Abstract
Background
Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is a life‐threatening disease. Most often women become symptomatic only in the advanced stages of the disease, increasing the difficulty of treatment. Whilst the disease responds well to surgery and chemotherapy, the relapse rate is high. New treatments to prevent disease recurrence or progression, prolong survival, and increase the quality of life are needed.
Objectives
To assess the effectiveness and safety of interferon after surgery in the treatment of advanced (stage II‐IV) EOC.
Search methods
The Cochrane Gynaecological Cancer Review Group Specialized Register, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) Issue 1, 2012, MEDLINE and EMBASE were searched to January 2012. Handsearching of conference proceedings was also undertaken. Reference lists of reviews and included trials were screened and experts in the field were contacted for additional trials. Clinical trials registers were searched for ongoing trials.
Selection criteria
Randomised controlled trials (RCTs) involving participants with advanced EOC that compared post‐operative chemotherapy alone with post‐operative interferon therapy in combination with chemotherapy or post‐operative chemotherapy followed by interferon or observation alone
Data collection and analysis
Two review authors (AL and AM) independently screened the search results for relevant trials and extracted pre‐specified information from each included trial. Data were managed using Review Manager 5.1. Hazard ratios (HR) were calculated for time‐to‐event outcomes and risk ratios (RR) for dichotomous outcomes, with corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Main results
Five trials, including 1476 participants, were included in the review. Two trials compared interferon with observation alone and three trials compared interferon plus chemotherapy with chemotherapy alone. A meta‐analysis of two trials involving 370 participants found no significant difference in both overall survival (HR 1.14, 95% CI 0.84 to 1.55) and progression free survival (HR 0.99, 95% CI 0.79 to 1.24) between the interferon and observation alone groups in post‐surgical women who had undergone first‐line chemotherapy for advanced EOC. One trial with 293 participants found that while no significant difference was observed in incidence of nausea or vomiting between the two treatment groups, significantly more flu‐like symptoms (RR 2.25, 95% CI 1.73 to 2.91) and fatigue (RR 1.54, 95% CI 1.27 to 1.88) were reported in the interferon group. For the second comparison, a meta‐analysis of two trials comprising 244 participants found that although there was no significant difference in overall survival between the interferon plus chemotherapy and the chemotherapy alone group (HR 1.14, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.76), women in the interferon plus chemotherapy group had worse progression free survival than those in the chemotherapy alone group (HR 1.43, 95% CI 1.02 to 2.00). Compared to chemotherapy alone, adding interferon to chemotherapy did not alter the incidence of adverse events in post‐surgical women with advanced EOC.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice
Based on low quality evidence, the addition of interferon to first‐line chemotherapy did not alter the overall survival in post‐surgical women with advanced EOC compared with chemotherapy alone. There is low quality evidence to suggest that interferon in combination with chemotherapy worsened the progression free survival in post‐surgical women with advanced EOC compared with chemotherapy alone. There is not enough evidence that interferon therapy alone alters overall survival or progression free survival compared to observation alone in post‐surgical women who have undergone first‐line chemotherapy.
Implications for research
Three of the five trials included in this review were stopped early and were, therefore, underpowered to detect any true effect of the intervention. The trials did not report the results of important outcomes in a uniform manner, preventing statistical aggregation of the results. Trial methodology was poorly reported resulting in unclear risk of bias. For clear recommendations to be made regarding the effectiveness of interferon in the treatment of advanced EOC, long‐term, well conducted and adequately powered RCTs would be needed. However, the available data do not suggest that interferon has an adequately advantageous effect to warrant further investigation.
Plain language summary
Interferon therapy after surgery in women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer
Epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is a potentially life‐threatening condition. EOC usually develops in women above 50 years of age and is rarely seen in women younger than 35 years old. Early symptoms of the disease are usually mild and vague, making this disease difficult to detect at an early stage. Patients with EOC are relatively asymptomatic until the disease has progressed to an advanced stage.
Although EOC initially responds well to surgery and chemotherapy, there is a high rate of recurrence within 12 to 24 months of treatment. Interferons are proteins that are made and released by host cells in response to the presence of pathogens. They are named after their ability to 'interfere' with viral replication within host cells. Interferon serves two important functions. It signals neighbouring cells and triggers their resistance mechanisms; and it activates other immune cells that kill invading pathogens. This review assessed the effectiveness of interferon therapy in reducing the rate of recurrence or prolonging the time between chemotherapy and subsequent recurrence of the disease.
Five trials, including 1476 participants, were included in the review. Three of the five trials were stopped early. The risk of bias of most of the trials was high or unclear due to incomplete reporting of methods and results. Most of the trials were not large enough to detect any true effect of the intervention. Trials either did not report the results of important outcomes or the results of important outcomes were not uniform between the trials.
The evidence from the three trials suggested that the addition of interferon to first‐line chemotherapy did not alter the overall survival in post‐surgical women with advanced EOC compared with chemotherapy alone. On the contrary, there is evidence that interferon in combination with chemotherapy worsened progression free survival in post‐surgical women with advanced EOC compared with chemotherapy alone. Furthermore, there is not enough evidence that interferon therapy alone improves overall survival or progression free survival in post‐surgical women who have undergone first‐line chemotherapy when compared with observation alone.
Summary of findings
Background
Description of the condition
Worldwide, epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC) is the sixth most common cancer among women. There are more than 200,000 new cases diagnosed each year, accounting for approximately 4% of all cancers diagnosed in women. EOC is less common in women under the age of 35 years, and its incidence increases with age (GLOBOCAN 2002). In Europe, approximately 37% of women with EOC are alive five years after diagnosis (EUROCARE 2003). This is largely because the early stages of the disease often present with very few, if any, specific symptoms so most women present with advanced stage disease (Jemal 2008).
According to the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO), ovarian cancer is staged as follows (FIGO nomenclature, Rio de Janeiro 1988).
Stage I: the cancer is limited to the ovaries.
Stage II: the cancer involves one or both ovaries with spread to other pelvic organs or surfaces.
Stage III: the cancer spreads outside the pelvis to the abdominal area, including spread to the liver surface.
Stage IV: the cancer spreads to the liver or outside the peritoneal cavity to areas such as the chest or brain.
More details are given in Table 3.
1. Table 1: FIGO staging for ovarian cancer.
| STAGE I | The cancer is limited to the ovaries |
| IA | Limited to one ovary and the outer ovarian capsule is not ruptured. There is no tumor on the external surface of the ovary and there is no ascites and/or the washings are negative |
| IB | Cancer is present in both ovaries, but the outer capsule is intact and there is no tumor on external surface. There is no ascites and the washings are negative |
| IC | The cancer is either Stage IA or IB level but the capsule is ruptured or there is tumor on the ovarian surface or malignant cells are present in ascites or washings |
| STAGE II | Cancer involves one or both ovaries with spread to other pelvic organs or surfaces |
| IIA | Extension or implants onto the uterus and/or fallopian tube. The washings are negative washings and there is no ascites |
| IIB | Extension or implants onto other pelvic tissues. The washings are negative and there is no ascites |
| IIC | Pelvic extension or implants like Stage IIA or IIB but with positive pelvic washings |
| STAGE III | Cancer spread outside the pelvis to the abdominal area, including metastases to liver surface |
| IIIA | Tumor is grossly confined to the pelvis but with micro‐scopic peritoneal metastases beyond pelvis to abdominal peritoneal surfaces or the omentum |
| IIIB | Same as IIIA but with macro‐scopic peritoneal or omental metastases beyond pelvis less than 2 cm in size |
| IIIC | Same as IIIA but with peritoneal or omental metastases beyond pelvis, larger than 2 cm or lymph node metastases to inguinal, pelvic, or para‐aortic areas |
| STAGE IV | Metastases or spread to the liver or outside the peritoneal cavity to areas such as the chest or brain |
Patients with EOC are often relatively asymptomatic until the disease has progressed to an advanced stage. Some early symptoms may include bloating, pelvic or abdominal pain, difficulty eating or feeling full quickly, or a frequent need to urinate. The symptoms are usually mild and often go undetected (Twombly 2007). The five‐year survival rates of stage II, III and IV invasive EOC patients are 66%, 34% and 18% respectively (ACS 2013).
Several risk factors for EOC have been identified and include the following: a family history of the disease, refractory infertility or nulliparity (not having borne children), and certain mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 tumour suppressor genes. Multiparity (having given birth two or more times), use of oral contraceptives, and tubal ligation or hysterectomy have been shown to reduce the risk of EOC. Five years of oral contraceptive use by women, including those with a family history of the disease, can reduce their risk of EOC by up to 50% (Holschneider 2000).
Description of the intervention
While EOC responds well to surgery and chemotherapy, trials show that within 12 to 24 months post‐surgery and first‐line chemotherapy, 80% of patients experience disease recurrence or progression (Sourbier 2012). There is a need to explore new treatments that could prevent disease recurrence or progression after first‐line treatment. A recent Cochrane review concluded that there is not sufficient evidence that maintenance chemotherapy is more beneficial than observation alone for advanced EOC (Mei 2010; Mei 2011). Maintenance whole abdominal radiotherapy may improve the five‐year progression free survival (PFS) (Pickel 1999; Sorbe 2003; Mei 2011); however, it is rarely recommended because of its severe side effects. Interferons (IFNs) could be potentially useful in the treatment of EOC (Mei 2011).
In the 1980s, interferon‐alpha (INFα) was assessed as a maintenance therapy for patients with multiple myeloma (a cancer of the plasma cells in bone marrow). As a single agent, interferon has a low response rate in myeloma patients with responses of approximately 15%. However, in patients who demonstrated no evidence of disease progression following primary chemotherapy, maintenance chemotherapy with low‐dose subcutaneous INFα improved progression free and overall survival (Mandelli 1990; Hall 2004). INFα has been shown to have an in vitro activity against EOC cell lines (Epstein 1980; Hall 2004) and a limited clinical benefit in advanced EOC (Freedman 1983; Einhorn 1988; Hall 2004). It can be hypothesized that subcutaneous INFα may act as an effective maintenance therapy in patients with advanced EOC and thus improve overall survival (Hall 2004).
How the intervention might work
Interferons (IFNs) are a family of cytokines that demonstrate antiviral, immunomodulatory and antiproliferative activities. The IFNs are classified as type I (α, β, τ, and ω), II (γ) or III (λ) according to structural homology, cell‐surface receptor‐binding and functional activity. Type I IFNs are secreted at low levels by almost all cell types. IFNα and IFNβ are used clinically to treat viral infections, such as hepatitis B and C, and to treat certain malignancies such as malignant melanoma, hairy cell leukaemia, Kaposi’s sarcoma, chronic myelogenous leukaemia and renal cell carcinoma (Schroder 2004; Maher 2007; Tsuno 2009).
In addition to their structural differences, INFs alpha (α) and gamma (γ) differ in some respects. INFα is known for its ability to make cells resistant to viral infections while INFγ is known for its ability to regulate overall immune system functioning. Also, while INFα is produced by almost every cell in the body, INFγ is produced only by specialised cells in the immune system, known as T lymphocytes and natural killer cells.
INFα is a cytokine with multiple targets and mechanisms of action that are believed to contribute to its well‐known anti‐tumour activity, including inhibition of cell proliferation, induction of differentiation (cell maturation) or apoptosis (programmed cell death), stimulation of the immune system, and angiostatic activity (prevention of blood vessel growth) (Gresser 2002; Dunn 2006; Gresser 2007; Moserle 2008). INFα has been widely used to treat patients with solid tumours, including EOC, generally with unsatisfactory clinical results (Moserle 2008). Nevertheless, major clinical responses have occasionally been reported in some patients (Berek 1985; Nardi 1990; Willemse 1990; Moserle 2008), prompting the conduct of several large scale clinical trials. The tumour or host features underlying positive and negative outcomes of INFα therapy remain unknown for most cancers (Moserle 2008).
Why it is important to do this review
Due to the lack of sustained response to chemotherapy for the treatment of advanced EOC, there is a need to explore other potential treatment modalities such as the use of INF. This review aimed to assess the effectiveness and safety of interferon in the treatment of advanced (stage II‐IV) EOC.
Objectives
To assess the effectiveness and safety of interferon after surgery in the treatment of advanced (stage II‐IV) EOC.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
Randomised controlled trials (RCTs).
Types of participants
Post‐operative patients (adult women aged 18 years and above) with diagnosed Stage II, III (micro or macro) or IV EOC.
Types of interventions
Intervention
Post‐operative treatment with interferon alone or interferon combined with other cytotoxic agents. Type I interferons (alpha (α) and beta (β)) and Type II interferons (gamma (γ)) will be included. Some of the commercially available brands of interferon include interferon alfacon‐1 (Infergen), interferon‐alfa‐2a (Roferon‐A), pegylated interferon alfa‐2a, interferon alfa‐n3 (Alferon‐N), interferon alfa‐2b, pegylated interferon alfa‐2b, interferon beta‐1a (Avonex), interferon beta‐1b (Betaseron), and interferon gamma‐1B (Actimmune).
Control
Any post‐operative chemotherapy regimen or placebo.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
1. Overall survival (OS): time (in days) from the date of randomisation until death.
2. Progression free survival (PFS): time (in days) from randomisation to progression of disease or death (whichever occurs first). Disease progression is defined as the appearance of one or more new lesions or unequivocal progress of existing lesions, or both.
Secondary outcomes
1. Quality of life (QoL), measured using a scale that has been validated through reporting of norms in a peer‐reviewed publication.
2. Response (number of patients showing complete clinical response) as defined according to internationally agreed criteria (e.g. World Health Organization (WHO)).
3. Adverse events:
toxicity (flu‐like symptoms, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, etc),
other adverse events (neurological, dyspnoea, depression and anxiety, skin change or rash, alopecia, arthralgia or arthritis, insomnia, haematological, hepatic, other).
Search methods for identification of studies
A comprehensive and exhaustive search of the literature was executed in an attempt to identify all relevant trials regardless of language or publication status (published, unpublished, in press, and in progress).
Electronic searches
We searched the following databases and trial registers for relevant trials: Cochrane Gynaecological Cancer Review Group Specialized Register; Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) Issue 1, 2012; MEDLINE and EMBASE to January 2012. All relevant articles found were identified on PubMed and further searches were carried out for newly published articles using the 'related articles' feature.
The MEDLINE, EMBASE and CENTRAL search strategIes are presented in Appendix 1.
We searched the reference lists of all included trials for relevant trials. We also contacted authors of included trials and experts in the field of ovarian cancer and gynaecology to identify any additional published or unpublished trials.
Searching other resources
Handsearching
The following sources were handsearched for relevant trials or conference reports and abstracts.
Gynaecology Oncology (Annual Meeting of the American Society of Gynaecologic Oncologists), from November 1972 to June 2012 (Volume 1 to Volume 125, Issue 3).
International Journal of Gynaecological Cancer (Annual Meeting of the International Gynaecologic Cancer Society), 1991 to July 2012 (Volume 1 to Volume 22, Issue 6).
British Journal of Cancer, July 1973 to June 2012 (Volume 28 to 107, Issue 1)
Grey literature
Metaregister, Physicians Data Query, www.controlled‐trials.com/rct, www.clinicaltrials.gov, www.cancer.gov/clinicaltrials, and Gynaecology Oncologists of Canada (www.g‐o‐c.org) were searched for ongoing trials.
Data collection and analysis
Selection of studies
Two review authors, Aramide Lawal (AL) and Alfred Musekiwa (AM), independently screened the results of the search to select potentially relevant trials and applied the eligibility criteria using a pre‐designed eligibility form based on the inclusion criteria. Corresponding full text articles were retrieved and used to apply the eligibility criteria. Each of the articles were scrutinized to ensure that multiple publications from the same trial were included only once. Where eligibility was unclear, we sought clarification from the trial authors and re‐assessed the corresponding articles. We resolved any differences between the eligibility results by consensus. We excluded trials that did not meet the inclusion criteria and stated the reasons in the 'Characteristics of excluded studies' table.
Data extraction and management
Using a specially designed pre‐piloted data extraction form, two review authors (AL and AM) independently extracted information on methods, participants, interventions, and outcomes from each included trial. We extracted the number of participants randomised in each group and the numbers analysed for each outcome. We included dichotomous and time‐to‐event outcomes. For each dichotomous outcome we extracted the number of participants experiencing the event in each treatment group. For each time‐to‐event outcome, we extracted the number of participants experiencing the event, the median (range) survival for each treatment group and, where reported, the hazard ratio with corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) and Log‐rank P value. We used some of these data to estimate the log hazard ratio and its standard error using Parmar's methods (Parmar 1998).
The following information was also extracted: trial author(s), year of publication, country of origin, journal citation (including language), trial setting, trial design and methodology, details of the participants (demographic characteristics, total number enrolled, age, comorbidities, and patient characteristics), criteria for participant inclusion and exclusion, ovarian cancer details at diagnosis (FIGO stage, histological cell type, tumour grade, extent of disease, disease free interval, number of recurrences), interferon details and control or comparison details (route of administration, dosage, duration), duration of follow‐up, risk of bias in trial, and details about each of the primary and secondary outcomes. Trial authors were contacted in the case of unclear or missing data. We resolved any disagreements regarding extracted data by consensus.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors (AL and AM) independently assessed the risk of bias in included studies using the Cochrane Collaboration's tool (Higgins 2011). This included assessment of the following.
-
Selection bias:
random sequence generation,
allocation concealment.
Performance bias:
blinding of participants and personnel (patients and treatment providers).
-
Detection bias:
blinding of outcome assessment.
-
Attrition bias:
-
incomplete outcome data. We recorded the proportion of participants whose outcomes were not reported at the end of the trial. We coded a satisfactory level of loss to follow‐up for each outcome as:
low risk of bias, if fewer than 20% of patients were lost to follow‐up and reasons for loss to follow‐up were similar in both treatment arms,
high risk of bias, if more than 20% of patients were lost to follow‐up or reasons for loss to follow‐up differed between treatment arms,
unclear risk of bias, if loss to follow‐up was not reported.
-
-
Reporting bias:
selective reporting of outcomes.
Other possible sources of bias.
We categorized our judgements as 'yes', 'no', or 'unclear', indicating a low, high, or unclear risk of bias, respectively. The results were summarized using the 'risk of bias summary' and the 'risk of bias graph' in addition to the 'risk of bias tables'. Where necessary, we contacted the trial authors for clarification. We resolved any disagreements regarding risk of bias assessment by consensus.
Measures of treatment effect
We used Review Manager 5.1 (Revman 5) to calculate hazard ratios for time‐to‐event outcomes and risk ratios for dichotomous outcomes. For time‐to‐event outcomes, we calculated the log hazard ratios and their corresponding standard errors using Parmar's methods (Parmar 1998). These values were then entered into Revman 5 using the generic inverse variance method of meta‐analysis. We presented hazard ratios (HR) and risk ratios (RR) with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Dealing with missing data
Where data from the trial reports were insufficient, unclear or missing, we contacted the trial authors by e‐mail for additional information or clarification. We carried out analyses according to the intention‐to‐treat (ITT) principle where there were no missing data. In the case of missing data, we carried out analyses according to the available case analysis. We did not impute missing outcome data for any of the outcomes.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We assessed statistical heterogeneity by visually inspecting the forest plots to detect overlapping CIs, by estimation of the percentage heterogeneity between trials that cannot be ascribed to sampling variation (Higgins 2003), and also by a formal statistical test of the significance of the heterogeneity (Deeks 2001). We could not carry out subgroup analyses because there were only two trials per meta‐analysis. We used the guidance in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011) for interpreting the heterogeneity results. Where substantial heterogeneity was detected, we did not report the pooled result of the meta‐analysis but instead reported results from each trial separately.
Assessment of reporting biases
We could not construct funnel plots to assess the potential for small trial effects, such as publication bias, because we only had two trials per meta‐analysis.
Data synthesis
We decided a priori to use the random‐effects method irrespective of the results of the tests for heterogeneity. We calculated hazard ratios for time‐to‐event outcomes and risk ratios (RR) for dichotomous outcomes using Revman 5. Corresponding 95% CIs were also calculated. None of the trials included in the review compared multiple treatment regimes or assessed a continuous outcome.
We compared the effectiveness of interferon versus observation alone as well as interferon in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone.
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
The pre‐specified subgrouping to investigate for possible sources of heterogeneity across trials was:
FIGO stage of EOC (II, III, and IV).
Although we had planned to conduct subgroup analyses in the case of statistically significant heterogeneity between trials, this could not be done because there were only two trials per meta‐analysis.
Sensitivity analysis
Because of the small number of trials per meta‐analysis, we did not perform sensitivity analysis to assess the influence of risk of bias (allocation concealment) on the findings.
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
A total of 462 records were obtained from electronic databases and an additional 36 records were identified from other sources (see Figure 1). Following de‐duplication of the records a total of 461 records were assessed for eligibility. Ten full text articles were obtained. Five trials were deemed eligible for inclusion in the review. Two trials were excluded from the review; the reasons are set out in the Characteristics of excluded studies table. We were unclear about the eligibility of three trials as we were unable to obtain the full texts of these trials (Kosmidis 1997; Sumrit 1998; Zhyl'chuk 1998). Information on these trials has been included in the Characteristics of studies awaiting classification table.
1.
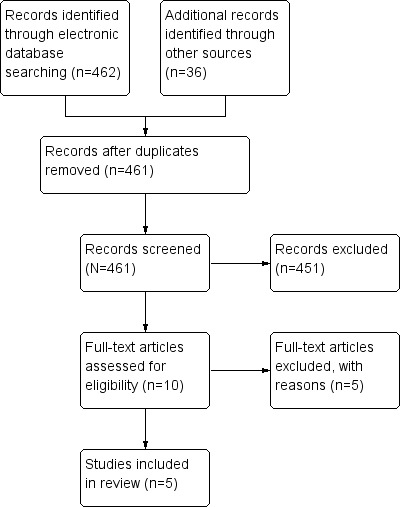
Study flow diagram.
Included studies
Details of all the included trials are presented in the table Characteristics of included studies. Four of the five trials were multicentre trials (Windbichler 2000; Hall 2004; Alberts 2006; Alberts 2008). The five trials included a total of 1476 randomised participants, and sample sizes ranged from 70 (Alberts 2006) to 847 (Alberts 2008) participants.
Settings
The trials were conducted in the United Kingdom (Hall 2004), Austria (Windbichler 2000), Italy (Bruzzone 1997) and the United States of America (USA) (Alberts 2006). The Alberts 2008 trial enrolled participants from Europe and North and South America. All trials were carried out in a secondary care setting. No trials were reported by primary care physicians or clinics.
Participants
The participants were women with histologically proven, advanced (FIGO stage II‐IV) EOC who had undergone debuking surgery. Trials included women with adequate bone marrow, hepatic and renal function. According to the inclusion criteria of this review only participants with FIGO stage II‐IV EOC were to be included. Windbichler 2000, however, enrolled participant with FIGO Stage Ic‐IV EOC and 11% of the included participants were classified as having FIGO Stage Ic EOC. The results of this trial were not analysed by the FIGO stage of the participants, so we were unable to tease out the information pertinent to our review. We did not feel justified in excluding this trial since only 11% of the participants had FIGO Stage Ic EOC, hence this trial was included. Alberts 2008 included a majority of participants with FIGO Stage III EOC, with 76.5% and 76.7% in the experimental and comparison groups respectively. The percentage of women with Stage IV EOC was 23.5% and 23.3% respectively. Alberts 2006 did not report on the FIGO staging of the participants. Windbichler 2000 stated that the percentage of women with FIGO Ic, II, III and IV EOC in the interferon group were 11%, 14%, 74% and 1% respectively, whilst the percentages in the chemotherapy group were 16%, 9%, 69% and 6% respectively. Hall 2004 reported that the percentages of women with FIGO Stage I, II, III and IV EOC in the interferon group were 7%, 22%, 63% and 15%, whereas in the chemotherapy group the percentages were 8%, 13%, 64% and 15% respectively. Bruzzone 1997 reported the percentages of women with FIGO I/II, III, IV EOC in the intervention group to be 4%, 83% and 13%, and in the control group 86% of women had FIGO stage III and 14% had stage IV disease.
Windbichler 2000 included women aged less than 75 years and excluded those with severe cardiovascular disease, life expectancy less than three months, recent malignancy or thromboembolic disease. Bruzzone 1997 enrolled women aged between 18 and 75 years and excluded those with extra‐abdominal localisation of disease (Stage IV) and previous malignancies. Hall 2004 enrolled women with no evidence of disease progression after post‐operative chemotherapy. Alberts 2006 included women with not more than 120 days between chemotherapy and second‐look surgery who had a patent intraperitoneal space at the time of second‐look surgery. Alberts 2008 enrolled previously untreated histologically diagnosed women following the initial surgery and who were randomised within 12 weeks after that surgery.
Intervention
The trials investigated the effectiveness of interferon with or without chemotherapy, either as part of the first‐line therapy following surgery (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000; Alberts 2008) or as a form of maintenance therapy following surgery and first‐line chemotherapy (Hall 2004; Alberts 2006).
Two forms of interferon were investigated, INFα (Bruzzone 1997; Hall 2004; Alberts 2006) and INFγ (Windbichler 2000; Alberts 2008). The interferon therapy was administered subcutaneously in two trials (Hall 2004; Alberts 2008) and intraperitoneally in three trials (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000; Alberts 2006).
The chemotherapy received by the women, either in conjunction with the interferon therapy or prior to interferon therapy, also differed between trials (see the details outlined in the table Characteristics of included studies).
The duration of treatment with interferon therapy varied from four years and four months (Bruzzone 1997) to 11 years (Alberts 2006). Duration of treatment was not specified in Alberts 2008.
The control groups received chemotherapy only or observation only. In both Alberts 2006 and Hall 2004 the control group received chemotherapy after surgery and was then observed while the intervention group received interferon. In Windbichler 2000 the control group received cisplatin (100 mg/m2) and cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2) every four weeks for six cycles, that is 24 weeks, and in Bruzzone 1997 the control group received three courses of carboplatin (400 mg/m2) every 28 days for three weeks. In Alberts 2008 the control group received chemotherapy, which included paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) over 3 hrs followed by carboplatin every three weeks continously. A total of six cycles were given unless disease progression or dose‐limiting toxicity occurred, or patients refused further treatment.
Outcomes
Primary outcomes including overall survival were reported by all included trials. Progression free survival was reported by Bruzzone 1997, Hall 2004, Alberts 2008 and Windbichler 2000. Treatment failure free survival was, however, only reported by Alberts 2008.
Secondary outcomes including adverse events were reported in three trials (Hall 2004; Alberts 2006; Alberts 2008). Response outcomes were reported by Windbichler 2000 and toxicity was reported by Windbichler 2000, Hall 2004 and Bruzzone 1997.
Excluded studies
Two trials were excluded because they were not randomised controlled trials but controlled clinical trials (Cardamakis 1999; Berek 2000). One trial (Kosmidis 1997) did not contain sufficient data for analysis because the outcomes that were measured and reported on were not relevant to our review. We have requested additional information from the authors, but we have not yet received a response. This study in addition to two further trials are awaiting classification because full text articles could not be found even after extensive searching and contacting the authors of the respective papers (Sumrit 1998; Zhyl'chuk 1998).
Risk of bias in included studies
Summaries of the risk of bias across included trials are provided in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
2.
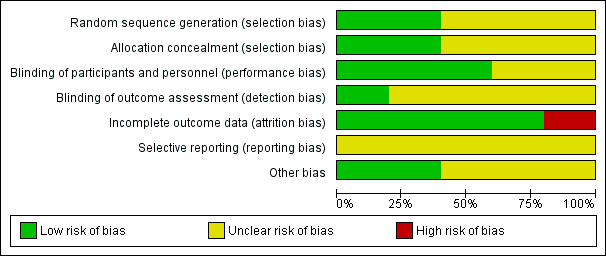
Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included trials.
3.
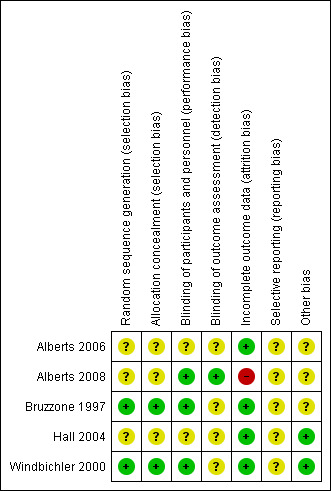
Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
Allocation
Bias related to randomisation was judged to be low in two trials (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000) and unclear in the remaining three (Hall 2004; Alberts 2006; Alberts 2008). Windbichler 2000 had computer generated randomised lists and Bruzzone 1997 used random number tables and specific lists of randomisation lists in blocks of varying sizes. The remaining trials were unclear and we have requested clarification from authors and are awaiting their responses.
Blinding
Where blinding of participants was not reported on, or not described, we judged the trial to be at unclear risk when the control participants did not receive any treatment (Hall 2004; Alberts 2006). Where blinding of participants was not reported on but the control group received chemotherapy alone we judged the risk of bias to be of unclear (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000; Alberts 2008). Adequate blinding of outcome assessors was described in Alberts 2008. Blinding of outcome assessors was not described in any of the other trials and the bias was therefore judged as unclear risk of bias (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000; Hall 2004; Alberts 2006).
Incomplete outcome data
The risk of bias due to attrition was judged to be low in three of the five included trials. Five out of 57 people were lost to follow‐up in the intervention group as well as the same proportion in the control group in one trial (Bruzzone 1997), and at least 96% received the intervention in another trial (Hall 2004). In one trial (Alberts 2008) the incidence of withdrawal was 24% and 17% in the intervention and control groups respectively, and another trial recorded 9% and 10% withdrawals due to disease progression in the intervention and control groups respectively (Windbichler 2000). Alberts 2006 recorded 8% loss to follow‐up in the intervention group and none in the control group.
Selective reporting
None of the trial protocols were obtained. Therefore, the risk of bias was judged as unclear for all of the included trials.
Other potential sources of bias
Three of the included trials were stopped early and were therefore judged to have unclear risk of bias. Two of these trials were stopped early due to poor accrual of participants (Bruzzone 1997; Alberts 2006) and the other trial was stopped early based on a decision made by the Data and Safety Monitoring Board (Alberts 2008).
Effects of interventions
Summary of findings for the main comparison. Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for women with advanced (Stage II‐IV) epithelial ovarian cancer who have undergone surgery.
| Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone for women with advanced (Stage II‐IV) epithelial ovarian cancer who have undergone surgery | ||||||
| Patient or population: Women with advanced (Stage II‐IV) epithelial ovarian cancer who have undergone surgery Settings: Secondary care settings Intervention: Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone post‐surgery for advanced ovarian surgery | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of Participants (trials) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Interferon + Chemotherapy versus Chemotherapy alone | |||||
| Overall survival | Study population | HR 1.14 (0.74‐1.76) | 244 (2 trials) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low1,4 | ||
| 318 per 1000 | 378 per 1000 (295 to 483) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 309 per 1000 | 368 per 1000 (287 to 470) | |||||
| Progression‐free survival | Study population | HR 1.43 (1.02 to 2.00) | 244 (2 trials) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low,3,2 | ||
| 607 per 1000 | 546 per 1000 (297 to 1000) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 603 per 1000 | 543 per 1000 (295 to 1000) | |||||
| Adverse event (flu‐like symptoms) | Study population | RR 6.49 (0.41 to 102.25) | 230 (2 trials) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low1,3 | ||
| 87 per 1000 | 564 per 1000 (36 to 1000) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 100 per 1000 | 649 per 1000 (41 to 1000) | |||||
| Adverse event (fatigue) | Study population | RR 1.17 (0.82 to 1.68) | 97 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low3,4 | ||
| 511 per 1000 | 597 per 1000 (419 to 858) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 511 per 1000 | 598 per 1000 (419 to 858) | |||||
| Adverse event (neurotoxicity) | Study population | RR 0.87 (0.57 to 1.33) | 230 (2 trials) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low3, 4 | ||
| 270 per 1000 | 235 per 1000 (154 to 359) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 244 per 1000 | 212 per 1000 (139 to 325) | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across trials) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: Confidence interval; RR: Risk ratio | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High quality: Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: We are very uncertain about the estimate. | ||||||
1 High risk of bias due to study being stopped early
2 Significant heterogeneity between the trials 3 The method of randomisation was not described and allocation concealment was not mentioned 4 Small sample size, potentially underpowered study
Summary of findings 2. Interferon versus observation alone for women with advanced (Stage II‐IV) epithelial ovarian cancer.
| Interferon versus observation alone for women with advanced (Stage II‐IV) epithelial ovarian cancer | ||||||
| Patient or population: women with advanced (Stage II‐IV) epithelial ovarian cancer who have undergone surgery Settings: Secondary care settings Intervention: Interferon versus observation alone post‐surgery for advanced epithelial ovarian cancer | ||||||
| Outcomes | Illustrative comparative risks* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | No of Participants (trials) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Assumed risk | Corresponding risk | |||||
| Control | Interferon versus observation alone | |||||
| Overall survival | Study population | HR 1.14 (0.84 to 1.55) | 370 (2 trials) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝1,3 low |
||
| 140 per 1000 | 74 per 1000 (35 to 153) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 306 per 1000 | 178 per 1000 (88 to 329) | |||||
| Progression‐free survival | Study population | HR 0.99 (0.79 to 1.24) | 370 (2 trials) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low1,2 | ||
| 571 per 1000 | 629 per 1000 (429 to 920) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 571 per 1000 | 628 per 1000 (428 to 919) | |||||
| Adverse event (flu‐like symptoms) | Study population | RR 2.25 (1.73 to 2.91) | 293 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low1,2 | ||
| 315 per 1000 | 710 per 1000 (546 to 918) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 315 per 1000 | 709 per 1000 (545 to 917) | |||||
| Adverse event (fatigue) | Study population | RR 1.54 (1.27 to 1.88) | 293 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low1,2 |
||
| 477 per 1000 | 734 per 1000 (605 to 896) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 477 per 1000 | 735 per 1000 (606 to 897) | |||||
| Adverse event (nausea/ vomiting) | Study population | RR 1.21 (0.91 to 1.62) | 293 (1 study) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ low1,2 | ||
| 349 per 1000 | 422 per 1000 (318 to 565) | |||||
| Moderate | ||||||
| 349 per 1000 | 422 per 1000 (318 to 565) | |||||
| *The basis for the assumed risk (e.g. the median control group risk across trials) is provided in footnotes. The corresponding risk (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: Confidence interval; RR: Risk ratio; OR: Odds ratio | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High quality: Further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect. Moderate quality: Further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate. Low quality: Further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate. Very low quality: We are very uncertain about the estimate. | ||||||
1Method of randomisation and allocation concealment were not reported on resulting in a potential high risk of selection bias. Participants were not blinded to the treatment which may have affected the performance of the control group resulting in a potentially high risk of performance bias. 2 Small sample size, potentially underpowered study
3 Imprecise effect estimate as evidenced by wide confidence interval.
Interferon versus observation alone
Two trials assessed the effect of interferon versus observation alone (Hall 2004; Alberts 2006).
Primary outcomes
1. Overall survival (OS)
Meta‐analysis of the two trials, assessing 370 women, found no significant difference in overall survival between the interferon and observation alone groups (HR 1.14, 95% CI 0.84 to 1.55, Figure 4, Analysis 1.1). The percentage of the variability in effect estimates that was due to heterogeneity rather than chance might not be important (I2 = 16%).
4.
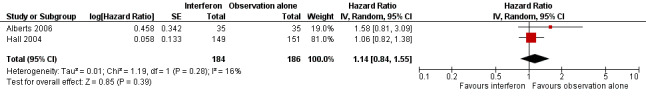
Forest plot of comparison: 1 Interferon versus observation alone, outcome: 1.1 Overall survival.
1.1. Analysis.
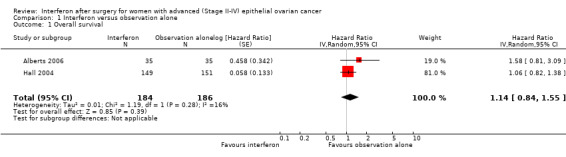
Comparison 1 Interferon versus observation alone, Outcome 1 Overall survival.
2. Progression free survival (PFS)
Meta‐analysis of the two trials, assessing 370 women, found no significant difference in progression free survival between the interferon and observation alone groups (HR 0.99, 95% CI 0.79 to 1.24, Analysis 1.2). The percentage of the variability in effect estimates that was due to heterogeneity rather than chance might not be important (I2 = 0%). Hall 2004 followed up patients for two years (15%, 63%, 14% and 7% of women had stage FIGO Stage I, II, III and IV EOC respectively). The period of follow‐up was not stated in Alberts 2006 and 64%, 26% and 10% of the women had FIGO Stage III, II and I EOC respectively.
1.2. Analysis.
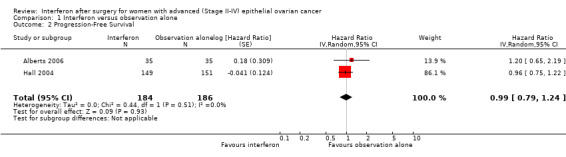
Comparison 1 Interferon versus observation alone, Outcome 2 Progression‐Free Survival.
Secondary outcomes
1. Quality of life (QoL)
This outcome was not reported by the two trials assessing this comparison.
2. Response
This was defined by the number of women with a complete clinical response.
This outcome was not reported by the two trials assessing this comparison.
3. Adverse events
Toxicity (flu‐like symptoms, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, etc)
Alberts 2006 reported toxicity adverse events only for the interferon arm and not for the observation alone arm.
Hall 2004, assessing 293 women, reported significantly more flu‐like symptoms (RR 2.25, 95% CI 1.73 to 2.91, Analysis 1.3) and fatigue (RR 1.54, 95% CI 1.27 to 1.88, Analysis 1.4) in the interferon group compared to the observation alone group, but there was no significant difference in the number of women experiencing nausea or vomiting between the two treatment groups (RR 1.21, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.62, Analysis 1.5).
1.3. Analysis.
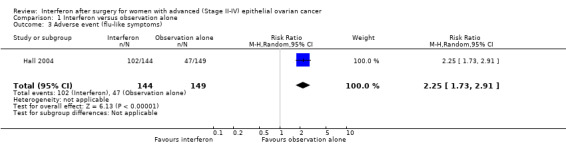
Comparison 1 Interferon versus observation alone, Outcome 3 Adverse event (flu‐like symptoms).
1.4. Analysis.
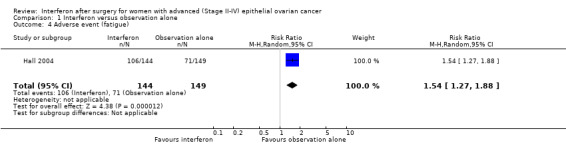
Comparison 1 Interferon versus observation alone, Outcome 4 Adverse event (fatigue).
1.5. Analysis.
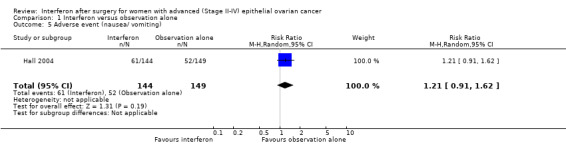
Comparison 1 Interferon versus observation alone, Outcome 5 Adverse event (nausea/ vomiting).
Other adverse events (neurological, dyspnoea, depression and anxiety, skin change or rash, alopecia, arthralgia or arthritis, insomnia, haematological, hepatic, other)
Both trials (Hall 2004; Alberts 2006) reported other adverse events only for the interferon group and not for the observation alone group.
Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone
Three trials compared the effect of interferon therapy in combination with chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000; Alberts 2008).
Primary outcomes
1. Overall survival (OS)
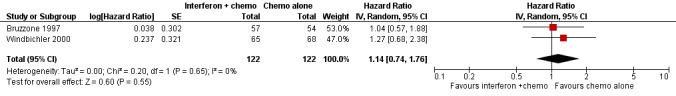
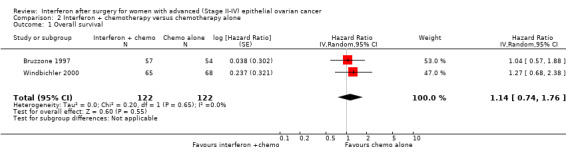
Meta‐analysis of two trials (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000), assessing 244 women, found no significant difference in overall survival between the interferon plus chemotherapy and the chemotherapy alone groups (HR 1.14, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.76, Figure 5, Analysis 2.1). The percentage of the variability in effect estimates that was due to heterogeneity rather than chance might not be important (I2 = 0%). The remaining trial (Alberts 2008) could not be included in the meta‐analysis because it failed to report the hazard ratio for EOC patients separately, orsufficient information to enable the calculation of the hazard ratio.
5.
Forest plot of comparison: 2 Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone, outcome: 2.1 Overall survival.
2.1. Analysis.
Comparison 2 Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone, Outcome 1 Overall survival.
2. Progression free survival (PFS)
Meta‐analysis of two trials (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000), assessing 244 participants, found that women in the interferon plus chemotherapy group had a higher risk of disease progression compared to the chemotherapy alone group (HR 1.43, 95% CI 1.02 to 2.00, Figure 6, Analysis 2.2). The percentage of the variability in effect estimates that was due to heterogeneity rather than chance might not be important (I2 = 0%). The remaining trial (Alberts 2008) could not be included in the meta‐analysis because it failed to report the hazard ratio for EOC patients separately, or sufficient information to enable the calculation of the hazard ratio.
6.
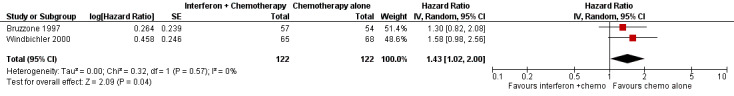
Forest plot of comparison: 2 Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone, outcome: 2.2 Progression free survival.
2.2. Analysis.
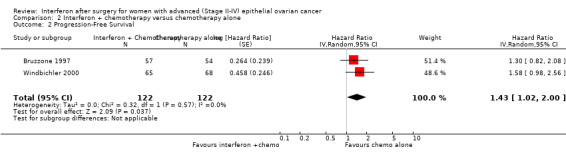
Comparison 2 Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone, Outcome 2 Progression‐Free Survival.
Secondary outcomes
1. Quality of life (QoL)
This outcome was not reported by any of the three trials assessing this comparison.
2. Response
One trial (Windbichler 2000), assessing 81 participants, found no significant difference in the number of women with a complete clinical response between the two treatment groups (RR 1.23, 95% CI 0.87 to 1.73, Analysis 2.3).
2.3. Analysis.
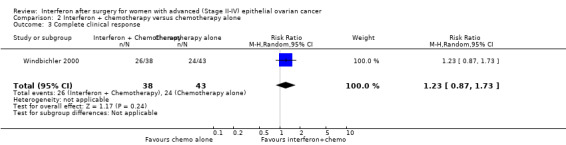
Comparison 2 Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone, Outcome 3 Complete clinical response.
This outcome was not reported by the other two trials assessing this comparison.
3. Adverse events
Alberts 2008 did not report adverse event results for each arm of EOC patients separately, or any relative measure for the two groups.
Toxicity (flu‐like symptoms, fatigue, nausea and vomiting, etc)
Flu‐like symptoms
One trial (Windbichler 2000), assessing 133 participants, found that treatment with interferon plus chemotherapy significantly increased the risk of flu‐like symptoms compared to chemotherapy alone (RR 23.54, 95% CI 5.95 to 93.09, Analysis 2.4). Another trial (Bruzzone 1997), assessing 97 participants, found no significant difference in the risk of flu‐like symptoms between the two treatment groups (RR 2.00, 95% CI 0.95 to 4.19, Analysis 2.4). These two trials were not pooled in a meta‐analysis because of high heterogeneity.
2.4. Analysis.
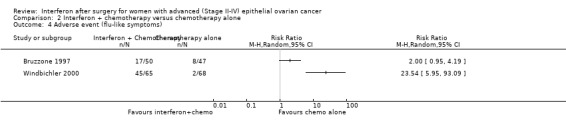
Comparison 2 Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone, Outcome 4 Adverse event (flu‐like symptoms).
Fatigue
One trial (Bruzzone 1997), assessing 97 participants, found no significant difference in the number of women experiencing fatigue between the two treatment groups (RR 1.18, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.68, Analysis 2.5). Windbichler 2000 did not report on fatigue.
2.5. Analysis.
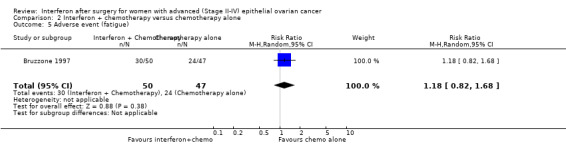
Comparison 2 Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone, Outcome 5 Adverse event (fatigue).
Neither Bruzzone 1997 nor Windbichler 2000 reported on nausea or vomiting.
Other adverse events (neurological, dyspnoea, depression and anxiety, skin change or rash, alopecia, arthralgia or arthritis, insomnia, haematological, hepatic, other)
The following adverse events were reported by both Bruzzone 1997 and Windbichler 2000. The numbers used in the calculations of treatment effects were derived from the percentages reported.
Neurotoxicity
A meta‐analysis of results from Bruzzone 1997 and Windbichler 2000, assessing 230 participants, found no significant difference in the incidence of neurotoxicity between the two treatment groups (RR 0.87, 95% CI 0.57 to 1.33, Analysis 2.6). The percentage of the variability in effect estimates that was due to heterogeneity rather than chance might not be important (I2 = 0%).
2.6. Analysis.
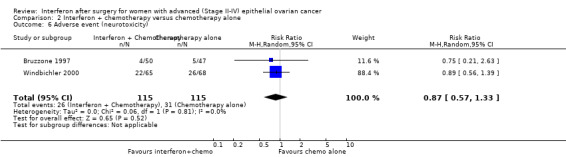
Comparison 2 Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone, Outcome 6 Adverse event (neurotoxicity).
Alopecia
A meta‐analysis of results from Bruzzone 1997 and Windbichler 2000, assessing 230 participants, found no significant difference in the incidence of alopecia between the two treatment groups (RR 0.96, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.23, Analysis 2.7). The percentage of the variability in effect estimates that was due to heterogeneity rather than chance might not be important (I2 = 0%).
2.7. Analysis.
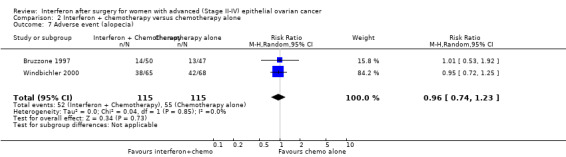
Comparison 2 Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone, Outcome 7 Adverse event (alopecia).
Anaemia
A meta‐analysis of results from Bruzzone 1997 and Windbichler 2000, assessing 230 participants, found no significant difference in the incidence of anaemia between the two treatment groups (RR 1.13, 95% CI 0.83 to 1.55, Analysis 2.8). The percentage of the variability in effect estimates that was due to heterogeneity rather than chance might not be important (I2 = 0%).
2.8. Analysis.
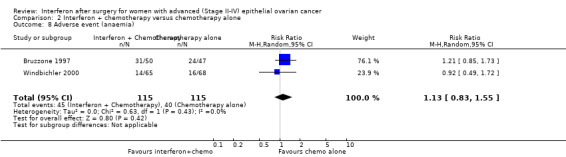
Comparison 2 Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone, Outcome 8 Adverse event (anaemia).
Discussion
Summary of main results
Five trials, with a total of 1476 women, were included in the review. Two trials assessed the effectiveness of interferon therapy compared with observation alone in post‐surgical women who had undergone first‐line chemotherapy for advanced EOC (Hall 2004; Alberts 2006). Three trials investigated the effectiveness of adding interferon to first‐line chemotherapy compared to chemotherapy alone in post‐surgical women with advanced EOC (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000; Alberts 2008).
A meta‐analysis of two trials (Hall 2004; Alberts 2006) found no significant difference in both overall survival and progression free survival between the interferon and observation alone groups in post‐surgical women who have undergone first‐line chemotherapy for advanced EOC.
One trial (Hall 2004) found that while no significant difference was observed in the number of women experiencing nausea or vomiting between the two treatment groups, significantly more flu‐like symptoms and fatigue were reported in the interferon group compared to the observation group.
A meta‐analysis of two trials (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000) found no significant difference in overall survival between the interferon plus chemotherapy and chemotherapy alone groups in post‐surgical women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. However, meta‐analysis of the same two trials found that women in the interferon plus chemotherapy group had a higher risk of disease progression compared to the chemotherapy alone group.
Based on the results of a meta‐analysis of two trials (Bruzzone 1997; Windbichler 2000), the addition of interferon to first‐line chemotherapy did not significantly increase the incidence of neurotoxic events, alopecia or anaemia compared to chemotherapy alone. While Windbichler 2000 reported a significant increase in flu‐like symptoms in the interferon and chemotherapy group compared to the chemotherapy alone group, Bruzzone 1997 reported no significant difference between the two groups for the incidence of flu‐like symptoms or fatigue.
It is also important to note that three of the five included trials were stopped early. Bruzzone 1997 was stopped early due to toxicities and the higher costs in the interferon arm, considering the absence of a clinically important survival advantage. Alberts 2006 was stopped early due to poor accrual of participants. Alberts 2008 was stopped early following a protocol‐defined second interim analysis, which revealed a significantly shorter overall survival time in women receiving interferon with chemotherapy compared to chemotherapy alone. Stopping a trial early may result in the study being underpowered to detect a true effect if the effect size is small.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
A substantial amount of information on important outcomes has been requested from the trial authors, but has not yet been received. Four of the five included trials were conducted in developed countries. In one trial women were recruited from countries in Europe and North and South America, thus making the findings somewhat more applicable to developed and developing countries. In undeveloped settings, the cost implications of interferon therapy versus the effectiveness of the treatment would have to be considered more closely. There were no trials completed within the last three years that met the inclusion criteria of the review. There remains a possibility that interferon therapy is more effective with some of the newer chemotherapy regimes, but this has not been tested. Most of the included trials failed to measure or report on important secondary outcomes such as clinical response, quality of life or the cost implications of interferon therapy.
Quality of the evidence
GRADE assessments
GRADEPro was used to create 'Summary of findings' tables for the various outcomes. In determining the level of evidence for each outcome, both the efficacy results and the assessment of the risk of bias were integrated into a final assessment of the level of evidence and full details of the decision provided in footnotes. All primary and secondary outcomes were rated as critical and received a score of ‘9’ indicating the highest level of importance to patients.
Interferon and chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone
See Table 1 for the complete assessment and rationale for ratings.
For the outcome of overall survival the level of evidence was rated as low. The evidence is based on the findings of two trials. The reasons for downgrading this outcome is due to the method of randomisation not being described in the included trials and allocation concealment either not being described or undertaken, as well as one trial being stopped early.
For disease progression and adverse events (flu‐like symptoms, fatigue and neurotoxicity) the level of evidence was rated as low. Reasons for this rating included lack of reporting on the method of randomisation, allocation concealment either not described or undertaken in the trials, significant heterogeneity between the trials, high risk of bias due to stopping the trial early, and small sample sizes and potential for a study to be underpowered to detect the true effect of the intervention on the outcome in question.
Interferon versus observation alone
See Table 2 for the complete assessment and rationale for ratings.
For the outcome of overall survival the level of evidence was rated as low. The evidence was based on the findings of two small trials with unclear or potentially high risk of selection bias and performance bias. In addition to this, the wide confidence intervals reflect imprecise estimates of effect for this outcome.
For disease progression and adverse events (nausea and vomiting, flu‐like symptoms and fatigue) the level of evidence was rated as low. Evidence for these outcomes was based on the findings of one study that did not report the method of randomisation or describe how allocation concealment was conducted, or if it was conducted, resulting in unclear or potentially high risk of selection bias. The small sample size and potential for a study to be underpowered to detect the true effect of the intervention on the outcome in question also led to the quality of the evidence being downgraded.
Based on the low quality of evidence for the outcomes reported, there is insufficient evidence for a robust conclusion regarding the effectiveness of interferon in the treatment of advanced EOC. This is based on the results of the four trials that were included in the meta‐analyses. The key methodological shortcomings were the absence of the method of randomisation and allocation concealment, significant heterogeneity between trials, small sample sizes as well as early stoppage of trials.
Potential biases in the review process
Biases in the review process were minimised by performing a comprehensive search of the literature, independently selecting and appraising the trials, and extracting the data in duplicate. Where data were missing, we sought additional information and data direct from authors, where this was possible to do so. At the time of the review submission, we were unable to get information on various methodological aspects of the trials (for example method of randomisation and allocation concealment) as well as important outcomes (for example number of deaths, number of participants with disease progression or recurrence) from the relevant authors.
The following aspects of the included trials could introduce bias into the results of the review.
Although all of the included trials investigated interferon, the interventions evaluated in the trials were similar but not identical.
Interferon was administered either subcutaneously or intraperitoneally.
The chemotherapy regimes used, either in combination with interferon or prior to interferon therapy, were similar but not identical.
The review is at risk of publication bias for less prominent trials. We attempted to reduce this risk by identifying relevant conference abstracts, by handsearching relevant conference proceedings. Furthermore, there are two trials awaiting assessment as we could not get hold of the full text articles. It is not known what effect the results of these trials might have on the validity of this review.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
Windbichler 2000 concluded that the inclusion of intraperitoneal INFγ in first‐line chemotherapy prolongs progression free survival. This finding is similar to that of a pilot study by Berek 2000, which found surgically documented responses in the size of ovarian tumours following the use of INFα. Overall this review concluded that interferon, with or without chemotherapy, was no more effective than chemotherapy alone or observation alone in improving overall survival or progression free survival in post‐surgical women with advanced epithelial ovarian cancer (EOC).
In a study by Freedman 1983, where human leukocyte INFα was administered to 15 patients with EOC after previous chemotherapy or therapeutic irradiation, one objective response was observed. In another study by Epstein 1980, which determined the in vitro sensitivity of human ovarian carcinoma cells to the antiproliferative effects of human leukocyte interferon, tumour colony cells were found to be responsive to interferon. In a preliminary trial by Jui‐Tung 1992, where INFα and INFγ with sizofiran were given to post‐operative patients, it was found that there were no recurrences in those patients. There was also significant difference in survival in the patients treated with interferon.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
Based on low quality evidence, the addition of interferon to first‐line chemotherapy, compared with chemotherapy alone, did not alter the overall survival in post‐surgical women with advanced EOC. There is low quality evidence to support that interferon in combination with chemotherapy, compared with chemotherapy alone, worsened the progression free survival in post‐surgical women with advanced EOC. There is not enough evidence that interferon therapy alone alters overall survival or progression free survival compared to observation alone in post‐surgical women who have undergone first‐line chemotherapy.
Implications for research.
Three of the five trials included in this review were stopped early and may be underpowered to detect the true effect of the intervention. The trials did not report the results of important outcomes in a uniform manner, preventing statistical aggregation of the results. Trial methodology was poorly reported, resulting in unclear risk of bias. For clear recommendations to be made regarding the effectiveness of interferon in the treatment of advanced EOC, long‐term, well conducted and adequately powered RCTs would be needed to investigate the effects of interferon on overall survival, progression free survival, complete clinical response, quality of life, adverse events and cost implications. Improved trial planning and conduct are necessary to avoid early stoppage of trials. However, the available data do not suggest that interferon has a clinically significant effect in EOC, either alone or combined with conventional chemotherapy, hence conducting further studies might not be ethical.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 17 July 2018 | Amended | Next stage expected date amended. |
| 28 June 2018 | Review declared as stable | Intervention no longer in general use. |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 2, 2012 Review first published: Issue 6, 2013
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 April 2015 | Amended | Contact details updated. |
| 24 February 2015 | Amended | Contact details updated. |
| 11 February 2015 | Amended | Contact details updated. |
| 27 March 2014 | Amended | Contact details updated. |
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Jo Morrison for clinical advice. We would also like to thank Charles Okwundu for his advice and editing input during the protocol phase of the review.
The National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) is the largest single funder of the Cochrane Gynaecological Cancer Group.
The views and opinions expressed therein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the NIHR, NHS or the Department of Health
Appendices
Appendix 1. MEDLINE search strategy
Medline Ovid
1 exp Ovarian Neoplasms/ 2 (ovar* adj5 (cancer* or tumor* or tumour* or neoplas* or malignan* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma*)).mp. 3 1 or 2 4 exp Interferons/ 5 interferon*.mp. 6 (Infergen or Roferon‐A or Alferon‐N or Avonex or Betaseron or Actimmune).mp. 7 4 or 5 or 6 8 randomized controlled trial.pt. 9 controlled clinical trial.pt. 10 randomized.ab. 11 placebo.ab. 12 drug therapy.fs. 13 randomly.ab. 14 trial.ab. 15 groups.ab. 16 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 17 3 and 7 and 16
key:
mp=title, abstract, original title, name of substance word, subject heading word, protocol supplementary concept, rare disease supplementary concept, unique identifier, pt=publication type, ab=abstract, fs=floating subheading
Appendix 2. EMBASE search strategy
Embase Ovid
1 exp ovary cancer/ 2 (ovar* adj5 (cancer* or tumor* or tumour* or neoplas* or malignan* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma*)).mp. 3 1 and 2 4 exp interferon/ 5 interferon*.mp. 6 (Infergen or Roferon‐A or Alferon‐N or Avonex or Betaseron or Actimmune).mp. 7 4 or 5 or 6 8 crossover procedure/ 9 double‐blind procedure/ 10 randomized controlled trial/ 11 single‐blind procedure/ 12 random*.mp. 13 factorial*.mp. 14 (crossover* or cross over* or cross‐over*).mp. 15 placebo*.mp. 16 (double* adj blind*).mp. 17 (singl* adj blind*).mp. 18 assign*.mp. 19 allocat*.mp. 20 volunteer*.mp. 21 8 or 9 or 10 or 11 or 12 or 13 or 14 or 15 or 16 or 17 or 18 or 19 or 20 22 3 and 7 and 21
key:
mp=title, abstract, subject headings, heading word, drug trade name, original title, device manufacturer, drug manufacturer, device trade name, keyword
Appendix 3. CENTRAL search strategy
CENTRAL
#1 MeSH descriptor Ovarian Neoplasms explode all trees #2 (ovar* near/5 (cancer* or tumor* or tumour* or neoplas* or malignan* or carcinoma* or adenocarcinoma*)) #3 (#1 OR #2) #4 MeSH descriptor Interferons explode all trees #5 interferon* #6 (Infergen or Roferon‐A or Alferon‐N or Avonex or Betaseron or Actimmune) #7 (#4 OR #5 OR #6) #8 (#3 AND #7)
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Interferon versus observation alone.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Overall survival | 2 | 370 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.84, 1.55] |
| 2 Progression‐Free Survival | 2 | 370 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.79, 1.24] |
| 3 Adverse event (flu‐like symptoms) | 1 | 293 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.25 [1.73, 2.91] |
| 4 Adverse event (fatigue) | 1 | 293 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.54 [1.27, 1.88] |
| 5 Adverse event (nausea/ vomiting) | 1 | 293 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.21 [0.91, 1.62] |
Comparison 2. Interferon + chemotherapy versus chemotherapy alone.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Overall survival | 2 | 244 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 1.14 [0.74, 1.76] |
| 2 Progression‐Free Survival | 2 | 244 | Hazard Ratio (Random, 95% CI) | 1.43 [1.02, 2.00] |
| 3 Complete clinical response | 1 | 81 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.23 [0.87, 1.73] |
| 4 Adverse event (flu‐like symptoms) | 2 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | Totals not selected | |
| 5 Adverse event (fatigue) | 1 | 97 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.18 [0.82, 1.68] |
| 6 Adverse event (neurotoxicity) | 2 | 230 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.87 [0.57, 1.33] |
| 7 Adverse event (alopecia) | 2 | 230 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.74, 1.23] |
| 8 Adverse event (anaemia) | 2 | 230 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.13 [0.83, 1.55] |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Alberts 2006.
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial Trial duration: 11 years, from March 1988 to June 1999 Trial location: USA ‐ 66 participants from South West Oncology Group (SWOG) and 4 from Gynecologic Oncology Group (GOG) |
|
| Participants | Number of participants: 70 randomised (35 treatment group, 35 observation alone) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria: not specified |
|
| Interventions | Intervention: Alpha‐interferon (IFNα‐26, Schering‐Plough Kenilworth, NJ) in weekly doses of 50x106 IU (for 6 doses) Control: observation alone |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Ethics approval: the trial received local institutional review board (IRB) review and approval according to institutional guidelines Informed consent: IRB approved consent forms were signed by the patients Funding: source of funding/conflict of interest not declared Correspondence with authors: dalberts@azcc.arizona.edu on the 3rd July 2012 |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | It is reported that patients were randomised but the method of randomisation is not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported on |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not reported on. Control group was merely observed |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Loss to follow‐up was minimal and similar in both groups (3/35 intervention, 0/35 control) |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol was not obtained |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Trial stopped early due to poor accrual of patients |
Alberts 2008.
| Methods | This was a multicentre, open‐label, two‐arm phase III randomised controlled trial Trial duration: enrolment from January 29, 2002 to March 31, 2004. Trial duration not specified Trial location: Europe, North and South America |
|
| Participants | Number of participants: 847 participants (426 intervention, 421 control), 774 ovarian cancer (OC), 73 primary peritoneal carcinoma (PPC) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria: not stated |
|
| Interventions | Intervention: Chemotherapy plus interferon‐gamma 1b (IFN‐γ 1b) Chemotherapy included paclitaxel (175 mg/m2 over 3 hours) followed by carboplatin (AUC 6) every 3 weeks. A total of 6 cycles of chemotherapy were given unless disease progression or dose‐limiting toxicity occurred or patients refused further treatment Interferon therapy included 100μg administered subcutaneously, 3 times weekly (every other day; no more than 3 days in a 7‐day period) continuously (including the 3 weeks following the last dose of chemotherapy) Control: Chemotherapy alone consisting of Paclitaxel (175 mg/m2 over 3 hours) followed by carboplatin (AUC 6) every 3 weeks. A total of 6 cycles of chemotherapy were given unless disease progression or dose‐limiting toxicity occurred or patients refused further treatment |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Ethics approval: this was not reported on Informed consent: patients provided informed consent between January 29, 2002 and March 31, 2004 Funding: this was not reported on Correspondence with authors: dalberts@azcc.arizona.edu on 3rd July 2012 |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned how randomisation was carried out |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not reported on |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Open‐label trial but unlikely to affect outcomes. Control group received chemotherapy alone |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Disease progression was assessed by an endpoint review committee blinded to the treatment assignment using serial CT scans, MRIs, physical exams, and CA‐125 levels |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | High risk | ITT analysis was done 79% of participants adhered to treatment (i.e, undertook at least 5 out of 6 courses) in the treatment arm and 86% adhered in the control arm. 34% of adherent participants died in the intervention arm while 28% died in the control arm. 61% of non‐adherent participants died in the intervention arm while 45% of non‐adherent participants died in the control arm. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol was not available |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Study stopped early due to DSMB (data and safety monitoring board) recommendation ‐ this was due to the study finding a statistically significant difference between treatment groups that crossed the pre‐specified boundaries for inferiority and futility. |
Bruzzone 1997.
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial Trial duration: 4 years June 1990 to October 1992 Trial location: Italy (North West Oncology group) |
|
| Participants | Number of participants: 111 randomised (57 experimental group, 54 control) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria:
|
|
| Interventions | Intervention: Intraperitoneal INF‐alpha 25,000,000 U on day 1 followed by intraperitoneal carboplatin 400mg/m2 on day 2 every 28 days for 3 courses Control: Intraperitoneal carboplatin 400mg/m2 every 28 days |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Ethics approval: not reported on Informed consent: participants signed informed consent forms before enrolment into study Funding: source of funding not reported on. Probably under auspices of North West Oncology Group Correspondence with authors: National Institute for Cancer Research and Co‐operative Centers of the North West Oncology Group on 3rd July 2012 |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomisation was performed using random number tables and specific lists of randomisation numbers |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Treatment allocation was conducted centrally by telephoning the trial office at the Cancer Institute whenever a patient was enrolled |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Blinding of participants was not reported on but measured outcomes unlikely to be affected by lack of blinding as control group received chemotherapy only |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Loss to follow‐up low and similar in both groups (5/57 intervention, 5/54 control). Intention‐to‐treat analysis was also conducted |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Trial protocol not obtained |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Trial stopped early due to due to toxicities and the higher costs in the interferon arm considering the absence of impressive survival advantage |
Hall 2004.
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial Trial duration: 7 years and 5 months, from February 1990 to July 1997 Trial location: 14 centres across the United Kingdom |
|
| Participants | Number of participants: 300 randomised (interferon‐149, control‐151) Inclusion criteria: Patients had histologically proven epithelial ovarian cancer that showed no evidence of disease progression after post‐operative chemotherapy. The percentage of participants with FIGO stage I, II, III and IV ovarian cancer in the interferon group was 7%, 22%, 63% and 15% while in the chemotherapy group was 8%, 13%, 64% and 15% respectively Exclusion criteria: not specified |
|
| Interventions | Intervention: Interferon‐alpha: INF‐α 2a (Roferon‐A, Roche) (4.5 mega‐units subcutaneously 3 days per week). Interferon was continued until disease progression or in response to toxicity or patient request Control: No maintenance treatment |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Ethics approval: study was approved by the Local Research Ethics Commitee of each participating centre Informed consent: written informed consent was obtained from patients prior to randomisation Funding: not mentioned Correspondence with authors: g.hall@leeds.ac.uk on date on 3rd July 2012 |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described how randomisation was done |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not mentioned |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not described if participants were blinded to the treatment assigned. Control group did not receive any treatment |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not described if outcome assessors were blinded to treatment assignment but inlikely to have any effect on the outcomes |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Intention‐to‐treat (ITT) analysis was done on all the patients. Eight patients (2 interferon and 6 observation) died without any follow‐up visits). 144 of 149 participants in the interferon group received at least one injection |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol was not available |
| Other bias | Low risk | No reason to suspect other bias |
Windbichler 2000.
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial Trial duration: 7 years and 3 months, from December 1991 to March 1998 Trial location: 12 Austrian gynaecological and medical centres |
|
| Participants | Number of participants: 148 randomized (75 intervention group, 73 control group) Inclusion criteria:
Exclusion criteria: Patients with concomitant severe cardiovascular disease, life expectancy of less than 3 months, recent second malignancy or history of thromboembolic disease |
|
| Interventions | Intervention: Intraperitoneal treatment with interferon‐gamma (IFN‐γ) consisting of 0.1 mg subcutaneously on days 1,3,5, 15, 17 and 19 of each 28‐day cycle PLUS standard chemotherapy given every 4 weeks consisting of 100mg/m2 cisplatin and 600mg/m2 cyclophosphamide Control: Standard chemotherapy given every 4 weeks consisting of 100mg/m2 cisplatin and 600mg/m2 cyclophosphamide |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Ethics approval: study protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of the University of Innsbruck Medical School as well as the respective committees of the other participating centres Informed consent: all participants signed written consent forms before being enrolled Funding: not mentioned Correspondence with authors: To C Marth. Department of Obstetrics and Gynaecology, University Hospital, Anichstrasse 35, A‐6020 Innsbruck, Austria 3rd July 2012 |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomisation lists were computer generated |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Patients were allocated to a treatment arm by the study centre by means of fax transmission |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Not mentioned but unlikely to affect the study outcomes. Control group received chemotherapy only |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not mentioned. Unlikely to affect the study as outcomes are objective. All slides were reviewed by one pathologist |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Intention‐to‐treat analysis was done. In the treatment group 6 of 65 patients discontinued due to disease progression. Of the remaining 59 participants, 32 completed 6 cycles of treatment. In the control group, 7 of the 68 participants discontinued due to disease progression. Of the remaining 61 patients, 39 completed 6 cycles of chemotherapy |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Protocol was not available |
| Other bias | Low risk | No reason to suspect other bias |
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Berek 2000 | Not a randomised controlled trial |
| Cardamakis 1999 | Not a randomised controlled trial |
| Sumrit 1998 | Abstract or full article not found |
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
Kosmidis 1997.
| Methods | Not specified |
| Participants | 83 women with median age 56 years. 74% had stage III while 435 had serious and 25% had mucinous adenocarcinoma. 30% had an optimal operation with residual disease and treated with chemotherapy. Of the 86 women 44 had complete clinical remission (cCR) and they were randomised to receive either interferon‐alpha 2b or observation alone |
| Interventions | Intervention: Intraperitoneal interferon was given Control: Patients were observed |
| Outcomes |
|
| Notes | The full text article has been requested from authors but we have not received any response. |
Zhyl'chuk 1998.
| Methods | Not specified |
| Participants | Participants with different histologic forms of ovarian cancer |
| Interventions | Adjuvant interferon |
| Outcomes | CA‐125 levels |
| Notes | The full text article has been requested from authors but we have not received any response. |
Differences between protocol and review
We have used the Parmar's methods to calculate hazard ratios and their corresponding standard errors. This was not specified in the protocol.
Contributions of authors
AL developed the protocol with the assistance of AM. AM wrote the data collection and analysis section and also assisted in the writing of the background. LN wrote various sections of the review and edited all of the versions of the review.
Sources of support
Internal sources
Wits Reproductive Health & HIV Institute (WRHI), University of Wits, Johannesburg, South Africa.
Faculty of Health Sciences, Stellenbosch University, Cape Town, South Africa.
External sources
No sources of support supplied
Declarations of interest
Aramide Lawal: none known
Alfred Musekiwa: none known
Liesl Grobler: none known
Stable (no update expected for reasons given in 'What's new')
References
References to studies included in this review
Alberts 2006 {published data only}
- Alberts DS, Hannigan EV, Liu P, Jiang C, Wilczynski S, Copeland L, Markman M. Randomized trial of adjuvant intraperitoneal alpha‐interferon in stage III ovarian cancer patients who have no evidence of disease after primary surgery and chemotherapy: An intergroup study. Gynecologic Oncology 2006;100:133‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Alberts 2008 {published data only}
- Alberts DS, Marth C, Alvarez RD, Johnson G, Bidzinski M, Kardatzke DR, et al. Randomized phase 3 trial of interferon gamma‐1b plus standard carboplatin/paclitaxel versus carboplatin/paclitaxel alone for first‐line treatment of advanced ovarian and primary peritoneal carcinomas: Results from a prospectively designed analysis of progression‐free survival. Gynecologic Oncology 2008;109:174‐81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bruzzone 1997 {published data only}
- Bruzzone M, Rubagotti A, Gadducci A, Catsafados E. Intraperitoneal carboplatin with or without interferon‐alpha in advanced ovarian cancer patients with minimal residual disease at second look: a prospective randomized trial of 111patients. G.O.N.O. Gruppo Oncologic Nord Ovest. Journal of Gynecologic Oncology 1997;63(3):499‐505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hall 2004 {published data only}
- Hall GD, Brown JM, Coleman RE, Stead M, Metcalf KS, Peel KR, et al. Maintenance treatment with interferon for advanced ovarian cancer: results from the Northern and Yorkshire gynaecology group randomised phase III study. British Journal of Cancer 2004;91:621‐6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Windbichler 2000 {published data only}
- Windbichler GH, Hausmaninger H, Stummvoll W, Graf AH, Kainz C, Lahodny J, et al. Interferon‐gamma in the first‐line therapy of ovarian cancer: a randomized phase III trial. British Journal of Cancer 2000;82(6):1138‐44. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Berek 2000 {published data only}
- Berek JS, Markman M, Stonebraker B, Lentz SS. Interferon plus chemotherapy for primary treatment of ovarian cancer. Lancet 2000;356(9223):6‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cardamakis 1999 {published data only}
- Cardamakis E, Ginopoulos P, Dimopoulos D, Avaraki M. Treatment of women with minimal residual ovarian cancer after cytoreductive surgery of stage III: Interferon alpha‐2 plus carboplatin and cyclophosphamide versus carboplatin and cyclophosphamide. International Journal of Gynaecological Cancer 1999;9:20. [Google Scholar]
Sumrit 1998 {published data only}
- Senapad S, Neungton S, Teerapakawong C, Piamsomboon S, Theerasakvichaya S, Suphanich A. Outcome of the ovarian epithelial Cancer stage I‐II treated with cyclophosphamide plus cisplatinum or carboplatin. Siriraj Medical Journal 1998 October;50(10):925‐32. [Google Scholar]
References to studies awaiting assessment
Kosmidis 1997 {published data only}
- Kosmidis P, Bafaloukos D, Skarlos D, Pavlidis N, Aravantinos G. Intraperitoneal (IP) Interferon A2b (INF) consolidation in ovarian cancer patients following carboplatin chemotherapy. European Journal of Cancer September 1997;33(8):88‐9. [Google Scholar]
Zhyl'chuk 1998 {published data only}
- Zhyl'chuk V, Alistratov OV, Vorontsova AL. [Increasing the efficacy of treating patients with extensive ovarian cancer by using laferon]. Lik Sprava [Ukranian] May 1998;3:117‐9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
ACS 2013
- Anonymous. Survival rates for ovarian cancer, by stage. http://www.cancer.org/cancer/ovariancancer/detailedguide/ovarian‐cancer‐survival‐rates (accessed 31 March 2013) March 2013.
Berek 1985
- Berek JS, Hacker NF, Lichenstein A. Intraperitoneal recombinant α‐interferon for "salvage" immunotherapy in Stage III epithelial ovarian cancer:a Gynecology Oncology Group Study. Cancer Research 1985;45:4447‐53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Deeks 2001
- Deeks JJ, Altman DG, Bradburn MJ. Statistical methods for examining heterogeneity and combining results from several studies in meta‐analysis. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG (editors). Systematic Reviews in Health Care: Meta‐analysis in Context (2nd edition). London (UK): BMJ Publication Group, 2001. [Google Scholar]
Dunn 2006
- Dunn GP, Koebel CM, Schreiber RD. Interferons, immunity and cancer immunoediting. Nature Reviews. Immunology 2006;6:836‐48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Einhorn 1988
- Einhorn N, Ling P, Einhorn S, Strander H. A phase II study on escalating interferon doses in advanced ovarian carcinoma. American Journal of Clinical Oncology 1988;11:3‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Epstein 1980
- Epstein LB, Shen JT, Abele JS, Reese CC. Sensitivity of human ovarian carcinoma cells to interferon and other antitumor agents as assessed by an in vitro semi‐solid agar technique. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1980;350:228‐44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
EUROCARE 2003
- Sant M, Aareleid T, Berrino F, Bielska Lasota M, Carli PM, Faivre J, et al. and the EUROCARE Working Group. EUROCARE ‐ 3: survival of cancer patients diagnosed 1990‐94 ‐ results and commentary. Annals of Oncology 2003;14 Suppl 5:v61‐118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
FIGO nomenclature, Rio de Janeiro 1988
- Reprinted from Heintz A, Odicino F, Maisonneuve P, Maisonneuve P, Quinn MA, Benedet JL, Creasman WT, et al. Carcinoma of the ovary. International Journal Gynecology and Obstetrics 2006;95(1):S163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Freedman 1983
- Freedman RS, Gutterman JU, Wharton JT, Rutledge FN. Leukocyte interferon (IFN alpha) in patients with epithelial ovarian carcinoma. Journal of Biological Response Modifiers 1983;2:133‐8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
GLOBOCAN 2002
- Ferlay J, Bray F, Pisani P, Parkin DM. GLOBOCAN 2002. Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide. IARC CancerBase No. 5, version 2.0. IARCPress, Lyon 2004. [Google Scholar]
Gresser 2002
- Gresser I, Belardelli F. Endogenous type I interferons as a defense against tumors. Cytokine Growth Factor Reviews 2002;13:111‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gresser 2007
- Gresser I. The anti‐tumor effects of interferon: a personal history. Biochimie 2007;89(6):723‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2003
- Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Measuring inconsistency in meta‐analyses. BMJ 2003;327(7414):557‐60. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0. [updated March 2011]. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. [Google Scholar]
Holschneider 2000
- Holschneider CH, Berek JS. Ovarian cancer: Epidemiology, biology, and prognostic factors. Seminars on Surgical Oncology 2000;19(1):3‐10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jemal 2008
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T. Cancer Statistics. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians 2008;58:71‐96. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jui‐Tung 1992
- Jui‐Tung Chen, Katsuhiko Hasumi, Kazumasa Masubuchi. Interferon‐α, interferon‐γ and sizofiran in the adjuvant therapy in ovarian cancer — a preliminary trial. Biotherapy December 1992;5(4):275‐80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Maher 2007
- Maher SG, Romero‐Weaver AL, Scarzello AJ. Interferon: cellular executioner or white knight?. Current Medicinal Chemistry 2007;14:1279‐89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mandelli 1990
- Mandelli F, Avvisati G, Amadori S, Boccadoro M, Gernone A, Lauta VM, et al. Maintenance treatment with recombinant interferon alfa‐2b in patients with multiple myeloma responding to conventional induction chemotherapy. New England Journal of Medicine 1990;322:1430‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mei 2010
- Mei L, Chen H, Wei DM, Fang F, Liu GJ, Xie HY, et al. Maintenance chemotherapy for ovarian cancer. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010;Issue 9:[DOI: 10, 1002/14651858.CD007414.pub2]. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mei 2011
- Mei L, Chen H, Chen F, Feng D, Fang F. Maintenance bioimmunotherapy for epithelial ovarian cancer (Protocol). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011;Issue 5:[DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009137]. [Google Scholar]
Moserle 2008
- Moserle L, Indraccolo S, Ghisi M. The side population of ovarian cancer cells is a primary target of INF‐α antitumor effects. Cancer Research 2008;68(14):5658‐68. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Nardi 1990
- Nardi M, Cognetti F, Pollera CF. Intraperitoneal recombinant α2‐interferon alternating with cisplatin as salvage therapy for minimal residual‐disease ovarian cancer: a phase II study. Journal of Clinical Oncology 1990;8:1036‐41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Parmar 1998
- Parmar MKB, Torri V, Stewart L. Extracting summary statistics to perform meta‐analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Statistics in Medicine 1998;17:2815‐34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Pickel 1999
- Pickel H, Lahousen M, Petru E, Stettner H, Hackl A, Kapp K, et al. Consolidation radiotherapy after carboplatin‐based chemotherapy in radically operated advanced ovarian cancer. Gynecology Oncology 1999;72:215‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Revman 5 [Computer program]
- The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). The Cochrane Collaboration, Version 5.0. Copenhagen. The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration 2008.
Schroder 2004
- Schroder K, Hertzog PJ, Ravasi T. Interferon‐γ: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. Journal of Leukocyte Biology 2004;75:163‐89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sorbe 2003
- Sorbe B. Consolidation treatment of advanced (FIGO stage III) ovarian carcinoma in complete surgical remission after induction chemotherapy: a randomized controlled clinical trial comparing whole abdominal radiotherapy, chemotherapy and no further treatment. International Journal of Gynecological Cancer 2003;13:278‐86. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sourbier 2012
- Sourbier C. Ovarian cancer: emerging molecular‐targeted therapies. Biologics: Targets and Therapy 2012;6:147‐54. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tsuno 2009
- Tsuno T, Mejido J, Zhao T. IRF9 is a key factor for eliciting the antiproliferative activity of IFN‐α. Journal of Immunotherapy 2009;32(8):803‐16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Twombly 2007
- Twombly R. Cancer killer may be silent "no more". Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2007;99(18):1359‐61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Willemse 1990
- Willemse PH, Vries EG, Mulder NH. Intraperitoneal human recombinant interferon α2b in minimal residual ovarian cancer. European Journal of Cancer 1990;26:353‐8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


