Watch a video presentation of this article
Watch the interview with the author
Abbreviations.
ADH, antidiuretic hormone; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; HRS, hepatorenal syndrome; NE, norepinephrine; PRA, plasma renin activity; RAAS, renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system; SBP, spontaneous bacterial peritonitis; SNS, sympathetic nervous system.
Temporal Relationship Between Circulatory and Renal Dysfunction and Ascites Formation
Sodium retention, an impairment of free water excretion, and a reduction in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) are the most relevant renal abnormalities in cirrhosis. Their main consequences are ascites, dilutional hyponatremia, and hepatorenal syndrome (HRS).1 These complications appear sequentially in parallel with a progressive deterioration of circulatory function2 (Fig. 1).
Figure 1.
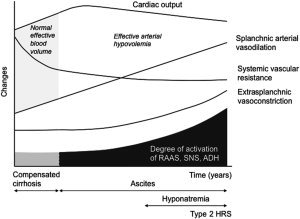
Mechanisms of circulatory and renal dysfunction in cirrhosis. The main mechanism is progressive splanchnic arterial vasodilation due to the overproduction of vasodilator molecules. During the initial phases of decompensated cirrhosis when the activation of vasoconstrictor systems is moderate, patients develop sodium retention and ascites. In subsequent stages, the activation of ADH leads to dilutional hyponatremia. Finally, in the most advanced phases when circulatory dysfunction is extreme, the renal vasodilatory systems are overcome, and patients develop severe renal vasoconstriction and type 2 HRS. These patients also present with cardiac dysfunction.
Phase 1: Hyperdynamic Circulation Keeps Patients Free of Ascites Despite the Progression of Splanchnic Arterial Vasodilation
Splanchnic arterial vasodilation is an important feature associated with portal hypertension. It increases portal venous inflow and maintains the progression of portal hypertension despite the collateral circulation, and it impairs systemic circulatory function. In compensated cirrhosis, splanchnic arterial vasodilation is not followed by an impairment of the effective arterial blood volume because patients develop parallel increases in plasma volume and cardiac output (hyperdynamic circulation). During this phase, the arterial pressure, renal function, plasma renin activity (PRA), plasma norepinephrine (NE) level, and antidiuretic hormone (ADH) concentration are normal.
Phase 2: The Onset of Sodium Retention and Ascites Develop in the Absence of Activation of the Renin‐Angiotensin‐Aldosterone System (RAAS) and the Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
With the progression of cirrhosis, patients become unable to excrete their regular sodium intake. Sodium is then retained with water and accumulates as ascites. During this phase, in comparison with phase 1, patients display higher portal pressures, probably higher peripheral vascular resistance, increased cardiac output, and moderately reduced sodium excretion. In contrast, renal perfusion, GFR, free water excretion, PRA, NE, and ADH are normal.3, 4 Sodium retention is, therefore, unrelated to activation of the renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system (RAAS) and the SNS, the two most important antinatriuretic systems so far identified. Plasma levels of endogenous natriuretic hormones are increased.5 The mechanism of sodium retention during this phase is unknown.
Phase 3: Activation of the Endogenous Vasoconstrictor Systems Is Initially Associated With Intense Sodium Retention but Preserved Renal Perfusion, GFR, and Renal Ability to Excrete Free Water
When sodium retention is intense, PRA and NE are increased.2, 3 The plasma volume and the peripheral vascular resistance, however, do not differ from the previous phase despite marked activation of the renin‐angiotensin system and the SNS.3 This feature is compatible with a progression in splanchnic arterial vasodilation compensated by vasoconstriction in extrasplanchnic organs (Table 1). Renal, cerebral, and muscular blood flow is reduced in these patients.6 Cardiac output in phase 3, although higher than normal, is lower than that in phase 2,3 and this indicates that circulatory dysfunction is also related to a decrease in cardiac function. Arterial pressure during this phase is critically dependent on the increased activity of the renin‐angiotensin system and the SNS, and the administration of drugs that interfere with these systems may precipitate arterial hypotension.3 Renal perfusion and GFR are normal or are only moderately reduced because the vasoconstrictor effect of angiotensin and catecholamines is antagonized by intrarenal vasodilator prostaglandins.7 Renal perfusion is, therefore, dependent on prostaglandin synthesis, and severe renal failure may develop with nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs. Prostaglandins also inhibit the effects of ADH and prevent the development of significant hyponatremia.8
Table 1.
Systemic Hemodynamic and Neurohormonal Parameters in Patients With Nonazotemic Cirrhosis and Ascites Who Did or Did Not Develop Type 2 HRS During Follow‐Up3
| Parameter | Baseline Data for Patients Not Developing Type 2 HRS (n = 39) | Data for Patients Developing Type 2 HRS (n = 15) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Type 2 HRS | ||
| Mean arterial pressure (mm Hg) | 88 ± 9 | 86 ± 10 | 79 ± 7 |
| PRA (ng/mL·hour−1) | 3.1 ± 2.3 | 7.5 ± 3.7 | 11.9 ± 4.8 |
| NE (pg/mL) | 222 ± 68 | 442 ± 155 | 629 ± 320 |
| Systemic vascular resistance (dyn·s/cm−5) | 962 ± 256 | 1032 ± 251 | 1014 ± 276 |
| Cardiac output (L/minute) | 7.2 ± 1.8 | 6.2 ± 1.4 | 5.8 ± 1.2 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 87 ± 15 | 84 ± 12 | 80 ± 14 |
These results are indicative of a progressive deterioration of cardiocirculatory function. The absence of significant changes in systemic vascular resistance between the groups is compatible with peripheral arterial vasodilatation compensated by the vasoconstrictor effect of the RAAS and the SNS. The lack of an increase in the heart rate indicates an impairment in cardiac chronotropic function. HRS developed in patients with severe impairment of systemic hemodynamics. The data are presented as means and standard deviations.
Phase 4: Dilutional Hyponatremia Develops When the Renal Ability to Excrete Free Water Is Severely Reduced
In comparison with phase 3, PRA and NE are higher and renal perfusion and GFR are lower in patients with dilutional hyponatremia (<130 mEq/L). The renal ability to excrete free water, which is approximately 10 mL/minute in healthy subjects and 4 to 5 mL/minute in patients with cirrhosis in phase 3, is <1 mL/minute in patients with hyponatremia. This reduction in free water clearance is related to high plasma levels of ADH.7 Dilutional hyponatremia produces a depletion of brain osmolytes and predisposes patients to brain edema and hepatic encephalopathy.
Phase 5: Type 2 HRS Represents the Extreme Expression of Circulatory Dysfunction
Type 2 HRS (defined as a serum creatinine level > 1.5 mg/dL or a GFR < 40 mL/minute) is secondary to intense renal vasoconstriction.2, 3 It develops in the setting of both severe deterioration of circulatory function and extreme overactivity of endogenous vasoconstrictor systems that together overcome the effect of intrarenal vasodilatory mechanisms (Table 1). The cardiac output in patients with type 2 HRS is lower than that in patients without HRS.3, 9 A significant number of these patients may even present with normal or reduced cardiac output, which indicates the disappearance of hyperdynamic circulation. Sodium retention in patients with type 2 HRS is due to reduced filtered sodium and markedly increased sodium reabsorption in the proximal tubule. The delivery of sodium to the distal nephron, the site of action of diuretics, is very low.
The Time Course of Circulatory and Renal Dysfunction Is Not Uniform
The time course from compensated cirrhosis to type 2 HRS is not uniform. Although it may take a decade or even longer if the progression of liver failure and/or fibrosis is delayed (i.e., alcohol withdrawal in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis or viral suppression), it can progress faster if there is rapid deterioration of these factors. The time course of circulatory and renal dysfunction may also be accelerated by complications associated with the underlying disease. Patients at any phase of the disease may progress to HRS (either type 1 or 2) within a few days or weeks of acute bacterial infections, toxic, viral, or acute alcoholic hepatitis superimposed on cirrhosis, large‐volume paracentesis without albumin, or major surgery. Studies in patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) have shown that this rapid progression occurs in the setting of an exaggerated inflammatory response leading to intense acute arterial vasodilation and a reduction in cardiac output10 (Table 2).
Table 2.
Functional Parameters in Patients Who Did or Did Not Develop Type 1 HRS After SBP10
| Parameter | Type 1 HRS (n = 8) | No Type 1 HRS (n = 15) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBP Diagnosis | SBP Resolution | SBP Diagnosis | SBP Resolution | |
| Mean arterial pressure (mm Hg) | 83 ± 7 | 73 ± 8* | 83 ± 10 | 83 ± 8 |
| PRA (ng/mL·hour−1) | 18.4 ± 11.2† | 28.3 ± 12.4* | 3.9 ± 3.6 | 2.8 ± 3.6 |
| NE (pmol/L) | 4711 ± 1336† | 7625 ± 2453* | 1862 ± 1017 | 1874 ± 1153 |
| Systemic vascular resistance (dyn·s/cm−5) | 1137 ± 220† | 1268 ± 320 | 893 ± 196 | 968 ± 226 |
| Cardiac output (L/minute) | 5.7 ± 0.9† | 4.6 ± 0.7* | 7.4 ± 1.9 | 6.8 ± 2.0 |
| Heart rate (bpm) | 93 ± 13 | 87 ± 9 | 87 ± 16 | 79 ± 16 |
Two hemodynamic studies were performed: one at the diagnosis of SBP and the other after the resolution of the infection. The time that elapsed between the studies was <7 days. The data are presented as means and standard deviations.
Significantly different in comparison with the values at the diagnosis of SBP.
Significantly different in comparison with the values at the diagnosis of SBP in the group without type 1 HRS.
Key Factors Associated With Circulatory Dysfunction, Renal Dysfunction, and Ascites Formation
Splanchnic Arterial Vasodilation and Renal Dysfunction
Splanchnic arterial vasodilation in cirrhosis is related to an increase in the local release of vasodilatory substances, including nitric oxide and endogenous cannabinoids. The translocation of bacteria or bacterial products from the intestinal lumen to the intestinal extracellular space and the activation of the intestinal nonadrenergic, noncholinergic nervous systems are probably important mechanisms in this process. In cirrhosis, there is also increased angiogenesis in the splanchnic area secondary to local activation of proangiogenic factors. These two mechanisms lead the splanchnic circulation to be resistant to the vasoconstrictor effect of angiotensin II, catecholamines, and vasopressin. As a result, extrasplanchnic organs become the main sites regulating arterial pressure in cirrhosis. In patients with cirrhosis and renal failure with or without bacterial infections, there is marked systemic inflammation that impairs the microcirculatory function in the kidneys and other organs. Both features account for the predisposition of patients with cirrhosis to develop extrahepatic organ failure, including HRS.
Reduction in Cardiac Output
Although diastolic dysfunction (impaired ventricular relaxation) is a frequent event in cirrhosis, it is usually low‐grade and does not participate in the reduction in cardiac output. In contrast, the cardiac chronotropic and inotropic response to SNS activity is severely impaired. The most plausible mechanism of circulatory dysfunction in cirrhosis is, therefore, an insufficient cardiac chronotropic and inotropic response to the sympathetic nervous overactivity associated with the progression of splanchnic vasodilation.
Potential conflict of interest: Nothing to report.
References
- 1. Arroyo V, Gines P, Gerbes AL, Dudley FJ, Gentilini P, Laffy G, et al. Definition and diagnostic criteria of refractory ascites and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. International Ascites Club. Hepatology 1996; 23: 164‐176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Schrier RW, Arroyo V, Bernardi M, Epstein M, Henriksen JH, Rodés J. Peripheral arterial vasodilation hypothesis: a proposal for the initiation of renal sodium and water retention in cirrhosis. Hepatology 1988; 8: 1151‐1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Ruiz‐del‐Arbol L, Monescillo A, Arocena C, Valer P, Gines P, Moreira V, et al. Circulatory function and hepatorenal syndrome in cirrhosis. Hepatology 2005; 42: 439‐447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Salo J, Guevara M, Fernandez‐Esparrach G, Bataller R, Gines A, Jimenez W, et al. Impairment of renal function during moderate physical exercise in patients with ascites: relationship with the activity of neurohormonal systems. Hepatology 1997; 25: 1338‐1342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Gines P, Jimenez W, Arroyo V, Navasa M, Lopez C, Tito L, et al. Atrial natriuretic factor in cirrhosis with ascites: plasma levels, cardiac release and splanchnic extraction. Hepatology 1988; 8: 636‐642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Guevara M, Bru C, Gines P, Fernandez‐Esparrach G, Sort P, Bataller R, et al. Increased cerebrovascular resistance in cirrhotic patients with ascites. Hepatology 1988; 28: 39‐44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Arroyo V, Gines P, Rimola A, Gaya J. Renal function abnormalities, prostagandins and effects of nonsteroidal anti‐inflammatory drugs in cirrhosis with ascites. An overview with emphasis on pathogenesis. Am J Med 1986; 25: 104‐122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Perez‐Ayuso RM, Arroyo V, Camps J, Rimola A, Gaya J, Rivera F, et al. Evidence that renal prostaglandins are involved in renal water metabolism in cirrhosis. Kidney Int 1984; 26: 72‐80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Krag A, Bendtsen F, Henriksen JH, Moller S. Low cardiac output predicts development of hepatorenal syndrome and survival in patients with cirrhosis and ascites. Gut 2010; 59: 105‐110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Ruiz‐del‐Arbol L, Urman J, Fernandez J, Gonzalez M, Navasa M, Monescillo A, et al. Systemic, renal, and hepatic hemodynamic derangement in cirrhotic patients with spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Hepatology 2003; 38: 1210‐1218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


