Abstract
Background
The effect of mutations conferring antibiotic resistance can depend on the genetic background. To determine if a previously de novo acquired antibiotic resistance influences the adaptation to a second antibiotic, antibiotic resistance was selected for by exposure to stepwise increasing sublethal levels of amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, kanamycin, or tetracycline. E. coli populations adapted to either a single or two antibiotics sequentially were characterized using whole genome population sequencing and MIC measurements.
Results
In a wild-type background, adaptation to any of the antibiotics resulted in the appearance of well-known mutations, as well as a number of mutated genes not known to be associated with antibiotic resistance. Development of a second resistance in a strain with an earlier acquired resistance to a different antibiotic did not always result in the appearance of all mutations associated with resistance in a wild-type background. In general, a more varied set of mutations was acquired during secondary adaptation. The ability of E. coli to maintain the first resistance during this process depended on the combination of antibiotics used. The maintenance of mutations associated with resistance to the first antibiotic did not always predict the residual MIC for that compound.
Conclusions
In general, the data presented here indicate that adaptation to each antibiotic is unique and independent. The mutational trajectories available in already resistant cells appear more varied than in wild-type cells, indicating that the genetic background of E. coli influences resistance development. The observed mutations cannot always fully explain the resistance pattern observed, indicating a crucial role for adaptation on the gene expression level in de novo acquisition of antibiotic resistance.
Keywords: Bactericidal antibiotics, de novo resistance, Mutations, Whole genome sequencing
Background
To be able to predict, prevent, or slow down development of antibiotic resistance, the molecular mechanisms that drive development of antibiotic resistance need to be understood. Antibiotic resistance can develop in three distinct ways: through horizontal gene transfer, chromosomal mutations, or phenotypic adaptation. In Escherichia coli, the first stages of de novo development of antibiotic resistance occur on a phenotypic level, controlled by adaptation on the gene expression level [1]. After this initial stage, mutations appear that, in most cases, confer a reduction in bacterial fitness [1–3]. Often, this is followed by the appearance of compensatory mutations that reduce the loss in fitness without reducing the acquired resistance [4].
Antibiotic resistance can be selected for by exposure to stepwise increasing sublethal levels of the antibiotic [5]. Although each antibiotic class has a specific cellular target, the radical-based theory suggests that as a secondary effect increased levels of cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) occur as a result of a pathway common to all bactericidal antibiotics [6, 7]. Following this logic, similar mutations might occur in cells with acquired resistance to different bactericidal antibiotics. During evolution experiments exposing E. coli to steadily increasing levels of antibiotics, cells with an earlier acquired resistance to a bactericidal antibiotic adapt to a second bactericidal, but not bacteriostatic, antibiotic at a more rapid rate, corroborating this theory [8].
The effect of resistance associated mutations varies depending on the genetic background, such as the presence of other resistance mutations, a phenomenon known as epistasis [9, 10]. The fitness cost incurred by mutations determines the evolutionary pathways available [11], suggesting that the evolutionary history of bacteria may influence the type or number of mutations that are acquired upon exposure to an antibiotic. In this study, we investigate if a previously de novo acquired antibiotic resistance influences the adaptation to a second antibiotic. Whole genome population sequencing was applied to E. coli strains with de novo acquired resistance to either one or to two antibiotics sequentially. We previously reported on larger genomic changes that occur during adaptation to a single antibiotic, or two antibiotics successively [12]. In this study, we provide a comprehensive overview of the different mutations that are acquired when wild-type or antibiotic-resistant E. coli is exposed to amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, kanamycin, or tetracycline.
Results
This study addressed three questions: 1) which mutations are associated with the development of resistance by E. coli wild-type against specific antibiotics? 2) Are the same mutations observed when cells made resistant against one antibiotic become resistant to a second one? 3) Are initial mutations lost when cells resistant to one antibiotic are made resistant to another one? To answer these questions, strains exposed to only amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, or kanamycin, all bactericidal antibiotics from different classes, or the bacteriostatic antibiotic tetracycline were compared to cells made resistant to two of these antibiotics successively. Resistant strains were generated by exposing wild-type E. coli or a strain with an earlier acquired resistance to increasing but sublethal concentrations of any of these antibiotics [8]. The initial resistance was selected for in duplicate strains. Two replicates of each of these strains were made resistant to a second antibiotic, resulting in four strains with the same exposure history (Fig. 1). Genomic DNA was isolated from the entire population at selected time points for whole genome sequencing at an average read depth of 226 to identify genetic changes associated with acquired resistance to a single and to subsequent antibiotics.
Fig. 1.
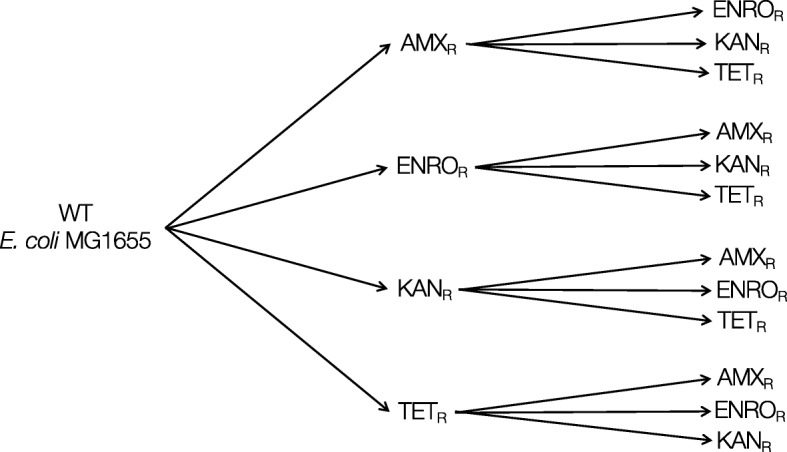
Set-up of evolution experiments inducing resistance. Duplicate strains of wild-type E. coli MG1655 were made resistant by exposure to increasing non-lethal concentrations of amoxicillin (AMX), enrofloxacin (ENRO), kanamycin (KAN), or tetracycline (TET). Two replicates of each of the primary resistant strains were subsequently made resistant to one of the three other antibiotics using the same approach. As a result 4 replicates were obtained of all double exposed strains
Adaptation of the wild-type to amoxicillin (Table 1) resulted in two well-scrutinized mutations in the ampC promoter [1, 13], and in mutations in ompR, citF, and rpoD, all with a population frequency of 1. One of the replicate strains acquired a mutation in waaB in addition to these mutations. In the wild-type strain adapted to enrofloxacin, either ten or eleven genes were mutated, and a low-frequency mutation occurred in mutL. Mutations in gyrA, parC, parE, soxR, and acrR, commonly associated with resistance to fluoroquinolones [14–16] were accompanied by less frequently observed mutations in the genes proY and yciO. In addition, mutations in the 5′ UTR of rpsJ, ybjL or ybjM, and gtlB were detected. When wild-type cells were exposed to kanamycin, mutations accumulated in sbmA, sapF, cpxA, npr, fusA, and the 5′ UTR of uidA. Interestingly, a mutation in gyrB, most often associated with resistance to fluoroquinolones [17], was identified with a population frequency of 1 in both wild-type-adapted strains. Development of resistance to tetracycline in wild-type E. coli resulted in mutations in acrR and acrB, ompF, mlaA. A mutation in rpoC was only detected in a strain with partial resistance to tetracycline.
Table 1.
Mutations associated with resistance to amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, kanamycin, or tetracycline in wild-type E. coli
| Exposure to amoxicillin | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WT | WT | ||||
| Gene product | Gene | Mutation | 40 μg/ml | 1280 μg/ml | 1280 μg/ml |
| B-lactamase | ampC | G23 T (promoter) | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| C-11 T (promoter) | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Transcriptional regulator | ompR | E88A | 1 | 1 | |
| Citrate lyase | citF | G432A | 1 | 0.97 | |
| Sigma 70 | rpoD | D445V | 0.96 | 1 | |
| UDP-D-galactose | waaB | Del C3803246 (FS297) | 1 | ||
| Exposure to enrofloxacin | |||||
| WT | WT | ||||
| Gene product | Gene | Mutation | 1024 μg/ml | 1024 μg/ml | |
| DNA gyrase subunit A | gyrA | D87G | 1 | ||
| S83 L | 1 | 1 | |||
| D87N | 1 | ||||
| DNA gyrase subunit B | gyrB | S463F | 1 | ||
| DNA topoisomerase IV subunit A | parC | S80R | 1 | 1 | |
| DNA topoisomerase IV subunit B | parE | Ins Q458 | 0.94 | 1 | |
| Cryptic proline/histidine transporter | proY | A235S | 1 | 1 | |
| Transcriptional regulator | acrR | Del 485,885–11 (FS42) | 1 | 1 | |
| Transcriptional regulator | soxR | T133S, del 4,277,899–903 (FS144) | 1 | 1 | |
| S10 subunit of 30S | rpsJ | 5′ UTR (G3453306 T) | 1 | 1 | |
| Putative transport protein/Putative inner membrane protein | ybjL/ybjM* | 5′ UTR (A889923G) | 1 | 1 | |
| Glutamate synthase subunit | gltB | 5′ UTR (C3354487T) | 1 | 1 | |
| Putative RNA binding protein | yciO | N64Y | 1 | 1 | |
| Mismatch repair protein | mutL | W390 L | 0.12 | ||
| Exposure to kanamycin | |||||
| WT | WT | ||||
| Gene product | Gene | Mutation | 32 μg/mL | 1024 μg/mL | 1024 μg/mL |
| Peptide antibiotic transporter | sbmA | Del 397,306–27 (FS 222) | 1 | 1 | |
| ATP binding protein of putrescine ABC exporter | sapF | L181Q | 1 | 1 | |
| Sensor protein of Cpx TCS | cpxA | Q242L | 1 | 1 | |
| DNA gyrase subunit B | gyrB | S464Y | 1 | 1 | |
| Phosphorelay protein | npr | L23R | 1 | 1 | |
| Elongation factor G | fusA | Q242L | 1 | ||
| A608V | 0.19 | ||||
| F05 L | 0.74 | 1 | |||
| β-D-glucuronidase | uidA | 5′ UTR (T1696220C) | 1 | ||
| Exposure to tetracycline | |||||
| WT | |||||
| Gene product | Gene | Mutation | 16 μg/mL | 64 μg/mL | |
| Multidrug efflux pump RND permease | acrB | I45L | 1 | 1 | |
| Transcriptional regulator | acrR | P85Q | 1 | 1 | |
| Outer membrane porin F | ompF | T71S | 0.65 | 0.04 | |
| Ins 7 nt after G986771 (FS71) | 0.60 | ||||
| Outer membrane lipoprotein | mlaA | Del N41/F42 | 0.9 | ||
| RNA polymerase subunit β’ | rpoC | G367C | 0.34 | ||
Numbers shown indicate frequency of mutation in population. Del = deletion, Ins = insertion, underlined letters and numbers indicate nucleotides and their genomic position, * indicates that mutation could affect either gene. For amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, and kanamycin, two independent strains were sequenced
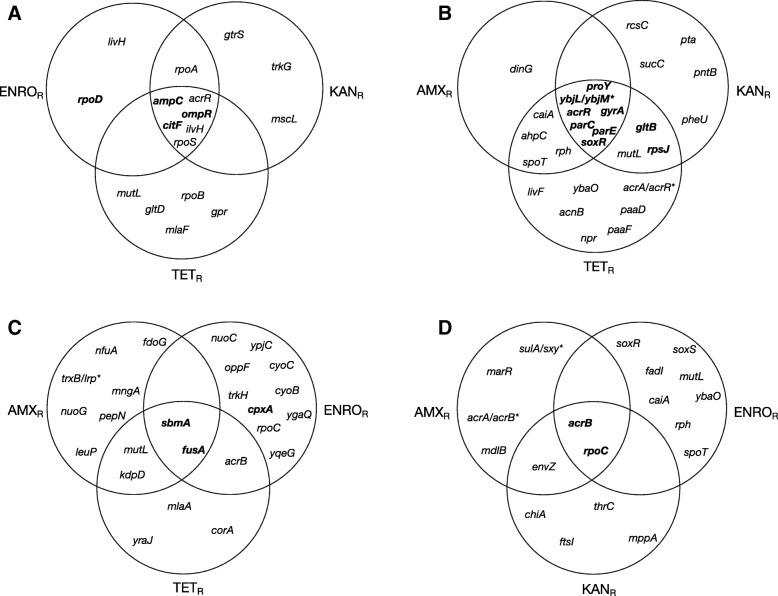
Development of secondary resistance does not always result in the appearance of all mutations associated with resistance to that specific antibiotic in a wild-type strain (Fig. 2, Tables 2, 3, 4 and 5). This is most apparent in the strains adapted to kanamycin (Fig. 2c), where only mutations in sbmA and fusA are acquired by all strains. A high degree of variability can be observed between the replicates, as indicated by the frequencies displayed in Tables 2, 3, 4 and 5(column headed “Strains”), suggesting that secondary adaptation allows for more flexibility than primary development of resistance. Moreover, selected resistance to a second antibiotic results in the appearance of mutations that are acquired by multiple strains already resistant to another antibiotic but not by wild-type strains, such as rpoA during secondary amoxicillin resistance development (Fig. 2a), caiA, ahpC, rph, and spoT during adaptation to enrofloxacin (Fig. 2b), kdpD and acrB during development of resistance to kanamycin as a second antibiotic (Fig. 2c), or envZ when already resistant cells adapt to tetracycline (Fig. 2d). Within different antibiotic-resistant populations, a mutL mutation was identified in several samples, with a population frequency varying from 0.09 to 0.20.
Fig. 2.
Overlap of mutations associated with resistance to amoxicillin (a), enrofloxacin (b), kanamycin (c), or tetracycline (d) in strains with a previously acquired resistance to a different antibiotic. AMXR: amoxicillin resistant, ENROR: enrofloxacin resistant, KANR: kanamycin resistant, TETR: tetracycline resistant. Mutations associated with resistance in a wild-type background are shown in bold. Mutations associated with the previous resistance have been omitted from the figure
Table 2.
Mutations associated with resistance to amoxicillin in strains with a previously acquired resistance to enrofloxacin, kanamycin, or tetracycline
| Gene product | Gene | Mutation | Pop. frequency | Strains |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transcriptional regulator | acrR | L204R, Del C205 | 0.98–1 | E1/4, K2/4 T2/4 |
| B-lactamase | ampC | C35A (promoter) | 1 | E4/4, K3/4, T1/4 |
| C-11 T (promoter) | 1 | E4/4, K3/4, T1/4 | ||
| Ins T after C4379837 (promoter) | 1 | K1/4 | ||
| Ins T after A4379015 (promoter) | 1 | T1/4 | ||
| Citrate lyase | citF | G432A | 1 | E4/4, K3/4, T1/4 |
| Glutamate synthase subunit | gltD | A80A | 0.18 | T1/4 |
| L-glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate reductase | gpr | L180F | 1 | T2/4 |
| CPS-53 glucosyl transferase | gtrS | V351 V | 0.96 | K1/4 |
| Acetolactate synthase/acetohydroxybutanoate synthase subunit | ilvH | G52C | 0.60–1 | E2/4, K2/4, T1/4 |
| Branched chain amino acid/phenylalanine ABC transporter membrane subunit | livH | G239R | 0.18 | E1/4 |
| Intermembrane phospholipid transport system subunit | mlaF | Ins AIT between T38-A39 | 0.65–0.66 | T2/4 |
| Large conductance mechanosensitive channel | mscL | L45Q | 0.98 | K1/4 |
| Mismatch repair protein | mutL | W390 L | 0.11–0.2 | T2/4 |
| Transcriptional regulator | ompR | E88A | 1 | E4/4, K3/4, T1/4 |
| RNA polymerase subunit α | rpoA | C269S | 1 | E1/4, K1/4 |
| RNA polymerase subunit β | rpoB | E564A | 0.15 | T1/4 |
| Sigma 70 | rpoD | D445V | 1 | E4/4 |
| Alternative sigma factor σS | rpoS | E16Stop | 0.96–1 | K2/4, T1/4 |
| Del Q59-E330 | 0.91–1 | T2/4 | ||
| Potassium ion transporter | trkG | G159D | 1 | K1/4 |
Del = deletion, Ins = insertion, underlined letters and numbers indicate nucleotides and their genomic position. Population frequency indicates the mutational frequency in the sequenced population. Strains indicates the prevalence of a mutation within different replicates. E: population with previously acquired resistance to enrofloxacin, K: population with previously acquired resistance to kanamycin, T: population with previously acquired resistance to tetracycline. X/Y: X indicates number of replicates with particular mutation, Y indicates total number of replicates that were sequenced. Mutations associated with resistance in a wild-type background are shown in bold. Mutations associated with the previous resistance have been omitted from the table
Table 3.
Mutations associated with resistance to enrofloxacin in strains with a previously acquired resistance to amoxicillin, kanamycin, or tetracycline
| Gene product | Gene | Mutation | Pop. frequency | Strains |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multidrug efflux pump membrane fusion lipoprotein/transcriptional regulator | acrA/acrR* | 5′ UTR (Del 485,695–711) | 1 | T1/3 |
| Transcriptional regulator | acrR | Del 485,885–11 (FS42) | 1 | A3/4, K1/4, T2/3 |
| Aconitate hydratase B/2-methylisocitrate dehydratase | acnB | G362 V, Del L363-V865 | 1 | T1/3 |
| Alkyl hydroperoxide reductase | ahpC | Del F38 | 0.40–1 | A2/4, T1/3 |
| Crotonobetainyl-CoA reductase | caiA | C154A, F155P, I156T, T157P, S158R, S159 T, A160S, Y161W, Del T162-R380 | 1 | A2/4, T1/4 |
| ATP-dependent helicase | dinG | Del Q641-R716 | 0.89 | A1/4 |
| Glutamate synthase subunit | gltB | 5′ UTR (C3354487T) | 1 | K1/4, T2/3 |
| DNA gyrase subunit A | gyrA | S83 L | 1 | A4/4, E1/4, T3/3 |
| D87G | 1 | A3/4, K2/4, T1/3 | ||
| D87N | 1 | K2/4, T2/3 | ||
| Branched chain amino acid/phenylalanine ABC transporter membrane subunit | livF | G239F | 0.87 | T1/4 |
| Mismatch repair protein | mutL | W390 L | 0.09–0.14 | K1/4, T2/3 |
| Phosphorelay protein | npr | L23R | 1 | T1/3 |
| Phenylacetate degradation protein | paaD | A8S | 1 | T1/3 |
| Putative 2,3-dehydroadipyl-CoA hydratase | paaF | V35 L | 1 | T1/3 |
| DNA topoisomerase IV subunit A | parC | S80R | 0.94–1 | A3/4, K4/4, T3/3 |
| DNA topoisomerase IV subunit B | parE | Ins Q458 | 0.97–1 | A3/4, K2/4, T2/3 |
| E459Q | 0.03 | A1/4 | ||
| S425P | 0.81 | K2/4 | ||
| Ins S after A457 | 0.95 | T1/3 | ||
| tRNA-Phe | pheU | 5′ UTR (G4362633 T) | 1 | K1/4 |
| Cryptic proline/histidine transporter | proY | A235S | 1 | A3/4, K1/4, T2/3 |
| Pyridine nucleotide transhydrogenase subunit β | ptnB | V434 V | 0.57 | K1/4 |
| Phosphate acetyltransferase | pta | Del T431-Q714 | 0.56 | K1/4 |
| Sensory histidine kinase | rcsC | E44K | 1 | K2/4 |
| Truncated RNase PH | rph | Del R676 | 1 | A2/4, T1/3 |
| S10 subunit of 30S | rpsJ | 5′ UTR (G3453306 T) | 1 | K1/4, T2/3 |
| Bifunctional (p) ppGpp synthase/hydrolase | spoT | Ins C after T3815879 (FS223) | 1 | A2/4, T1/4 |
| Transcriptional regulator | soxR | T113S, del 4,277,899–903 (FS14) | 1 | A3/4, K1/4, T1/3 |
| Ins G136 | 0.15 | K1/4 | ||
| L139F, del T after C4277882 | 0.85 | K1/4 | ||
| A146E | 1 | K1/4 | ||
| Del R139-N154 | 1 | K1/4 | ||
| Succinyl-CoA synthetase subunit β | sucC | Del A218-N221 | 0.51 | K1/4 |
| DNA-binding transcriptional activator | ybaO | T33P | 1 | T1/4 |
| Putative RNA binding protein | yciO | N64Y | 1 | A1/4 |
| Putative transport protein/Putative inner membrane protein | ybjL/ybjM * | 5′ UTR (A889923G) | 1 | A3/4, K1/4, T2/3 |
Del = deletion, Ins = insertion, underlined letters and numbers indicate nucleotides and their genomic position, * indicates that mutation could affect either gene. Population frequency indicates the mutational frequency in the sequenced population. Strains indicates the prevalence of a mutation within different replicates. E: population with previously acquired resistance to enrofloxacin, K: population with previously acquired resistance to kanamycin, T: population with previously acquired resistance to tetracycline. X/Y: X indicates number of replicates with particular mutation, Y indicates total number of replicates that were sequenced. Mutations associated with resistance in a wild-type background are shown in bold. Mutations associated with the previous resistance have been omitted from the table
Table 4.
Mutations associated with resistance to kanamycin in strains with a previously acquired resistance to amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, or tetracycline
| Gene product | Gene | Mutation | Pop. frequency | Strains |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multidrug efflux pump RND permease | acrB | V139F | 0.73–1 | E2/3 |
| Inner membrane magnesium ion transporter | corA | Del V264-F266 | 0.93 | T1/4 |
| Sensor protein of Cpx two-component system | cpxA | Q242L | 1 | E2/3 |
| Cytochrome bo3 ubiquinol oxidase subunit 1 | cyoB | G662C | 0.86–0.93 | E2/3 |
| Del G448658 (FS661) | 0.13 | E1/3 | ||
| Start1L | 0.12 | E1/3 | ||
| Cytochrome bo3 ubiquinol oxidase subunit 3 | cyoC | Start1I | 0.86–0.93 | E2/3 |
| Del C448658 (FS1) | 0.13 | E1/3 | ||
| N661Stop | 0.12 | E1/3 | ||
| Formate dehydrogenase O subunit α | fdoG | V226 L | 0.36–0.58 | A2/3 |
| Elongation factor G | fusA | T393I | 1 | A1/3 |
| F605 L | 1 | E3/3, T3/4 | ||
| P610L | 0.92–0.97 | A2/3 | ||
| P610T | 0.96 | T1/4 | ||
| sensory histidine kinase | kdpD | Q728P | 0.36–0.61 | A1/3, T1/4 |
| tRNA-Leu | leuP | V16 V | 0.67 | A1/3 |
| Outer membrane lipoprotein | mlaA | Q728P | 0.88 | T1/4 |
| Del F42-N43 | 0.92 | T1/4 | ||
| 2-O-α-mannosyl-D-glycerate specific PTS permease | mngA | F431 L | 0.28–0.59 | A2/3 |
| Mismatch repair protein | mutL | W390 L | 0.11–0.13 | A1/4, T2/4 |
| Iron-sulfur cluster carrier protein | nfuA | Ins 8 nt after G3546085 (FS154) | 0.23 | A1/3 |
| NADH:quinone oxidoreductase subunit CD | nuoC | Del R471-L474 | 0.93 | E1/3 |
| NADH:quinone oxidoreductase subunit G | nuoG | Ins C after A2399396 (FS257) | 0.4 | A1/3 |
| Murein/oligopeptide ABC transporter subunit | oppF | L888Stop | 0.74–1 | E2/3 |
| Ins SIQ after L187 | 0.14 | E1/3 | ||
| Aminopeptidase N | pepN | V809E | 0.57 | A1/3 |
| RNA polymerase subunit β’ | rpoC | G367C | 0.16 | E1/3 |
| ATP binding protein of putrescine ABC exporter | sapF | L181Q | 1 | T2/4 |
| Peptide antibiotic transporter | sbmA | Ins G after T393897 (FS88) | 0.99 | E1/3 |
| W98Stop | 0.44 | A1/3 | ||
| Y162Stop | 0.11 | T1/4 | ||
| W179Stop | 0.53–0.60 | T2/4 | ||
| S250Stop | 0.44 | A1/3 | ||
| L369 L | 0.14 | T2/4 | ||
| I370L | 0.14 | T2/4 | ||
| Uncharacterized protein | ygaQ | Q417K | 1 | E2/3 |
| Uncharacterized protein | ypjC | 5′ UTR (T2785462C) | 1 | E2/3 |
| Putative transporter | yqeG | P282P | 0.22 | E1/3 |
| Putative fimbrial usher protein | yraJ | Q614L | 0.18 | T1/4 |
| H615H | 0.19 | T1/4 |
Del = deletion, Ins = insertion, underlined letters and numbers indicate nucleotides and their genomic position. Population frequency indicates the mutational frequency in the sequenced population. Strains indicates the prevalence of a mutation within different replicates. A: population with previously acquired resistance to amoxicillin, E: population with previously acquired resistance to enrofloxacin, T: population with previously acquired resistance to tetracycline. X/Y: X indicates number of replicates with particular mutation, Y indicates total number of replicates that were sequenced. Mutations associated with resistance in a wild-type background are shown in bold. Mutations associated with the previous resistance have been omitted from the table
Table 5.
Mutations associated with resistance to tetracycline in strains with a previously acquired resistance to amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, or kanamycin
| Gene product | Gene | Mutation | Pop. frequency | Strains |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multidrug efflux pump membrane fusion lipoprotein/multidrug efflux pump RND permease | acrA/acrB* | 5′ UTR (Del 485,695–711) | 0.77 | A1/4 |
| Multidrug efflux pump RND permease | acrB | V139F | 1 | A1/4, E4/4 |
| S665A | 1 | A1/4 | ||
| Transcriptional regulator | acrR | I45L | 0.97 | K1/1 |
| P85Q | 1 | A3/4, K1/4 | ||
| E130K | 1 | K1/1 | ||
| R442Q | 1 | K1/1 | ||
| Crotonobetainyl-CoA reductase | caiA | C154A, F155P, I156T, T157P, S158R, S159 T, A160S, Y161W, Del T162-R380 | 1 | E1/4 |
| Endochitinase | chiA | W702R | 1 | K1/1 |
| Membrane associated sensor kinase | envZ | P247S | 0.24–0.95 | A1/4, K1/1 |
| 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase | fadI | L246 L | 1 | E2/4 |
| Peptidoglycan DD-transpeptidase | ftsI | A513S | 1 | K1/1 |
| DNA-binding transcriptional repressor | marR | Ins C after A1619472 (FS118) | 1 | A1/4 |
| ABC transporter family protein | mdlB | A16A | 1 | A2/4 |
| mlaA | Del F42-N43 | 0.93 | K1/1 | |
| Murein tripeptide ABC transporter periplasmic binding protein | mppA | F244F | 1 | K1/1 |
| Mismatch repair protein | mutL | W390 L | 0.1 | E1/4 |
| Outer membrane porin F | ompF | Ins 7 nt after G986771 (FS71) | 0.04 | E1/4 |
| Truncated RNase PH | rph | Del R676 | 1 | E1/4 |
| RNA polymerase subunit β’ | rpoC | Del T208-K213 | 1 | E1/4 |
| DNA-binding transcriptional dual regulator | soxR | T145S, G146 T, A147L, R148A, L149G, L150R, Del E151-N155 | 1 | E1/4 |
| DNA-binding transcriptional dual regulator | soxS | S2F | 0.98–1 | E3/4 |
| Bifunctional (p) ppGpp synthase/hydrolase | spoT | Ins C after T3815879 (FS223) | 1 | E1/4 |
| DNA-binding transcriptional activator | ybaO | T33P | 1 | E1/4 |
Numbers shown indicate frequency of mutation in population. Del = deletion, Ins = insertion, underlined letters and numbers indicate nucleotides and their genomic position. Population frequency indicates the mutational frequency in the sequenced population. Strains indicates the prevalence of a mutation within different replicates. A: population with previously acquired resistance to amoxicillin, E: population with previously acquired resistance to enrofloxacin, K: population with previously acquired resistance to kanamycin. X/Y: X indicates number of replicates with particular mutation, Y indicates total number of replicates that were sequenced. Mutations associated with resistance in a wild-type background are shown in bold. Mutations associated with the previous resistance have been omitted from the table
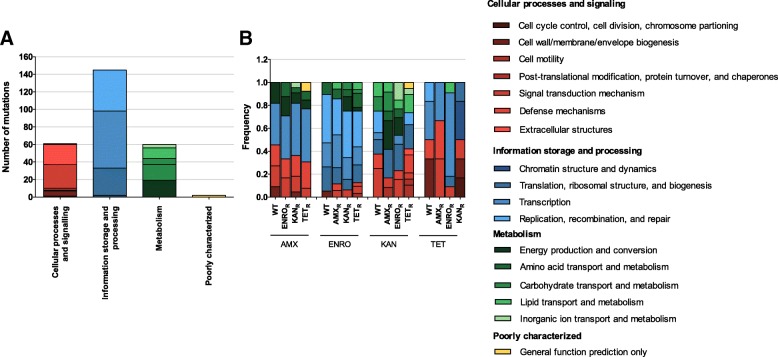
All genes containing a mutation were functionally annotated using clusters of orthologous groups (COG) analysis and clustered according to the four different categories (Fig. 3). The majority of mutations occur in genes involved in information storage and processing in general (145/268) and transcription (65/268) (Fig. 3a). For development of resistance to amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, and kanamycin, no major shift in the function of the mutated genes could be detected (Fig. 3b). For tetracycline, the total number of mutations is significantly lower than the numbers observed with the other three antibiotics, making the comparison slightly problematic.
Fig. 3.
Functional annotation of mutated genes associated with antibiotic resistance. All genes containing a mutations were classified using cluster of orthologous groups (COG) classifications and grouped by the four main categories (a) or by resistant strain (b). The genes were classified into COG categories using IMG/M (https://img.jgi.doe.gov)
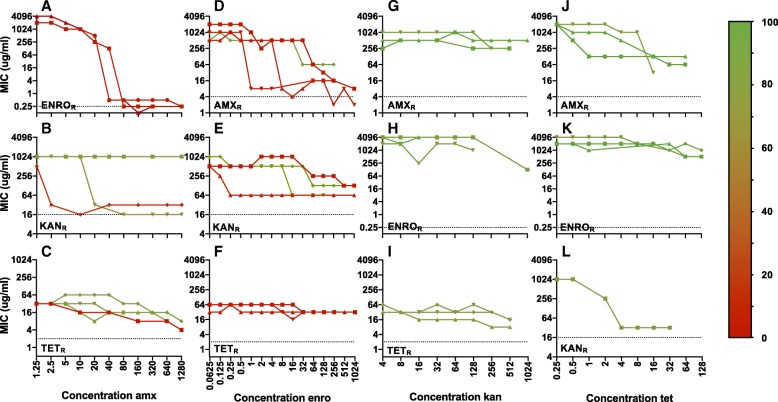
The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of the first antibiotic was measured in all strains exposed to two antibiotics sequentially, to determine if the original resistance could be maintained during development of resistance to a second antibiotic (Fig. 4). In general, the ability of E. coli to maintain its original resistance appears to depend on the combination of antibiotics used. Amoxicillin resistance is compatible with kanamycin and tetracycline exposure, but not with enrofloxacin. For enrofloxacin resistance, the same applies. Acquired resistance to kanamycin resistance can co-exist with enrofloxacin resistance, but not with resistance to other antibiotics. Tetracycline resistance persists after exposure to kanamycin, but not to enrofloxacin. Exposure to amoxicillin results in a mixed pattern.
Fig. 4.
MIC values over time in resistant strains exposed to a second antibiotic. Plots show MIC (ug/ml) of the first de novo acquired resistance, indicated on the X-axes, when exposed to amoxicillin (amx, a-c), enrofloxacin (enro, d-f), kanamycin (kan, g-i), or tetracycline (tet, j-l). The dotted black lines indicate the MICs for wild-type E. coli MG1655. Different lines in each plot indicate the different replicates. The percentage of residual mutations was determined by dividing the number of original mutations still present at the end of the experiment by the number of mutations observed in the beginning and multiplying this number by 100. The percentages are indicated in the plots using colors based on the gradient shown on the right
The percentage of residual mutations was determined by dividing the number of original mutations still present in the strain at the end of the experiment by the number of mutations acquired by the parental strain and multiplying this number by 100 (Fig. 4). When comparing the residual MIC with the number of original mutations still present for most antibiotic combinations, loss of resistance can be correlated with loss of mutations and vice versa. However, a clear correlation cannot always be established. For amoxicillin and enrofloxacin resistance, the absence of mutations correlates to the loss of the original resistance. Resistance to kanamycin and tetracycline, in contrast, is partially or fully maintained, but this does not coincide with the maintenance of the original resistance mutations, suggesting that either the additionally acquired mutations also contribute to the original resistance, or that subsequent adaptation on a gene expression level maintains the level of resistance to the first antibiotic.
Discussion
Taken together, the data presented in this study indicate that the mutations involved in de novo acquisition of resistance to each antibiotic are unique for each specific antibiotic. The shared killing mechanism proposed for all bactericidal antibiotics [6, 7] and the reduction of ROS levels measured in resistant strains [8] suggest that common mutations may occur during adaptation. However, no common mutation shared by all populations resistant to one of the bactericidal antibiotics could be identified. The one common mutation identified throughout the dataset is a mutL W390 L mutation (Tables 2, 3, 4 and 5). In E. coli, MutL is essential for mismatch repair [18]. Defects in mismatch repair are often observed in antibiotic-resistant strains [19, 20] and are known to increase mutation rates over 200-fold [21]. Considering its role in DNA mismatch repair, the mutation frequency varying between 0.09–0.20 most likely provides the population with a source of increased variation without causing deleterious effects on the entire population.
In all resistant strains, most shared mutations that are acquired by both the wild-type and strains with acquired resistance mostly have a frequency of (close to) 1, indicating fixation in the population. For each antibiotic, mutations previously associated with that antibiotic resistance were observed (Table 1). The occurrence of the same mutations in replicates concurs with the earlier observation that while the initial mutations during the development of resistance may vary, at the higher concentrations a single mutation or set of mutations becomes dominant [1]. From a mechanistic point of view, acquired antibiotic resistance can be classified into three groups: 1) prevention of access to target by reduction of permeability (ompR for amoxicillin, soxR for enrofloxacin, sbmA and sapF for kanamycin, ompF for tetracycline) or increased efflux (acrR and soxR for enrofloxacin, acrB and acrR for tetracycline), 2) modification of target (gyrA, parC, and parE for enrofloxacin), or 3) antibiotic modification (ampC for amoxicillin). The effect of other mutations identified in this dataset is not always clear and could vary. Some mutations appear to have a non-structural function, such as mutations found in the 5′ UTR region of rpsJ, gltB, and ybjL or ybjM in strains with acquired resistance to enrofloxacin, by potentially influencing gene expression or translation [22, 23]. Mutations in sigma factors, for example rpoD in amoxicillin resistance, rpoC in tetracycline resistance, or rpoS during secondary adaptation to amoxicillin or tetracycline, can redirect expression of an entire set of genes [24].
Protein moonlighting is a phenomenon in which proteins, often metabolic proteins or molecular chaperones, fulfil more than one biological function [25]. Metabolic proteins from the glycolytic or glyoxylate cycle often function as moonlighting enzymes [26]. CitF, encoding isocitrate lyase, is a candidate for such a role.
Interestingly, a number of synonymous mutations were also identified (Tables 2, 3, 4 and 5). Synonymous mutations are now recognized to have a range of, mostly deleterious, effects on cells, including altering mRNA structure [27, 28], rate of translation [29], protein folding [30], and fitness [31]. So far, synonymous mutations contributing to antibiotic resistance development have been described in TEM-1 β-lactamase [32], gyrA, and rpoB [33].
Not all mutations identified in the resistant strains are necessarily functionally relevant. Through genetic hitchhiking, mutations can increase in frequency because they are genetically linked to mutations that do provide a survival advantage under antibiotic pressure [34, 35].
Most resistance mutations in bacteria confer a fitness cost [36], which can be reduced by the appearance of compensatory mutations [37] or additional resistance mutations [38]. E. coli with acquired resistance to amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, or tetracycline is able to maintain the level of resistance when cultured under the same conditions in the absence of antibiotics [5]. It is therefore likely that some of the mutations observed in this dataset do not confer resistance themselves, but compensate for the fitness cost associated with resistance mutations. In general, mutations observed in this data set either interfere directly with the target-drug interaction, or they facilitate development of resistance by adjusting other cellular processes and thereby compensating for metabolic costs.
The observation that not all mutations associated with a particular resistance in wild-type E. coli appeared during secondary adaptation to the same antibiotic confirms that the effect of a single mutation on phenotype or fitness can depend on the genetic background [11, 39]. For some mutations that do not appear during secondary adaptation, the associated fitness cost could be too high in that particular genetic background. Alternatively, the mutation might not be necessary for resistance. Although no cross-resistance between resistant strains from this study has been found [8], the different genetic background itself could contribute to the ability to become resistant to a second antibiotic. Another explanation could be that the particular mutation is a compensatory mutation that is no longer necessary because of the different genetic background [38].
The mutations identified in strains exposed to a second antibiotic do not appear to be random, as the population frequency is high (Tables 2, 3, 4 and 5) and mutations appear in replicate strains (Fig. 2). The higher number of mutations could be necessary to compensate for the mutations already present in the resistant strains, or could represent alternative pathways to adaptation to the second antibiotic. In addition, a much higher degree of variability was displayed during secondary adaptation, both in the population frequencies of the mutations (Tables 2, 3, 4 and 5), as well as in the incidence of mutations among replicates (Tables 2, 3, 4 and 5). This confirms that, in addition to the different selective strength [40, 41], the genetic background can influence the mutational trajectories available [11, 42].
In an antibiotic-free environment, strains with acquired resistance to amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, and tetracycline maintain this resistance for at least two weeks after daily passaging [5]. When transferred to an environment with a different antibiotic, depending on the antibiotic combination, the original resistance is lost, partially maintained or fully preserved (Fig. 4). This suggests that the cellular adjustments necessary for adaptation to a new antibiotic are not always compatible with the earlier acquired mutations, which can have implications for the de novo development of multidrug resistance.
During resistance development, adaptation to one antibiotic can result in an increased or decreased susceptibility to other antibiotics, a concept known as collateral sensitivity or collateral resistance. This is a concept often employed to develop strategies to limit resistance development [43–47], but is not observed in the resistant strains generated in this study [8] and can therefore not explain the drug-specific effect on loss or maintenance of resistance. Similar experiments in Pseudomonas aeruginosa show a very similar pattern on resensitization of antibiotic resistant strains, where the effect clearly seems to depend on the combination of the antibiotics, but no explanation is available as of yet [48] .
The loss of resistance is not always correlated with the loss of the associated mutations. Resistance to kanamycin and tetracycline (Fig. 4) appears to be partially maintained, but no mutations associated with resistance could be identified in those samples. The residual resistance could be explained by the genetic background contributing to resistance, such as gyrB during adaptation to kanamycin and enrofloxacin, or acrR during adaptation to enrofloxacin or tetracycline, although no cross-resistance between resistant strains has been observed [8]. Alternatively, adaptation on a gene expression level could contribute to residual levels of resistance.
Conclusion
The acquisition of drug resistance involves changes at various levels of cellular organization, including the genome, transcripts, and metabolites, highlighting that a complex interaction network is involved [49]. The data presented in this study support this notion. Development of resistance in strains with a previously acquired resistance does not result in the accumulation of the same mutations observed during primary adaptation in wild-type E. coli. This observation suggests that the genetic background of the strain itself plays an important role in resistance development. Moreover, mutations alone cannot always fully explain the resistance pattern observed, supporting the earlier suggested role for adaptation on the gene expression level in de novo acquisition of antibiotic resistance [50].
Methods
Bacterial strains, growth media, antibiotics, and MIC measurement
In all experimental tracks inducing resistance by exposing cells to step-wise increasing concentrations of the antibiotic [5], E. coli MG1655 wild-type strains were used as starting point. The choice of starting concentrations was based on MIC measurements.
Evolution experiments were performed as follows: wild-type E. coli was exposed to either 1.25 μg/ml amoxicillin, 0.0625 μg/ml enrofloxacin, 4 μg/ml kanamycin, or 0.5 μg/ml tetracycline. Cells were grown overnight at 37 °C, and OD600 were measured after 24 h. When the OD600 of the exposed culture was at least 75% of the OD600 of a reference culture that was not exposed to antibiotics, the population was considered adapted and the antibiotic concentration was doubled. Using the exposed population, new flasks were re-inoculated to a final OD600 of 0.1, with the flasks with the lower concentration now serving as the reference culture. The initial adaptation to each antibiotic was performed in duplicate.
After development of resistance to one antibiotic, two duplicates of each duplicate strain were used for exposure to a second antibiotic, resulting in four strains with an identical exposure history, as depicted in Fig. 1. To re-start the evolution experiments, flasks were re-inoculated with one of the resistant strains to a final OD600 of 0.1. Strains with acquired resistance to one or two antibiotics were compared [8]. When a population was considered adapted, glycerol stocks were made and stored at -80 °C. When relevant, cells from glycerol stocks were plated on LB agar and grown in Evans medium with the appropriate antibiotic.
Stock solutions of amoxicillin, enrofloxacin, kanamycin, or tetracycline (10 mg/mL) were filter sterilized and stored at 4 °C for maximally 2 weeks. Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) were determined as described before [51]. Measurements were performed in 96-well ThermoScientific Multiskan FC spectrophotometer plate readers, shaken and at 37 °C in a final volume of 150 μl with a starting OD595 of 0.05. Antibiotic concentrations increasing by a factor of 2 and ranging from 0.0625 to 4096 μg/ml were applied. The lowest concentrations that limited final OD after 23 h to 0.2 or less was reported as MIC.
Whole genome sequencing
Glycerol stocks of selected strains were plated on LB agar, and over 100 single colonies were combined to grow a liquid culture (Evans minimal medium) in the presence of the antibiotic. The culture was still growing when samples were taken to freeze at -80 °C. We then used roughly 109 cells (corresponding to 2 mL of a culture with an OD600 of 1) for genomic DNA isolation. Genomic DNA was isolated using the DNeasy blood and tissue kit (Qiagen). DNA was isolated from the wild-type, the duplicates of the single exposure strains and all four replicates of the double exposure strains. A wild-type E. coli MG1655 was submitted to the same protocol and used as control. In this control two point mutations were observed when compared to the MG1655 reference strain. These point mutations were observed in all strains and are not reported.
gDNA libraries were generated according to the manufacturers’ protocols using the Ion Xpress™ Plus gDNA Fragment Library Preparations (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Bar-coded libraries were prepared according to the Ion Plus fragment library kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) and the Ion Xpress DNA bar-coding kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the 200-base-read Ion Proton libraries instructions of the manufacturer. The size distribution and yield of the barcoded libraries were assessed using the 2200 TapeStation System with Agilent High Sensitivity D1000 ScreenTapes (Agilent Technologies). Sequencing templates were prepared on the Ion Chef System using the Ion PI Hi-Q Chef Kit (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Sequencing was performed on an Ion Proton System using a Ion PI v3 chip (Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the instructions of the manufacturer.
For quality control procedures, the FASTQ files of individual samples were assessed with fastqc (http://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/). Several quality metrics (sequencing depth, read length distribution, read quality distribution, mean read quality along the read, base frequency at each read position) were compared across samples in relation to the experimental factors using in-house software based on samtools and R (https://www.r-project.org/). To map all accepted reads to the E. coli K-12 MG1655 reference genome, Tmap was applied (https://github.com/iontorrent/TMAP/blob/master/doc/tmap-book.pdf). The Ion Proton system generates sequencing reads of variable lengths, and Tmap combines a short read algorithm [52] and long read algorithms [52, 53] in a multistage mapping approach. The genes were classified into COG categories using IMG/M (https://img.jgi.doe.gov).
The average sequencing depth was 226. Torrent Variant Caller (Thermo Fisher Scientific) was used to identify deviations, such as single-nucleotide polymorphisms, insertions, and deletions from the reference genome. The Torrent Variant Caller is based on Freebayes [54] and capable of somatic variant calling. Overall, parameters such as the minimum phred-scaled call quality, the minimum coverage, and the maximum strand bias, were set such that variants were called with relatively high reliability, at the cost of sensitivity. On the other hand, the minimum observed allele frequency required for a non-reference variant call was set relatively low (5%) to enable detection of low frequency events in the bacterial populations. Mutation frequency was calculated as the ratio of the number of reads containing a genetic variation to the overall read number. To differentiate between sequencing errors and true mutations, genetic deviations were excluded if either of the following conditions applied: 1) the mutations appeared in a homopolymer region, or 2) the Phred quality score was < 30 and the same mutation was not identified in a different sample with a Phred quality score of ≥30. Mutations also present in the wild-type were excluded from the analysis.
Sequencing reads were mapped directly to the MG1655 genome to enable detection of mutations and short indels. For the detection of long inserts the single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) calling algorithm was used. Locations with a high number of called mutations were assumed to be alignment artifacts due to inserts in the genome under study and were detected with the cn.mops package [55]. The regions containing these alignment artefacts were subsequently amplified with PCR and sequenced by Sanger sequencing to achieve a more reliable analysis than the alternative, de novo assembly of the entire genome, would allow [12].
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Wim de Leeuw for assistance with bioinformatics analysis.
Funding
This study was supported by the Netherlands Food and Consumer Product Safety Authority. The funding body had no role in the design of the study, data collection, analysis, interpretation of data, or writing the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
The binary alignment/map (bam) files of the sequenced strains have been deposited in the NCBI database and can accessed at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Traces/study/?acc=PRJNA489357
Abbreviations
- COG
clusters of orthologous groups
- MIC
minimal inhibitory concentration
- ROS
reactive oxygen species
- SNP
single nucleotide polymorphism
Authors’ contributions
MH and BtK conceived the project. MH performed experiments. MJ performed the bioinformatic analysis. MH and BtK wrote the manuscript. SB contributed to the final manuscript. All authors critically reviewed the manuscript and approved the final version.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Handel N, Schuurmans JM, Feng Y, Brul S, ter Kuile BH. Interaction between mutations and regulation of gene expression during development of de novo antibiotic resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014;58(8):4371–4379. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02892-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bagel S, Hullen V, Wiedemann B, Heisig P. Impact of gyrA and parC mutations on quinolone resistance, doubling time, and supercoiling degree of Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1999;43(4):868–875. doi: 10.1128/AAC.43.4.868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Vogwill T, MacLean RC. The genetic basis of the fitness costs of antimicrobial resistance: a meta-analysis approach. Evol Appl. 2015;8(3):284–295. doi: 10.1111/eva.12202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Maisnier-Patin S, Andersson DI. Adaptation to the deleterious effects of antimicrobial drug resistance mutations by compensatory evolution. Res Microbiol. 2004;155(5):360–369. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2004.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.van der Horst MA, Schuurmans JM, Smid MC, Koenders BB, ter Kuile BH. De novo acquisition of resistance to three antibiotics by Escherichia coli. Microb Drug Resist. 2011;17(2):141–147. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2010.0101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kohanski MA, Dwyer DJ, Hayete B, Lawrence CA, Collins JJ. A common mechanism of cellular death induced by bactericidal antibiotics. Cell. 2007;130(5):797–810. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2007.06.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Dwyer DJ, Belenky PA, Yang JH, MacDonald IC, Martell JD, Takahashi N, et al. Antibiotics induce redox-related physiological alterations as part of their lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2014;111(20):E2100–E2109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1401876111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hoeksema M, Brul S, Ter Kuile BH. Influence of reactive oxygen species on De novo Acquisition of Resistance to bactericidal antibiotics. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2018;62(6):e02354–e02317. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02354-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Knopp M, Andersson DI. Predictable phenotypes of antibiotic resistance mutations. mBio. 2018;9(3):e00770–e00718. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00770-18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Durao P, Trindade S, Sousa A, Gordo I. Multiple resistance at no cost: rifampicin and streptomycin a dangerous liaison in the spread of antibiotic resistance. Mol Biol Evol. 2015;32(10):2675–2680. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Weinreich DM, Watson RA, Chao L. Perspective: sign epistasis and genetic constraint on evolutionary trajectories. Evolution. 2005;59(6):1165–1174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Hoeksema M, Jonker MJ, Bel K, Brul S, Ter Kuile BH. Genome rearrangements in Escherichia coli during de novo acquisition of resistance to a single antibiotic or two antibiotics successively. BMC Genomics. 2018;19(1):973. doi: 10.1186/s12864-018-5353-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Corvec S, Caroff N, Espaze E, Marraillac J, Reynaud A. 11 mutation in the ampC promoter increasing resistance to beta-lactams in a clinical Escherichia coli strain. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2002;46(10):3265–3267. doi: 10.1128/AAC.46.10.3265-3267.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ruiz J. Mechanisms of resistance to quinolones: target alterations, decreased accumulation and DNA gyrase protection. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2003;51(5):1109–1117. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkg222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Koutsolioutsou A, Pena-Llopis S, Demple B. Constitutive soxR mutations contribute to multiple-antibiotic resistance in clinical Escherichia coli isolates. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005;49(7):2746–2752. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.7.2746-2752.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Vinue L, Hooper DC, Jacoby GA. Chromosomal mutations that accompany qnr in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2018;51(3):479–483. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2018.01.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Karczmarczyk M, Martins M, Quinn T, Leonard N, Fanning S. Mechanisms of fluoroquinolone resistance in Escherichia coli isolates from food-producing animals. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(20):7113–20. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00600-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Acharya S, Foster PL, Brooks P, Fishel R. The coordinated functions of the E. Coli MutS and MutL proteins in mismatch repair. Mol Cell. 2003;12(1):233–246. doi: 10.1016/S1097-2765(03)00219-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Taddei F, Matic I, Godelle B, Radman M. To be a mutator, or how pathogenic and commensal bacteria can evolve rapidly. Trends Microbiol. 1997;5(11):427–428. doi: 10.1016/S0966-842X(97)01157-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.LeClerc JE, Li B, Payne WL, Cebula TA. High mutation frequencies among Escherichia coli and Salmonella pathogens. Science (New York, NY) 1996;274(5290):1208–1211. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5290.1208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Marinus MG. DNA methylation and mutator genes in Escherichia coli K-12. Mutat Res. 2010;705(2):71–76. doi: 10.1016/j.mrrev.2010.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Caroff N, Espaze E, Gautreau D, Richet H, Reynaud A. Analysis of the effects of −42 and −32 ampC promoter mutations in clinical isolates of Escherichia coli hyperproducing ampC. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2000;45(6):783–788. doi: 10.1093/jac/45.6.783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rinder H, Thomschke A, Rusch-Gerdes S, Bretzel G, Feldmann K, Rifai M, et al. Significance of ahpC promoter mutations for the prediction of isoniazid resistance in mycobacterium tuberculosis. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1998;17(7):508–511. doi: 10.1007/BF01691135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gruber TM, Gross CA. Multiple sigma subunits and the partitioning of bacterial transcription space. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003;57:441–466. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Jeffery CJ. An introduction to protein moonlighting. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014;42(6):1679–1683. doi: 10.1042/BST20140226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Henderson B, Martin A. Bacterial virulence in the moonlight: multitasking bacterial moonlighting proteins are virulence determinants in infectious disease. Infect Immun. 2011;79(9):3476–3491. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00179-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Goodman DB, Church GM, Kosuri S. Causes and effects of N-terminal codon bias in bacterial genes. Science (New York, NY) 2013;342(6157):475–479. doi: 10.1126/science.1241934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kudla G, Murray AW, Tollervey D, Plotkin JB. Coding-sequence determinants of gene expression in Escherichia coli. Science. 2009;324(5924):255–258. doi: 10.1126/science.1170160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sørensen Michael A., Pedersen Steen. Absolute in vivo translation rates of individual codons in Escherichia coli. Journal of Molecular Biology. 1991;222(2):265–280. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90211-N. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang G, Hubalewska M, Ignatova Z. Transient ribosomal attenuation coordinates protein synthesis and co-translational folding. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009;16(3):274–280. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Firnberg E, Labonte JW, Gray JJ, Ostermeier M. A comprehensive, high-resolution map of a gene's fitness landscape. Mol Biol Evol. 2014;31(6):1581–1592. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msu081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schenk MF, Szendro IG, Krug J, de Visser JA. Quantifying the adaptive potential of an antibiotic resistance enzyme. PLoS Genet. 2012;8(6):e1002783. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Lai CC, Chen CC, Lu YC, Chuang YC, Tang HJ. The clinical significance of silent mutations with respect to ciprofloxacin resistance in MRSA. Infect Drug Resist. 2018;11:681–687. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S159455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kim Y, Stephan W. Detecting a local signature of genetic hitchhiking along a recombining chromosome. Genetics. 2002;160(2):765–777. doi: 10.1093/genetics/160.2.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lang GI, Rice DP, Hickman MJ, Sodergren E, Weinstock GM, Botstein D, et al. Pervasive genetic hitchhiking and clonal interference in forty evolving yeast populations. Nature. 2013;500(7464):571–574. doi: 10.1038/nature12344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Melnyk AH, Wong A, Kassen R. The fitness costs of antibiotic resistance mutations. Evol Appl. 2015;8(3):273–283. doi: 10.1111/eva.12196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Maisnier-Patin S, Berg OG, Liljas L, Andersson DI. Compensatory adaptation to the deleterious effect of antibiotic resistance in Salmonella typhimurium. Mol Microbiol. 2002;46(2):355–366. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2002.03173.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Trindade S, Sousa A, Xavier KB, Dionisio F, Ferreira MG, Gordo I. Positive epistasis drives the acquisition of multidrug resistance. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(7):e1000578. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wong A. Epistasis and the evolution of antimicrobial resistance. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:246. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wistrand-Yuen E, Knopp M, Hjort K, Koskiniemi S, Berg OG, Andersson DI. Evolution of high-level resistance during low-level antibiotic exposure. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1599. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04059-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mira PM, Meza JC, Nandipati A, Barlow M. Adaptive landscapes of resistance genes change as antibiotic concentrations change. Mol Biol Evol. 2015;32(10):2707–2715. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Borrell S, Teo Y, Giardina F, Streicher EM, Klopper M, Feldmann J, et al. Epistasis between antibiotic resistance mutations drives the evolution of extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis. Evol Med Public Health. 2013;2013(1):65–74. doi: 10.1093/emph/eot003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Barbosa C, Trebosc V, Kemmer C, Rosenstiel P, Beardmore R, Schulenburg H, et al. Alternative evolutionary paths to bacterial antibiotic resistance cause distinct collateral effects. Mol Biol Evol. 2017;34(9):2229–2244. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msx158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Imamovic L, Sommer MO. Use of collateral sensitivity networks to design drug cycling protocols that avoid resistance development. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5(204):204ra132. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3006609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Lazar V, Pal Singh G, Spohn R, Nagy I, Horvath B, Hrtyan M, et al. Bacterial evolution of antibiotic hypersensitivity. Mol Syst Biol. 2013;9:700. doi: 10.1038/msb.2013.57. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Munck C, Gumpert HK, Wallin AI, Wang HH, Sommer MO. Prediction of resistance development against drug combinations by collateral responses to component drugs. Sci Transl Med. 2014;6(262):262ra156. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rodriguez de Evgrafov M, Gumpert H, Munck C, Thomsen TT, Sommer MO. Collateral resistance and sensitivity modulate evolution of high-level resistance to drug combination treatment in Staphylococcus aureus. Mol Biol Evol. 2015;32(5):1175–1185. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msv006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yen P, Papin JA. History of antibiotic adaptation influences microbial evolutionary dynamics during subsequent treatment. PLoS Biol. 2017;15(8):e2001586. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2001586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Suzuki S, Horinouchi T, Furusawa C. Prediction of antibiotic resistance by gene expression profiles. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5792. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Handel N, Schuurmans JM, Brul S, ter Kuile BH. Compensation of the metabolic costs of antibiotic resistance by physiological adaptation in Escherichia coli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(8):3752–3762. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02096-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Schuurmans JM, Nuri Hayali AS, Koenders BB, ter Kuile BH. Variations in MIC value caused by differences in experimental protocol. J Microbiol Methods. 2009;79(1):44–47. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2009.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Li H, Durbin R. Fast and accurate short read alignment with burrows-wheeler transform. Bioinformatics. 2009;25(14):1754–1760. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Ning Z, Cox AJ, Mullikin JC. SSAHA: a fast search method for large DNA databases. Genome Res. 2001;11(10):1725–1729. doi: 10.1101/gr.194201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Garrison EM, Gabor. Haplotype-based variant detection from short-read sequencing. eprint arXiv. 2012:1207.3907v2.
- 55.Klambauer G, Schwarzbauer K, Mayr A, Clevert DA, Mitterecker A, Bodenhofer U, et al. Cn. MOPS: mixture of Poissons for discovering copy number variations in next-generation sequencing data with a low false discovery rate. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(9):e69. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The binary alignment/map (bam) files of the sequenced strains have been deposited in the NCBI database and can accessed at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Traces/study/?acc=PRJNA489357