Abstract
Significance.
Visual performance with wavefront-guided (WFG) contact lenses has only been reported immediately after manufacture without time for habituation, and comparison has only been made with clinically unrefined predicate conventional lenses. We present comparisons of habitual corrections, best conventional scleral lenses, and WFG scleral lenses after habituation to all corrections.
Purpose.
To compare, in a cross-over design, optical and visual performance of eyes with corneal ectasias wearing dispensed best conventional scleral lens corrections and dispensed individualized WFG scleral lens corrections.
Methods.
Ten subjects (20 eyes) participated in a randomized cross-over study where best conventional scleral lenses and WFG scleral lenses (customized through the 5th radial order) were worn for eight weeks each. These corrections, as well as each subject’s habitual correction and normative data for normal eyes, were compared using (1) residual higher-order aberrations (HORMS), (2) visual acuity (VA), (3) letter contrast sensitivity (CS), and (4) visual image quality (logVSX). Correlations were performed between Pentacam biometric measures and gains provided by WFG lenses.
Results.
Mean HORMS reduced 48% from habitual to conventional, and 43% from conventional to WFG. Mean logMAR VA improved from habitual (+0.12) to conventional (−0.03) and further with WFG (−0.09); six eyes gained >1 line with WFG over conventional. Area under CS curve improved 26% from habitual to conventional and 14% from conventional to WFG. Eyes achieving normal levels: HORMS: conventional 40%, WFG 85%; VA: conventional 50%, WFG 85%; CS: conventional 60%, WFG 90%. LogVSX improved 16% from habitual to conventional and 25% further with WFG. Reduction in aberrations with WFG lenses best correlated with posterior cornea radius of curvature.
Conclusions.
Visual performance was superior to that reported with non-habituated WFG lens wear; with WFG lenses HORMS and logVSX significantly improved, allowing more eyes to reach normal levels of optical and visual performance than with conventional lenses.
Keywords: corneal ectasia, scleral lens, wavefront aberration, wavefront-guided corrections, visual performance
Decreased visual performance in corneal ectasias such as keratoconus is predominantly optical in origin, typically resulting from bilaterally-asymmetric elevated higher-order aberrations caused by the rotationally-asymmetric irregular profiles of anterior and posterior corneal surfaces.1–3 Onset of most ectatic conditions is during adolescence and these individuals usually experience normal visual stimulation throughout critical periods of development and undergo typical neural development. Hence, if the aberrated optics of these eyes can be appropriately corrected, normal levels of visual performance are expected to recover after habituation to the improved retinal image.
Current standards of care for corneal ectasias are rigid corneal or scleral lenses, which partially mask anterior cornea irregularities through approximate refractive index matching of the post-lens tear film and cornea, and by providing a new optically well-formed first surface for the eye. Those refractive indices are, however, not perfectly matched and residual anterior corneal surface aberrations remain, as do aberrations from the irregular posterior corneal surface1–3 which cannot be masked by rigid contact lenses.
Wavefront-guided contact lens technology is designed to specifically target the unique aberrations of individual eyes, particularly the elevated levels of residual aberrations experienced by highly aberrated eyes wearing conventional contact lenses.2,4–6
While customized wavefront-guided contact lenses have been manufactured and demonstrated with varying levels of efficacy in laboratory settings,7–16 and studied using simulations and theoretical modelling,17–25 those studies that measured visual performance with these lenses7–16 did so immediately after manufacturing and fitting the lenses without allowing time for the visual systems of the wearers to habituate to the new percept.
Previous studies compared wavefront-guided lenses with habitual or conventional lenses that served as predicate stepping-stones (for wavefront-guided lenses) and were not necessarily clinically optimized in terms of their fit and optics.10–12,14,16 In some studies, sphero-cylindrical components of the wavefront-guided lenses have been corrected using spectacle trial lenses before evaluating visual performance11,14,15 and, consequently, lenses were not dispensed.
Allowing the visual system time to adapt is common clinical practice when dispensing progressive addition lenses, large changes in prescriptions, high cylinders, or after ocular surgery. Likewise, when highly aberrated eyes are acutely corrected (without providing time for adaptation) with adaptive optics, visual performance is improved, but not to normal levels,26 and further gains are only achieved after habituation or training.27
Given that the visual system is adapted to its habitual aberration structure,26,28 and given the considerable reduction in aberration magnitude imparted by wavefront-guided lenses (in this study and others14,16) along with the reversal2,3 in key aberrations (such as coma) associated with directional blur, patients should habituate to the corrections before visual performance is evaluated. While visual performance reported with wavefront-guided lenses has been improved, we postulate it has hitherto remained worse than normal (despite reduced levels of aberration12–14,16,29) due to insufficient habituation time and / or the interaction of residual aberrations being detrimental to visual image quality.
As wavefront-guided technology becomes more accessible, it is important to present controlled comparisons of state of the art wavefront-guided scleral lenses with the best conventional scleral lenses prescribed in practice. In fact, first achieving clinically typical performance with best conventional scleral lenses is an essential prerequisite in appreciating any real gains in performance provided by wavefront-guided lenses and in identifying which eyes would benefit most from wavefront-guided lenses over conventional lenses.
Therefore, this paper presents comparison of three corrections: (1) the subject’s habitual correction, (2) a best conventional scleral lens, (3) and a best individualized wavefront-guided scleral lens, after lenses were dispensed and worn as part of daily life by eyes with corneal ectasias, which allowed approximately eight weeks of habituation to each new correction in a cross-over manner. This comparison is presented in terms of (1) residual higher-order root mean square (RMS) wavefront error, (2) high contrast visual acuity, (3) letter contrast sensitivity, and (4) the visual image quality metric logVSX (the logarithm of the visual Strehl ratio). Correlations between ocular biometric measures and the reduction in higher-order aberrations provided by the wavefront-guided lenses over conventional lenses are examined.
METHODS
This research adhered to the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Prior to data collection, the nature and potential consequences of the study were explained to each subject and University of Houston Institutional Review Board approved informed consent was signed.
Subjects
Ten subjects (nine male, one female) with corneal ectasia were recruited; nine were diagnosed with bilateral keratoconus and one with bilateral pellucid marginal degeneration. These conditions characteristically present with bilaterally-asymmetric disease severities,4,30 and the ectasias of some fellow eyes were quite mild (these eyes stood to benefit less from wavefront-guided lenses than more severe ectasias). Nonetheless, both eyes of each subject (20 eyes) were included because each eye presented unique optical and fitting challenges. Appropriate statistical methods31,32 (see Results) were used to account for any dependency between right and left eyes of each individual.
Table 1 classifies the severity of the subjects in terms of the ABCD Keratoconus Grading System,33 which incorporates anterior (“A”) and posterior (“B”) corneal radii of curvature and thinnest pachymetry (“C”), all determined by Topometric KC Staging software on the Pentacam HR (Oculus Inc., Arlington WA), as well as best-corrected distance VA (“D”). Grading ranges from 0 (normal) to 4 (most severe).
Table 1.
Severity of ectasia according the ABCD system42 of the right and left eyes of each subject, where stage 0 is least severe and stage 4 is most severe. Dimensions: A: anterior radius of curvature; B: posterior radius of curvature; C: thinnest pachymetry; D: best corrected distance vision with each correction.
| S 01 | S 02 | S 03 | S 04 | S 05 | S 06 | S 07 | S 08 | S 09 | S 10 | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimension | R | L | R | L | R | L | R | L | R | L | R | L | R | L | R | L | R | L | R | L |
| A: | 1 | 0 | 4 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| B: | 2 | 2 | 4 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 0 | 2 |
| C: | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| D (habitual): | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| D (conventional): | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| D(wavefront): | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Five subjects used spectacles for the habitual correction measurements; three used contact lenses on both eyes (two wore scleral lenses, one wore hybrid lenses); one used a toric soft lens on one eye and was unaided in the other; and one subject performed the habitual correction measurements unaided. Mean (± SD) age of the subjects was 34.4 ±11.1 years (range: 24 to 55). Inclusion criteria: no corneal scarring over the central 7 mm of the pupil and unremarkable systemic and other ocular health.
Performance Measures
Performance measures were recorded monocularly.
Higher-order Root Mean Square Wavefront Error
Three wavefront error measurements recorded using a COAS HD wavefront sensor (Johnson and Johnson Vision, Santa Ana CA) and described by a 10th radial order normalized Zernike polynomial fit, were averaged over a common dilated pupil size.
High contrast Visual Acuity
High contrast visual acuity was measured in a darkened room and calculated with per-letter scoring, terminating after five missed letters, as the mean of three unique ETDRS logMAR charts displayed with –100% Weber contrast (Display++ monitor; Cambridge Research Systems, Kent UK) and background luminance of 116 cd/m2 (Minolta LS-110, Konica Minolta, Ramsey, NJ).
Letter Contrast Sensitivity
Using the same monitor and darkened room, letter contrast sensitivity was measured using letter sizes having fundamental-spatial frequencies of 4, 8, and 16 cycles per degree (20/150, 20/75, and 20/37.5 respectively) and area under the log contrast sensitivity function curve34 was calculated. For each letter size, contrast threshold was estimated to the nearest 0.2 log unit, after which three measures of contrast threshold were determined using rows of unique Sloan letters that began at a contrast level 0.4 log units above the initial estimate and reduced in steps of 0.1 log units per line until five letters were missed.
The Logarithm of the Visual Strehl Ratio (logVSX)
Visual image quality was quantified using logVSX,35 a single value metric combining comprehensive description of the optics (here, wavefront error of an eye wearing a correction) with a measure of the neural processing of the visual system. LogVSX has been shown predictive of subjective best focus,35,36 and able to identify spectacle prescriptions equivalent to subjective refraction.37 Change in logVSX has been well correlated with change in logMAR visual acuity.38,39
VSX ranges from 0 (worst) to 1 (best). The (base 10) logarithm of 1 is 0, thus, the closer the value of logVSX to 0 (the less negative the value), the better the visual image quality. LogVSX was calculated from mean wavefront error (of the corrected eyes) over 5 mm pupil diameters.
Study Format and Lens Designs
The study protocol began with measurement of the four outcomes using the habitual correction. Thereafter, fitting (but not necessarily dispensing) of conventional scleral lenses commenced, which involved adjusting the designs of the lenses to provide healthy, comfortable fits that were rotationally and translationally stable, and to refine sphere, cylinder, and axis.
The macro design of the conventional and wavefront-guided scleral lenses is described in detail elsewhere.16 Briefly, lenses were manufactured at the Visual Optics Institute, University of Houston, College of Optometry, using a DAC 2X-ALM OTT ophthalmic lens lathe (DAC International, Carpinteria, CA) and Boston XO material (Bausch + Lomb, Rochester, NY). Overall diameter ranged from 17 to 18.1 mm. The front surface was aspheric, designed to render the lens free of spherical aberration when on the eye and included a 10 mm central optic zone. The posterior surface contained six curves; the fifth curve was a toric annulus designed to impart rotational stability.40,41
After allowing 30 minutes for settling on the eye, lens engravings were monitored to quantify lens rotation and the orientation of the peripheral toric annulus was adjusted in subsequent lens designs to compensate for the observed rotation.16,41 When a stable and correctly-oriented lens with a clinically acceptable fit was achieved, the location of the pupil center relative to the geometric center of the lens was measured such that the wavefront-guided prescription could be offset in opposite xy-directions relative to the lens center to compensate. Most scleral lenses rested inferior and temporal relative to the center of the pupil14 and, consequently, most wavefront-guided prescriptions were offset superior and nasal relative to the lens center (Figure 1). Thresholds for tolerable lens movements are inversely proportional to the magnitudes of wavefront-guided prescriptions,17,18,22,24,25 and therefore varied across the range of ectasia severities included here.
Figure 1.
(A) Scleral lens positioned inferiorly and temporally with a small amount of anti-clockwise rotation on a left eye. (B) Distribution of xy-offsets of wavefront-guided prescriptions (relative to the geometric lens center (0,0)) to compensate for lens displacement. Offset of the wavefront-guided prescription compensates for lens misalignment and positions the prescription over the center of the pupil, while observed rotation is corrected by rotation of a peripheral posterior toric curve.
Wavefront-guided lenses were designed using the macro parameters of the stable conventional lens. Residual wavefront error was measured through the stable lens after dilation (one drop 1% tropicamide, one drop 2.5% phenylephrine), and an offset wavefront-guided prescription targeting residual aberrations up to the fifth Zernike radial order42 was imparted into the anterior lens surface.
Median diameter of the wavefront-guided prescription was 8 mm (mean 7.84 mm); this was limited on the low end by the maximum dilated pupil size, and the wavefront error measurements for eyes with larger pupils were scaled43 down to 8 mm.
At this point, a cross-over study design was initiated where each subject wore a best conventional scleral lens daily for approximately eight weeks and a wavefront-guided scleral lens daily for an additional eight weeks. This provided an opportunity for the visual system of each subject to habituate to the retinal image formed by each lens in their everyday environment, and follow-up visits provided opportunities (if needed) for refinement of the optics and the fit of each lens (which necessitated manufacture of new lenses). Subjects generally conformed to the eight week time period; some subjects wore a lens type for slightly longer, for example, due to travel or work obligations, illness, or natural disaster (hurricane Harvey). The order of lens wear was randomized; three subjects wore conventional lenses first and seven wore wavefront-guided lenses first. Some subjects that wore the wavefront-guided lenses first, expressed such substantial unhappiness during the conventional lens (second) part of the cross-over that we will re-evaluate this randomization during future studies. One subject did not complete the conventional lens part of the cross-over, but still wore the wavefront-guided lens for eight weeks.
At the final visit with each lens, visual acuity and contrast sensitivity were measured with the lenses through natural pupils, and residual wavefront error was measured over dilated pupils.
RESULTS
Both statistical and clinical significance are considered. All standard deviations were calculated using ANOVA and components of variance analyses to account for any dependence of right and left eyes.31,32 Similarly, p-values were calculated using split-plot ANOVAs.31,32 Plots for individual eyes use lines to track each eye across the three (categorical) corrections and any given eye is consistently represented by the same color, symbol, and line across all four outcomes. The best conventional lens for 18 eyes was spherical and for two eyes was sphero-cylindrical.
Higher-order Root Mean Square Wavefront Error
Higher-order RMS results were scaled43 to a 5 mm pupil diameter to better agree with habitual physiological pupil sizes and pupil sizes during visual acuity and contrast sensitivity measures, and are presented up to the 6th radial order.
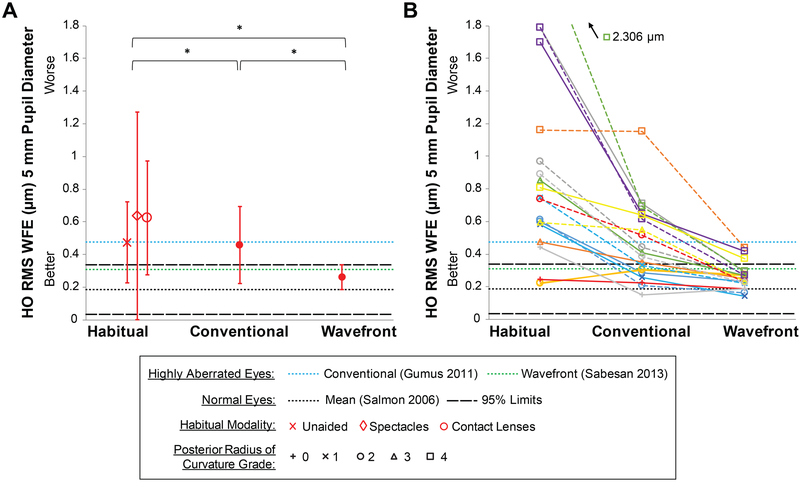
Mean ±SD higher-order RMS wavefront error decreased from the habitual correction (0.886 ±0.589 μm, mean across modalities) to conventional lenses (0.458 ±0.238 μm), and further decreased to within normal limits with wavefront-guided lenses (0.260 ±0.077 μm) (Figure 2). These represent statistically significant reductions of 48% (P = .02) from habitual to conventional, 43% (P = .004) from conventional to wavefront-guided, and 71% (P = .001) from habitual to wavefront-guided. Note the reduction in variability with wavefront-guided lenses.
Figure 2.
Higher-order root mean square (HO RMS) wavefront error (WFE) across the three corrections for (A) the mean of all eyes and (B) all individual eyes. Error bars are one standard deviation. In (B) two eyes of a subject are plotted in the same color; right eyes solid; left eyes dashed; symbols indicate severity grade of posterior radius of curvature.33 The 95% limits for normal eyes (Salmon and van de Pol44) are plotted as well as mean levels for eyes with keratoconus wearing conventional scleral lenses (Gumus et al.6) and wavefront-guided scleral lenses (Sabesan et al.14). Study data is scaled43 in the Discussion for comprehensive comparison with literature; here available data for contact lens related norms have been approximated to a common 5mm using the ratio of pupil sizes.
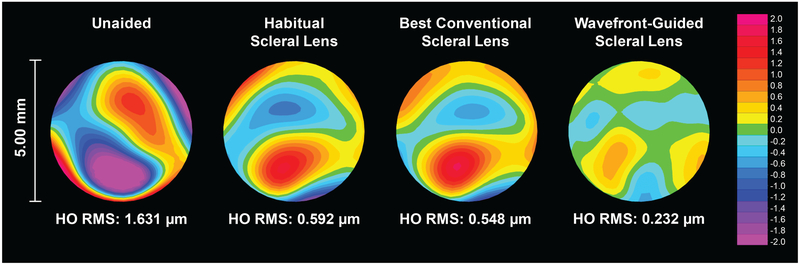
The unique reduction in higher-order RMS wavefront error for each eye may be better appreciated as the percentage of eyes within age-matched normal (normal eye)44 limits: 15% of eyes were within normal limits wearing the habitual correction; 40% with best conventional scleral lenses; and 85% with wavefront-guided lenses. A representative example of higher-order wavefront error maps (across unaided and the three corrections) for one subject with moderate keratoconus is shown in Figure 3.
Figure 3.
Higher order wavefront error maps for the left eye (corresponding to the dashed yellow line in Figure 2B) of a 33 year old male subject with moderate keratoconus.
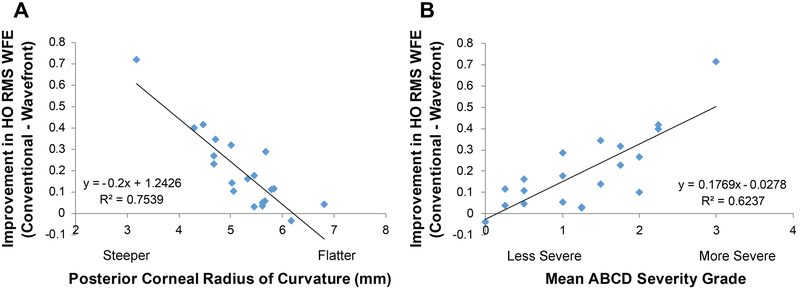
Reduction in higher-order aberrations by wavefront-guided lenses over conventional lenses was best correlated (Figure 4) with posterior corneal radius of curvature (dimension “B”)33 (R2 = 0.75) followed by the mean severity grading (averaging across dimensions ABC and D for the conventional lens) (R2 = 0.62).
Figure 4.
Biometric measures that correlated best with improvement in higher-order root mean square (HO RMS) wavefront error (WFE) from best conventional lenses to wavefront-guided lenses were (A) posterior corneal radius of curvature and (B) mean severity of ectasia33 (average across severity dimensions “A” anterior corneal radius of curvature, “B” posterior corneal radius of curvature, “C” thinnest pachymetry (all measured with a Pentacam), and “D” distance visual acuity with the best conventional lens).
Visual Acuity
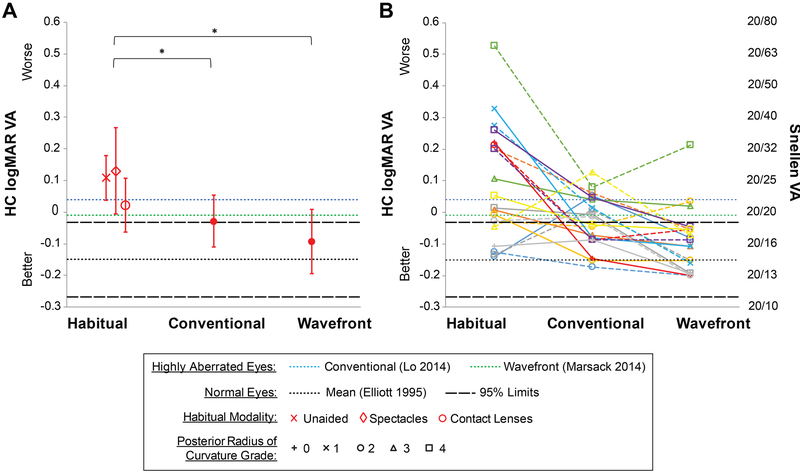
Mean ±SD logMAR visual acuity improved from the habitual correction (+0.09 ±0.18, mean across modalities) to conventional lenses (−0.03 ±0.09), and improved further with wavefront-guided lenses (−0.09 ±0.10) (Figure 5). Disease severity dimension “D” (best corrected distance visual acuity) thus varies dependent on which correction (habitual, conventional, wavefront-guided) is used; for example, subjects in each severity grade of “D” (0:1:2:3:4) were 8:10:2:0:0 with habitual, 12:8:0:0:0 with conventional, and 17:3:0:0:0 with wavefront-guided corrections.
Figure 5.
High contrast (HC) logMAR visual acuity (VA) across the three corrections for (A) the mean of all eyes and (B) all individual eyes. Error bars are one standard deviation. In (B) two eyes of a subject are plotted in the same color; right eyes solid; left eyes dashed; symbols indicate severity grade of posterior radius of curvature.33 Age-matched 95% limits for normal eyes (Elliott et al.45) are plotted as well as levels for eyes with keratoconus wearing conventional (Lo et al.47) and wavefront-guided scleral lenses (Marsack et al.16).
Mean improvements from habitual to conventional and from habitual to wavefront-guided were statistically significant (P = .048 and P = .007 respectively). Mean improvement from conventional to wavefront-guided was not (P = .07), however, from an individual perspective, six eyes showed clinically significant improvements of greater than one line of logMAR visual acuity and substantially more eyes reached normal45 levels: habitual correction 25%; conventional lenses 50%; wavefront-guided lenses 85%.
Letter Contrast Sensitivity
At each fundamental spatial frequency, the majority of eyes improved in letter contrast sensitivity from the habitual correction to conventional scleral lenses, and improved further with wavefront-guided lenses.
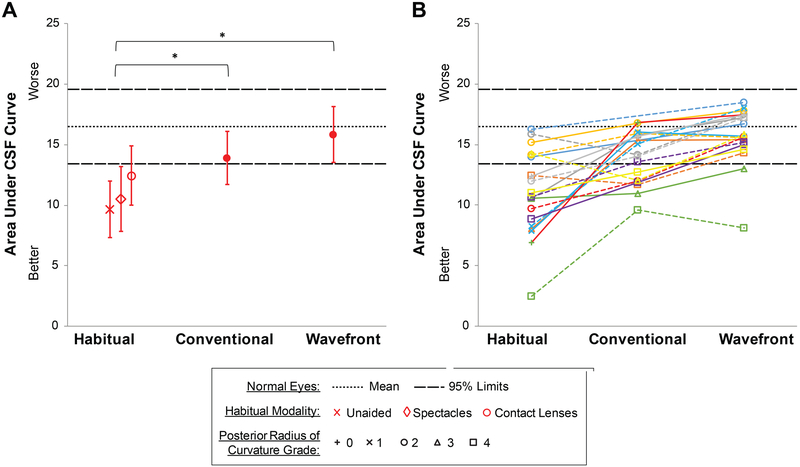
Mean ±SD area under the log contrast sensitivity function34 (Figure 6) improved from the habitual correction (11.07 ±3.48, mean across modalities) to conventional lenses (13.91 ±2.20), and improved further with wavefront-guided lenses (15.82 ±2.34). These correspond to significant gains of 26% (P = .009) from habitual to conventional and 43% (P < .001) from habitual to wavefront-guided. The 14% gain from conventional to wavefront-guided was not significant (P = .09). Eyes within normal limits: habitual correction 30%; conventional lenses 60%; wavefront-guided lenses 90%.
Figure 6.
Area under the log contrast sensitivity function (CSF) across the three corrections for (A) the mean of all eyes and (B) all individual eyes. Error bars are one standard deviation. In (B) two eyes of a subject are plotted in the same color; right eyes solid; left eyes dashed; symbols indicate severity grade of posterior radius of curvature.33 Age-matched 95% limits for normal eyes were measured on the same instrument system.
The Visual Image Quality Metric logVSX (The Visual Strehl Ratio)
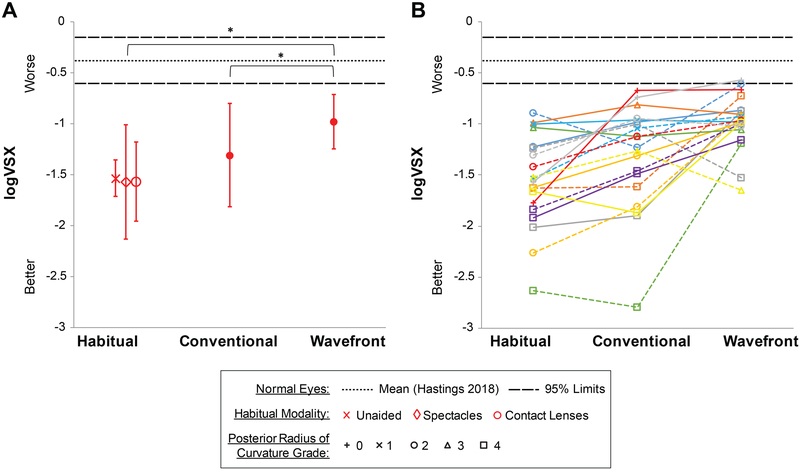
A similar pattern of gains was found for logVSX (Figure 7): mean ±SD metric value improved from the habitual correction (−1.55 ±0.48, mean across modalities) to conventional lenses (−1.31 ±0.51), and improved further with wavefront-guided lenses (−0.98 ±0.27). Wavefront-guided lenses provided 37% and 25% statistically significant (P < .0001 and P = .019 respectively) better visual image quality than the habitual and conventional corrections. The 16% improvement from habitual to conventional was not significant (P = .11). While the pattern of results for logVSX agrees with the other outcomes and best visual image quality was provided by the wavefront-guided lenses, the majority (18) of eyes did not reach the high logVSX levels theoretically obtained by objectively best-correcting normal eyes.46
Figure 7.
Visual image quality metric logVSX (the visual Strehl ratio) across the three corrections for (A) the mean of all eyes (B) all individual eyes. Error bars are one standard deviation. In (B) two eyes of a subject are plotted in the same color; right eyes solid; left eyes dashed; symbols indicate severity grade of posterior radius of curvature.33 Age-matched 95% limits are for objectively best-corrected normal eyes (Hastings et al.46).
DISCUSSION
This study sought to determine the benefit of transferring individuals with corneal ectasia from their habitual correction to best conventional scleral lenses and to personalized wavefront-guided lenses by dispensing each type of lens and allowing approximately eight weeks of habituation to the retinal image formed by each.
Best Conventional Scleral Lenses
Achieving equivalent, or better than, clinically representative performance with best conventional scleral lenses is an essential prerequisite in appreciating any gains in performance provided by wavefront-guided lenses.
Mean residual levels of higher-order RMS wavefront error with best conventional lenses (0.30 μm over a 4 mm pupil; 0.46 μm over 5mm; 0.58 μm over 6mm) were equivalent to, or better than, reports of highly aberrated eyes wearing conventional scleral lenses6,14,16 or corneal rigid gas permeable lenses.2,4,5 Similarly, best conventional scleral lenses provided mean visual acuity (−0.03) better than or equivalent to reports of highly aberrated eyes wearing conventional scleral lenses47 or corneal rigid gas permeable lenses.48 Despite differences in methodology discussed below, letter contrast sensitivity with the best conventional scleral lenses was also equivalent to that of highly aberrated eyes wearing corneal rigid gas permeable lenses.49 In this study, the magnitudes and distributions of residual higher-order aberrations, through best conventional lenses, interacted such that all eyes remained outside the objectively optimized logVSX levels of best-corrected normal eyes.46
Comparison of Wavefront-guided lenses with other Studies
Comparisons are made with (1) attempts to correct measured aberrations of real eyes and (2) benchmark modalities of clinical practice.
Higher-order Root Mean Square Wavefront Error
Mean higher-order RMS levels with wavefront-guided lenses reported here (0.19 μm over a 4 mm diameter pupil; 0.26 μm over 5mm; 0.33 μm over 6mm) are statistically equivalent to previous reports of wavefront-guided scleral lenses,14,16 significantly better than reports of wavefront-guided soft lenses,10,11,13 better than that of conventional scleral lenses in this study and others,6,14,16 and better than reports of highly aberrated eyes wearing corneal rigid gas permeable lenses.2,4,5
Visual Acuity
Visual acuity is a variable subjective quantity50 that can be relatively insensitive to visual blur,51 which could have contributed to lack of significance in gain between best conventional and wavefront-guided lenses. Nonetheless, mean logMAR visual acuity with wavefront-guided lenses in this study (−0.09) is clinically equivalent or better than other reports of scleral wavefront-guided lenses,14,16 better than wavefront-guided soft lenses,7,13,15 better than that conventional scleral lenses in this study and elsewhere,47 and better than reports of highly aberrated eyes wearing corneal rigid gas permeable lenses.48 These differences may be due to habituation.
Letter Contrast Sensitivity
Letter contrast sensitivity was compared with performance of well-corrected normal eyes on the same instrument system. Firstly, because common letter contrast sensitivity charts52 typically only test one low spatial frequency (1 to 2 cycles per degree). Secondly, contrast sensitivity with wavefront-guided lenses7,14 or corneal rigid gas permeable lenses,49 has been studied using sine-wave gratings. While the fundamental frequencies of letter and sine-wave stimuli can be equivalent, sine-wave gratings are insensitive to phase errors present in normal53 – and amplified in highly aberrated – eyes54 that can affect visual perception.55
Sabesan et al.14 presented change in contrast sensitivity with wavefront-guided lenses as a multiple of contrast sensitivity with conventional lenses. This can be bias the performance of the wavefront-guided lenses because the conventional lenses were unrefined predicate lenses, as has been common practice.10–12,16 Overall, we found an opposite pattern of contrast sensitivity results in that performance with wavefront-guided lenses in this study gained more at higher spatial frequencies than at lower spatial frequencies. Comparing with their Figure 5, mean log contrast sensitivity reported here was equivalent for 4 cycles per degree (1.64 ±0.14); significantly better for 8 cycles per degree (1.41 ±0.19); and mean log contrast sensitivity reported here for 16 cycles per degree (1.01 ±0.25) was significantly better than at the highest spatial frequency (12 cycles per degree) they reported. These differences may be due to habituation.
The Visual Image Quality Metric (logVSX)
Wavefront-guided lenses were designed to correct measured residual aberrations from the second through fifth radial orders. Although the total magnitude (RMS) of higher-order aberrations was reduced to within normal levels for 85% of eyes, the distribution and magnitude of individual aberration terms residual through the wavefront-guided lenses interacted visually such that logVSX for the majority of eyes did not reach the objectively optimized levels of best-corrected normal eyes.46 Considering, the realistic variability of subjective refraction, 14 eyes reached the logVSX limits (−0.580 ±0.239; 5 mm pupil diameter) calculated from the typical subjective refraction of 200 young normal eyes.56
This indicates that further improvement in visual quality is possible as wavefront-guided corrections continue to be improved and might involve, for example, targeting particular aberrations such that the residual distributions of higher-order aberrations better resemble those of normal eyes.
Who Will Benefit Most from Wavefront-guided Lenses?
Health care is evolving towards personalized treatments tailored to the individual needs of each specific patient. Wavefront-guided contact lenses are serving as an ophthalmic application of such individualized medicine for corneal ectasias. However, the investments of time, technology, and cost involved in fitting wavefront-guided products are greater than conventional corrections, making them more comparable to prosthetic devices. Although the choice of corrections is influenced by the visual quality expectations of an individual in addition to the investments of time and money, it is desirable – perhaps even ethically necessary – to estimate the benefits that an individual could gain from wavefront-guided lenses over conventional scleral lenses. This is pertinent given that we are in the infancy of the clinical translation of wavefront-guided lenses, which will become more widely accessible, further improved, and an option for certain individuals with normal eyes wishing to reduce higher-order aberrations.
Residual higher-order RMS wavefront error through best conventional scleral lenses best predicted (R2 = 0.94) the additional reduction in higher-order aberrations achieved by wavefront-guided lenses over conventional lenses. This is not surprising because wavefront-guided lenses were designed to specifically target residual higher-order RMS wavefront error. Estimating a patient’s potential gains using residual higher-order RMS wavefront error through a conventional lens is reasonable because a best conventional lens is a prerequisite for a wavefront-guided lens. However, as visual processing is better understood and visual image quality metrics better developed, it is likely that the field should strive to optimize these metrics as opposed to simplistically targeting a reduction in aberration terms.
Of the biometric measures, posterior corneal radius of curvature best correlated (R2 = 0.75) with the reduction in higher-order aberrations provided by wavefront-guided lenses, followed by mean disease severity (averaging grading dimensions A, B, C, and D for the conventional lens) (R2 = 0.62), both of which can be evaluated with Pentacam software (Oculus Inc., Arlington WA).
Based on posterior corneal radius of curvature, the present sample of eyes could be divided into: (1) those of severity grades 0 and 1 (>5.7 mm) and (2) those of severity grades 2, 3, and 4 (<5.7 mm). Seventy-five percent of eyes in the first group were within normal levels of higher-order RMS wavefront error with a best conventional lens, compared with 31% of eyes in the second group. Eyes in the first group experienced a mean reduction of 0.057 μm in higher-order RMS wavefront error (5 mm pupil) with the wavefront-guided lens over the conventional, while a mean reduction of 0.233 μm was experienced by the second group. A greater sample of eyes is needed before this threshold criterion could be confidently advocated.
If these insights were followed, some eyes fit with wavefront-guided lenses in this study would not be fit in practice – these eyes experienced smaller gains with the wavefront-guided lenses. Both eyes of each subject were fit here by experimental design to gain insights into who would benefit most. Given the bilateral-asymmetry that characterizes corneal ectasias and the current state of wavefront-guided lenses, these individuals might currently be well served wearing a wavefront-guided lens on their more severe eye and a conventional lens on the less severe eye.
Predicting the individual benefit in this way only considers the unique optical challenges presented by each eye but neglects the many traditional challenges of scleral lens fitting; both sets of challenges need to be resolved for the successful fitting of wavefront-guided lenses. In this study, as is true of clinical practice, the challenges of fitting a stable scleral lens were sometimes significant. In contrast, the incorporation of the wavefront-guided correction was relatively easy (requiring an additional two to three visits) once a stable well-fitting conventional scleral lens was achieved. Identifying individuals that stand to benefit from wavefront-guided lenses is important because the eyes in this study that experienced substantial gains, reported the investment of time to fit wavefront-guided lenses as worthwhile, and described the gains in visual performance and quality as life-changing.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Funded by the National Institutes of Health/National Eye Institute: NIH/NEI R01EY019105; NIH/NEI R01EY008520; NIH/NEI P30EY07551.
The authors thank Drs. Katrina Parker, Maria Walker, Anita Ticak, Amber Gaume Giannoni, Eric Ritchey, Anna-Kaye Logan, Tiffany Chen, Sheila Morrison, Jan Bergmanson, Judith Perrigin, and Norman Leach of the University Eye Institute at the University of Houston College of Optometry; Drs Ayeswarya Ravikumar and Yue Shi; Dr Larry Thibos and Hope Queener for contributions to the visual image quality metric-, contact lens design-, and statistics-software, and Kimberly Thompson for assistance with figures.
Portions of these findings were presented at the International Society for Contact Lens Research (ISCLR) 2017 meeting in Stevenson OR, the Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO) 2018 meeting in Honolulu HI, and the International Society of Contact Lens Specialists (ISCLS) 2018 meeting in Washington DC.
Contributor Information
Gareth D. Hastings, Visual Optics Institute, College of Optometry, University of Houston, Houston, Texas.
Raymond A. Applegate, Visual Optics Institute, College of Optometry, University of Houston, Houston, Texas.
Lan Chi Nguyen, Visual Optics Institute, College of Optometry, University of Houston, Houston, Texas.
Matthew J. Kauffman, Visual Optics Institute, College of Optometry, University of Houston, Houston, Texas.
Roxana T. Hemmati, Visual Optics Institute, College of Optometry, University of Houston, Houston, Texas; Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, Texas.
Jason D. Marsack, Visual Optics Institute, College of Optometry, University of Houston, Houston, Texas.
REFERENCES
- 1.Tomidokoro A, Oshika T, Amano S, Higaki S, et al. Changes in Anterior and Posterior Corneal Curvatures in Keratoconus. Ophthalmology 2000;107:1328–32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Choi J, Wee W, Lee J, Kim M. Changes of Ocular Higher Order Aberration in On-and Off-eye of Rigid Gas Permeable Contact Lenses. Optom Vis Sci 2007;84:42–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen M, Yoon G. Posterior Corneal Aberrations and their Compensation Effects on Anterior Corneal Aberrations in Keratoconic Wyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2008;49:5645–52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kosaki R, Maeda N, Bessho K, Hori Y, et al. Magnitude and Orientation of Zernike Terms in Patients with Keratoconus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2007;48:3062–68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Negishi K, Kumanomido T, Utsumi Y, Tsubota K. Effect of Higher-order Aberrations on Visual Function in Keratoconic Eyes with a Rigid Gas Permeable Contact Lens. Am J Ophthalmol 2007;144:924–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gumus K, Gire A, Pflugfelder S. The Impact of the Boston Ocular Surface Prosthesis on Wavefront Higher-order Aberrations. Am J Ophthalmol 2011;151:682–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.López-Gil N, Chateau N, Castejón-Monchón J, Artal P, et al. Correcting Ocular Aberrations by Soft Contact Lenses. S Afr Optom 2003;62:173–7. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jeong T, Yoon G. Customized Correction of Wavefront Aberrations in Abnormal Human Eyes by using a Phase Plate and a Customized Contact Lens. J Korean Phys Soc 2006;49:121–5. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chen M, Sabesan R, Ahmad K, Yoon G. Correcting Anterior Corneal Aberration and Variability of Lens Movements in Keratoconic Eyes with Back-surface Customized Soft Contact Lenses. Opt Lett 2007;32:3203–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Marsack JD, Parker KE, Niu Y, Pesudovs K, et al. On-Eye Performance of Custom Wavefront-Guided Soft Contact Lenses in a Habitual Soft Lens-wearing Keratoconic Patient. J Refract Surg 2007;23:960–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sabesan R, Jeong T, Carvalho L, Cox I, et al. Vision Improvement by Correcting Higher-Order Aberrations with Customized Soft Contact Lenses in Keratoconic Eyes. Opt Lett 2007;32:1000–2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Marsack JD, Parker KE, Applegate RA. Performance of Wavefront-guided Soft Lenses in Three Keratoconus Subjects. Optom Vis Sci 2008;85:E1172–8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Katsoulos C, Karageorgiadis L, Vasileiou N, Mousafeiropoulos T, et al. Customized Hydrogel Contact Lenses for Keratoconus Incorporating Correction for Vertical Coma Aberration. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2009;29:321–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sabesan R, Johns L, Tomashevskaya O, Jacobs D, et al. Wavefront-guided Scleral Lens Prosthetic Device for Keratoconus. Optom Vis Sci 2013;90:314–23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jinabhai A, O’Donnell C, Tromans C, Radhakrishnan H. Optical Quality and Visual Performance with Customised Soft Contact Lenses for Keratoconus. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2014;34:528–39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Marsack JD, Ravikumar A, Nguyen LC, Ticak A, et al. Wavefront-guided Scleral Lens Correction in Keratoconus. Optom Vis Sci 2014;91:1221–30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Guirao A, Williams D, Cox I. Effect of Rotation and Translation on the Expected Benefit of an Ideal Method to Correct the Eye’s Higher-order Aberrations. J Opt Soc Am (A) 2001;18:1003–15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Guirao A, Cox I, Williams D. Method for Optimizing the Correction of the Eye’s Higher-order Aberrations in the Presence of Decentrations. J Opt Soc Am (A) 2002;19:126–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.De Brabander J, Chateau N, Marin G, Lopez-Gil N, et al. Simulated Optical Performance of Custom Wavefront Soft Contact Lenses for Keratoconus. Optom Vis Sci 2003;80:637–43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ho A Aberration Correction with Soft Contact Lens: Is the Postlens Tear Film Important? Eye Contact Lens 2003;29:S182–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Thibos LN, Cheng X, Bradley A. Design Principles and Limitations of Wavefront Guided Contact Lenses. Eye Contact Lens 2003;29:S167–70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.López-Gil N, Castejón-Mochón J, Fernández-Sánchez V. Limitations of the Ocular Wavefront Correction with Contact Lenses. Vision Res 2009;49:1729–37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Jinabhai A, Charman W, O’Donnell C, Radhakrishnan H. Optical Quality for Keratoconic Eyes with Conventional RGP Lens and Simulated, Customised Contact Lens Corrections: A Comparison: Simulating Customised Corrections for Keratoconus Patients. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2012;32:200–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shi Y, Queener HM, Marsack JD, Ravikumar A, et al. Optimizing Wavefront-guided Corrections for Highly Aberrated Eyes in the Presence of Registration Uncertainty. J Vis 2013;13:1–15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shi Y, Applegate RA, Wei X, Ravikumar A, et al. Registration Tolerance of a Custom Correction to Maintain Visual Acuity. Optom Vis Sci 2013;90:1370–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sabesan R, Yoon G. Visual Performance after Correcting Higher-order Aberrations in Keratoconic eyes. J Vis 2009;9:1–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sabesan R, Barbot A, Yoon G. Enhanced Neural Function in Highly Aberrated Eyes following Perceptual Learning with Adaptive Optics. Vision Res 2017;132:78–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Artal P, Chen L, Fernández E, Singer B, et al. Neural Compensation for the Eye’s Optical Aberrations. J Vis 2004;281–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sabesan R, Yoon G. Neural Compensation for Long-term Asymmetric Optical Blur to Improve Visual Performance in Keratoconic Eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2010;51:3835–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zadnik K, Steger-May K, Fink B, Joslin C, et al. Between-eye Asymmetry in Keratoconus. Cornea 2002;21:671–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Armstrong R, Eperjesi F, Gilmartin B. The Application of Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) to Different Experimental Designs in Optometry. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2002;22:248–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Armstrong R Statistical Guidelines for the Analysis of Data Obtained from One or Both Eyes. Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2013;33:7–14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Belin M, Duncan J, Ambrosio R Jr, Gomes J. Keratoconus: The ABCD Grading System. Int J Keratoconus Ectatic Corneal Dis 2015;4:85–93. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Applegate RA, Hilmantel G, Howland HC. Area under Log Contrast Sensitivity Function: A Concise Method of Following Changes in Visual Performance In: OSA Technical Digest Series. Vision Science and Its Applications, vol 1. St. Louis, MO: Optical Society of America; 1997;1:98–101. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Thibos L, Hong X, Bradley A, Applegate R. Accuracy and Precision of Objective Refraction from Wavefront Aberrations. J Vis 2004;4:329–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Cheng X, Bradley A, Thibos L. Predicting Subjective Judgment of Best Focus with Objective Image Quality Metrics. J Vis 2004;4:310–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hastings GD, Marsack JD, Nguyen LC, Cheng H, et al. Is an Objective Refraction Optimised using the Visual Strehl Ratio Better than a Subjective Refraction? Ophthalmic Physiol Opt 2017;37:317–25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Schoneveld P, Pesudovs K, Coster D. Predicting Visual Performance from Optical Quality Metrics in Keratoconus. Clin Exp Optom 2009;92:289–96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ravikumar A, Sarver E, Applegate R. Change in Visual Acuity is Highly Correlated with Change in Six Image Quality Metrics Independent of Wavefront Error and/or Pupil Diameter. J Vis 2012;12:1–13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Visser E, Visser R, Van Lier H. Advantages of Toric Scleral Lenses. Optom Vis Sci 2006;83:233–6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ticak A, Marsack J, Koenig D, Ravikumar A, et al. A Comparison of Three Methods to Increase Scleral Contact Lens On-Eye Stability: Eye Contact Lens 2015;41:386–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Marsack JD, Pesudovs K, Sarver E, Applegate RA. Impact of Zernike-fit Error on Simulated High- and Low-contrast Acuity in Keratoconus: Implications for Using Zernike-based Corrections. J Opt Soc Am (A) 2006;23:769–76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Schwiegerling J Scaling Zernike Expansion Coefficients to Different Pupil Sizes. J Opt Soc Am (A) 2002;19:1937–45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Salmon T, van de Pol C. Normal-Eye Zernike Coefficients and Root-mean-square Wavefront Errors. J Cataract Refract Surg 2006;32:2064–74. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Elliott D, Yang K, Whitaker D. Visual Acuity Changes throughout Adulthood in Normal, Healthy Eyes: Seeing Beyond 6/6. Optom Vis Sci 1995;72:186–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Hastings GD, Marsack JD, Thibos LN, Applegate RA. Normative Best-corrected Values of the Visual Image Quality Metric VSX as a Function of Age and Pupil Size. J Opt Soc Am (A) 2018;35:732–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Lo H, Yeh S, Cheng H. Scleral Contact Lenses for Visual Rehabilitation in Keratoconus and Irregular Astigmatism after Refractive Surgery. Taiwan J Ophthalmol 2014;4:73–6. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Schornack M, Patel S. Scleral Lenses in the Management of Keratoconus: Eye Contact Lens 2010;36:39–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yang B, Liang B, Liu L, Liao M, et al. Contrast Sensitivity Function after Correcting Residual Wavefront Aberrations during RGP Lens Wear. Optom Vis Sci 2014;91:1271–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Raasch T, Bailey I, Bullimore M. Repeatability of Visual Acuity Measurement. Optom Vis Sci 1998;75:342–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ravikumar A, Applegate R, Shi Y, Bedell H. Six Just-noticeable Differences in Retinal Image Quality in 1 Line of Visual Acuity: Toward Quantification of Happy versus Unhappy Patients with 20/20 Acuity. J Cataract Refract Surg 2011;37:1523–9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pelli D, Robson J, Wilkins A. The Design of a New Letter Chart for Measuring Contrast Sensitivity. Clin Vis Sci 1988;2:187–99. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Charman W, Walsh G. The Optical Phase Transfer Function of the Eye and the Perception of Spatial Phase. Vision Res 1985;25:619–23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Pantanelli S, MacRae S, Jeong T, Yoon G. Characterizing the Wave Aberration in Eyes with Keratoconus or Penetrating Keratoplasty Using a High-dynamic Range Wavefront Sensor. Ophthalmology 2007;114:2013–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Sarver E, Applegate R. The Importance of the Phase Transfer Function to Visual Function and Visual Quality Metrics. J Refract Surg 1995 2004;20:S504–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Thibos L, Hong X, Bradley A, Cheng X. Statistical Variation of Aberration Structure and Image Quality in a Normal Population of Healthy Eyes. J Opt Soc Am (A) 2002;19:2329–48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]