Abstract
All-trans retinoic acid (atRA) is used to treat certain cancers and dermatologic diseases. A common adverse effect of atRA is hypercholesterolemia; cytochrome P450 (CYP) 7A repression is suggested as a driver. However, the underlying molecular mechanisms remain unclear. We investigated CYP7A1 expression in the presence of atRA in human hepatocytes and hepatic cell lines. In HepaRG cells, atRA increased cholesterol levels dose-dependently alongside dramatic decreases in CYP7A1 expression. Lentiviral-mediated CYP7A1 overexpression reversed atRA-induced cholesterol accumulation, suggesting that CYP7A1 repression mediated cholesterol accumulation. In CYP7A1 promoter reporter assays and gene-knockdown studies, altered binding of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 α (HNF4α) to the proximal promoter was essential for atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression. Pharmacologic inhibition of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and ERK pathways attenuated atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression and cholesterol accumulation. Overexpression of AP-1 (c-Jun/c-Fos), a downstream target of JNK and ERK, repressed CYP7A1 expression. In DNA pull-down and chromatin immunoprecipitation assays, AP-1 exhibited sequence-specific binding to the proximal CYP7A1 promoter region overlapping the HNF4α binding site, and atRA increased AP-1 but decreased HNF4α recruitment to the promoter. Collectively, these results indicate that atRA activates JNK and ERK pathways and the downstream target AP-1 represses HNF4α transactivation of the CYP7A1 promoter, potentially responsible for hypercholesterolemia.
Keywords: cytochrome P450, cholesterol metabolism, nuclear receptors, retinoids/vitamin A, toxicology
Retinoids (vitamin A and its derivatives) modulate physiological processes including proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis, via regulation of multiple genes (1, 2). These regulatory effects of retinoids are mediated mainly by retinoic acids (RAs), the bioactive metabolites of retinoids. All-trans RA (atRA) is the most biologically active RA and is used effectively for the treatment of cancers and dermatological disorders (3–6). Of note, one of the most prevalent side effects of retinoid drug therapy is hypercholesterolemia (affecting 31% of patients) that potentially promotes atherosclerosis (6–8).
Cholesterol homeostasis is regulated mainly by the rates of cholesterol synthesis and elimination in the liver. These processes are modulated by the levels of the enzymes catalyzing the rate-limiting steps: the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate by HMG-CoA reductase (HMGCR) for cholesterol synthesis (9) and cytochrome P450 7A1 (CYP7A1)-mediated conversion of cholesterol to bile acids for elimination (10). Previous studies reported that atRA represses CYP7A1 expression in HepG2 cells and human hepatocytes, as well as in mouse liver (11, 12), but the detailed molecular mechanism of how atRA leads to CYP7A1 repression is unclear. Furthermore, the effects of retinoids on HMGCR expression/activity in the liver remain unknown.
The expression of CYP7A1 is tightly controlled at transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels (13–18). Multiple microRNAs are known to decrease mRNA stability by targeting sequences in the 3′-untranslated region of CYP7A1 mRNA (19). The promoter of CYP7A1 contains conserved response elements for multiple transcription factors with different functionality (20). For example, pregnane X receptor (PXR) represses the CYP7A1 promoter (21, 22), whereas hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α (HNF4α) and liver receptor homolog-1 (LRH-1) activates the promoter (13, 23–25).
HNF4α is functionally modulated by multiple mechanisms, including intracellular signaling and protein-protein interactions. For example, activation of MAPKs, such as c-Jun N-terminal kinases (JNKs), ERKs, and p38, can inhibit HNF4α activity (23, 26, 27). The AP-1 protein family members serve as downstream effectors of ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Upon activation, these proteins form homodimers or heterodimers to regulate the expression of their target genes. Bile acids are known to activate c-Jun, a member of the AP-1 protein family, that interacts with HNF4α, leading to CYP7A1 repression (28). Additionally, transcriptional activity of HNF4α can be inhibited by its interaction with corepressors, such as small heterodimer partner (SHP) (29–31). Of note, atRA is known to induce SHP expression in human hepatocytes (11) and activate MAPK in multiple tissues, including breast cancer and intestinal cells (32, 33).
Retinoids can regulate gene transcription by binding to their cognate receptors, RA receptors (RARs) and retinoid X receptors (RXRs). The complex subsequently binds to the RAR response element (RARE), two direct repeats of hexameric sequences (AGGTCA-like) with 5 base pair spacers (i.e., DR5), and modulates the promoter activities of target genes (34, 35). Functional RARE was previously identified in the Cyp7a1 promoter of rodents (13), but it is unknown whether the respective sequences in the human CYP7A1 promoter are functional. RXR binding of retinoids can also lead to activation of its permissive binding partners, including PXR (36) and farnesoid X receptor (FXR). FXR transactivates the SHP promoter, and SHP, in turn, can repress HNF4α transactivation of the CYP7A1 promoter (24, 25, 37).
In this study, we report that atRA increases cholesterol levels, potentially by reducing CYP7A1 expression. We found that atRA activates the MAPK/AP-1 signaling pathway and inhibits the recruitment of HNF4α to the CYP7A1 promoter, leading to CYP7A1 repression. Results from transient transfection and promoter reporter assays also suggest that the involvement of multiple nuclear receptors (i.e., PXR, FXR, LRH-1, RAR, RXR, and SHP) in the atRA action on CYP7A1 expression is unlikely.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Cell culture
HepaRG cells were purchased from Biopredic International (Saint Grégoire, France) and cultured in Williams’ medium E supplemented with 10% FBS (Gemini, West Sacramento, CA), 5 µg/ml insulin, 2 mM l-glutamine, and 50 µM hydrocortisone hemisuccinate for 2 weeks. Confluent HepaRG cells were cultured in the same medium containing 2% DMSO (differentiation medium) for another 2 weeks. Medium was replaced every 2–3 days. Fully differentiated HepaRG cells were used as a liver model.
Primary human hepatocytes were obtained from the Liver Tissue Cell Distribution System (Pittsburgh, PA; funded by National Institutes of Health Contract HHSN276201200017C). Upon receipt, medium was replaced with Williams’ medium E supplemented with 0.1 µM dexamethasone, 2 mM l-glutamine, and 1% ITS solution (catalog no. I3146, Sigma). After stabilization for 24 h, cells were used for experiments.
HEK293T and HepG2 cells were obtained from ATCC (Manassas, VA) and cultured in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS and 2 mM l-glutamine. All cells were maintained at 37°C in a humidified incubator containing 5% CO2.
atRA treatment
A stock solution of atRA (catalog no. PHR1187, Sigma) was prepared at a concentration of 10 mM in DMSO. Cells were starved in FBS-free medium overnight before atRA treatment. The final DMSO concentrations in medium were 2.01% or 0.01% (2.01% for differentiated HepaRG cells, 0.01% for human hepatocytes and HepG2 cells). The media containing atRA were replaced every 24 h.
Total cholesterol quantification
Total cholesterol levels were determined using the cholesterol assay kit (Cell Biolabs, San Diego, CA), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells were washed with ice-cold PBS and homogenized in a mixture of chloroform, isopropanol, and NP-40 (7:11:0.1). After centrifugation at 15,000 g, organic phase was transferred to a new tube and dried until the solvents were removed. The dried pellets were dissolved in the assay diluent that contains cholesterol esterase and incubated with the cholesterol reaction reagent for 45 min at 37°C. Absorbance was measured at 540 nm.
Total RNA extraction and qPCR
Total RNA was extracted using Trizol reagent (Thermo Fisher) and was reverse-transcribed into cDNA using a High-Capacity cDNA reverse-transcription kit (Thermo Fisher). Quantitative PCR (qPCR) was performed using the StepOnePlusTM real-time PCR system with PrimeTime probes (Integrated DNA Technologies, Coralville, IA). The following probes were used: CYP7A1 (Hs.PT.58.21408221), HMGCR (Hs.PT.58.41105492), HNF4A (Hs.PT.58.22303533), SHP (Hs.PT.58.38586840), ABCA1 (Hs.PT.58.27452429), ABCG5 (Hs.PT.58.40909601), ABCG8 (Hs.PT.58.40210561), and GAPDH (Hs.PT.39a.22214836). The values were expressed as mRNA levels normalized to those of GAPDH (2-ΔΔct method).
Western blot analysis
Cells were lysed in RIPA buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 0.25% deoxycholic acid, 1% NP-40, and 1 mM EDTA) containing protease/phosphatase inhibitor cocktails (Roche, Mannheim, Germany). Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to a PVDF membrane. Membranes were incubated with 5% skim milk in TBS containing 0.1% Tween 20 (TBST) for 1 h and incubated with primary Abs against CYP7A1 (catalog no. ab79847, Abcam), HNF4α (catalog no. PP-H1415-00, R&D Systems), SHP (catalog no. sc-271511, Santa Cruz), p-P38 [catalog no. 4511, Cell Signaling Technology (CST)], P38 (catalog no. 8690, CST), p-JNK (catalog no. 4668, CST), JNK (catalog no. 9252, CST), p-ERK (catalog no. 4370, CST), ERK (catalog no. 4695, CST), p-MAPKAPK-2 (p-MK2; catalog no. 3007, CST), MAPKAPK-2 (MK2; catalog no. 3042, CST), p-c-Jun (catalog no. 2361, CST), c-Jun (catalog no. 9165, CST), c-Fos (catalog no. 2250, CST), and RARα (catalog no. sc-773, Santa Cruz) at 4°C overnight. Membranes were washed with TBST and incubated with secondary Ab for 1 h. Proteins were visualized with chemiluminescent substrate (Thermo Fisher).
Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay
Cells were fixed in medium containing 1% paraformaldehyde at room temperature for 10 min and incubated in 125 mM glycine solution for 5 min to quench cross-links. Cells were washed with PBS and lysed in hypotonic buffer solution (20 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 10 mM KCl, 0.5% NP-40, and protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktails; Roche) for 10 min. After centrifugation at 10,000 g at 4°C for 1 min, supernatants were discarded, and nuclear pellets were rinsed with PBS and sonicated in RIPA buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 0.25% deoxycholic acid, 1% NP-40, 1 mM EDTA, and protease and phosphatase inhibitor cocktails) to shear DNA to the length ranging from 200 to 1,000 bp. After centrifugation at 16,000 g at 4°C for 10 min, supernatants were incubated with Ab-conjugated Dynabeads (Thermo Fisher) overnight. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP)-grade Abs against HNF4α (catalog no. PP-H1415-00, R&D Systems), c-Jun (catalog no. 9165, CST), and c-Fos (catalog no. 2250, CST) were conjugated to Dynabeads. The beads were washed with low-salt buffer (20 mM Tris, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, and 1 mM EDTA), high-salt buffer (20 mM Tris pH 8.0, 500 mM NaCl, 1% Triton X-100, and 1 mM EDTA), and TE buffer (10 mM Tris, pH 8.0, and 1 mM EDTA). Immune complexes were eluted in elution buffer (1% SDS and 0.1 M NaHCO3), and cross-linking was reversed by adding NaCl and heating at 65°C, followed by protease K treatment. DNA fragments were recovered using a Qiaquick PCR kit (Qiagen) and quantified by qPCR. The following PrimeTime probes were used to detect CYP7A1 promoter region: 5′-ggtctctgattgctttggaac-3′ (forward), 5′-catagtatccagatccattaacttgag-3′ (reverse), and 5′-acctgtggacttagttcaaggcca-3′ (probe). The signal was normalized by that from the amplified fragment without immunoprecipitation and expressed as percent input.
Nuclear extraction
Cells were washed with PBS and lysed in cytoplasmic extract buffer (20 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 10 mM KCl, 0.5% NP-40, and protease/phosphatase inhibitor cocktails) for 10 min. The cytosolic fraction was isolated by centrifugation at 10,000 g at 4°C for 1 min. The pellets were rinsed with ice-cold PBS and lysed in nuclear extract buffer (20 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 1.5 mM MgCl2, 0.42 M NaCl, 0.2 mM EDTA, 25% glycerol, and protease/phosphatase inhibitor cocktails) at 4°C for 1 h. The nuclear fraction was isolated by centrifugation at 16,000 g at 4°C for 10 min. The supernatants were used in the DNA pull-down assay.
DNA pull-down assay
The 5′ biotin-labeled oligonucleotides and nonlabeled oligonucleotides (competitor) were synthesized by Integrated DNA Technologies. The oligonucleotide sequences were as follows: WT, 5′-cctgtggacttagttcaaggccagttactacc-3′; m1, cctgccacattagttcaaggccagttactacc-3′; and m2, 5′-cctgtggacttctcccaaggccagttactacc-3′. Duplex oligonucleotides (4 μg)-conjugated Dynabeads (M-280 Streptavidin, Thermo Fisher) were incubated with nuclear extracts (200 μg) at room temperature for 2 h. The beads were washed with PBS, and proteins were eluted by boiling in 1× sample buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 6.8, 10% glycerol, 5% 2-mercaptoethanol, 2% SDS, and 0.2% bromophenol blue). The proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE followed by Western blot analysis.
Plasmids
The insert DNA of the CYP7A1 promoter between −200 and +50 was synthesized by Genscript (Piscataway, NJ) and cloned into pGL3 vector to generate pGL3-CYP7A1 (−200/+50) plasmid. Deletion fragments of the CYP7A1 promoter were PCR-amplified using pGL3-CYP7A1 (−200/+50) as a template and cloned into pGL3 vector to generate pGL3-CYP7A1 (−100/+50 and −50/+50) plasmids. The mutations in pGL3-CYP7A1 constructs were made by Genscript. Expression vectors for c-Jun and c-Fos were purchased from Genscript. pcDNA3-HNF4A plasmid was received from Frances M. Sladek (University of California, Riverside, CA).
Luciferase reporter assay
HepG2 cells were transfected with promoter reporter constructs with or without expression vectors using FuGENE HD reagent (Promega) for 24 h and treated with atRA for 24 h. Luciferase activity was measured using GloMax luminometer (Promega) and normalized to the Renilla luciferase activity.
Lentiviral infection
Flag-tagged CYP7A1 clone was purchased from Genscript. Coding region of Flag-CYP7A1 was PCR-amplified and cloned into VVPW lentiviral expression vector (gift of G. L. Gusella, Mount Sinai Hospital, New York) to create VVPW-Flag-CYP7A1 plasmid. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with VVPW-Flag-CYP7A1, pCMV-VSVG, and psPAX2 plasmids (38, 39) in a ratio of 3:2:1 using FuGENE HD reagent according to the manufacturer’s instructions to produce virus harboring Flag-CYP7A1. Control virus was produced using empty VVPW vector together with pCMV-VSVG and psPAX2. After 12 h transfection, medium was replaced, and viruses were produced for 48 h. Medium containing virus particles was filtered through a 0.45 µm filter, concentrated by Lenti-X Concentrator (Clontech). The viral particles were titrated by a Lenti-X titration kit (Takara). HepaRG cells and human hepatocytes were transduced with equal amounts of lentiviral particles in the presence of polybrene (2 µg/ml).
Gene knockdown
Gene expression was silenced by siRNA transfection using Dharmafect 1 (Dharmacon, Lafayette, CO), according to the manufacturer’s instruction. The following siRNAs (Dharmacon) were used: control (catalog no. D-001206-14), HNF4A (catalog no. M-003406-02), and SHP (catalog no. M-003410-01).
Statistical analysis
All values were presented as means ± SD. For comparison of two groups, statistical differences were determined by Student’s t-test. For statistical testing of multiple groups, one-way ANOVA followed by posthoc Tukey’s test was performed.
RESULTS
atRA treatment increases cholesterol levels through CYP7A1 repression
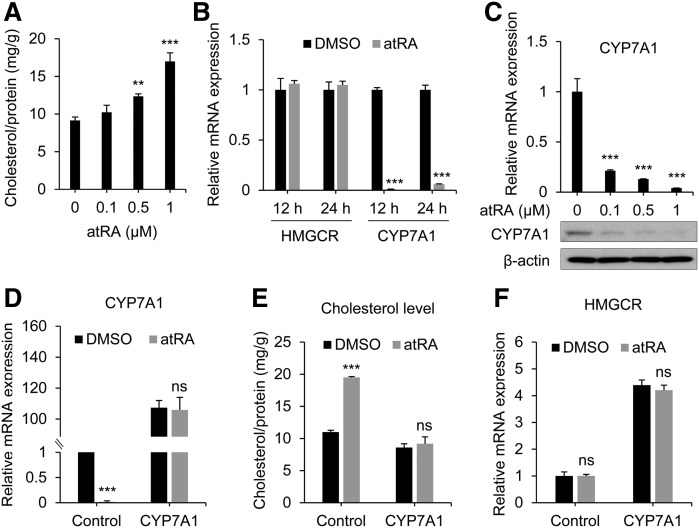
We first examined whether atRA affects total cholesterol level in human liver cells. Primary hepatocytes and differentiated HepaRG cells have been used to recapitulate the processes of the intact liver (40, 41) and thus were chosen as model systems. atRA increased total cholesterol levels in HepaRG cells in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 1A), consistent with clinical results (6–8). To understand the mechanism by which atRA treatment results in cholesterol accumulation, we analyzed mRNA expression levels of hepatic genes involved in cholesterol homeostasis. The mRNA level of HMGCR (the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol biosynthesis) was not altered by atRA. On the other hand, the mRNA level of CYP7A1 (the rate-limiting enzyme in cholesterol elimination) was dramatically decreased upon atRA treatment (Fig. 1B). atRA repressed CYP7A1 expression at both mRNA and protein levels in a concentration-dependent manner (Fig. 1C). To gauge the importance of CYP7A1 in atRA-induced cholesterol accumulation, we next examined whether increased cholesterol level upon atRA treatment can be reversed by CYP7A1 overexpression. HepaRG cells were infected with lentivirus carrying Flag-CYP7A1, followed by atRA treatment and cholesterol measurement. CYP7A1 expression was dramatically increased in the infected cells and not affected by atRA treatment (Fig. 1D). Consistently, the basal levels of intracellular cholesterol level were ∼20% lower in CYP7A1-overexpressing cells and not affected by atRA treatment (Fig. 1E). Of note, CYP7A1 overexpression led to compensatory increases in HMGCR expression (Fig. 1F), potentially accounting for the relatively small decreases in basal cholesterol levels (despite the dramatic increases in CYP7A1 expression in Flag-CYP7A1-infected cells). Similar findings were observed in primary human hepatocytes (supplemental Fig. S1). These results suggest that CYP7A1 repression contributes to cholesterol accumulation by atRA.
Fig. 1.
atRA induces cholesterol accumulation in HepaRG cells. A: HepaRG cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of atRA for 48 h, and total cholesterol levels were measured (n = 3, mean ± SD). ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 versus control. B: HepaRG cells were treated with atRA (1 µM) for 24 h, and mRNA levels were measured by qPCR (n = 3, mean ± SD). *** P < 0.001 versus control. C: HepaRG cells were treated with indicated concentrations of atRA for 48 h, and mRNA (upper) and protein (lower) levels were determined by qPCR and Western blot analysis, respectively. *** P < 0.001 versus control. D–F: HepaRG cells were infected with 1 × 107 particles of Flag-CYP7A1 lentivirus (or control) in 6-well plates and treated with atRA (1 µM) or DMSO for 72 h. D, F: mRNA levels were measured by qPCR (n = 3, mean ± SD). *** P < 0.001 versus DMSO-treated group. E: Cholesterol levels were measured (n = 3, mean ± SD). *** P < 0.001 versus DMSO-treated group. ns, not significant.
HNF4α is an essential contributor to CYP7A1 repression by atRA
CYP7A1 mRNA level is known to be regulated at both transcriptional (i.e., promoter activity) and posttranscriptional (i.e., mRNA stability) levels (19). We first examined whether atRA affects mRNA stability of CYP7A1 by monitoring mRNA decay. The decay rate of CYP7A1 mRNA was similar between atRA- and DMSO-treated HepaRG cells (supplemental Fig. S2), suggesting that posttranscriptional regulation is not involved in decreased CYP7A1 mRNA level by atRA.
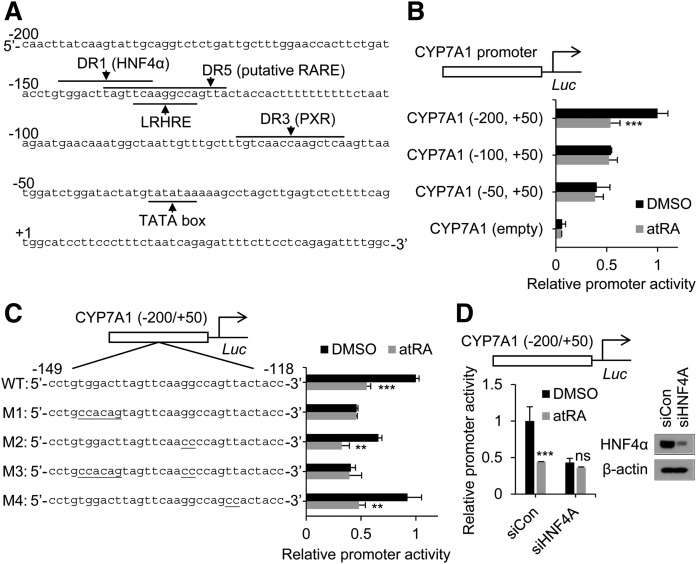
Multiple response elements for different transcription factors have been reported in the CYP7A1 promoter (Fig. 2A) (20). To map the promoter region responsible for CYP7A1 repression by atRA, we generated 5′-deletion constructs of the CYP7A1 promoter and performed promoter reporter assays. To this end, HepG2 cells were used as a transfection host because transfection efficiency in differentiated cells (e.g., primary hepatocytes or HepaRG) is low (42). CYP7A1 repression by atRA disappeared when the −200/−100 region of the CYP7A1 promoter was deleted (Fig. 2B), indicating that the region is critical for atRA response. The region harbors HNF4α/LRH-1 binding sites and putative RARE (DR5) (Fig. 2A). To identify response element(s) responsible for atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression, we generated mutant constructs for HNF4α/LRH-1 binding sites or DR5 and examined the effect of mutation on atRA response using a promoter reporter assay. Mutation in the LRH-1 binding site or DR5 (M2 and M4, respectively; Fig. 2C) had no effect on atRA response; however, the mutation in the HNF4α binding site (M1 and M3) abrogated atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression (Fig. 2C). To confirm the role of HNF4α in atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression, we knocked down HNF4A expression using siRNA and examined its effects on CYP7A1 promoter activity. HNF4α depletion led to decreased CYP7A1 promoter activity at basal levels (Fig. 2D), consistent with the critical role of HNF4α as an activator of the CYP7A1 promoter (13, 23, 24). Of note, it also abrogated atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression (Fig. 2D). Similar results were obtained upon HNF4A knockdown in human hepatocytes (supplemental Fig. S3). These results indicate that HNF4α (but not LRH-1, RAR, or PXR) is a critical component in the regulatory pathways for atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression in human liver cells.
Fig. 2.
The HNF4α response element is essential for atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression. A: Previously reported hormone response elements in the human CYP7A1 promoter. B, C: HepG2 cells were transfected with CYP7A1 promoter luciferase vectors (indicated constructs) and treated with atRA (1 µM), and promoter activity was measured (n = 3, mean ± SD). ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 versus DMSO-treated group. D: HepG2 cells were transfected with siRNA (20 nM) targeting HNF4A (siHNF4A) or control siRNA (siCon). After 24 h, the cells were transfected with CYP7A1 promoter luciferase vector, followed by treatment with atRA (1 µM) or DMSO for 24 h (n = 3, mean ± SD). Also shown is the Western blot image of the siRNA-transfected cells at 48 h posttransfection. *** P < 0.001 versus DMSO-treated group. ns, not significant.
To further rule out the involvement of genomic mechanisms in CYP7A1 repression by atRA, HepaRG cells were treated with RAR and RXR antagonists (ANG193109 and UVI3003, respectively), and CYP7A1 response to atRA was examined. CYP26A1 expression was examined as a marker of RAR/RXR action. AGN193109 and UVI3003 decreased atRA-mediated induction of CYP26A1 (supplemental Fig. S4) as expected; however, these agents had minimal effects on CYP7A1 repression by atRA, verifying insignificant roles of genomic mechanisms in atRA action on CYP7A1.
SHP induction does not play a role in CYP7A1 repression by atRA
To determine whether CYP7A1 repression by atRA is mediated via atRA effects on HNF4A expression, we measured HNF4A mRNA levels following atRA treatment in multiple liver cells (i.e., primary human hepatocytes and HepaRG and HepG2 cells). mRNA levels of CYP26A1, a marker gene for atRA action, were dramatically increased in all cells (supplementary Fig. S5). Interestingly, whereas CYP7A1 expression was significantly decreased in all cells, the effects of atRA on HNF4A mRNA levels were variable in these cells (i.e., no changes in HNF4A expression in HepG2 cells and two of four different batches of human hepatocytes) (supplemental Fig. S5). This result suggests that CYP7A1 repression by atRA can be mediated by altered HNF4α activity alone (i.e., without changes in its expression).
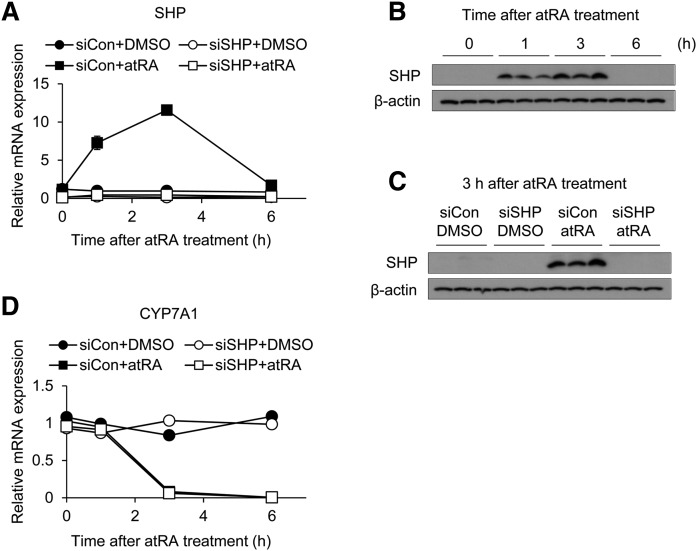
Transcriptional activity of HNF4α can be modulated by protein interactions with other transcription factors, such as corepressor SHP (29–31). Considering that atRA increases SHP expression in the liver (11), we examined whether SHP is required for atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression. To this end, we depleted SHP using siRNA transfection in HepaRG cells and human hepatocytes and examined whether it affects CYP7A1 repression by atRA. atRA increased SHP expression in HepaRG cells, in agreement with the previous study (11), and this was abrogated in cells transfected with SHP siRNA (Fig. 3A–C). Despite the lack of SHP induction, atRA repressed CYP7A1 expression (Fig. 3D). Similar results were obtained in a batch of human hepatocytes (supplemental Fig. S6). These results suggest that SHP is dispensable for atRA-mediated repression of CYP7A1.
Fig. 3.
SHP does not contribute to CYP7A1 repression by atRA. HepaRG cells were transfected with siRNA (50 nM) targeting SHP (siSHP) or control siRNA (siCon), followed by treatment with atRA (1 µM) or DMSO for the time periods indicated. mRNA and protein levels were determined by qPCR (n = 3, mean ± SD) (A, D) and Western blot analysis (B, C), respectively.
atRA represses CYP7A1 expression via JNK and ERK activation
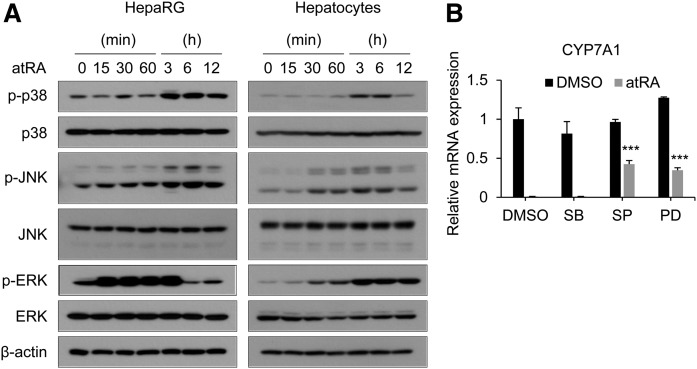
atRA activates MAPKs in multiple cell types, including breast cancer cells (33, 43). To determine whether atRA is capable of activating MAPK signaling pathways in liver cells, we treated HepaRG cells and primary human hepatocytes with atRA and detected phosphorylated JNK, ERK, or p38 proteins. Western blot analysis showed that atRA activates all three MAPK pathways in both HepaRG cells and primary human hepatocytes; however, the time profiles of activation for JNK and ERK differed (Fig. 4A). For example, ERK activation occurred rapidly (peaking at 15 min) in HepaRG, whereas it gradually increased over time in human hepatocytes (Fig. 4A). To identify MAPK pathways responsible for CYP7A1 repression by atRA, we treated HepaRG cells with a specific MAPK inhibitor (i.e., SB203580, SP600125, and PD98059 for p38, JNK, and ERK, respectively) and examined atRA-induced CYP7A1 repression. Treatment with inhibitors completely blocked phosphorylation of respective proteins as expected (supplemental Fig. S7). Although SB203580 had a minimal effect on CYP7A1 repression by atRA, individual treatment with SP600125 or PD98059 led to partial reversal of atRA action (Fig. 4B). These results indicate the involvement of JNK and ERK pathways in CYP7A1 regulation by atRA.
Fig. 4.
atRA activates MAPK pathways to regulate CYP7A1 expression. A: HepaRG cells and human hepatocytes were treated with atRA (1 µM) for the time periods indicated. Protein levels were determined by Western blot analysis. B: mRNA levels of CYP7A1 in the cells were measured by qPCR. (n = 3, mean ± SD). *** P < 0.001 versus DMSO-treated group. PD, PD98059; SB, SB203580; SP, SP600125.
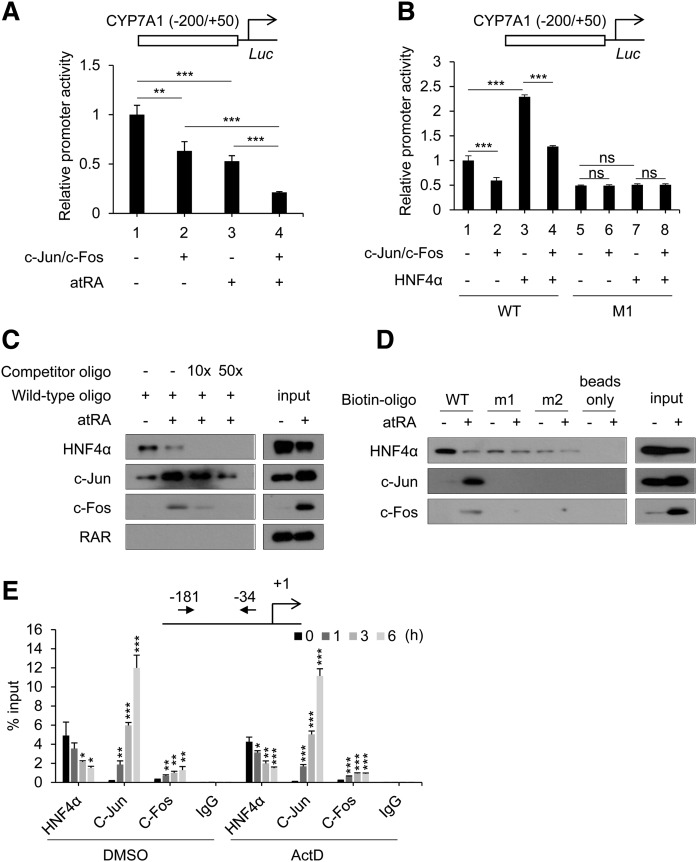
AP-1 (c-Jun/c-Fos) binds to the HNF4α binding site to repress CYP7A1 transcription
AP-1 proteins are downstream targets of JNK and ERK (44). To determine whether AP-1 proteins are involved in CYP7A1 repression by atRA, we overexpressed AP-1 components (i.e., c-Jun and c-Fos) and examined their effects on CYP7A1 promoter activity in HepG2 cells. AP-1 overexpression led to a significant decrease in CYP7A1 promoter activity (Fig. 5A, lane 1 vs. 2). atRA treatment in AP-1 overexpressed cells further repressed CYP7A1 promoter activity (Fig. 5A, lane 2 vs. 4), suggesting enhanced activities of overexpressed AP-1 proteins via phosphorylation.
Fig. 5.
AP-1 proteins are recruited to the HNF4α-binding site of the CYP7A1 promoter in a HNF4α-dependent manner. A: HepG2 cells were cotransfected with CYP7A1 promoter luciferase vector and expression vectors (c-Jun and c-Fos) and treated with atRA (1 µM) for 24 h, and promoter activity was measured (n = 3, mean ± SD). * P < 0.05; *** P < 0.001. B: HepG2 cells were cotransfected with CYP7A1 promoter luciferase vector and HNF4α expression vectors, and promoter activity was measured (n = 3, mean ± SD). *** P < 0.001; ns, not significant. M1, mutated HNF4 binding site. C, D: HepaRG cells were treated with atRA (1 µM) for 3 h. Western blot analysis was performed after DNA pull-down using the biotinylated oligonucleotides indicated and nuclear extracts. E: HepaRG cells were pretreated with Actinomycin D (ActD; 2 µg/ml) for 1 h and treated with atRA (1 µM) for the time periods indicated, and ChIP assay was performed (n = 3, mean ± SD). * P < 0.05; ** P < 0.01; *** P < 0.001 versus control (0 h).
To explore the possibility that AP-1 proteins directly regulate the CYP7A1 promoter (not involving HNF4α), promoter reporter assays were performed using luciferase vector harboring the CYP7A1 promoter with a mutation in its HNF4α response element (M1). The activity of the WT CYP7A1 promoter was repressed upon overexpression of AP-1 proteins (Fig. 5B, lane 1 vs. 2 or 3 vs. 4); however, it was abrogated when the HNF4α response element in the CYP7A1 promoter was mutated (Fig. 5B, lane 5 vs. 6 or 7 vs. 8), suggesting that AP-1 action on the CYP7A1 promoter is HNF4α binding site-dependent. The expression of c-Jun, one of the AP-1 components, was knocked down in HepaRG cells, and CYP7A1 response to atRA was examined. CYP7A1 repression by atRA was maintained in c-Jun-knocked-down cells (supplemental Fig. S8), suggesting potential involvement of non-AP-1 mechanisms in atRA action on CYP7A1 expression.
Next, we examined the recruitment of HNF4α and AP-1 proteins on the CYP7A1 promoter by DNA pull-down assays. To this end, oligonucleotides harboring HNF4α-binding element of CYP7A1 (−149/−118) were used. RAR recruitment was examined as a negative control based on the results from promoter reporter assays (Fig. 2C). RAR did not bind to the oligonucleotide, as expected (Fig. 5C). atRA decreased HNF4α and increased c-Jun/c-Fos bound to the DNA. The changes in HNF4α, c-Jun, and c-Fos binding to the oligonucleotide appear partly due to altered expression levels of the proteins in atRA-treated cells. For example, atRA led to a dramatic increase in c-Fos protein levels (Fig. 5C), consistent with a previous report that phosphorylation leads to transactivation of c-Fos promoter and stabilization of c-Fos protein (45–47). The binding of HNF4α, c-Jun, and c-Fos decreased dramatically after the addition of unlabeled WT oligonucleotides, indicating that the proteins bind specifically to the oligonucleotide.
To confirm whether AP-1 recruitment to the DNA is HNF4α-dependent, oligonucleotides harboring mutated HNF4α response element (i.e., m1 and m2) were generated, and DNA pull-down assays were performed. The binding of HNF4α to the m1 and m2 oligonucleotides dramatically decreased, whereas AP-1 proteins did not interact with m1 or m2 oligonucleotides, regardless of atRA treatment (Fig. 5D), suggesting that AP-1 binding to the CYP7A1 promoter is HNF4α-dependent. ChIP assay in HepaRG cells revealed that the binding of AP-1 to the region of the CYP7A1 promoter was increased during atRA treatment, whereas the binding of HNF4α was decreased (Fig. 5E), in agreement with the results from the DNA pull-down assay.
Considering that our results indicate the involvement of nongenomic mechanisms in the atRA action, the changes in the recruitments of AP-1 proteins and HNF4α were further examined upon blockade of transcription. HepaRG cells were pretreated with actinomycin D followed by atRA treatment and ChIP assays. Actinomycin D pretreatment did not affect the temporal changes in AP-1 and HNF4α recruitment to the CYP7A1 promoter (Fig. 5E). Together, these results indicate that AP-1, upon activation by atRA, decreases HNF4α transactivation of the CYP7A1 promoter by inhibiting HNF4α recruitment to the promoter.
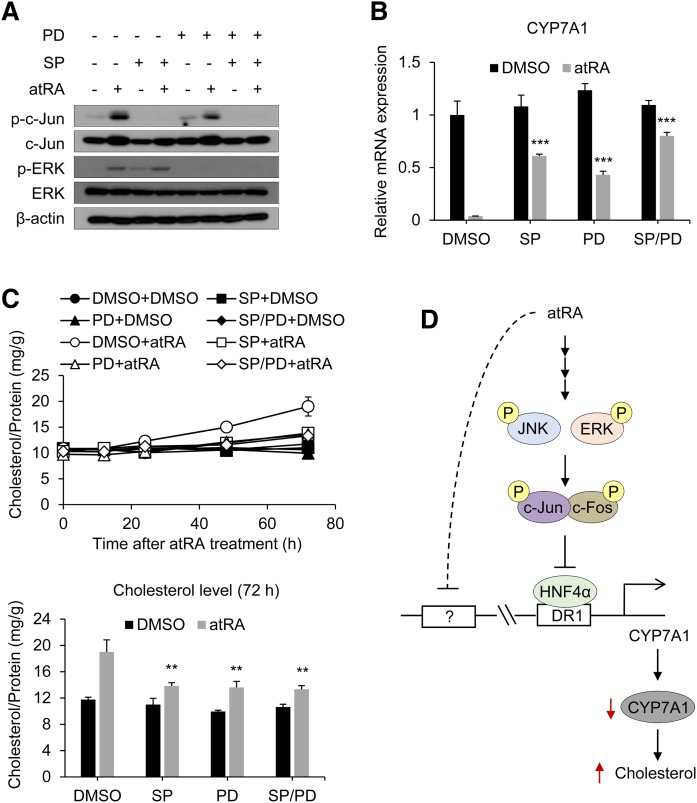
JNK/ERK signaling pathways play a crucial role in atRA-induced cholesterol accumulation
To further define the roles of JNK and ERK pathways in atRA-induced cholesterol accumulation, we examined the effects of JNK and ERK inhibitors (i.e., SP600125 and PD98059, respectively) on atRA-induced cholesterol accumulation in HepaRG cells. Inhibition of JNK and ERK pathways (Fig. 6A) led to significant decreases in atRA-induced CYP7A1 repression (Fig. 6B) and cholesterol accumulation (Fig. 6C). Although combined treatment with SP600125 and PD98059 failed to completely abrogate atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression or cholesterol accumulation, the results suggest that JNK/ERK, AP-1, and HNF4α signaling cascade is a major pathway for atRA repression of CYP7A1 transcription.
Fig. 6.
JNK/ERK inhibition reverses atRA-induced cholesterol accumulation. A, B: HepaRG cells were pretreated with SP600125 (SP; 50 µM) and/or PD98059 (PD; 50 µM) for 1 h and treated with atRA (1 µM) for 3 h. A: Protein levels were determined by Western blot analysis. B: mRNA levels were determined by qPCR (n = 3, mean ± SD). *** P < 0.001 versus atRA-treated group. C: HepaRG cells were pretreated with SP600125 (50 µM) and/or PD98059 (50 µM) for 1 h and treated with atRA (1 µM) for the time periods indicated. Total cholesterol levels were measured. Total cholesterol levels at the 72 h time point are presented (n = 3, mean ± SD). ** P < 0.01 versus atRA-treated group. D: A model depicting mechanisms for CYP7A1 repression by atRA is shown.
DISCUSSION
Retinoids, including atRA, are commonly used to treat certain cancers or dermatological diseases, but are often accompanied by hypercholesterolemia. The molecular mechanisms underlying atRA-induced hypercholesterolemia remain unclear. In this study, we conducted a thorough investigation of the mechanisms. To this end, liver cells of human origin were used, in consideration of previously reported interspecies differences in the regulation of CYP7A1 (22, 48). Our results indicate that atRA activates JNK/ERK signaling pathways, and subsequent inhibition of HNF4α transactivation of the CYP7A1 promoter potentially contributes to hypercholesterolemia by atRA.
The liver is a major organ for the maintenance of cholesterol homeostasis by controlling cholesterol synthesis and elimination. These processes are governed mainly by the actions of two rate-limiting enzymes, HMGCR and CYP7A1. In human hepatocytes and HepaRG cells, atRA had no effects on HMGCR expression, but dramatically decreased CYP7A1 expression at both mRNA and protein levels. Overexpression of CYP7A1 protected the cells from atRA-induced cholesterol accumulation. These results suggest that hypercholesterolemia by atRA is caused by downregulation of CYP7A1, consistent with the idea that CYP7A1 plays a critical role in maintaining cholesterol homeostasis, as previously shown in humans or mice with CYP7A1 deficiency (49, 50).
CYP7A1 expression is regulated at both transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels (51, 52). CYP7A1 mRNA half-life was not affected by atRA treatment, suggesting that atRA-induced CYP7A1 repression is likely mediated by its effects on the CYP7A1 promoter. Indeed, results from promoter reporter assays revealed that atRA decreases CYP7A1 promoter activity. The human CYP7A1 promoter harbors at least two AGGTCA-like repeating sequences, providing potential binding sites for nuclear receptors such as HNF4α, LRH-1, RAR, and PXR. Our results from the CYP7A1 promoter reporter assay using deletion or site-specific mutated constructs indicate that the HNF4α binding site is critical for atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression. Moreover, depletion of HNF4α abrogated atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression in HepG2 and human hepatocytes, supporting the idea that HNF4α is a critical component in CYP7A1 regulation by atRA in human liver tissue. These results also suggest that the involvement of other potential transcriptional regulators in CYP7A1 repression by atRA (e.g., RAR) is minor, if any.
Our results showed minimal effects of atRA on HNF4A expression in HepG2 cells and two (out of four) batches of human hepatocytes. Importantly, CYP7A1 repression by atRA was still observed in these cells, suggesting that atRA action on CYP7A1 expression occurs mainly through atRA modulating HNF4α activity (rather than HNF4A expression). Corepressors, including SHP, are known to interact with HNF4α and alter DNA binding affinity of HNF4α (53–55). atRA was previously shown to induce SHP expression in human hepatocytes (11), suggesting the potential roles of SHP in CYP7A1 repression by atRA. However, SHP knockdown (using siRNA) had a minimal effect on atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression, indicating minor roles of SHP in atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression. This appears in line with previous findings that SHP expression was not essential in CYP7A1 repression in cholestasis (56). Of note, SHP is a representative target gene of FXR, a permissive binding partner of RXR. Our findings also suggest that FXR/RXR (in addition to SHP) is a minor player in atRA-induced cholesterol accumulation. This notion is consistent with a previous report where FXR knockdown (using siRNA) had no effect on CYP7A1 repression by atRA in primary human hepatocytes (11).
The rapid changes in HNF4α activity and the lack of actinomycin D effects on the temporal changes in HNF4α recruitment to the CYP7A1 promoter (Fig. 5E) suggest that the activation is likely mediated by nongenomic actions of atRA. Our results in HepaRG cells indicate important roles of MAPK in altered HNF4α action by atRA. Although atRA activated three MAPK pathways (i.e., ERK, JNK, and p38), the study using pharmacological inhibitors revealed that JNK and ERK signaling pathways (but not p38) are critical in atRA-mediated CYP7A1 repression. Previous studies have shown that bile acids activate JNK, and its downstream target c-Jun inhibits coactivator binding to HNF4α via direct interaction with HNF4α (28, 57). Our results showed that, similarly to bile acids, atRA activates MAPK pathways. Subsequent activation of AP-1 proteins c-Jun and c-Fos led to increases in c-Jun and c-Fos binding to the HNF4α response element of CYP7A1 and decreased CYP7A1 promoter activity. Together, these results suggest that atRA activation of ERK/JNK and subsequent AP-1 proteins repress HNF4α transactivation of the CYP7A1 promoter (Fig. 6D).
To evaluate the role of JNK/ERK signaling in atRA-induced cholesterol accumulation, we examined the effects of pharmacological inhibition of JNK/ERK pathways on cholesterol level in atRA-treated HepaRG cells. Individual inhibition of JNK and ERK signaling rescued HepaRG cells from cholesterol accumulation during atRA treatment. Of note, the JNK and ERK inhibitors lacked additive or synergistic effects on cholesterol accumulation, and the combination treatment failed to fully reverse cholesterol accumulation in atRA-treated cells. Additionally, c-Jun knockdown failed to abrogate CYP7A1 repression by atRA, suggesting the presence of additional pathways (not involving MAPK/AP-1) in CYP7A1 repression by atRA (Fig. 6D). Although our study focused on the promoter region (−200/+50) of CYP7A1, other transcription factors, including estrogen-related receptor γ, are known to regulate CYP7A1 transcription by binding to (∼1.5 kilobase) upstream enhancer region (58). Whether these regulatory factors contribute to atRA-induced cholesterol accumulation in liver cells remains to be investigated.
How atRA triggers the activation of the MAPK pathway remains unclear. Stress signals such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) can activate MAPK signaling pathways, and retinoids were previously shown to cause mitochondrial swelling and decrease mitochondria membrane potential (59), a condition that induces ROS accumulation. Indeed, we found in HepaRG cells that atRA increased ROS level by 2-fold at 1 h after treatment (supplemental Fig. S9). However, inhibition of ROS accumulation by N-acetyl-cysteine did not affect atRA-mediated MAPK activation or CYP7A1 repression (supplemental Fig. S9), suggesting minimal roles of ROS in MAPK activation by atRA.
Conversion to bile acids followed by biliary excretion is a major elimination pathway of cholesterol from the body (60). The dramatic reduction in CYP7A1 expression upon atRA treatment suggests subsequent decreases in biliary elimination of cholesterol as bile acids, and this may trigger compensatory stimulation of other elimination pathways for cholesterol. ABCA1 is a membrane transporter expressed ubiquitously (including liver) and is involved in cholesterol removal from tissues to systemic circulation as HDL (61). ABCG5 and ABCG8, located at the canalicular membranes of hepatocytes, facilitate efflux of cholesterol into bile for excretion into the intestine (60). In HepaRG cells, atRA had minimal effects on ABCA1 expression (supplemental Fig. S10). On the other hand, it decreased ABCG5 and ABCG8 expression by ∼2-fold, potentially due to the repressive effects of atRA on HNF4α action on their promoters (62). Of note, the latter finding suggests the possibility that decreased biliary transport of cholesterol via ABCG5 and ABCG8 may underlie intracellular cholesterol accumulation upon atRA treatment. Interestingly, however, animal studies have shown decreased (rather than increased) hepatic cholesterol levels when Abcg5 and Abcg8 are deleted (60, 63). The roles of ABCG5/8 in atRA effects on hepatic cholesterol accumulation remain to be clarified.
In conclusion, we showed that atRA causes cholesterol accumulation in human liver cells in part by downregulation of CYP7A1 transcription. This is triggered by activation by ERK/JNK signaling and subsequent downstream effector AP-1 proteins, leading to decreased HNF4α transactivation of the CYP7A1 promoter. These results provide mechanistic insights into atRA-induced cholesterol disorder.
Supplementary Material
Footnotes
Abbreviations:
- atRA
- all-trans retinoic acid
- ChIP
- chromatin immunoprecipitation
- CST
- Cell Signaling Technology
- CYP7A1
- cytochrome P450 7A1
- FXR
- farnesoid X receptor
- HMGCR
- HMG-CoA reductase
- HNF4α
- hepatocyte nuclear factor 4α
- JNK
- c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- LRH-1
- liver receptor homolog-1
- PXR
- pregnane X receptor
- qPCR
- quantitative PCR
- RA
- retinoic acid
- RAR
- retinoic acid receptor
- RARE
- retinoic acid receptor response element
- ROS
- reactive oxygen species
- RXR
- retinoid X receptor
- SHP
- small heterodimer partner
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grants R01HD089455 and R01GM112746. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
The online version of this article (available at http://www.jlr.org) contains a supplement.
REFERENCES
- 1.Clagett-Dame M., and Knutson D.. 2011. Vitamin A in reproduction and development. Nutrients. 3: 385–428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Mark M., Ghyselinck N. B., and Chambon P.. 2009. Function of retinoic acid receptors during embryonic development. Nucl. Recept. Signal. 7: e002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Schlenk R. F., Dohner K., Kneba M., Gotze K., Hartmann F., Del Valle F., Kirchen H., Koller E., Fischer J. T., Bullinger L., et al. . 2009. Gene mutations and response to treatment with all-trans retinoic acid in elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Results from the AMLSG Trial AML HD98B. Haematologica. 94: 54–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Schlenk R. F., Frohling S., Hartmann F., Fischer J. T., Glasmacher A., del Valle F., Grimminger W., Gotze K., Waterhouse C., Schoch R., et al. . 2004. Phase III study of all-trans retinoic acid in previously untreated patients 61 years or older with acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 18: 1798–1803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Venditti A., Stasi R., Del Poeta G., Buccisano F., Aronica G., Bruno A., Pisani F., Caravita T., Masi M., Tribalto M., et al. . 1995. All-trans retinoic acid and low-dose cytosine arabinoside for the treatment of ‘poor prognosis’ acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 9: 1121–1125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zane L. T., Leyden W. A., Marqueling A. L., and Manos M. M.. 2006. A population-based analysis of laboratory abnormalities during isotretinoin therapy for acne vulgaris. Arch. Dermatol. 142: 1016–1022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bershad S., Rubinstein A., Paterniti J. R., Le N. A., Poliak S. C., Heller B., Ginsberg H. N., Fleischmajer R., and Brown W. V.. 1985. Changes in plasma lipids and lipoproteins during isotretinoin therapy for acne. N. Engl. J. Med. 313: 981–985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Brelsford M., and Beute T. C.. 2008. Preventing and managing the side effects of isotretinoin. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 27: 197–206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Goldstein J. L., and Brown M. S.. 1990. Regulation of the mevalonate pathway. Nature. 343: 425–430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vlahcevic Z. R., Pandak W. M., and Stravitz R. T.. 1999. Regulation of bile acid biosynthesis. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 28: 1–25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Cai S. Y., He H., Nguyen T., Mennone A., and Boyer J. L.. 2010. Retinoic acid represses CYP7A1 expression in human hepatocytes and HepG2 cells by FXR/RXR-dependent and independent mechanisms. J. Lipid Res. 51: 2265–2274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Schmidt D. R., Holmstrom S. R., Fon Tacer K., Bookout A. L., Kliewer S. A., and Mangelsdorf D. J.. 2010. Regulation of bile acid synthesis by fat-soluble vitamins A and D. J. Biol. Chem. 285: 14486–14494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Crestani M., Sadeghpour A., Stroup D., Galli G., and Chiang J. Y.. 1998. Transcriptional activation of the cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A) by nuclear hormone receptors. J. Lipid Res. 39: 2192–2200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Crestani M., Stroup D., and Chiang J. Y.. 1995. Hormonal regulation of the cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7). J. Lipid Res. 36: 2419–2432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hylemon P. B., Gurley E. C., Stravitz R. T., Litz J. S., Pandak W. M., Chiang J. Y., and Vlahcevic Z. R.. 1992. Hormonal regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA levels and transcriptional activity in primary rat hepatocyte cultures. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 16866–16871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pandak W. M., Li Y. C., Chiang J. Y., Studer E. J., Gurley E. C., Heuman D. M., Vlahcevic Z. R., and Hylemon P. B.. 1991. Regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA and transcriptional activity by taurocholate and cholesterol in the chronic biliary diverted rat. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 3416–3421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stravitz R. T., Hylemon P. B., Heuman D. M., Hagey L. R., Schteingart C. D., Ton-Nu H. T., Hofmann A. F., and Vlahcevic Z. R.. 1993. Transcriptional regulation of cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase mRNA by conjugated bile acids in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 13987–13993. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Wang D. P., Stroup D., Marrapodi M., Crestani M., Galli G., and Chiang J. Y.. 1996. Transcriptional regulation of the human cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A) in HepG2 cells. J. Lipid Res. 37: 1831–1841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Song K. H., Li T., Owsley E., and Chiang J. Y.. 2010. A putative role of micro RNA in regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase expression in human hepatocytes. J. Lipid Res. 51: 2223–2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Stroup D., Crestani M., and Chiang J. Y.. 1997. Identification of a bile acid response element in the cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene CYP7A. Am. J. Physiol. 273: G508–G517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Bhalla S., Ozalp C., Fang S., Xiang L., and Kemper J. K.. 2004. Ligand-activated pregnane X receptor interferes with HNF-4 signaling by targeting a common coactivator PGC-1alpha. Functional implications in hepatic cholesterol and glucose metabolism. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 45139–45147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Li T., and Chiang J. Y.. 2005. Mechanism of rifampicin and pregnane X receptor inhibition of human cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene transcription. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 288: G74–G84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.De Fabiani E., Mitro N., Anzulovich A. C., Pinelli A., Galli G., and Crestani M.. 2001. The negative effects of bile acids and tumor necrosis factor-alpha on the transcription of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene (CYP7A1) converge to hepatic nuclear factor-4: a novel mechanism of feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis mediated by nuclear receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 30708–30716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kir S., Zhang Y., Gerard R. D., Kliewer S. A., and Mangelsdorf D. J.. 2012. Nuclear receptors HNF4alpha and LRH-1 cooperate in regulating Cyp7a1 in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 287: 41334–41341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lu T. T., Makishima M., Repa J. J., Schoonjans K., Kerr T. A., Auwerx J., and Mangelsdorf D. J.. 2000. Molecular basis for feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis by nuclear receptors. Mol. Cell. 6: 507–515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Guo H., Gao C., Mi Z., Zhang J., and Kuo P. C.. 2007. Characterization of the PC4 binding domain and its interactions with HNF4alpha. J. Biochem. 141: 635–640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Vető B., Bojcsuk D., Bacquet C., Kiss J., Sipeki S., Martin L., Buday L., Bálint B. L., and Aranyi T.. 2017. The transcriptional activity of hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha is inhibited via phosphorylation by ERK1/2. PLoS One. 12: e0172020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Li T., Jahan A., and Chiang J. Y.. 2006. Bile acids and cytokines inhibit the human cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene via the JNK/c-jun pathway in human liver cells. Hepatology. 43: 1202–1210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lee Y. K., Dell H., Dowhan D. H., Hadzopoulou-Cladaras M., and Moore D. D.. 2000. The orphan nuclear receptor SHP inhibits hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 and retinoid X receptor transactivation: two mechanisms for repression. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20: 187–195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Shimamoto Y., Ishida J., Yamagata K., Saito T., Kato H., Matsuoka T., Hirota K., Daitoku H., Nangaku M., Yamagata K., et al. . 2004. Inhibitory effect of the small heterodimer partner on hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 mediates bile acid-induced repression of the human angiotensinogen gene. J. Biol. Chem. 279: 7770–7776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhou T., Zhang Y., Macchiarulo A., Yang Z., Cellanetti M., Coto E., Xu P., Pellicciari R., and Wang L.. 2010. Novel polymorphisms of nuclear receptor SHP associated with functional and structural changes. J. Biol. Chem. 285: 24871–24881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Namachivayam K., K. MohanKumar, D. Arbach, R. Jagadeeswaran, S. K. Jain, V. Natarajan, D. Mehta, R. P. Jankov, and A. Maheshwari. 2015. All-trans retinoic acid induces TGF-beta2 in intestinal epithelial cells via RhoA- and p38alpha MAPK-mediated activation of the transcription factor ATF2. PLoS One. 10: e0134003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang Q., and Wieder R.. 2004. All-trans retinoic acid potentiates Taxotere-induced cell death mediated by Jun N-terminal kinase in breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 23: 426–433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., and Dejean A.. 1990. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 343: 177–180. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.O’Reilly K., Bailey S. J., and Lane M. A.. 2008. Retinoid-mediated regulation of mood: possible cellular mechanisms. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood). 233: 251–258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Pérez E., Bourguet W., Gronemeyer H., and de Lera A. R.. 2012. Modulation of RXR function through ligand design. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1821: 57–69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Goodwin B., Jones S. A., Price R. R., Watson M. A., McKee D. D., Moore L. B., Galardi C., Wilson J. G., Lewis M. C., Roth M. E., et al. . 2000. A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol. Cell. 6: 517–526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kistler A. D., Singh G., Altintas M. M., Yu H., Fernandez I. C., Gu C., Wilson C., Srivastava S. K., Dietrich A., Walz K., et al. . 2013. Transient receptor potential channel 6 (TRPC6) protects podocytes during complement-mediated glomerular disease. J. Biol. Chem. 288: 36598–36609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ren G., Tardi N. J., Matsuda F., Koh K. H., Ruiz P., Wei C., Altintas M. M., Ploegh H., and Reiser J.. 2018. Podocytes exhibit a specialized protein quality control employing derlin-2 in kidney disease. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 314: F471–F482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Kanebratt K. P., and Andersson T. B.. 2008. Evaluation of HepaRG cells as an in vitro model for human drug metabolism studies. Drug Metab. Dispos. 36: 1444–1452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Gerets H. H., Tilmant K., Gerin B., Chanteux H., Depelchin B. O., Dhalluin S., and Atienzar F. A.. 2012. Characterization of primary human hepatocytes, HepG2 cells, and HepaRG cells at the mRNA level and CYP activity in response to inducers and their predictivity for the detection of human hepatotoxins. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 28: 69–87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Gardmo C., Kotokorpi P., Helander H., and Mode A.. 2005. Transfection of adult primary rat hepatocytes in culture. Biochem. Pharmacol. 69: 1805–1813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Yen A., Roberson M. S., Varvayanis S., and Lee A. T.. 1998. Retinoic acid induced mitogen-activated protein (MAP)/extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) kinase-dependent MAP kinase activation needed to elicit HL-60 cell differentiation and growth arrest. Cancer Res. 58: 3163–3172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Karin M. 1995. The regulation of AP-1 activity by mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 16483–16486. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chen R. H., Abate C., and Blenis J.. 1993. Phosphorylation of the c-Fos transrepression domain by mitogen-activated protein kinase and 90-kDa ribosomal S6 kinase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 90: 10952–10956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Murphy L. O., Smith S., Chen R. H., Fingar D. C., and Blenis J.. 2002. Molecular interpretation of ERK signal duration by immediate early gene products. Nat. Cell Biol. 4: 556–564. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Nakakuki T., Birtwistle M. R., Saeki Y., Yumoto N., Ide K., Nagashima T., Brusch L., Ogunnaike B. A., Okada-Hatakeyama M., and Kholodenko B. N.. 2010. Ligand-specific c-Fos expression emerges from the spatiotemporal control of ErbB network dynamics. Cell. 141: 884–896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Goodwin B., Watson M. A., Kim H., Miao J., Kemper J. K., and Kliewer S. A.. 2003. Differential regulation of rat and human CYP7A1 by the nuclear oxysterol receptor liver X receptor-alpha. Mol. Endocrinol. 17: 386–394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Erickson S. K., Lear S. R., Deane S., Dubrac S., Huling S. L., Nguyen L., Bollineni J. S., Shefer S., Hyogo H., Cohen D. E., et al. . 2003. Hypercholesterolemia and changes in lipid and bile acid metabolism in male and female cyp7A1-deficient mice. J. Lipid Res. 44: 1001–1009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pullinger C. R., Eng C., Salen G., Shefer S., Batta A. K., Erickson S. K., Verhagen A., Rivera C. R., Mulvihill S. J., Malloy M. J., et al. . 2002. Human cholesterol 7α-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) deficiency has a hypercholesterolemic phenotype. J. Clin. Invest. 110: 109–117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Li T., Francl J. M., Boehme S., and Chiang J. Y.. 2013. Regulation of cholesterol and bile acid homeostasis by the cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase/steroid response element-binding protein 2/microRNA-33a axis in mice. Hepatology. 58: 1111–1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tarling E. J., Clifford B. L., Cheng J., Morand P., Cheng A., Lester E., Sallam T., Turner M., and de Aguiar Vallim T. Q.. 2017. RNA-binding protein ZFP36L1 maintains posttranscriptional regulation of bile acid metabolism. J. Clin. Invest. 127: 3741–3754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ruse M. D. Jr., Privalsky M. L., and Sladek F. M.. 2002. Competitive cofactor recruitment by orphan receptor hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha1: modulation by the F domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22: 1626–1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Sladek F. M., Ruse M. D. Jr., Nepomuceno L., Huang S. M., and Stallcup M. R.. 1999. Modulation of transcriptional activation and coactivator interaction by a splicing variation in the F domain of nuclear receptor hepatocyte nuclear factor 4alpha1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19: 6509–6522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Zhang Y., Hagedorn C. H., and Wang L.. 2011. Role of nuclear receptor SHP in metabolism and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1812: 893–908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Kerr T. A., Saeki S., Schneider M., Schaefer K., Berdy S., Redder T., Shan B., Russell D. W., and Schwarz M.. 2002. Loss of nuclear receptor SHP impairs but does not eliminate negative feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis. Dev. Cell. 2: 713–720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gupta S., Stravitz R. T., Dent P., and Hylemon P. B.. 2001. Down-regulation of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase (CYP7A1) gene expression by bile acids in primary rat hepatocytes is mediated by the c-Jun N-terminal kinase pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 15816–15822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Zhang Y., Kim D. K., Lee J. M., Park S. B., Jeong W. I., Kim S. H., Lee I. K., Lee C. H., Chiang J. Y., and Choi H. S.. 2015. Orphan nuclear receptor oestrogen-related receptor gamma (ERRgamma) plays a key role in hepatic cannabinoid receptor type 1-mediated induction of CYP7A1 gene expression. Biochem. J. 470: 181–193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Rigobello M. P., Scutari G., Friso A., Barzon E., Artusi S., and Bindoli A.. 1999. Mitochondrial permeability transition and release of cytochrome c induced by retinoic acids. Biochem. Pharmacol. 58: 665–670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Yu L., Hammer R. E., Li-Hawkins J., Von Bergmann K., Lutjohann D., Cohen J. C., and Hobbs H. H.. 2002. Disruption of Abcg5 and Abcg8 in mice reveals their crucial role in biliary cholesterol secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 99: 16237–16242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Basso F., Freeman L., Knapper C. L., Remaley A., Stonik J., Neufeld E. B., Tansey T., Amar M. J., Fruchart-Najib J., Duverger N., et al. . 2003. Role of the hepatic ABCA1 transporter in modulating intrahepatic cholesterol and plasma HDL cholesterol concentrations. J. Lipid Res. 44: 296–302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sumi K., Tanaka T., Uchida A., Magoori K., Urashima Y., Ohashi R., Ohguchi H., Okamura M., Kudo H., Daigo K., et al. . 2007. Cooperative interaction between hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha and GATA transcription factors regulates ATP-binding cassette sterol transporters ABCG5 and ABCG8. Mol. Cell. Biol. 27: 4248–4260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Wang J., Mitsche M. A., Lutjohann D., Cohen J. C., Xie X. S., and Hobbs H. H.. 2015. Relative roles of ABCG5/ABCG8 in liver and intestine. J. Lipid Res. 56: 319–330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.