Description
A 30-year-old woman with a history of symptomatic Osgood-Schlatter disease (OSD) in childhood presented to her primary care physician with pain in her right knee, gradually worsening over the past 6 months. Until this period of persistent pain, the patient reported occasional intermittent right knee pain over the years that would self-resolve, precluding a doctor’s visit. The patient had sustained no trauma to the knee. She was a former collegiate athlete and participated in vigorous exercise on a daily basis, to include running, weight-lifting and plyometric activities. Conservative therapy, to include rest, activity modification, ice and anti-inflammatory medications, had not relieved the pain.
On exam there was significant bony prominence over the tibial tuberosity on the right knee, absent on the left. There was no swelling, effusion or atrophy of surrounding muscles. The patella tendon continued to track midline without lateral or medial translation. Crepitus of the patella was observed with extension and flexion. Tenderness to palpation over the tibial tuberosity was noted, absent elsewhere. Full range of motion was intact. There was no pain with seated passive or active range of motion, however a sharp pain over the tibial tuberosity was noted with squatting.
Plain films were obtained which were notable for diffuse bony ossicles from fragmentation of the apophysis in the affected knee, with oedematous changes surrounding the ossicles in the plane of the patella tendon (figure 1), particularly when compared with the unaffected knee (figure 2). Given the pain was localised to the tuberosity and area overlying the fragmented ossicles, the patient’s pain was felt to be caused by persistently symptomatic OSD.
Figure 1.
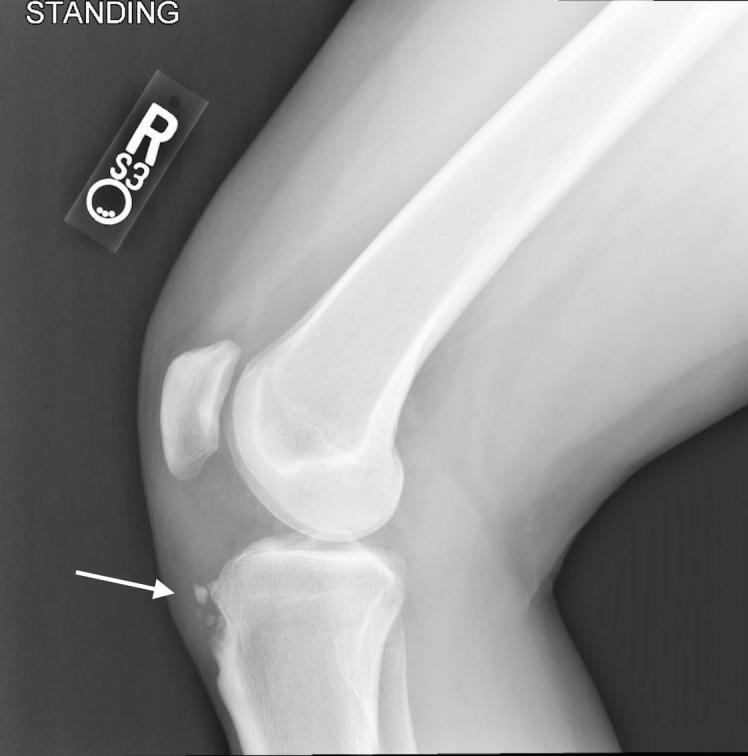
Lateral weight-bearing film of the right knee demonstrating multiple well-corticated ossific fragments seen adjacent to a prominent tibial tuberosity.
Figure 2.
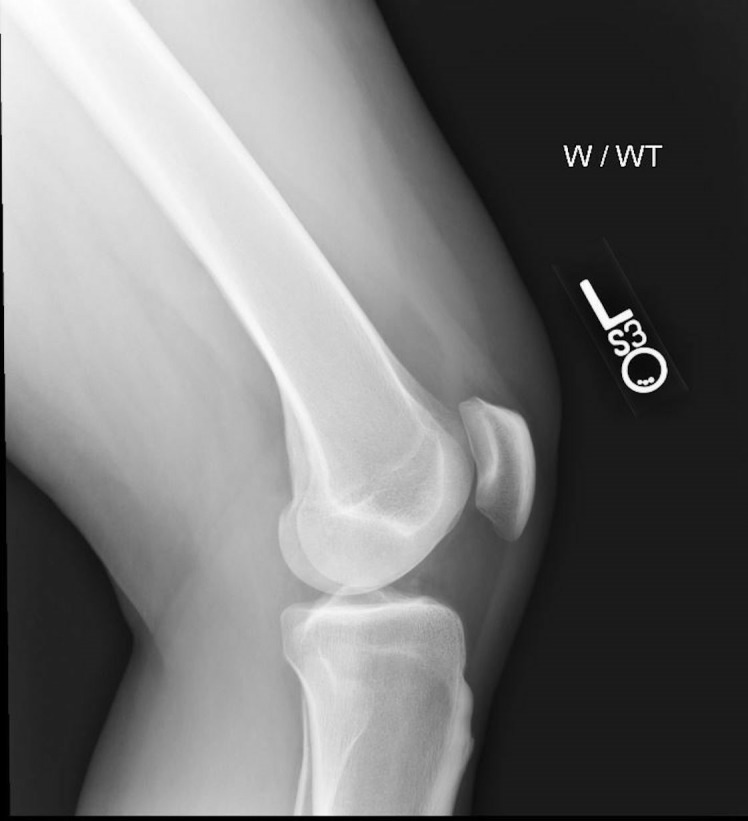
Lateral weight-bearing film of the left knee for comparison, demonstrating normal osseous mineralisation and alignment.
OSD, also known as osteochondrosis of the tibial tubercle, is believed to be caused by repetitive strain of the patellar tendon at the tibial insertion site. It is a common childhood condition affecting primarily adolescent boys who partake in running and jumping activities, however is seen with increasing frequency in women; this trend is felt to parallel the increasing participation of women in sport. Most cases resolve with supportive treatment and rarely are symptomatic into adulthood.1 Treatment involves limiting activity until inflammation resolves and exercises that strengthen the surrounding musculature to reduce stress across the tibial tuberosity. Isometric strength drills targeting the hamstring, quadriceps, iliotibial band and gastrocnemius muscle can progress to dynamic movements, with stretching to augment pain reduction. In severe cases, surgical intervention with ossicle removal and tibial reduction osteotomy may be considered.2
With our patient, treatment with physical therapy and strict activity modification was initiated. Surgical removal of the ossicles was considered, but the patient wished to forgo surgery given equivocal outcomes in the literature.3 After 6 months, the patient’s pain largely resolved although she continues to have persistent pain with kneeling and occasional flares of acute pain over the tibial tuberosity with squatting.
This case represents, to our knowledge, the first known report of persistently symptomatic Osgood-Schlatter syndrome in a skeletally mature female adult. The case underscores the importance of considering OSD in the differential for anterior knee pain.
Learning points.
Osgood-Schlatter disease (OSD) should be on the differential for anterior knee pain.
OSD can cause pain in the skeletally mature adult.
Less commonly, OSD can affect women.
Footnotes
Contributors: CEM contributed the text of the manuscript and CMK contributed with edits.
Funding: The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests: None declared.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Patient consent for publication: Obtained.
References
- 1. Gholve PA, Scher DM, Khakharia S, et al. . Osgood schlatter syndrome. Curr Opin Pediatr 2007;19:44–50. 10.1097/MOP.0b013e328013dbea [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Choi W, Jung K. Intra-articular large ossicle associated to Osgood-Schlatter disease. Cureus 2018;10:e3008 10.7759/cureus.3008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Bloom OJ, Mackler L, Barbee J. Clinical inquiries. What is the best treatment for Osgood-Schlatter disease? J Fam Pract 2004;53:153–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


