Abstract
Background
Sometimes it is necessary to bring on labour artificially because of safety concerns for the mother or baby. This review is one of a series of reviews of methods of labour induction using a standardised protocol.
Objectives
To determine the effects of NO donors (isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN), isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN), nitroglycerin and sodium nitroprusside) for third trimester cervical ripening or induction of labour, in comparison with placebo or no treatment or other treatments from a predefined hierarchy.
Search methods
We searched Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth's Trials Register (15 August 2016) and the reference lists of trial reports.
Selection criteria
Clinical trials comparing NO donors for cervical ripening or labour induction with other methods listed above it on a predefined list of methods of labour induction. Interventions include NO donors (isosorbide mononitrate, isosorbide dinitrate, nitroglycerin and sodium nitroprusside) compared with other methods listed above it on a predefined list of methods of labour induction.
Data collection and analysis
This review is part of a series of reviews focusing on methods of induction of labour, based on a generic protocol. Three review authors independently assessed trials for inclusion, assessed risk of bias and extracted data. In this update, the quality of the evidence for the main comparison was assessed using the GRADE approach.
Main results
We included 23 trials (including a total of 4777 women). Included studies compared NO donors with placebo, vaginal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), intracervical PGE2, vaginal misoprostol and intracervical Foley catheter. The majority of the included studies were assessed as being at low risk of bias.
Nitric oxide versus placebo
There was no evidence of a difference for any of the primary outcomes analysed: vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours (risk ratio (RR) 0.97, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.83 to 1.15; one trial, 238 women; low‐quality evidence), uterine hyperstimulation with fetal heart rate (FHR) changes (RR 0.09, 95% CI 0.01 to 1.62; two trials, 300 women; low‐quality evidence), caesarean section (RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.88 to 1.11; nine trials, 2624 women; moderate‐quality evidence) or serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death (average RR 1.61, 95% CI 0.08 to 33.26; two trials, 1712 women; low‐quality evidence). There were no instances of serious maternal morbidity or death (one study reported this outcome).
There was a reduction in an unfavourable cervix at 12 to 24 hours in women treated with NO donors (average RR 0.78, 95% CI 0.67 to 0.90; four trials, 762 women), and this difference was observed in both subgroups of standard release and slow release formulation. Women who received NO donors were less likely to experience uterine hyperstimulation without FHR rate changes (RR 0.05, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.80; one trial, 200 women), and more likely to experience side effects, including nausea, headache and vomiting.
Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins
There was no evidence of any difference between groups for uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes or caesarean section (RR 0.97, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.21; three trials, 571 women). Serious neonatal morbidity and serious maternal morbidity were not reported. There were fewer women in the NO donor group who did not achieve a vaginal delivery within 24 hours (RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.47 to 0.86; one trial, 400 primiparae women).
Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins
One study reported a reduction in the number of women who had not achieved a vaginal delivery within 24 hours with NO donors (RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.47 to 0.86; one trial, 400 women). This result should be interpreted with caution as the information was extracted from an abstract only and a full report of the study is awaited. No differences were observed between groups for uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.01 to 7.74; one trial, 42 women) or serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.01 to 7.74; one trial, 42 women). Fewer women in the NO donor group underwent a caesarean section in comparison to women who received intracervical prostaglandins (RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.44 to 0.90; two trials, 442 women). No study reported on the outcome serious maternal morbidity or death.
Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol
There was a reduction in the rate of uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes with NO donors (RR 0.07, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.37; three trials, 281 women). There were no differences in caesarean section rates (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.21; 761 women; six trials) and no cases of serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death were reported. One study found that women in the NO donor group were more likely to not deliver within 24 hours (RR 5.33, 95% CI 1.62 to 17.55; one trial, 150 women). Serious maternal morbidity or death was not reported.
In terms of secondary outcomes, there was an increase in cervix unchanged/unfavourable with NO (RR 3.43, 95% CI 2.07 to 5.66; two trials, 151 women) and an increase in the need for oxytocin augmentation with NO induction (RR 2.67, 95% CI 1.31 to 5.45; 7 trials; 767 women), although there was evidence of significant heterogeneity which could not be fully explained. Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR was lower in the NO group, as was meconium‐stained liquor, Apgar score less than seven at five minutes and analgesia requirements.
Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical catheter
There was no evidence on any difference between the effects of NO and the use of a Foley catheter for induction of labour for caesarean section (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.39 to 2.59; one trial, 80 women). No other primary outcomes were reported. One study of 75 participants did not contribute any data to the review.
For all comparisons, women who received NO donors were more likely to experience side effects such as headache, nausea or vomiting.
Authors' conclusions
Available data suggests that NO donors can be a useful tool in the process of induction of labour causing the cervix to be more favourable in comparison to placebo. However, additional data are needed to assess the true impact of NO donors on all important labour process and delivery outcomes.
Plain language summary
Nitric oxide donors for cervical ripening and induction of labour
What is the issue?
Sometimes it is necessary to bring on labour artificially in the third trimester because of safety concerns for the mother or her baby. Most commonly used cervical ripening or induction agents also cause uterine activity or contraction, which requires close monitoring of mother and baby within a hospital environment.
Why is this important?
Nitric oxide (NO) donor agents such as isosorbide mononitrate, Isosorbide dinitrate, nitroglycerin and sodium nitroprusside are thought to bring on ripening of the cervix (neck of the womb) without producing contractions and could be used in an outpatient setting. There are increasing data to support their use for this purpose.
What evidence did we find?
We searched for evidence on 15th August 2016 and identified a further 13 studies. The review now includes a total of 23 studies involving 4777 women. The five main primary outcomes (after the administration of NO donors) included: vaginal delivery not achieved within 24 hours; uterine hyperstimulation with changes in the fetal heart rate; caesarean section; serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death; and serious maternal morbidity or death. The evidence for the five primary outcomes was mainly found to be of low quality. There was no evidence of a difference for any of the primary outcomes analysed. There was evidence from four trials to suggest that NO donors were superior to placebo in bringing on ripening of the cervix. Women who received NO donors were also more likely to experience side effects such as headache, nausea or vomiting.
What does this mean?
NO donor leads to little or no difference on the majority of labour process and delivery outcomes. However, there was some evidence to suggest that it probably helps in causing the cervix to be more favourable at 12 to 24 hours after administration. Additional studies are needed to see the true impact of NO donors in bringing on induction of labour and its effect on caesarean section rates.
Summary of findings
Summary of findings for the main comparison. Nitric oxide donors versus placebo for cervical ripening and induction of labour.
| Nitric oxide donors for cervical ripening and induction of labour | ||||||
| Patient or population: pregnant women undergoing cervical ripening and induction of labour Setting: outpatient and inpatient settings in India, UK, Sweden, Sri Lanka, France and Iran Intervention: nitric oxide donors Comparison: placebo/no intervention | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | № of participants (studies) | Quality of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Risk with placebo/no intervention (all women) | Risk with (1.1) Nitric oxide donors | |||||
| Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | Study population | RR 0.97 (0.83 to 1.15) | 238 (1 RCT) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ LOW 1 | ||
| 711 per 1000 | 689 per 1000 (590 to 817) | |||||
| Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | Study population | RR 0.09 (0.01 to 1.62) | 300 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ LOW 2 3 | ||
| 33 per 1000 | 3 per 1000 (1 to 54) | |||||
| Caesarean section | Study population | RR 0.99 (0.88 to 1.11) | 2624 (9 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊕⊝ MODERATE 4 | ||
| 280 per 1000 | 277 per 1000 (246 to 311) | |||||
| Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | Study population | RR 1.61 (0.08 to 33.26) | 1712 (2 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ LOW 5 6 | ||
| 1 per 1000 | 2 per 1000 (0 to 39) | |||||
| Serious maternal morbidity or death | Study population | not estimable | 1362 (1 RCT) | There were no events for this outcome. | ||
| 0 per 1000 | 0 per 1000 (0 to 0) | |||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: Confidence interval; FHR: Fetal heart rate; RCT: randomised controlled trial; RR: Risk ratio. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence High quality: We are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect Moderate quality: We are moderately confident in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different Low quality: Our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: The true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect Very low quality: We have very little confidence in the effect estimate: The true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect | ||||||
1 Only one study with few events, small sample size and wide confidence interval.
2 High risk of bias for allocation concealment and blinding.
3 Only two studies with few or no events, small sample size and wide confidence interval.
4 High risk of bias for allocation concealment, blinding and selective outcome reporting.
5 Confidence intervals do not overlap (opposite directions of effect) and I2 = 48%.
6 Only two studies with few events and wide confidence intervals.
Background
Description of the condition
It is often necessary to bring on labour artificially because of safety concerns for the mother or baby. This review is one of a series of reviews of methods of labour induction using a standardised protocol. For more detailed information on the rationale for this methodological approach, please refer to the currently published 'generic' protocol (Hofmeyr 2009). The generic protocol describes how a number of standardised reviews were combined to compare various methods of preparing the cervix of the uterus and inducing labour. The initial series of 21 reviews were developed simultaneously (Alfirevic 2014; Boulvain 2005; Boulvain 2016; Bricker 2000; French 2001; Hapangama 2009; Hofmeyr 2003; Howarth 2001; Hutton 2001; Jozwiak 2012; Kavanagh 2001; Kavanagh 2005; Kavanagh 2006a; Kavanagh 2006b; Kelly 2001a; Kelly 2013b; Luckas 2000; Smith 2003; Smith 2013; Thomas 2001; Thomas 2014).
Induction of labour occurs in approximately 20% of pregnancies in the UK. The ideal agent for induction of labour would induce cervical ripening without causing uterine contractions (Calder 1998). Currently, most commonly used cervical ripening or induction agents result in uterine activity or contractions, or both. These necessitate close monitoring of mother and baby within a hospital environment. Cervical ripening without uterine contractility could occur safely in an outpatient setting and it may be expected that this would result in greater maternal satisfaction and lower costs.
Description of the intervention
Nitric oxide (NO) is thought to be an essential mediator in the process of cervical ripening (Chwalisz 1998). There is increasing evidence that the use of NO donors (including isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN), isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN), nitroglycerin and sodium nitroprusside) allow cervical ripening to occur in the absence of uterine contractions and this may be performed in an outpatient environment (Agarwal 2012; Bullarbo 2007; Chanrachakul 2000; Chanrachakul 2002; Osman 2006; Rezk 2014; Schmitz 2014).
How the intervention might work
The major physiological effect of NO (a free radical gas with a half‐life of less than four seconds) is the relaxation of smooth muscle (Buhimschi 1995). NO itself is endogenously supplied from L‐arginine through the action of the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) (Arnold 1977), which has been identified as being present in the human cervix (Telfer 1995). This NO product reacts with soluble guanylate cyclase, the product of which raises the concentration of intracellular cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP). cGMP causes the dephosphorylation of myosin light chains within the smooth muscle structure leading to its relaxation. Significantly, the cervix is largely composed of connective tissue, including smooth muscle. Previous studies have confirmed that this smooth muscle component of the cervix has a functional role in cervical ripening (Bryman 1986). Several animal experiments have independently come to the conclusion that NO is an important mediator in the cervical ripening process (Calder 1998; Chwalisz 1998). Specifically, when the NO donor sodium nitroprusside was applied to the cervixes of pregnant guinea pigs, ripening occurred in the same way as during normal labour, but significantly labour itself was not induced (Qing 1996). Further to this, and in opposition to the adverse effects of prostaglandin use, NO also inhibits myometrial contraction and promotes uterine blood flow (Ekerhord 1998; Izurni 1993). NO donors have even been proposed as realistic tocolytic agents in the management of preterm labour (Lees 1994; Norman 1997).
NO donors have successfully been used for cervical ripening, not for pre‐induction ripening, but to ripen the cervix in preparation for first trimester surgical termination of pregnancy (Thompson 1997), where they have been shown to have fewer adverse effects than prostaglandins (Thompson 1998).
Why it is important to do this review
There is increasing focus on agents that allow safe initiation of the labour process without uterine contractions and where possible away from a hospital environment. NO donors may represent such a group of agents. This review allows us to examine the efficacy of these agents for induction of labour.
Objectives
To determine the effects of NO donors (ISMN, ISDN, nitroglycerin and sodium nitroprusside) for third trimester cervical ripening or induction of labour, in comparison with placebo or no treatment or other treatments from a predefined hierarchy.
This review is part of a series of review focusing on induction of labour. Within all previous reviews there has been no distinction between cervical ripening and later stages of the induction process. The primary aim of all induction agents is to induce the labour not solely to produce cervical ripening. NO donors in some ways only aim to produce cervical ripening, but for the purpose of this review they have been examined alongside other similar agents and we have used similar outcomes to all the other reviews in the series.
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
Randomised controlled trials comparing NO donors for cervical ripening or labour induction to other methods listed above it on a predefined list of methods of labour induction (seeMethods). Cluster trials were eligible for inclusion. Quasi‐randomised and cross‐over trials were not eligible for inclusion.
Types of participants
Pregnant women due for third trimester induction of labour, carrying a viable fetus.
Types of interventions
NO donors (isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN), isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN), nitroglycerin and sodium nitroprusside) compared to other methods listed above it on a predefined list of methods of labour induction (seeMethods).
For the purposes of most of the comparisons, the main agent used was ISMN. Hence unless specified in the analysis all included studies used this agent, and it was administered in single or multiple doses using a standard release formulation. In one trial a slow‐release compound was used and this was analysed within a separate subgroup within this comparison. Another trial used isosorbide dinitrate as a NO donor.
Studies were analysed as a whole group (all women), and also according to status of the cervix, membrane status and parity, as specified in the generic protocol Hofmeyr 2009.
Primary comparisons
NO donors versus placebo/no treatment.
NO donors versus vaginal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2).
NO donors versus intracervical PGE2.
NO donors versus vaginal misoprostol.
NO donors versus intracervical Foley catheter.
Types of outcome measures
Clinically relevant outcomes for trials of methods of cervical ripening and labour induction have been prespecified by two authors of labour induction reviews (Justus Hofmeyr and Zarko Alfirevic).
Primary outcomes
Five primary outcomes were chosen as being most representative of the clinically important measures of effectiveness and complications.. 1. Vaginal delivery not achieved within 24 hours (or period specified by trial authors). 2. Uterine hyperstimulation with fetal heart rate (FHR) changes. 3. Caesarean section. 4. Serious neonatal morbidity or perinatal death (e.g. seizures, birth asphyxia defined by trialists, neonatal encephalopathy, disability in childhood). 5. Serious maternal morbidity or death (e.g. uterine rupture, admission to intensive care unit, septicaemia).
Perinatal and maternal morbidity and mortality are composite outcomes. This is not an ideal solution because some components are clearly less severe than others. It is possible for one intervention to cause more deaths, but less severe morbidity. However, in the context of labour induction at term this is unlikely. All of these events are rare, and a modest change in their incidence is easier to detect if composite outcomes are presented. We have explored the incidence of individual components as secondary outcomes (see below).
Secondary outcomes
Secondary outcomes relate to measures of effectiveness, complications and satisfaction.
Measures of effectiveness
6. Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12 to 24 hours. 7. Oxytocin augmentation.
Complications
8. Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes. 9. Uterine rupture. 10. Epidural analgesia. 11. Instrumental vaginal delivery. 12. Meconium‐stained liquor. 13. Apgar score less than seven at five minutes. 14. Neonatal intensive care unit admission. 15. Neonatal encephalopathy. 16. Perinatal death. 17. Disability in childhood. 18. Maternal side effects (all). 19. Maternal nausea. 20. Maternal vomiting. 21. Maternal diarrhoea. 22. Other maternal side effects. 23. Postpartum haemorrhage (as defined by the trial authors). 24. Serious maternal complications (e.g. intensive care unit admission, septicaemia but excluding uterine rupture). 25. Maternal death.
Measures of satisfaction
26. Woman not satisfied. 27. Caregiver not satisfied.
'Uterine rupture' includes all clinically significant ruptures of unscarred or scarred uteri. We have excluded trivial scar dehiscence noted incidentally at the time of surgery.
Additional outcomes may appear in individual reviews.
While we have sought all the above outcomes, we have included only those with data in the analysis tables.
The terminology of uterine hyperstimulation is problematic (Curtis 1987). In the reviews, we use the term 'uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes' to include uterine tachysystole (more than five contractions per 10 minutes for at least 20 minutes) and uterine hypersystole/hypertonus (a contraction lasting at least two minutes) and 'uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes' to denote uterine hyperstimulation syndrome (tachysystole or hypersystole with FHR changes such as persistent decelerations, tachycardia or decreased short‐term variability).
We have included outcomes in the analysis: if reasonable measures were taken to minimise observer bias; and data were available for analysis according to original allocation.
In more recent reviews and updates the following outcomes have been added.
28. Neonatal infection. 29. Neonatal antibiotics. 30. Chorioamnionitis. 31. Endometritis. 32. Maternal antibiotics.
In addition, in view of the nature of the trials and the intervention studied, we have examined some additional outcomes in this review. These include the following.
33. Additional induction agents required. 34. Initiation of cervical ripening to delivery interval (in days).
Search methods for identification of studies
The following methods section of this review is based on a standard template used by the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group.
Electronic searches
We searched Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth’s Trials Register by contacting their Information Specialist (15 August 2016).
The Register is a database containing over 22,000 reports of controlled trials in the field of pregnancy and childbirth. For full search methods used to populate Pregnancy and Childbirth’s Trials Register including the detailed search strategies for CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase and CINAHL; the list of handsearched journals and conference proceedings, and the list of journals reviewed via the current awareness service, please follow this link to the editorial information about the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth in the Cochrane Library and select the ‘Specialized Register ’ section from the options on the left side of the screen.
Briefly, Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth’s Trials Register is maintained by their Information Specialist and contains trials identified from:
monthly searches of the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL);
weekly searches of MEDLINE (Ovid);
weekly searches of Embase (Ovid);
monthly searches of CINAHL (EBSCO);
handsearches of 30 journals and the proceedings of major conferences;
weekly current awareness alerts for a further 44 journals plus monthly BioMed Central email alerts.
Search results are screened by two people and the full text of all relevant trial reports identified through the searching activities described above is reviewed. Based on the intervention described, each trial report is assigned a number that corresponds to a specific Pregnancy and Childbirth review topic (or topics), and is then added to the Register. The Information Specialist searches the Register for each review using this topic number rather than keywords. This results in a more specific search set which has been fully accounted for in the relevant review sections (Included studies; Excluded studies; Studies awaiting classification).
Searching other resources
We searched the reference lists of trial reports by hand.
We did not apply any language or date restrictions.
Data collection and analysis
To avoid duplication of data the labour induction methods have been listed in a specific order, from one to 27. Each review includes comparisons between one of the methods (from two to 28), with only those methods above it on the list. Thus, the review of intravenous oxytocin (4) includes only comparisons with intracervical prostaglandins (3), vaginal prostaglandins (2) or placebo (1). Methods identified in the future will be added to the end of the list. The current list is as follows:
placebo/no treatment;
vaginal prostaglandins (Thomas 2014);
intracervical prostaglandins (Boulvain 2008);
intravenous oxytocin (Alfirevic 2009);
amniotomy (Bricker 2000);
intravenous oxytocin with amniotomy (Howarth 2001);
vaginal misoprostol (Hofmeyr 2003);
oral misoprostol (Alfirevic 2014);
mechanical methods including extra‐amniotic Foley catheter (Jozwiak 2012);
membrane sweeping (Boulvain 2005);
extra‐amniotic prostaglandins (Hutton 2001);
intravenous prostaglandins (Luckas 2000);
oral prostaglandins (French 2001);
mifepristone (Hapangama 2009);
estrogens (Thomas 2001);
corticosteroids (Kavanagh 2006a);
relaxin (Kelly 2001a);
hyaluronidase (Kavanagh 2006b);
castor oil, bath, and/or enema (Kelly 2013b);
acupuncture (Smith 2013);
breast stimulation (Kavanagh 2005);
sexual intercourse (Kavanagh 2001);
homoeopathic methods (Smith 2003);
nitric oxide;
buccal or sublingual misoprostol (Muzonzini 2004);
hypnosis;
other methods for induction of labour.
For methods used in the previous version of this review, seeKelly 2011.
For this update, the following methods were used for assessing the reports that were identified as a result of the updated search.
The following methods section of this review is based on a standard template used by the Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth Group.
Selection of studies
Three review authors independently assessed for inclusion all the potential studies we identified as a result of the search strategy. We resolved any disagreement through discussion.
Data extraction and management
We used a standardised form to extract data. For eligible studies, all three review authors extracted the data using the agreed form. We resolved discrepancies through discussion. We entered data into Review Manager software (RevMan 2014) and checked for accuracy.
When information regarding any of the above was unclear, we attempted to contact authors of the original reports to provide further details.
The following methods section of this review is based on a standard template used by Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
All three review authors independently assessed risk of bias for each study using the criteria outlined in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2011). We resolved any disagreement by discussion.
(1) Random sequence generation (checking for possible selection bias)
We described for each included study the method used to generate the allocation sequence in sufficient detail to allow an assessment of whether it should produce comparable groups.
We assessed the method as:
low risk of bias (any truly random process, e.g. random number table; computer random number generator);
high risk of bias (any non‐random process, e.g. odd or even date of birth; hospital or clinic record number);
unclear risk of bias.
(2) Allocation concealment (checking for possible selection bias)
We described for each included study the method used to conceal allocation to interventions prior to assignment and assess whether intervention allocation could have been foreseen in advance of, or during recruitment, or changed after assignment.
We assessed the methods as:
low risk of bias (e.g. telephone or central randomisation; consecutively numbered sealed opaque envelopes);
high risk of bias (open random allocation; unsealed or non‐opaque envelopes, alternation; date of birth);
unclear risk of bias.
(3.1) Blinding of participants and personnel (checking for possible performance bias)
We described for each included study the methods used, if any, to blind study participants and personnel from knowledge of which intervention a participant received. We considered studies to be at low risk of bias if they were blinded, or if we judged that the lack of blinding would be unlikely to have affected the results. We assessed blinding separately for different outcomes or classes of outcomes.
We assessed the methods as:
low, high or unclear risk of bias for participants;
low, high or unclear risk of bias for personnel;
low, high or unclear risk of bias for outcome assessors.
(3.2) Blinding of outcome assessment (checking for possible detection bias)
We described for each included study the methods used, if any, to blind outcome assessors from knowledge of which intervention a participant received. We assessed blinding separately for different outcomes or classes of outcomes.
We assessed methods used to blind outcome assessment as:
low, high or unclear risk of bias.
(4) Incomplete outcome data (checking for possible attrition bias due to the amount, nature and handling of incomplete outcome data)
We described for each included study, and for each outcome or class of outcomes, the completeness of data including attrition and exclusions from the analysis. We stated whether attrition and exclusions were reported and the numbers included in the analysis at each stage (compared with the total randomised participants), reasons for attrition or exclusion where reported, and whether missing data were balanced across groups or were related to outcomes. Where sufficient information was reported, or was supplied by the trial authors, we re‐included missing data in the analyses which we undertook.
We assessed methods as:
low risk of bias (e.g. no missing outcome data; missing outcome data balanced across groups);
high risk of bias (e.g. numbers or reasons for missing data imbalanced across groups; ‘as treated’ analysis done with substantial departure of intervention received from that assigned at randomisation);
unclear risk of bias.
(5) Selective reporting (checking for reporting bias)
We described for each included study how we investigated the possibility of selective outcome reporting bias and what we found.
We assessed the methods as:
low risk of bias (where it is clear that all of the study’s pre‐specified outcomes and all expected outcomes of interest to the review have been reported);
high risk of bias (where not all the study’s pre‐specified outcomes have been reported; one or more reported primary outcomes were not pre‐specified; outcomes of interest are reported incompletely and so cannot be used; study fails to include results of a key outcome that would have been expected to have been reported);
unclear risk of bias.
(6) Other bias (checking for bias due to problems not covered by (1) to (5) above)
We described for each included study any important concerns we have about other possible sources of bias.
We assessed whether each study was free of other problems that could put it at risk of bias:
low risk of other bias;
high risk of other bias;
unclear whether there is risk of other bias.
(7) Overall risk of bias
We made explicit judgements about whether studies were at high risk of bias, according to the criteria given in the Handbook (Higgins 2011). With reference to (1) to (6) above, we assessed the likely magnitude and direction of the bias and whether we considered it is likely to impact on the findings. We explored the impact of the level of bias through undertaking sensitivity analyses ‐ seeSensitivity analysis.
Assessment of the quality of the evidence using the GRADE approach
For this update, we assessed the quality of the evidence using the GRADE approach as outlined in the GRADE handbook in order to assess the quality of the body of evidence relating to the following outcomes for the main comparison NO donors versus placebo.
Vaginal delivery not achieved within 24 hours (or period specified by trial authors).
Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
Caesarean section.
Serious neonatal morbidity or perinatal death (e.g. seizures, birth asphyxia defined by trialists, neonatal encephalopathy, disability in childhood).
Serious maternal morbidity or death (e.g. uterine rupture, admission to intensive care unit, septicaemia).
We used the GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool to import data from Review Manager 5.3 (RevMan 2014) in order to create a ’Summary of findings’ table. A summary of the intervention effect and a measure of quality for each of the above outcomes was produced using the GRADE approach. The GRADE approach uses five considerations (study limitations, consistency of effect, imprecision, indirectness and publication bias) to assess the quality of the body of evidence for each outcome. The evidence can be downgraded from 'high quality' by one level for serious (or by two levels for very serious) limitations, depending on assessments for risk of bias, indirectness of evidence, serious inconsistency, imprecision of effect estimates or potential publication bias.
Measures of treatment effect
Dichotomous data
For dichotomous data, we present results as summary risk ratio (RR) with 95% confidence intervals (CI).
Continuous data
No continuous data were analysed in this review. In future updates, if available, we will use the mean difference if outcomes are measured in the same way between trials. We will use the standardised mean difference to combine trials that measure the same outcome, but use different methods.
Unit of analysis issues
Cross‐over trials were not eligible for inclusion due to the nature of their design. No cluster‐randomised controlled trials were included in the review. In future updates of this review, if cluster‐randomised trials became available, we plan to include them.
Cluster‐randomised trials
If identified in future updates, we will include cluster‐randomised trials in the analyses along with individually‐randomised trials. We will adjust their sample sizes or standard errors using the methods described in the Handbook [Section 16.3.4 or 16.3.6] using an estimate of the intracluster correlation co‐efficient (ICC) derived from the trial (if possible), from a similar trial or from a study of a similar population. If we use ICCs from other sources, we will report this and conduct sensitivity analyses to investigate the effect of variation in the ICC. If we identify both cluster‐randomised trials and individually‐randomised trials, we plan to synthesise the relevant information. We will consider it reasonable to combine the results from both if there is little heterogeneity between the study designs and the interaction between the effect of intervention and the choice of randomisation unit is considered to be unlikely.
We will also acknowledge heterogeneity in the randomisation unit and perform a sensitivity analysis to investigate the effects of the randomisation unit.
Dealing with missing data
For included studies, we noted levels of attrition. We explored the impact of including studies with high levels of missing data in the overall assessment of treatment effect by using sensitivity analysis.
For all outcomes, we carried out analyses, as far as possible, on an intention‐to‐treat basis, i.e. we attempted to include all participants randomised to each group in the analyses, and all participants were analysed in the group to which they were allocated, regardless of whether or not they received the allocated intervention. The denominator for each outcome in each trial was the number randomised minus any participants whose outcomes were known to be missing.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We assessed statistical heterogeneity in each meta‐analysis using the Tau², I² and Chi² statistics. We regarded heterogeneity as substantial if the Tau² is greater than zero and either an I² was greater than 30% or there was a low P value (less than 0.10) in the Chi² test for heterogeneity.
Assessment of reporting biases
In future updates of this review, if there are 10 or more studies in a meta‐analysis, we will investigate reporting biases (such as publication bias) using funnel plots. We will assess funnel plot asymmetry visually. If we detect asymmetry visual assessment, we will perform exploratory analyses to investigate it.
Data synthesis
We carried out statistical analysis using Review Manager software (RevMan 2014). We used fixed‐effect meta‐analysis for combining data where it was reasonable to assume that studies were estimating the same underlying treatment effect: i.e. where trials were examining the same intervention, and the trials’ populations and methods were judged sufficiently similar. If there was clinical heterogeneity sufficient to expect that the underlying treatment effects differed between trials, or if we detected substantial statistical heterogeneity, we used random‐effects meta‐analysis to produce an overall summary, if we considered an average treatment effect across trials was clinically meaningful. We treated the random‐effects summary as the average of the range of possible treatment effects and discussed the clinical implications of treatment effects differing between trials. If the average treatment effect was not clinically meaningful, we did not combine trials.
Where we used random‐effects analyses, we presented the results as the average treatment effect with its 95% CI, and the estimates of Tau² and I².
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
Where we identified substantial heterogeneity, we investigated it using subgroup analyses and sensitivity analyses. We considered whether an overall summary was meaningful, and if it was, used random‐effects analysis to produce it.
We carried out the following subgroup analyses.
Slow release versus standard release (Analysis 1.6; Analysis 1.22)
One type of NO donor versus a different NO donor (Analyses 7 to 24)
1.6. Analysis.
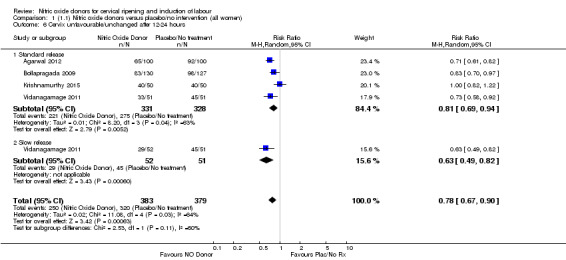
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 6 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
1.22. Analysis.
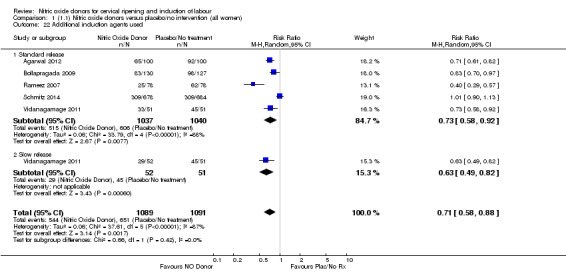
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 22 Additional induction agents used.
We carried out subgroup analyses for all outcomes in the above analyses.
We assessed subgroup differences by interaction tests available within RevMan (RevMan 2014). We reported the results of subgroup analyses quoting the Chi² statistic and P value, and the interaction test I² value.
Sensitivity analysis
We planned to perform sensitivity analysis on the basis of trial quality.
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
In total, we considered 36 trials. We excluded 13 (for details, seeCharacteristics of excluded studies), and included 23 (involving a total of 4777 women) (for details, seeCharacteristics of included studies).
Included studies
Ten studies compared nitric oxide (NO) donors with placebo (Agarwal 2012; Bollapragada 2009; Bullarbo 2007; Haghighi 2015; Krishnamurthy 2015; Nicoll 2001; Rameez 2007; Schmitz 2014; Vidanagamage 2011; Yazdizadeh 2013).
Three studies compared NO donors with vaginal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) (Chanrachakul 2000; Osman 2006; Romero‐Gutierrez 2011).
Seven studies compared NO donors with vaginal misoprostol (Chanrachakul 2002; Guha 2015; Haghighi 2013; Perche 2009; Razaq 2011; Sharma 2005; Soliman 2013).
One study had three arms and compared NO donors with both intracervical PGE2 and vaginal misoprostol (Sharma 2005).
One study had three arms and compared NO donors with vaginal misoprostol and with a combination of vaginal misoprostol and NO donor, which is a complex intervention. We have not included the data from this arm of the study in the review (Soliman 2013).
One study compared NO donors with intracervical PGE2 only (Kadian 2008).
Two studies compared NO donors with intracervical catheter (Movahed 2016; Rezk 2014), however Movahed 2016 did not contribute any data to the review.
One study had three arms and compared standard dose ISMN and sustained release ISMN with placebo (Vidanagamage 2011) (to allow inclusion of both intervention arms from this trial, we did not pool the results within the comparison).
Where isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN) was used:
a dose of 40 mg was used in all but one study, where the dose was 60 mg (Rameez 2007). In one study, a sustained release formulation of 60 mg isosorbide mononitrate (ISMN) was used (Vidanagamage 2011);
a single dose was given in five studies (Bullarbo 2007; Chanrachakul 2002; Nicoll 2001; Rezk 2014; Vidanagamage 2011); multiple planned doses were used in four studies (Agarwal 2012; Bollapragada 2009; Schmitz 2014; Yazdizadeh 2013); and multiple doses as required were used in six studies (Guha 2015; Krishnamurthy 2015; Perche 2009; Sharma 2005; Schmitz 2014; Soliman 2013);
all but one study used the ISMN vaginally.
Where isosorbide dinitrate (ISDN) was used:
a dose of 40 mg was used in four studies (Haghighi 2013; Haghighi 2015; Kadian 2008; Osman 2006), in three studies a maximum of two doses were used, in one a single dose of 40 mg was used (Osman 2006);
a dose of 20 mg was used in one study (Romero‐Gutierrez 2011) to a maximum of three doses;
a dose of 20 mg used orally in the third arm of one trial (Haghighi 2015) to a maximum of two doses.
Where glyceryl trinitrate (GTN) was used:
a dose of 500 mcg was used in both studies (Chanrachakul 2000; Sharma 2005).
Additonal induction agents
In addition to the study medication, additional agents were used for cervical ripening prior to amniotomy and intravenous oxytocin in four studies. In five trials, this was additional doses of vaginal PGE2 (Agarwal 2012; Bollapragada 2009; Bullarbo 2007; Osman 2006; Schmitz 2014), and in two studies this additional ripening was effected using an intracervical extra amniotic Foley catheter (Rameez 2007; Vidanagamage 2011).
Trial setting
Five trials were conducted in an outpatient setting (Agarwal 2012; Bollapragada 2009; Bullarbo 2007; Rezk 2014; Schmitz 2014).
This information is summarised in Characteristics of included studies.
Excluded studies
We excluded 13 studies (for details, seeCharacteristics of excluded studies).
Risk of bias in included studies
Risk of bias assessments are summarised in Figure 1 and Figure 2.
1.
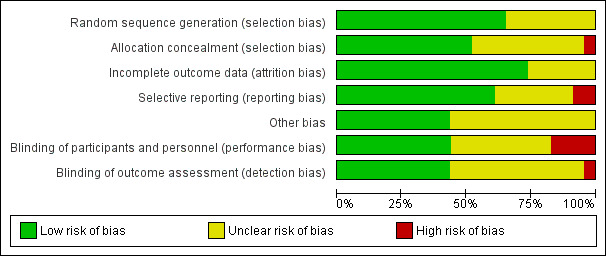
'Risk of bias' graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
2.
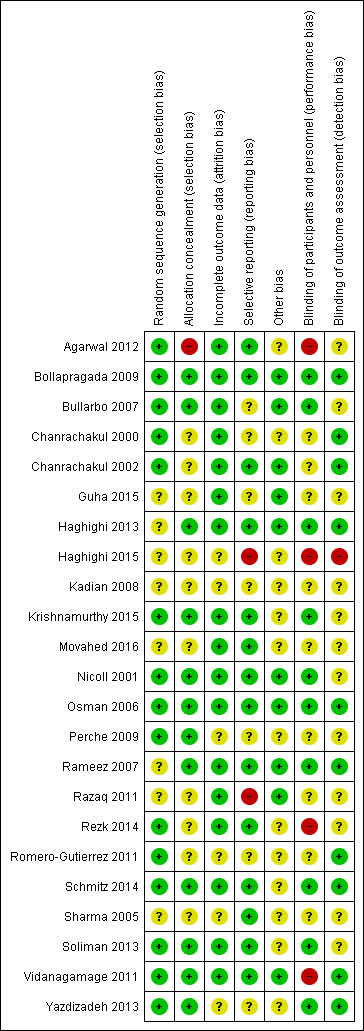
'Risk of bias' summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
Allocation
Randomisation sequence was computer‐generated in nine studies (Agarwal 2012; Bollapragada 2009; Chanrachakul 2000; Chanrachakul 2002; Krishnamurthy 2015; Osman 2006; Rezk 2014; Schmitz 2014; Soliman 2013). Random number tables were used in six studies (Bullarbo 2007; Nicoll 2001; Perche 2009; Romero‐Gutierrez 2011; Vidanagamage 2011; Yazdizadeh 2013) and sequence generation method was 'unclear' in eight studies (Guha 2015; Haghighi 2013; Haghighi 2015; Kadian 2008; Movahed 2016; Rameez 2007; Razaq 2011; Sharma 2005). One study stated that randomisation occurred in blocks, but no mention of the method of sequence generation was made (Rameez 2007).
Allocation concealment was performed by using centrally‐dispensed (pharmacy) packs of study medication including suitable dummies in one study (Bollapragada 2009). Sequentially‐numbered, opaque and sealed envelopes were used in eight studies (Bullarbo 2007; Haghighi 2013; Krishnamurthy 2015; Nicoll 2001; Osman 2006; Rameez 2007; Soliman 2013; Vidanagamage 2011). One study used sealed envelopes (Perche 2009), and another study used coded drug boxes (Yazdizadeh 2013). One study used a web‐based application to assign women and the allocation was reported as being unavailable to the research team (Schmitz 2014). Ten studies were unclear on how allocation was concealed (Chanrachakul 2000; Chanrachakul 2002; Guha 2015; Haghighi 2015; Kadian 2008; Movahed 2016; Razaq 2011; Rezk 2014; Romero‐Gutierrez 2011; Sharma 2005). One study used open allocation (Agarwal 2012).
Blinding
Blinding was achieved by using suitable dummies in 10 studies (Bollapragada 2009; Bullarbo 2007; Haghighi 2013; Krishnamurthy 2015; Nicoll 2001; Osman 2006; Rameez 2007; Schmitz 2014; Soliman 2013; Yazdizadeh 2013). No dummies were used in two studies, but it was stated that the outcome assessor was unaware of allocation in both (Chanrachakul 2000; Chanrachakul 2002). In six studies no details were given regarding blinding of any groups (Guha 2015; Kadian 2008; Movahed 2016; Perche 2009; Razaq 2011; Sharma 2005). Two studies were single blind study (Agarwal 2012; Rezk 2014). In one study, women were blinded but it is unclear if therapist was blinded as well (Romero‐Gutierrez 2011). In one study the therapist was aware of the intervention given (Vidanagamage 2011). One study was unblinded (Haghighi 2015).
Incomplete outcome data
There were no trials where there was evidence of significant levels of attrition bias, though six were assessed as unclear (Haghighi 2015; Kadian 2008; Perche 2009; Romero‐Gutierrez 2011; Sharma 2005; Yazdizadeh 2013).
Selective reporting
Two studies were assessed as having a high risk of reporting bias as neither study clearly specified which outcomes would be reported (Haghighi 2015; Razaq 2011).
Other potential sources of bias
No other bias was identified in 10 of the studies (Bollapragada 2009; Bullarbo 2007; Chanrachakul 2002; Guha 2015; Haghighi 2013; Nicoll 2001; Osman 2006; Rameez 2007; Razaq 2011; Vidanagamage 2011), with the remaining studies assessed as unclear risk.
Effects of interventions
See: Table 1
Comparison 1: Nitric oxide versus placebo (10 studies, 2799 women)
Primary outcomes
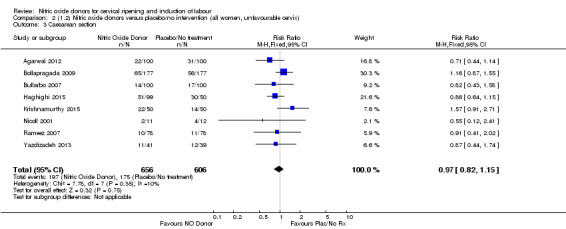
There was no evidence of a difference for any of the primary outcomes when NO donors were compared to placebo for induction of labour: vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours (risk ratio (RR 0.97, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.83 to 1.15; one trial, 238 women, low‐quality evidence, Analysis 1.1); uterine hyperstimulation with fetal heart rate (FHR) changes (RR 0.09, 95% CI 0.01 to 1.62; two trials, 300 women, low‐quality evidence,Analysis 1.2); caesarean section (RR 0.99, 95% CI 0.88 to 1.11; nine trials, 2624 women, moderate‐quality evidenceAnalysis 1.3); or serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death (average RR 1.61, 95% CI 0.08 to 33.26; I² = 48%, two trials, 1712 women, low‐quality evidence,Analysis 1.4). There were no instances of serious maternal morbidity or death in the one study reporting this outcome (Schmitz 2014).
1.1. Analysis.
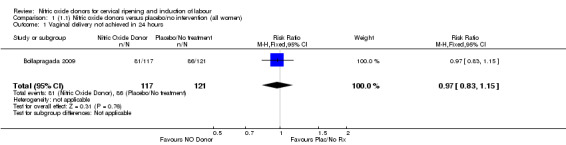
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
1.2. Analysis.
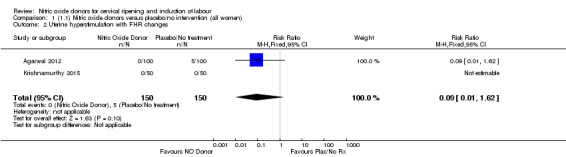
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
1.3. Analysis.
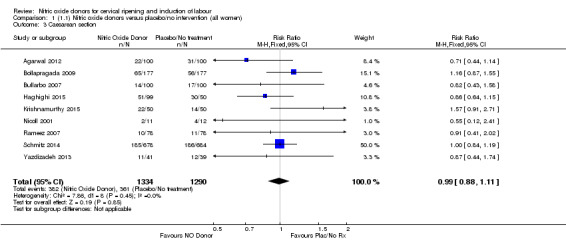
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
1.4. Analysis.
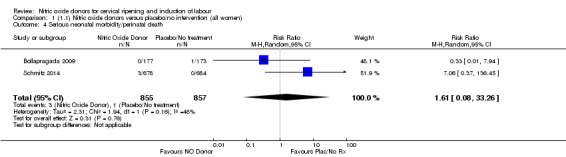
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
Clinical subgroups
There was no evidence of a difference for any of the primary outcomes in any of the clinical subgroups examined:
unfavourable cervix (Analysis 2.1; Analysis 2.2; Analysis 2.3; Analysis 2.4);
intact membranes and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 3.1; Analysis 3.2; Analysis 3.3; Analysis 3.4);
all primiparae (Analysis 4.1; Analysis 4.3; Analysis 4.4);
all primiparae and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 5.1; Analysis 5.3; Analysis 5.4);
all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix (Analysis 6.1; Analysis 6.2; Analysis 6.3).
2.1. Analysis.
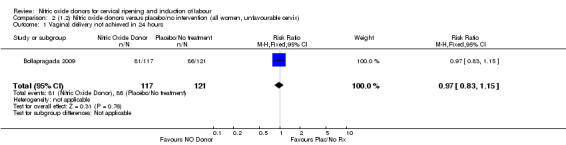
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
2.2. Analysis.
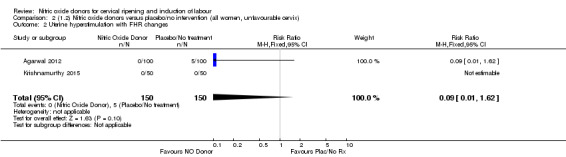
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
2.3. Analysis.
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
2.4. Analysis.
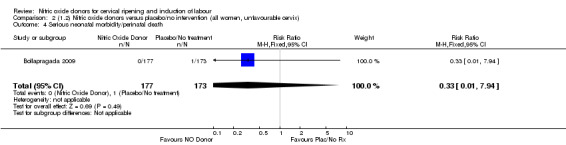
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
3.1. Analysis.
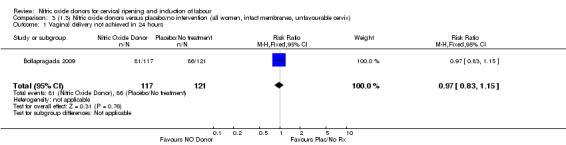
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
3.2. Analysis.
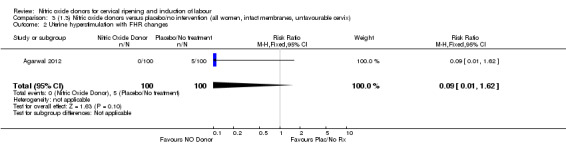
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
3.3. Analysis.
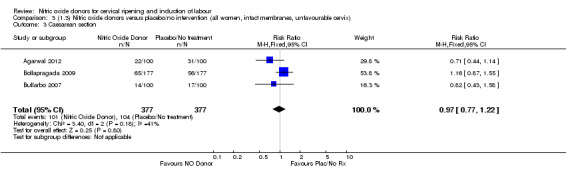
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
3.4. Analysis.
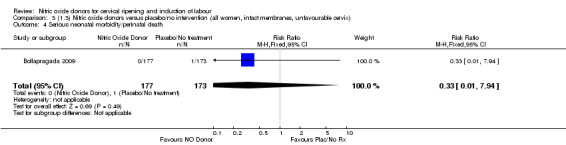
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
4.1. Analysis.
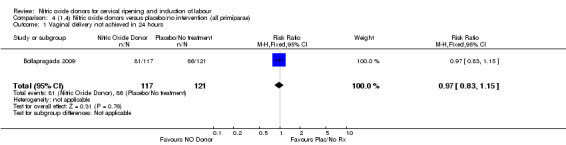
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
4.3. Analysis.
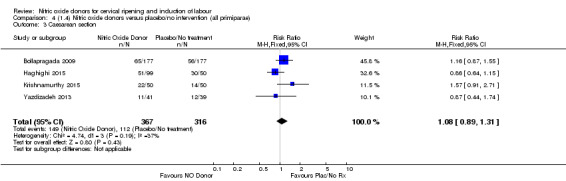
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
4.4. Analysis.
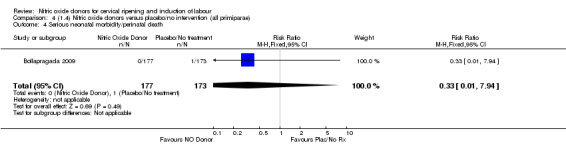
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
5.1. Analysis.
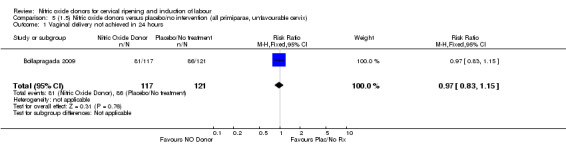
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
5.3. Analysis.
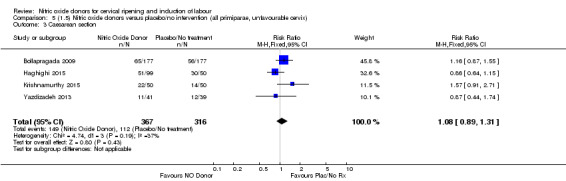
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
5.4. Analysis.
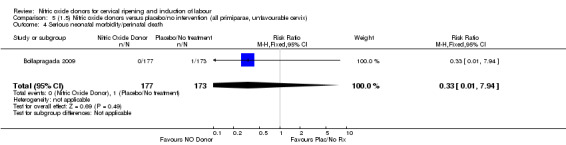
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
6.1. Analysis.
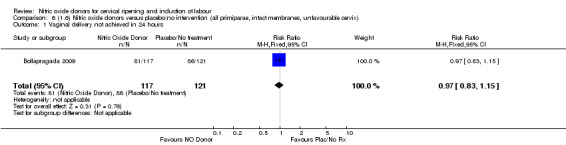
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
6.2. Analysis.
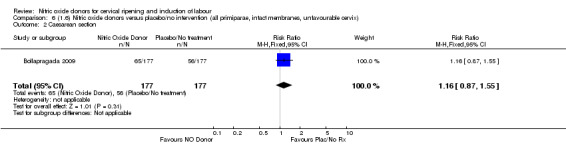
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
6.3. Analysis.
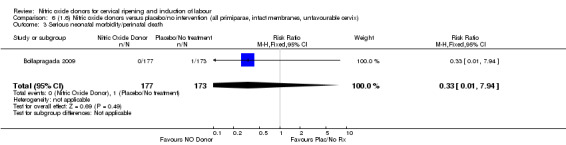
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
Secondary outcomes
There was a reduction in the proportion of women with an unfavourable cervix at 12 to 24 hours in those women who were treated with NO donors compared to placebo ( average RR 0.78, 95% CI 0.67 to 0.90; Tau² = 0.02; I² =64%, four trials, 762 women, Analysis 1.6). A difference was also observed in each of the subgroups: in four studies (Agarwal 2012; Bollapragada 2009; Krishnamurthy 2015; Vidanagamage 2011), there was a reduction in the proportion of women with an unfavourable cervix at 12 to 24 hours in those women who were treated with NO donors compared to placebo in comparison to placebo (RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.73 to 0.87; I² = 63%, four trials, 659 women, Analysis 1.6.1); additionally, there was evidence of a similar reduction in the proportion of women with an unfavourable cervix when treated with a slow release formulation in one study (Vidanagamage 2011) (RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.49 to 0.82, one trial, 103 women, Analysis 1.6.2). No evidence of a difference was observed between subgroups (Test for subgroup differences: Chi² = 1.69, df = 1 (P = 0.10), I² = 62.8%).
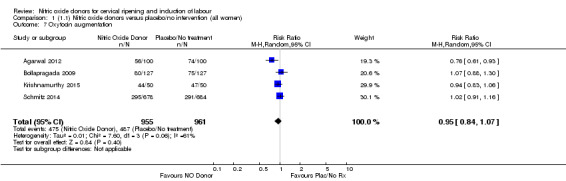
There were no differences observed between groups in rates of oxytocin augmentation (RR 0.95, 95% CI 0.84 to 1.07; four trials, 1916 women, I² = 61% Analysis 1.7) and there was evidence of substantial heterogeneity. No woman in the NO donor group experienced uterine hyperstimulation without FHR rate changes (RR 0.05, 95% CI 0.00 to 0.80; one trial, 200 women, Analysis 1.8).
1.7. Analysis.
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 7 Oxytocin augmentation.
1.8. Analysis.
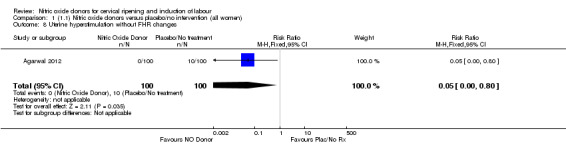
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 8 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
Induction of labour with NO when compared to placebo was associated with an increase in all maternal side effects (RR 2.82, 95% CI 2.49 to 3.20; one trial, 1362 women; Analysis 1.15), nausea (average RR 2.44, 95% CI 1.47 to 4.05; three trials, 1782 women; I² = 55%), headache (average RR 6.59, 95% CI 3.97 to 10.95; six trials, 2085 women, Analysis 1.17), and vomiting (RR 2.42, 95% CI 1.54 to 3.81; one trial, 1362 women, Analysis 1.18). There was significant heterogeneity associated with the result for maternal headache, despite using a random‐effects model (Heterogeneity: Tau² = 0.23; Chi² = 19.91, df = 5 (P = 0.001); I² = 75%). However, this was due to the results from one study (Bollapragada 2009) and the heterogeneity disappears if the results from this trial are excluded, resulting in a greater effect of NO. Despite close scrutiny of this trial, it was not possible to understand why the result for this trial would be so different to the others in this comparison.
1.15. Analysis.
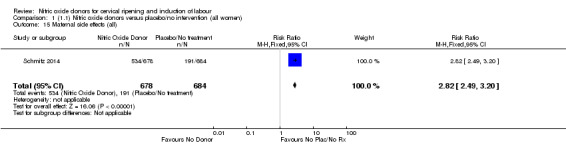
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 15 Maternal side effects (all).
1.17. Analysis.
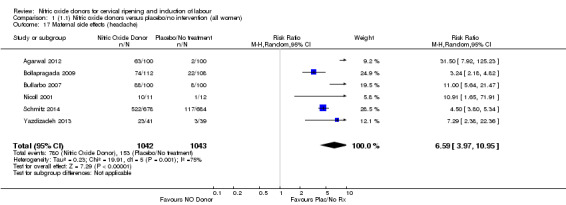
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 17 Maternal side effects (headache).
1.18. Analysis.
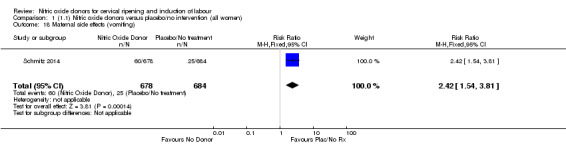
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 18 Maternal side effects (vomiting).
When compared to placebo, the use of NO (in a standard release formulation) for induction of labour resulted in the use of less additional induction agents (average RR 0.73, 95% CI 0.58 to 0.92; five studies, 2077 women, Analysis 1.22). However, there was evidence of significant heterogeneity in this result (Heterogeneity: Tau² = 0.06; Chi² = 33.79, df = 4 (P < 0.00001, I² = 88%). This is generated by one study (Rameez 2007). This study again is comparable to others in this group and hence it is unclear why this difference is seen. The same benefit was seen when a slow release formulation was used in one additional study (Vidanagamage 2011), compared to placebo.
No differences were observed for any of the other secondary outcomes analysed (Analysis 1.7; Analysis 1.9; Analysis 1.10; Analysis 1.11; Analysis 1.12; Analysis 1.13; Analysis 1.14; Analysis 1.19; Analysis 1.20; Analysis 1.21; Analysis 1.22).
1.9. Analysis.
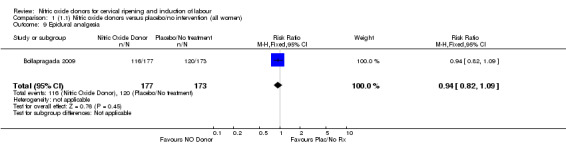
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 9 Epidural analgesia.
1.10. Analysis.
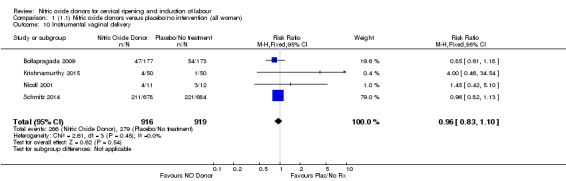
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 10 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
1.11. Analysis.
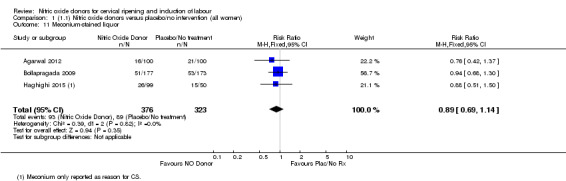
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 11 Meconium‐stained liquor.
1.12. Analysis.
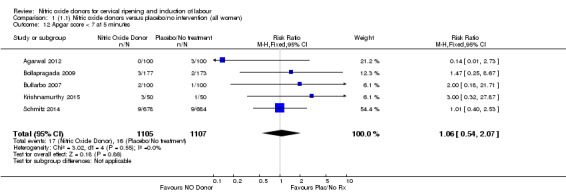
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 12 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
1.13. Analysis.
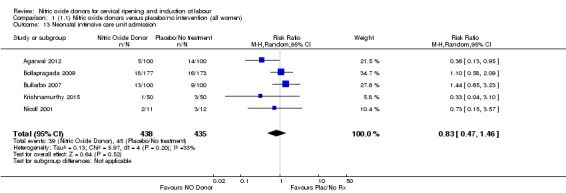
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 13 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
1.14. Analysis.
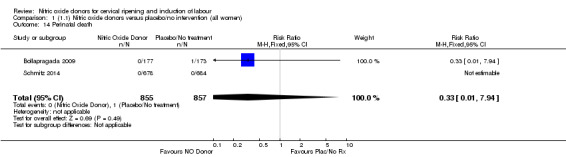
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 14 Perinatal death.
1.19. Analysis.
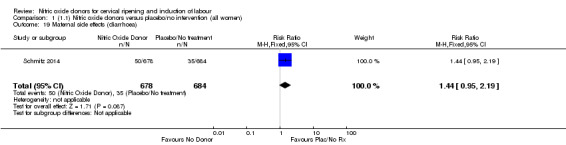
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 19 Maternal side effects (diarrhoea).
1.20. Analysis.
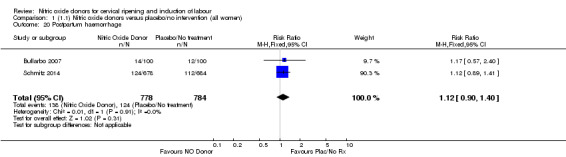
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 20 Postpartum haemorrhage.
1.21. Analysis.
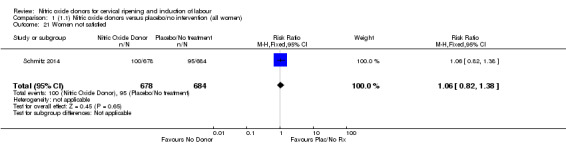
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 21 Women not satisfied.
None of the following secondary outcomes were reported and analysed: uterine rupture; neonatal encephalopathy; disability in childhood; other maternal side effects; serious maternal complications; maternal death; caregiver not satisfied; neonatal infection; neonatal antibiotics; chorioamnionitis; endometritis; maternal antibiotics; initiation of cervical ripening to delivery interval (in days).
Clinical subgroups
The results for the majority of secondary outcomes were the same in the clinical subgroups analysed. The only difference related to the maternal side effect of nausea, where no differences were observed between groups for the following clinical subgroups:
intact membranes and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 3.15);
all primiparae (Analysis 4.13);
all primiparae and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 5.13);
all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix (Analysis 6.12).
3.15. Analysis.
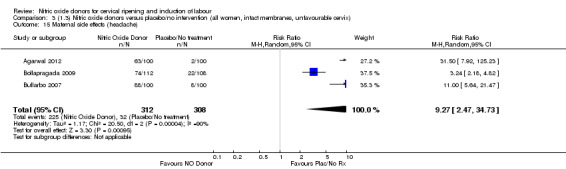
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 15 Maternal side effects (headache).
4.13. Analysis.
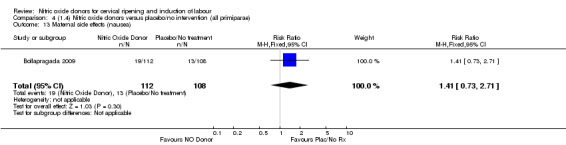
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 13 Maternal side effects (nausea).
5.13. Analysis.
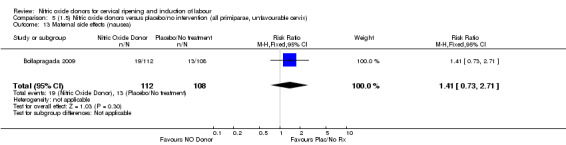
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 13 Maternal side effects (nausea).
6.12. Analysis.
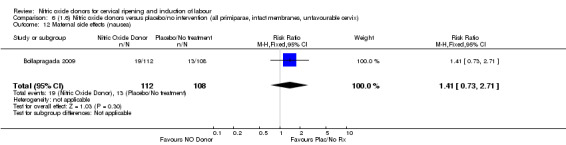
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Maternal side effects (nausea).
Comparison 2: Nitric oxide versus vaginal prostaglandins (three studies, 578 women)
Primary outcomes
There was no evidence of any difference between the effects of NO and vaginal prostaglandins for the two of the primary outcomes analysed:
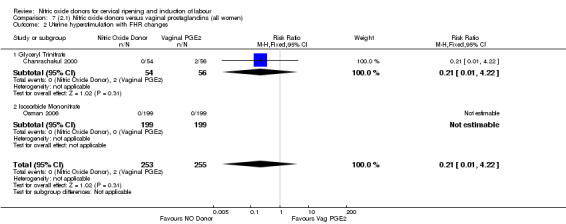
uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes (RR 0.21, 95% CI 0.01 to 4.22; two trials, 508 women, (Analysis 7.2);
caesarean section (RR 0.97, 95% CI 0.78 to 1.21; three trials, 571 women, Analysis 7.4).
7.2. Analysis.
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
7.4. Analysis.
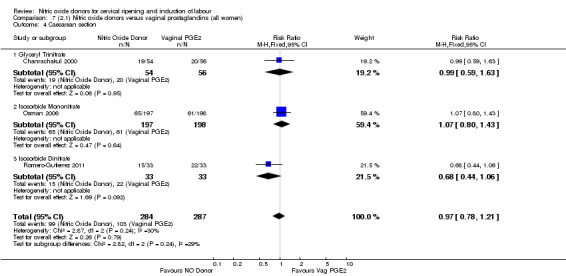
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 4 Caesarean section.
There were fewer women in the NO donor group who did not achieve a vaginal delivery within 24 hours in comparison to vaginal prostaglandins (Analysis 7.1). This result should be interpreted with caution as the information was extracted from an abstract only and a full report of the study is awaited.
7.1. Analysis.
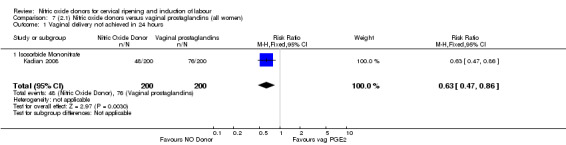
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
Serious neonatal morbidity and serious maternal morbidity were not reported in any of the trials for all women.
There was no evidence of a difference for two of the primary outcomes (uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes and caesarean section) in any of the other clinical subgroups examined:
unfavourable cervix (Analysis 8.1; Analysis 8.2);
intact membranes and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 9.1; Analysis 9.2);
primiparae (Analysis 10.2; Analysis 10.3);
all primiparae and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 11.1; Analysis 11.2);
all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix (Analysis 12.1; Analysis 12.2).
8.1. Analysis.
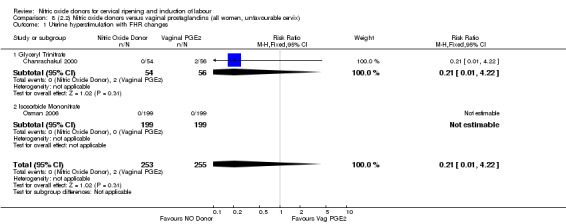
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
8.2. Analysis.
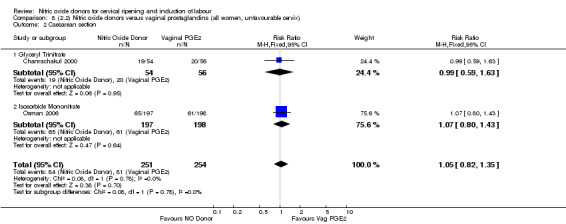
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
9.1. Analysis.
Comparison 9 (2.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
9.2. Analysis.
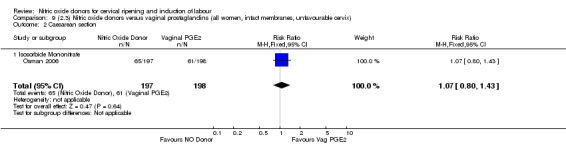
Comparison 9 (2.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
10.2. Analysis.
Comparison 10 (2.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
10.3. Analysis.
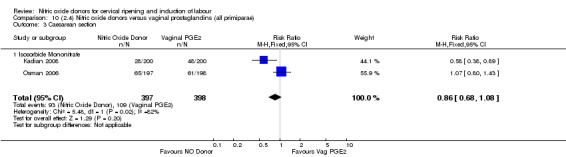
Comparison 10 (2.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
11.1. Analysis.
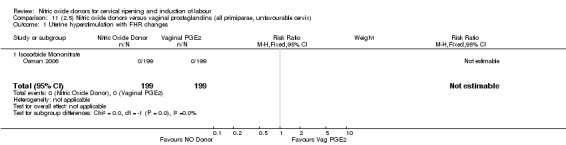
Comparison 11 (2.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
11.2. Analysis.
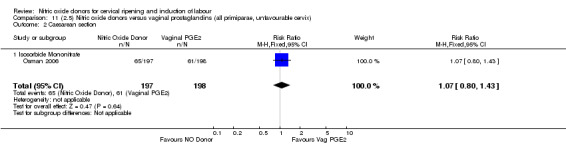
Comparison 11 (2.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
12.1. Analysis.
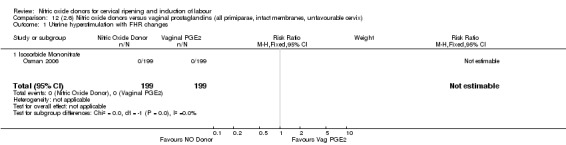
Comparison 12 (2.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
12.2. Analysis.
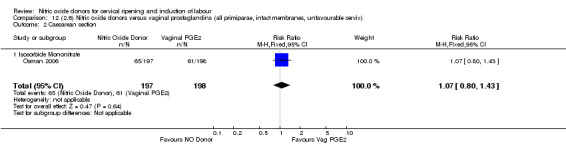
Comparison 12 (2.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
Subgroup analysis
There was no evidence of any difference between the different types of NO donor used (glyceral trinitrate; isosorbide mononitrate; isosorbide dinitrate) for any of the primary outcomes analysed.
Secondary outcomes
There were no cases of uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes reported in the NO donor group compared to five cases in the vaginal prostaglandin group (RR 0.09, 95% CI 0.01 to 1.66; one trial, 110 women, Analysis 7.3). There were no differences observed between groups for any of the following outcomes:
7.3. Analysis.
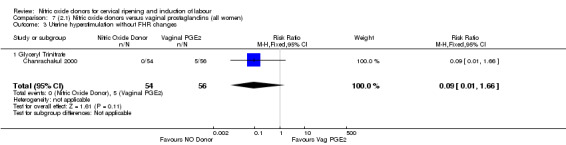
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 3 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
epidural analgesia (RR 1.04, 95% CI 0.91 to 1.18; one trial, 394 women, Analysis 7.8);
instrumental vaginal delivery (RR 1.02, 95% CI 0.76 to 1.37; one trial, 395 women, Analysis 7.5);
meconium‐stained liquor (RR 0.86, 95% CI 0.32 to 2.28; one trial, 66 women, Analysis 7.6);
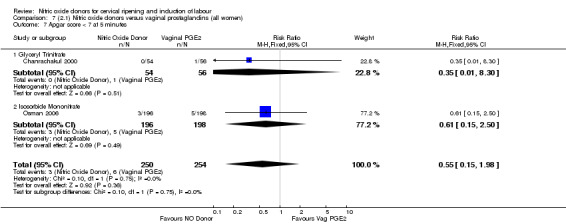
Apgar score less than seven at five minutes (RR 0.55, 95% CI 0.15 to 1.98; two trials, 504 women, Analysis 7.7);
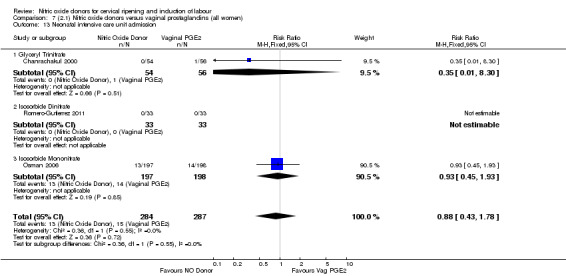
Neonatal intensive care unit admission (RR 0.88, 95% CI 0.43 to 1.78; three trials, 571 babies, Analysis 7.13);
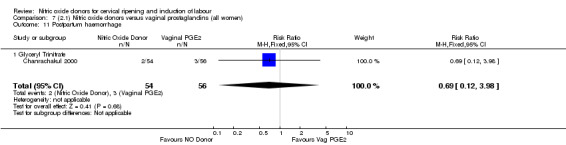
postpartum haemorrhage (RR 0.69, 95% CI 0.12 to 3.98; one trial, 110 women, Analysis 7.11);
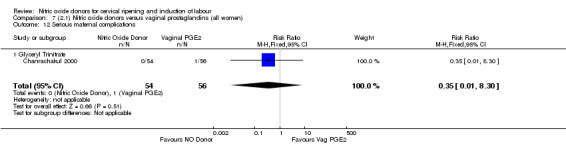
serious maternal complications (RR 0.35, 95% CI 0.01 to 8.30; one trial, 110 women, Analysis 7.12).
7.8. Analysis.
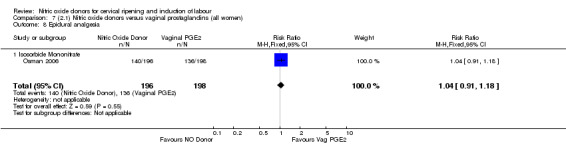
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 8 Epidural analgesia.
7.5. Analysis.
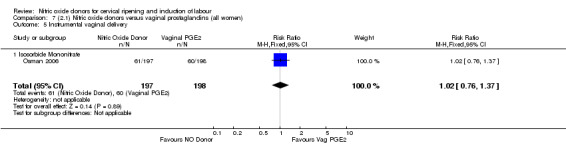
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
7.6. Analysis.
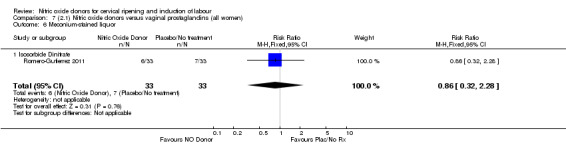
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 6 Meconium‐stained liquor.
7.7. Analysis.
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
7.13. Analysis.
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 13 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
7.11. Analysis.
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 11 Postpartum haemorrhage.
7.12. Analysis.
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 12 Serious maternal complications.
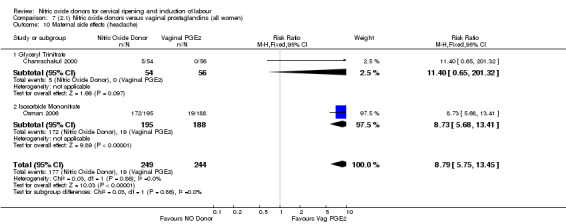
There was evidence of an increase in the rates of nausea (RR 1.79, 95% CI 1.10 to 2.93; one study, 385 women, Analysis 7.9) and an increase in the rates of headache (RR 8.79, 95% CI 5.75 to 13.45; two studies, 493 women, Analysis 7.10) when induction was undertaken using NO.
7.9. Analysis.
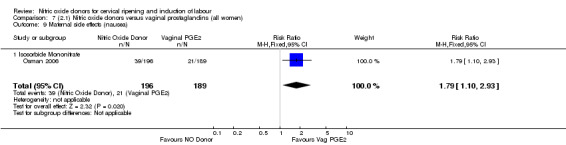
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (nausea).
7.10. Analysis.
Comparison 7 (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
None of the following secondary outcomes were reported and analysed: cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12 to 24 hours; uterine rupture; neonatal encephalopathy; perinatal death; disability in childhood; maternal death; woman not satisfied; caregiver not satisfied; neonatal infection; neonatal antibiotics; chorioamnionitis; endometritis; maternal antibiotics; additional induction agents required; initiation of cervical ripening to delivery interval (in days).
Clinical subgroups
The results for all of the secondary outcomes were the same in the clinical subgroups analysed:
unfavourable cervix (Analysis 8.3 to Analysis 8.11);
intact membranes and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 9.3 to Analysis 9.8);
primiparae (Analysis 10.4 to Analysis 10.9);
all primiparae and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 11.3 to Analysis 11.8);
all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix (Analysis 12.3 to Analysis 12.8).
8.3. Analysis.
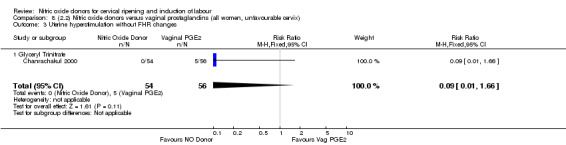
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
8.11. Analysis.
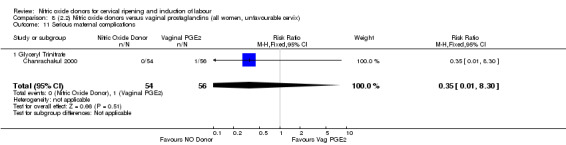
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Serious maternal complications.
9.3. Analysis.
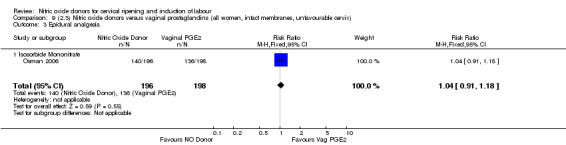
Comparison 9 (2.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Epidural analgesia.
9.8. Analysis.
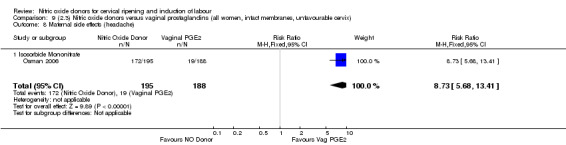
Comparison 9 (2.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Maternal side effects (headache).
10.4. Analysis.
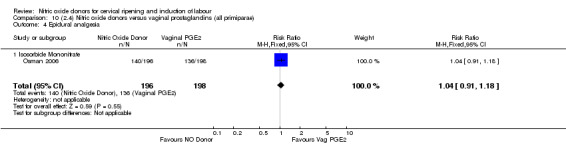
Comparison 10 (2.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 4 Epidural analgesia.
10.9. Analysis.
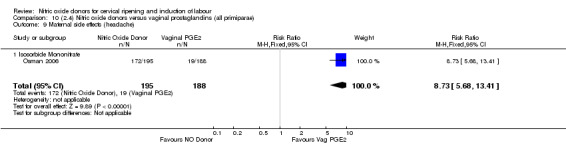
Comparison 10 (2.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (headache).
11.3. Analysis.
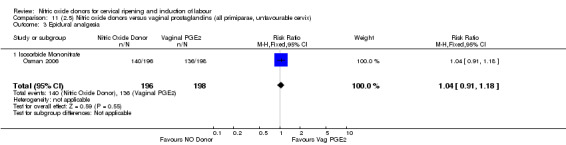
Comparison 11 (2.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Epidural analgesia.
11.8. Analysis.
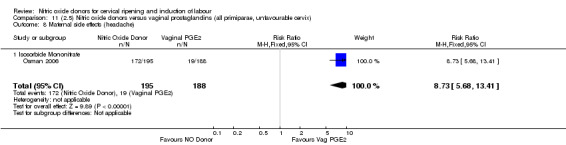
Comparison 11 (2.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Maternal side effects (headache).
12.3. Analysis.
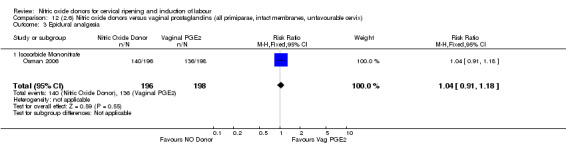
Comparison 12 (2.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Epidural analgesia.
12.8. Analysis.
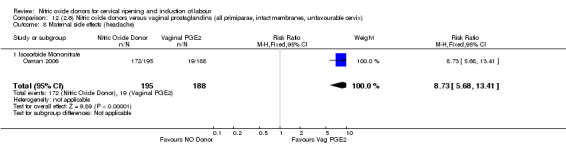
Comparison 12 (2.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Maternal side effects (headache).
Subgroup analysis
There was no evidence of any difference between the different types of NO donor used (glyceral trinitrate; isosorbide mononitrate; isosorbide dinitrate) for any of the secondary outcomes analysed.
Comparison 3: Nitric oxide versus intracervical prostaglandins (two studies, 442 women)
Primary outcomes
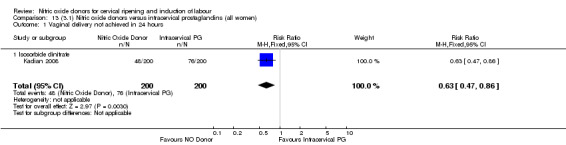
One study (Kadian 2008), reported a reduction in the number of women who had not achieved a vaginal delivery within 24 hours when induction was undertaken with NO donors in comparison to intracervical prostaglandins (RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.47 to 0.86; one trial, 400 women, Analysis 13.1). This result should be interpreted with caution as the information was extracted from an abstract only and a full report of the study is awaited. No differences were observed between groups for uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.01 to 7.74; one trial, 42 women, Analysis 13.2) or serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.01 to 7.74; one trial, 42 women, Analysis 13.4). Fewer women in the NO donor group underwent a caesarean section in comparison to women who received intracervical prostaglandins (RR 0.63, 95% CI 0.44 to 0.90; two trials, 442 women, Analysis 13.3). No study reported on the outcome serious maternal morbidity or death.
13.1. Analysis.
Comparison 13 (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
13.2. Analysis.
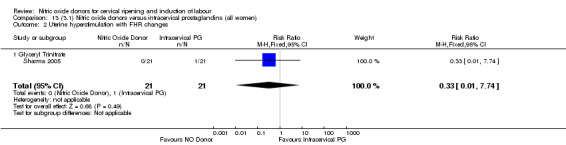
Comparison 13 (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
13.4. Analysis.
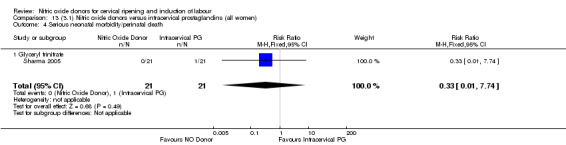
Comparison 13 (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
13.3. Analysis.
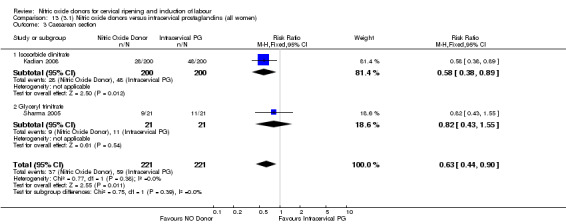
Comparison 13 (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
Clinical subgroups
The results for two of the primary outcomes, uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes and serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death, were the same in the clinical subgroups analysed:
unfavourable cervix (Analysis 14.2; Analysis 14.4);
intact membranes and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 15.2; Analysis 15.4);
primiparae (Analysis 16.1; Analysis 16.3);
all primiparae and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 17.1; Analysis 17.3);
all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix (Analysis 18.1; Analysis 18.3).
14.2. Analysis.
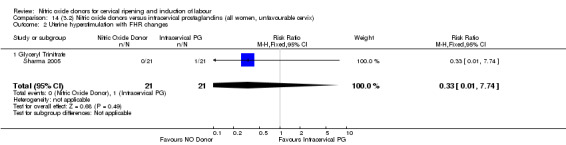
Comparison 14 (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
14.4. Analysis.
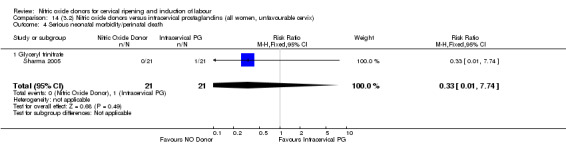
Comparison 14 (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
15.2. Analysis.
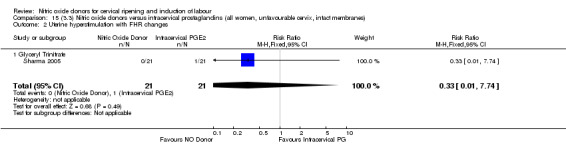
Comparison 15 (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
15.4. Analysis.
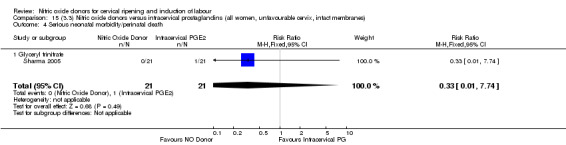
Comparison 15 (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
16.1. Analysis.
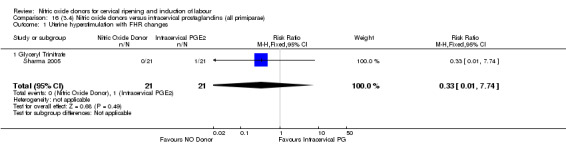
Comparison 16 (3.4) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
16.3. Analysis.
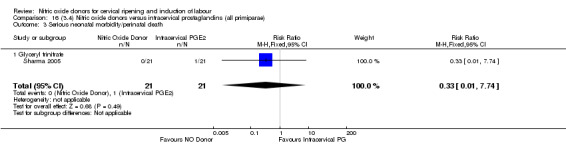
Comparison 16 (3.4) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
17.1. Analysis.
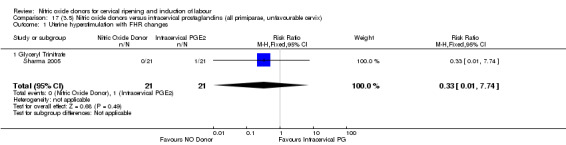
Comparison 17 (3.5) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
17.3. Analysis.
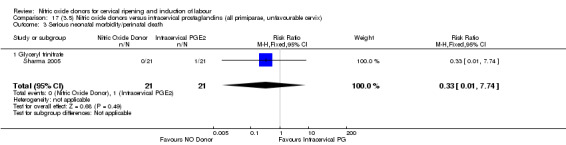
Comparison 17 (3.5) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
18.1. Analysis.
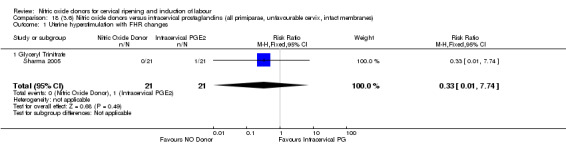
Comparison 18 (3.6) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
18.3. Analysis.
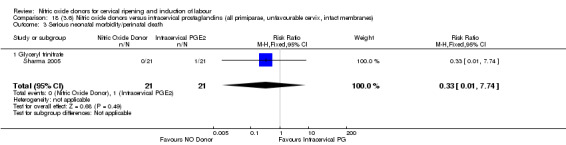
Comparison 18 (3.6) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
For caesarean section, there were no differences between groups according to the clinical subgroups, although only one study was included in any clinical subgroup:
unfavourable cervix (Analysis 14.3);
intact membranes and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 15.3);
primiparae (Analysis 16.2);
all primiparae and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 17.2);
all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix (Analysis 18.2).
14.3. Analysis.
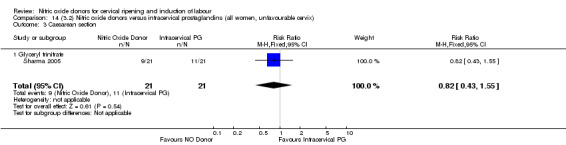
Comparison 14 (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
15.3. Analysis.
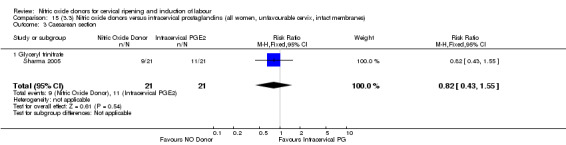
Comparison 15 (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
16.2. Analysis.
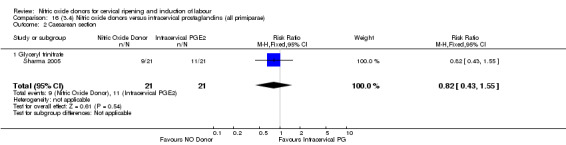
Comparison 16 (3.4) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
17.2. Analysis.
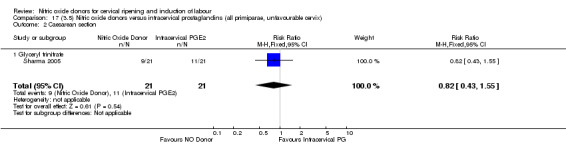
Comparison 17 (3.5) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
18.2. Analysis.
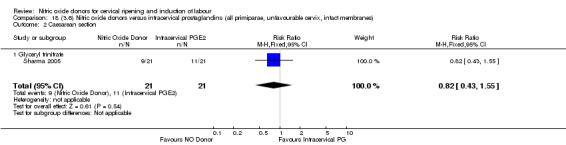
Comparison 18 (3.6) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
Subgroup analysis
There were too few studies to determine whether there was evidence of a difference between the different types of NO donor for caesarean section (Analysis 13.3). It was not possible to perform subgroup analysis for any other primary outcomes.
Secondary outcomes
There were no differences observed between groups for any of the following outcomes:
cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12 to 24 hours (RR 1.29, 95% CI 0.59 to 2.81; one trial, 42 women, Analysis 13.5);
oxytocin augmentation (RR 0.89, 95% CI 0.43 to 1.85; one trial, 42 women, Analysis 13.6);
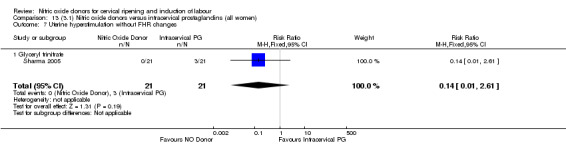
uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes (RR 0.14, 95% CI 0.01 to 2.61; one trial, 42 women, Analysis 13.7);
instrumental vaginal delivery (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.07 to 14.95; one trial, 42 women, Analysis 13.8);
perinatal death (RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.01 to 7.74)(RR 0.33, 95% CI 0.01 to 7.74; one trial, 42 women, Analysis 13.9).
13.5. Analysis.
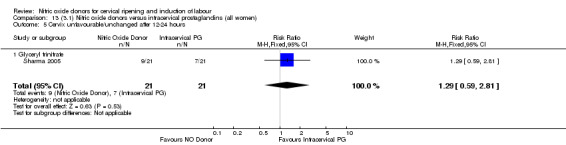
Comparison 13 (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
13.6. Analysis.
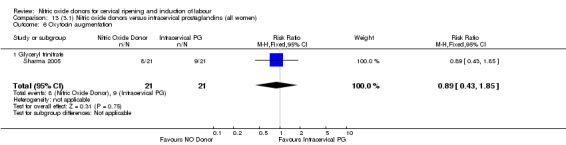
Comparison 13 (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 6 Oxytocin augmentation.
13.7. Analysis.
Comparison 13 (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
13.8. Analysis.
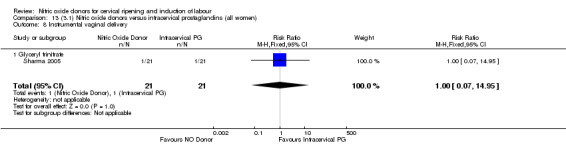
Comparison 13 (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 8 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
13.9. Analysis.
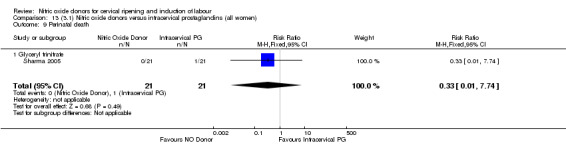
Comparison 13 (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 9 Perinatal death.
The only difference observed related to maternal side effects of headache. Nitric oxide when compared to intracervical prostaglandins resulted in an increase in maternal headache (RR 10.00, 95% CI 1.40 to 71.32; one study, 42 women; Analysis 13.10).
13.10. Analysis.
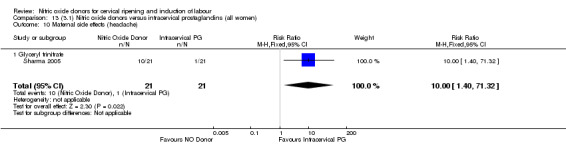
Comparison 13 (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
None of the following secondary outcomes were reported and analysed: uterine rupture; epidural analgesia; meconium‐stained liquor; Apgar score less than seven at five minutes; neonatal intensive care unit admission; neonatal encephalopathy; disability in childhood; postpartum haemorrhage; serious maternal complications; maternal death; woman not satisfied; caregiver not satisfied; neonatal infection; neonatal antibiotics; chorioamnionitis; endometritis; maternal antibiotics; additional induction agents required; initiation of cervical ripening to delivery interval (in days).
Clinical subgroups
The results for all secondary outcomes did not change when analysed in clinical subgroups:
unfavourable cervix (Analysis 14.5; Analysis 14.6; Analysis 14.7; Analysis 14.8; Analysis 14.9; Analysis 14.10);
intact membranes and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 15.5; Analysis 15.6; Analysis 15.7; Analysis 15.8; Analysis 15.9; Analysis 15.10);
primiparae (Analysis 16.4; Analysis 16.5; Analysis 16.6; Analysis 16.7; Analysis 16.8; Analysis 16.9);
all primiparae and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 17.4; Analysis 17.5; Analysis 17.6; Analysis 17.7; Analysis 17.8; Analysis 17.9);
all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix (Analysis 18.4; Analysis 18.5; Analysis 18.6; Analysis 18.7; Analysis 18.8; Analysis 18.9).
14.5. Analysis.
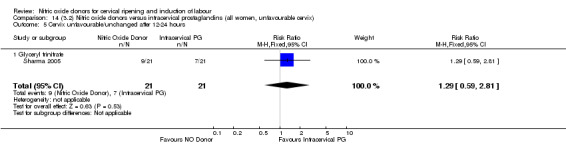
Comparison 14 (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
14.6. Analysis.
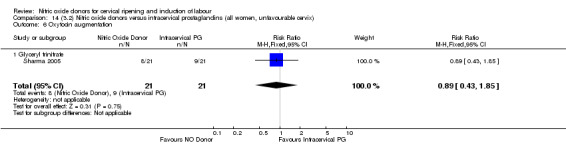
Comparison 14 (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Oxytocin augmentation.
14.7. Analysis.
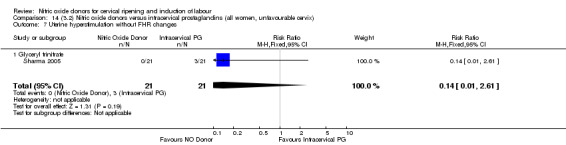
Comparison 14 (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
14.8. Analysis.
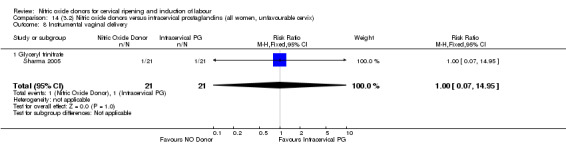
Comparison 14 (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
14.9. Analysis.
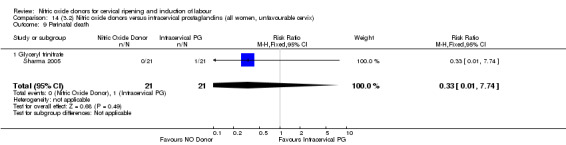
Comparison 14 (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Perinatal death.
14.10. Analysis.
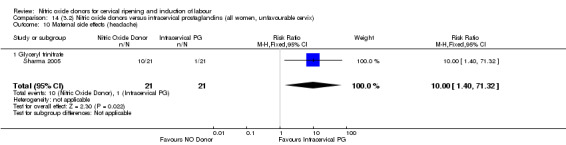
Comparison 14 (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
15.5. Analysis.
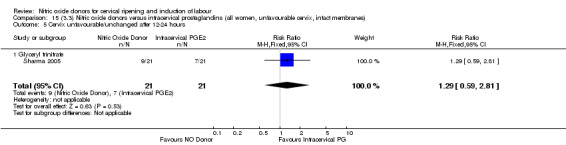
Comparison 15 (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
15.6. Analysis.
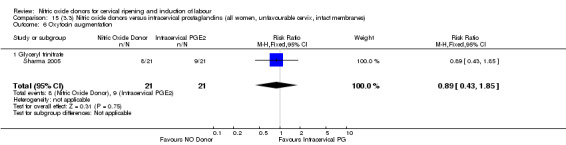
Comparison 15 (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 6 Oxytocin augmentation.
15.7. Analysis.
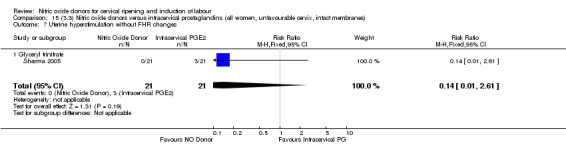
Comparison 15 (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
15.8. Analysis.
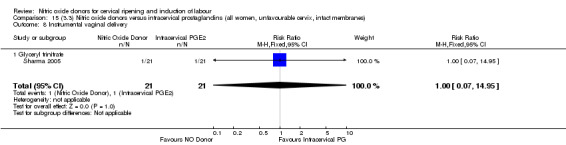
Comparison 15 (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 8 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
15.9. Analysis.
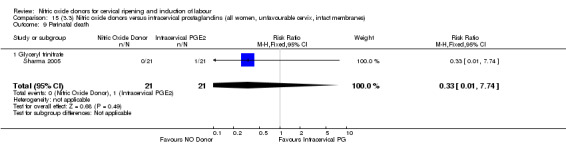
Comparison 15 (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 9 Perinatal death.
15.10. Analysis.
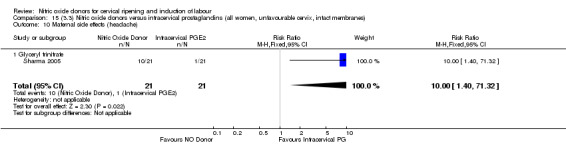
Comparison 15 (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
16.4. Analysis.
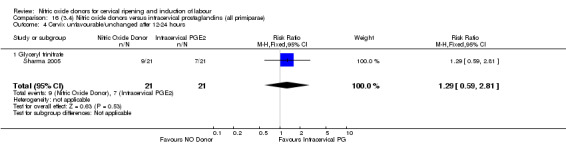
Comparison 16 (3.4) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
16.5. Analysis.
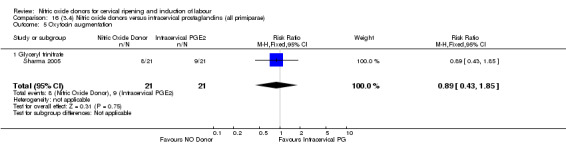
Comparison 16 (3.4) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 5 Oxytocin augmentation.
16.6. Analysis.
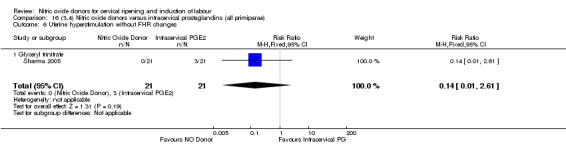
Comparison 16 (3.4) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 6 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
16.7. Analysis.
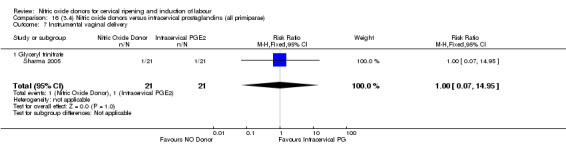
Comparison 16 (3.4) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
16.8. Analysis.
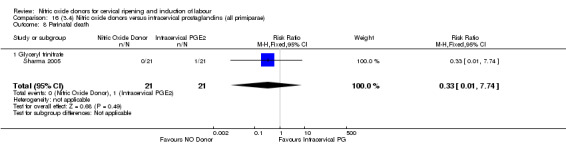
Comparison 16 (3.4) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 8 Perinatal death.
16.9. Analysis.
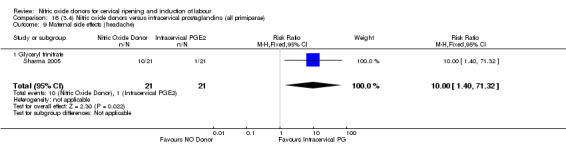
Comparison 16 (3.4) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (headache).
17.4. Analysis.
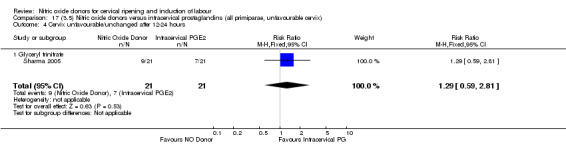
Comparison 17 (3.5) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
17.5. Analysis.
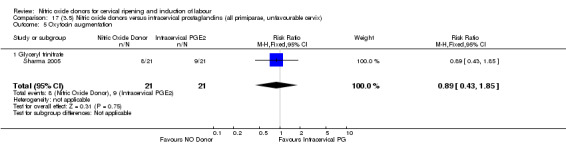
Comparison 17 (3.5) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Oxytocin augmentation.
17.6. Analysis.
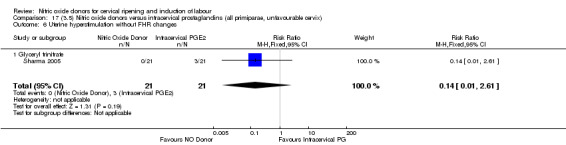
Comparison 17 (3.5) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
17.7. Analysis.
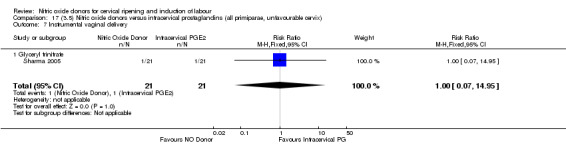
Comparison 17 (3.5) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
17.8. Analysis.
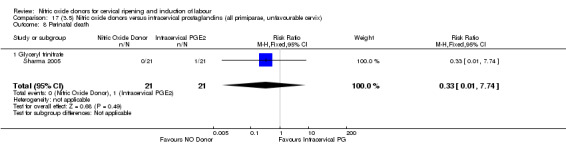
Comparison 17 (3.5) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Perinatal death.
17.9. Analysis.
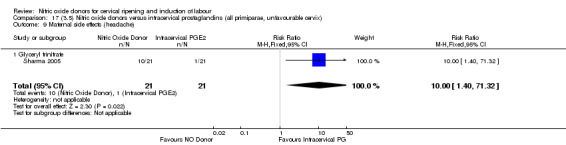
Comparison 17 (3.5) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (headache).
18.4. Analysis.
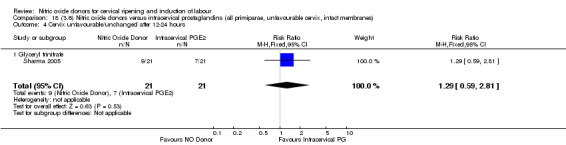
Comparison 18 (3.6) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
18.5. Analysis.
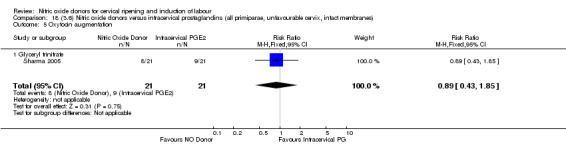
Comparison 18 (3.6) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 5 Oxytocin augmentation.
18.6. Analysis.
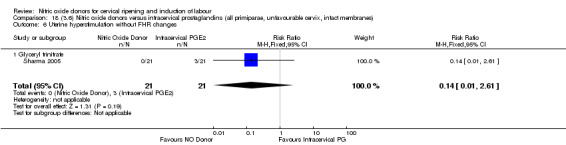
Comparison 18 (3.6) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 6 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
18.7. Analysis.
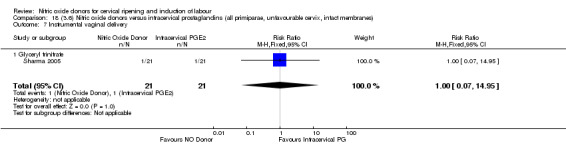
Comparison 18 (3.6) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
18.8. Analysis.
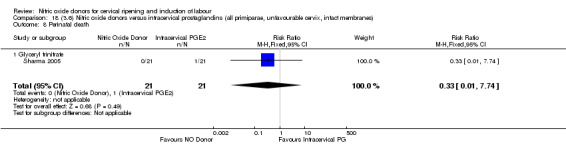
Comparison 18 (3.6) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 8 Perinatal death.
18.9. Analysis.
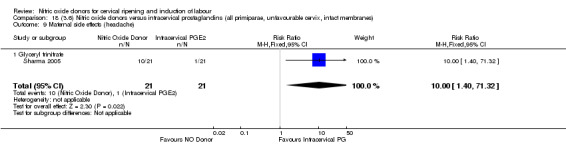
Comparison 18 (3.6) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (headache).
Subgroup analysis
There were not enough data to carry out planned subgroup analysis.
Comparison 4: Nitric oxide versus vaginal misoprostol (seven studies, 917 women)
Primary outcomes
There was a reduction in the rate of uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes when induction was conducted with NO compared with vaginal misoprostol (RR 0.07, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.37; three trials, 281 women, Analysis 19.2). There were no differences in caesarean section rates (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.82 to 1.21; 6 studies; 761 women Analysis 19.3), and no cases of serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death were reported (Analysis 19.4). The primary outcomes vaginal delivery not achieved within 24 hours and serious maternal morbidity or death were not reported in any of the studies.
19.2. Analysis.
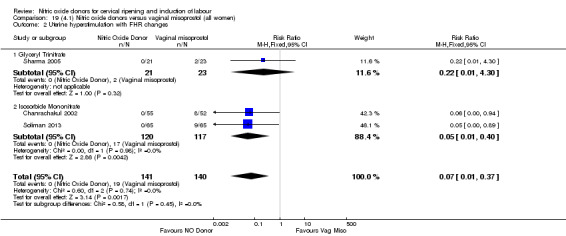
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
19.3. Analysis.
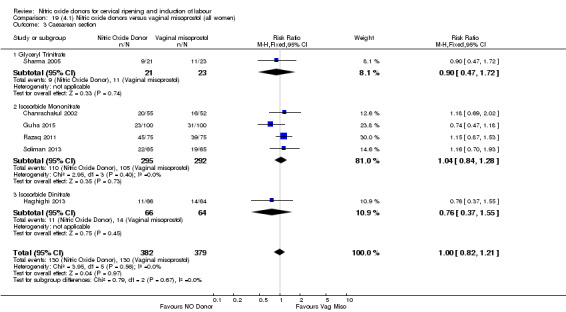
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
19.4. Analysis.
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
Clinical subgroups
Results were largely similar across clinical subgroups:
unfavourable cervix (Analysis 20.1; Analysis 20.2; Analysis 20.3);
intact membranes and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 21.1; Analysis 21.2; Analysis 21.3);
primiparae (Analysis 22.2; Analysis 22.3; Analysis 22.4);
all primiparae and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 23.1; Analysis 23.2; Analysis 23.3);
all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix (Analysis 24.1; Analysis 24.2; Analysis 24.3).
20.1. Analysis.
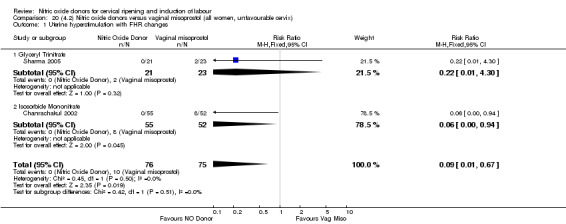
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
20.2. Analysis.
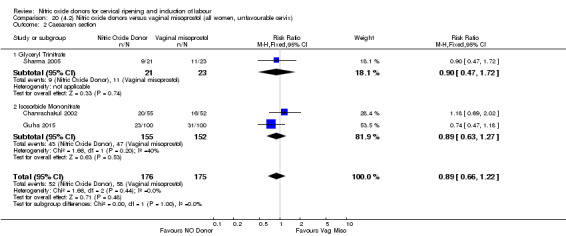
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
20.3. Analysis.
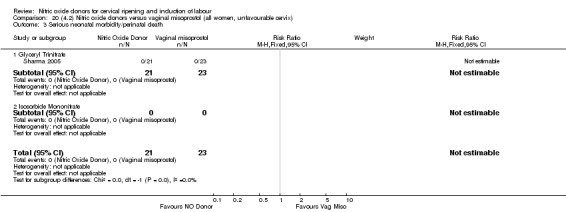
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
21.1. Analysis.
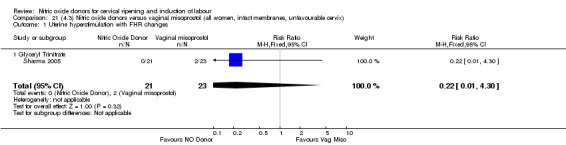
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
21.2. Analysis.
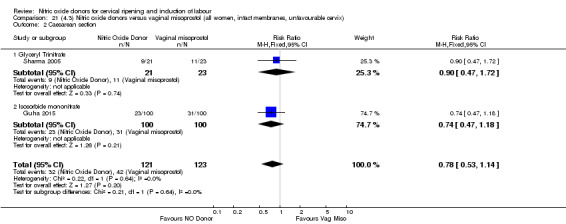
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
21.3. Analysis.
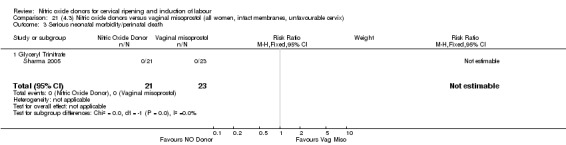
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
22.2. Analysis.
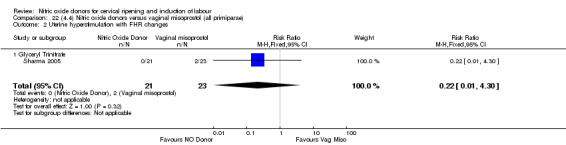
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
22.3. Analysis.
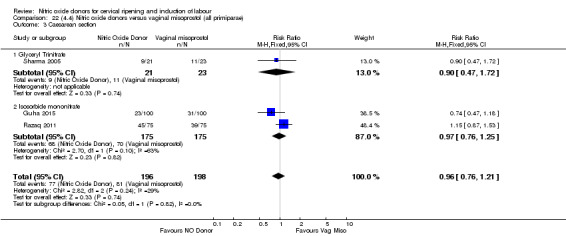
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 3 Caesarean section.
22.4. Analysis.
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
23.1. Analysis.
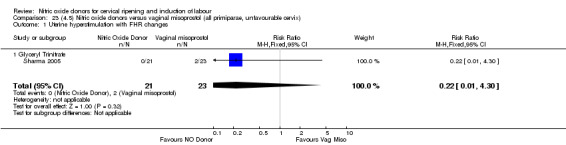
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
23.2. Analysis.
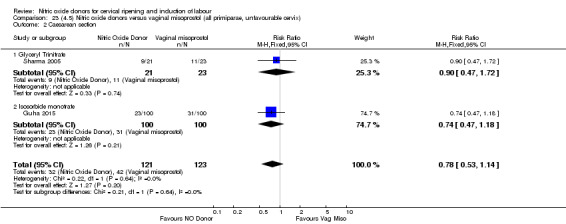
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
23.3. Analysis.
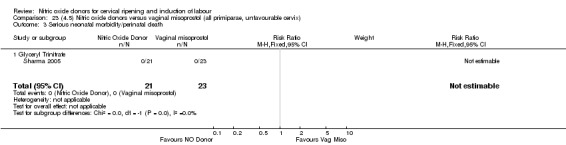
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
24.1. Analysis.
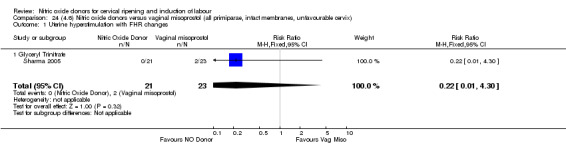
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
24.2. Analysis.
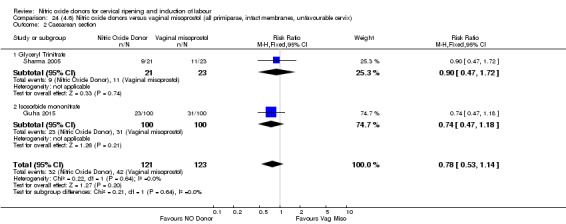
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Caesarean section.
24.3. Analysis.
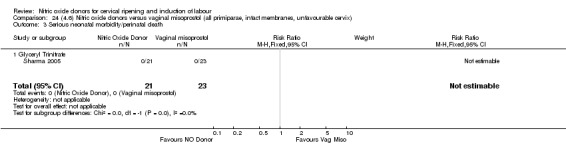
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death.
Subgroup analysis
There was no evidence of any difference between the different types of NO donor used (glyceral trinitrate; isosorbide mononitrate; isosorbide dinitrate) for any of the primary outcomes analysed.
Secondary outcomes
There was an increase in cervix unchanged/unfavourable when induction with NO was compared with vaginal misoprostol (RR 3.43, 95% CI 2.07 to 5.66; two trials, 151 women, Analysis 19.5).
19.5. Analysis.
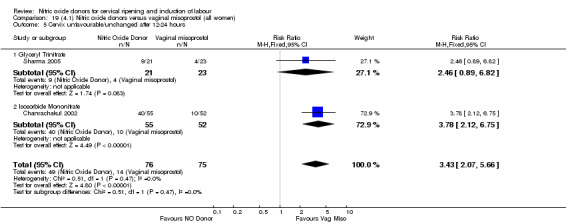
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
There was an increase in the need for oxytocin augmentation with NO induction compared with vaginal misoprostol (RR 2.67, 95% CI 1.31 to 5.45; seven trials, 767 women, Analysis 19.6). However, there was evidence of significant heterogeneity between the studies despite the use of a random‐effects model (Heterogeneity: Tau² = 0.84; Chi² = 108.82, df = 6 (P < .00001): I² = 94%). Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR was lower in the NO group in comparison to the vaginal misoprostol group (RR 0.06, 95% CI 0.01 to 0.32; three trials, 367 women, Analysis 19.7), as was meconium‐stained liquor (RR 0.29, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.65; two trials, 260 women, Analysis 19.10), Apgar score less than seven at five minutes (RR 0.16, 95% CI 0.07 to 0.38; six trials, 777 women, Analysis 19.11) and analgesia requirements (RR 0.26, 95% CI 0.13 to 0.49; one trial, 130 women, Analysis 19.17).
19.6. Analysis.
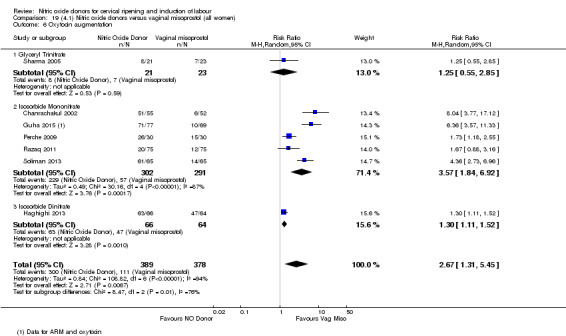
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 6 Oxytocin augmentation.
19.7. Analysis.
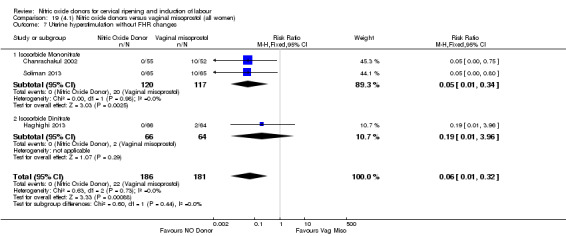
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
19.10. Analysis.
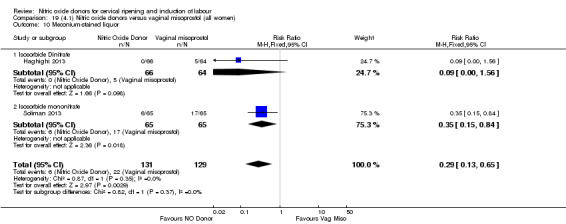
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 10 Meconium‐stained liquor.
19.11. Analysis.
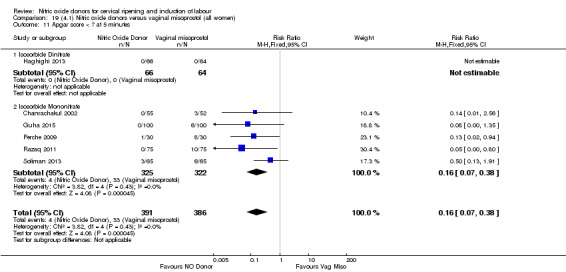
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 11 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
19.17. Analysis.
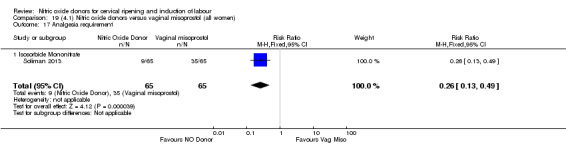
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 17 Analgesia requirement.
NO was associated with an increase in maternal headache when compared with vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour (RR 10.98, 95% CI 4.05 to 29.73; four trials, 341 women, Analysis 19.15).
19.15. Analysis.
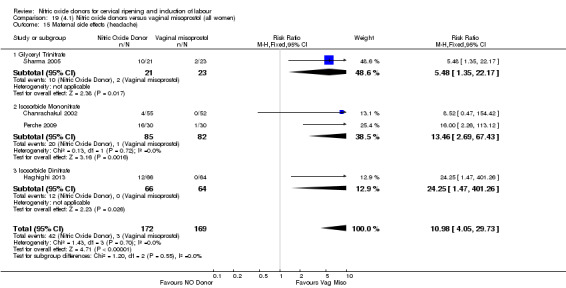
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 15 Maternal side effects (headache).
No differences between groups were observed for instrumental vaginal delivery (RR 1.10, 95% CI 0.07 to 16.43; one trial, 44 women, Analysis 19.9), neonatal intensive care unit admission (RR 0.19, 95% CI 0.09 to 0.43; four trials, 587 women, Analysis 19.12), or postpartum haemorrhage (RR 1.33, 95% CI 0.57 to 3.06; four trials, 587 women, Analysis 19.16). There were no cases of perinatal death reported in the two studies that reported it (Analysis 19.13).
19.9. Analysis.
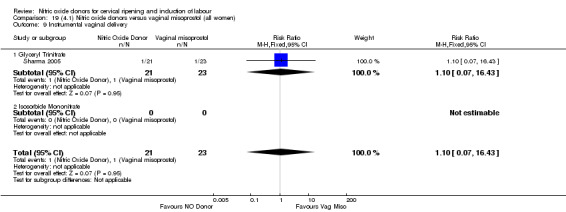
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 9 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
19.12. Analysis.
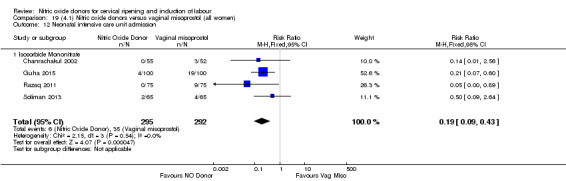
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 12 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
19.16. Analysis.
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 16 Postpartum haemorrhage.
19.13. Analysis.
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 13 Perinatal death.
None of the following secondary outcomes were reported and analysed: uterine rupture; epidural analgesia; neonatal encephalopathy; disability in childhood; serious maternal complications; maternal death; caregiver not satisfied; neonatal infection; neonatal antibiotics; chorioamnionitis; endometritis; maternal antibiotics; additional induction agents required. Initiation of cervical ripening to delivery interval was reported in three trials, Krishnamurthy 2015, Movahed 2016 and Razaq 2011, but data were presented in mean minutes (Krishnamurthy 2015; Movahed 2016) and hours (Razaq 2011), respectively rather than days as specified for this review and so has not been analysed. Women not satisfied were described in Guha 2015. Due to lack of clarity of how this outcome was reported (the percentages of women reporting satisfaction levels add up to over 100%), the data were not used in the analysis.
Clinical subgroups
Result were largely similar across clinical subgroups:
unfavourable cervix (Analysis 20.4; Analysis 20.5; Analysis 20.6; Analysis 20.7; Analysis 20.8; Analysis 20.9; Analysis 20.10; Analysis 20.11; Analysis 20.12; Analysis 20.13);
intact membranes and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 21.4; Analysis 21.5; Analysis 21.6; Analysis 21.7; Analysis 21.8; Analysis 21.9; Analysis 21.10);
primiparae (Analysis 22.5; Analysis 22.6; Analysis 22.7; Analysis 22.10; Analysis 22.12);
all primiparae and unfavourable cervix (Analysis 23.3; Analysis 23.4; Analysis 23.5; Analysis 23.6; Analysis 23.9; Analysis 23.11);
all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix (Analysis 24.4; Analysis 24.5; Analysis 24.6; Analysis 24.9; Analysis 24.11).
20.4. Analysis.
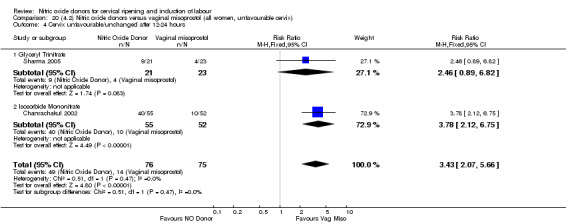
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
20.5. Analysis.
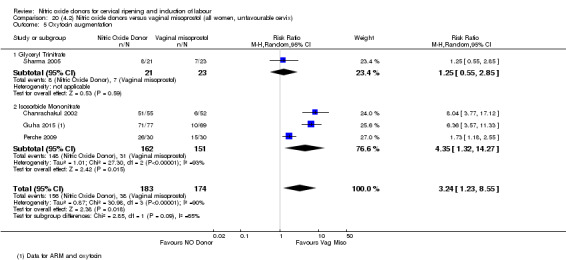
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Oxytocin augmentation.
20.6. Analysis.
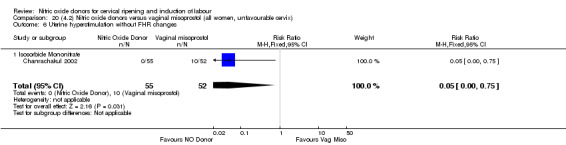
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
20.7. Analysis.
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
20.8. Analysis.
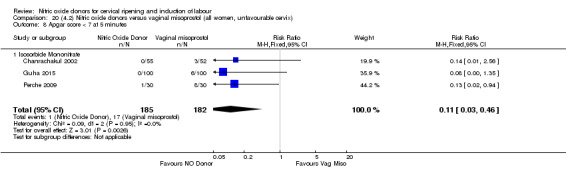
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
20.9. Analysis.
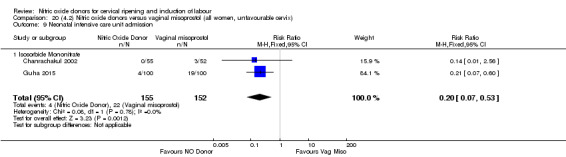
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
20.10. Analysis.
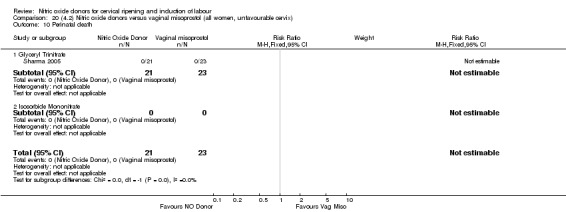
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Perinatal death.
20.11. Analysis.
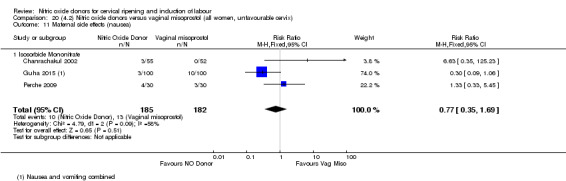
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Maternal side effects (nausea).
20.12. Analysis.
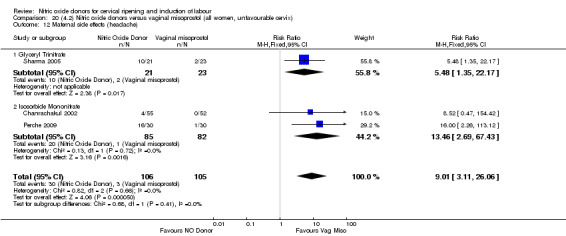
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Maternal side effects (headache).
20.13. Analysis.
Comparison 20 (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 13 Postpartum haemorrhage.
21.4. Analysis.
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
21.5. Analysis.
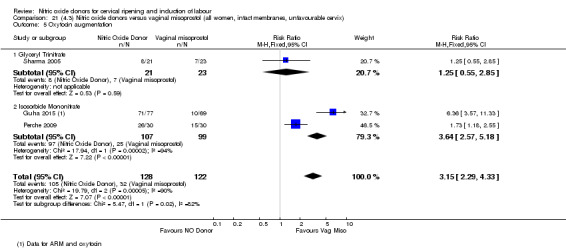
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Oxytocin augmentation.
21.6. Analysis.
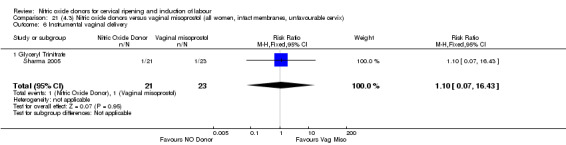
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
21.7. Analysis.
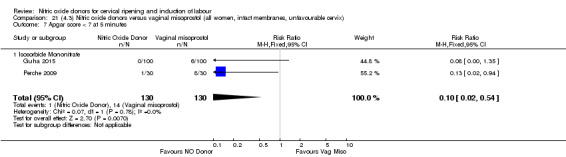
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
21.8. Analysis.
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Perinatal death.
21.9. Analysis.
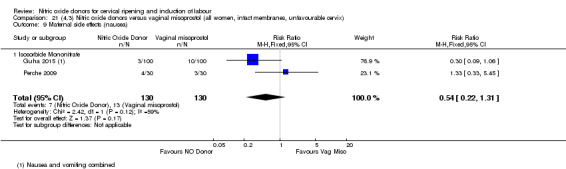
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (nausea).
21.10. Analysis.
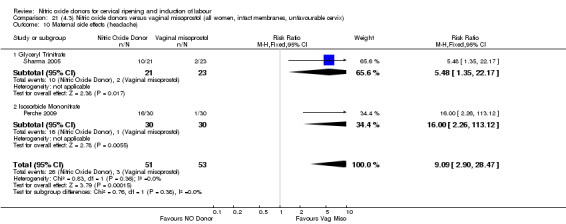
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
22.5. Analysis.
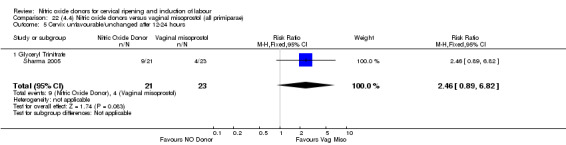
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
22.6. Analysis.
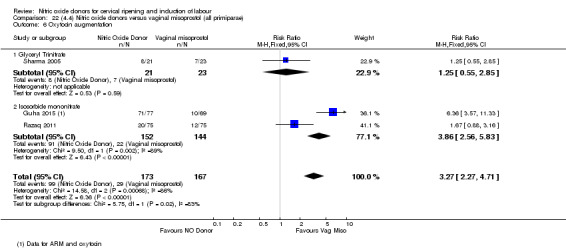
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 6 Oxytocin augmentation.
22.7. Analysis.
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
22.10. Analysis.
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 10 Perinatal death.
22.12. Analysis.
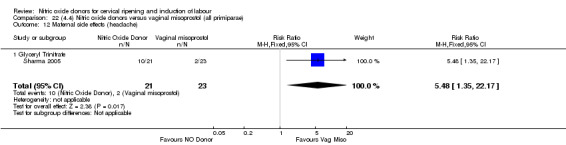
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 12 Maternal side effects (headache).
23.4. Analysis.
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
23.5. Analysis.
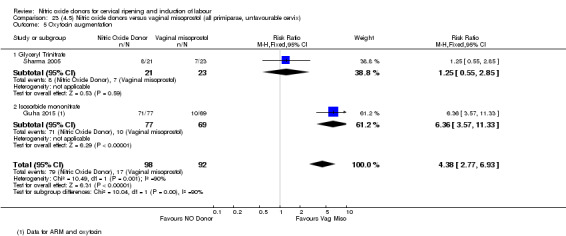
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Oxytocin augmentation.
23.6. Analysis.
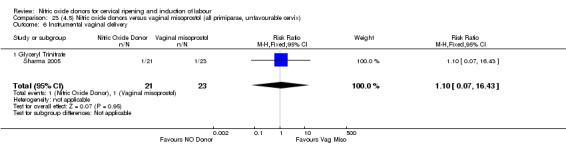
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
23.9. Analysis.
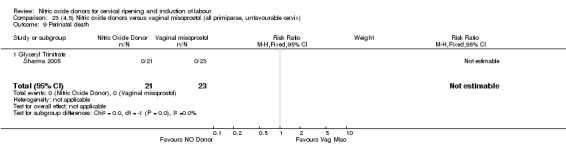
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Perinatal death.
23.11. Analysis.
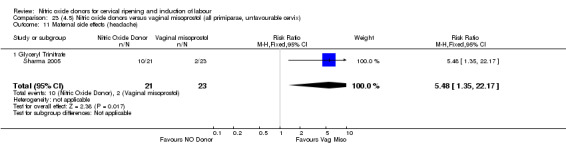
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Maternal side effects (headache).
24.4. Analysis.
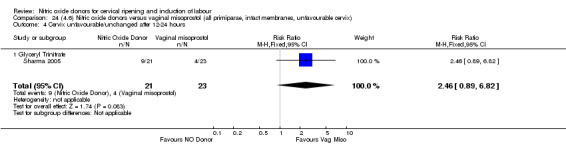
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
24.5. Analysis.
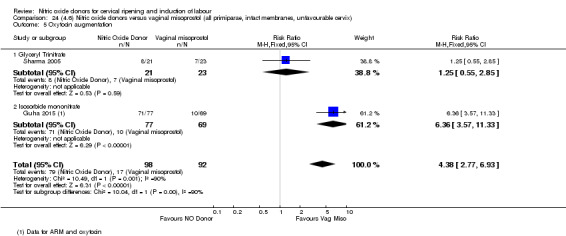
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Oxytocin augmentation.
24.6. Analysis.
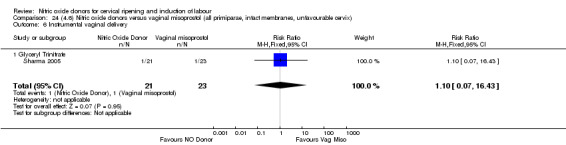
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
24.9. Analysis.
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Perinatal death.
24.11. Analysis.
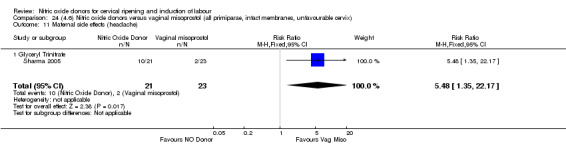
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Maternal side effects (headache).
Subgroup analysis
There was no evidence of any difference between the different types of NO donor used (glyceral trinitrate; isosorbide mononitrate; isosorbide dinitrate) for any of the secondary outcomes analysed.
Comparison 5: Nitric oxide versus intracervical catheter (two studies, 155 women)
Analyses 25 to 30
One study (Movahed 2016) did not contribute any data.
Primary outcomes
There was no evidence on any difference between the effects of NO and the use of a Foley catheter for induction of labour for caesarean section (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.39 to 2.59; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.1). None of the other primary outcomes were reported: vaginal delivery not achieved within 24 hours; uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes; serious neonatal morbidity or perinatal death or; or serious maternal morbidity or death.
25.1. Analysis.
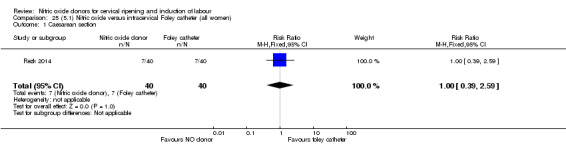
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 1 Caesarean section.
Clinical subgroups
Since there was only one study in this comparison with one outcome (caesarean section), the results were the same for the one outcome analysed.
Subgroup analysis
It was not possible to carry out subgroup analysis with a single study.
Secondary outcomes
There was evidence of an increase in the use of oxytocin augmentation when comparing NO donors to the use of a Foley catheter for induction of labour (RR 1.65, 95% CI 1.17 to 2.32; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.2). Additionally there was evidence of an increase in the rates of maternal headache in association with NO donors when compared to Foley catheter (RR 3.33, 95% CI 0.99 to 11.22; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.10). There was no evidence of a difference in maternal satisfaction between the use of NO donors or Foley catheter for induction of labour (RR 1.75, 95% CI 0.56 to 5.51; one trial, 80 women, participants, Analysis 25.12).
25.2. Analysis.
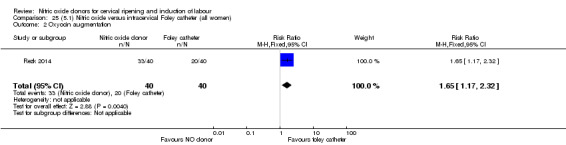
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 2 Oxyocin augmentation.
25.10. Analysis.
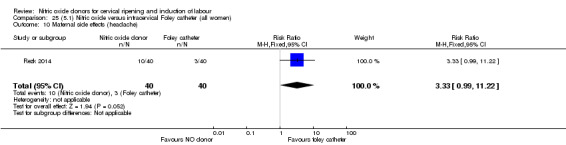
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
25.12. Analysis.
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 12 Women not satisfied.
There were no differences observed between groups for any of the following outcomes:
oxytocin augmentation (RR 1.65, 95% CI 1.17 to 2.32; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.2);
uterine rupture (not estimable as no events in either group, Analysis 25.3);
epidural analgesia (RR 1.00, 95% CI 0.39 to 2.59; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.4);
instrumental vaginal delivery (RR 0.80, 95% CI 0.23 to 2.76; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.5);
meconium‐stained liquor (RR 2.00, 95% CI 0.19 to 21.18; one trial, 80, Analysis 25.6);
Apgar score less than seven at five minutes (RR 1.67, 95% CI 0.95 to 2.93; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.7);
neonatal intensive care unit admission (RR 2.50, 95% CI 0.51 to 12.14; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.8);
maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting) (RR 3.00, 95% CI 0.33 to 27.63; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.9);
postpartum haemorrhage (RR 2.00, 95% CI 0.90 to 4.43; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.11);
other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia) (RR 0.42, 95% CI 0.16 to 1.07; one trial, 80 women, Analysis 25.13).
25.3. Analysis.
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 3 Uterine rupture.
25.4. Analysis.
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 4 Epidural analgesia.
25.5. Analysis.
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
25.6. Analysis.
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 6 Meconium‐stained liquor.
25.7. Analysis.
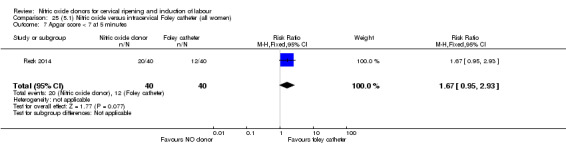
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
25.8. Analysis.
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
25.9. Analysis.
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting).
25.11. Analysis.
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 11 Postpartum haemorrhage.
25.13. Analysis.
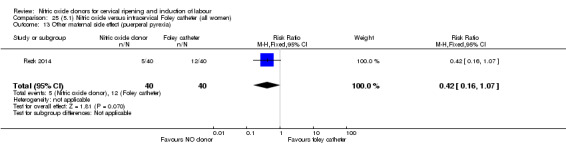
Comparison 25 (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women), Outcome 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia).
None of the following secondary outcomes were reported and analysed: cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12 to 24 hours; uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes; neonatal encephalopathy; perinatal death; disability in childhood; serious maternal complications; maternal death; caregiver not satisfied; neonatal infection; neonatal antibiotics; chorioamnionitis; endometritis; maternal antibiotics.
Clinical subgroups
Since there was only one study in this comparison and the results were the same for all clinical subgroups.
Subgroup analysis
It was not possible to carry out subgroup analysis with a single study.
Discussion
Summary of main results
Nitric oxide (NO) donors reduce the proportion of women with an unfavourable cervix at 12 to 24 hours when compared to placebo for induction of labour.
NO donors increase the proportion of women with an unfavourable cervix at 12 to 24 hours when compared to vaginal misoprostol.
NO donors when compared to placebo, vaginal or intracervical prostaglandins, vaginal misoprostol and intracervical Foley catheter resulted in a higher rate of maternal headache when used for induction of labour.
Induction of labour with NO donors resulted in a greater proportion of women remaining undelivered at 24 to 48 hours when compared with vaginal or intracervical prostaglandins.
NO donors were associated with a reduction in the rate of uterine hyperstimulation with fetal heart rate (FHR) changes when compared with vaginal misoprostol for induction of labour.
NO donors when compared to intracervical prostaglandins resulted in fewer women undergoing a caesarean section.
NO donors were associated with a reduction in the rate of uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes when compared with placebo or vaginal misoprostol.
There was no evidence of any difference between NO donors and Foley catheter for any of the reported outcomes, apart from an increase in headache with NO donors.
There are very limited data available to compare NO donors to any other induction agent. There is evidence to suggest that NO is more effective in causing cervical ripening in comparison to placebo however, these results needs further evaluation as this did not affect the induction to delivery interval or delivery outcomes in this comparison. Vaginal misoprostol appears to be more effective than NO donors for induction of labour.
In two studies, we noted the use of a complex intervention in the form of vaginal prostaglandin along with NO donor in some women (Agarwal 2012; Bollapragada 2009). In both of these studies, the use of additional induction agents was determined by the response of the cervix following initial treatment with NO donors or placebo. If the cervix remained unfavourable (as defined by the authors), then vaginal prostaglandin was administered. If the cervix was favourable then additional vaginal prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) was not used. Hence for a proportion of these women a complex intervention was used. It is difficult to determine the effect of NO donor alone on the favourability of cervix in these studies.
It is therefore possible that the true effect of NO donors would be better evaluated through a trial comparing NO donors plus vaginal PGE2 versus other interventions.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
There are limited data within the trials on the whole; furthermore, there are limited numbers of studies within each comparison group, making interpretation difficult. There are insufficient data to understand if we have a complete view of the effect of NO donor use in the cervical ripening.
As mentioned earlier in the review, NO donors work primarily to promote cervical ripening, hence the comparison to other, more traditional induction of labour agents may not be appropriate. The outcomes used to evaluate these agents look at the entire journey from the first stages of induction through to delivery. Furthermore, many of the recent studies looking at the use of NO donors have been performed within an outpatient setting where most standard ripening agents are not routinely used at present.
Quality of the evidence
The risk of bias was found to be low in the majority of studies for all domains. The more recent trials were found to be at the lowest risk of bias. The quality of the evidence was assessed using the GRADE approach for the five primary outcomes for the comparison of nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (see Table 1). The evidence was assessed as being low for vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours, uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes, and serious maternal morbidity. The main reason for downgrading the evidence for these outcomes was due to concerns over imprecision (few events, small sample sizes and wide confidence intervals) and because most of the data were from single studies. The evidence was assessed as being of moderate quality for caesarean section and was downgraded due to limitations in design (high risk of bias for allocation concealment, selective outcome reporting and blinding).
Potential biases in the review process
We attempted to minimise bias during the review process by having three people assess the eligibility of studies, assess risk of bias and extract data with a third person involved to check or review each area. We attempted to be as inclusive as possible in our search.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
There have been no formal systematic reviews of the use of NO donors compared to other induction agents.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
Available data suggest that nitric oxide (NO) donors can be a useful tool in the process of induction of labour causing the cervix to be more favourable in comparison to placebo. However, further complex interventional trials are needed to study its true effect on labour process and delivery outcomes.
Implications for research.
More studies are required to examine how NO donors may work alongside established induction of labour protocols, especially those based in outpatient settings. There is also a need to further develop a more robust set of outcome measures which allow the efficacy of the cervical ripening phase of the induction process to be effectively evaluated.
An ideal study to determine the effect of NO donor would involve complex intervention. In this, women could be randomised into two groups, one receiving placebo + prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) and another receiving NO donor + PGE2 regardless of the favourability of the cervix. Then the need for oxytocin, length of the labour and delivery outcomes to be assessed.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 15 August 2016 | New citation required but conclusions have not changed | Thirteen trials added for this update. This update includes a total of 23 studies. Conclusions remain the same. |
| 15 August 2016 | New search has been performed | Search updated: 13 new studies included (Agarwal 2012; Guha 2015; Haghighi 2013; Haghighi 2015; Krishnamurthy 2015; Movahed 2016; Razaq 2011; Rezk 2014; Romero‐Gutierrez 2011; Schmitz 2014; Soliman 2013; Vidanagamage 2011; Yazdizadeh 2013) and four excluded (Abdellah 2011; Ahmed 2014; El‐Khayat 2016; Ziard 2012). One study previously in awaiting classification has been excluded in this update (Vaisanen‐Tommiska 2008). A 'Summary of findings' table was added for this update. |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 1, 2008 Review first published: Issue 6, 2011
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 12 November 2008 | Amended | Converted to new review format. |
Acknowledgements
Josephine Kavanagh for her input on the protocol for this review.
We are grateful to Luciana Figuera for the translation of the paper Perche 2009 and to Bita Mesgarpour for the translation of the paper (Movahed 2016).
This project was supported by the National Institute for Health Research, via Cochrane Infrastructure funding to Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth. The views and opinions expressed therein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect those of the Systematic Reviews Programme, NIHR, NHS or the Department of Health.
We thank Anna Cuthbert, Research Assistant, Cochrane Pregnancy and Childbirth, for her help with the 2016 update.
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 238 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.83, 1.15] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 2 | 300 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.09 [0.01, 1.62] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 9 | 2624 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.88, 1.11] |
| 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 2 | 1712 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.61 [0.08, 33.26] |
| 5 Serious maternal morbidity or death | 1 | 1362 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 6 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 4 | 762 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.67, 0.90] |
| 6.1 Standard release | 4 | 659 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.69, 0.94] |
| 6.2 Slow release | 1 | 103 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.49, 0.82] |
| 7 Oxytocin augmentation | 4 | 1916 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.95 [0.84, 1.07] |
| 8 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.05 [0.00, 0.80] |
| 9 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.82, 1.09] |
| 10 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 4 | 1835 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.83, 1.10] |
| 11 Meconium‐stained liquor | 3 | 699 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.69, 1.14] |
| 12 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 5 | 2212 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.54, 2.07] |
| 13 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 5 | 873 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.47, 1.46] |
| 14 Perinatal death | 2 | 1712 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 15 Maternal side effects (all) | 1 | 1362 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.82 [2.49, 3.20] |
| 16 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 3 | 1782 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.44 [1.47, 4.05] |
| 17 Maternal side effects (headache) | 6 | 2085 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 6.59 [3.97, 10.95] |
| 18 Maternal side effects (vomiting) | 1 | 1362 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.42 [1.54, 3.81] |
| 19 Maternal side effects (diarrhoea) | 1 | 1362 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.44 [0.95, 2.19] |
| 20 Postpartum haemorrhage | 2 | 1562 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.12 [0.90, 1.40] |
| 21 Women not satisfied | 1 | 1362 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.06 [0.82, 1.38] |
| 22 Additional induction agents used | 5 | 2180 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.71 [0.58, 0.88] |
| 22.1 Standard release | 5 | 2077 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.73 [0.58, 0.92] |
| 22.2 Slow release | 1 | 103 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.49, 0.82] |
1.5. Analysis.
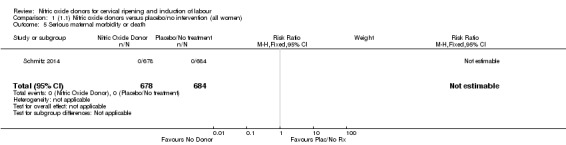
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 5 Serious maternal morbidity or death.
1.16. Analysis.
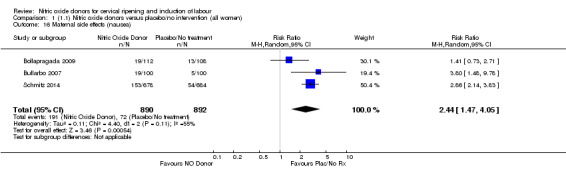
Comparison 1 (1.1) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women), Outcome 16 Maternal side effects (nausea).
Comparison 2. (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 238 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.83, 1.15] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 2 | 300 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.09 [0.01, 1.62] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 8 | 1262 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.82, 1.15] |
| 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 3 | 557 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.81 [0.73, 0.89] |
| 6 Oxytocin augmentation | 3 | 554 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.82, 1.03] |
| 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.05 [0.00, 0.80] |
| 8 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.82, 1.09] |
| 9 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 3 | 473 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.68, 1.28] |
| 10 Meconium‐stained liquor | 3 | 699 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.69, 1.14] |
| 11 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 4 | 850 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.13 [0.42, 2.98] |
| 12 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 5 | 873 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.57, 1.30] |
| 13 Perinatal death | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 14 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 2 | 420 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.06 [1.22, 3.50] |
| 15 Maternal side effects (headache) | 5 | 723 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 7.04 [5.13, 9.66] |
| 16 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.17 [0.57, 2.40] |
| 17 Additional induction agents used | 2 | 413 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.66 [0.57, 0.77] |
2.5. Analysis.
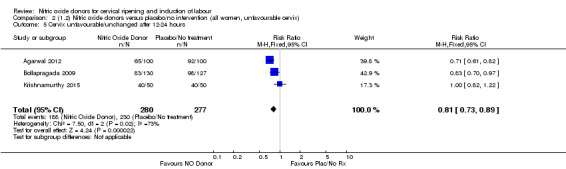
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
2.6. Analysis.
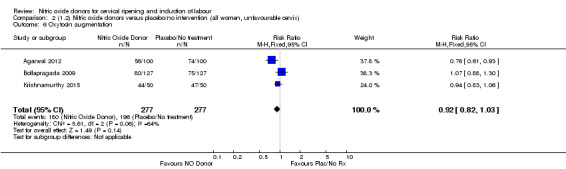
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Oxytocin augmentation.
2.7. Analysis.
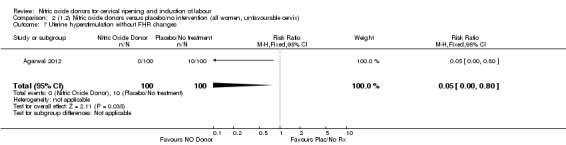
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
2.8. Analysis.
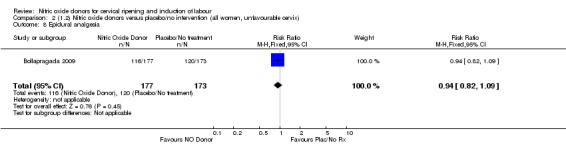
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Epidural analgesia.
2.9. Analysis.
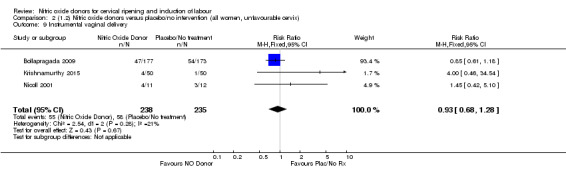
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
2.10. Analysis.
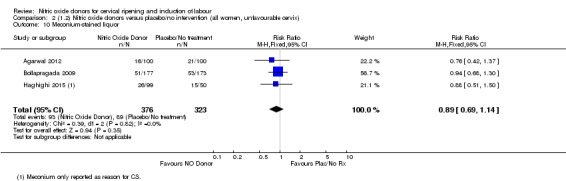
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Meconium‐stained liquor.
2.11. Analysis.
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
2.12. Analysis.
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
2.13. Analysis.
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 13 Perinatal death.
2.14. Analysis.
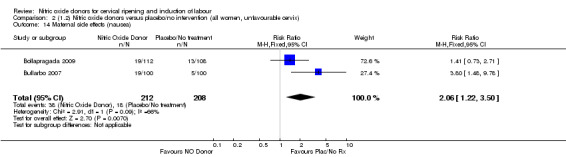
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 14 Maternal side effects (nausea).
2.15. Analysis.
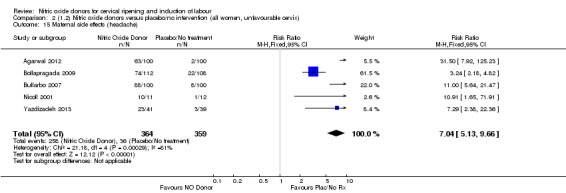
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 15 Maternal side effects (headache).
2.16. Analysis.
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 16 Postpartum haemorrhage.
2.17. Analysis.
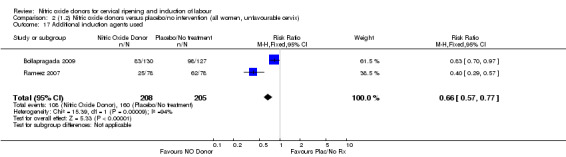
Comparison 2 (1.2) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 17 Additional induction agents used.
Comparison 3. (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 238 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.83, 1.15] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.09 [0.01, 1.62] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 3 | 754 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.77, 1.22] |
| 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 2 | 457 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.72 [0.61, 0.85] |
| 6 Oxytocin augmentation | 2 | 454 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.79, 1.05] |
| 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.05 [0.00, 0.80] |
| 8 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.82, 1.09] |
| 9 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.61, 1.18] |
| 10 Meconium‐stained liquor | 2 | 550 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.67, 1.18] |
| 11 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 3 | 750 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.84 [0.27, 2.59] |
| 12 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 3 | 750 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.42, 1.84] |
| 13 Perinatal death | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 14 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 2 | 420 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.18 [0.82, 5.77] |
| 15 Maternal side effects (headache) | 3 | 620 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 9.27 [2.47, 34.73] |
| 16 Postpartum haemorrhage | 2 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.55, 2.07] |
| 17 Additional induction agents used | 1 | 257 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.70, 0.97] |
3.5. Analysis.
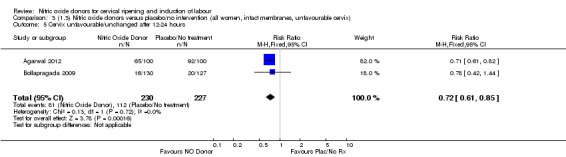
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
3.6. Analysis.
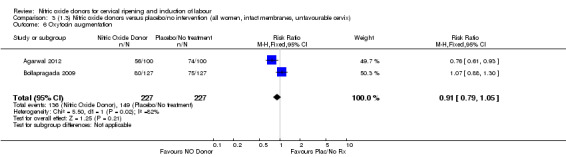
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Oxytocin augmentation.
3.7. Analysis.
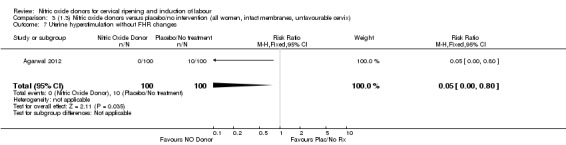
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes.
3.8. Analysis.
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Epidural analgesia.
3.9. Analysis.
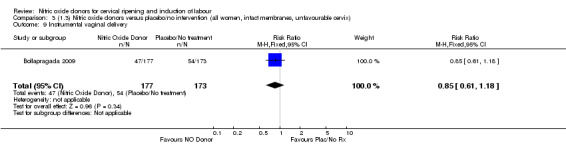
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
3.10. Analysis.
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Meconium‐stained liquor.
3.11. Analysis.
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
3.12. Analysis.
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
3.13. Analysis.
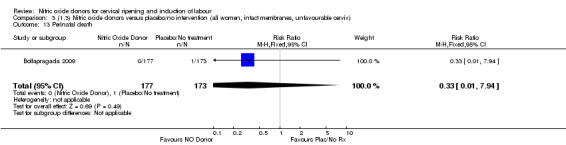
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 13 Perinatal death.
3.14. Analysis.
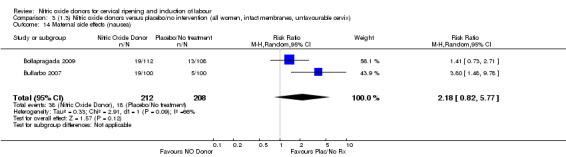
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 14 Maternal side effects (nausea).
3.16. Analysis.
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 16 Postpartum haemorrhage.
3.17. Analysis.
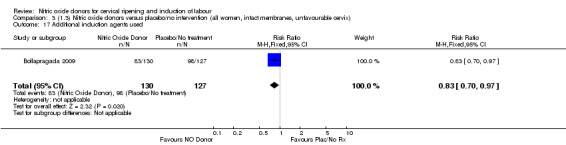
Comparison 3 (1.3) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 17 Additional induction agents used.
Comparison 4. (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 238 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.83, 1.15] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 100 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 4 | 683 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.08 [0.89, 1.31] |
| 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 2 | 357 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.77, 0.99] |
| 6 Oxytocin augmentation | 2 | 354 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.89, 1.16] |
| 7 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.82, 1.09] |
| 8 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 2 | 450 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.66, 1.25] |
| 9 Meconium‐stained liquor | 2 | 499 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.70, 1.22] |
| 10 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 2 | 450 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.50, 7.77] |
| 11 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 2 | 450 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.53, 1.80] |
| 12 Perinatal death | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 13 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 220 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.41 [0.73, 2.71] |
| 14 Maternal side effects (headache) | 2 | 300 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.10 [1.97, 8.56] |
| 15 Additional induction agents used | 1 | 257 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.70, 0.97] |
4.2. Analysis.
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
4.5. Analysis.
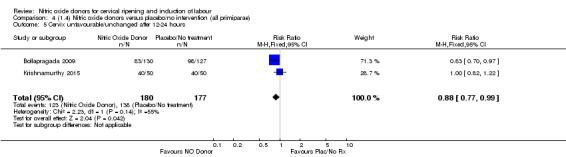
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
4.6. Analysis.
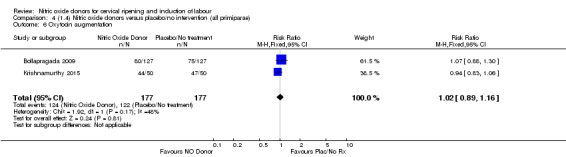
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 6 Oxytocin augmentation.
4.7. Analysis.
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 7 Epidural analgesia.
4.8. Analysis.
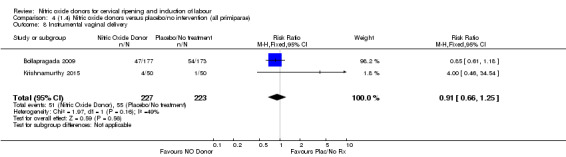
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 8 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
4.9. Analysis.
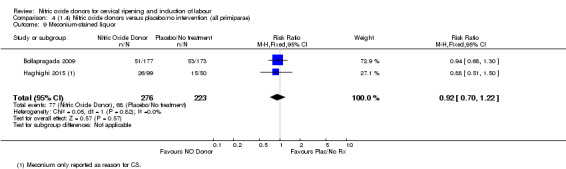
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 9 Meconium‐stained liquor.
4.10. Analysis.
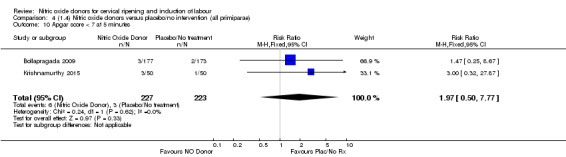
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 10 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
4.11. Analysis.
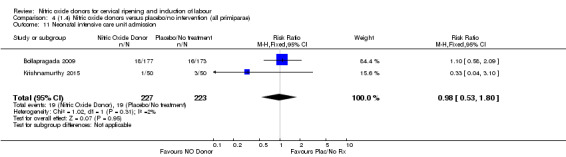
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 11 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
4.12. Analysis.
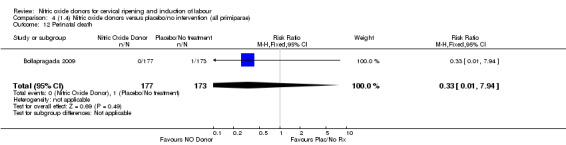
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 12 Perinatal death.
4.14. Analysis.
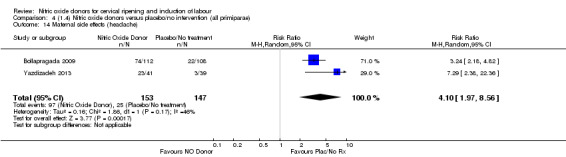
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 14 Maternal side effects (headache).
4.15. Analysis.
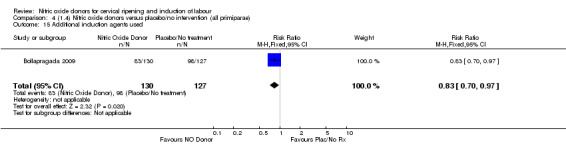
Comparison 4 (1.4) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae), Outcome 15 Additional induction agents used.
Comparison 5. (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 238 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.83, 1.15] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 100 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 4 | 683 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.08 [0.89, 1.31] |
| 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 2 | 357 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.77, 0.99] |
| 6 Oxytocin augmentation | 2 | 354 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.89, 1.16] |
| 7 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.82, 1.09] |
| 8 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 2 | 450 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.91 [0.66, 1.25] |
| 9 Meconium‐stained liquor | 2 | 499 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.92 [0.70, 1.22] |
| 10 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 2 | 450 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.97 [0.50, 7.77] |
| 11 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 2 | 450 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.98 [0.53, 1.80] |
| 12 Perinatal death | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 13 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 220 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.41 [0.73, 2.71] |
| 14 Maternal side effects (headache) | 2 | 300 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.73 [2.56, 5.43] |
| 15 Additional induction agents used | 1 | 257 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.70, 0.97] |
5.2. Analysis.
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes.
5.5. Analysis.
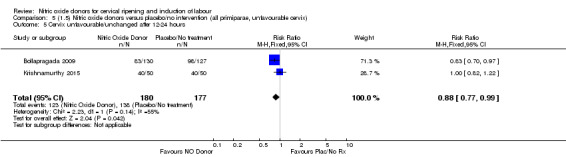
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
5.6. Analysis.
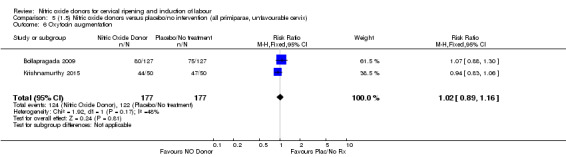
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Oxytocin augmentation.
5.7. Analysis.
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Epidural analgesia.
5.8. Analysis.
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
5.9. Analysis.
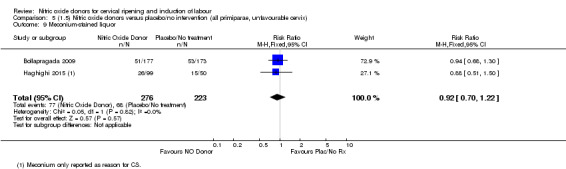
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Meconium‐stained liquor.
5.10. Analysis.
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
5.11. Analysis.
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
5.12. Analysis.
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Perinatal death.
5.14. Analysis.
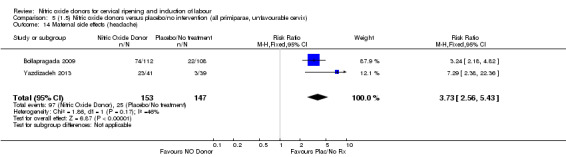
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 14 Maternal side effects (headache).
5.15. Analysis.
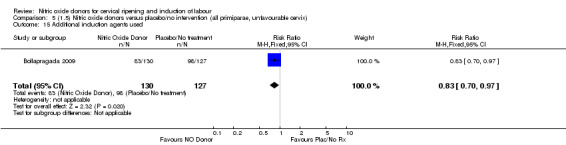
Comparison 5 (1.5) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 15 Additional induction agents used.
Comparison 6. (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 238 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.83, 1.15] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 1 | 354 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.16 [0.87, 1.55] |
| 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 257 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.42, 1.44] |
| 5 Oxytocin augmentation | 1 | 254 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.88, 1.30] |
| 6 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.82, 1.09] |
| 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.85 [0.61, 1.18] |
| 8 Meconium‐stained liquor | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.94 [0.68, 1.30] |
| 9 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.47 [0.25, 8.67] |
| 10 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.58, 2.09] |
| 11 Perinatal death | 1 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.94] |
| 12 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 220 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.41 [0.73, 2.71] |
| 13 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 220 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.24 [2.18, 4.82] |
| 14 Additional induction agents used | 1 | 257 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.70, 0.97] |
6.4. Analysis.
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours.
6.5. Analysis.
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Oxytocin augmentation.
6.6. Analysis.
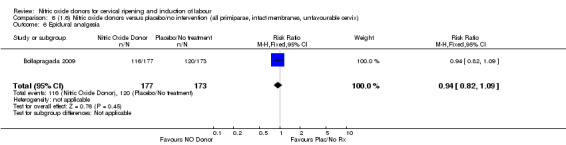
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Epidural analgesia.
6.7. Analysis.
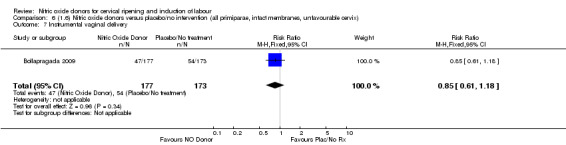
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
6.8. Analysis.
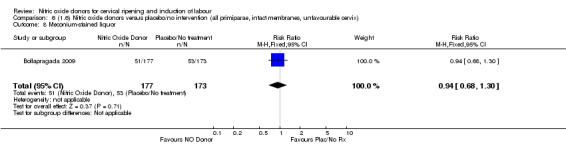
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Meconium‐stained liquor.
6.9. Analysis.
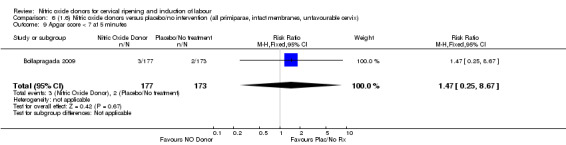
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
6.10. Analysis.
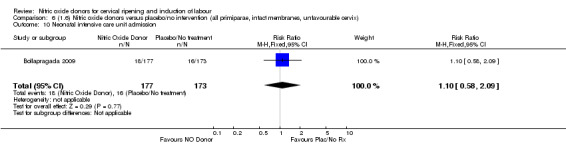
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
6.11. Analysis.
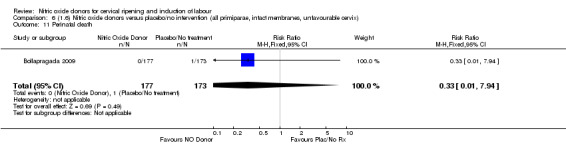
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Perinatal death.
6.13. Analysis.
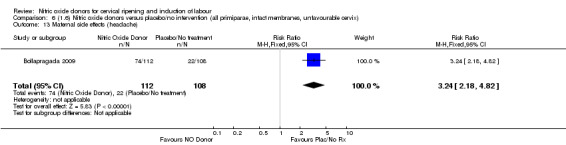
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 13 Maternal side effects (headache).
6.14. Analysis.
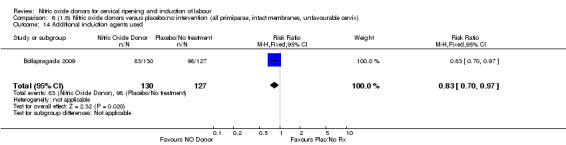
Comparison 6 (1.6) Nitric oxide donors versus placebo/no intervention (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 14 Additional induction agents used.
Comparison 7. (2.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.47, 0.86] |
| 1.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.47, 0.86] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 2 | 508 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.01, 4.22] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.01, 4.22] |
| 2.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.09 [0.01, 1.66] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.09 [0.01, 1.66] |
| 4 Caesarean section | 3 | 571 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.78, 1.21] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.59, 1.63] |
| 4.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.80, 1.43] |
| 4.3 Isosorbide Dinitrate | 1 | 66 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.68 [0.44, 1.06] |
| 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 5.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 6 Meconium‐stained liquor | 1 | 66 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.32, 2.28] |
| 6.1 Isosorbide Dinitrate | 1 | 66 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.32, 2.28] |
| 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 2 | 504 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.55 [0.15, 1.98] |
| 7.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.01, 8.30] |
| 7.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.50] |
| 8 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 9.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 2 | 493 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.79 [5.75, 13.45] |
| 10.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 11.4 [0.65, 201.32] |
| 10.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 383 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.73 [5.68, 13.41] |
| 11 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.12, 3.98] |
| 11.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.12, 3.98] |
| 12 Serious maternal complications | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.01, 8.30] |
| 12.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.01, 8.30] |
| 13 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 3 | 571 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.43, 1.78] |
| 13.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.01, 8.30] |
| 13.2 Isosorbide Dinitrate | 1 | 66 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 13.3 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.45, 1.93] |
Comparison 8. (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 2 | 508 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.01, 4.22] |
| 1.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.01, 4.22] |
| 1.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 2 | 505 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.05 [0.82, 1.35] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.99 [0.59, 1.63] |
| 2.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.80, 1.43] |
| 3 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.09 [0.01, 1.66] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.09 [0.01, 1.66] |
| 4 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 4.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 5.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 6 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 2 | 504 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.55 [0.15, 1.98] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.01, 8.30] |
| 6.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.50] |
| 7 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 2 | 505 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.88 [0.43, 1.78] |
| 7.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.01, 8.30] |
| 7.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.45, 1.93] |
| 8 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (headache) | 2 | 493 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.79 [5.75, 13.45] |
| 9.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 11.4 [0.65, 201.32] |
| 9.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 383 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.73 [5.68, 13.41] |
| 10 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.12, 3.98] |
| 10.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.69 [0.12, 3.98] |
| 11 Serious maternal complications | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.01, 8.30] |
| 11.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 110 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.01, 8.30] |
8.4. Analysis.
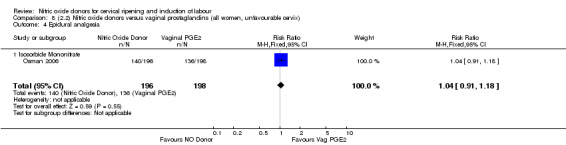
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Epidural analgesia.
8.5. Analysis.
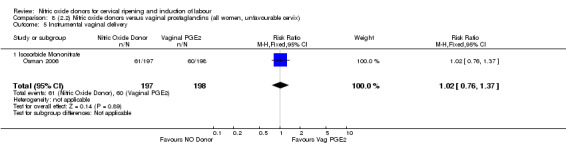
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
8.6. Analysis.
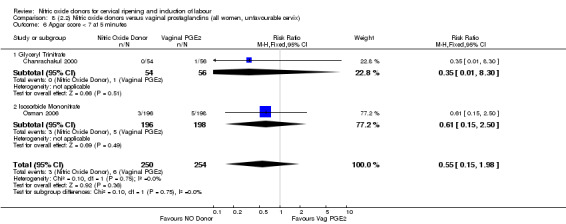
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
8.7. Analysis.
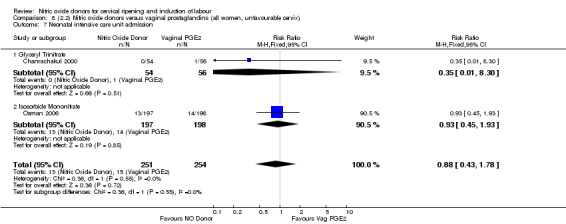
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
8.8. Analysis.
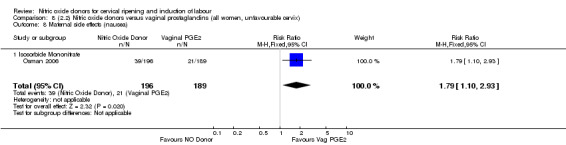
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Maternal side effects (nausea).
8.9. Analysis.
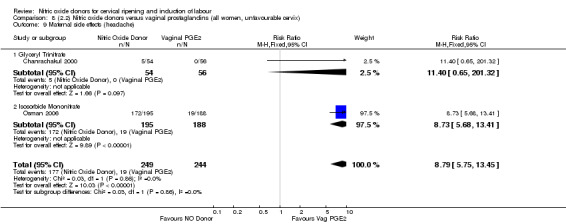
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (headache).
8.10. Analysis.
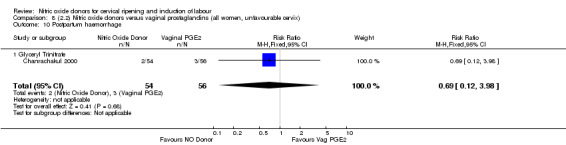
Comparison 8 (2.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Postpartum haemorrhage.
Comparison 9. (2.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 1.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.80, 1.43] |
| 2.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.80, 1.43] |
| 3 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 3.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 4 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 4.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 5 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.50] |
| 5.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.50] |
| 6 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.45, 1.93] |
| 6.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.45, 1.93] |
| 7 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 7.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 8 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 383 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.73 [5.68, 13.41] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 383 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.73 [5.68, 13.41] |
9.4. Analysis.
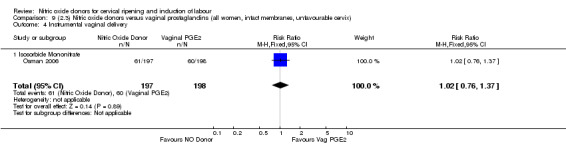
Comparison 9 (2.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
9.5. Analysis.
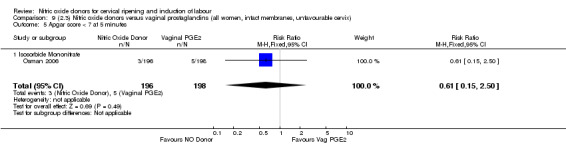
Comparison 9 (2.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
9.6. Analysis.
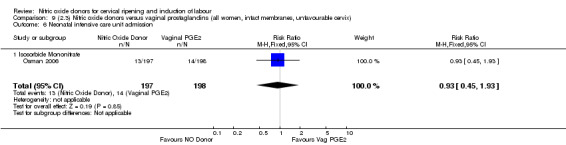
Comparison 9 (2.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
9.7. Analysis.
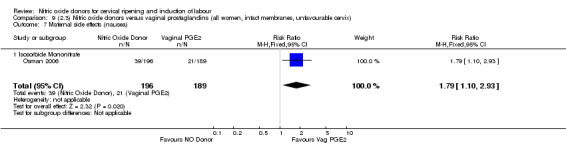
Comparison 9 (2.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Maternal side effects (nausea).
Comparison 10. (2.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.47, 0.86] |
| 1.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.47, 0.86] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 2 | 795 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.68, 1.08] |
| 3.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 795 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.86 [0.68, 1.08] |
| 4 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 4.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 5.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 6 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.50] |
| 6.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.50] |
| 7 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.45, 1.93] |
| 7.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.45, 1.93] |
| 8 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 383 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.73 [5.68, 13.41] |
| 9.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 383 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.73 [5.68, 13.41] |
10.1. Analysis.
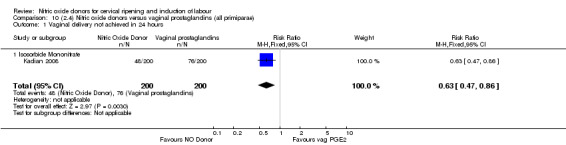
Comparison 10 (2.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
10.5. Analysis.
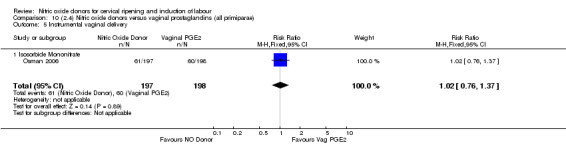
Comparison 10 (2.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
10.6. Analysis.
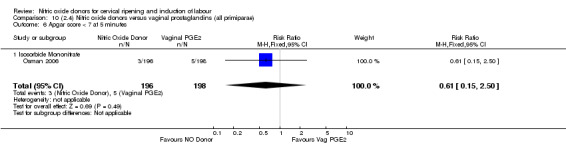
Comparison 10 (2.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 6 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
10.7. Analysis.
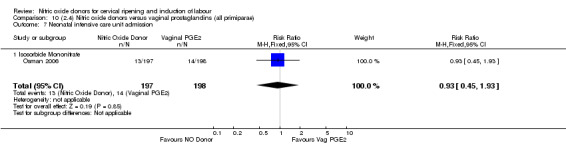
Comparison 10 (2.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 7 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
10.8. Analysis.
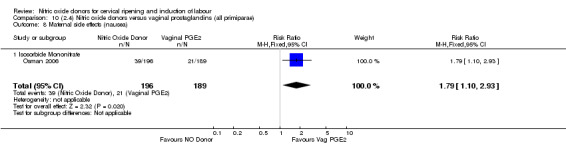
Comparison 10 (2.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae), Outcome 8 Maternal side effects (nausea).
Comparison 11. (2.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 1.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.80, 1.43] |
| 2.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.80, 1.43] |
| 3 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 3.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 4 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 4.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 5 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.50] |
| 5.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.50] |
| 6 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.45, 1.93] |
| 6.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.45, 1.93] |
| 7 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 7.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 8 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 383 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.73 [5.68, 13.41] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 383 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.73 [5.68, 13.41] |
11.4. Analysis.
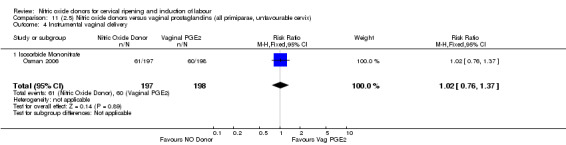
Comparison 11 (2.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
11.5. Analysis.
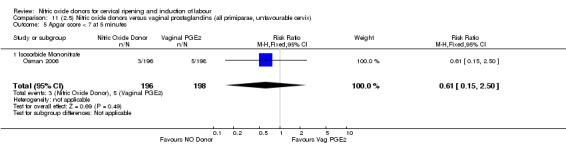
Comparison 11 (2.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
11.6. Analysis.
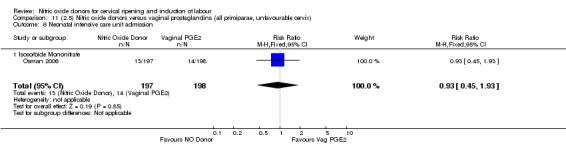
Comparison 11 (2.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
11.7. Analysis.
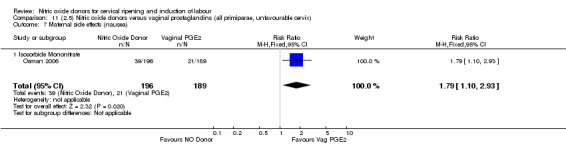
Comparison 11 (2.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Maternal side effects (nausea).
Comparison 12. (2.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 1.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 398 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.80, 1.43] |
| 2.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.07 [0.80, 1.43] |
| 3 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 3.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.91, 1.18] |
| 4 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 4.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.02 [0.76, 1.37] |
| 5 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.50] |
| 5.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.61 [0.15, 2.50] |
| 6 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.45, 1.93] |
| 6.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 395 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.45, 1.93] |
| 7 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 7.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 385 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.79 [1.10, 2.93] |
| 8 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 383 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.73 [5.68, 13.41] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 383 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 8.73 [5.68, 13.41] |
12.4. Analysis.
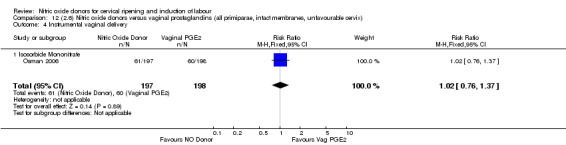
Comparison 12 (2.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
12.5. Analysis.
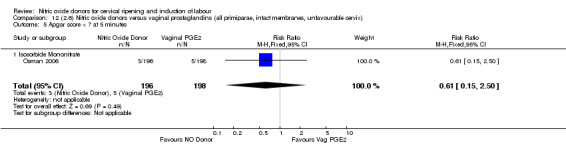
Comparison 12 (2.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
12.6. Analysis.
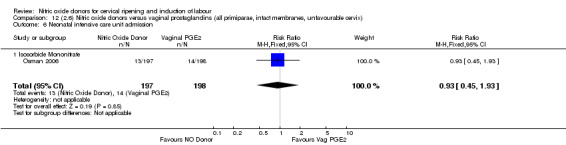
Comparison 12 (2.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
12.7. Analysis.
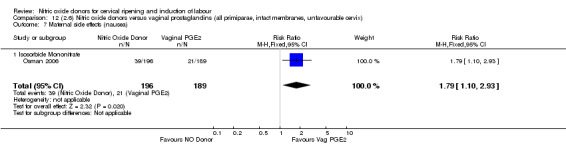
Comparison 12 (2.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal prostaglandins (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Maternal side effects (nausea).
Comparison 13. (3.1) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.47, 0.86] |
| 1.1 Isosorbide dinitrate | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.47, 0.86] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 2 | 442 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.44, 0.90] |
| 3.1 Isosorbide dinitrate | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.58 [0.38, 0.89] |
| 3.2 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 6 Oxytocin augmentation | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 7.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 8 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 8.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 9 Perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 9.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
| 10.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
Comparison 14. (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.47, 0.86] |
| 1.1 Isosorbide dinitrate | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.47, 0.86] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 6 Oxytocin augmentation | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 7.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 8 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 8.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 9 Perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 9.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
| 10.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
14.1. Analysis.
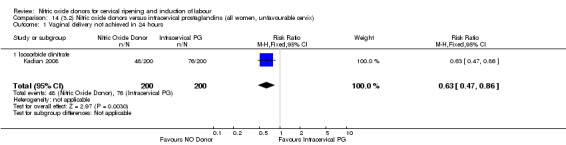
Comparison 14 (3.2) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
Comparison 15. (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.47, 0.86] |
| 1.1 Isosorbide dinitrate | 1 | 400 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.63 [0.47, 0.86] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 6 Oxytocin augmentation | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 7.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 8 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 8.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 9 Perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 9.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
| 10.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
15.1. Analysis.
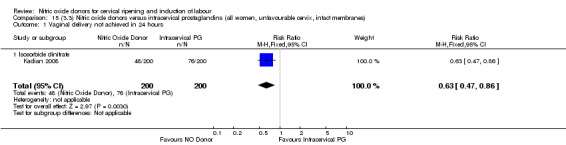
Comparison 15 (3.3) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all women, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
Comparison 16. (3.4) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 1.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 5 Oxytocin augmentation | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 6 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 7.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 8 Perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 8.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
| 9.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
Comparison 17. (3.5) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 1.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 5 Oxytocin augmentation | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 6 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 7.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 8 Perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 8.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
| 9.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
Comparison 18. (3.6) Nitric oxide donors versus intracervical prostaglandins (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix, intact membranes).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 1.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.82 [0.43, 1.55] |
| 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.59, 2.81] |
| 5 Oxytocin augmentation | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.43, 1.85] |
| 6 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.14 [0.01, 2.61] |
| 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 7.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.07, 14.95] |
| 8 Perinatal death | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 8.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.33 [0.01, 7.74] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
| 9.1 Glyceryl trinitrate | 1 | 42 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.0 [1.40, 71.32] |
Comparison 19. (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 150 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.33 [1.62, 17.55] |
| 1.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 150 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.33 [1.62, 17.55] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 3 | 281 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.07 [0.01, 0.37] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.30] |
| 2.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 237 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.05 [0.01, 0.40] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 6 | 761 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.82, 1.21] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.47, 1.72] |
| 3.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 4 | 587 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.04 [0.84, 1.28] |
| 3.3 Isosorbide Dinitrate | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.76 [0.37, 1.55] |
| 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 2 | 151 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.43 [2.07, 5.66] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 [0.89, 6.82] |
| 5.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 107 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.78 [2.12, 6.75] |
| 6 Oxytocin augmentation | 7 | 767 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 2.67 [1.31, 5.45] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.55, 2.85] |
| 6.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 5 | 593 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.57 [1.84, 6.92] |
| 6.3 Isosorbide Dinitrate | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.30 [1.11, 1.52] |
| 7 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 3 | 367 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.06 [0.01, 0.32] |
| 7.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 237 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.05 [0.01, 0.34] |
| 7.2 Isosorbide Dinitrate | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.19 [0.01, 3.96] |
| 8 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.45, 1.31] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.45, 1.31] |
| 9 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 9.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 9.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 10 Meconium‐stained liquor | 2 | 260 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.29 [0.13, 0.65] |
| 10.1 Isosorbide Dinitrate | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.09 [0.00, 1.56] |
| 10.2 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.35 [0.15, 0.84] |
| 11 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 6 | 777 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.07, 0.38] |
| 11.1 Isosorbide Dinitrate | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 11.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 5 | 647 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.07, 0.38] |
| 12 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 4 | 587 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.19 [0.09, 0.43] |
| 12.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 4 | 587 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.19 [0.09, 0.43] |
| 13 Perinatal death | 2 | 194 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 13.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 13.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 150 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 14 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 5 | 647 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.17 [0.63, 2.17] |
| 14.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 5 | 647 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.17 [0.63, 2.17] |
| 15 Maternal side effects (headache) | 4 | 341 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 10.98 [4.05, 29.73] |
| 15.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.48 [1.35, 22.17] |
| 15.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 167 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 13.46 [2.69, 67.43] |
| 15.3 Isosorbide Dinitrate | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 24.25 [1.47, 401.26] |
| 16 Postpartum haemorrhage | 4 | 587 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.33 [0.57, 3.06] |
| 16.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 4 | 587 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.33 [0.57, 3.06] |
| 17 Analgesia requirement | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.26 [0.13, 0.49] |
| 17.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 130 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.26 [0.13, 0.49] |
| 18 Additional induction agents required | 1 | 150 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 16.67 [5.44, 51.09] |
| 18.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 150 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 16.67 [5.44, 51.09] |
19.1. Analysis.
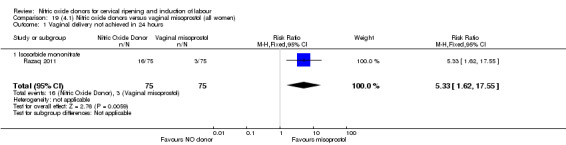
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
19.8. Analysis.
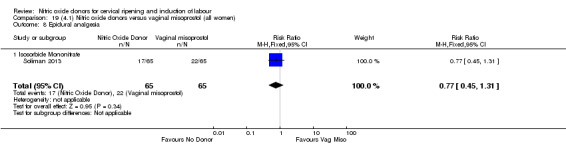
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 8 Epidural analgesia.
19.14. Analysis.
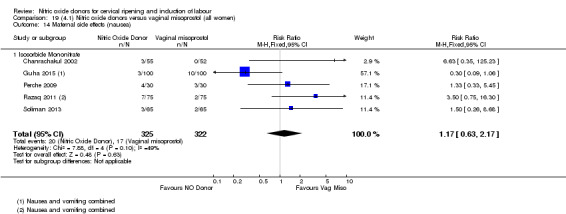
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 14 Maternal side effects (nausea).
19.18. Analysis.
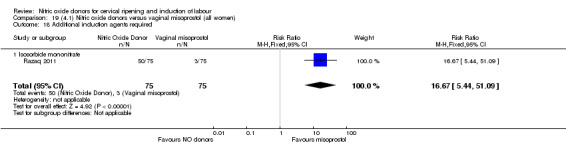
Comparison 19 (4.1) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women), Outcome 18 Additional induction agents required.
Comparison 20. (4.2) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 2 | 151 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.09 [0.01, 0.67] |
| 1.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.30] |
| 1.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 107 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.06 [0.00, 0.94] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 3 | 351 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.66, 1.22] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.47, 1.72] |
| 2.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 307 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.89 [0.63, 1.27] |
| 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 2 | 151 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.43 [2.07, 5.66] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 [0.89, 6.82] |
| 4.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 107 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.78 [2.12, 6.75] |
| 5 Oxytocin augmentation | 4 | 357 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 3.24 [1.23, 8.55] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.55, 2.85] |
| 5.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 3 | 313 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Random, 95% CI) | 4.35 [1.32, 14.27] |
| 6 Uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes | 1 | 107 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.05 [0.00, 0.75] |
| 6.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 107 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.05 [0.00, 0.75] |
| 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 7.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 7.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 8 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 3 | 367 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.11 [0.03, 0.46] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 3 | 367 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.11 [0.03, 0.46] |
| 9 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 2 | 307 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.20 [0.07, 0.53] |
| 9.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 307 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.20 [0.07, 0.53] |
| 10 Perinatal death | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 10.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 10.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 0 | 0 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 11 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 3 | 367 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.35, 1.69] |
| 11.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 3 | 367 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.77 [0.35, 1.69] |
| 12 Maternal side effects (headache) | 3 | 211 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 9.01 [3.11, 26.06] |
| 12.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.48 [1.35, 22.17] |
| 12.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 167 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 13.46 [2.69, 67.43] |
| 13 Postpartum haemorrhage | 2 | 307 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.47 [0.25, 8.61] |
| 13.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 307 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.47 [0.25, 8.61] |
Comparison 21. (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.30] |
| 1.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.30] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 2 | 244 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.53, 1.14] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.47, 1.72] |
| 2.2 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.47, 1.18] |
| 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 [0.89, 6.82] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 [0.89, 6.82] |
| 5 Oxytocin augmentation | 3 | 250 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.15 [2.29, 4.33] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.55, 2.85] |
| 5.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 206 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.64 [2.57, 5.18] |
| 6 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 2 | 260 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.10 [0.02, 0.54] |
| 7.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 260 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.10 [0.02, 0.54] |
| 8 Perinatal death | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 8.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 2 | 260 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.54 [0.22, 1.31] |
| 9.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 2 | 260 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.54 [0.22, 1.31] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 2 | 104 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 9.09 [2.90, 28.47] |
| 10.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.48 [1.35, 22.17] |
| 10.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 60 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 16.0 [2.26, 113.12] |
| 11 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.18, 21.71] |
| 11.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.18, 21.71] |
21.11. Analysis.
Comparison 21 (4.3) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Postpartum haemorrhage.
Comparison 22. (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours | 1 | 150 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.33 [1.62, 17.55] |
| 1.1 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 150 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.33 [1.62, 17.55] |
| 2 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.30] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.30] |
| 3 Caesarean section | 3 | 394 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.96 [0.76, 1.21] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.47, 1.72] |
| 3.2 Isosorbide mononitrate | 2 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.97 [0.76, 1.25] |
| 4 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 2 | 194 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4.2 Isosorbide Mononitrate | 1 | 150 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 5 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 [0.89, 6.82] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 [0.89, 6.82] |
| 6 Oxytocin augmentation | 3 | 340 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.27 [2.27, 4.71] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.55, 2.85] |
| 6.2 Isosorbide mononitrate | 2 | 296 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.86 [2.56, 5.83] |
| 7 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 7.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 8 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 2 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.06 [0.01, 0.44] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 2 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.06 [0.01, 0.44] |
| 9 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 2 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.06, 0.42] |
| 9.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 2 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.16 [0.06, 0.42] |
| 10 Perinatal death | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 10.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 11 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 2 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.37, 1.89] |
| 11.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 2 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.83 [0.37, 1.89] |
| 12 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.48 [1.35, 22.17] |
| 12.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.48 [1.35, 22.17] |
| 13 Postpartum haemorrhage | 2 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.50, 3.33] |
| 13.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 2 | 350 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.29 [0.50, 3.33] |
| 14 Additional induction agents required | 1 | 150 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 16.67 [5.44, 51.09] |
| 14.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 150 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 16.67 [5.44, 51.09] |
22.1. Analysis.
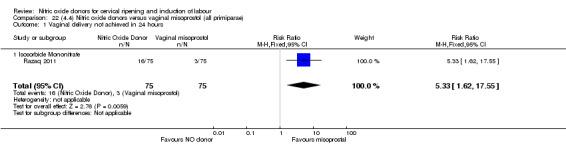
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 1 Vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours.
22.8. Analysis.
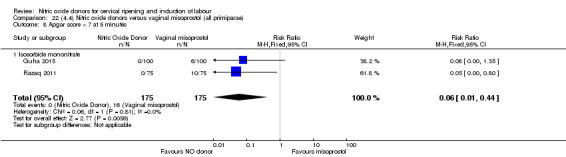
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 8 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
22.9. Analysis.
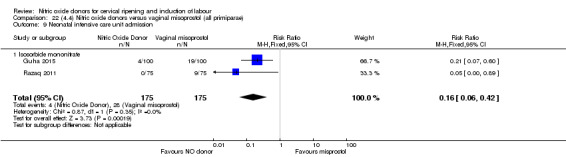
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 9 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
22.11. Analysis.
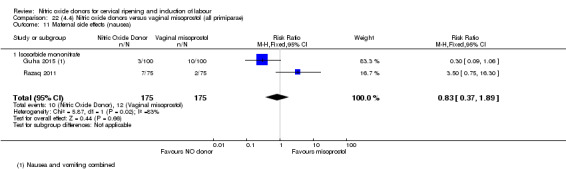
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 11 Maternal side effects (nausea).
22.13. Analysis.
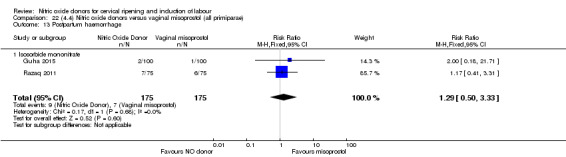
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 13 Postpartum haemorrhage.
22.14. Analysis.
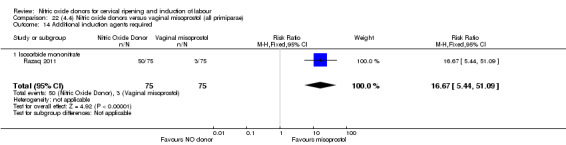
Comparison 22 (4.4) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae), Outcome 14 Additional induction agents required.
Comparison 23. (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.30] |
| 1.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.30] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 2 | 244 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.53, 1.14] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.47, 1.72] |
| 2.2 Isosorbide monotrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.47, 1.18] |
| 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 [0.89, 6.82] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 [0.89, 6.82] |
| 5 Oxytocin augmentation | 2 | 190 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.38 [2.77, 6.93] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.55, 2.85] |
| 5.2 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 146 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 6.36 [3.57, 11.33] |
| 6 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.08 [0.00, 1.35] |
| 7.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.08 [0.00, 1.35] |
| 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.07, 0.60] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.07, 0.60] |
| 9 Perinatal death | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 9.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.3 [0.09, 1.06] |
| 10.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.3 [0.09, 1.06] |
| 11 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.48 [1.35, 22.17] |
| 11.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.48 [1.35, 22.17] |
| 12 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.18, 21.71] |
| 12.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.18, 21.71] |
23.7. Analysis.
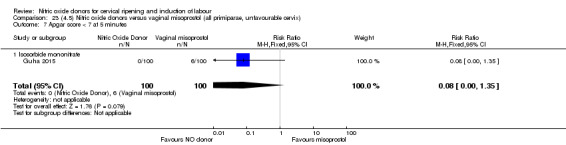
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
23.8. Analysis.
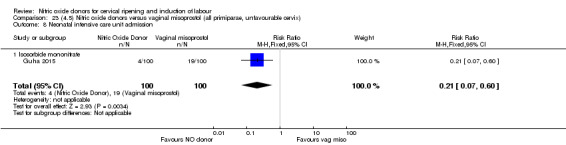
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
23.10. Analysis.
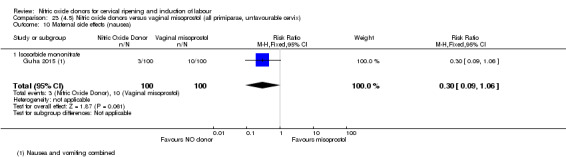
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (nausea).
23.12. Analysis.
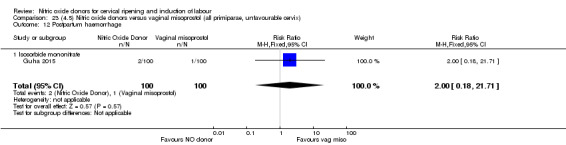
Comparison 23 (4.5) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Postpartum haemorrhage.
Comparison 24. (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.30] |
| 1.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.22 [0.01, 4.30] |
| 2 Caesarean section | 2 | 244 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.78 [0.53, 1.14] |
| 2.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.90 [0.47, 1.72] |
| 2.2 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.74 [0.47, 1.18] |
| 3 Serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 3.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12‐24 hours | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 [0.89, 6.82] |
| 4.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.46 [0.89, 6.82] |
| 5 Oxytocin augmentation | 2 | 190 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 4.38 [2.77, 6.93] |
| 5.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.25 [0.55, 2.85] |
| 5.2 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 146 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 6.36 [3.57, 11.33] |
| 6 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 6.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.10 [0.07, 16.43] |
| 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.08 [0.00, 1.35] |
| 7.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.08 [0.00, 1.35] |
| 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.07, 0.60] |
| 8.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.21 [0.07, 0.60] |
| 9 Perinatal death | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 9.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (nausea) | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.3 [0.09, 1.06] |
| 10.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.3 [0.09, 1.06] |
| 11 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.48 [1.35, 22.17] |
| 11.1 Glyceryl Trinitrate | 1 | 44 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 5.48 [1.35, 22.17] |
| 12 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.18, 21.71] |
| 12.1 Isosorbide mononitrate | 1 | 200 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.18, 21.71] |
24.7. Analysis.
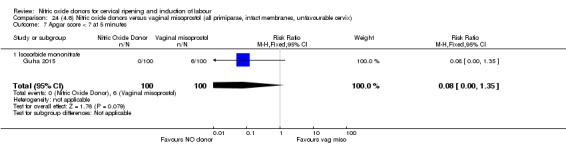
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
24.8. Analysis.
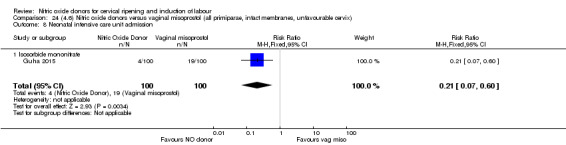
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
24.10. Analysis.
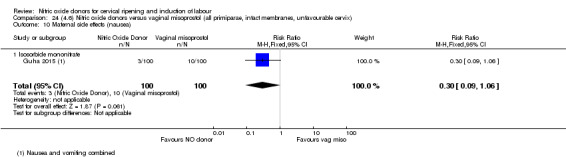
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (nausea).
24.12. Analysis.
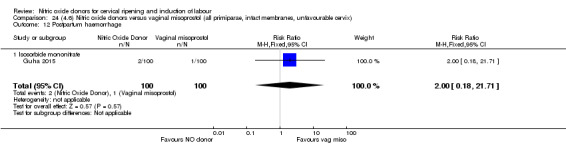
Comparison 24 (4.6) Nitric oxide donors versus vaginal misoprostol (all primiparae, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Postpartum haemorrhage.
Comparison 25. (5.1) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Caesarean section | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 2 Oxyocin augmentation | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [1.17, 2.32] |
| 3 Uterine rupture | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.8 [0.23, 2.76] |
| 6 Meconium‐stained liquor | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.19, 21.18] |
| 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.67 [0.95, 2.93] |
| 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.5 [0.51, 12.14] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.33, 27.63] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.33 [0.99, 11.22] |
| 11 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.90, 4.43] |
| 12 Women not satisfied | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.75 [0.56, 5.51] |
| 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.16, 1.07] |
Comparison 26. (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Caesarean section | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 2 Oxyocin augmentation | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [1.17, 2.32] |
| 3 Uterine rupture | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.8 [0.23, 2.76] |
| 6 Meconium‐stained liquor | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.19, 21.18] |
| 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.67 [0.95, 2.93] |
| 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.5 [0.51, 12.14] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.33, 27.63] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.33 [0.99, 11.22] |
| 11 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.90, 4.43] |
| 12 Women not satisfied | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.75 [0.56, 5.51] |
| 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.16, 1.07] |
26.1. Analysis.
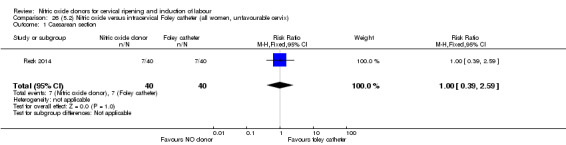
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Caesarean section.
26.2. Analysis.
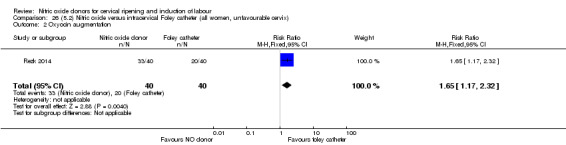
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Oxyocin augmentation.
26.3. Analysis.
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Uterine rupture.
26.4. Analysis.
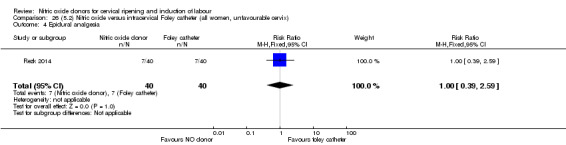
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Epidural analgesia.
26.5. Analysis.
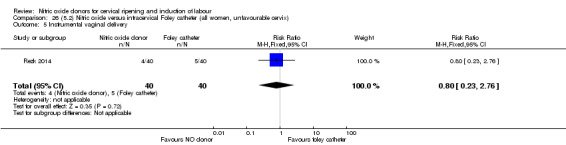
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
26.6. Analysis.
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Meconium‐stained liquor.
26.7. Analysis.
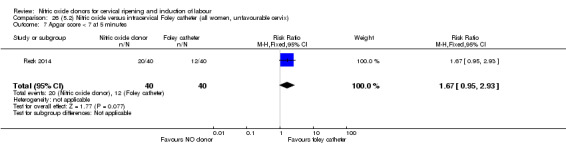
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
26.8. Analysis.
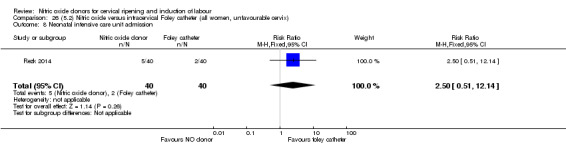
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
26.9. Analysis.
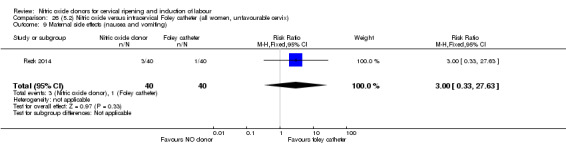
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting).
26.10. Analysis.
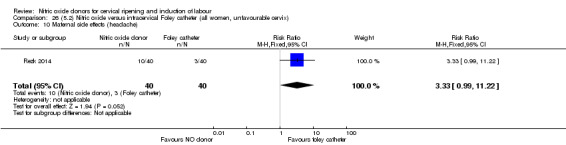
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
26.11. Analysis.
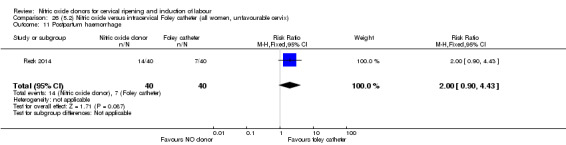
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Postpartum haemorrhage.
26.12. Analysis.
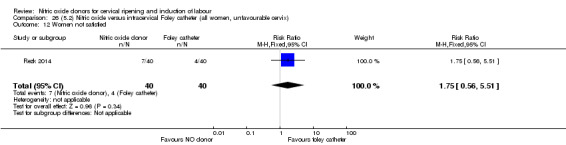
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Women not satisfied.
26.13. Analysis.
Comparison 26 (5.2) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia).
Comparison 27. (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Caesarean section | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 2 Oxyocin augmentation | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [1.17, 2.32] |
| 3 Uterine rupture | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.8 [0.23, 2.76] |
| 6 Meconium‐stained liquor | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.19, 21.18] |
| 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.67 [0.95, 2.93] |
| 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.5 [0.51, 12.14] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.33, 27.63] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.33 [0.99, 11.22] |
| 11 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.90, 4.43] |
| 12 Women not satisfied | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.75 [0.56, 5.51] |
| 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.16, 1.07] |
27.1. Analysis.
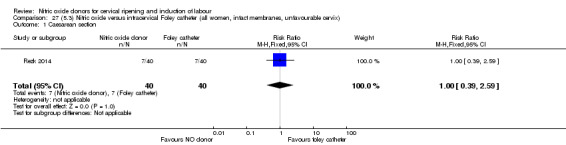
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Caesarean section.
27.2. Analysis.
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Oxyocin augmentation.
27.3. Analysis.
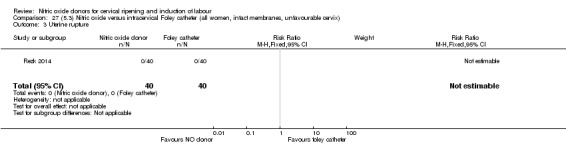
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Uterine rupture.
27.4. Analysis.
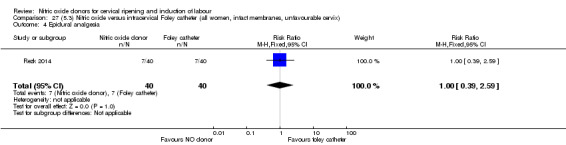
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Epidural analgesia.
27.5. Analysis.
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
27.6. Analysis.
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Meconium‐stained liquor.
27.7. Analysis.
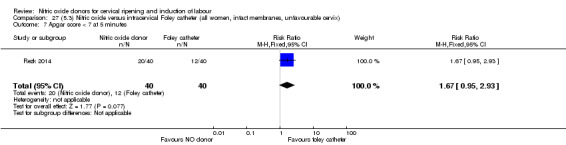
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
27.8. Analysis.
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
27.9. Analysis.
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting).
27.10. Analysis.
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
27.11. Analysis.
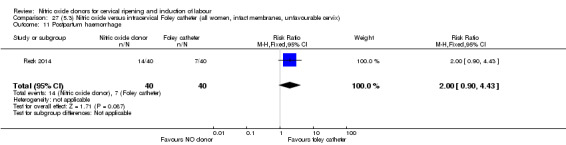
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Postpartum haemorrhage.
27.12. Analysis.
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Women not satisfied.
27.13. Analysis.
Comparison 27 (5.3) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia).
Comparison 28. (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Caesarean section | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 2 Oxyocin augmentation | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [1.17, 2.32] |
| 3 Uterine rupture | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.8 [0.23, 2.76] |
| 6 Meconium‐stained liquor | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.19, 21.18] |
| 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.67 [0.95, 2.93] |
| 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.5 [0.51, 12.14] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.33, 27.63] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.33 [0.99, 11.22] |
| 11 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.90, 4.43] |
| 12 Women not satisfied | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.75 [0.56, 5.51] |
| 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.16, 1.07] |
28.1. Analysis.
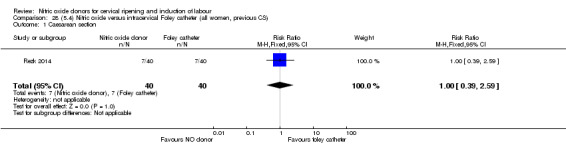
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 1 Caesarean section.
28.2. Analysis.
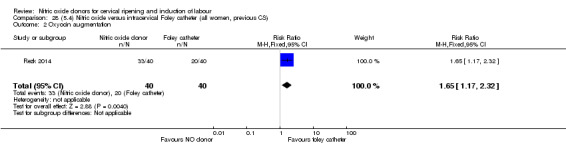
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 2 Oxyocin augmentation.
28.3. Analysis.
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 3 Uterine rupture.
28.4. Analysis.
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 4 Epidural analgesia.
28.5. Analysis.
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
28.6. Analysis.
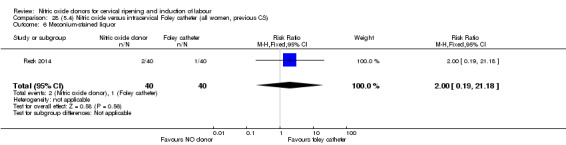
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 6 Meconium‐stained liquor.
28.7. Analysis.
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
28.8. Analysis.
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
28.9. Analysis.
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting).
28.10. Analysis.
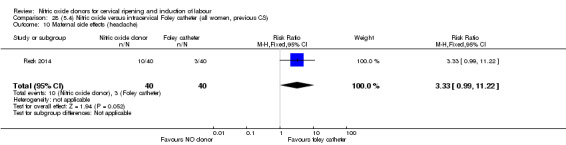
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
28.11. Analysis.
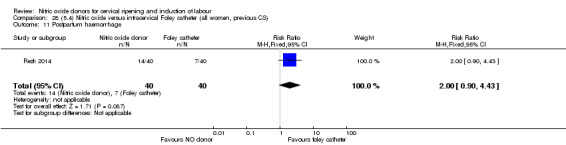
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 11 Postpartum haemorrhage.
28.12. Analysis.
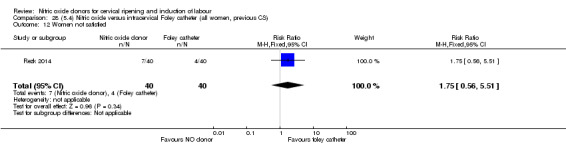
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 12 Women not satisfied.
28.13. Analysis.
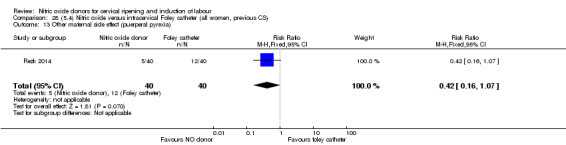
Comparison 28 (5.4) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous CS), Outcome 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia).
Comparison 29. (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Caesarean section | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 2 Oxyocin augmentation | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [1.17, 2.32] |
| 3 Uterine rupture | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.8 [0.23, 2.76] |
| 6 Meconium‐stained liquor | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.19, 21.18] |
| 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.67 [0.95, 2.93] |
| 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.5 [0.51, 12.14] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.33, 27.63] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.33 [0.99, 11.22] |
| 11 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.90, 4.43] |
| 12 Women not satisfied | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.75 [0.56, 5.51] |
| 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.16, 1.07] |
29.1. Analysis.
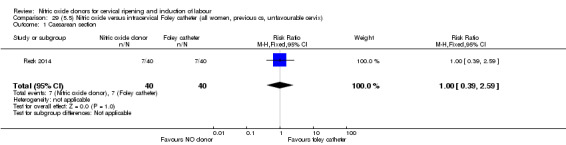
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Caesarean section.
29.2. Analysis.
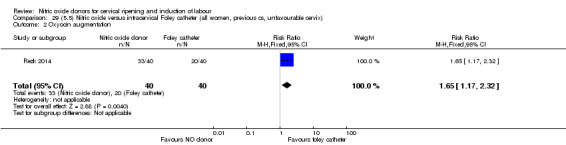
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Oxyocin augmentation.
29.3. Analysis.
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Uterine rupture.
29.4. Analysis.
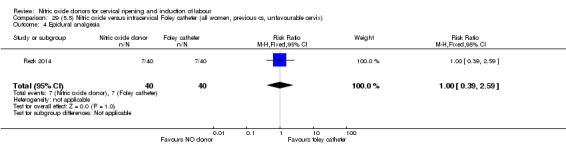
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Epidural analgesia.
29.5. Analysis.
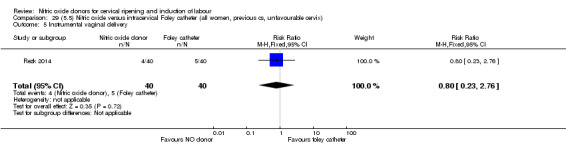
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
29.6. Analysis.
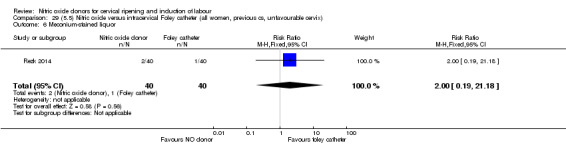
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Meconium‐stained liquor.
29.7. Analysis.
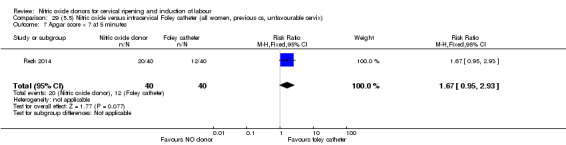
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
29.8. Analysis.
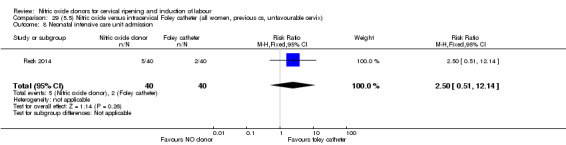
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
29.9. Analysis.
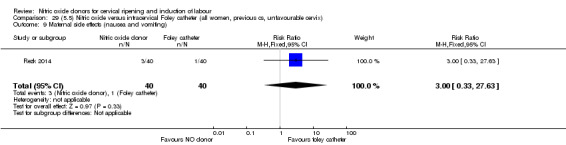
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting).
29.10. Analysis.
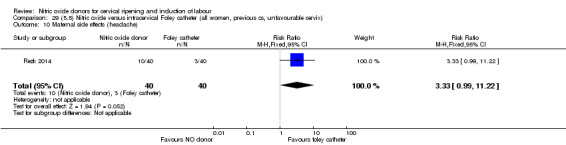
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
29.11. Analysis.
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Postpartum haemorrhage.
29.12. Analysis.
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Women not satisfied.
29.13. Analysis.
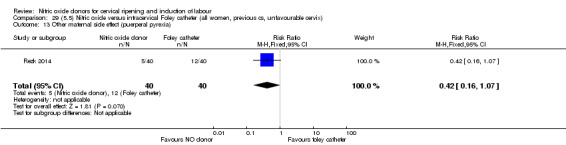
Comparison 29 (5.5) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia).
Comparison 30. (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix).
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Caesarean section | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 2 Oxyocin augmentation | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.65 [1.17, 2.32] |
| 3 Uterine rupture | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.0 [0.0, 0.0] |
| 4 Epidural analgesia | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.0 [0.39, 2.59] |
| 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.8 [0.23, 2.76] |
| 6 Meconium‐stained liquor | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.19, 21.18] |
| 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.67 [0.95, 2.93] |
| 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.5 [0.51, 12.14] |
| 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.0 [0.33, 27.63] |
| 10 Maternal side effects (headache) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 3.33 [0.99, 11.22] |
| 11 Postpartum haemorrhage | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 2.0 [0.90, 4.43] |
| 12 Women not satisfied | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.75 [0.56, 5.51] |
| 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia) | 1 | 80 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.42 [0.16, 1.07] |
30.1. Analysis.
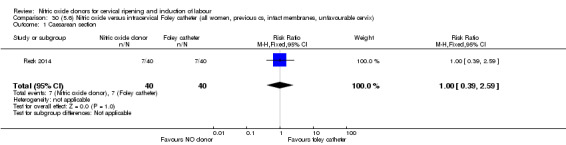
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 1 Caesarean section.
30.2. Analysis.
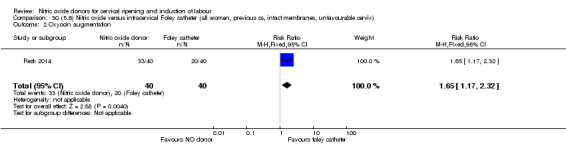
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 2 Oxyocin augmentation.
30.3. Analysis.
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 3 Uterine rupture.
30.4. Analysis.
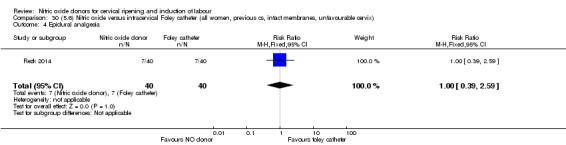
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 4 Epidural analgesia.
30.5. Analysis.
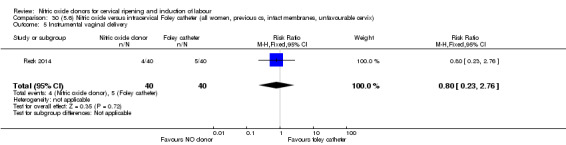
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 5 Instrumental vaginal delivery.
30.6. Analysis.
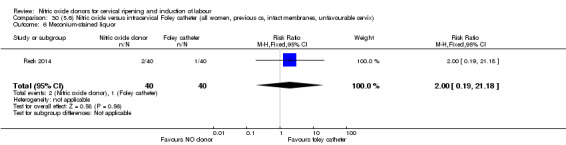
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 6 Meconium‐stained liquor.
30.7. Analysis.
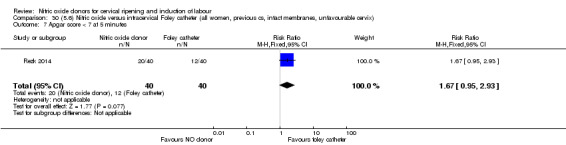
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 7 Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes.
30.8. Analysis.
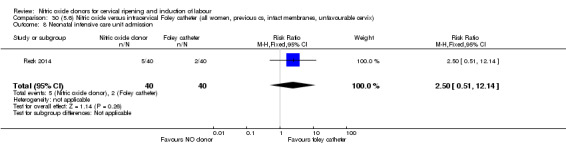
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 8 Neonatal intensive care unit admission.
30.9. Analysis.
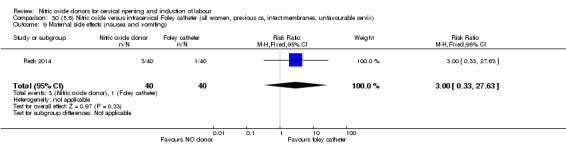
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 9 Maternal side effects (nausea and vomiting).
30.10. Analysis.
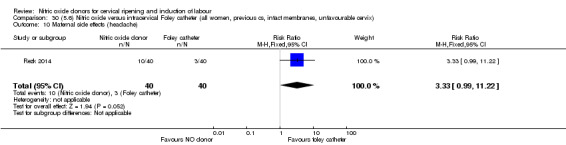
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 10 Maternal side effects (headache).
30.11. Analysis.
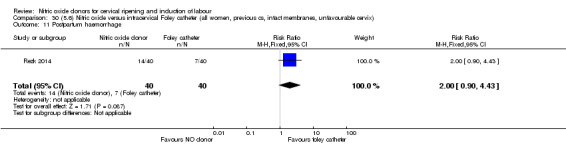
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 11 Postpartum haemorrhage.
30.12. Analysis.
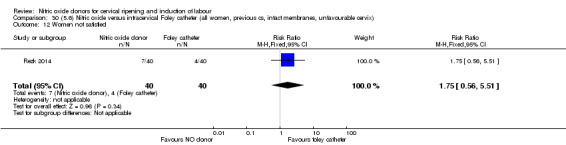
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 12 Women not satisfied.
30.13. Analysis.
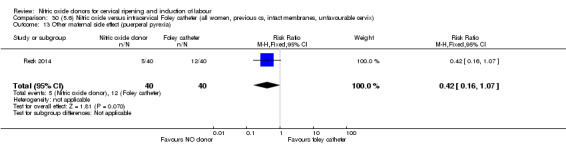
Comparison 30 (5.6) Nitric oxide versus intracervical Foley catheter (all women, previous cs, intact membranes, unfavourable cervix), Outcome 13 Other maternal side effect (puerperal pyrexia).
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Agarwal 2012.
| Methods | A single‐blind randomised placebo‐controlled trial in an outpatient setting. Study conducted between February 2010 to January 2011 at Safdarjung hospital, New Delhi, India. | |
| Participants | Study conducted on 200 postdate pregnant women with unfavourable cervix. Inclusion criteria: included all women with singleton pregnancy more than 36 weeks with Bishop score less than 6 and no uterine contractions. Exclusion criteria: included pregnant women with malpresentation, previous caesarean section, diabetes, hypertension/ PET, vaginal bleeding, ruptured membranes, oligohydramnios, IUGR, women with heart disease or any contraindication to receive ISMN such as allergy to the drugs, bronchial asthma, hypotension and palpitations. |
|
| Interventions | After recording a baseline Bishop score 200 participants were either given two 40 mg tablets of ISMN (100 women) or two, 40 mg tablets of pyridoxine as placebo (100 women). They were instructed to self‐administer at home, vaginally, 1 of the tablets at 9 AM and the other at 9 PM the same day, and to report to the hospital the next day at 9 AM for admission. Participants were also instructed to report immediately to the hospital if they had labour pains, vaginal bleeding or leakage, or decrease fetal movements. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: caesarean section, uterine hyperstimulation with and without FHR changes, cervix unfavourable after 12‐24 hours, oxytocin augmentation, postpartum haemorrhage and headache. Fetal: meconium‐stained liquor, Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes and NICU admission. |
|
| Notes | The study used 1 dose of 0.5 mg intracervical PGE2 in both ISMN and placebo groups if the Bishop score was < 6 on admission. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated sequence was used for randomisation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Open allocation sequence used. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | ITT was applied.100 women in ISMN group and 100 women in placebo group entered the study. 100 participants were included in the outcome analysis in each arm. No dropouts reported. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Single‐blind randomised control trial. Participants were blinded, but therapist were not blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
Bollapragada 2009.
| Methods | Double‐blind randomised controlled trial in an outpatient setting. Recruitment between March 2005 and December 2006 at Princess Royal Maternity Hospital, Glasgow. | |
| Participants | Women scheduled for admission for cervical ripening and labour induction. Inclusion criteria: included all of the following: nulliparity, singleton fetus, cephalic presentation, ≥ 37 completed weeks' gestation, modified Bishop score < 7, and willingness to self‐administer vaginal tablets. Exclusion criteria: included women < 16 years of age, those who needed delivery within the next 48 hours in the fetal or maternal interest or who had ruptured membranes. |
|
| Interventions | 350 were randomised. 177 were prescribed 40 mg ISMN tablets and 173 received placebo, with instructions to self‐administer the tablets vaginally at home at 48, 32 and 16 hours prior to scheduled time of admission. After admission to hospital, induction of labour was with vaginal prostaglandins until cervical ripening (described as Bishop score > 6) was achieved or 3 doses of prostaglandin tablets (3 mg each) were administered. Once the cervix was ripe fetal membranes were ruptured and oxytocin administered if required. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: elapsed time from admission to delivery, operative delivery rates (caesarean section and instrumental vaginal delivery), vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours, cervix unfavourable/unchanged at 12 to 24 hours, oxytocin augmentation, epidural analgesia, maternal side effects, postpartum haemorrhage, requirement for additional inpatient cervical ripening agents. various outcomes relating to maternal satisfaction. Neonatal: serious neonatal morbidity/perinatal death, meconium‐stained liquor, admission and duration of NICU admission, 5‐minute Apgar score of less than 7. |
|
| Notes | Detailed economic data also included. Protocol published previously. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Centrally‐generated randomisation schedule in permuted blocks of 4. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Pharmacy at Western Infirmary in Glasgow prepared identical treatment packs, labelled with relevant unique study number. Allocation via automated interactive telephone response service. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 47 in ISMN arm and 46 in placebo arm withdrawn after randomisation. Majority went into spontaneous labour. 11 withdrawals in total, 2 diagnosed with breech presentations and hence excluded. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Patients, therapists, outcome assessors and analysts blinded to allocation. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Patients, therapists, outcome assessors and analysts blinded to allocation. |
Bullarbo 2007.
| Methods | Double‐blind randomised controlled trial in an outpatient setting. Recruitment between November 2002 and April 2005, at the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Sahlgrenska University Hospital, Gothenberg, Sweden. | |
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria: uncomplicated pregnancy, singleton pregnancy, cephalic presentation, gestational age at least 42 weeks, Bishop score < 5, normal AFI > 5 cm, reactive fetal heart pattern, intact membranes. Exclusion criteria: regular uterine contractions, cardiorespiratory disease, history of headaches, history of alcohol abuse, intolerance to ISMN, serious disease defined as daily use of medication. |
|
| Interventions | 200 women randomised, 100 received vaginally‐administered ISMN, 40 mg and 100 received placebo tablet. Subsequently in women where regular contractions were not established an amniotomy was performed or 1 mg of prostaglandin given. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: caesarean section, maternal side effects, postpartum haemorrhage. Neonatal: Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes, NICU admission. Non‐prespecified: cervix unfavourable after outpatient ripening. |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random number tables. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed sequentially numbered envelopes. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Limited reporting in this area. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Suitable dummies used. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
Chanrachakul 2000.
| Methods | Randomly allocated by computer programme. Inpatient setting. Recruitment between January 1999 and September 1999 in Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand. | |
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria: singleton pregnancy, cephalic presentation, Bishop score < 6, reactive non‐stress test. Exclusion criteria: fetal malpresentations, previous scarred uterus or contraindications to receive nitric oxide donors or prostaglandins. |
|
| Interventions | 112 women randomised, 110 analysed. 54 women received vaginal GTN (500 µg) versus 56 women who received vaginal PGE2 (3 mg). Both groups reviewed at 3, 6,12 and 24 hours. Both medications repeated after 6 hours if Bishop score < 6. At 24 hours (or earlier if possible) both groups had forewater amniotomy and oxytocin. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: uterine hyperstimulation both with and without FHR changes, caesarean section, maternal headache, postpartum haemorrhage, serious maternal complications. Neonatal: Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes, NICU admission. |
|
| Notes | Data also presented within abstract from FIGO 2000. Also early data from study presented within Chanrachakul et all 2000, but not mentioned in final report. May represent salami slicing/duplicate publication. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details given. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 2 women excluded due to incomplete data. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Limited reporting in this area. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Limited reporting in this area. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Limited reporting in this area. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Outcome assessor unaware of allocation. |
Chanrachakul 2002.
| Methods | Randomly allocated by computer‐generated number. Inpatient setting. Recruitment between December 1999 and September 2000 in Ramathibodi Hospital, Mahidol University, Thailand. | |
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria: singleton pregnancy, cephalic presentation, Bishop score < 6, reactive non‐stress test. Exclusion criteria: fetal malpresentations. contraindications to receive nitric oxide donors or prostaglandins. |
|
| Interventions | 110 women randomised, 107 analysed. 55 women received vaginal ISMN tablet (40 mg) versus 52 women who received vaginal misoprostol (50 µg). Both groups reviewed at 6, 12 and 24 hours. At 24 hours (or earlier if possible) both groups had forewater amniotomy and oxytocin. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: uterine hyperstimulation both with and without FHR changes, caesarean section, cervix unfavourable/unchanged after 12 to 24 hours, oxytocin augmentation, maternal nausea or headache and postpartum haemorrhage. Neonatal: Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes, NICU admission. |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details given. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 2 sets of incomplete data and 1 woman withdrawn due to an undiagnosed breech presentation. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No mention of suitable dummies used. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Outcome assessor not aware of treatment allocation. |
Guha 2015.
| Methods | An inpatient single‐centre randomised trial carried out at Rajshahi College Hospital, Bangledesh between January 2008 and June 2009. | |
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria: nulliparous, singleton, term pregnancy, intact membranes, Bishop score 4 or less, cephalic presentation. Exclusion criteria: fetal compromise of sufficient severity, cephalopelvic disproportion, non‐cephalic presentation. |
|
| Interventions | 200 women randomised. 100 women received vaginal 40 mg IMN tablets and 100 women received 50 mcg misoprostol (1/4 of 200 mcg tablet) administered into posterior vaginal fornix. All women were assessed every 6 hours and re‐administered the medication if Bishop score was not more than 6 or labour pains were established for a maximum of 4 doses. | |
| Outcomes |
Maternal outcomes: maternal demographics, adverse outcomes, mode of delivery, maternal complications (hyperstimulation, tachysystole, fever, nausea and vomiting, headache, hypotension, postpartum atony), change in Bishop score after medication. Neonatal outcomes: general neonatal outcomes (not clearly specified). |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | 'Randomly divided' but no detail given. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details given. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Outcomes do not appear to be prespecified in text. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No details given. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No details given. |
Haghighi 2013.
| Methods | A randomised double‐blind clinical trial, conducted between January 2009 and November 2010, in Shahid Akbar‐abadi Obstetrics and Gynaecology Centre, a University hospital in Tehran, Iran. | |
| Participants | 136 women scheduled for induction pf labour were recruited for the study. Inclusion criteria: primiparous, singleton, term or post‐term pregnant women with Bishop score < 5 and cephalic presentation were included in the study. Exclusion criteria: EFW > 4 kg, oligohydramnios, IUGR, non reassuring FHR, ruptured membranes, any contraindication to prostaglandins or ISDN, BMI > 30, placenta praevia, vaginal bleeding, uterine contractions, suspected chorioamnionitis. |
|
| Interventions | 132 participants were randomly assigned to either misoprostol group or ISDN. 64 in misoprostol group and 66 in ISDN group. 2 women in misoprostol group had caesarean section on request and hence were excluded. Women in misoprostol group had 25 mcg PGE1 and women in ISDN group had 40 mg ISDN, maximum of 2 doses were inserted vaginally after 4 hours if the Bishop score was < 8 or uterine contractions < 3 in 10 min with duration of < 40 seconds. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: changes in Bishop score after the drug administration, need for stimulation, time from initial dose to active phase of labour and to delivery, method of delivery, complications of ISDN. Fetal: 1 and 5 min Apgar score < 7. |
|
| Notes | After 2 doses of the drug, oxytocin was used and women had caesarean section delivery if labour not established 6 hours after oxytocin infusion. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Block randomisation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Numbered sealed opaque envelopes were used. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | The study drop outs were explained and participants were analysed in their respective groups. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Double‐blind trial. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Double‐blind trial. |
Haghighi 2015.
| Methods | Non‐blinded parallel randomised controlled trial conducted on the midwifery ward of Shahid Akbar Abadi Hospital, Tehran, Iran. Used block randomisation. | |
| Participants | 149 nulliparous women were recruited to this study Inclusion criteria: nulliparous women, singleton, cephalic presentation, gestation over 40 weeks and 4 days, Bishop score less than 5, no contraindications for ISDN, no previous caesarean section, no uterine scar, no underlying disease, not required to have reactive nonstress test or normal biophysical profile ultrasound. |
|
| Interventions | 149 nulliparous women were randomised into 3 groups: 50 received 40 mg ISDN, maximum 2 doses inserted vaginally after 4 hours, 49 received 20 mg ISDN orally, maximum 2 doses 4 hourly, 50 were the control and received no medication. | |
| Outcomes | Suggested to be Bishop score change but prespecified outcomes are not explicit. | |
| Notes | Monitiored for 4 hours following administration of medication then discharged home for 24 hours. We combined the oral and vaginal ISDN groups to create a single pair‐wise comparison with the control. |
|
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | 'selected by simple random sampling method' |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details given. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Total numbers of groups are not given in the results tables. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Outcomes not prespecified. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | None noted. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | No blinding. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | No blinding. |
Kadian 2008.
| Methods | Prospective study. Post Graduate Institute of Medical Sciences, India. Setting unclear. | |
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria: primigravidae, singleton pregnancy, cephalic presentation unfavourable cervix. Exclusion criteria: unclear. |
|
| Interventions | 400 women randomised 200 received intracervically administered ISDN, 40 mg and 200 received 0.5 mg PGE2 vaginal gel, which was repeated after 6 hours if Bishop score remained low. Subsequently oxytocin was started after 12 hours in both groups. |
|
| Outcomes | Maternal: vaginal delivery not achieved in 24 hours, caesarean section. | |
| Notes | Limited data extraction as report in abstract format only. Authors contacted. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | 'randomised.' |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details given. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Full report awaited. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Full report awaited. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Full report awaited. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No mention if suitable dummies used. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No mention if suitable dummies used. |
Krishnamurthy 2015.
| Methods | Randomly allocated using computer generated random number table. Allocation concealed using sequentially numbered opaque envelopes.Inpatient setting in India. | |
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria: primigravida, singleton, cephalic presentation, 38 weeks gestation or more, modified Bishop score of less than 6. Exclusion criteria: under 18 years old, uterine scar, ruptured membranes, uterine contractions, medical complications, contraindications to vaginal delivery or isosorbide mononitrite therapy. |
|
| Interventions | 100 recruited, 100 randomised into 2 groups: 50 women received 40 mg isosorbide mononitrite inserted vaginally into posterior fornix, second dose given 12 hours later if Bishop score still less than 6, 50 received 40 mg placebo (pyridoxine) administered the same way as intervention. | |
| Outcomes |
Maternal: change in modified Bishop Score at 12 and 24 hours after drug insertion, time from initiation of cervical ripening till delivery, labour duration, need of oxytocin augmentation, mode of delivery, uterine hyperstimulation, tachysystole, headache, tachycardia, palpitations, hypotension, nausea and vomiting, proportions of unripe cervix (Bishop Score < 6) at 24 hr after first drug insertion. Neonatal: Apgar scores < 7 at 1 min and 5 min, fetal distress, NICU admissions, length of neonatal stay in NICU. |
|
| Notes | Absense of headache, nausea, vomiting and palpitations only mentioned referring to IMN group in text. No side effects mentioned for control group. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomly allocated into 2 groups using a computer‐generated random number table. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Opaque, sequentially numbered envelopes |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | 'drug insertion was done by a senior resident who was not part of the investigation'. Dummy used as placebo therefore assuming patients blinded as well. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not stated. |
Movahed 2016.
| Methods | Randomised clinical trial with 3 treatment arms. Recruitment period unclear, conducted at University Hospital in Qazvin, Iran. | |
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria: nulliparous women, 39 weeks gestation or over with Bishop score less than 4. Exclusion criteria: vaginal bleeding, membrane rupture, active genital herpes infection, history of myomectomy, non‐reassuring fetal heart status, history of heart disease. |
|
| Interventions | 75 women randomised into 3 groups: 25 women received ISMN, 25 received transvaginal catheter and 25 received Laminaria. | |
| Outcomes |
Maternal: interval between time of induction and cervical ripening, interval between oxytocin administration and full cervical dilatation, duration of second and third labour phases, mode of delivery, maternal complications. Neonatal: complications. |
|
| Notes | Non‐English language. Laminaria not eligible as an intervention for this review. No data suitable for analysis. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Participants 'randomly divided' by choosing colourful cards. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details given. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No mention of suitable dummies used. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | No details given. |
Nicoll 2001.
| Methods | Randomly allocated using random number tables in permuted blocks of 12. Concealment sealed, opaque sequentially numbered envelopes. Inpatient setting. Recruitment between August 1998 and July 1999 Dept of Obstetrics and Gynecology, University of Glasgow and Glasgow Royal Maternity Hospital. | |
| Participants |
Inclusion criteria: not stated. Exclusion criteria: Bishop score > 7, multiple pregnancy, history of antepartum haemorrhage, pregnancy‐induced hypertension or pre‐eclampsia, breech presentation, fetal abdominal circumference < 5th percentile, AFI < 5th percentile, history of cardiorespiratory disease, history of headache. |
|
| Interventions | 38 recruited, 36 women randomised into 3 groups 13 women received vaginally‐administered ISMN (20 mg), 11 women received vaginally‐administered ISMN (40 mg), 12 women received a vaginal examination only. Women who failed to achieve a Bishop score of > 7, 360 minutes after treatment allocation underwent an amniotomy. The women filled out a symptom questionnaire and had their cervical score assessed pretreatment administration and 360 minutes after administration. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: caesarean section, instrumental vaginal delivery and maternal side effects (headache). Neonatal: NICU admission. |
|
| Notes | Only data comparing the 40 mg ISMN group to placebo were analysed. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Randomly allocated using random number tables in permuted blocks of 12. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed, opaque sequentially numbered envelopes. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | This was a double‐blinded study and independent observer administrated the treatment. The assessment of the cervix was carried out by the same assessor to reduce individual variation. The patient was not aware of the treatment given. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | The assessment of the cervix was carried out by the same assessor to reduce individual variation. |
Osman 2006.
| Methods | Double‐blind randomised controlled trial in an inpatient setting. Recruitment between September 2001 and November 2003 at Princess Royal Maternity Hospital, Glasgow. | |
| Participants | Women scheduled for admission for cervical ripening and labour induction. Inclusion criteria: included all of the following: nulliparity, singleton fetus, cephalic presentation, ≥ 38 completed weeks' gestation, modified Bishop score < 6, and normal admission CTG. Exclusion criteria: included women < 16 years of age, ≥ 1 birth at > 23 weeks' gestation, previous caesarean section, those who needed delivery within the next 48 hours in the fetal or maternal interest or who had ruptured membranes. |
|
| Interventions | 400 were randomised. 200 were prescribed 40 mg ISMN tablets and 200 received 2 mg vaginal PGE2. After 24 hours if the Bishop score was < 6 then a 1 mg 'rescue' dose of PGE2 gel was given. | |
| Outcomes |
Maternal: uterine hyperstimulation with FHR changes, caesarean section, epidural analgesia, instrumental vaginal delivery, maternal side effects (nausea and headache). Neonatal: Apgar score at 5 minutes, NICU admission. |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated in permuted blocks. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Centrally‐dispensed sealed opaque sequentially numbered envelopes. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Patient and outcome assessors unaware of allocation. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Patient and outcome assessors unaware of allocation. |
Perche 2009.
| Methods | Double‐blind randomised controlled trial (setting unclear). Recruitment period not stated, at Urquinana Central Hospital, Maracaibo, Zuilia State, Venezuela. | |
| Participants | Women scheduled for admission for cervical ripening and labour induction. Inclusion criteria: included all of the following: singleton fetus, term pregnancies, modified Bishop score < 6, and not in labour. Exclusion criteria: Bishop score > 7, ruptured membranes, chorioamnionitis, bleeding. |
|
| Interventions | 60 were randomised. 30 were prescribed 40 mg ISMN tablets and 30 received 50 mcg vaginal misoprostol. These medications were repeated every 4 hours for 24 hours. no further details of subsequent treatments were given. | |
| Outcomes | Oxytocin augmentation, Apgar score < 7 at 5 minutes, maternal side effects. | |
| Notes | Original trial report in Spanish and translated prior to extraction. The authors are grateful to Luciana Figuera for her translation. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random number tables. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed envelopes. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Limited reporting unable to make judgement. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Limited reporting unable to make judgement. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Limited reporting unable to make judgement. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Limited reporting unable to make judgement. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Limited reporting unable to make judgement. |
Rameez 2007.
| Methods | Double‐blind randomised controlled trial (stratified by parity) in an inpatient setting. Recruitment between August 2003 and April 2004 at the University Obstetric Unit, Teaching Hospital, Galle, Sri Lanka. | |
| Participants | Women scheduled for admission for cervical ripening and labour induction. Inclusion criteria: included all of the following: uncomplicated singleton fetus, cephalic presentation, ≥ 41 completed weeks' gestation, modified Bishop score < 5. Exclusion criteria: any medical or obstetric problems or contraindications to ISMN. |
|
| Interventions | 156 were randomised. 78 were prescribed 60 mg ISMN tablets and 78 received placebo (vitamin C) re‐examined after 48 hours. If cervix favourable (Bishop score ≥ 7) then they were induced the same day with amniotomy and oxytocin. if unfavourable then an intracervical extra amniotic Foley catheter was used to induce further ripening. |
|
| Outcomes | Maternal: caesarean section, additional induction agents used. | |
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Block randomisation (stratified by parity). |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed, opaque sequentially numbered envelopes. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Outcome assessor unaware of allocation. Suitable dummies used so patient blinded as well. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Outcome assessor unaware of allocation. Suitable dummies used so patient blinded as well. |
Razaq 2011.
| Methods | Prospective randomised control trial carried out at Al‐Elwiya Maternity Teaching Hospital, Baghdad. | |
| Participants | 150 pregnant women were randomised. Inclusion criteria: primiparous women, singleton fetus with uncomplicated pregnancy, admitted for post‐dates induction. Exclusion criteria: obstetric, gynaecological or medical problems. |
|
| Interventions | Out of 150 women randomised, 75 received 40 mg IMN vaginally in the form of two 20 mg tablets and 75 received 50 mcg misoprostol vaginally. The process was repeated in the misoprostol group every 6 hours if the Bishop scores did not improve for a maximum of 3 doses. | |
| Outcomes |
Maternal: delivery interval, mode of delivery, adverse effects. Neonatal: general outcomes (not prespecified). |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | 'Randomised', no further details given. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | High risk | Outcomes not clearly specified in the text. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Unclear. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Unclear. |
Rezk 2014.
| Methods | A single‐centre balanced randomised parallel group study carried out at Menoufia University Hospital, Egypt between January 2013 and January 2014 in an outpatient setting. | |
| Participants | 80 pregnant women with previous 1 caesarean section were randomised. Inclusion criteria: women with 37 weeks and beyond gestation, intact membranes, Bishop score less than 6, reactive non‐stress test, normal umbilical artery dopplers indices, absence of labour and willingness to participate were included. Exclusion criteria: women with intrauterine fetal death, twin pregnancy, polyhydramnios, placenta praevia, severe anaemia, severe hypertension, uncontrolled diabetes, coagulopathy and any contraindication to labour induction were excluded from the study. |
|
| Interventions | Out of 80 women who were recruited for the study, 40 had Foley catheter inserted (control) and 40 received single‐dose 40 mg ISMN vaginally. Foley catheter was either removed at 12 hours or expelled spontaneously. Women in ISMN group were examined every 3 hours for the next 24 hours. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: caesarean section, oxytocin augmentation, uterine rupture, epidural analgesia, instrumental delivery, nausea and vomiting, headache, puerperal pyrexia and women not satisfied with the treatment. Fetal: meconium‐stained liquor, Apgar score less than 7 at 5 minutes and NICU admission. |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated sequence was used for randomisation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Unclear. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Blinding of the patient and therapist is not feasible. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not feasible. |
Romero‐Gutierrez 2011.
| Methods | Double‐blind randomised controlled trial using random number tables. Trial conducted at Mexican Social Security Institute's High speciality medical unit number 48 in Leon, Guanajuato. Patients were recruited between February 1 to August 31, 2009. | |
| Participants | Total number of participants in the study were 66. Divided in to intervention and control group. Each group had 33 participants. Inclusion criteria: women with singleton pregnancy, cephalic presentation at 41 weeks and 6 days gestation with Bishop score less than 6 were recruited for the study. Exclusion criteria: women with acute fetal distress, cephalopelvic disproportion, allergy to Isosorbide or dinoprostone, cardiothoracic condition, placenta praevia, oligohydramnios with AFI < 5, caesarean section and premature membrane rupture were excluded. |
|
| Interventions | 66 were randomised. 33 received 0.5 mcg of dinoprostone (control group) and another 33 received 20 mg of ISDN (experimental group). In both groups the medication was applied vaginally at 6 hours intervals for a maximum of 3 doses. | |
| Outcomes |
Maternal: length of labour and caesarean section. Fetal: meconium liquor, NICU admission, Apgar score to the minute and at 5 minutes. |
|
| Notes | Spanish paper. Available information limited by language. Cost‐analysis for both the drugs administered. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random number tables were used. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No information available. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Article did not indicate whether any patients withdrew or dropped out. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | No information available. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Limited information. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Patients were blinded but it is unclear if therapist was blinded as well. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Unclear. |
Schmitz 2014.
| Methods | Double‐blind multicentre randomised controlled trial conducted in 11 French university hospital referral maternity units. Trial conducted between June 25, 2009, and November 14, 2012 in an outpatient setting. | |
| Participants | Total of 1373 women were randomised and included in the trial. 11 women were later excluded as they did not meet the inclusion criteria. ITT analysis was applied. Inclusion criteria: nulliparous women with singleton pregnancy, cephalic presentation, intact membranes, Bishop score less than 6 and at 41 + 0 weeks of gestation were included in the study. Exclusion criteria: women less than 18 years, with no social security coverage, on antihypertensive treatment, fetal death and known to have contraindication to ISMN were excluded from the study. |
|
| Interventions | 1373 women were randomised into 2 groups. 684 women were given placebo and 678 women were given 40 mg ISMN. 11 women were excluded and ITT analysis was applied. In each group women received 3 doses of the medication vaginally at 48 hours interval. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: caesarean section, serious maternal morbidity or death, oxytocin augmentation, instrumental vaginal delivery, maternal side effects, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, headache, postpartum haemorrhage, severe postpartum haemorrhage and women not satisfied with the treatment. We have assumed that the data of severe postpartum haemorrhage are included in the postpartum haemorrhage and hence have only considered postpartum haemorrhage data. Fetal: serious neonatal morbidity or perinatal death and Apgar score less than 7 at 5 minutes. We did not include the data on NICU as the trial only mentioned the number of NICU admissions for 5 days or more and data for all admissions are not available. |
|
| Notes | ||
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated sequence was used for randomisation in permuted blocks. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Central randomisation: a web‐based application was used to assign women and the allocation was available to any of the research team. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Low risk. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Patient and therapist both blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Outcome assessor and analyst blinded. |
Sharma 2005.
| Methods | 'Randomised' Inpatient setting. Recruitment between November 2001 and November 2003, Deptartment of Obstetrics and Gynecology, at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi. | |
| Participants | Women scheduled for admission for cervical ripening and labour induction. Inclusion criteria: included all of the following: nulliparity, singleton fetus, modified Bishop score < 6. Exclusion criteria: previous caesarean section and ruptured membranes. |
|
| Interventions | 65 were randomised into 3 groups. 21 were prescribed 500 mcg GTN (misoprostol) tablets, 21 received 0.5 mg intracervical PGE2 and 23 received 50 mcg of vaginal misoprostol. Women were reassessed at 6 hours and if possible amniotomy was performed. If Bishop score < 6 then further dose of same drug was given. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: uterine hyperstimulation with and without FHR changes, caesarean section, cervix unfavourable at 12 to 24 hours, oxytocin augmentation, instrumental vaginal delivery and maternal side effects (headache). Neonatal: perinatal death, serious neonatal morbidity or death. |
|
| Notes | 2 patients (1 from GTN and 1 from misoprostol group excluded due to being delivered by caesarean section after first dose of medication. Not clear if included in final data on caesarean section. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | "Randomised." |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | No details given. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | May be concern over 2 post randomisation exclusions. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not stated. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Not stated. |
Soliman 2013.
| Methods | A prospective double‐blind randomised clinical trial conducted in Tanta University Hospital, Egypt between April 2010 and March 2012. | |
| Participants | 196 women participated in this study. Inclusion criteria: nulliparous women, gestational age of at least 37 weeks, with singleton fetus and vertex presentation, Bishop score less than 6 and intact membranes, reactive non‐stress test, normal umbilical artery doppler indices, absence of labour and willingness to participate were included in the study. Exclusion criteria: women excluded from study were multiparous, with multiple pregnancy, fetal malpresentation, premature rupture of membranes, regular uterine contractions, major cephalopelvic disproportion and with contraindications to ISMN or misoprostol. |
|
| Interventions | 200 women were randomised into 3 groups and 196 women were analysed. 4 dropouts noted, 2 each in ISMN and misoprostol group as they did not meet the inclusion criteria. 65 women received 50 mcg of misoprostol vaginally. 65 women received 40 mg ISMN and 66 women had both 40 mg ISMN and 50 mcg misoprostol. 3 doses of the medication was inserted vaginally at 0, 6 and 12 hours. |
|
| Outcomes |
Maternal: caesarean section, uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes, oxytocin augmentation, epidural analgesia, analgesia required, nausea and vomiting, headache and postpartum haemorrhage. Fetal: meconium‐stained liquor, Apgar score less than 7 in 5 minutes and NICU admission. |
|
| Notes | In this review we have not used the combination treatment data because it is a complex intervention. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Computer‐generated sequence used for randomisation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sealed, opaque and sequentially numbered envelopes were used. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Unclear. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Patient and therapist were blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Unclear. |
Vidanagamage 2011.
| Methods | A double blind randomised controlled trial conducted between March 2006 and April 2007 at the University Obstetic Unit, Teaching Hopital Mahamodara Galle, Sri Lanka. The study was conducted an inpatient setting. | |
| Participants | Women with post‐term pregnancy and unfavourable cervix. Incusion criteria: singleton pregnancy with cephalic presentation, gestation between 40 weeks + 5 days and 41 weeks and Bishop score < 5. Exclusion criteria: women with any medical or obstetrics problems and with any contraindication to the use of ISMN were excluded from the study. |
|
| Interventions | 156 women were recruited to the study and randomised into 3 groups. 52 women in group A received ISMN 40 mg tablets, 52 women in group B received 60 mg ISMN‐SR tab, and rest 52 women in group C received 100 mg vitamin C tablets. | |
| Outcomes |
Maternal: changes in the mean Bishop score at 6 hours and 48 hours, caesarean section rate, uterine hyperstimulation without FHR changes. Fetal: mean 5 minute Apgar score of babies delivered within 72 hours of the intervention. |
|
| Notes | Randomised controlled trial with 3 study arms. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Stratified block randomisation. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Sequentially numbered sealed opaque envelopes. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Other bias | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | High risk | Therapist aware of the intervention given. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
Yazdizadeh 2013.
| Methods | A randomised double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial conducted in Sina Hospital (an education hospital in Ahvaz, Iran) between June to October 2010. Trial was conducted in an outpatient setting. | |
| Participants | 90 primiparous women presenting to the hospital with any sign of labour were recruited for the study. Inclusion criteria: primiparous women, between age 18‐35 years, Bishop score < 6, BMI between 19.8‐26, cephalic presentation, singleton fetus, normal stress test or biophysical profile in last 48 hours and gestation age of 40‐42 weeks. Exclusion criteria: women with headache, alcohol abuse, polyhydramnios, placenta praevia or abruption and with any contraindication to induction of labour were excluded from the study. |
|
| Interventions | 90 women recruited in the study were randomised into 2 groups. ISMN group received 2 doses of 40 mg ISMN vaginally at 0 and 12 hours. The other group received placebo tablets vaginally at 0 and 12 hours. | |
| Outcomes |
Maternal: changes in Bishop score, duration between drug administration to active phase of labour, induction to delivery interval, amount of oxytocin used, length of second and third stages of labour and caesarean section rates. Fetal: Apgar scores at 1st and 5th minute after birth. |
|
| Notes | This trial recruited women coming with signs of labour. | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Low risk | Random number tables. |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Low risk | Coded drug boxes. |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | 10 dropouts from the study not explained. |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Unclear risk | Unclear. |
| Other bias | Unclear risk | Unclear. |
| Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Both patient and therapist blinded. |
| Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias) All outcomes | Low risk | No evidence to the contrary. |
AFI: amniotic fluid index BMI: body mass index CTG: cardiotocograph EFW: estimated fetal weight FHR: fetal heart rate GTN: glyceral trinitrate ISDN: isosorbide dinitrate ISMN: isosorbide mononitrate ITT: intention‐to‐treat IUGR: intrauterine growth restriction mcg: microgram mg: milligram NICU: neonatal intensive care unit PET: pre‐eclamptic toxaemia PGE2: prostaglandin E2
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Abdellah 2011 | This study compared used complex intervention. An ISMN and misoprostol combination was compared against placebo and misoprostol combination. Hence was excluded. |
| Ahmed 2014 | This study was excluded as there were no extractable data. It has not been possible to contact the authors for clarification. |
| Bates 2003 | Study outcome measures relate to pharmacokinetic characteristics (serum concentration) of NO donor (ISMN) administration, rather than to clinical outcomes. |
| Collingham 2010 | Study intervention involves the use of ISMN with or without oral misoprostol. Hence as a complex intervention is excluded from review. |
| Ekerhovd 2003 | Study setting inappropriate. Participants received NO donor (ISMN) before elective caesarean section rather than for the indication of post‐term pregnancy and thus induction of labour. |
| El‐Khayat 2016 | Randomised trial comparing misoprostol with intracervical Foley catheter plus NO donor (IMN). Complex intervention which does not allow direct comparison for NO donor efficiency. |
| Habib 2008 | Randomised trial comparing ISMN to placebo. Subsequent treatment was dependent on Bishop score and if less than 6 the patients received up to 3 doses of vaginal PGE2 (3 mg) if more than 6 patients received an amniotomy and intravenous oxytocin. Hence intervention is complex and it is not possible to separate out those women who did or did not have prostaglandins in addition to oxytocin. |
| Helal 2004 | The published study has large sections that appears to be similar to a previous paper (Nicoll et al 2000: study ID 11517) which is already included in our review. In particular the entire introduction section, large sections of the methods, and parts of the comments section does not appear to be original work. |
| Moghtadaei 2007 | Study intervention involved use of ISMN with concurrent oxytocin compared to extra‐amniotic saline as complex intervention is excluded from review. |
| Nunes 2006 | Randomised trial comparing GTN (500 micrograms) with concomitant vaginal PGE2 (2 mg) to GTN alone. Hence excluded as is a complex intervention. |
| Vaisanen‐Tommiska 2008 | The primary focus of this study is to examine NO levels. No relevant data are extractable. |
| Wolfler 2006 | Study comparison inappropriate for review criteria. Study compared NO donor (ISMN) and PGE2 (dinoprostone) to PGE2 (dinoprostone) alone. This study design does not allow a direct comparison for NO donor efficacy. |
| Ziard 2012 | Randomised trial comparing 2 regimens of ISMN administration which is an inappropriate comparison for this review. |
GTN: glyceral trinitrate ISMN: isosorbide mononitrate NO: nitric oxide PGE2: prostaglandin E2
Characteristics of studies awaiting assessment [ordered by study ID]
Ghanaie 2013.
| Methods | |
| Participants | |
| Interventions | |
| Outcomes | |
| Notes | Non‐English language ‐ in Farsi. Awaiting translation. |
Differences between protocol and review
We have re‐structured the comparisons to make the ‘all women’ comparisons sequential and re‐ordered outcomes to put the five primary outcomes first, followed by the secondary outcomes in the order stated in the methods text. A 'Summary of findings' table has been incorporated for this update.
In more recent reviews and updates the following outcomes have been added:
28. neonatal infection; 29. neonatal antibiotics; 30. chorioamnionitis; 31. endometritis; 32. maternal antibiotics.
In addition, in view of the nature of the trials and the intervention studied, we have examined some additional outcomes in this review. These include: 33. additional induction agents required; 34. initiation of cervical ripening to delivery interval (in days).
Contributions of authors
Tony Kelly (TK) completed the initial review of baseline evidence and drafted the text of the original protocol and review. For the purposes of this update Arpita Ghosh (AG) has been the main author and has worked alongside TK and Katherine Lattey (KL). All three authors reviewed all trials and judged suitability and inclusion. All three authors carried out data extraction and resolved any discrepancies by discussion. The final review was drafted by AG, TK and KL.
Declarations of interest
Arpita Ghosh: none known.
Katherine R Lattey: none known.
Anthony J Kelly: none known.
New search for studies and content updated (no change to conclusions)
References
References to studies included in this review
Agarwal 2012 {published data only}
- Agarwal K, Batra A, Dabral A, Aggarwal A. Evaluation of isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening prior to induction of labor for postdated pregnancy in an outpatient setting. International Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2012;118(3):205‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bollapragada 2009 {published data only}
- Bollapragada S, Mackenzie F, Norrie J, Petrou S, Reid M, Greer I, et al. IMOP: randomised placebo controlled trial of outpatient cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) prior to induction of labour ‐ clinical trial with analyses of efficacy, cost effectiveness and acceptability. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth 2006;6:25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollapragada SS, MacKenzie F, Norrie J, Petrou S, Reid M, Greer IA, et al. Randomized placebo controlled trial of outpatient cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) prior to induction of labour ‐ clinical trial with analyses of efficacy, cost effectiveness and acceptability. The IMOP study [abstract]. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2007;27(Suppl 1):S22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollapragada SS, MacKenzie F, Norrie JD, Eddama O, Petrou S, Reid M, et al. Randomised placebo‐controlled trial of outpatient (at home) cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate (IMN) prior to induction of labour‐clinical trial with analyses of efficacy and acceptability. The IMOP study. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2009;116(9):1185‐95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eddama O, Petrou S, Schroeder L, Bollapragada SS, Mackenzie F, Norrie J, et al. The cost‐effectiveness of outpatient (at home) cervical ripening with isosorbide mononitrate prior to induction of labour. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2009;116(9):1196‐203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman J. Pharmacokinetics of nitric oxide donors administered per vaginam in the third trimester of pregnancy. National Research Register (www.controlled‐trials.com) (accessed 26 July 2001).
- Reid M, Lorimer K, Norman JE, Bollapragada SS, Norrie J. The home as an appropriate setting for women undertaking cervical ripening before the induction of labour. Midwifery 2011;27:30‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bullarbo 2007 {published data only}
- Bullarbo M, Eriksson O, Andersch B, Granstrom L, Norstrom A, Erkerhovd E. Outpatient vaginal administration of the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening and labor induction postterm: a randomized controlled study. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2007;196:50.e1‐50.e5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullarbo M, Norstrom A, Andersch B, Ekerhovd E. Isosorbide mononitrate induces increased cervical expression of cyclooxygenase‐2, but not of cyclooxygenase‐1, at term. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology 2007;130(2):160‐4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chanrachakul 2000 {published data only}
- Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y, Punyavachira P. Potential efficacy of nitric oxide for cervical ripening on pregnancy at term. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2000;71:217‐9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y, Punyavachira P. Randomised comparison of glyceryl trinitrate and prostaglandin E2 for cervical ripening at term. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2000;96:549‐53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanrachakul B, Herbutya Y. Phase II to determine the potential efficacy and safety of nitric oxide for cervical ripening in pregnancy at term. XVI FIGO World Congress of Obstetrics & Gynecology (Book 4); 2000 Sept 3‐8; Washington DC, USA. 2000:68‐9.
Chanrachakul 2002 {published data only}
- Chanrachakul B, Herabutya Y, Punyavachira P. Randomized trial of isosorbide mononitrate versus misoprostol for cervical ripening at term. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2002;78:139‐45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Guha 2015 {published data only}
- Guha K, Fatema A, Biswas PK, Haque E. Isosorbide mononitrate versus misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labour at term. Mymensingh Medical Journal : Mmj 2015;24(2):346‐51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Haghighi 2013 {published data only}
- Haghighi L, Homam H, Raoofi Z, Najmi Z. Intravaginal isosorbide dinitrate or misoprostol for cervical ripening prior to induction of labour: A randomised controlled trial. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2013;33(3):272‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Haghighi 2015 {published data only}
- Haghighi L, Moukhah S, Goshtasbi A. Comparing the effect of oral and vaginal isosorbide dinitrate in pre‐induction cervical ripening in term pregnancy: A controlled clinical trial. Advanced Biomedical Research 2015;4:129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moukhah S, Ahmadi F. Preinduction cervical ripening using oral and vaginal isosorbide dinitrate in patients with term pregnancy: A randomized clinical trial. Koomesh 2016;17(4):863‐70. [Google Scholar]
Kadian 2008 {published data only}
- Kadian ND. Comparison of nitric oxide donor isosorbide dinitrate (IDN) and dinoprostone for cervical ripening before induction of labor at term. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2008;115(s1):76. [Google Scholar]
Krishnamurthy 2015 {published data only}
- Krishnamurthy R, Pallavee P, Ghose S. Evaluation of isosorbide mononitrate for preinduction of cervical ripening: A randomized placebo‐controlled trial. Journal of Family and Reproductive Health 2015;9:75‐81. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Movahed 2016 {published data only}
- Movahed F, Seyed E, Pakniat H, Iranipour M, Yazdi Z. Comparison of the effects of transcervical catheter, laminaria and isosorbide mononitrate on cervical ripening. Journal of Babol University of Medical Sciences 2016;18(3):19‐24. [Google Scholar]
Nicoll 2001 {published data only}
- Nicoll AE, Mackenzie F, Greer IA, Norman JE. Vaginal application of the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for preinduction cervical ripening: a randomized controlled trial to determine effects on maternal and fetal hemodynamics. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2001;184:958‐64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Osman 2006 {published data only}
- Osman I, MacKenzie F, Norrie J, Murray HM, Greer IA, Norman JE. The "PRIM" study: a randomized comparison of prostaglandin E2 gel with the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening before the induction of labor at term. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2006;194(4):1012‐21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osman I, MacKenzie F, Norrie J, Murray HM, Greer IA, Norman JE. The 'PRIM' study ‐ a randomised comparison of prostaglandin with isosorbide mononitrate for pre‐induction cervical ripening at term [abstract]. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2005;112(4):512. [Google Scholar]
- Osman I, Mackenzie F, Norrie J, Greer A, Norman JE. The 'PRIM' study ‐ a randomised comparison of prostaglandin with isosorbide mononitrate for preinduction cervical ripening at term [abstract]. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2004;24(Suppl 1):S67. [Google Scholar]
- Osman I, Norman J, Mackenzie F, Murray H, Norrie J, Greer I. The "PRIM" study: a randomised comparison of prostaglandin E2 gel with the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening prior to the induction of labour at term [abstract]. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2004;191(6 Suppl 1):S184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Perche 2009 {published data only}
- Perche S, Guerra M, Reyna E, Hidalgo M, Santos J, Mejia J, et al. Vaginal isosorbide mononitrate or misoprostol for cervical ripening in term pregnancies. Clinica e Investigacion en Ginecologia y Obstetricia 2009;36(6):203‐8. [Google Scholar]
Rameez 2007 {published data only}
- Rameez MF, Goonewardene IM. Nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for pre‐induction cervical ripening at 41 weeks' gestation: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2007;33(4):452‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Razaq 2011 {published data only}
- Razaq A. Isosorbide mononitrate versus misoprostol for cervical ripening. Al‐Kindy College Medical Journal 2011;8(1):69‐74. [Google Scholar]
Rezk 2014 {published data only}
- Rezk M, Sanad Z, Dawood R, Masood A, Emarh M, Halaby AA. Intracervical foley catheter versus vaginal isosorbid mononitrate for induction of labor in women with previous one cesarean section. Journal of Clinical Gynecology and Obstetrics 2014;3(2):55‐61. [Google Scholar]
Romero‐Gutierrez 2011 {published data only}
- Romero‐Gutierrez G, Gonzalez OEB, Ponce‐Ponce de Leon A. Isosorbide and dinoprostone for induction of labor [Isosorbide y dinoprostona en induccion del trabajo de parto]. Ginecologia y Obstetricia de Mexico 2011;79(5):285‐91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schmitz 2014 {published data only}
- Schmitz T, Closset E, Fuchs F, Maillard F, Rozenberg P, Anselem O, et al. Outpatient cervical ripening with nitric oxide (NO) donors for prolonged pregnancy in nullipara: the NOCETER randomized, multicentre, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2014;210(1 Suppl):S19. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz T, Fuchs F, Closset E, Rozenberg P, Winer N, Perrotin F, et al. Outpatient cervical ripening by nitric oxide donors for prolonged pregnancy: a randomized controlled trial. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2014;124(6):1089‐97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sharma 2005 {published data only}
- Sharma Y, Kumar S, Mittal S, Misra R, Dadhwal V. Evaluation of glyceryl trinitrate, misoprostol, and prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening in term pregnancy. Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology Research 2005;31(3):210‐5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Soliman 2013 {published data only}
- Soliman AT. A comparison of isosorbide mononitrate, misoprostol, and combination therapy for preinduction cervical ripening at term: a randomized controlled trial. Tanta Medical Journal 2013;41(4):310‐7. [Google Scholar]
Vidanagamage 2011 {published data only}
- Vidanagamage RS, Goonewardene IM. The efficacy of two different doses of vaginal isosorbide mononitrate in pre induction cervical ripening: a double blind randomised controlled trial. Ceylon Medical Journal 2011;56(3):91‐100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Yazdizadeh 2013 {published data only}
- Yazdizadeh H, Abedi P, Najar S, Angali KA. The impact of isosorbide mononitrate on cervical ripening and labor induction in primiparous women with term pregnancy: A double‐blind, randomized, controlled trial. Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research 2013; Vol. 18, issue 3:246‐50. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
References to studies excluded from this review
Abdellah 2011 {published data only}
- Abdellah MS, Hussien M, AboAlhassan A. Intravaginal administration of isosorbide mononitrate and misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labour: a randomized controlled trial. Archives of Gynecology and Obstetrics 2011;284(1):25‐30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ahmed 2014 {published data only}
- Ahmed WAS, Ahmed MR, Madny EH, Mohamed RM, Elshahat AM. A comparison between two different doses of vaginal isosorbide mononitrate versus misoprostol in pre‐induction cervical ripening at term: a randomized controlled study. Journal of Maternal‐Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2014;27(Suppl 1):150. [Google Scholar]
Bates 2003 {published data only}
- Bates CD, Nicoll AE, Mullen AB, Mackenzie F, Thomson AJ, Norman JE. Serum profile of isosorbide mononitrate after vaginal administration in the third trimester. BJOG: an international journal of obstetrics and gynaecology 2003;110:64‐7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Collingham 2010 {published data only}
- Collingham J, Fuh K, Caughey A, Pullen K, Lyell D, Druzin M, et al. Randomized clinical trial of cervical ripening and labor induction using oral misoprostol with or without intravaginal isosorbide mononitrate. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2008;199(6 Suppl 1):S57. [Google Scholar]
- Collingham JP, Fuh KC, Caughey AB, Pullen KM, Lyell DJ, El‐Sayed YY. Oral misoprostol and vaginal isosorbide mononitrate for labor induction: a randomized controlled trial. Obstetrics & Gynecology 2010;116(1):121‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ekerhovd 2003 {published data only}
- Ekerhovd E, Bullarbo M, Andersch B, Norstrom A. Vaginal administration of the nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate for cervical ripening at term: a randomized controlled study. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2003;189:1692‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
El‐Khayat 2016 {published data only}
- El‐Khayat W, Alelaiw H, El‐Kateb A, Elsemary A. Comparing vaginal misoprostol versus foley catheter plus vaginal isosorbide mononitrate for labor induction. Journal of Maternal‐Fetal & Neonatal Medicine 2016;29(3):487‐92. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Habib 2008 {published data only}
- Habib SM, Emam SS, Saber AS. Outpatient cervical ripening with nitric oxide donor isosorbide mononitrate prior to induction of labor. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics 2008;101(1):57‐61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Helal 2004 {published data only}
- Helal AMM, Abd El‐Razek MME, Ahmed RE. Randomized double‐blind controlled study to determine the effect of vaginally applied nitric oxide donor (isosorbide mononitrate) for preinduction cervical ripening on maternal & fetal hemodynamics and the ripening of the cervix. El‐Minia Medical Bulletin 2004;15(1):32‐42. [Google Scholar]
Moghtadaei 2007 {published data only}
- Moghtadaei P. A randomized trial comparing outpatient vaginal isosorbide‐mononitrate versus extra‐amnion saline infusion with concurrent oxytocin for cervical ripening and labor induction in nulliparous women. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2007;197(6 Suppl 1):S103. [Google Scholar]
- Moghtadei P, Sardari F. A randomized trial comparing outpatient vaginal isosorbide mononitrate versus extra‐amnion saline infusion with concurrent oxytocin for cervical ripening and labor induction in nulliparous women. Journal of Maternal‐Fetal and Neonatal Medicine 2008;21(Suppl 1):77. [Google Scholar]
Nunes 2006 {published data only}
- Nunes FP, Campos AP, Pedroso SR, Leite CF, Avillez TP, Rodrigues RD, et al. Intravaginal glyceryl trinitrate and dinoprostone for cervical ripening and induction of labor. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2006;194(4):1022‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Vaisanen‐Tommiska 2008 {published data only}
- Vaisanen‐Tommiska M, Mikkola T, Ylikorkala O. Vaginal nitro induces cervical nitric oxide release in women postterm. 36th Nordic Congress of Obstetrics and Gynecology; 2008 June 14‐17; Reykjavik, Iceland. 2008:123.
Wolfler 2006 {published data only}
- Wolfler MM, Facchinetti F, Venturini P, Huber A, Helmer H, Husslein P, et al. Induction of labor at term using isosorbide mononitrate simultaneously with dinoprostone compared to dinoprostone treatment alone: a randomized, controlled trial. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 2006;195(6):1617‐22. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ziard 2012 {published data only}
- Ziard MH, Goonewardene IMR. Efficacy of two different treatment regimens of vaginal nitric oxide donor (iso‐sorbidemononitrate) used for pre‐induction cervical ripening. Sri Lanka Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 2012;34(Suppl 1):81, Abstract no: OP 13. [Google Scholar]
References to studies awaiting assessment
Ghanaie 2013 {published data only}
- Ghanaie MM, Mirblouk F, Godarzi R, Shakiba M. Effect of outpatient isosorbide mononitrate on success of labor induction. Journal of Babol University of Medical Sciences 2013;15(2):12‐7. [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Alfirevic 2009
- Alfirevic Z, Kelly AJ, Dowswell T. Intravenous oxytocin alone for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003246.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Alfirevic 2014
- Alfirevic Z, Aflaifel N, Weeks A. Oral misoprostol for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001338.pub3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Arnold 1977
- Arnold WP, Mittal CK, Katsuki S, Murad F. Nitric oxide activates guanylate cyclase and increases guanosine 3':5'‐cyclic monophosphate levels in various tissue preparations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1977;74:3203‐7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Boulvain 2005
- Boulvain M, Stan C, Irion O. Membrane sweeping for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000451.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Boulvain 2008
- Boulvain M, Kelly AJ, Irion O. Intracervical prostaglandins for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006971] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Boulvain 2016
- Boulvain M, Irion O, Dowswell T, Thornton JG. Induction of labour at or near term for suspected fetal macrosomia. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 5. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000938.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bricker 2000
- Bricker L, Luckas M. Amniotomy alone for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2000, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002862] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bryman 1986
- Bryman I, Norström A, Lindblom B. Influence of prostaglandins and adrenoceptor agonists on contractile activity in the human cervix at term. Obstetrics & Gynecology 1986;67:574‐8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Buhimschi 1995
- Buhimschi I, Yallampalli C, Dong Y. Involvement of nitric‐oxide‐cyclic guanosine monophosphate pathway in control of human uterine contractility during pregnancy. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1995;172:1577‐84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Calder 1998
- Calder AA. Nitric oxide: another factor in cervical ripening. Human Reproduction 1998;13:250‐1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Chwalisz 1998
- Chwalisz K, Garfield RE. Nitric oxide as the final mediator of cervical ripening. Human Reproduction 1998;13:245‐52. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Curtis 1987
- Curtis P, Evans S, Resnick J. Uterine hyperstimulation. The need for standard terminology. Journal of Reproductive Medicine 1987;32:91‐5. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ekerhord 1998
- Ekerhord E, Brannstrom M, Delbo D, Norstrom A. Nitric oxide mediated inhibition of contractile activity in the human cervix. Molecular Human Reproduction 1998;4:915‐20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
French 2001
- French L. Oral prostaglandin E2 for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003098] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hapangama 2009
- Hapangama D, Neilson JP. Mifepristone for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002865.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JPT, Green S, editors. Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Hofmeyr 2003
- Hofmeyr GJ, Gülmezoglu AM, Pileggi C. Vaginal misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 10. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000941] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hofmeyr 2009
- Hofmeyr GJ, Alfirevic Z, Kelly AJ, Kavanagh J, Thomas J, Neilson JP, et al. Methods for cervical ripening and labour induction in late pregnancy: generic protocol. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2009, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002074] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Howarth 2001
- Howarth GR, Botha DJ. Amniotomy plus intravenous oxytocin for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003250] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hutton 2001
- Hutton E, Mozurkewich E. Extra‐amniotic prostaglandin for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003092] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Izurni 1993
- Izurni H, Yallampall C, Carfield R. Gestational changes in L‐arginine‐induced relaxation of pregnant rat and human myometrial smooth muscle. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology 1993;169(5):1327‐37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Jozwiak 2012
- Jozwiak M, Bloemenkamp WM, Kelly A, Mol BWJ, Irion O, Boulvain M. Mechanical methods for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001233.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kavanagh 2001
- Kavanagh J, Kelly AJ, Thomas J. Sexual intercourse for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003093] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kavanagh 2005
- Kavanagh J, Kelly AJ, Thomas J. Breast stimulation for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2005, Issue 3. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003392.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kavanagh 2006a
- Kavanagh J, Kelly AJ, Thomas J. Corticosteroids for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003100.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kavanagh 2006b
- Kavanagh J, Kelly AJ, Thomas J. Hyaluronidase for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2006, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003097.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kelly 2001a
- Kelly AJ, Kavanagh J, Thomas J. Relaxin for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 2. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003103] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Kelly 2013b
- Kelly AJ, Kavanagh J, Thomas J. Castor oil, bath and/or enema for cervical priming and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 7. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003099.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Lees 1994
- Lees C, Campbell S, Jaunaax E, Brown R, Ramsey B, Cibb D. Arrest of pre‐term labour and prolongation of gestation with glyceryl trinitrate, a nitric oxide donor. Lancet 1994;343:1325‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Luckas 2000
- Luckas M, Bricker L. Intravenous prostaglandin for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2000, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002864] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Muzonzini 2004
- Muzonzini G, Hofmeyr GJ. Buccal or sublingual misoprostol for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2004, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD004221.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Norman 1997
- Norman J, Ward I, Martin W, Cameron A, McGrath J, Creer I. Effects of cGMP and the nitric oxide donors glyceryl trinitrate and sodium nitroprusside on contractions in vitro of isolated myometrial tissue from pregnant women. Journal of Repoductive Fertility 1997;110:249‐54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Qing 1996
- Qing S, Bier H, Garfiled R. Local application of nitric oxide (NO) donors induces cervical ripening. Journal of the Society of Gynaecological Investigation 1996;3:462. [Google Scholar]
RevMan 2014 [Computer program]
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Smith 2003
- Smith CA. Homoeopathy for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003399] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Smith 2013
- Smith CA, Crowther CA, Grant SJ. Acupuncture for induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2013, Issue 8. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002962.pub3] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Telfer 1995
- Telfer J, Lyall F, Norman J. Identification of nitric oxide synthase in human uterus. Human Reproduction 1995;10:19‐23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thomas 2001
- Thomas J, Kelly AJ, Kavanagh J. Oestrogens alone or with amniotomy for cervical ripening or induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003393] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thomas 2014
- Thomas J, Fairclough A, Kavanagh J, Kelly AJ. Vaginal prostaglandin (PGE2 and PGF2a) for induction of labour at term. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2014, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003101.pub3] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thompson 1997
- Thompson A, Luman C, Cameron A. Nitric oxide donors induce ripening of the human uterine cervix: a randomised control trial. British Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology 1997;104:1054‐7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Thompson 1998
- Thompson A, Lunan C, Ledingham M, Howat R, Cameron I, Greer I. Randomised trial of nitric oxide donors versus prostaglandins for cervical ripening before first trimester termination of pregnancy. Lancet 1998;352:1093‐6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Kelly 2008
- Kelly AJ, Kavanagh J. Nitric oxide donors for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008, Issue 1. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006901] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Kelly 2011
- Kelly AJ, Munson C, Minden L. Nitric oxide donors for cervical ripening and induction of labour. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 6. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD006901.pub2] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


