Abstract
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is most likely caused by killing of β cells by autoreactive CD8+ T cells. Methods to isolate and identify these cells are limited by their low frequency in the peripheral blood. We analyzed CD8+ T cells, reactive with diabetes antigens, with T cell libraries and further characterized their phenotype by CyTOF using class I MHC tetramers. In the libraries, the frequency of islet antigen specific CD45RO+IFNγ+CD8+ T cells was higher in patients with T1D compared to healthy control (HC) subjects. Antigen specific cells from the libraries of patients with T1D were reactive with ZnT8186–194 whereas those from HC recognized ZnT8186–194 and other antigens. ZnT8186–194-reactive CD8+ cells expressed an activation phenotype in T1D patients. We found T cell receptor sequences that were used in multiple library wells from patients with T1D but these sequences were private and not shared between individuals. These sequences could identify the antigen specific T cells on a repeated draw, ex vivo in the IFNγ+ CD8+ T cell subset. We conclude that CD8+ T cell libraries can identify antigen specific T cells in patients with T1D. The T cell clonotypes can be tracked in vivo with identification of the TCR gene sequences.
Keywords: Type 1 diabetes, autoimmunity, T cell libraries, CD8, ZnT8, CyTOF
Introduction
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is believed to be caused by destruction of insulin producing-pancreatic cells by antigen specific T cells. Human data, including histologic studies of islets from patients with T1D have identified CD8+ T cells as the mediators of islet destruction although CD4+ antigen reactive T cell lines from patients can cause insulitis and facilitate the action of CD8+ cells (1–3). A number of potential targets of autoreactive CD8+ T cells have been identified including peptides from insulin, preproinsulin, and proinsulin, as well as IGRP, ZnT8, and GAD65(4–7).
Islet antigen specific CD8+ T cells can be found in healthy control subjects as well as patients with T1D, by FACS, even at similar frequencies, and therefore, the presence or absence of cells is not a sufficient explanation for susceptibility to disease. The phenotypes of the islet antigen specific CD8+ T cells, identified by FACS, showed a greater proportion of CD45RO+ T cells in T1D patients (6). Curiously, in a recent analysis, islet antigen reactive cells were found within the naïve, CD45RA compartment, raising questions about whether these cells had been activated during the development of diabetes(8). Furthermore, in the previous studies, it was not possible to clarify whether the differences that were observed between individuals in the cells were due to activation, differentiation, or proliferation, or control of the antigen specific cells by other factors such as Tregs which may also be dysfunctional in patients with T1D(9). Because of the very low frequency of the antigen specific T cells in the peripheral blood, qualitative analyses of the cells have been challenging with conventional methods such as MHC tetramers and ELISpots, and there are very limited data on the cellular characteristics of the cells including their T cell receptor (TCR) sequences(10). In this regard, CyTOF, which enables detection of more than 40 markers on a per cell basis can greatly improve data acquisition from rare cells.
T cell library assays were originally developed by Geiger et al. to detect and characterize rare antigen specific T cells within cell compartments(11, 12). T cells were sorted on the basis of phenotype and polyclonally expanded. They were tested for functional responses to primary antigens and recall antigen. CD4+ T cells specific for peptides from pathogens could be detected at a frequency ranging from 5–170/106 naïve cells. Cao et al. applied this method for study of autoreactive CD4+ T cells in patients with multiple sclerosis(13). The libraries are useful in a number of ways. Since cells are sorted directly ex vivo on the basis of phenotypes, the frequency of antigen reactive cells can be compared among subpopulations. In addition, functional features and TCRs may be identified on the expanded antigen-reactive cells. T cell libraries were initially developed for analysis of antigen specific human CD4+ T cells, but CD8+ T cells are more difficult to grow and expand for extended periods of time, and the frequency of precursors in the naïve population has not been evaluated.
To study antigen specific CD8+ T cells in patients with T1D, we developed methods to create CD8+ T cell libraries and methods to phenotype the antigen specific T cells by CyTOF. We used these methods to study the CD45RA+ (majority of naïve cells) and memory (CD45RO+) CD8+ cells in patients with T1D and HC subjects. Using the libraries, we were able to identify which antigens are recognized by the cells and to isolate TCRs from the antigen reactive cells.
Methods
Study subjects
Peripheral blood was drawn from patients with T1D after written informed consent. Leukocytes from healthy donors were purchased from New York Blood Center or were from healthy volunteers. All participants were HLA-A2+ which was screened by staining of PBMC with mAb BB7.2 which recognizes the α chain of HLA-A2, followed by flow cytometry analysis. Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects. The studies were approved by the Institutional Review Boards at the University of Colorado, Columbia University, and Yale University.
Antibodies and reagents
The following monoclonal antibodies were used for flow cytometry analysis and cell sorting; anti-CD8 (TONBO Biosciences), anti-CD4 (BD Biosciences), anti-CD45RA (BioLegend), anti-CD45RO (BD Biosciences). LIVE/DEAD fixable yellow dead cell stain kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Recombinant human IL-2 was obtained through the AIDS Research and Reference Reagent Program (Division of AIDS, National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases). Recombinant human IL-7 and IL-15 were purchased from BioLegend.
T2 peptide binding assay
The peptides IGRP228–236, PPI2–10, PPI34–42, and PPI90–99 were synthesized by AnaSpec. All the other peptides (Supplemental Figure 1) were synthesized by GenScript. To verify HLA-A2 binding, HLA-A2 TAP-deficient T2 cells were incubated with peptide and β2m in serum free medium overnight, and analyzed for expression of HLA-A2 with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled HLA-A2 specific antibody (BD Biosciences)(14).
Cell purification and sorting
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated by Ficoll-Hypaque gradient centrifugation. CD8+ T cells were selected with human CD8+ T cell isolation kit (STEMCELL Technologies). CD8+ T cells were sorted into CD45RA+ or CD45RO+ fractions on a FACSAria (BD Biosciences) to a purity of >98% as verified by post-sort analysis.
CD8+ T cell library assay
CD8+CD45RA+ and CD8+CD45RO+ cells sorted from PBMC were cultured in 96-well round-bottom plates (Corning) at 2 × 103 cells per well in complete DMEM medium (supplemented with 5 mM HEPES; pH7.3 (AmericanBio), 0.1 mM nonessential amino acids (Gibco), 1 mM sodium pyruvate (Gibco), 50 U/ml penicillin (Gibco), 50 U/ml streptomycin (Gibco), and 5% human serum (Sigma-Aldrich)) in the presence of 1 ug/ml PHA, 20 U/ml IL-2, 20 ng/ml IL-7, and 20 ng/ml IL-15 with irradiated (45 Gy) allogeneic feeder cells (2 × 104 cells per well). These initial cultures were without added peptides. Fresh cytokines were added every 3 days. On day 10, the libraries were screened by culturing ~5 × 105 cells with K562 HLA-A2+4–1BBL+ cells (~105 cells)(kind gift of J Riley, Univ PA) which were either unpulsed or pulsed for 3 hours with islet Ag peptide pools (PPI2–10, PPI15–24, PPI34–42, IGRP228–236, IA-2797–805, and ZnT8186–194) or viral peptides (InfluenzaM158–66 and EBVBMLF-1280–288). Culture supernatant was harvested on day 6 following peptide pool stimulation for cytokine measurements by ELISA (IFNγ) or Luminex (TNF, IL-6, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-8, IL-2, IL-17A, IL-10, and IL-1β). In some experiments, CD45RO+CD8+ T cell libraries with positive or negative responses to islet Ag peptides were further expanded by adding IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15 every 2~4 days for another 14 days and then restimulated with irradiated K562 HLA-A2+ 4–1BBL+ cells pulsed with individual islet Ag peptides. IFNγ was measured in supernatants after 6 days of stimulation.
CyTOF analysis
CyTOF Helios (Fluidigm) was used. Heavy metal conjugated antibodies or purified antibodies were purchased from Fluidigm, CyTOF Core at Brigham and Women’s Hospital Harvard Medical School, and eBiosciences. Some antibodies were conjugated using Maxpar antibody labeling kit (Fluidigm) or cisplatin as reported previously(15). Biotinylated HLA-A2 monomers loaded with PPI2–10, PPI34–42, and IGRP228–236 peptides were provided by NIH and those with PPI15–24, IA-2797–805, and ZnT8186–194 peptides were tetramerized using a standard protocol (NIH tetramer core facility). Streptavidin cDNA sequence was mutated with six cysteine residues at C-terminus. The mutant streptavidin was purified and conjugated with heavy metal as previously described (16). Tetramer barcoding technology was employed to distinguish ZnT8-tetramer+ cells and other islet Ag-tetramer+ cells and also to increase the specificity of the tetramer staining by triple tetramer staining.
For the analysis, previously frozen CD8+ T cells were isolated from PBMC using EasySep human CD8+ T cell isolation kit (Stem Cell). They were pretreated with dasatinib(17) and stained with HLA-A2 tetramers and antibodies. Dead cell staining by Cell-ID cisplatin, surface marker staining, fix and permeabilization using Foxp3 staining buffer set (eBiosciences), and intracellular staining were performed. Cell-ID intercalator-Ir (Fluidigm) was used to identify genomic DNA-containing single cells. 0.1X volume of EQ four element calibration beads were added to samples for normalization. For each sample, healthy PBMC were also input as reference cells using anti-CD45 based barcoding technique (18). CyTOF data was analyzed using Cytobank (cytobank.org) and using SAUCIE(19). SAUCIE, a deep learning method for single-cell analysis, identified and clustered several distinct cell types in the samples. SAUCIE was chosen for clustering because the correct number of cell types/clusters was not known ahead of time, and it automatically fits the appropriate number of clusters based on the data. All cells from T1D patients were clustered together, and then separately all those from the healthy references. The mean expression profile of each cluster was then analyzed for marker-marker relationships that differ between the two groups.
T cell receptor studies
Positive wells were selected on the basis of IFNγ production to the pool of peptides and the TCR Vβ and Vα chains were sequenced (Adaptive Biotech, Seattle, WA). The frequencies of the CDR3s were determined after alignment. Primers were prepared for PCR analysis of the specific sequences.
To identify the TCRs ex vivo, PBMCs were stimulated with the ZnT8186–194 peptide for 6 hours and IFNγ+ and – CD8+ cells, identified with anti-CD8 mAb(HIT8a, PerCP-Cy5.5, Biolegend) and an anti-IFNγ antibody (130–054–201, Miltenyi), were sorted by a flow cytometer. The TCR sequence was identified in the sorted subpopulations by RT-PCR.
Statistical analysis:
Unless indicated the mean±SEM is shown. Comparisons were made using the indicated statistical tests using GraphPad software (version 7.03). For library studies, wells with > mean+3SD of the IFNγ levels for wells cultured with APCs that had been cultured with DMSO were calculated for each subject (RO+ and RA+ cells separately) were considered positive. The percent+ library wells are presented as the (number positive wells/total number of wells) * 100. For CyTOF analysis, two way ANOVAs were performed comparing grouped data with post-hoc testing of individual markers.
Results
Analysis of antigen specific cells with CD8+ T cell libraries
We tested previously identified peptides from the Immune Epitope Database (http://www.iebd.org) and published reports in a T2 binding assay to verify binding and stability to HLA-A2 (5, 7, 14, 20–27). From the original 10, we selected 6 on the basis of this assay (Supplemental Figure 1): 3 from preproinsulin (PPI)(2–10, 15–24, and 34–42); 1 from islet-specific glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit-related protein (IGRP)(228–236); 1 from islet antigen 2 (IA-2)(797–805); and 1 from the β cell zinc transporter (ZnT8)(186–194) (5, 7, 20–27). To improve the efficiency of the analysis, the 6 peptides were pooled for the initial library screening.
We modified previous methods to facilitate expansion of CD8+ T cells with good reproducibility (Supplemental Figure 2). The subsets of cells were first cultured with PHA and feeder cells with a cocktail of common γ chain cytokines, IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15. We then used HLA-A2+, 4–1BBL+, K562 cell line as antigen presenting cells to eliminate the need for large volumes of blood samples to obtain APCs of sufficient number.
We used previously frozen PBMC from patients with T1D (Table 1) and HC subjects. We sorted CD8+ cells from between 10–40 million PBMCs into CD45RO+ (memory) and CD45RA+ subpopulations, the majority of the latter are naïve cells. Between 8 and 100 wells were plated from each subject (median=59 and 60 for CD45RO+ and CD45RA+). Because of limited cell availability, the assays with CD8+CD45RO+ cells were performed with all subjects (29 patients and 13 HC) but the CD45RA studies were done with 25 patients and 13 HC subjects.
Table 1.
Demographic data of patients analyzed by libraries
| N | 29 |
| Age (years) | 24.9±2.88 (SEM), range 14–63 |
| Gender (M/F) | 11/18 |
| Disease duration (years) | 16.7±2.52 (SEM), range 0–50 yrs |
| GADA positive | 75% |
| IA-2A positive | 58% |
| ZnT8 positive | 42% |
includes samples and data from 3 concordant triplets and 2 concordant twins ages 63 and 32 yrs.
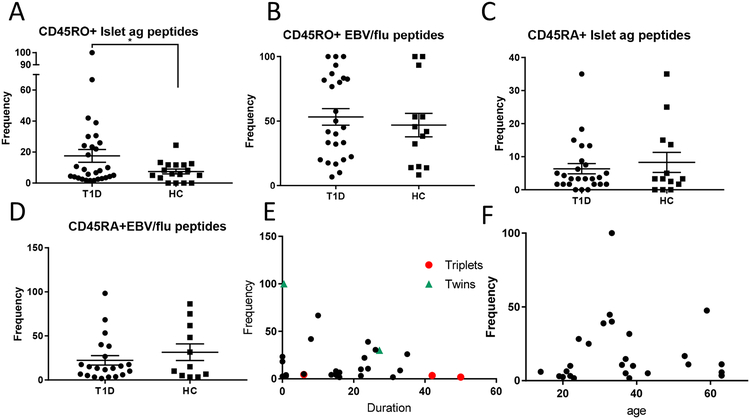
IFNγ production to islet antigen peptides was measured in a total of 1934 CD45RO and 1528 CD45RA library wells. In the CD45RO+ fraction, the frequency of wells showing positive responses against islet antigen peptides in T1D patients was significantly higher than in cells from the HC wells (Figure 1A, p=0.028 and Supplemental Figure 2) but the frequency of CD45RO+EBV/flu-reactive cells was similar in the patients and HC subjects (Figure 1B). The frequency of islet antigen reactive wells (i.e. those with positive IFNγ levels/total library wells*100) was lower among the CD8+CD45RA+ vs CD8+CD45RO+ cells overall (6.35±1.53% vs 17.6±4.12%, p=0.016) in patients with T1D, but there was not a significant difference in the frequency of CD8+CD45RA+ islet antigen positive wells between the patients and HC subjects (Figure 1C). The frequency of the viral peptide reactive wells in the CD45RA+ populations was, again, similar in the patients and healthy controls (Figure 1D). The differences in the frequency of the positive CD45RO+ wells in patients vs HC were not due to the background IFNγ production because the levels in the wells challenged with DMSO-treated K562 cells were similar (mean+3SD: 329±80 pg/ml and 288±60 pg/ml, p=ns) in T1D patients and HC subjects.
Figure 1. Analysis of autoantigen reactive CD8+ T cells by T cell libraries.
Libraries were prepared from CD8+CD45RO+ cells sorted from the peripheral blood as described from 29 patients with T1D and 15 HC. Each well was expanded with irradiated allogeneic PBMC+IL-2, IL-7, and IL-15 as described in Materials and Methods. After 10 days the wells were washed and stimulated with K562 cells that had been pulsed with 6 diabetes peptides, peptides from EBV/flu, or treated with DMSO alone. IFNγ levels in the supernatants were measured by ELISA after 6 days. Data from a representative patient and HC subject are shown in Supplemental Figure 2B. The frequencies of positive wells that were above the threshold, which was mean+3SD of DMSO wells were calculated for each subject. There was a significantly greater proportion of positive wells from CD45RO+ cells from patients with T1D reactive with islet antigens (A)(*p=0.028, t-test with Welch’s correction) compared to HC, but not to peptides from EBV/flu (B). CD45RA+CD8+ cells were sorted from 25 and 13 of the T1D patients and HC respectively. (C,D) There was not a significant difference between the frequency of islet antigen-reactive (C) or EBV/flu reactive cells (D). The relationship between frequency of CD45RO+ CD8+ islet antigen-reactive cells and diabetes duration (E) or age (F) are shown (p=ns, Spearman corr). The orange and green dots represent samples from concordant identical triplets and twins respectively.
Among patients with T1D, although there was a decline in the frequency of positive wells with duration of disease overall, the relationship was not statistically significant (Figure 1E, r2=0.043, p=ns), and we did not find a relationship between age or age at diagnosis and the frequency of positive wells in the CD45RO+ libraries (Figure 1F and not shown). Among our subjects were identical triplets and twins that were concordant for T1D (orange and green in Figure 1E). Among these genetically identical sibs, the sib with the shortest duration of disease had a higher frequency of positive libraries.
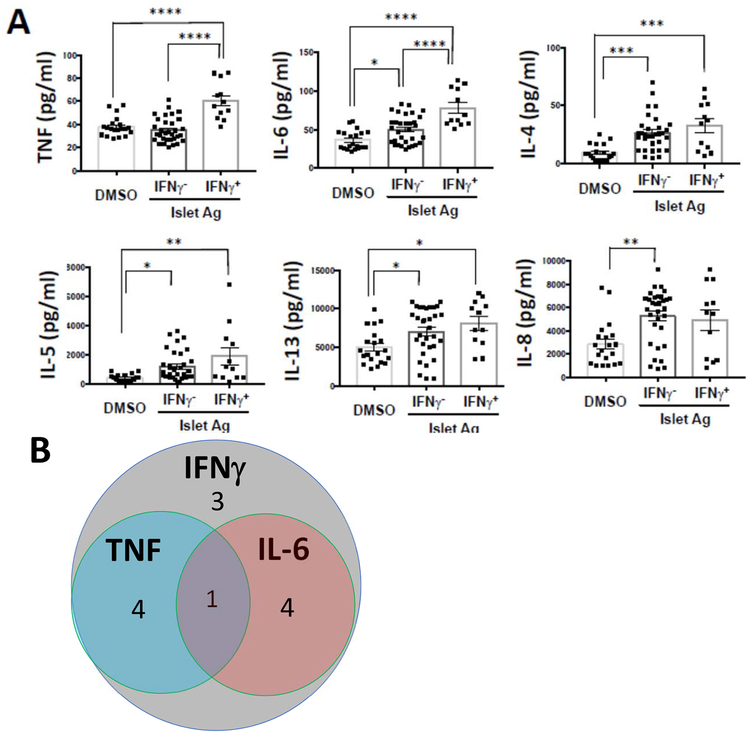
We selected positive wells on the basis of IFNγ production but it was possible that other cytokines were produced or multiple antigen reactive cells were in the wells. We compared the levels of other cytokines in the culture supernatants in the IFNγ+ and – wells (Figure 2A). There was significantly greater release of TNF and IL-6 in the IFNγ+ vs IFNγ-wells (p=0.0001). IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and IL-8 were increased in both the IFN- and (with the exception of IL-8) IFNγ+ wells but were not significantly different between the IFNγ+ and IFNγ-wells. IL-17, IL-2, and IL-10 levels were below the limits of detection even in the IFNγ-wells. The overlap of cytokine release in individual positive wells is shown in Figure 2B.
Figure 2. Multiple cytokines are found in the supernatants from library wells from patients with T1D:
(A) Cytokines in the supernatants of IFNγ positive wells (n=12 from 5 subjects with T1D) and IFNγ negative wells (n=32 from 5 subjects with T1D), as well as non-peptide stimulated (DMSO) wells (n=20 from 3 subjects with T1D) were measured with Luminex assay. The levels of IL-2, IL-17, and IL-10 were below the limit of detection. (* p<0.05, ** p<0.01, *** p<0.001, **** p<0.0001, ANOVA with multiple comparisons) The data were combined from 3 independent experiments. (B) Venn diagram is showing the overlap of cytokines from IFNγ positive (n=12 wells from 3 subjects with T1D), TNF positive and IL-6 positive wells. The number of wells are indicated in the graph. The positive was defined by thresholds of mean+3SD of individual cytokines. In addition to IFNγ, which was used to identify the positive wells, other cytokines (TNF, IL-6, IL-4, IL-5, IL-13) were increased in the positive and negative wells but IL-8 was also increased in the IFNγ-cells.
Identification of antigens recognized by CD45RO+CD8+ T cells
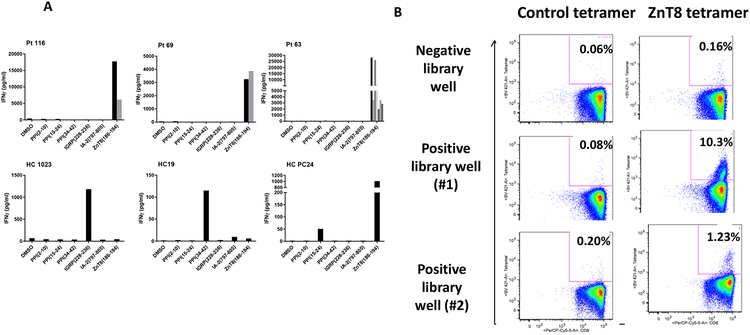
To determine which of the 6 peptides from the pool were responsible for the IFNγ production, we expanded the positive cells from 4 pts with T1D and 3 HC with cytokines and challenged them with the APC cell line pulsed with the individual peptides. In all 21 positive wells from the 4 patients with T1D, the IFNγ response was to ZnT8186–194 (Data on 3 of the 4 are shown in Figure 3A). We confirmed the high frequency of ZnT8-specific cells by flow cytometry by staining positive wells from 3 patients with T1D (Pt 116, 39 yoM, T1Dx16 yrs; Pt 69, 23yoM, T1Dx22 yrs; Pt 63, 27 yoF, T1Dx23yrs) and 3 HC subjects. The wells were expanded with cytokines and stained with class I MHC tetramers loaded with the ZnT8186–194 peptide. The frequency of the tetramer+ cells was as high as 10% (Figure 3B). In HC subjects we found responses to other peptides such as IGRP228–236 and PPI34–42 as well as ZnT8186–194 (Figure 3A).
Figure 3. Recognition of ZnT8(186–194) by cells from positive libraries from patients with T1D:
(A) Positive wells from the CD8+ T cell libraries from 4 patients with T1D and 3 HC subjects were further expanded with cytokines and challenged with K562 cells pulsed with each individual peptide used in the original pool. The levels of IFNγ were measured after 6 days. The data are from 11 wells from the 3 patients described in the text (Pt 116, Pt 69, and Pt 63) with T1D and 3 HC subjects (HC1023, 19, PC24). Each graph represents the analysis of positive wells from an individual patient. The bars (black and grey) represent the cytokine responses of different positive wells to the peptides. There were positive responses to ZnT8186–194 in wells from the patients with T1D but responses to IGRP228–236, PPI34–42, PPI15–24, and ZnT8186–194 in the HC subjects. (B) The CD45RO+ cells from one library well without and two library wells with an IFNγ response to the peptide pulsed K562 cells from Pt 63 were expanded in cytokines and stained with tetramers loaded with ZnT8186–194 peptide or control tetramer and analyzed by flow cytometry. The percentages refer to the frequency of tetramer+ cells in the CD8+ gate.
Analysis of the phenotypes of antigen specific CD8+ T cells by CyTOF
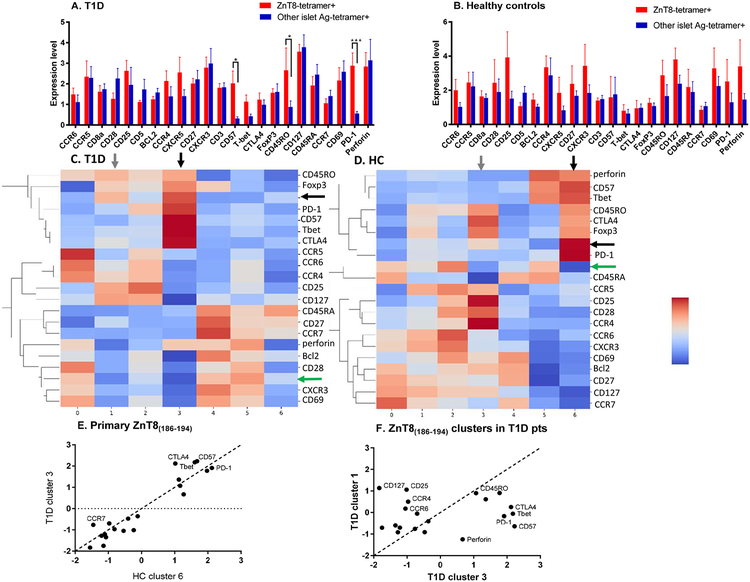
To determine whether the phenotype of the ZnT8-reactive cells in vivo could account for our findings, we compared the phenotypes of the ZnT8-specific CD8+ cells to cells reactive with the other 5 peptides in our pool using CyTOF in a subset of the patients and HCs (n=6 each). This subset of subjects showed a frequency of positive library wells that was representative of the larger group (T1D patients 14.8±4.69% vs HC 4.89±1.91%, p=0.054).. The cells were analyzed directly ex vivo without culture. We modified streptavidin using methods that had been described by Newell et al. and tetramerized the peptide-loaded monomers with streptavidin conjugated to 147Sm, 165Ho, 166Er, and 167Er so that the cells could be identified by CyTOF (Supplemental Figure 3A) (16). “Tetramer Positive” cells were identified by simultaneous staining with tetramers loaded with 3 heavy metals. In preliminary studies, we confirmed the specificity of tetramer binding by competing for tetramer binding with free peptides (not shown). Using barcoding, we compared the frequency and features of the ZnT8186–194 specific CD8+ cells with the CD8+ T cells specific for other peptides within each individual in paired comparisons between the CD8+ T cells reactive with ZnT8186–194 or the other 5 peptides. We did not identify significant differences in markers between ZnT8186–194 reactive and other peptide-reactive CD8+ T cells in the HC subjects (n=6) but we did when comparing the ZnT8186–194 reactive CD8+ T cells to CD8+ cells specific for other peptides in patients with T1D (n=6)(Figure 4A, B). The ZnT8186–194 reactive cells showed increased expression of CD45RO (p=0.017), CD57 (p=0.028), and PD-1 (p=0.0003) compared to those reactive to other peptides (Figure 4A). To distinguish the individuals cells on the basis of associated markers, we performed a cluster analysis of the tetramer+ cells using SAUCIE (19). Heatmaps were generated to identify markers that associated with the tetramer+ cells in the clusters (Figure 4 C, D). In the T1D patients and HC subjects, the ZnT8186–194-reactive cells were identified in two clusters. The dominant clusters in the T1D and HC subjects were cluster 3 and 6 respectively (black horizontal and vertical arrows), but some cells were also found in clusters 1 and 3 respectively (black horizontal and gray vertical arrows). The T cells reactive to other diabetes antigens were distributed in 3 clusters (clusters 0, 4, 5 in the T1D patients and clusters 0, 2, 5 in the HC subjects, green arrows)(Figures 4C, D). The frequency of all tetramer+ cells was modestly greater in the T1D vs HC subjects Supplemental Figure 3B, p=0.046) but particularly among the ZnT8186–194-reactive cells (Supplemental Figure 3B, p=0.02, Mann-Whitney). The average expression of markers within the clusters was compared to identify phenotypic differences between them (Figures 4E, F). There was increased expression of CD57, Tbet, and CTLA-4 in the dominant clusters from patients with T1D vs HC (Figure 4E), and increased expression of CD57, PD-1, Tbet, Perforin, and CTLA-4 in cluster 3 vs cluster 1 in patients with T1D. The number of ZnT8186–914-reactive cells in the two clusters was variable but median number was higher in the patients with T1D compared to HC subjects (median 4 and 3.5 for clusters 1 and 3 respectively in T1D and 1 and 0 for clusters 3 and 6 respectively for HC subjects)
Figure 4. CyTOF analysis of antigen specific T cells:
(A and B) Using bar-coded tetramers, we analyzed the expression of the indicated markers on CD8+ T cells that were specific for ZnT8186–194 (red) or specific for CD8+ T cells reactive with the 5 other islet antigen peptides that were pooled (IGRP228–236, PPI2–10, PPI34–42, PPI15–24, IA-2797–805)(blue). The results of 6 healthy controls and 6 patients with T1D from 2 independent experiments are shown. Values were normalized with the signal intensity of reference cells that were added to all of the assays and the intensity of the signals were compared between the ZnT8 tetramer+ and other tetramer+ cells using two-way ANOVA for paired comparisons with post-hoc analysis of the individual markers (mean±SEM). The expression of CD45RO (*p<0.05), CD57 (*p<0.05), and PD-1 (***p<0.001) were increased in the ZnT8-tetramer+ cells from patients with T1D. (C, D) The CyTOF data were analyzed by SAUCIE to identify clusters among the tetramer+ cells and their associated markers. In patients with T1D and HC subjects the ZnT8186–194–reactive cells were found most commonly in clusters 3 and 6 respectively (black horizontal and vertical arrows), but some cells were also found in clusters 1 and 3 respectively (black horizontal and gray vertical arrows). The T cells reactive to other diabetes antigens were distributed in 3 clusters (clusters 0, 4, 5 in the T1D patients and clusters 0, 2, 5 in the HC subjects, green arrows). (E, F) The average values of markers within the dominant clusters of the ZnT8186–194–reactive cells in the T1D patients (cluster 3) and HC subjects (cluster 6). The dotted line is the line of identity. In F the differences between the two clusters of ZnT8186–194–reactive cells are shown.
Identification of T cell receptor sequences of ZnT8-reactive CD8+ T cells in libraries and in vivo
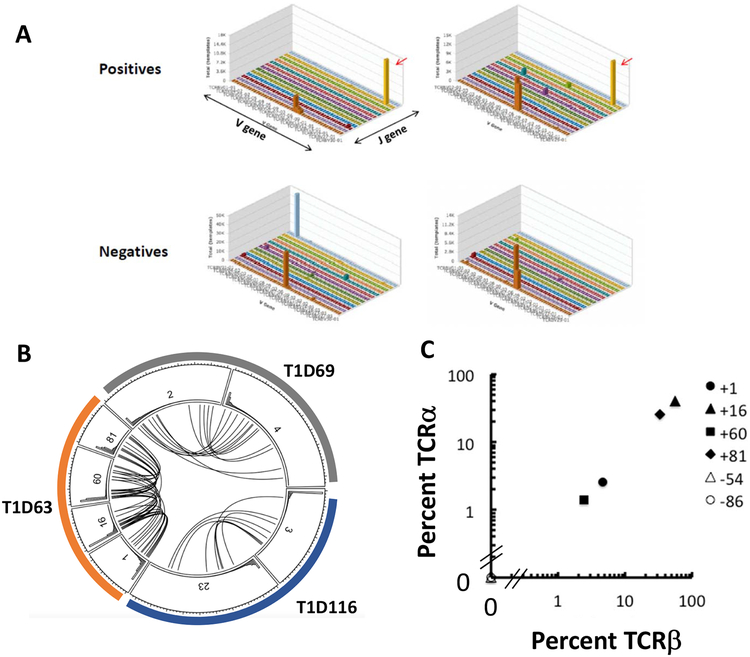
We selected positive wells with ZnT8186–194 reactive-cells from 4 patients, and 3 positive wells from HCs and sequenced of the Vβ and Vα chains. We identified CDR3 sequences that were present in the wells at a frequency of ≥ 0.05% (i.e. 1:2000 which corresponds to at least 1 cell/well). We then looked for these same sequences in other positive wells from the same individual and other patients (Figure 5A,B, Supplemental Table 1). We found multiple wells from the same individual that shared CDR3 sequences but these sequences were private and not shared between individuals. We identified Vα chains, that corresponded to the Vβ chains in multiple wells (Figure 5C, r2=1.0, p<0.0001). We then confirmed our sequencing results by screening multiple wells from the CD45RO+ and RA+ libraries from the same patient by PCR. The identified TCR sequence was found in 4/4 CD45RO+ positive wells but was also identified in 1/3 positive wells in the CD45RA+ libraries from the same patient (Figure 6A). It was not identified in the negative wells from the libraries.
Figure 5. TCR sequences of islet antigen reactive wells:
(A) The frequency of TCRβ V-J sequences of representative positive wells and negative wells from a single patient (Pt 63) representative of 3 are shown in 3D plots. Red arrow indicates shared V-J usage among the positive wells, which was not observed in the negative wells. (B)The circos plot shows data from individual wells from 3 patients with T1D (colors, T1D63, T1D69, and T1D116). The lines between the subdivisions connect common TCRβ sequences. The numbers identify the library well number. (C) In a representative analysis, the frequencies of the TCRα and the TCRβ chains were compared and found to match between each library well with a positive IFNγ response (r2=1.0, p<0.0001). Well numbers appear to the right of the plot.
Figure 6. Identification of TCR sequences in library wells and in vivo:
(A) The Vα and Vβ sequences, identified in 5C above from pt 63, were detected, using PCR for the TCR chains, in positive (+) but not negative (−) library wells (selected for IFNγ responses). (DW=control well) There were multiple wells in the CD45RO libraries but a single positive well from the CD45RA+ libraries in which the Vα and Vβ sequences were identified. (B) PBMC isolated in a repeat draw from the same patient were cultured with ZnT8186–194 peptide. IFNγ+CD8+ and IFNγ−CD8+ T cells were identified with a capture assay and sorted. The presence of the TCR Vα and Vβ chains were again identified by PCR (arrow) in the IFNγ+ cells.
Finally, we then obtained a new sample from the same donor 9 months later and stimulated the PBMC with the ZnT8186–194 peptide. IFNγ+ and - CD8+ cells were identified with an IFNγ-capture antibody and sorted. The TCR α and β chain sequences were found among the IFNγ+ cells but were not detected among the IFNγ-cells (Figure 6B).
Discussion
Studies from preclinical models and autopsy material suggest that CD8+ T cells are the mediators of β cell destruction in T1D(1, 2). They are the dominant T cells found in human insulitis, and a limited number of CD8+ T cell clones have been isolated that can kill β cells(28, 29). However, many laboratories have not identified differences in the frequency of islet antigen-specific CD8+ T cells between T1D patients and HC subjects with Class I MHC tetramers(6, 8). Our results with CD8+ T cell libraries, in which we find a higher frequency of islet antigen reactive cells in the CD45RO+CD8+ cells show that there are differences in the frequency of functionally active diabetes antigen reactive T cells that may not be identified by staining of the T cell receptors with tetramers. In the T cell libraries, we did not find a difference in the frequency of the diabetes antigen specific CD8+CD45RA+ T cells consistent with the notion that autoantigen reactive cells may be detected in HC subjects. Moreover, in contrast to the antigen reactive memory cells from HCs, which recognized a variety of islet antigenic peptides, the CD45RO+ cells from patients with T1D were dominated by reactivity to ZnT8186–194 and these antigen specific cells that showed an activated phenotype when compared to T cells reactive to other diabetes antigen peptides when analyzed by CyTOF.
The libraries enabled us to identify frequently used TCRs by antigen reactive cells with these tools, we could track the cells in vivo. The same CDR3 sequence, from one library well was found in multiple wells from the same individual frequently in the CD45RO+ but also in a smaller proportion of CD45RA+ library wells. However, the α and β chain sequences that were expanded in the positive wells were private and not shared between individuals. These findings are consistent with the notion that in patients with T1D and HC there is a similar frequency of autoantigen reactive CD45RA+ cells. In patients, these T cells are activated and expanded during disease progression.
T cell libraries were originally used to identify antigen specific T cells, separated on the basis of phenotype among PBMC(11). To overcome difficulties in expanding CD8+ cells and overcoming practical challenges in obtaining a sufficient number of antigen presenting cells, particularly in young subjects, we modified the cocktail of cytokines used to expand the cells and used K562 cells expressing HLA-A2 and costimulatory 4–1BBL molecules instead of autologous monocytes. We used pooled peptides to screen for islet antigen reactive cells to increase the odds of finding islet antigen positive wells in our screening assay. We cannot be certain that the K562 cell line can present antigen to all antigen reactive cells and there may be antigenic peptides that were not included in our pool. The frequency of T1D antigen reactive cells, using data from all subjects was about 1 per 2×104 CD45RO+CD8+ T cells (or approximately 2/100,000 CD8+ T cells) which is in the range of the frequency of ZnT8-reactive cells in total PBMCs reported by Scotto et al with ELIspot assays, but their assays did not differentiate the frequency of the antigen reactive cells in CD8 T cell subsets (25). We selected the antigen reactive cells on the basis of IFNγ production because that cytokine has been linked with pathogenic cells in T1D(30–32), but other pathologic cytokines including TNF and IL-6 were secreted(33). The multiplicity of cytokines may reflect more than 1 antigen specific cell in each library well, as this would explain our finding of IL5 and IL13 in IFNγ+ wells. It is possible that studies based on the production of other cytokines may identify other antigen specificities that are recognized in patients with diabetes.
Analysis of antigen specificity is dependent the selection of peptides used for study and methods of analysis. Data from other studies including analysis of islet-infiltrating cells has shown that other antigens are also recognized(5, 6, 8, 20, 21) but these cells were identified by tetramer staining. We selected peptides for study on the basis of binding in the T2 assay and peptides with very low binding affinity could have been missed. In addition, a potential limitation of our analysis is that the peptides selected were chosen for their binding to HLA-A*0201 but our screening for HLA-A2 involved an antibody (BB7.2) that can recognize other genotypes. Our analysis with the peptides from EBV/flu ensure that the HLA-A2 was capable of binding the peptides and none of the individuals without positive wells in the diabetes peptide libraries had positive wells with the peptides from EBV/flu. The ZnT8186–194 peptide was the predominant antigen recognized by the cells in patients with T1D. It is a transporter protein that maintains the zinc level of the insulin secretion granule(34, 35). The high frequency of the ZnT8-reactive cells that we identified in the libraries may reflect a higher frequency and/or growth advantage of precursor cells that have been activated consistent with our detection of the TCRs in the RO and RA libraries. Interestingly, we had the opportunity to analyze a single at-risk subject (an autoantibody+ relative without diabetes) but in this subject, the frequency of positive wells was relatively low compared to patients with diabetes (3.2%). Further prospective studies are needed to differentiate whether more autoantigens are recognized early in the course of disease with is focusing of the autoreactive repertoire towards ZnT8-reactive cells in diabetes progressors.
Unlike results using Class I multimers reported by Culina et al, we found that the frequency of ZnT8186–194-reactive CD8+ T cells was increased in patients vs HC subjects but the differences we found were in the CD45RO+ and not the CD45RA+ which these investigators found to be expressed on the ZnT8186–194 – reactive cells. (8). Culina et al identified cells based on multimer staining whereas we began with sorting of the cells into subsets and then challenging with antigen after expansion. Because CD45RA+ cells are more numerous than CD45RO+ cells, the majority of the antigen specific cells are likely to be in the CD45RA compartment even if their frequency is less. It is possible that differences between individuals may be overlooked if the sequence of the analysis begins with selection of the tetramer+ cells. Second, the libraries require functional readouts – expansion to the non-specific stimuli and cytokines in the first 10 days and then responses to antigen. The tetramer studies are based on the presence or an antigen specific T cell receptor. Indeed other functional assays (e.g. ELISPOT) have consistently identified a difference in the frequency of the ZnT8-reactive cells in patients with T1D vs healthy control subjects(8, 25, 36). Therefore, the library studies provide an opportunity to identify cells within a select subpopulation that is technically challenging when antigen specific cells are infrequent.
Features of the antigen specific cells that were found by CyTOF ex vivo that may account for differences in responses in the libraries. The increased CD57 expression on cells that expressed CD45RO, which is associated with chronic antigen activation and IFNγ production, suggests these cells had been stimulated in vivo by antigen(37). Our cluster analysis showed that the ZnT8186–914 and other antigen-specific T cells were heterogeneous rather than uniform populations on the basis of their expression of markers. Clusters of the ZnT8186–914 – reactive cells differed in certain markers that are likely to be of pathologic significance such as perforin and Tbet, a transcription factor associated with IFNγ production. Whether β cell killing occurs may be more dependent on the relative proportion of functional subsets. This information also suggests that agents that target specific molecules may be useful for therapy.
A limitation of our study is that we did not perform sequencing on a single cell basis, and therefore, the presumed Vα/Vβ chain combination can only be inferred on the basis of frequencies. Further studies using cloned cells isolated from the libraries should resolve any question about the chain pairing. Nonetheless, the sequencing information enabled us to identify the antigen-reactive cells in the same subject on a second occasion. This tool may be useful in tracking antigen specific cells within an individual over time and avoid the technical difficulties associated with other methods. Lastly, the TCR sequence data may enable future construction of cellular therapies that can use the TCRs from islet antigen specific cells to direct immune cells to the islets.
In summary, we have used CD8 T cell libraries and CyTOF to identify and characterize antigen specific T cells in patients with T1D. These methods will be useful for characterizing these cells, tracking them in patients, and even for designing new therapies that target the pathogenic cells.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Klementy Shchetynsky and the Yale CyTOF core facility for technical assistance. We also thank Dr. Peter Cresswell for the T2 cells and helpful discussions. HO, PPH, ALP, MA, SK, PC, HU, DE, AF performed the studies analyzed data, and prepared the manuscript. AKS and KCH analyzed the data and prepared the manuscript. KCH is the guarantor of the work.
Supported by grants R01DK057846, UC4DK104205 from the NIH, grant 20130068 from the JDRF, and support from the Brehm Coalition, Helmsley Foundation, and the Howalt family.
References
- 1.Coppieters KT, Dotta F, Amirian N, Campbell PD, Kay TW, Atkinson MA, Roep BO, and von Herrath MG. 2012. Demonstration of islet-autoreactive CD8 T cells in insulitic lesions from recent onset and long-term type 1 diabetes patients. J Exp Med 209: 51–60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Itoh N, Hanafusa T, Miyazaki A, Miyagawa J, Yamagata K, Yamamoto K, Waguri M, Imagawa A, Tamura S, Inada M, and et al. 1993. Mononuclear cell infiltration and its relation to the expression of major histocompatibility complex antigens and adhesion molecules in pancreas biopsy specimens from newly diagnosed insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. J Clin Invest 92: 2313–2322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Viehmann Milam AA, Maher SE, Gibson JA, Lebastchi J, Wen L, Ruddle NH, Herold KC, and Bothwell AL. 2014. A humanized mouse model of autoimmune insulitis. Diabetes 63: 1712–1724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dolton G, Lissina A, Skowera A, Ladell K, Tungatt K, Jones E, Kronenberg-Versteeg D, Akpovwa H, Pentier JM, Holland CJ, Godkin AJ, Cole DK, Neller MA, Miles JJ, Price DA, Peakman M, and Sewell AK. 2014. Comparison of peptide-major histocompatibility complex tetramers and dextramers for the identification of antigen-specific T cells. Clin Exp Immunol 177: 47–63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Skowera A, Ellis RJ, Varela-Calvino R, Arif S, Huang GC, Van-Krinks C, Zaremba A, Rackham C, Allen JS, Tree TI, Zhao M, Dayan CM, Sewell AK, Unger WW, Drijfhout JW, Ossendorp F, Roep BO, and Peakman M. 2008. CTLs are targeted to kill beta cells in patients with type 1 diabetes through recognition of a glucose-regulated preproinsulin epitope. J Clin Invest 118: 3390–3402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Skowera A, Ladell K, McLaren JE, Dolton G, Matthews KK, Gostick E, Kronenberg-Versteeg D, Eichmann M, Knight RR, Heck S, Powrie J, Bingley PJ, Dayan CM, Miles JJ, Sewell AK, Price DA, and Peakman M. 2015. beta-cell-specific CD8 T cell phenotype in type 1 diabetes reflects chronic autoantigen exposure. Diabetes 64: 916–925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Pinkse GG, Tysma OH, Bergen CA, Kester MG, Ossendorp F, van Veelen PA, Keymeulen B, Pipeleers D, Drijfhout JW, and Roep BO. 2005. Autoreactive CD8 T cells associated with beta cell destruction in type 1 diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 102: 18425–18430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Culina S, Lalanne AI, Afonso G, Cerosaletti K, Pinto S, Sebastiani G, Kuranda K, Nigi L, Eugster A, Osterbye T, Maugein A, McLaren JE, Ladell K, Larger E, Beressi JP, Lissina A, Appay V, Davidson HW, Buus S, Price DA, Kuhn M, Bonifacio E, Battaglia M, Caillat-Zucman S, Dotta F, Scharfmann R, Kyewski B, Mallone R, and G. ImMaDiab Study. 2018. Islet-reactive CD8(+) T cell frequencies in the pancreas, but not in blood, distinguish type 1 diabetic patients from healthy donors. Sci Immunol 3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.McClymont SA, Putnam AL, Lee MR, Esensten JH, Liu W, Hulme MA, Hoffmuller U, Baron U, Olek S, Bluestone JA, and Brusko TM. 2011. Plasticity of human regulatory T cells in healthy subjects and patients with type 1 diabetes. J Immunol 186: 3918–3926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Herold KC, Brooks-Worrell B, Palmer J, Dosch HM, Peakman M, Gottlieb P, Reijonen H, Arif S, Spain LM, Thompson C, Lachin JM, and G. Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet Research. 2009. Validity and reproducibility of measurement of islet autoreactivity by T-cell assays in subjects with early type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 58: 2588–2595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Geiger R, Duhen T, Lanzavecchia A, and Sallusto F. 2009. Human naive and memory CD4+ T cell repertoires specific for naturally processed antigens analyzed using libraries of amplified T cells. J Exp Med 206: 1525–1534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lindestam Arlehamn CS, Gerasimova A, Mele F, Henderson R, Swann J, Greenbaum JA, Kim Y, Sidney J, James EA, Taplitz R, McKinney DM, Kwok WW, Grey H, Sallusto F, Peters B, and Sette A. 2013. Memory T cells in latent Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection are directed against three antigenic islands and largely contained in a CXCR3+CCR6+ Th1 subset. PLoS Pathog 9: e1003130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cao Y, Goods BA, Raddassi K, Nepom GT, Kwok WW, Love JC, and Hafler DA. 2015. Functional inflammatory profiles distinguish myelin-reactive T cells from patients with multiple sclerosis. Sci Transl Med 7: 287ra274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stuber G, Leder GH, Storkus WT, Lotze MT, Modrow S, Szekely L, Wolf H, Klein E, Karre K, and Klein G. 1994. Identification of wild-type and mutant p53 peptides binding to HLA-A2 assessed by a peptide loading-deficient cell line assay and a novel major histocompatibility complex class I peptide binding assay. Eur J Immunol 24: 765–768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Mei HE, Leipold MD, and Maecker HT. 2016. Platinum-conjugated antibodies for application in mass cytometry. Cytometry A 89: 292–300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Newell EW, Sigal N, Bendall SC, Nolan GP, and Davis MM. 2012. Cytometry by time-of-flight shows combinatorial cytokine expression and virus-specific cell niches within a continuum of CD8+ T cell phenotypes. Immunity 36: 142–152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Lissina A, Ladell K, Skowera A, Clement M, Edwards E, Seggewiss R, van den Berg HA, Gostick E, Gallagher K, Jones E, Melenhorst JJ, Godkin AJ, Peakman M, Price DA, Sewell AK, and Wooldridge L. 2009. Protein kinase inhibitors substantially improve the physical detection of T-cells with peptide-MHC tetramers. J Immunol Methods 340: 11–24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kleinsteuber K, Corleis B, Rashidi N, Nchinda N, Lisanti A, Cho JL, Medoff BD, Kwon D, and Walker BD. 2016. Standardization and quality control for high-dimensional mass cytometry studies of human samples. Cytometry A 89: 903–913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Amodio M, Srinivasan D, and Van Dijk D. 2017. Exploring Single-Cell Data with Multitasking Deep Neural Networks. bioRxiv. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Blancou P, Mallone R, Martinuzzi E, Severe S, Pogu S, Novelli G, Bruno G, Charbonnel B, Dolz M, Chaillous L, van Endert P, and Bach JM. 2007. Immunization of HLA class I transgenic mice identifies autoantigenic epitopes eliciting dominant responses in type 1 diabetes patients. J Immunol 178: 7458–7466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mallone R, Martinuzzi E, Blancou P, Novelli G, Afonso G, Dolz M, Bruno G, Chaillous L, Chatenoud L, Bach JM, and van Endert P. 2007. CD8+ T-cell responses identify beta-cell autoimmunity in human type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 56: 613–621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hassainya Y, Garcia-Pons F, Kratzer R, Lindo V, Greer F, Lemonnier FA, Niedermann G, and van Endert PM. 2005. Identification of naturally processed HLA-A2--restricted proinsulin epitopes by reverse immunology. Diabetes 54: 2053–2059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Takaki T, Marron MP, Mathews CE, Guttmann ST, Bottino R, Trucco M, DiLorenzo TP, and Serreze DV. 2006. HLA-A*0201-restricted T cells from humanized NOD mice recognize autoantigens of potential clinical relevance to type 1 diabetes. J Immunol 176: 3257–3265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Takahashi K, Honeyman MC, and Harrison LC. 2001. Cytotoxic T cells to an epitope in the islet autoantigen IA-2 are not disease-specific. Clin Immunol 99: 360–364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Scotto M, Afonso G, Larger E, Raverdy C, Lemonnier FA, Carel JC, Dubois-Laforgue D, Baz B, Levy D, Gautier JF, Launay O, Bruno G, Boitard C, Sechi LA, Hutton JC, Davidson HW, and Mallone R. 2012. Zinc transporter (ZnT)8(186–194) is an immunodominant CD8+ T cell epitope in HLA-A2+ type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetologia 55: 2026–2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Angelini DF, Serafini B, Piras E, Severa M, Coccia EM, Rosicarelli B, Ruggieri S, Gasperini C, Buttari F, Centonze D, Mechelli R, Salvetti M, Borsellino G, Aloisi F, and Battistini L. 2013. Increased CD8+ T cell response to Epstein-Barr virus lytic antigens in the active phase of multiple sclerosis. PLoS Pathog 9: e1003220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zhou V, Yassai MB, Regunathan J, Box J, Bosenko D, Vashishath Y, Demos W, Lee F, and Gorski J. 2013. The functional CD8 T cell memory recall repertoire responding to the influenza A M1(58–66) epitope is polyclonal and shows a complex clonotype distribution. Hum Immunol 74: 809–817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kronenberg D, Knight RR, Estorninho M, Ellis RJ, Kester MG, de Ru A, Eichmann M, Huang GC, Powrie J, Dayan CM, Skowera A, van Veelen PA, and Peakman M. 2012. Circulating preproinsulin signal peptide-specific CD8 T cells restricted by the susceptibility molecule HLA-A24 are expanded at onset of type 1 diabetes and kill beta-cells. Diabetes 61: 1752–1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Unger WW, Pearson T, Abreu JR, Laban S, van der Slik AR, der Kracht SM, Kester MG, Serreze DV, Shultz LD, Griffioen M, Drijfhout JW, Greiner DL, and Roep BO. 2012. Islet-specific CTL cloned from a type 1 diabetes patient cause beta-cell destruction after engraftment into HLA-A2 transgenic NOD/scid/IL2RG null mice. PLoS One 7: e49213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cardozo AK, Proost P, Gysemans C, Chen MC, Mathieu C, and Eizirik DL. 2003. IL-1beta and IFN-gamma induce the expression of diverse chemokines and IL-15 in human and rat pancreatic islet cells, and in islets from pre-diabetic NOD mice. Diabetologia 46: 255–266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cnop M, Welsh N, Jonas JC, Jorns A, Lenzen S, and Eizirik DL. 2005. Mechanisms of pancreatic beta-cell death in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: many differences, few similarities. Diabetes 54 Suppl 2: S97–107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Eizirik DL, and Darville MI. 2001. beta-cell apoptosis and defense mechanisms: lessons from type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 50 Suppl 1: S64–69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Rabinovitch A, and Suarez-Pinzon WL. 2007. Roles of cytokines in the pathogenesis and therapy of type 1 diabetes. Cell Biochem Biophys 48: 159–163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wenzlau JM, Juhl K, Yu L, Moua O, Sarkar SA, Gottlieb P, Rewers M, Eisenbarth GS, Jensen J, Davidson HW, and Hutton JC. 2007. The cation efflux transporter ZnT8 (Slc30A8) is a major autoantigen in human type 1 diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104: 17040–17045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Chimienti F, Devergnas S, Pattou F, Schuit F, Garcia-Cuenca R, Vandewalle B, Kerr-Conte J, Van Lommel L, Grunwald D, Favier A, and Seve M. 2006. In vivo expression and functional characterization of the zinc transporter ZnT8 in glucose-induced insulin secretion. J Cell Sci 119: 4199–4206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Enee E, Kratzer R, Arnoux JB, Barilleau E, Hamel Y, Marchi C, Beltrand J, Michaud B, Chatenoud L, Robert JJ, and van Endert P. 2012. ZnT8 is a major CD8+ T cell-recognized autoantigen in pediatric type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 61: 1779–1784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Bandres E, Merino J, Vazquez B, Inoges S, Moreno C, Subira ML, and Sanchez-Ibarrola A. 2000. The increase of IFN-gamma production through aging correlates with the expanded CD8(+high)CD28(−)CD57(+) subpopulation. Clin Immunol 96: 230–235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.