedCalc statistical software for biomedical research (https://www.medcalc.org).
3. Results
The predictions for missense variants in the GJB2 (Cх26), GJB6 (Сх30), and GJB3 (Cx31) genes by the in silico tools in comparison with their established clinical significance are presented in Table 1. Predictions for studied missense variants (3 pathogenic, 6 benign) were different in every analyzed in silico tool. Only the c.269T>C (p.Leu90Pro) variant of the GJB2 gene was evaluated by all programs as a damaging variant.
Table 1.
Evaluation of missense variants by predictive in silico tools.
| Gene | Missense variants |
Clinical significance | SIFT | FATHMM | MutationAssessor | Polyphen-2 | CONDEL | MutationTaster | MutPred | Align GVGD | PROVEAN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
GJB2 (Cx26) |
c.79G>A p.Val27Ile rs2274084 |
Benign |
Tolerated score: 0.21 |
Damaging score: -5.59 |
Medium FI score: 2.28 VC score: 2.16 VS score: 2.40 |
Probably damaging HumDiv score: 1.000 HumVar score: 0.998 |
Deleterious Calculated Condel score: 0.612278613903 |
Polymorphism score: 29 |
hypotheses are absent general score: 0.321 |
Unclassified Class C25 GV 0.00 GD 29.61 |
Neutral score: -0.660 |
| c.101T>C p.Met34Thr rs35887622 |
Pathogenic |
Damaging score: 0.01 |
Damaging score: -5.41 |
Medium FI score: 2.315 VC score: 2.43 VS score: 2.20 |
Benign HumDiv score: 0.038 HumVar score: 0.083 |
Deleterious Calculated Condel score: 0.58786807751 |
Disease causing score: 81 |
hypotheses are absent general score: 0.969 |
Deleterious Class C65 GV 0.00 GD 81.04 |
Deleterious score: -3.801 |
|
| c.109G>A p.Val37Ile rs72474224 |
Pathogenic | Tolerated score: 0.34 |
Damaging score: -5.46 |
Medium FI score: 2.095 VC score: 2.58 VS score: 1.61 |
Probably damaging HumDiv score: 1.000 HumVar score: 0.996 |
Deleterious Calculated Condel score: 0.61487213316 |
Disease causing score: 29 |
hypotheses are absent general score: 0.902 |
Unclassified Class C25 GV 0.00 GD 29.61 |
Neutral score: -0.857 |
|
| c.269T>C p.Leu90Pro rs80338945 |
Pathogenic |
Damaging score: 0 |
Damaging score: -5.64 |
Medium FI score: 3.33 VC score: 4.26 VS score: 2.40 |
Probably damaging HumDiv score: 1.000 HumVar score: 0.996 |
Deleterious Calculated Condel score: 0.676708483818 |
Disease causing score: 98 |
Confident hypotheses: Gain of sheet (P = 0.039) general score:0.915 |
Deleterious C65 GV 0.00 GD 97.78 |
Deleterious score: -6.482 |
|
| c.341A>G p.Glu114Gly rs2274083 |
Benign |
Tolerated score: 0.16 |
Damaging score: -4.58 |
Medium FI score: 2.005 VC score: 2.40 VS score: 161 |
Benign HumDiv score: 0.001 HumVar score: 0.001 |
Deleterious Calculated Condel score: 0.556433693212 |
Polymorphism score: 98 |
hypotheses are absent general score: 0.232 |
Deleterious Class C65 GV 0.00 GD 97.85 |
Neutral score: -0.123 |
|
| c.368C>A p.Thr123Asn rs111033188 |
Benign |
Tolerated score: 0.59 |
Damaging score: -4.42 |
Neutral FI score: -0.305 VC score: -0.61 VS score: - 0 |
Benign HumDiv score: 0.000 HumVar score: 0.000 |
Neutral Calculated Condel score: 0.513276654484 |
Disease causing score: 53 |
hypotheses are absent general score: 0.201 |
Deleterious Class C55 GV 0.00 GD 64.77 |
Neutral score: 0.797 |
|
| c.457G>A p.Val153Ile rs111033186 |
Benign |
Tolerated score: 1 |
Damaging score: -3.69 |
Neutral FI score: -0.305 VC score: -0.43 VS score: -0.18 |
Benign HumDiv score: 0.003 HumVar score: 0.007 |
Neutral Calculated Condel score: 0.491937780564 |
Disease causing score: 29 |
hypotheses are absent general score: 0.488 |
Unclassified Class C25 GV 0.00 GD 29.61 |
Neutral score: 0.138 |
|
|
| |||||||||||
|
GJB6 (Cx30) |
c.301G>A p.Glu101Lys rs571454176 |
Benign |
Тolerated score:0.69 |
Damaging score: -5.26 |
Neutral FI score: -0.37 VC score: -0.74 VS score: 0 |
Benign HumDiv score: 0.193 HumVar score: 0.058 |
Neutral Calculated Condel score: 0.505405538667 |
Disease causing Score: 56 |
Actionable hypotheses: Gain of MoRF binding (P = 0.0064) Gain of ubiquitination at E101 (P = 0.0276) Gain of methylation at E101 (P = 0.0345) general score: 0.506 |
Deleterious Class C55 GV 0.00 GD 56.87 |
Neutral score: -1.273 |
|
| |||||||||||
|
GJB3 (Cx31) |
с.580G>A p.Ala194Thr rs121908852 |
Benign |
Тolerated score: 0.91 |
Damaging score: -3.67 |
Low FI score: 1.085 VC score: -0.54 VS score: 2.71 |
Benign HumDiv score: 0.163 HumVar score: 0.110 |
Deleterious Calculated Condel score: 0.529626647419 |
Disease causing Score: 58 |
hypotheses are absent general score: 0.399 |
Deleterious Class C55 GV 0.00 GD 58.02 |
Neutral score: 1.636 |
Note. The correct results (both “true” positive and “true” negative results) are highlighted by bold font.
The informative parameters of the compared programs are presented in Table 2. The accuracy of the clinical significance predictions for missense variants among the analyzed nine programs varies from 33% (FATHMM) to 89% (SIFT and PROVEAN). The SIFT and PROVEAN showed high sensitivity and specificity parameters: 67% and 100%, respectively. The programs MutationAssessor, FATHMM, MutationTaster, and CONDEL had 100% sensitivity, but showed a low specificity, between 33% and 67%, and CONDEL showed total absence of specificity. High rates of predictability of positive and negative results were provided by the SIFT and PROVEAN programs (PPV = 100% and NPV = 86% for both programs) while the FATHMM and Align GVGD programs were the most inaccurate, which resulted in a decrease in almost all of the analyzed parameters. However, FATHMM showed 100% sensitivity since all missense variants were classified by this program as equally damaging.
Table 2.
Performance of in silico tools.
| in silico Tools | Accuracy | Sensitivity | Specificity | PPV | NPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIFT | 89% | 67% | 100% | 100% | 86% |
| MutationAssessor | 78% | 100% | 67% | 60% | 100% |
| FATHMM | 33% | 100% | 0% | 33% | 0% |
| Polyphen-2 | 78% | 67% | 83% | 67% | 50% |
| MutationTaster | 56% | 100% | 33% | 43% | 33% |
| PROVEAN | 89% | 67% | 100% | 100% | 86% |
| Align GVGD | 44% | 33% | 33% | 33% | 67% |
| MutPred | 67% | 33% | 83% | 50% | 71% |
| CONDEL | 67% | 100% | 50% | 50% | 100% |
Note. Accuracy (Aс) - the proportion of the correct test results (that is the sum of true positive and true negative results) among all the patients examined. In our case, this is the proportion of correct estimates of pathogenic and benign variants; Sensitivity (Se) - the ability of the diagnostic method to give the correct result which is defined as the proportion of true positive results among all performed tests. In our case, this is the proportion of true positive results, that is, the correct identification of pathogenic variants; Specificity (Sp) - the ability of the diagnostic method not to give false positive results in the absence of disease, which is defined as the proportion of true negative results among healthy individuals in studied group. In our case, this is a share of true negative results, that is, a correct identification of benign variants; Positive predictive values (PPV) - prediction of pathogenic variants; Negative predictive values (NPV) - prediction of benign variants.
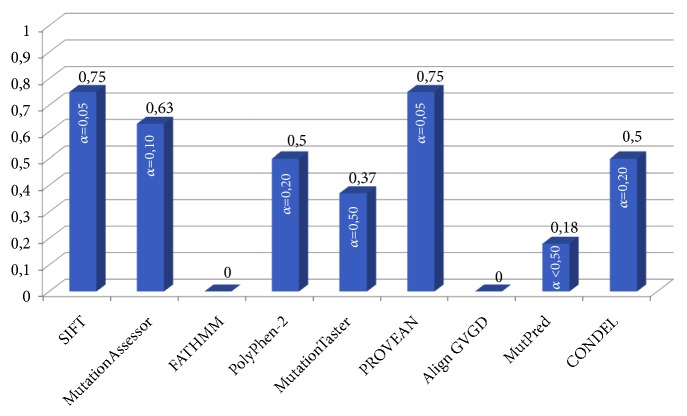
The overall correlation coefficients are presented in Figure 2. The SIFT and PROVEAN programs demonstrate the highest correlation of in silico predictions with observed clinical significance of missense substitutions (r = 0.75) which corresponds to their analytical parameters (Table 2). The average values of correlation were shown for MutationAssessor (r = 0.63), PolyPhen-2 (r = 0.5), and CONDEL (r = 0.5) which also correspond to their analytical parameters (Table 2). The MutationTaster demonstrated a weak correlation (r=0.37), MutPred showed very weak correlation (r = 0.18), and the FATHMM and Align GVGD programs showed no correlation between the observed values (r = 0).
Figure 2.
The correlation coefficient (r) histogram. Note. r: the relationship between the known clinical significance of missense variants and in silico evaluation given by 9 predictive tools; α: the level of significance of the correlation coefficient: the critical value for the significance level and the sample size n=9 is 0.933, so the correlation is significant at p<0.001 [23].
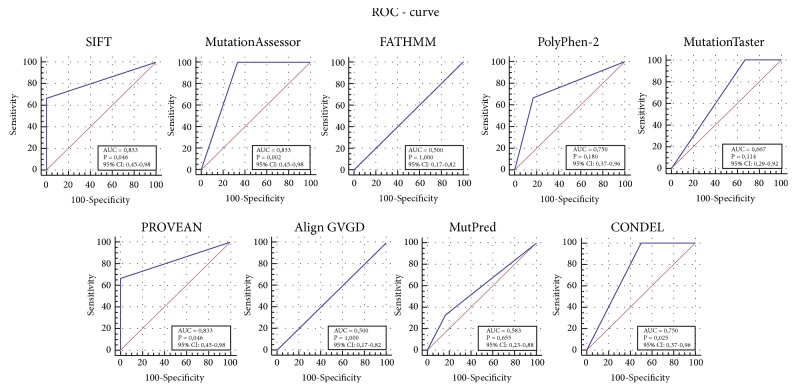
The result of ROC curve analysis is shown in Figure 3. The resulting ROC curves demonstrated that the largest coefficient of the area under the curve was shown by three programs: SIFT (AUC = 0.833, p = 0.046, 95% CI: 0.45-0.98), PROVEAN (AUC = 0.833, p = 0.046, 95% CI: 0.45-0.98), and MutationAssessor (AUC = 0.833, p = 0.002, 95% CI: 0.45-0.98). For PolyPhen-2 and CONDEL, the area of the curve was in the range of 0.7-0.8 (AUC = 0.750, p = 0.175, 95% CI: 0.37-0.96), and for MutationTaster it was in the range of 0.6-0.7 (AUC = 0.665, p = 0.114, 95% CI: 0.29-0.92). Two programs, FATHMM and Align GVGD, showed a complete lack of information in the predictions (AUC = 0.500, p = 1.000, 95% CI: 0.17-0.82).
Figure 3.
ROC curves expressing the relationship of the sensitivity and specificity of the tested programs. These graphs illustrate performance of studied in silico tools. The overall accuracy of the tests can be described as the area under the ROC curve (AUC); a higher AUC score indicates a better performance. The diagonal line shows the relationship between true-positive and false-positive values of absolutely uninformative in silico tools (FATHMM and Align GVGD). 95% CI indicates 95% confidence interval (Binomial Exact). The ROC curves were constructed using the MedCalc statistical software for biomedical researches (https://www.medcalc.org).
4. Discussion
For the first time, we analyzed the informative parameters of nine predictive in silico tools, obtained by predictions of the clinical significance of missense variants of GJB2 (Cx26), GJB6 (Cx30), and GJB3 (Cx31) connexin genes associated with hearing impairment. The capabilities of in silico prediction tools were demonstrated by testing nine missense variants with confirmed clinical significance of GJB2 (Cх26), GJB6 (Cx30), and GJB3 (Cx31) genes detected earlier in the study of congenital hearing impairment in the Sakha Republic of Russia [14, 15]. The results of this study may be applicable for analysis of novel missense variants of the GJB2 (Cx26), GJB6 (Cx30), and GJB3 (Cx31) genes.
We focused on nine programs chosen according to the following criteria: predicting the impact of missense variants on the function or structure of the protein, differing in computational methods and/or tools, popularity (the top programs included in the dbNSFP [44]), and free online access. Parameters such as accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity were chosen to assess their predictive abilities. Without these parameters, it is not possible to fully evaluate the accuracy of a test [42].
As a result, the SIFT and PROVEAN programs showed the highest sensitivity (Se = 67%) and specificity (Sp = 100%). Thus, the requirement for maximum total sensitivity and specificity in our study was 167% (Se + Sp), while the required balance between sensitivity and specificity was 33% (∆ Se - Sp). The accuracy (Ac) of the predictions of the SIFT and PROVEAN programs was 89%. This result can be considered as the best in this study; it can also be compared to accuracy of predictions published earlier in other studies: 80% - 90% [6, 7, 28, 36, 45]. A lower accuracy was shown by MutationAssessor (Ac = 78%), CONDEL (Ac = 67%), and MutationTaster (Ac = 56%) that were highly sensitive (Se = 100%), but not very specific (Sp = 33-67%). These results indicate a low accuracy of predictions for neutral variants. Align GVGD (Ac = 44%) and FATHMM (Ас = 33%) produced a large number of incorrect pathogenicity predictions and thus were unacceptable for testing variants of the studied genes.
In addition to the obtained characteristics of accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity, we also used correlation coefficients (r) and areas under the ROC curve (AUC) as alternative indicators of the quality of the tested programs. We compared the values of r and AUC with the quantitative values of the exact predictions of the in silico tools under study. For instance, the highest values of r = 0.75 were shown by the SIFT and PROVEAN programs that gave the highest number of correct predictions. As is known, the higher the predictive power of the model, the closer the ROC curve to the upper left corner, where the fraction of true-positive cases is 100% (ideal sensitivity) and the share of false-positive cases is zero [42]. The resulting ROC curves demonstrated that the curves of SIFT and PROVEAN were closest to the ideal chart, with the largest area under the curve: AUC = 0.83 (95% confidence interval is 0.45-0.98), which indicates a very good quality of predictions. The ROC curves of FATHMM and Align GVGD on the diagonal line indicated an absolute lack of informativeness (AUC = 0.500, which corresponds to random guessing); as a result, they had the most erroneous predictions. Our results confirmed that the best programs for bioinformatic analysis of missense variants of the GJB2 (Cx26), GJB6 (Cx30), and GJB3 (Cx31) connexin genes are SIFT and PROVEAN.
The resulting performance of the PROVEAN and SIFT tools turned out to be fully comparable, as previously described [40, 41]. Note that both programs have the same algorithm of assessing variants by whether they occur in evolutionary conserved region or not, which uses the most popular service, BLASTP (Basic Local Alignment Search Tool) [3, 24, 27, 40, 41]. Thus, we can assume that both tools have the same predictability. However, it should be noted that SIFT predicts the effects of all possible substitutions at each position in the protein sequence calculated from a Dirichlet mixture. On the other hand, PROVEAN provides a generalized approach to predict the functional effects of protein sequence variations computed based on BLOSUM62 [40]. The obtained data indicate that, with a wide choice of predictive programs, it is important to consider their methods and tools used for analysis. Also, it should be considered that any computer analysis of biological data is an in silico experiment, which has only a more or less reliable prediction that must be verified by other comprehensive structural/functional studies.
5. Conclusion
In summary, the analysis of all obtained informative parameters (accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity) of the nine in silico tools along with the correlation coefficient and the area under the ROC curve showed that SIFT and PROVEAN were the tools with the best pathogenicity prediction power; MutationAssessor, PolyPhen-2, and CONDEL performed at an average level; MutationTaster and MutPred were below average; and Align GVGD and FATHMM were uninformative. The results of this study may be applicable for analysis of novel missense variants of the GJB2 (Cx26), GJB6 (Cx30), and GJB3 (Cx31) genes.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation (Grant #6.1766.2017), the NEFU in Yakutsk (project: “Genetic features of the population of Sakha Republic: gene pool structure, cold adaptation, psychogenetic characteristics, prevalence of certain genetic and infectious diseases”), the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (Grants #17-29-06-016_ofi_m, #18-015-00212_А, #18-013-00738_А, #18-05-600035_Arctica, and #18-34-00439_mol_а), and the Program for Support of the Bioresource Collections of FASO of Russia “Genome of Sakha Republic”, YSC CMP (BRK 0556-2017-0003).
Data Availability
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1: description of the in silico tools; Table S2: sequence identifiers.
References
- 1.Hamosh A., Scott A. F., Amberger J. S., Bocchini C. A., McKusick V. A. Online mendelian inheritance in man (OMIM), a knowledgebase of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Research. 2005;33:D514–D517. doi: 10.1093/nar/gki033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stenson P. D., Mort M., Ball E. V., et al. The human gene mutation database: 2008 update. Genome Medicine. 2009;1(13) doi: 10.1186/gm13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ng P. C., Henikoff S. Predicting the effects of amino acid substitutions on protein function. Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics. 2006;7:61–80. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genom.7.080505.115630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Richards S., Aziz N., Bale S., et al. ACMG laboratory quality assurance committee. standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: a joint consensus recommendation of the american college of medical genetics and genomics and the association for molecular pathology. Genetics in Medicine. 2015;17(5):405–423. doi: 10.1038/gim.2015.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Thusberg J., Vihinen M. Pathogenic or not? and if so, then how? Studying the effects of missense mutations using bioinformatics methods. Human Mutation. 2009;30(5):703–714. doi: 10.1002/humu.20938. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Thusberg J., Olatubosun A., Vihinen M. Performance of mutation pathogenicity prediction methods on missense variants. Human Mutation. 2011;32(4):358–368. doi: 10.1002/humu.21445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Walters-Sen L. C., Hashimoto S., Thrush D. L., et al. Variability in pathogenicity prediction programs: impact on clinical diagnostics. Molecular Genetics & Genomic Medicine. 2015;3(2):99–110. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Thompson B. A., Greenblatt M. S., Vallee M. P., et al. Calibration of multiple in silico tools for predicting pathogenicity of mismatch repair gene missense substitutions. Human Mutation. 2013;34(1):255–265. doi: 10.1002/humu.22214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Galehdari H., Saki N., Mohammadi-asl J., Rahim F. Meta-analysis diagnostic accuracy of SNP-based pathogenicity detection tools: a case of UTG1A1 gene mutations. International Journal of Molecular Epidemiology and Genetics. 2013;4(2):77–85. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kerr I. D., Cox H. C., Moyes K., et al. Assessment of in silico protein sequence analysis in the clinical classification of variants in cancer risk genes. Journal of Community Genetics. 2017;8(2):87–95. doi: 10.1007/s12687-016-0289-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ernst C., Hahnen E., Engel C., et al. Performance of in silico prediction tools for the classification of rare BRCA1/2 missense variants in clinical diagnostics. BMC Medical Genomics. 2018;11(35) doi: 10.1186/s12920-018-0353-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Moles-Fernández A., Duran-Lozano L., Montalban G., et al. Computational tools for splicing defect prediction in breast/ovarian cancer genes: how efficient are they at predicting RNA alterations? Frontiers in Genetics. 2018;9(366) doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Yilmaz A. Bioinformatic analysis of GJB2 gene missense mutations. Cell Biochemistry and Biophysics. 2015;71(3):1623–1642. doi: 10.1007/s12013-014-0385-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Barashkov N. A., Pshennikova V. G., Posukh O. L., et al. Spectrum and frequency of the GJB2 gene pathogenic variants in a large cohort of patients with hearing impairment living in a subarctic region of Russia (the Sakha Republic) PLoS ONE. 2016;11(5) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0156300.e0156300 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pshennikova V. G., Barashkov N. A., Solovyev A. V., et al. Analysis of GJB6 (Сx30) and GJB3 (Сx31) genes in deaf patients with monoallelic mutations in GJB2 (Сx26) gene in the Sakha Republic (Yakutia) Russian Journal of Genetics. 2017;53(6):705–715. doi: 10.1134/S1022795417030103. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Teryutin F. M., Barashkov N. A., Kunelskaya N. L., et al. Variability of auditory threshold at deaf patients with splice site c.-23+1G>A mutation in GJB2 gene (Konneksin 26) Yakut Medical Journal. 2015;2(50):167–172. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Landrum M. J., Lee J. M., Riley G. R., et al. ClinVar: public archive of relationships among sequence variation and human phenotype. Nucleic Acids Research. 2014;42(1):980–985. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Landrum M. J., Lee J. M., Benson M., et al. ClinVar: public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016;44(D1):862–868. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Lek M., Karczewski K. J., Minikel E. V., et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature. 2016;536(7616):285–291. doi: 10.1038/nature19057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Auton A., Brooks L. D., Durbin R. M., et al. A global reference for human genetic variation. Nature. 2015;526:68–74. doi: 10.1038/nature15393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ng P. C., Henikoff S. Predicting deleterious amino acid substitutions. Genome Research. 2001;11(5):863–874. doi: 10.1101/gr.176601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Maeda S., Nakagawa S., Suga M., et al. Structure of the connexin 26 gap junction channel at 3.5 A resolution. Nature. 2009;458(7238):597–602. doi: 10.1038/nature07869. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Glantz S. A. Primer of Biostatistics. McGraw-Hill, Health Professions Division; 1997. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ng P. C., Henikoff S. Accounting for human polymorphisms predicted to affect protein function. Genome Research. 2002;12(3):436–446. doi: 10.1101/gr.212802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ng P. C., Henikoff S. SIFT: predicting amino acid changes that affect protein function. Nucleic Acids Research. 2003;31(13):3812–3814. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkg509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kumar P., Henikoff S., Ng P. C. Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nature Protocols. 2009;4(7):1073–1082. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2009.86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Shihab H. A., Gough J., Cooper D. N., et al. Predicting the functional, molecular, and phenotypic consequences of amino acid substitutions using hidden Markov models. Human Mutation. 2013;34(1):57–65. doi: 10.1002/humu.22225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Shihab H. A., Gough J., Cooper D. N., Day I. N. M., Gaunt T. R. Predicting the functional consequences of cancer-associated amino acid substitutions. Bioinformatics. 2013;29(12):1504–1510. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shihab H. A., Gough J., Mort M., Cooper D. N., Day I. N. M., Gaunt T. R. Ranking non-synonymous single nucleotide polymorphisms based on disease concepts. Human Genomics. 2014;8(1) doi: 10.1186/1479-7364-8-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Reva B., Antipin Y., Sander C. Determinants of protein function revealed by combinatorial entropy optimization. Genome Biology. 2007;8(11):p. 232. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-11-r232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Reva B., Antipin Y., Sander C. Predicting the functional impact of protein mutations: application to cancer genomics. Nucleic Acids Research. 2011;39(17):p. e118. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Adzhubei I. A., Schmidt S., Peshkin L., et al. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nature Methods. 2010;7(4):248–249. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0410-248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.González-Pérez A., López-Bigas N. Improving the assessment of the outcome of nonsynonymous SNVs with a consensus deleteriousness score, Condel. American Journal of Human Genetics. 2011;88(4):440–449. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2011.03.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Schwarz J. M., Cooper D. N., Schuelke M., Seelow D. Mutationtaster2: mutation prediction for the deep-sequencing age. Nature Methods. 2014;11(4):361–362. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.2890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Schwarz J. M., Rödelsperger C., Schuelke M., Seelow D. MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nature Methods. 2010;7(8):575–576. doi: 10.1038/nmeth0810-575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sherry S. T., Ward M., Sirotkin K. dbSNP-database for single nucleotide polymorphisms and other classes of minor genetic variation. Genome Research. 1999;9(8):677–679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Li B., Krishnan V. G., Mort M. E., et al. Automated inference of molecular mechanisms of disease from amino acid substitutions. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(21):2744–2750. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tavtigian S. V., Deffenbaugh A. M., Yin L., et al. Comprehensive statistical study of 452 BRCA1 missense substitutions with classification of eight recurrent substitutions as neutral. Journal of Medical Genetics. 2006;43(4):295–305. doi: 10.1136/jmg.2005.033878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Mathe E., Olivier M., Kato S., Ishioka C., Hainaut P., Tavtigian S. V. Computational approaches for predicting the biological effect of p53 missense mutations: a comparison of three sequence analysis based methods. Nucleic Acids Research. 2006;34(5):1317–1325. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkj518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Choi Y., Sims G. E., Murphy S., Miller J. R., Chan A. P. Predicting the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. PLOS ONE. 2012;7(10) doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0046688.46688 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Choi Y., Chan A. P. PROVEAN web server: a tool to predict the functional effect of amino acid substitutions and indels. Bioinformatics. 2015;31(16):2745–2747. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btv195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Fletcher R. H., Fletcher S. W. Clinical Epidemiology: The Essentials. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zou K. H. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) literature research. 2002, http://splweb.bwh.harvard.edu:8000/pages/ppl/zou/roc.html.
- 44.Liu X., Wu C., Li C., Boerwinkle E. dbNSFP v3.0: a one-stop database of functional predictions and annotations for human nonsynonymous and splice-site SNVs. Human Mutation. 2016;37(3):235–241. doi: 10.1002/humu.22932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Dong C., Wei P., Jian X., et al. Comparison and integration of deleteriousness prediction methods for nonsynonymous SNVs in whole exome sequencing studies. Human Molecular Genetics. 2015;24(8):2125–2137. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddu733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1: description of the in silico tools; Table S2: sequence identifiers.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.