Figure 1.
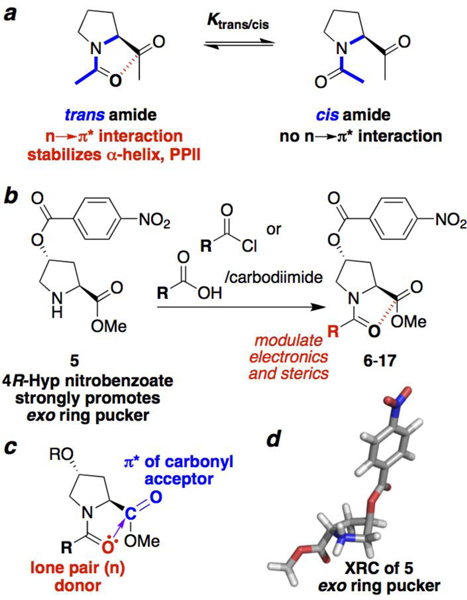
Proline cis-trans isomerism to probe n→π* interactions. (a) Proline trans and cis amide bonds (blue) are in slow exchange on the NMR timescale. Only the trans amide bond may be stabilized by an n→π* interaction. Thus, molecular properties that promote an n→π* interaction lead to a larger Ktrans/cis. (b) Synthesis of peptides with different acyl N-caps from the common intermediate 5. (c) Overlap of the donor (red) carbonyl Oi lone pair (n) with the acceptor carbonyl Ci+1=Oi+1 (blue) π* molecular orbital leads to electron delocalization. The extent of orbital overlap is associated with the Oi…Ci+1 distance (purple), with n→π* interactions exhibiting distances significantly below the 3.22 Å sum of the van der Waals radii of O and C. (d) Crystal structure of 5, which exhibits an exo ring pucker due to the strong stereoelectronic effect of the nitrobenzoate ester.
