Abstract
Background
Metabolomics represents a powerful tool for exploring modulation of the human metabolome in response to food intake. However, the choice of multivariate statistical approach is not always evident, especially for complex experimental designs with repeated measurements per individual. Here we have investigated the serum metabolic responses to two breakfast meals: an egg and ham based breakfast and a cereal based breakfast using three different multivariate approaches based on the Projections to Latent Structures framework.
Methods
In a cross over design, 24 healthy volunteers ate the egg and ham breakfast and cereal breakfast on four occasions each. Postprandial serum samples were subjected to metabolite profiling using 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy and metabolites were identified using 2D nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Metabolic profiles were analyzed using Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Discriminant Analysis and Effect Projections and ANOVA-decomposed Projections to Latent Structures.
Results
The Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Discriminant Analysis model correctly classified 92 and 90% of the samples from the cereal breakfast and egg and ham breakfast, respectively, but confounded dietary effects with inter-personal variability. Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Effect Projections removed inter-personal variability and performed perfect classification between breakfasts, however at the expense of comparing means of respective breakfasts instead of all samples. ANOVA-decomposed Projections to Latent Structures managed to remove inter-personal variability and predicted 99% of all individual samples correctly. Proline, tyrosine, and N-acetylated amino acids were found in higher concentration after consumption of the cereal breakfast while creatine, methanol, and isoleucine were found in higher concentration after the egg and ham breakfast.
Conclusions
Our results demonstrate that the choice of statistical method will influence the results and adequate methods need to be employed to manage sample dependency and repeated measurements in cross-over studies. In addition, 1H nuclear magnetic resonance serum metabolomics could reproducibly characterize postprandial metabolic profiles and identify discriminatory metabolites largely reflecting dietary composition.
Trial registration
Registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, identifier: NCT02039596. Date of registration: January 17, 2014.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (10.1186/s12937-019-0446-2) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Metabolomics, Nutrition, NMR, OPLS-DA, OPLS-EP, ANOVA-PLS, Postprandial, Serum, Breakfast
Background
To establish associations and causation between diet and health, objective and reliable methods are needed to measure dietary exposure [1]. Unfortunately, few such methods exist. Instead, subjective assessment methods are commonly used and these include dietary records, food diaries, 24-h dietary recalls, food frequency questionnaires and diet history records. These methods rely on subjects’ own reports of their diets [2]. As such, they are associated with difficulties in estimation of consumption over time and of portion size, variation in dietary intake, cognitive processes such as episodic and generic memory as well as bias in over- and under-reporting of foods [2]. Despite validation efforts, random and systematic errors in subjective dietary assessment methods limit the possibility to measure true dietary intake [3]. A few single dietary biomarkers are today used to validate or to substitute subjective dietary assessment methods [1, 4–6]. Still, currently used dietary biomarkers do not always correlate well with the nutrients or foods they are intended to indicate and they fail to reflect the complex matrix of an overall diet [3]. Providing accurate and reliable measurements of dietary exposure constitutes one of the most challenging problems in nutrition research today [7].
Metabolomics concentrates on the high-throughput characterization of small molecule metabolites (< 1.5 kDa) in biological samples and is therefore a method suitable to explore metabolic effects of dietary exposures [8]. Using metabolomics, food-derived metabolites and the change in endogenous metabolites can be identified including amino acids, alkaloids, polyphenols and metabolites of microbial origin. Metabolomics in nutrition has been described as: “The study of endogenous and gut microbiota metabolic response to food (general diet or intervention) and the identification of metabolites that originate from food and could be used as biomarkers of exposure of these foods” [9]. In the area of nutritional metabolomics, potential biomarkers for individual food items and diets have been identified in both urine and plasma/serum [10]. However, further studies are needed to deepen the understanding of the food metabolome and to identify additional potential nutritional biomarkers for food items and complex diets. Controlled dietary intervention studies, where true consumption can be monitored in a supervised fashion, provide an opportunity to investigate the metabolic response of different foods or diets using metabolomics. In clinical studies that use metabolomics to explore the response to different exposures, it is not self-explanatory what method to apply regarding data analysis. Multivariate methods based on projections to latent structures (PLS) with different extensions are frequently applied, and orthogonal projections to latent structures with discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) has become a standard method in metabolomics [11–13]. These multivariate methods are in their standard form suitable only for independent data, as they do not by themselves separate within- from between-individual effects but rather the average effect between two or more sample classes [14]. However, clinical studies may entail sample dependency from repeated measures on the same investigated unit. Using an independent test on dependent data generates less robust models and potentially both false positive and negative discriminatory metabolites. OPLS-EP is an extension of the OPLS-DA method developed to handle dependent data by data pre-processing [15]. Using OPLS-EP the variation within and between subjects is separated and intrinsic differences in treatment effects between individuals can be identified [15]. However, a drawback lies in that only one measurement per treatment can be used and, consequently, averages must be used from repeated measurements on the same individual instead of concurrently examining all samples. ANOVA decompositioning of multivariate data offers a means to subtract study factors from measured variables, thus providing the possibility to focus on the reproducible within-person effect (i.e. treatment) while still keeping all individual samples in the analysis [16, 17].
The aim of the present study was to explore the outcome, discriminative potential, reproducibility of metabolic profiles, and biological relevance of discriminatory metabolites, of three different multivariate models, OPLS-DA, OPLS-Effect Projections (EP), and ANOVA-PLS. This was performed in a nutritional cross-over intervention study with the aim to investigate the serum metabolic response to two isocaloric breakfast meals using 1H NMR metabolomics. We have previously described the urine metabolome of the same diet [18].
Materials and methods
Ethical approval, recruitment and subject screening
The project was approved by the Regional Ethical Review Board in Gothenburg, Sweden (reference number 561–12), adhered to the Helsinki Declaration, and registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (identifier: NCT02039596).
Volunteers were recruited by advertisement at the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, and Chalmers University of Technology in Gothenburg, Sweden. Before entering the study participants provided written informed consent.
In total, 24 healthy volunteers, 12 males and 12 females, were enrolled in the study (Table 1). Volunteers were considered suitable if apparently healthy (normal serum electrolytes, iron status, creatinine, liver transaminases, bilirubin and alkaline phosphatase, C-reactive protein, plasma glucose, and thyroid status), with no regular use of medications (contraceptives were permitted), and BMI > 18.5 and < 30 kg/m2. Screening included a three-day weighed-food diary a short lifestyle questionnaire that included questions regarding food and alcohol consumption, use of nicotine, drugs, herbal remedies and supplements and level of physical activity. Body composition was measured with bioimpedance (ImpediMed Bioimp Version 5.3.1.1). Exclusion criteria included: aged <18 or >65 years, pregnancy or lactation, use of nicotine, natural remedies and/or herbal tea, alcohol consumption higher than 5 units per week (1 unit = 12 g alcohol), allergies to food items included in the study, and the practice of an extreme diet or intent to change physical activity and/or dietary habits before or during the intervention.
Table 1.
Anthropometric characteristics of included volunteers (n = 24)
| Characteristics | Males (n = 12) | Females (n = 12) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean ± SD | min/max | mean ± SD | min/max | |
| Age (year) | 27.3 ± 11.2 | 19.0/54.0 | 24.4 ± 8.2 | 18.0/46.0 |
| Height (cm) | 184.3 ± 6.0 | 172.0/192.0 | 169.2 ± 6.1 | 159.0/177.0 |
| Body weight (kg) | 77.5 ± 7.8 | 66.8/91.3 | 66.2 ± 7.1 | 56.6/77.4 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 22.8 ± 2.1 | 20.6/26.9 | 23.1 ± 2.3 | 19.5/26.7 |
| Fat mass (%) | 13.9 ± 5.9 | 6.7/24.7 | 26.9 ± 5.2 | 18.4/34.0 |
Study design
Study participants consumed the two different breakfasts, cereal breakfast (CB) and egg and ham breakfast (EHB), four times each, in the following order; abba/baab, where a = CB and b = EHB, Tuesday to Friday during two consecutive weeks (eight occasions in total). Breakfasts were consumed at the Department of Internal Medicine and Clinical Nutrition, University of Gothenburg, Sweden. The CB consisted of orange juice, oat puffs with milk, and a rye bread sandwich with hard cheese and fresh tomato. The EHB consisted of orange juice, scrambled eggs, white beans in tomato sauce, fried pork loin, tomato and toasted white bread with orange marmalade. Study participants choose either coffee (male n = 6, female n = 4) or tea (male n = 6, female n = 8), both with 20 ml of milk. Participants were also given a choice between a large (750 kcal) (male n = 12, female n = 1) or a small (500 kcal) (female n = 11) breakfast size.
The two breakfast meals had similar composition of protein, fat and carbohydrates. Breakfasts of 500 kcal comprised 20 g protein, 19 g fat and 60 g carbohydrates while the breakfasts of 750 kcal comprised 29 g protein, 34 g fat and 80 g carbohydrates (see supplementary file information of previous article [18] for detailed meal composition and Additional files 1, 2 and 3 for detailed description of breakfasts’ nutrients, amino acids and fatty acids).
Two weeks before and during the intervention, study participants were asked to refrain from using dietary supplements and occasional medications. The day before and during the intervention, volunteers were asked to abstain from drinking alcohol, engaging in strenuous exercise (> 2 h moderate intense physical activity, defined as 3–6 MET:s (metabolic equivalents)) [19], and eating fish. Volunteers did not have any other restrictions regarding food consumption.
To help stabilize background metabolic profiles further, a standardized evening meal of quenelles with tagliatelle in tomato sauce (488 kcal) was provided to be consumed between 18:00 and 20:00 h (Fig. 1). Volunteers were instructed to drink water for the evening meal, not eat anything further and only drink water before arriving to the test kitchen between 07.30 and 09.30 h where they consumed the breakfasts within 30 min. During the intervention, volunteers noted health status, occasional medications, and exact time of evening meal together with water intake during the overnight fast.
Fig. 1.
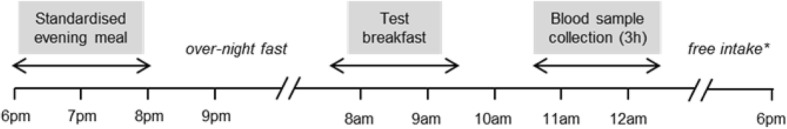
Study design of clinical intervention, Monday evening to Friday lunch during two consecutive weeks. *Volunteers were instructed to abstain from eating fish, dietary supplements and drinking alcohol during the intervention
Serum collection and preprocessing
Postprandial serum samples were collected after breakfast meals (3 h 15 min ± 22 min). In total, 192 samples were collected. Venous blood was drawn into 4 mL Z serum Separator Clot activator tubes (VACUETTE® TUBE Greiner Bio-One), allowed to clot at 4 °C for 30 min and centrifuged at 4 °C at 2600 x g for 10 min. 400 μL serum was aliquoted in 500 μL cryo vials and placed at − 20 °C within 1 h (57 min ± 11 min) and at − 80 °C within 2 h. Samples were stored at − 80 °C until analysis. 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy analysis was performed on all serum samples. Prior to 1H-NMR analysis, serum samples were thawed for 60 min at 4 °C, 100 μL serum was mixed with 100 μL phosphate buffer (75 mM Na2HPO4, 20% D2O, 0.2 mM imidazole, 4% NaN3, 0.08% TSP-d4, pH 7.4) in a deep well plate. 180 μL sample mix was transferred to 3.0 mm NMR tubes (Bruker BioSpin, 96 sample racks for SampleJet) using a SamplePro liquid handling robot (Bruker BioSpin, Rheinstetten, Germany). Samples were kept at 6 °C until analysis. For quality control three samples with pooled serum from four individuals in the dataset and three buffer samples were used on each 96 sample rack.
NMR spectroscopy analysis
All 1H NMR spectra were measured on an Oxford 800 MHz magnet equipped with a Bruker Avance III HD console and with a 3 mm TCI cryoprobe and a cooled (6 °C) SampleJet automatic sample changer for sample handling. All 1H NMR experiments were performed at 298 K. NMR data (1D perfect echo with excitation sculpting for water suppression) was recorded using the Bruker pulse sequence ‘zgespe’. The spectral width was 20 ppm, the relaxation delay was 1.34 s. The acquisition time was 2.04 s. With a total of 64 scans collected into 64 k data points, the measurement time for each sample was 4 min 19 s. All data sets were zero filled to 128 k and an exponential line-broadening of 0.3 Hz was applied before Fourier transformation. All data processing was performed with TopSpin 3.2pl6 (Bruker BioSpin, Rheinstetten, Germany). TSP-d4 was used for referencing. 1H NMR data were acquired for a total of 192 serum samples.
For annotation, pooled serum from all individuals in the dataset was utilized for natural abundance 1H-13C HSQC (‘hsqcetgpsisp2.24’) and 1H-1H TOCSY (‘mlevgpphw5’) experiments. The 1H-13C HSQC spectra were measured with acquisition times of 63.9 ms (1H) and 50.9 ms (13C), a 3 s pulse delay, 8 scans and acquisition of 2048 data points (1H) in 768 increments (13C). The 1H and 13C pulse widths were p1 = 7.44 μs and p3 = 9.3 μs, respectively. The 1H and 13C spectral widths were 20 ppm and 100.00 ppm, respectively. 1H-1H TOCSY spectra were acquired with the same proton pulse width as for the 1H-13C HSQC. The spectral widths were13.95 ppm in both dimensions, the acquisition times were 183.5 ms (F2) and 229 ms (F1), the 1H-1H TOCSY mixing times 80 ms and the pulse delay 2 s. 8 scans were used, 2048 points and 512 increments were acquired in the direct and indirect dimensions, respectively.
Sodium phosphate (Na2HPO4), imidazole, and sodium azide (NaN3) were bought from SigmaAldrich, deuterium oxide (D2O) from Cambridge Isotopes, and 3-(trimethylsilyl) propionic-2,2,3,3-d4 acid sodium salt (TSP-d4) from MerckMillipore.
Annotation of metabolites
1D proton, 2D 1H-13C HSQC, and 2D 1H-1H TOCSY spectra of pooled serum from all individuals in the dataset were used for metabolite identification. Chenomx NMR suite 8.1 (Chenomx Inc., Edmonton, Canada) was used for spectral line fitting of 1D proton spectra. Chemical shifts in 1D proton, 2D 1H-13C HSQC, and 2D 1H-1H TOCSY spectra were compared with reference spectra in the Human Metabolome Database (HMDB) [20].
Data pre-processing and statistical analyses
Data pre-processing
1H-NMR spectra were aligned using icoshift and manual integration of peaks was performed to a linear baseline on all spectra in parallel using an in-house MatLab (MathWorks, Natick, USA) routine. In total 296 peaks were integrated within chemical shift range of 0.721–8.362 ppm. Data were normalized using Probabilistic Quotient Normalization (PQN).
Principal component analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) was performed using SIMCA software v.14.1 (Umetrics AB, Umeå, Sweden) [21]. PCA models were used to explore clustering patterns of observations, trends in the data and outliers. Two samples were removed due to poor data quality. Samples from each breakfast group were modelled separately to identify outliers, resulting in exclusion of 2 of 96 for the CB samples and 6 of 96 for the EHB samples according to Hotellings T2 range (Tcrit 99%) and Distance to Model (DModX) (not exceeding 1.8). In total, 182 samples were included in further data analysis. Two variables were removed from the data set (imidazole (pH indicator)). In total, 294 variables were included in the model for further analysis.
Orthogonal projections to latent structures with discriminant analysis and orthogonal projections to latent structures with effect projections
Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Discriminant Analysis (OPLS-DA) is a multivariate analysis tool that is often used in metabolomics [13]. However, OPLS-DA does not account for dependent data, such as repeated measures on the same individual which is generated in cross-over studies [22, 23]. OPLS-Effect Projections (EP) is a newly developed multivariate analysis that considers pairwise dependent samples in cross-over studies [15]. Both methods were performed in the present study using SIMCA software v.14.1 (Umetrics AB, Umeå, Sweden).
In the OPLS-DA and OPLS-EP models, four additional, highly abundant signals from unidentified lipids were removed since they, as a consequence of using Pareto scaling, influenced the model merely on account of the magnitude of the peaks. However, these lipids did not differ significantly between breakfast treatments (Mann Whitney U-test p > 0.05). Furthermore, the use of T2-filtered NMR experiment on water samples negated any identification of individual hydrophobic lipids and fatty acids. Hence, lipid variables did not contribute to the biological understanding of the data and OPLS models were not discernably affected by the removal of these variables. The numbers of latent variables (LV) in the models were determined using cross validation and Q2.
The validity of the OPLS models was assessed using Coefficient of Variation- ANalysis Of VAriance testing of cross-validated predictive residuals (CV-ANOVA), the cumulative amount of explained variation in the data summarized by the model (R2X[cum] and R2Y[cum]) and the predictive ability of the model (Q2[cum]). In addition, permutation tests (n = 999) was used for validation. For the OPLS-EP model, scores in relation to the response vector (Y) was also used for validation [15].
Separation of classes and variables related to separation in the data according to classification of breakfast meals was evaluated using OPLS-DA. Prior to modeling, data were centered and Pareto scaled. Cross validation groups were set to 24 (i.e. to number of study participants) and assigned observations based on observation ID for each individual so that all samples from one individual were left out in one cross-validation round. Receiver operating curve (ROC) analysis was performed and the area under the curve (AUC) was used as an estimate of the predictive accuracy of each breakfast meal in the OPLS-DA model. To select class discriminating variables of interest for annotation, S-plot, loadings (pq > 0.1) and top ranked variables in variable importance (VIP) scores in the OPLS-DA model were assessed.
For the OPLS-EP analysis, an effect matrix was calculated with Excel 2010. Mean values for each breakfast meal were calculated and values from the CB were subtracted from the EHB values for each volunteer (n = 24) and variable (n = 290). The effect matrix, i.e. the difference between breakfast meals, was modeled in relation to a response vector (Y = 1). Prior to modeling in Simca, all data were Pareto scaled (ParN) but not centered, and cross validation groups were set to 7 (default). S-plot was used for selection of variables of interest for annotation.
ANOVA-decomposed projections to latent structures
Multilevel methods, such as OPLS-EP, are capable of managing sample dependency in a cross-over design, but are in this case limited to comparing mean values between treatments. To simultaneously manage sample dependency and include all samples in the analysis, ANOVA decomposition [16] of the data was performed, by the factors: Coffee/Tea; Gender; Individual; and Breakfast. The factor Size of breakfast was almost completely confounded by Gender, wherefore it was excluded from ANOVA decomposition. Following the ANOVA-PLS approach [17], residuals were then added back to the breakfast type data, and analyzed by PLS to investigate systematic differences in the metabolome as a consequence of breakfast type. This supervised model was constructed in a repeated double cross validation procedure (rdCV) [24, 25], and incorporated with unbiased variable selection obtained by recursive feature elimination in the inner rdCV loop [26]. All samples per individual were co-sampled into the same cross validation segments to avoid overfitting to dependent samples. This approach has previously proven successful for supervised multivariate modelling [27, 28] to produce robust predictive modelling with effective variable selection and minimized risk of false positive discovery and model overfitting. Model performance was further assessed by permutation tests (n = 300) [29]. These analyses were performed in R v. 3.4.2 using in-house scripts, available from the authors upon request.
Significance tests of variables in multivariate models
Univariate statistical analysis of variables was performed using Mann Whitney U-test for the OPLS-DA model and Wilcoxon signed rank test for the OPLS-EP model; both with Benjamini Hochberg correction at the 95% level. A variable was considered significant if p < 0.05. These calculations were performed in MatLab R2015a.
Results
Breakfast related metabolic profiles
Statistics for the final OPLS models are presented in Table 2. Overall, the OPLS-DA model correctly classified 92% of the postprandial samples from the CB and 90% of the postprandial samples from the EHB while the ANOVA-PLS correctly classified 99% of samples with respect to breakfast type (ppermutation = 6.70e-17) (Table 3). ANOVA decomposition of the original data showed that the residuals represented the largest source of variability in the data (49%). Structured variability was dominated by inter-individual variation (38%) while breakfast intervention-related variability comprised 3.6% (Fig. 2).
Table 2.
OPLS models statistics
| Model | Nr of LVa | n | R2X [cum]b | R2Y [cum]c | Q2 [cum]d | CV-ANOVAe (p-value) | Permutation test (Q2)f |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPLS-DAg | 1 + 2 + 0 | 182 | 0.428 | 0.712 | 0.619 | < 0.001 | −0.165 |
| OPLS-EPh | 1 + 2 + 0 | 24 | 0.656 | 0.966 | 0.922 | < 0.001 | – |
aLatent Variables
b Cumulative fraction of the sum of squares of X explained by the selected latent variables
c Cumulative fraction of the sum of squares of Y explained by the selected latent variables
d Cumulative fraction of the sum of squares of Y predicted by the selected latent variables, estimated by cross validation
e ANalysis Of VAriance testing of Cross-Validated predictive residuals
f The intercept between real and random models, degree of overfit
g Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Discriminant Analysis
h Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Effect Projections
– Not applicable
Table 3.
Classification of postprandial serum samples by different models
| True intake | Classification | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OPLS-DAa | ANOVA-PLSb | ||||
| CB | EHB | CB | EHB | Total (n) | |
| CBc | 85 (92%) | 7 (8%) | 91 (99%) | 1 (1%) | 92 |
| EHBd | 9 (10%) | 81 (90%) | 1 (1%) | 89 (99%) | 90 |
| Total | 94 | 88 | 92 | 90 | 182 |
aOrthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Discriminant Analysis (Cross-validated scores)
bANalysis Of Variance - Partial Least Squares
cCereal breakfast
dEgg and ham breakfast
Fig. 2.
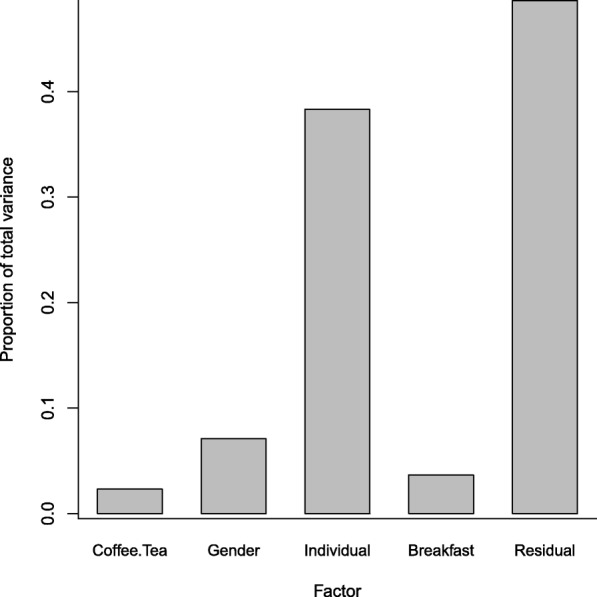
ANOVA decomposition visualising proportion of total variance in relation to different factors in postprandial (3 h) serum samples (n = 182) from 24 healthy volunteers
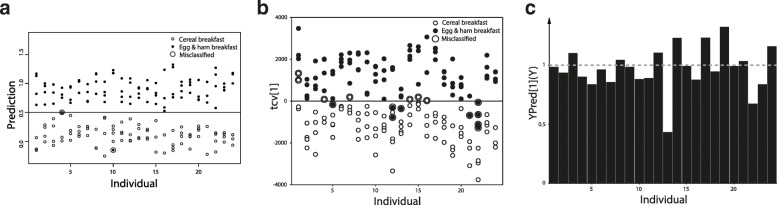
The ability of the OPLS-DA, OPLS-EP, and ANOVA-PLS models to discriminate between metabolic profiles of postprandial samples from volunteers who had consumed the CB and the EHB are displayed in Figs. 3 and 4. Seven out of 92 postprandial samples from the CB and nine out of 90 postprandial samples from the EHB were misclassified in the OPLS-DA model. However, when looking at the OPLS-DA model predictions (Fig. 3b), only two individuals have consistent erroneous breakfast predictions. The predictive accuracy for each breakfast meal by the OPLS-DA model, as illustrated by the area under the curve in ROC analysis, is displayed in Fig. 5. Metabolites discriminating in the OPLS-DA model were selected using a combination of S-plot (Additional file 4), loadings, and top ranked variables in VIP scores in the OPLS-DA model.
Fig. 3.
a Predicted values for breakfast classification in ANOVA-Partial Least Squares (PLS) model. The data were ANOVA-decomposed into the factors Coffee/Tea, Gender, Individual and Breakfast type and PLS analysis was performed on the Breakfast type data after addition of the residual matrix. Model included 290 variables and 182 postprandial observations from 24 healthy volunteers. b Breakfast dependent cross-validated scores (cross-validated x scores (tcv)) in orthogonal projections to latent structures with discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) model. Model included 290 variables and postprandial (3 h) serum samples (n = 182) from 24 healthy volunteers. c Predicted values in relation to response vector (Y) for volunteers in the in OPLS with effect projections (EP) model. The dotted line (Y = 1) indicates the response vector value for the model. The magnitude of the predicted effect for each volunteer is given by the height of the corresponding black bar. Deviations from the value 1 for a specific volunteer indicate a larger (> 1) or smaller (< 1) metabolic effect (difference between breakfast meals) in the model direction (metabolic profile) associated with the metabolism of foods included in the different breakfast meals. Model included 24 observations (equal to number of individuals) and 290 variables
Fig. 4.
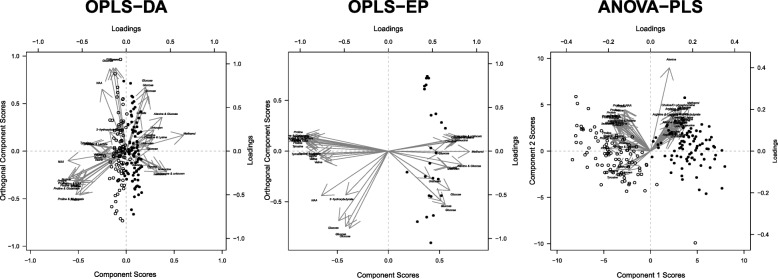
Biplot in Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Discriminant Analysis (OPLS-DA), OPLS with Effect Matrix (EP) and ANOVA-Partial Least Squares (PLS) models of observation scores and variable loadings. OPLS-DA and ANOVA-PLS models included 182 postprandial observations from 24 healthy volunteers and 290 variables while the OPLS-EP model 24 observations (equal to number of individuals) and 290 variables. Labeled metabolites denote selected discriminating metabolites in the different models
Fig. 5.
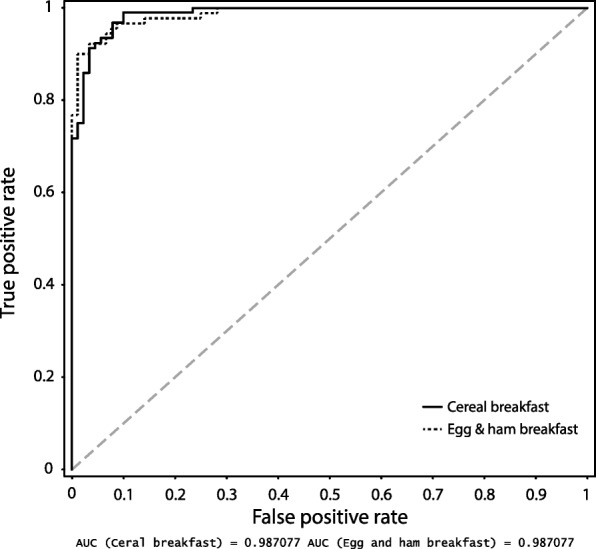
ROC curve in orthogonal projections to latent structures with discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) model comparing the postprandial metabolic response between cereal breakfast (CB) and egg & ham breakfast (EHB). In total 182 serum samples from 24 individuals were included in the model, 90 samples from volunteers who had consumed the EHB and 92 samples from volunteers who had consumed the CB. On average four samples per individual and breakfast meal. AUC = area under the curve
In the OPLS-EP model, all values above 0 in the OPLS-EP model correctly predicted the order of consumption of the EHB or the CB, whereas a negative value would predict the opposite. Only one individual displayed < 0.5 in predictive effect in relation to the response vector (Y), whereas remaining volunteers displayed > 0.75 in predictive effect (Fig. 3c). Again, metabolites increasing or decreasing in relation to the response vector were selected using S-plot (Additional file 5).
Further, the influence of a single meal on the postprandial metabolic profile the following day was studied by the difference in metabolic profiles between the same breakfast meal in relation to the breakfast meal served the day before. However, OPLS-DA models displayed low prediction (Q2) (data not shown) in class separation between breakfast meals, consistent with the ANOVA-PLS analysis showing no importance of the order of breakfast meals.
Discriminating metabolites
In total, seven unique metabolites were identified that were selected responsible for class separation in all models. Tyrosine, proline, and N-acetylated amino acid were found in significantly higher concentrations after consumption of the CB. In contrast, alanine, methanol, creatine, and isoleucine were found in significantly higher concentrations after consumption of the EHB.
For the OPLS models, five and six (excluding unknowns and glucose) metabolites were identified as discriminating in postprandial samples from the CB and the EHB respectively (Table 4). The ANOVA-PLS model unbiasedly selected two components and 48 variables corresponding to 12 metabolites as top predictors driving the separation between classes with three and nine metabolites responsible for class separation in postprandial samples from the CB and the EHB respectively. 3-hydroxybutyrate, valine, and glycine were selected as responsible for class separation in OPLS models but not in ANOVA models. In contrast, arginine, lysine, 4-aminobutyrate, choline, and glutamine were selected as top ranked variables in ANOVA-PLS but not in the OPLS models. All identifications of metabolites, except 3-hydroxybutyrate, were supported by 2D 1H-13C HSQC data.
Table 4.
Discriminating metabolites between breakfast meals in multivariate models
| Meal | Metabolite | Chemical shift (ppm) | p-valuea | Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CBb | Tyrosine | 7.19c, 6.89 | < 0.0001 | Alld |
| CB | Proline | 4.13e, 4.14, 4.15, 3.33, 3.34, 3.35, 2.37, 2.36, 2.35, 2.34, 2.33, 2.10, 2.09, 2.07f, 2.06, 2.03, 2.02, 2.01, 2.00, 1.99, 1.98, 1.97 | < 0.0001 | All |
| CB | NAAg | 2.09, 2.08, 2.06, 2.05, 2.03, 1.99 | < 0.0001 | All |
| CB | 3-hydroxybutyrate | 1.20 | 0.014 | OPLS-DAh, OPLS-EPi |
| CB | Valine | 1.05 , 1.04, 1.00, 0.99 | 0.0004 | OPLS-DA, OPLS-EP |
| CB | (Glucose)j | 5.24 , 3.91, 3.89 | 0.005 | OPLS-DA, OPLS-EP |
| CB | Unknown | 3.44, 1.15, 1.14 | – | ANOVA-PLSk |
| EHBl | Methanol | 3.37 | < 0.0001 | All |
| EHB | Creatine | 3.94, 3.04 | < 0.0001 | All |
| EHB | Isoleucine | 1.97, 1.98, 1.02, 1.01, 0.95, 0.94, 0.93 | < 0.0001 | All |
| EHB | (Alanine)m | 3.79 | < 0.0001 | All |
| EHB | Arginine | 1.89, 1.90, 1.91, 1.92 | < 0.0001 | ANOVA-PLS |
| EHB | Lysine | 3.03, 3.02, 1.90, 1.91, 1.92 | < 0.0001 | ANOVA-PLS |
| EHB | 4-aminobutyrate | 1.90 | < 0.0001 | ANOVA-PLS |
| EHB | Choline | 3.21 | < 0.0001 | ANOVA-PLS |
| EHB | Glutamine | 2.16 | < 0.0001 | ANOVA-PLS |
| EHB | (Glucose)j | 3.86, 3.74, 3.72 , 3.49 | 0.0006 | OPLS-DA, OPLS-EP |
| EHB | Lactate | 4.11 | 0.60 | OPLS-DA |
| EHB | Glycine | 3.57 | 0.0002 | OPLS-DA, OPLS-EP |
| EHB | Unknown | 4.05, 3.77, 3.73, 3.68, 2.56 | – | All |
aWilcoxon signed rank test
bCereal breakfast
cUnderscored chemical shift used for p-value calculation and variable rank number
dIncludes ANOVA-PLS, OPLS-DA, and OPLS-EP models
eBold chemical shifts indicate discriminating variable only in ANOVA-PLS model
fItalic chemical shifts indicate discriminating variable only in OPLS-DA and OPLS-EP models
gN-acetylated-amino acids
hOrthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Discriminant Analysis
iOrthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Effect Projections
jUnknown masked by glucose
kANalysis Of Variance – Partial Least Squares
lEgg and ham breakfast
mOverlap with glucose and unknown metabolites
– Not relevant
Discussion
Evaluating the outcome of three different multivariate statistical approaches, OPLS-DA, OPLS-EP and ANOVA-PLS, in a cross-over design, including 24 healthy volunteers, we explored the postprandial metabolic response to two isocaloric breakfast meals with similar macronutrient distribution, but with different food items.
Multivariate statistical modelling of metabolic profiles
The OPLS-DA model correctly classified of 92 and 90% of serum metabolic profiles the CB and the EHB meals, respectively (Table 3 and Fig. 3b). Moreover, the OPLS-DA model showed an overall difference in metabolic profiles between breakfast meals with a high degree of intra-individual similarity, although inter-individual variability was clearly discernible (Fig. 4). Similar to these findings, Lenz et al. (2003) [30] found relatively low inter- and intra-individual variation in 1H-NMR plasma metabolic profiles when providing a semi standardized diet during 2 days to healthy males. Likely, the confounding effect of inter-individual variability depends on the effect size of the intervention.
OPLS-EP takes pairwise sample dependency into account by modelling the effect matrix rather than the original data [15]. When better accounting for the paired structure of the data using OPLS-EP, the predictive ability of the model improved compared to the OPLS-DA model (Table 2). This confirms the confounding effect of inter-individual variability (Fig. 4). In addition, the OPLS-EP model classified all individuals correctly using 7-fold cross validation.
ANOVA-PLS was developed to allow for supervised PLS analysis of data decomposed by one or several factors, which makes it efficient to manage e.g. cross-over dependency by including Individual as a factor [17]. Although not shown here, it can be shown that multilevel approaches are special cases of ANOVA decomposition; the latter being the broader framework. In fact, their relation is conceptually similar to the difference between a paired t-test and a classical ANOVA. The ANOVA decomposition step thus manages not only to isolate inter-individual variation, but also to isolate other factors that may otherwise confound the analysis (in this case Coffee/Tea consumption and Gender), analogously to how such factors may be included in linear mixed models to account for confounding variables [16]. This approach provides a means to investigate contributions of the factors to the total variance by comparing sums of squares. In our data, the factor Individual was by far the major contributor to systematic variability, although overshadowed by the residual variability. This clearly indicates between sample fluctuations as the major source of variability, although the source of such fluctuations was not investigated. It is likely, however, that such variability is composed of both biological variation in the individual, pre-analytical sample management and instrumental variability [31]. It should be noted that the sums-of-squares in the currently used function were calculated sequentially (i.e. Type I sums-of-squares) and are thus sensitive to the order of factors if the design is not balanced. Sensitivity analysis, however, revealed only minor effect of the order of factors on both sums-of-squares and modelling outcomes in the present case.
Similar to OPLS-EP, classes were visibly separated in the ANOVA-PLS (Fig. 4). ANOVA-PLS thus managed to improve classification accuracy compared to OPLS-DA, even though this procedure employed a much stricter validation scheme than either of the OPLS methods [24]. This clearly shows the advantages of filtering out inter-individual variability prior to analysis to be able to focus on systematic differences between treatments. Using this approach, all samples were maintained in the analysis, leading to higher resolution in the multivariate model compared to OPLS-EP (Fig. 4). This also provided an opportunity to investigate whether effects were robust even with residual variability from multiple samples. ANOVA-PLS thus effectively combined the best aspects of discriminant and standard multilevel (such as Effect Projections) analyses for analysing complex cross-over data structures. Permutation analysis showed that the ANOVA-PLS was highly significant and devoid of overfitting (Additional file 6), since the permutation distribution median corresponded exactly to the expected value of 91 misclassifications for 182 randomly permuted observations in a two-class problem.
The order of individual breakfast meals did not have an impact on the metabolic profile in the present study, implying that foods in our breakfast meals do not influence the postprandial serum metabolic profiles measured by NMR after 24 h. Previously, the fat to carbohydrate ratio of an evening meal has been shown to impact the postprandial metabolic response in plasma 12 h after intake [32]. However, in our study the breakfast meals contained the same fat to carbohydrate ratio and this might explain why the postprandial response did not seem to be influenced by the type of breakfast consumed the day before. Moreover, white bean consumption has been shown to affect metabolite concentrations in urine up to 48 h after intake in a previous study [33]. However, the effect was not captured in serum, and this is in line with findings in the present study.
Discriminating metabolites
The cross-over design has the advantage of comparing each individual to themselves after the two different breakfasts. Given the use of proper statistical tools factors such as age [34], gender [35], BMI [36], insulin sensitivity [37], habitual diet [38], and habitual sleep [39], have minimal impact on the results. Although inter-personal variability confounded dietary effects in OPLS-DA, model predictions and biplots from all statistical methods provided similar output (Figs. 3 and 4). This was confirmed by the fact that discriminating metabolites selected from both OPLS models were, in fact, the same (Fig. 4 and Table 4). The difference in the ANOVA-PLS model is likely to a large extent dependent on the different procedures for variable selection. However, several variables were selected in all models (Fig. 4 and Table 4), suggesting that these may be the most robust findings.
The metabolites that were discriminating in all statistical analysis are thus discussed first. Variables including glucose, alanine, and lactate that discriminated between breakfasts in OPLS models had peaks overlapping with other metabolites or were not significant in univariate models and, since their relevance is therefore unclear, these metabolites are not discussed further.
Proline and tyrosine were found at higher concentrations in postprandial serum samples from the CB in relation to the EHB. Consistently, the CB had a higher proline content, with the major contribution from the cheese (Additional files 1 and 2). In contrast, there was little difference in total tyrosine content between the two breakfast meals, with sources as hard cheese in the CB and white beans and pork loin in the EHB. Tyrosine has previously been reported higher in postprandial serum samples, following a dairy meal compared to similar tyrosine content from fish, meat and lentils [40]. In our study the higher tyrosine in the CB may be related to the absorption and ratio between free and bound amino acids and/or the metabolic turnover of the different foods within the breakfasts [41].
The higher concentration of N-acetylated amino acids (NAA) in the CB compared to the EHB, might be related to a higher beta-oxidation rate of fatty acids, since the CB had a higher content of short chain fatty acids (Additional file 3) [42]. NAAs and N-acetylcysteine in particular, has shown various biological activities such as interaction with pathways regulating cell cycle and apoptosis, immune-modulation and gene expression among others [43, 44]. Unfortunately, however, it was not possible to unequivocally identify involved N-acetylated amino acids in this study.
For the EHB, methanol, creatine and isoleucine were higher than for the CB. The metabolism of fruit and vegetables, mainly due to the pectin content that is metabolized by the gut microflora, is believed to generate the majority of the serum methanol originating from the diet, other than alcoholic beverages [45, 46]. Together with the tomatoes and white beans, the orange marmalade, high in natural as well as added pectin, likely caused the higher methanol concentration after the EHB. In similarity with previous findings creatine was found in higher concentration in postprandial samples where volunteer had consumed red meat [47]. Leucine, as well as other branched amino acids has previously been shown to be associated with dietary intake of animal products and pulses [48] and the serum concentration of isoleucine likely reflects the higher intake in these products in the EHB.
In the OPLS models valine, 3-hydroxybutyrate, and glycine were selected as discriminating metabolites and these also differed between breakfast groups. Higher serum glycine was found after consuming the EHB that included both legumes and red meat, which are both major dietary sources of glycine. Glycine is a non-chiral amino acid that has also been identified as an endogenous metabolite in plasma [49]. Further, the EHB had a higher content of valine compared to the CB. Nevertheless, postprandial samples from the CB had higher concentrations of valine. The main food that contributed to the valine content in the CB was the hard cheese, whereas in the EHB it was white beans in tomato sauce. Our results suggest that absorption rates of valine differ between these foods. The ketone 3-hydroxybutyrate was higher after consumption of the CB. 3-hydroxybutyrate has previously been related to fat: carbohydrate ratio [32], but since macronutrients were balanced in the two breakfast meals we speculate that the observed difference in serum may be related to the composition of the fatty acid profiles of the meals (Additional file 3).
The ANOVA-PLS model also included arginine, lysine, glutamine, choline and, 4-aminobutyrate as discriminating metabolites. This reflected the fact that the EHB had higher content of all amino acids, except proline, tyrosine and tryptophan (Additional file 1), with white beans (arginine, lysine and, glutamine) and animal product as dietary sources. Animal products also constitute rich sources of choline [50] which might explain the higher serum concentration in volunteers who had consumed the EHB.
Strengths and limitations
Limitations of this study include that the study design did not allow us to investigate specificity of metabolic responses to the included foods, which is necessary for biomarker discovery and validation, or long-term metabolic effects. To evaluate potential health implications and/or biomarker applications of specific food items, other study designs are needed. However, the aim of this study was to evaluate the acute metabolic serum response between two complex meals. Further, specific N-acetylated amino acids, metabolites with low abundance in overlapping regions and individual fatty acids could not be identified. This inability is related to the NMR analysis of the current sample matrix. In addition, the included volunteers in the present study constituted a fairly homogenous group of individuals which is considered a limitation for the generalizability of the results. A larger and more heterogeneous group of volunteers may be preferable to reflect the metabolic response in the general population. Strengths of the study include the cross-over design to be able to focus on systematic intra-individual effects of dietary interventions, the standardized prior evening meal, the equal numbers of women and men, the repeated sampling which gave the opportunity to investigate sample-by-sample variability in relation to systematic dietary effects and, the application of several statistical tools.
Conclusions
In conclusion, all statistical models successfully separated metabolic profiles between the two breakfast meals, but with some limitations: OPLS-DA could not effectively manage sample dependency from the cross-over design, OPLS-EP could not manage repeated sampling per treatment, whereas ANOVA-PLS effectively managed both the cross-over and repeated measures design. When having dependent samples, OPLS-EP and ANOVA-PLS thus have the means to handle the data structure and generate more robust models with higher predictive performance than OPLS-DA. It is thus necessary that multivariate models considering sample dependency should be applied in cross-over metabolomics studies. Using NMR-metabolomics, especially when combined with appropriate multivariate models, it was possible to identify difference in serum metabolic profiles between two isocaloric meals with the same macronutrient composition yet including different foods. The differences in metabolites, discriminating between breakfast meals, largely mirrored differences in dietary composition. Thus, metabolomics holds the potential to complement traditional methods to evaluate dietary intake and compliance in intervention studies.
Additional files
Table S1. Amino acid content of breakfast meals (mg). (DOCX 92 kb)
Table S2. Amino acid content of individual foods (mg). (DOCX 94 kb)
Table S3. Fatty acid content of breakfast meals (g). (DOCX 92 kb)
S-plot in orthogonal projections to latent structures with discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) model comparing the postprandial metabolic response between cereal breakfast (CB) and egg & ham breakfast (EHB). The top box is displaying selected discriminating metabolites for the EHB while the bottom box is displaying selected discriminating metabolites for the CB. Grey circles indicate significant (p < 0.05) variables in Mann Whitney U-test. (EPS 5517 kb)
S-plot in orthogonal projections to latent structures with effect matrix (OPLS-EP) model comparing variables increasing and decreasing in relation to the response vector (Y). The top box is displaying selected metabolites increasing and the bottom box is displaying metabolites decreasing in relation to Y. Grey circles indicate significant (p < 0.05) variables in Wilcoxon signed rank test. (EPS 890 kb)
Permutation analysis of ANOVA-PLS, showing actual model misclassifications as vertical lines with p-value calculated as the cumulative probability of finding the actual model result is a Student’s t-distribution of misclassification results obtained from randomly permuted data (n = 300 per model). The permutation distribution had median value of 91 misclassifications, corresponding exactly to the expected value of 182 observations in a two-class problem. The results show strong predictive modelling performance with absence of overfitting in the validation frameworks. (EPS 418 kb)
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the volunteers for their commitment, Vibeke Malmros, Carin Lennartsson, and Elisabeth Gramatkovski for assistance in the clinical part of the study, and finally Pågen AB, and Scan AB for supplying bread and pork loin, respectively.
Funding
This research project was funded by The Swedish Research Council (project number: K2012-69X-22060-01-5) and the Swedish Nutrition Foundation.
Availability of data and materials
The dataset (excluding all participant background characteristics) analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA
ANalysis Of Variance
- BMI
Body Mass Index
- CB
Cereal Breakfast
- CV-ANOVA
Coefficient of Variation- ANalysis Of Variance
- EHB
Egg & Ham Breakfast
- HMDB
Human Metabolome Database
- HSQC
Heteronuclear Single-Quantum Correlation
- MET
Metabolic Equivalent
- NAA
N-acetylated amino acids
- NMR
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
- NOESY
Nuclear Overhauser Effect SpectroscopY
- OPLS-DA
Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Discriminant Analysis
- OPLS-EP
Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures with Effect Projections
- PCA
Principal Component Analysis
- PLS
Projektions to Latent Structures
- rdCV
Repeated double Cross Validation
- ROC
Receiver Operating Curve
- TOCSY
Total Correlation SpectroscopY
Authors’ contributions
AW, HL, GK, LE & MR designed the study, MR performed clinical study and sampling. AP & MR preprocessed samples. AP performed NMR-analysis. MR, AP & DM preprocessed NMR data. MR & DM performed OPLS analyses and univariate statistics. CB performed ANOVA-decomposed multivariate analyses and contributed to statistical inference. AP in collaboration with MR identified metabolites. MR interpreted the data in collaboration with HL & AP. MR wrote the manuscript in collaboration with CB, HL, AW, DM & AP. All authors read, revised and critically assessed and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The project was approved by the Regional Ethical Review Board in Gothenburg, Sweden (reference number 561–12), adhered to the Helsinki Declaration, and registered with ClinicalTrials.gov (identifier: NCT02039596). All volunteers gave written informed consent before entering the study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Millie Rådjursöga, Email: millie.radjursoga@gu.se.
Helen M. Lindqvist, Email: helen.lindqvist@gu.se
Anders Pedersen, Email: anders.pedersen@nmr.gu.se.
Göran B. Karlsson, Email: goran.karlsson@nmr.gu.se
Daniel Malmodin, Email: daniel.malmodin@gu.se.
Carl Brunius, Email: carl.brunius@chalmers.se.
Lars Ellegård, Email: lasse.ellegard@nutrition.gu.se.
Anna Winkvist, Email: anna.winkvist@nutrition.gu.se.
References
- 1.Bingham SA. Biomarkers in nutritional epidemiology. Public Health Nutr. 2002;5:821–827. doi: 10.1079/PHN2002368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Coulston AM, Boushey CJ, Ferruzzi G. Nutrition in the prevention and treatment of disease. 3. London: Academic Press; 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Jenab M, Slimani N, Bictash M, Ferrari P, Bingham SA. Biomarkers in nutritional epidemiology: applications, needs and new horizons. Hum Genet. 2009;125:507–525. doi: 10.1007/s00439-009-0662-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kaaks R, Riboli E, Sinha R. Biochemical markers of dietary intake. IARC Sci Publ. 1997;142:103–26. [PubMed]
- 5.Tasevska N, Runswick SA, McTaggart A, Bingham SA. Urinary sucrose and fructose as biomarkers for sugar consumption. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2005;14:1287–1294. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-04-0827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bingham S, Luben R, Welch A, Low YL, Khaw KT, Wareham N, Day N. Associations between dietary methods and biomarkers, and between fruits and vegetables and risk of ischaemic heart disease, in the EPIC Norfolk cohort study. Int J Epidemiol. 2008;37:978–987. doi: 10.1093/ije/dyn111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Primrose S, Draper J, Elsom R, Kirkpatrick V, Mathers JC, Seal C, Beckmann M, Haldar S, Beattie JH, Lodge JK, et al. Metabolomics and human nutrition. Br J Nutr. 2011;105:1277–1283. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510004812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Wishart DS. Metabolomics: applications to food science and nutrition research. Trends Food Sci Technol. 2008;19:482–493. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2008.03.003. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Fave G, Beckmann ME, Draper JH, Mathers JC. Measurement of dietary exposure: a challenging problem which may be overcome thanks to metabolomics? Genes Nutr. 2009;4:135–141. doi: 10.1007/s12263-009-0120-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Scalbert A, Brennan L, Manach C, Andres-Lacueva C, Dragsted LO, Draper J, Rappaport SM, van der Hooft JJ, Wishart DS. The food metabolome: a window over dietary exposure. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;99:1286–1308. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.113.076133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Wold S, Sjöström M, Eriksson L. PLS-regression: a basic tool of chemometrics. Chemom Intell Lab Syst. 2001;58:109–130. doi: 10.1016/S0169-7439(01)00155-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Trygg J, Wold S. Orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS) J Chemom. 2002;16:119–128. doi: 10.1002/cem.695. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Trygg J, Holmes E, Lundstedt T. Chemometrics in metabonomics. J Proteome Res. 2007;6:469–479. doi: 10.1021/pr060594q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Bylesjö M, Rantalainen M, Cloarec O, Nicholson JK, Holmes E, Trygg J. OPLS discriminant analysis: combining the strengths of PLS-DA and SIMCA classification. J Chemom. 2006;20:341–351. doi: 10.1002/cem.1006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Jonsson P, Wuolikainen A, Thysell E, Chorell E, Stattin P, Wikstrom P, Antti H. Constrained randomization and multivariate effect projections improve information extraction and biomarker pattern discovery in metabolomics studies involving dependent samples. Metabolomics. 2015;11:1667–1678. doi: 10.1007/s11306-015-0818-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Smilde AK, Jansen JJ, Hoefsloot HC, Lamers RJ, van der Greef J, Timmerman ME. ANOVA-simultaneous component analysis (ASCA): a new tool for analyzing designed metabolomics data. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3043–3048. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Thissen U, Wopereis S, van den Berg SA, Bobeldijk I, Kleemann R, Kooistra T, van Dijk KW, van Ommen B, Smilde AK. Improving the analysis of designed studies by combining statistical modelling with study design information. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009;10:52. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-52. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Radjursoga M, Karlsson GB, Lindqvist HM, Pedersen A, Persson C, Pinto RC, Ellegard L, Winkvist A. Metabolic profiles from two different breakfast meals characterized by 1H NMR-based metabolomics. Food Chem. 2017;231:267–274. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.03.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ministers NCo. Nordic Nutrition Recommendations 2012. Copenhagen: Nordic Council of Ministers; 2014.
- 20.Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Marcu A, Guo AC, Liang K, Vázquez-Fresno R, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Karu N, et al. HMDB 4.0: the human metabolome database for 2018. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:D608–D617. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wold S, Esbensen K, Geladi P. Principal component analysis. Chemom Intell Lab Syst. 1987;2:37–52. doi: 10.1016/0169-7439(87)80084-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Westerhuis JA, van Velzen EJ, Hoefsloot HC, Smilde AK. Multivariate paired data analysis: multilevel PLSDA versus OPLSDA. Metabolomics. 2010;6:119–128. doi: 10.1007/s11306-009-0185-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.van Velzen EJ, Westerhuis JA, van Duynhoven JP, van Dorsten FA, Hoefsloot HC, Jacobs DM, Smit S, Draijer R, Kroner CI, Smilde AK. Multilevel data analysis of a crossover designed human nutritional intervention study. J Proteome Res. 2008;7:4483–4491. doi: 10.1021/pr800145j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Westerhuis JA, Hoefsloot HCJ, Smit S, Vis DJ, Smilde AK, van Velzen EJJ, van Duijnhoven JPM, van Dorsten FA. Assessment of PLSDA cross validation. Metabolomics. 2008;4:81–89. doi: 10.1007/s11306-007-0099-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Filzmoser P, Liebmann B, Varmuza K. Repeated double cross validation. J Chemom. 2009;23:160–171. doi: 10.1002/cem.1225. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Shi Lin, Westerhuis Johan A, Rosén Johan, Landberg Rikard, Brunius Carl. Variable selection and validation in multivariate modelling. Bioinformatics. 2018;35(6):972–980. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bty710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Hanhineva K, Brunius C, Andersson A, Marklund M, Juvonen R, Keski-Rahkonen P, Auriola S, Landberg R. Discovery of urinary biomarkers of whole grain rye intake in free-living subjects using nontargeted LC-MS metabolite profiling. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2015;59:2315–2325. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201500423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Buck M, Nilsson LK, Brunius C, Dabire RK, Hopkins R, Terenius O. Bacterial associations reveal spatial population dynamics in Anopheles gambiae mosquitoes. Sci Rep. 2016;6:22806. doi: 10.1038/srep22806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Lindgren F, Hansen B, Karcher W, Sjöström M, Eriksson L. Model validation by permutation tests: applications to variable selection. J Chemom. 1996;10:521–532. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1099-128X(199609)10:5/6<521::AID-CEM448>3.0.CO;2-J. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Lenz EM, Bright J, Wilson ID, Morgan SR, Nash AF. A 1H NMR-based metabonomic study of urine and plasma samples obtained from healthy human subjects. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2003;33:1103–1115. doi: 10.1016/S0731-7085(03)00410-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Brunius Carl, Pedersen Anders, Malmodin Daniel, Karlsson B Göran, Andersson Lars I, Tybring Gunnel, Landberg Rikard. Prediction and modeling of pre-analytical sampling errors as a strategy to improve plasma NMR metabolomics data. Bioinformatics. 2017;33(22):3567–3574. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Robertson MD, Henderson RA, Vist GE, Rumsey RDE. Extended effects of evening meal carbohydrate-to-fat ratio on fasting and postprandial substrate metabolism. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;75:505–510. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/75.3.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Madrid-Gambin Francisco, Brunius Carl, Garcia-Aloy Mar, Estruel-Amades Sheila, Landberg Rikard, Andres-Lacueva Cristina. Untargeted 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics Analysis of Urine and Serum Profiles after Consumption of Lentils, Chickpeas, and Beans: An Extended Meal Study To Discover Dietary Biomarkers of Pulses. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2018;66(27):6997–7005. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chaleckis R, Murakami I, Takada J, Kondoh H, Yanagida M. Individual variability in human blood metabolites identifies age-related differences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113:4252–4259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1603023113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kochhar S, Jacobs DM, Ramadan Z, Berruex F, Fuerholz A, Fay LB. Probing gender-specific metabolism differences in humans by nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabonomics. Anal Biochem. 2006;352:274–281. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2006.02.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Moore SC, Matthews CE, Sampson JN, Stolzenberg-Solomon RZ, Zheng W, Cai Q, Tan YT, Chow WH, Ji BT, Liu DK, et al. Human metabolic correlates of body mass index. Metabolomics. 2014;10:259–269. doi: 10.1007/s11306-013-0574-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Chorell E, Ryberg M, Larsson C, Sandberg S, Mellberg C, Lindahl B, Antti H, Olsson T. Plasma metabolomic response to postmenopausal weight loss induced by different diets. Metabolomics. 2016;12:1573–90.
- 38.Bouchard-Mercier A, Rudkowska I, Lemieux S, Couture P, Vohl MC. The metabolic signature associated with the Western dietary pattern: a cross-sectional study. Nutr J. 2013;12:158. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-12-158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Xiao Q, Derkach A, Moore SC, Zheng W, Shu X-O, Gu F, Caporaso NE, Sampson JN, Matthews CE. Habitual sleep and human plasma metabolomics. Metabolomics. 2017;13:63. doi: 10.1007/s11306-017-1205-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ottosson F, Ericson U, Almgren P, Nilsson J, Magnusson M, Fernandez C, Melander O. Postprandial levels of branch chained and aromatic amino acids associate with fasting glycaemia. J Amino Acids. 2016;2016:8576730. doi: 10.1155/2016/8576730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ross AB, Svelander C, Undeland I, Pinto R, Sandberg AS. Herring and beef meals Lead to differences in plasma 2-Aminoadipic acid, beta-alanine, 4-Hydroxyproline, Cetoleic acid, and docosahexaenoic acid concentrations in overweight men. J Nutr. 2015;145:2456–2463. doi: 10.3945/jn.115.214262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.DeLany JP, Windhauser MM, Champagne CM, Bray GA. Differential oxidation of individual dietary fatty acids in humans. Am J Clin Nutr. 2000;72:905–911. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/72.4.905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Samuni Y, Goldstein S, Dean OM, Berk M. The chemistry and biological activities of N-acetylcysteine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830:4117–4129. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.04.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Fulghesu AM, Ciampelli M, Muzj G, Belosi C, Selvaggi L, Ayala GF, Lanzone A. N-acetyl-cysteine treatment improves insulin sensitivity in women with polycystic ovary syndrome. Fertil Steril. 2002;77:1128–1135. doi: 10.1016/S0015-0282(02)03133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lindinger W, Taucher J, Jordan A, Hansel A, Vogel W. Endogenous production of methanol after the consumption of fruit. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1997;21:939–943. doi: 10.1111/j.1530-0277.1997.tb03862.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Shindyapina AV, Petrunia IV, Komarova TV, Sheshukova EV, Kosorukov VS, Kiryanov GI, Dorokhov YL. Dietary methanol regulates human gene activity. PLoS One. 2014;9:e102837. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Harris RC, Nevill M, Harris DB, Fallowfield JL, Bogdanis GC, Wise JA. Absorption of creatine supplied as a drink, in meat or in solid form. J Sports Sci. 2002;20:147–151. doi: 10.1080/026404102317200855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Calbet JAL, Ponce-Gonzalez JG, Calle-Herrero J, Perez-Suarez I, Martin-Rincon M, Santana A, Morales-Alamo D, Holmberg HC. Exercise preserves lean mass and performance during severe energy deficit: the role of exercise volume and dietary protein content. Front Physiol. 2017;8:483. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00483.eCollection02017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.A J, Trygg J, Gullberg J, Johansson AI, Jonsson P, Antti H, Marklund SL, Moritz T. Extraction and GC/MS analysis of the human blood plasma metabolome. Anal Chem. 2005;77:8086–8094. doi: 10.1021/ac051211v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Mitchell SC, Zhang AQ, Smith RL. Chemical and biological liberation of trimethylamine from foods. J Food Compos Anal. 2002;15:277–282. doi: 10.1006/jfca.2002.1068. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Table S1. Amino acid content of breakfast meals (mg). (DOCX 92 kb)
Table S2. Amino acid content of individual foods (mg). (DOCX 94 kb)
Table S3. Fatty acid content of breakfast meals (g). (DOCX 92 kb)
S-plot in orthogonal projections to latent structures with discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) model comparing the postprandial metabolic response between cereal breakfast (CB) and egg & ham breakfast (EHB). The top box is displaying selected discriminating metabolites for the EHB while the bottom box is displaying selected discriminating metabolites for the CB. Grey circles indicate significant (p < 0.05) variables in Mann Whitney U-test. (EPS 5517 kb)
S-plot in orthogonal projections to latent structures with effect matrix (OPLS-EP) model comparing variables increasing and decreasing in relation to the response vector (Y). The top box is displaying selected metabolites increasing and the bottom box is displaying metabolites decreasing in relation to Y. Grey circles indicate significant (p < 0.05) variables in Wilcoxon signed rank test. (EPS 890 kb)
Permutation analysis of ANOVA-PLS, showing actual model misclassifications as vertical lines with p-value calculated as the cumulative probability of finding the actual model result is a Student’s t-distribution of misclassification results obtained from randomly permuted data (n = 300 per model). The permutation distribution had median value of 91 misclassifications, corresponding exactly to the expected value of 182 observations in a two-class problem. The results show strong predictive modelling performance with absence of overfitting in the validation frameworks. (EPS 418 kb)
Data Availability Statement
The dataset (excluding all participant background characteristics) analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.